Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, and Factoring Polynomials Using Algebra Tiles. This Lesson is Designed for 8 th Grade
|
|
|
- Sherilyn Stokes
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, and Factoring Polynomials Using Algebra Tiles This Lesson is Designed for 8 th Grade The Lesson will last 5 days and you will need: A Class Set of Algebra Tiles, Algebra Tiles for the Overhead, An Overhead
2 Basic operations with polynomials. 2 Objectives: When the students have completed this units they should be able to: NYS Standards: 1. Use physical models to perform operations with polynomials.(nys 8.A.5) 2. Multiply and divide monomials (NYS 8.A.6) 3. Add and subtract polynomials with integer coefficients. (NYS 8.A.7) 4. Multiply a binomial by a monomial or a binomial (NYS 8.A.8) Factor a trinomial in the form ax²+bx+c; a=1. (NYS 8.A.11.) NCTM Standards: 1. create and use representations to organize, record, and communicate mathematical ideas; 2. select, apply, and translate among mathematical representations to solve problems; 3. recognize and use connections among mathematical ideas; 4. understand how mathematical ideas interconnect and build on one another to produce a coherent whole; 5. communicate their mathematical thinking coherently and clearly to peers, teachers, and others; 6. model and solve contextualized problems using various representations, such as graphs, tables, and equations
3 3 An overview of the week. Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Introduce the students to the algebra tiles, show them what each tile represents and then use the tiles to model addition. Use the algebra tiles to model the subtract of polynomials Use algebra tiles to model the multiplication of a binomial by a monomial Use the algebra tiles to model the multiplication of a binomial by a binomial. Use the algebra tiles to factor trinomials.
4 Lesson 1, Day 1 Adding Polynomials 4 Objectives: After the lesson the students should be able to represent polynomials with the algebra tiles and be able to add polynomials with and without the algebra tiles. Standards met: Use physical models to perform operations with polynomials.(nys 8.A.5) Add and subtract polynomials with integer coefficients. (NYS 8.A.7) The beginning of the lesson will be devoted to passing out and explaining the symbolism of the algebra tiles. The students must understand what each tile represents so I will explain that: The blue square tile has lengths that measure x units long so its area is x*x = x². So, it represents x². The green rectangle has lengths x units by 1 unit long so its area is x*1=x. So, it represents x. The small yellow square tile has lengths 1 unit by 1 unit so its area is 1*1= 1. So, it represents 1. Note, the red sides of the tiles represent negative values, my students already know this because we used the small squares to add and subtract integers. They also know about zero pairs from adding and subtracting integers.
5 After I am done explaining the meaning of each tile I will have the students represent some different polynomials at their desk. 5 I will have the students represent the following polynomials with their algebra tiles: 1. x + 2 ans. 2. x²+2x+3 ans. 3. 2x²+2 Ans. 4. x²+2x-2 ans.
6 6 Now, after I believe all of the students know how to represent a polynomial using the algebra tiles I will them try some addition problems using what they have just learned. I will have the students simplify each of the following expression using the algebra tiles. 1. (2x+2) + (3x + 1) Ans. (Now combine every thing that is the same together) So, (2x+2) + (3x+1) = 5x (x²+2x+2) + (x²+2x+1) Ans. Combine everything that s the same So, (x²+2x+2) + (x²+2x+1) = 2x²+4x+3
7 3. (2x²+4x+1) + (x² + -1x +1) 7 Ans. Now, combine everything that is the same and cancel out if you can. So, (2x²+4x+1) + (x² + -1x +1) = 3x²+3x+2 Now, I will start asking the students to think of a rule that we can come up with so that we don t have to always use algebra tiles when we are adding polynomials. Hopefully they will notice that if you add the number in front of the variable with all of the of the other variables that are the same you will get the correct answer. After this rule I will tell them that the number in front of the variable is called the coefficient so our new rule will be to add the coefficients of the same terms or variables.
8 Day 1 Homework 8 For the following problems, draw a representation of each problem and then simplify the answer. 1. (2x + 1) + (2x +2) Model: Answer: 2. (x²+2x+1) + (x²+x+1) Model: Answer: 3. (x²+3x+2) + (2x+1) Model: Answer: 4. (3x+2) + (2x+ -1) Model: Answer:
9 Homework Day 1 Answers 9 For the following problems, draw a representation of each problem and then simplify the answer. 5. (2x + 1) + (2x +2) Model: Answer: 4x+3 6. (x²+2x+1) + (x²+x+1) Model: Answer: 2x²+3x+2 7. (x²+3x+2) + (2x+1) Model: Answer: x²+5x+3
10 10 8. (3x+2) + (2x+ -1) Model: Answer: 5x+3
11 11 Lesson 2, Day 2 Subtracting Polynomials Objectives: At the end of this lesson the students should be able to subtract polynomials with and without the use of algebra tiles. Standards Covered: Use physical models to perform operations with polynomials.(nys 8.A.5) Add and subtract polynomials with integer coefficients. (NYS 8.A.7) At the beginning of class I will choose 5 students to display their homework on the front board. We will discuss their answers as class and reestablish the rule we came up with yesterday about adding the coefficients of the like terms. We will then have a discussion about if they think the same rules will apply for subtraction. I will ask the students to make a guess on the answer to the problem (3x + 2) (2x + 2) and try to support their answer using the algebra tiles, reminding the students that the red side is the negative side. We will now show the terms cancel each other to give us an answer. (3x + 2) (2x + 2) Now, after canceling what terms are left? Ans. Is X
12 So, (3x + 2) (2x + 2) = x 12 Now, I will have the students try these next questions on their own using the algebra tiles and having them thinking about a rule for subtraction polynomials. 1. (3x² + 4x +3) (x² + 2x + 2) ans. So, (3x² + 4x +3) (x² + 2x + 2) = x²+2x+1 2. (x²+2x-2) (3x² + 2x +2) So, (x²+2x-2) (3x² + 2x +2)= -2x² - 4
13 3. (2x²-2x+4) (2x²+2x+4) 13 So, (2x²-2x+4) (2x²+2x+4) = -4x After these 4 examples we will come together as a class and see if we can find a rule that will apply when subtracting polynomials and hopefully the students will see that all you have to do is subtract the coefficients in front of the like terms.
14 Day 2 Homework 14 For homework, draw a representation of each problem then simplify each expression by using the model you drew. 1. (2x²+x+2) (x²+2x+4) Model: Ans: 2. (3x²+x-2) (x²-2x+2) Model: Ans: 3. (x²-2x+5) (3x²+2x+1) Model: Ans:
15 Day 2 Homework Answers 15 For homework, draw a representation of each problem then simplify each expression by using the model you drew. 1. (2x²+x+2) (x²+2x+4) Model: Ans: -x² - x-2 2. (3x²+x-2) (x²-2x+2) Model: Ans: 2x²+3x-4
16 3. (x²-2x+5) (3x²+2x+1) 16 Model: Ans: -2x²-4x+4
17 Day 3, Lesson 3 17 Objective: By the end of this the students should be able to multiply a binomial by a monomial. Standards Covered: Use physical models to perform operations with polynomials.(nys 8.A.5) Multiply a binomial by a monomial or a binomial (NYS 8.A.8) Today we will start the lesson by having 3 students come to the board and put their answers to the homework on the board. We will then go over the two rules we have made for adding and subtracting polynomials. Now we will introduce multiplying binomials by giving the students the worksheets below with the L bracket on it so that they can begin to model the multiplication.
18 18
19 19 After the students have the sheets above we will work on the following problem together and then the students will try some examples with a partner. Example: Multiply 3x * (2x + 3) First use your algebra tiles to model the two parts of the expression, one on the top of the L bracket and one the side. After you have modeled the two parts of the expression we will need to find what algebra tiles will we can place inside the bracket to form a rectangle with sides that are the same length as the two parts of our expression. This will give us our new expression. So, 3x * (2x + 3) is equal to 6x² + 9x
20 Now I will have the students try these problems with a partner Multiply 2* (2x + 3) So, the answer is 4x Multiply 4x * ( x 2)
21 2. Multiply 5 * (x + 2) So, 4x * ( x 2) = 4x² - 8x 21 So, 5*(x+2) = 5x +10
22 3. Multiply 2x * (x + 2) 22 So, 2x * (x + 2) = 2x² + 4x. After we have done these examples I will ask the students if they have noticed any patterns or anything that we can say may be a rule to use when multiplying polynomials. Hopefully the students will notice the use of the distributive property and see how the coefficients are being multiplied together and see that the variables are being multiplied together, using the rule for multiplying numbers with the same base which is adding the exponents
23 Day 3 Homework 23 Use the brackets below to represent the multiplication you are performing and then find the answer * (x + 3) Ans: 2. 3x * (2x -1) Ans:
24 3. x * ( 2x 2) 24 Ans: 4. 4 * ( 2x + 2)
25 Ans: Day 3 Homework 25 Use the brackets below to represent the multiplication you are performing and then find the answer * (x + 3) Ans: 2x x * (2x -1) Ans: 4x² - 2x
26 3. x * ( 2x 2) 26 Ans: -2x² + 4x 4. 4 * ( 2x + 2)
27 Ans: 8x + 8 Day 4, Lesson 4 27 Objective: At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to use what they have learned yesterday about distributing to multiply two binomials together. Standards covered: Use physical models to perform operations with polynomials.(nys 8.A.5) Multiply a binomial by a monomial or a binomial (NYS 8.A.8) At the beginning of the class I will have four students come to the board and write their homework answers on the board. We will then discuss their answers and go back over the distributive law and multiplying variables and coefficients. We then see if we can use these same concepts to multiply two binomials together. I will start with this example and then have the students work in pairs to solve some more examples. Example: (2x + 2) * ( x 1) Combine all like terms and cancel anything out that can be cancelled and your answer should be 2x² -2x +2
28 28 With a partner and using the algebra try to multiply the following binomials. Also, while you are working try to think of a rule that applies for all of the examples. 1. (3x + 2) * (x + 2) So, (3x + 2) * (x + 2) = 3x² + 8x (x 2) * (2x 3) So, (x 2) * (2x 3) = 2x² - 7x +6
29 3. (x+2) * (x-2) 29 So, (x+2) * (x-2) = x² (-2x + 2) * (2x + 3)
30 So, (-2x + 2) * (2x + 3) = -4x² -2x After the students have completed this activity we will discuss their outcomes and see if any of them have noticed any patterns that may lead to a rule for multiplying to binomials. Hopefully one of the students will notice that we are using the same procedure as yesterday but we are distributing twice through and then combing all of the like terms.
31 Day 4 Homework 31 Using the brackets below draw a model to represent the multiplication of the binomials and then use your model to multiply. 1. (x + 3) * ( x + 3) Ans: 2. (2x + 1) * ( 2x + 4)
32 Ans: 3. (2x -2) * (-x 3) 32 Ans: 4. (-2x + 1) * ( -3x + 1)
33 Ans: Day 4 Homework: Answers 33 Using the brackets below draw a model to represent the multiplication of the binomials and then use your model to multiply. 1. (x + 3) * ( x + 3) Ans: x² + 6x (2x + 1) * ( 2x + 4)
34 Ans: 4x² + 10x (2x -2) * (-x 3) 34 Ans: -2x² -4x (-2x + 1) * ( -3x + 1)
35 Ans: 6x² - 5x + 1 Day 5, Lesson 5 35 Objectives: At the end of this lesson the students will be able find the factors of a trinomial. Standards Met: Use physical models to perform operations with polynomials.(nys 8.A.5) Factor a trinomial in the form ax²+bx+c; a=1. (NYS 8.A.11.) At the beginning of the lesson we will go over the home work and discuss the rules used to answer the questions from the night before. I will then place a trinomial on the board and see if the students can guess what two binomials were multiplied together to get the trinomial. Then I will form the square, using the algebra tiles, which the trinomials make and see if that is easier for the students to find the two factors. Example: Find the factors of the trinomial x² + 2x + 1. See if the students can guess what the two factors are and then form the square or rectangle on the L bracket and see they can find the factors now. Now, after the students make their own square at their table, ask them if they can find the top and the side that what form this square. They should come up with this. So, the two factors of x² + 2x + 1 are (x+1)².
36 See if you can find the factors of the trinomials below x² + 3x + 2 Ans: So, the factors of x² + 3x + 2 are (x+2) and (x+1)
37 2. x² + 3x 37 Ans: So, the factors of x² + 3x are x and x + 3
38 3. x² - 5x Ans: So, the factors of x² -5x +6 are x -2 and x 3.
39 39 Now, after these examples I will ask the if they notice any patterns or common things happening in each example. After today they will probably only notice minor details and tomorrow they may be able form some strategies to find factors of polynomials. But, today hopefully they will notice that the last term in the trinomial is the product of the last two terms in the factors, and that both of the factors will start with x. For homework I will have the students draw the trinomials and find their factors and the next day of class we will discuss different strategies each student used to find the factors of the trinomials.
40 Homework Day 5 40 Draw the rectangle or square for each trinomial and then use that to find the two factors of the trinomial. 1. x² +4x + 4 Ans: 2. x² -2x + 1 Ans:
41 41 3. x² + 5x + 6 Ans: 4. x² -x 6 Ans:
42 42 Homework Day 5: Answers Draw the rectangle or square for each trinomial and then use that to find the two factors of the trinomial. 1. x² +4x + 4 Ans: (x+2) * (x+2) 2. x² -2x + 1 Ans: (x 1) * (x- 1)
43 43 3. x² + 5x + 6 Ans: (x+3)*(x+2) 4. x² -x 6 Ans: (x -3) * (x+2)
7 th Grade Integer Arithmetic 7-Day Unit Plan by Brian M. Fischer Lackawanna Middle/High School
 7 th Grade Integer Arithmetic 7-Day Unit Plan by Brian M. Fischer Lackawanna Middle/High School Page 1 of 20 Table of Contents Unit Objectives........ 3 NCTM Standards.... 3 NYS Standards....3 Resources
7 th Grade Integer Arithmetic 7-Day Unit Plan by Brian M. Fischer Lackawanna Middle/High School Page 1 of 20 Table of Contents Unit Objectives........ 3 NCTM Standards.... 3 NYS Standards....3 Resources
A Concrete Introduction. to the Abstract Concepts. of Integers and Algebra using Algebra Tiles
 A Concrete Introduction to the Abstract Concepts of Integers and Algebra using Algebra Tiles Table of Contents Introduction... 1 page Integers 1: Introduction to Integers... 3 2: Working with Algebra Tiles...
A Concrete Introduction to the Abstract Concepts of Integers and Algebra using Algebra Tiles Table of Contents Introduction... 1 page Integers 1: Introduction to Integers... 3 2: Working with Algebra Tiles...
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring
 1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
Using Algebra Tiles for Adding/Subtracting Integers and to Solve 2-step Equations Grade 7 By Rich Butera
 Using Algebra Tiles for Adding/Subtracting Integers and to Solve 2-step Equations Grade 7 By Rich Butera 1 Overall Unit Objective I am currently student teaching Seventh grade at Springville Griffith Middle
Using Algebra Tiles for Adding/Subtracting Integers and to Solve 2-step Equations Grade 7 By Rich Butera 1 Overall Unit Objective I am currently student teaching Seventh grade at Springville Griffith Middle
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials
 Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
NSM100 Introduction to Algebra Chapter 5 Notes Factoring
 Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Section 5.1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Factoring by Grouping Greatest Common Factor for a polynomial is the largest monomial that divides (is a factor of) each term of the polynomial. GCF is the
Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Student Activity
 Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Student Activity Materials: Algebra Tiles (student set) Worksheet: Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Algebra Tiles: Each algebra tile kits should contain
Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Student Activity Materials: Algebra Tiles (student set) Worksheet: Factoring Trinomials using Algebra Tiles Algebra Tiles: Each algebra tile kits should contain
SIMPLIFYING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS
 Tallahassee Community College 5 SIMPLIFYING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS In arithmetic, you learned that a fraction is in simplest form if the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of the numerator and the denominator is
Tallahassee Community College 5 SIMPLIFYING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS In arithmetic, you learned that a fraction is in simplest form if the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of the numerator and the denominator is
expression is written horizontally. The Last terms ((2)( 4)) because they are the last terms of the two polynomials. This is called the FOIL method.
 A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
Keystone Exams: Algebra I Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content. Pennsylvania
 Keystone Exams: Algebra I Assessment Anchors and Pennsylvania Algebra 1 2010 STANDARDS MODULE 1 Operations and Linear Equations & Inequalities ASSESSMENT ANCHOR A1.1.1 Operations with Real Numbers and
Keystone Exams: Algebra I Assessment Anchors and Pennsylvania Algebra 1 2010 STANDARDS MODULE 1 Operations and Linear Equations & Inequalities ASSESSMENT ANCHOR A1.1.1 Operations with Real Numbers and
Unit 7 Quadratic Relations of the Form y = ax 2 + bx + c
 Unit 7 Quadratic Relations of the Form y = ax 2 + bx + c Lesson Outline BIG PICTURE Students will: manipulate algebraic expressions, as needed to understand quadratic relations; identify characteristics
Unit 7 Quadratic Relations of the Form y = ax 2 + bx + c Lesson Outline BIG PICTURE Students will: manipulate algebraic expressions, as needed to understand quadratic relations; identify characteristics
Vieta s Formulas and the Identity Theorem
 Vieta s Formulas and the Identity Theorem This worksheet will work through the material from our class on 3/21/2013 with some examples that should help you with the homework The topic of our discussion
Vieta s Formulas and the Identity Theorem This worksheet will work through the material from our class on 3/21/2013 with some examples that should help you with the homework The topic of our discussion
Factoring Quadratic Trinomials
 Factoring Quadratic Trinomials Student Probe Factor x x 3 10. Answer: x 5 x Lesson Description This lesson uses the area model of multiplication to factor quadratic trinomials. Part 1 of the lesson consists
Factoring Quadratic Trinomials Student Probe Factor x x 3 10. Answer: x 5 x Lesson Description This lesson uses the area model of multiplication to factor quadratic trinomials. Part 1 of the lesson consists
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring
 Section 4 4: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring The last chapter introduced the distributive process. The distributive process takes a product of a monomial and a polynomial and changes the multiplication
Section 4 4: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring The last chapter introduced the distributive process. The distributive process takes a product of a monomial and a polynomial and changes the multiplication
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS
 MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
MATH 60 NOTEBOOK CERTIFICATIONS Chapter #1: Integers and Real Numbers 1.1a 1.1b 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.8 Chapter #2: Algebraic Expressions, Linear Equations, and Applications 2.1a 2.1b 2.1c 2.2 2.3a 2.3b 2.4 2.5
Exponents and Radicals
 Exponents and Radicals (a + b) 10 Exponents are a very important part of algebra. An exponent is just a convenient way of writing repeated multiplications of the same number. Radicals involve the use of
Exponents and Radicals (a + b) 10 Exponents are a very important part of algebra. An exponent is just a convenient way of writing repeated multiplications of the same number. Radicals involve the use of
How To Factor Quadratic Trinomials
 Factoring Quadratic Trinomials Student Probe Factor Answer: Lesson Description This lesson uses the area model of multiplication to factor quadratic trinomials Part 1 of the lesson consists of circle puzzles
Factoring Quadratic Trinomials Student Probe Factor Answer: Lesson Description This lesson uses the area model of multiplication to factor quadratic trinomials Part 1 of the lesson consists of circle puzzles
( ) FACTORING. x In this polynomial the only variable in common to all is x.
 FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS
 3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS RATIONAL NUMBERS In previous courses you have learned how to operate (do addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) on rational numbers (fractions). Rational numbers
3.1. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS RATIONAL NUMBERS In previous courses you have learned how to operate (do addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) on rational numbers (fractions). Rational numbers
Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III
 Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III Name Date Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Algebra Standard 10.0 A polynomial is a sum of one ore more monomials. Polynomial
Alum Rock Elementary Union School District Algebra I Study Guide for Benchmark III Name Date Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Algebra Standard 10.0 A polynomial is a sum of one ore more monomials. Polynomial
called and explain why it cannot be factored with algebra tiles? and explain why it cannot be factored with algebra tiles?
 Factoring Reporting Category Topic Expressions and Operations Factoring polynomials Primary SOL A.2c The student will perform operations on polynomials, including factoring completely first- and second-degree
Factoring Reporting Category Topic Expressions and Operations Factoring polynomials Primary SOL A.2c The student will perform operations on polynomials, including factoring completely first- and second-degree
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS
 POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Polynomial Division.. 314 The Rational Zero Test.....317 Descarte s Rule of Signs... 319 The Remainder Theorem.....31 Finding all Zeros of a Polynomial Function.......33 Writing a
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Polynomial Division.. 314 The Rational Zero Test.....317 Descarte s Rule of Signs... 319 The Remainder Theorem.....31 Finding all Zeros of a Polynomial Function.......33 Writing a
Name Intro to Algebra 2. Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring
 Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
Polynomial Expression
 DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to ingrid.stewart@csn.edu. Thank you! PLEASE NOTE
DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to ingrid.stewart@csn.edu. Thank you! PLEASE NOTE
Multiplying Binomials and Factoring Trinomials Using Algebra Tiles and Generic Rectangles
 Multiplying Binomials Standard: Algebra 10.0 Time: 55 mins. Multiplying Binomials and Factoring Trinomials Using Algebra Tiles and s Materials: Class set of Algebra Tiles or access to a computer for each
Multiplying Binomials Standard: Algebra 10.0 Time: 55 mins. Multiplying Binomials and Factoring Trinomials Using Algebra Tiles and s Materials: Class set of Algebra Tiles or access to a computer for each
Polynomials and Factoring. Unit Lesson Plan
 Polynomials and Factoring Unit Lesson Plan By: David Harris University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Math 410 Dr. Thomas, M D. 2 Abstract This paper will discuss, and give, lesson plans for all the topics
Polynomials and Factoring Unit Lesson Plan By: David Harris University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Math 410 Dr. Thomas, M D. 2 Abstract This paper will discuss, and give, lesson plans for all the topics
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: - Beginning Algebra CREDITS: 4 (Lec 4 / Lab 0) PREREQUISITES: MATH 0920: Fundamental Mathematics with a grade of C or better, Placement Exam,
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: - Beginning Algebra CREDITS: 4 (Lec 4 / Lab 0) PREREQUISITES: MATH 0920: Fundamental Mathematics with a grade of C or better, Placement Exam,
Algebra Cheat Sheets
 Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
Sheets Algebra Cheat Sheets provide you with a tool for teaching your students note-taking, problem-solving, and organizational skills in the context of algebra lessons. These sheets teach the concepts
When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property and take out the GCF.
 Factoring: reversing the distributive property. The distributive property allows us to do the following: When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property
Factoring: reversing the distributive property. The distributive property allows us to do the following: When factoring, we look for greatest common factor of each term and reverse the distributive property
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
 Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Adding and Subtracting Integers Unit. Grade 7 Math. 5 Days. Tools: Algebra Tiles. Four-Pan Algebra Balance. Playing Cards
 Adding and Subtracting Integers Unit Grade 7 Math 5 Days Tools: Algebra Tiles Four-Pan Algebra Balance Playing Cards By Dawn Meginley 1 Objectives and Standards Objectives: Students will be able to add
Adding and Subtracting Integers Unit Grade 7 Math 5 Days Tools: Algebra Tiles Four-Pan Algebra Balance Playing Cards By Dawn Meginley 1 Objectives and Standards Objectives: Students will be able to add
2.3. Finding polynomial functions. An Introduction:
 2.3. Finding polynomial functions. An Introduction: As is usually the case when learning a new concept in mathematics, the new concept is the reverse of the previous one. Remember how you first learned
2.3. Finding polynomial functions. An Introduction: As is usually the case when learning a new concept in mathematics, the new concept is the reverse of the previous one. Remember how you first learned
SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
 (Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
(Section 0.6: Polynomial, Rational, and Algebraic Expressions) 0.6.1 SECTION 0.6: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Be able to identify polynomial, rational, and algebraic
Mathematics Online Instructional Materials Correlation to the 2009 Algebra I Standards of Learning and Curriculum Framework
 Provider York County School Division Course Syllabus URL http://yorkcountyschools.org/virtuallearning/coursecatalog.aspx Course Title Algebra I AB Last Updated 2010 - A.1 The student will represent verbal
Provider York County School Division Course Syllabus URL http://yorkcountyschools.org/virtuallearning/coursecatalog.aspx Course Title Algebra I AB Last Updated 2010 - A.1 The student will represent verbal
Factors and Products
 CHAPTER 3 Factors and Products What You ll Learn use different strategies to find factors and multiples of whole numbers identify prime factors and write the prime factorization of a number find square
CHAPTER 3 Factors and Products What You ll Learn use different strategies to find factors and multiples of whole numbers identify prime factors and write the prime factorization of a number find square
In this section, you will develop a method to change a quadratic equation written as a sum into its product form (also called its factored form).
 CHAPTER 8 In Chapter 4, you used a web to organize the connections you found between each of the different representations of lines. These connections enabled you to use any representation (such as a graph,
CHAPTER 8 In Chapter 4, you used a web to organize the connections you found between each of the different representations of lines. These connections enabled you to use any representation (such as a graph,
Accommodated Lesson Plan on Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination for Diego
 Accommodated Lesson Plan on Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination for Diego Courtney O Donovan Class: Algebra 1 Day #: 6-7 Grade: 8th Number of Students: 25 Date: May 12-13, 2011 Goal: Students will
Accommodated Lesson Plan on Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination for Diego Courtney O Donovan Class: Algebra 1 Day #: 6-7 Grade: 8th Number of Students: 25 Date: May 12-13, 2011 Goal: Students will
Chris Yuen. Algebra 1 Factoring. Early High School 8-10 Time Span: 5 instructional days
 1 Chris Yuen Algebra 1 Factoring Early High School 8-10 Time Span: 5 instructional days Materials: Algebra Tiles and TI-83 Plus Calculator. AMSCO Math A Chapter 18 Factoring. All mathematics material and
1 Chris Yuen Algebra 1 Factoring Early High School 8-10 Time Span: 5 instructional days Materials: Algebra Tiles and TI-83 Plus Calculator. AMSCO Math A Chapter 18 Factoring. All mathematics material and
Curriculum Alignment Project
 Curriculum Alignment Project Math Unit Date: Unit Details Title: Solving Linear Equations Level: Developmental Algebra Team Members: Michael Guy Mathematics, Queensborough Community College, CUNY Jonathan
Curriculum Alignment Project Math Unit Date: Unit Details Title: Solving Linear Equations Level: Developmental Algebra Team Members: Michael Guy Mathematics, Queensborough Community College, CUNY Jonathan
Pre-Calculus II Factoring and Operations on Polynomials
 Factoring... 1 Polynomials...1 Addition of Polynomials... 1 Subtraction of Polynomials...1 Multiplication of Polynomials... Multiplying a monomial by a monomial... Multiplying a monomial by a polynomial...
Factoring... 1 Polynomials...1 Addition of Polynomials... 1 Subtraction of Polynomials...1 Multiplication of Polynomials... Multiplying a monomial by a monomial... Multiplying a monomial by a polynomial...
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives. Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers.
 Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
Math 0980 Chapter Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to Algebra: The Integers. 1. Identify the place value of a digit. 2. Write a number in words or digits. 3. Write positive and negative numbers used
a. You can t do the simple trick of finding two integers that multiply to give 6 and add to give 5 because the a (a = 4) is not equal to one.
 FACTORING TRINOMIALS USING THE AC METHOD. Factoring trinomial epressions in one unknown is an important skill necessary to eventually solve quadratic equations. Trinomial epressions are of the form a 2
FACTORING TRINOMIALS USING THE AC METHOD. Factoring trinomial epressions in one unknown is an important skill necessary to eventually solve quadratic equations. Trinomial epressions are of the form a 2
Algebra Unit Plans. Grade 7. April 2012. Created By: Danielle Brown; Rosanna Gaudio; Lori Marano; Melissa Pino; Beth Orlando & Sherri Viotto
 Algebra Unit Plans Grade 7 April 2012 Created By: Danielle Brown; Rosanna Gaudio; Lori Marano; Melissa Pino; Beth Orlando & Sherri Viotto Unit Planning Sheet for Algebra Big Ideas for Algebra (Dr. Small)
Algebra Unit Plans Grade 7 April 2012 Created By: Danielle Brown; Rosanna Gaudio; Lori Marano; Melissa Pino; Beth Orlando & Sherri Viotto Unit Planning Sheet for Algebra Big Ideas for Algebra (Dr. Small)
FACTORING QUADRATICS 8.1.1 and 8.1.2
 FACTORING QUADRATICS 8.1.1 and 8.1.2 Chapter 8 introduces students to quadratic equations. These equations can be written in the form of y = ax 2 + bx + c and, when graphed, produce a curve called a parabola.
FACTORING QUADRATICS 8.1.1 and 8.1.2 Chapter 8 introduces students to quadratic equations. These equations can be written in the form of y = ax 2 + bx + c and, when graphed, produce a curve called a parabola.
1.3 Algebraic Expressions
 1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
1.3 Algebraic Expressions A polynomial is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 The numbers a 1, a 2,..., a n are called coefficients. Each of the separate parts,
MTH 092 College Algebra Essex County College Division of Mathematics Sample Review Questions 1 Created January 17, 2006
 MTH 092 College Algebra Essex County College Division of Mathematics Sample Review Questions Created January 7, 2006 Math 092, Elementary Algebra, covers the mathematical content listed below. In order
MTH 092 College Algebra Essex County College Division of Mathematics Sample Review Questions Created January 7, 2006 Math 092, Elementary Algebra, covers the mathematical content listed below. In order
Examples of Tasks from CCSS Edition Course 3, Unit 5
 Examples of Tasks from CCSS Edition Course 3, Unit 5 Getting Started The tasks below are selected with the intent of presenting key ideas and skills. Not every answer is complete, so that teachers can
Examples of Tasks from CCSS Edition Course 3, Unit 5 Getting Started The tasks below are selected with the intent of presenting key ideas and skills. Not every answer is complete, so that teachers can
Polynomials and Factoring
 7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
CAHSEE on Target UC Davis, School and University Partnerships
 UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
A Systematic Approach to Factoring
 A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
A Systematic Approach to Factoring Step 1 Count the number of terms. (Remember****Knowing the number of terms will allow you to eliminate unnecessary tools.) Step 2 Is there a greatest common factor? Tool
Multiplying and Dividing Listen & Learn PRESENTED BY MATHMANIAC Mathematics, Grade 8
 Number Sense and Numeration Integers Multiplying and Dividing PRESENTED BY MATHMANIAC Mathematics, Grade 8 Integers Multiplying and Dividing Introduction Welcome to today s topic Parts of Presentation,
Number Sense and Numeration Integers Multiplying and Dividing PRESENTED BY MATHMANIAC Mathematics, Grade 8 Integers Multiplying and Dividing Introduction Welcome to today s topic Parts of Presentation,
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING
 POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
POLYNOMIALS and FACTORING Exponents ( days); 1. Evaluate exponential expressions. Use the product rule for exponents, 1. How do you remember the rules for exponents?. How do you decide which rule to use
Florida Math 0028. Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper
 Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
Florida Math 0028 Correlation of the ALEKS course Florida Math 0028 to the Florida Mathematics Competencies - Upper Exponents & Polynomials MDECU1: Applies the order of operations to evaluate algebraic
Factoring and Applications
 Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
Factoring and Applications What is a factor? The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) To factor a number means to write it as a product (multiplication). Therefore, in the problem 48 3, 4 and 8 are called the
Tool 1. Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
 Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Unit 3: Day 2: Factoring Polynomial Expressions
 Unit 3: Day : Factoring Polynomial Expressions Minds On: 0 Action: 45 Consolidate:10 Total =75 min Learning Goals: Extend knowledge of factoring to factor cubic and quartic expressions that can be factored
Unit 3: Day : Factoring Polynomial Expressions Minds On: 0 Action: 45 Consolidate:10 Total =75 min Learning Goals: Extend knowledge of factoring to factor cubic and quartic expressions that can be factored
Wentzville School District Algebra 1: Unit 8 Stage 1 Desired Results
 Wentzville School District Algebra 1: Unit 8 Stage 1 Desired Results Unit Title: Quadratic Expressions & Equations Course: Algebra I Unit 8 - Quadratic Expressions & Equations Brief Summary of Unit: At
Wentzville School District Algebra 1: Unit 8 Stage 1 Desired Results Unit Title: Quadratic Expressions & Equations Course: Algebra I Unit 8 - Quadratic Expressions & Equations Brief Summary of Unit: At
Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder).
 Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
Mathematics Georgia Performance Standards
 Mathematics Georgia Performance Standards K-12 Mathematics Introduction The Georgia Mathematics Curriculum focuses on actively engaging the students in the development of mathematical understanding by
Mathematics Georgia Performance Standards K-12 Mathematics Introduction The Georgia Mathematics Curriculum focuses on actively engaging the students in the development of mathematical understanding by
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials
 Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
Chapter R.4 Factoring Polynomials Introduction to Factoring To factor an expression means to write the expression as a product of two or more factors. Sample Problem: Factor each expression. a. 15 b. x
Vocabulary Words and Definitions for Algebra
 Name: Period: Vocabulary Words and s for Algebra Absolute Value Additive Inverse Algebraic Expression Ascending Order Associative Property Axis of Symmetry Base Binomial Coefficient Combine Like Terms
Name: Period: Vocabulary Words and s for Algebra Absolute Value Additive Inverse Algebraic Expression Ascending Order Associative Property Axis of Symmetry Base Binomial Coefficient Combine Like Terms
Multiplying and Factoring Notes
 Multiplying/Factoring 3 Multiplying and Factoring Notes I. Content: This lesson is going to focus on wrapping up and solidifying concepts that we have been discovering and working with. The students have
Multiplying/Factoring 3 Multiplying and Factoring Notes I. Content: This lesson is going to focus on wrapping up and solidifying concepts that we have been discovering and working with. The students have
Topic: Special Products and Factors Subtopic: Rules on finding factors of polynomials
 Quarter I: Special Products and Factors and Quadratic Equations Topic: Special Products and Factors Subtopic: Rules on finding factors of polynomials Time Frame: 20 days Time Frame: 3 days Content Standard:
Quarter I: Special Products and Factors and Quadratic Equations Topic: Special Products and Factors Subtopic: Rules on finding factors of polynomials Time Frame: 20 days Time Frame: 3 days Content Standard:
A. Factoring out the Greatest Common Factor.
 DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - FACTORING POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to ingrid.stewart@csn.edu. Thank you!
DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - FACTORING POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to ingrid.stewart@csn.edu. Thank you!
Solving Rational Equations
 Lesson M Lesson : Student Outcomes Students solve rational equations, monitoring for the creation of extraneous solutions. Lesson Notes In the preceding lessons, students learned to add, subtract, multiply,
Lesson M Lesson : Student Outcomes Students solve rational equations, monitoring for the creation of extraneous solutions. Lesson Notes In the preceding lessons, students learned to add, subtract, multiply,
Using Algebra Tiles from Polynomials to Factoring
 Using Algebra Tiles from Polynomials to Factoring For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Chris Mikles (888) 808-4276 mikles@cpm.org CPM Educational Program 203, all
Using Algebra Tiles from Polynomials to Factoring For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Chris Mikles (888) 808-4276 mikles@cpm.org CPM Educational Program 203, all
3.2. Solving quadratic equations. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes. Learning Style
 Solving quadratic equations 3.2 Introduction A quadratic equation is one which can be written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a, b and c are numbers and x is the unknown whose value(s) we wish to find.
Solving quadratic equations 3.2 Introduction A quadratic equation is one which can be written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where a, b and c are numbers and x is the unknown whose value(s) we wish to find.
CORRELATED TO THE SOUTH CAROLINA COLLEGE AND CAREER-READY FOUNDATIONS IN ALGEBRA
 We Can Early Learning Curriculum PreK Grades 8 12 INSIDE ALGEBRA, GRADES 8 12 CORRELATED TO THE SOUTH CAROLINA COLLEGE AND CAREER-READY FOUNDATIONS IN ALGEBRA April 2016 www.voyagersopris.com Mathematical
We Can Early Learning Curriculum PreK Grades 8 12 INSIDE ALGEBRA, GRADES 8 12 CORRELATED TO THE SOUTH CAROLINA COLLEGE AND CAREER-READY FOUNDATIONS IN ALGEBRA April 2016 www.voyagersopris.com Mathematical
Factoring. Factoring Monomials Monomials can often be factored in more than one way.
 Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Click on the links below to jump directly to the relevant section
 Click on the links below to jump directly to the relevant section What is algebra? Operations with algebraic terms Mathematical properties of real numbers Order of operations What is Algebra? Algebra is
Click on the links below to jump directly to the relevant section What is algebra? Operations with algebraic terms Mathematical properties of real numbers Order of operations What is Algebra? Algebra is
AIP Factoring Practice/Help
 The following pages include many problems to practice factoring skills. There are also several activities with examples to help you with factoring if you feel like you are not proficient with it. There
The following pages include many problems to practice factoring skills. There are also several activities with examples to help you with factoring if you feel like you are not proficient with it. There
No Solution Equations Let s look at the following equation: 2 +3=2 +7
 5.4 Solving Equations with Infinite or No Solutions So far we have looked at equations where there is exactly one solution. It is possible to have more than solution in other types of equations that are
5.4 Solving Equations with Infinite or No Solutions So far we have looked at equations where there is exactly one solution. It is possible to have more than solution in other types of equations that are
SOL Warm-Up Graphing Calculator Active
 A.2a (a) Using laws of exponents to simplify monomial expressions and ratios of monomial expressions 1. Which expression is equivalent to (5x 2 )(4x 5 )? A 9x 7 B 9x 10 C 20x 7 D 20x 10 2. Which expression
A.2a (a) Using laws of exponents to simplify monomial expressions and ratios of monomial expressions 1. Which expression is equivalent to (5x 2 )(4x 5 )? A 9x 7 B 9x 10 C 20x 7 D 20x 10 2. Which expression
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions
 6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet
 Name: Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet Date Section Learning Targets Assignment Tues 2/17 Find the prime factorization of an integer Find the greatest common factor (GCF) for a set of monomials.
Name: Factoring Algebra- Chapter 8B Assignment Sheet Date Section Learning Targets Assignment Tues 2/17 Find the prime factorization of an integer Find the greatest common factor (GCF) for a set of monomials.
Lesson 9.1 Solving Quadratic Equations
 Lesson 9.1 Solving Quadratic Equations 1. Sketch the graph of a quadratic equation with a. One -intercept and all nonnegative y-values. b. The verte in the third quadrant and no -intercepts. c. The verte
Lesson 9.1 Solving Quadratic Equations 1. Sketch the graph of a quadratic equation with a. One -intercept and all nonnegative y-values. b. The verte in the third quadrant and no -intercepts. c. The verte
Answers to Basic Algebra Review
 Answers to Basic Algebra Review 1. -1.1 Follow the sign rules when adding and subtracting: If the numbers have the same sign, add them together and keep the sign. If the numbers have different signs, subtract
Answers to Basic Algebra Review 1. -1.1 Follow the sign rules when adding and subtracting: If the numbers have the same sign, add them together and keep the sign. If the numbers have different signs, subtract
Hands-On Math Algebra
 Hands-On Math Algebra by Pam Meader and Judy Storer illustrated by Julie Mazur Contents To the Teacher... v Topic: Ratio and Proportion 1. Candy Promotion... 1 2. Estimating Wildlife Populations... 6 3.
Hands-On Math Algebra by Pam Meader and Judy Storer illustrated by Julie Mazur Contents To the Teacher... v Topic: Ratio and Proportion 1. Candy Promotion... 1 2. Estimating Wildlife Populations... 6 3.
Math 10C. Course: Polynomial Products and Factors. Unit of Study: Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address. Guiding Questions:
 Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
Using the Area Model to Teach Multiplying, Factoring and Division of Polynomials
 visit us at www.cpm.org Using the Area Model to Teach Multiplying, Factoring and Division of Polynomials For more information about the materials presented, contact Chris Mikles mikles@cpm.org From CCA
visit us at www.cpm.org Using the Area Model to Teach Multiplying, Factoring and Division of Polynomials For more information about the materials presented, contact Chris Mikles mikles@cpm.org From CCA
Math Common Core Sampler Test
 High School Algebra Core Curriculum Math Test Math Common Core Sampler Test Our High School Algebra sampler covers the twenty most common questions that we see targeted for this level. For complete tests
High School Algebra Core Curriculum Math Test Math Common Core Sampler Test Our High School Algebra sampler covers the twenty most common questions that we see targeted for this level. For complete tests
CPM Educational Program
 CPM Educational Program A California, Non-Profit Corporation Chris Mikles, National Director (888) 808-4276 e-mail: mikles @cpm.org CPM Courses and Their Core Threads Each course is built around a few
CPM Educational Program A California, Non-Profit Corporation Chris Mikles, National Director (888) 808-4276 e-mail: mikles @cpm.org CPM Courses and Their Core Threads Each course is built around a few
Contents. How You May Use This Resource Guide
 Contents How You May Use This Resource Guide ii 7 Factoring and Algebraic Fractions 1 Worksheet 7.1: The Box Problem......................... 4 Worksheet 7.2: Multiplying and Factoring Polynomials with
Contents How You May Use This Resource Guide ii 7 Factoring and Algebraic Fractions 1 Worksheet 7.1: The Box Problem......................... 4 Worksheet 7.2: Multiplying and Factoring Polynomials with
Big Bend Community College. Beginning Algebra MPC 095. Lab Notebook
 Big Bend Community College Beginning Algebra MPC 095 Lab Notebook Beginning Algebra Lab Notebook by Tyler Wallace is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Permissions beyond
Big Bend Community College Beginning Algebra MPC 095 Lab Notebook Beginning Algebra Lab Notebook by Tyler Wallace is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Permissions beyond
MATH 10034 Fundamental Mathematics IV
 MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:.
 MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
MATH 90 CHAPTER 6 Name:. 6.1 GCF and Factoring by Groups Need To Know Definitions How to factor by GCF How to factor by groups The Greatest Common Factor Factoring means to write a number as product. a
15.1 Factoring Polynomials
 LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
Direct Translation is the process of translating English words and phrases into numbers, mathematical symbols, expressions, and equations.
 Section 1 Mathematics has a language all its own. In order to be able to solve many types of word problems, we need to be able to translate the English Language into Math Language. is the process of translating
Section 1 Mathematics has a language all its own. In order to be able to solve many types of word problems, we need to be able to translate the English Language into Math Language. is the process of translating
is identically equal to x 2 +3x +2
 Partial fractions 3.6 Introduction It is often helpful to break down a complicated algebraic fraction into a sum of simpler fractions. 4x+7 For example it can be shown that has the same value as 1 + 3
Partial fractions 3.6 Introduction It is often helpful to break down a complicated algebraic fraction into a sum of simpler fractions. 4x+7 For example it can be shown that has the same value as 1 + 3
Factoring Flow Chart
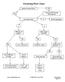 Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Polynomials and Quadratics
 Polynomials and Quadratics Want to be an environmental scientist? Better be ready to get your hands dirty!.1 Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials............703.2 They re Multiplying
Polynomials and Quadratics Want to be an environmental scientist? Better be ready to get your hands dirty!.1 Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials............703.2 They re Multiplying
Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method
 6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
USING ALGEBRA TILES EFFECTIVELY
 MATHEMATICS USING ALGEBRA TILES EFFECTIVELY TOOLS FOR UNDERSTANDING by Bettye C. Hall Reviewers James Gates, Ed.D. Yvonne S. Gentzler, Ph.D. AUTHOR Bettye C. Hall is the former Director of Mathematics
MATHEMATICS USING ALGEBRA TILES EFFECTIVELY TOOLS FOR UNDERSTANDING by Bettye C. Hall Reviewers James Gates, Ed.D. Yvonne S. Gentzler, Ph.D. AUTHOR Bettye C. Hall is the former Director of Mathematics
6706_PM10SB_C4_CO_pp192-193.qxd 5/8/09 9:53 AM Page 192 192 NEL
 92 NEL Chapter 4 Factoring Algebraic Epressions GOALS You will be able to Determine the greatest common factor in an algebraic epression and use it to write the epression as a product Recognize different
92 NEL Chapter 4 Factoring Algebraic Epressions GOALS You will be able to Determine the greatest common factor in an algebraic epression and use it to write the epression as a product Recognize different
Order of Operations More Essential Practice
 Order of Operations More Essential Practice We will be simplifying expressions using the order of operations in this section. Automatic Skill: Order of operations needs to become an automatic skill. Failure
Order of Operations More Essential Practice We will be simplifying expressions using the order of operations in this section. Automatic Skill: Order of operations needs to become an automatic skill. Failure
Gouvernement du Québec Ministère de l Éducation, 2004 04-00813 ISBN 2-550-43545-1
 Gouvernement du Québec Ministère de l Éducation, 004 04-00813 ISBN -550-43545-1 Legal deposit Bibliothèque nationale du Québec, 004 1. INTRODUCTION This Definition of the Domain for Summative Evaluation
Gouvernement du Québec Ministère de l Éducation, 004 04-00813 ISBN -550-43545-1 Legal deposit Bibliothèque nationale du Québec, 004 1. INTRODUCTION This Definition of the Domain for Summative Evaluation
Zero: If P is a polynomial and if c is a number such that P (c) = 0 then c is a zero of P.
 MATH 11011 FINDING REAL ZEROS KSU OF A POLYNOMIAL Definitions: Polynomial: is a function of the form P (x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + + a x + a 1 x + a 0. The numbers a n, a n 1,..., a 1, a 0 are called
MATH 11011 FINDING REAL ZEROS KSU OF A POLYNOMIAL Definitions: Polynomial: is a function of the form P (x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + + a x + a 1 x + a 0. The numbers a n, a n 1,..., a 1, a 0 are called
Linear Equations. 5- Day Lesson Plan Unit: Linear Equations Grade Level: Grade 9 Time Span: 50 minute class periods By: Richard Weber
 Linear Equations 5- Day Lesson Plan Unit: Linear Equations Grade Level: Grade 9 Time Span: 50 minute class periods By: Richard Weber Tools: Geometer s Sketchpad Software Overhead projector with TI- 83
Linear Equations 5- Day Lesson Plan Unit: Linear Equations Grade Level: Grade 9 Time Span: 50 minute class periods By: Richard Weber Tools: Geometer s Sketchpad Software Overhead projector with TI- 83
Learning Objectives 9.2. Media Run Times 9.3
 Unit 9 Table of Contents Unit 9: Factoring Video Overview Learning Objectives 9.2 Media Run Times 9.3 Instructor Notes 9.4 The Mathematics of Factoring Polynomials Teaching Tips: Conceptual Challenges
Unit 9 Table of Contents Unit 9: Factoring Video Overview Learning Objectives 9.2 Media Run Times 9.3 Instructor Notes 9.4 The Mathematics of Factoring Polynomials Teaching Tips: Conceptual Challenges
