page 1 INTRODUCTION A. Role of Kidneys: primarily regulation or homeostasis (rather than excretion)
|
|
|
- Tyrone Barber
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 page 1 INTRODUCTION A. Role of Kidneys: primarily regulation or homeostasis (rather than excretion) 1. Regulation of blood plasma and interstitial fluid composition (homeostasis), especially inorganic ions electrolyte balance (e.g. Na +, K +, Cl -, Ca 2+ ) and osmolality 2. Regulation of body fluid volume -- fluid balance 3. Regulation of blood plasma and interstitial fluid ph 4. Excretion of (non-volatile) metabolic end products (e.g. urea, uric acid, creatinine, NH 4 + ) and foreign solutes (e.g. some drugs) Note: The above are functions are vital; loss of renal function leads to debilitation beginning in about one day and terminating in death in one-two weeks 5. Endocrine organ, secreting a. renin, for regulation of Na +, ECF (extracellular fluid volume), vascular resistance b. erythropoietin, for regulation of erythrocyte production c. calcitriol, related to calcium regulation 6. Metabolic functions: e.g. peptide degradation, synthesis of NH 3 and H + B. General Renal Mechanism of Body Fluid Regulation: Selective withdrawal of substances from the blood plasma flowing through the kidneys and excretion these substances in the urine (main mechanism) Note: When renal function is measured, the values generally refer to both kidneys taken together; e.g. renal blood flow refers to the total blood flow rate through both kidneys, renal sodium excretion rate refers to the total excretion of sodium ion by both kidneys C.. Urine Formation Rate Normal 1 ml/min (1.5 L/day) Normal range ml/min (0.5-3 L/day) Oliguria < 0.4 ml/min (< 0.5 L/day) Anuria < 0.04 ml/min (< 50 ml/day) Polyuria > 2 ml/min (> 3 L/day)
2 page 2 INTRODUCTION (continued) D. Typical Composition of Urine (and Blood Plasma) E. Terms Plasma Urine Na mm/l Cl K HCO glucose 90 (5 mm/l) 0 mg/dl (mg%) plasma proteins 7 0 gm/dl (gm%) urea mg/dl uric acid 5 45 creatinine ph osmolar conc mosm/kg (Note: mg/dl = mg solute per 100 ml fluid; mg/dl = mg%) Plasma has a relatively constant composition Urine composition is variable in order to maintain homeostasis renal nephronephritis nephrology -uria glucosuria albuminuria anuria urology -emia uremia diuresis water diuresis osmotic diuresis diuretic refers to kidney refers to kidney or its functional unit (nephron) inflammation of the kidney medical specialty dealing with the kidney refers to urine composition or volume presence of glucose in the urine presence of albumin in urine no urine formation surgical specialty dealing with the urinary tract refers to blood high concentration of urea in blood plasma excretion of a large volume of urine excretion of a large volume of dilute urine excretion of a large volume of normal or high osmolarity a substance that causes diuresis diabetes certain diseases characterized by diuresis diabetes mellitus diuresis characterized by glucose containing urine diabetes insipidus diuresis characterized by dilute urine Clearance Volume of blood cleared of a substance by the kidneys per unit time (e.g. Na clearance, K clearance, glucose clearance)
3 page 3 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE RENAL SYSTEM A. Kidneys 1. Paired organs, located in the abdominal cavity just below the diaphragm 2. Supplied with blood by renal artery; after passing through the kidney, blood is returned to the heart by the renal vein 3. Forms urine, which is transported by the ureter to the bladder; excreted from the body at suitable intervals via the urethra (micturition reflex) Note: the ureter, bladder, and urethra do not change the composition of urine; when urine leaves the kidney, its composition is fixed 4. Divided into cortex (outer) and medulla (inner) regions B. Nephron 1. Functional unit: nephron (about one million per kidney); nephron divided into a. glomerular region (renal corpuscle) 1) glomerulus (capillary tuft) 2) Bowman's capsule (blind end of the nephron) b. proximal convoluted and straight tubule c. loop of Henle; dips deeply (juxtamedullary nephron) or slightly (cortical nephron) into the medulla; each has thick and thin segments 1) descending limb 2) hairpin turn 3) ascending limb Note: cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons are distinguished by the cortical location of their glomeruli and the depth to which their loops of Henle penetrate into the medulla d. distal convoluted and straight tubule e. collecting tubule/duct
4 page 4 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (continued) B. Nephron (continued) C. Vascular Bed
5 page 5 RENAL BLOOD FLOW A. Functional Anatomy of Microcirculation 1. Portal system (capillary beds in series), paralleling the nephron B. Values renal ==> afferent ==> glomerular ==> efferent ==> proximal peritubular ==> arteries arterioles capillaries arterioles capillaries vasa ==> distal peritubular ==> collecting duct ==> renal venules recta capillaries capillaries and veins 1. Normal (resting) blood flow: 1.2 L/min (20-25% of cardiac output) Normal (resting) plasma flow: 650 ml/min Note: the high blood flow is required to furnish the kidney with sufficient plasma for filtration, reabsorption, etc. 2. Range: the highest renal blood flow occurs at rest; progressively increasing activity or stress progressively reduces renal blood flow; under extreme conditions (e.g. shock), renal blood flow can be reduced to almost zero C. Control 1. Autonomic: major normal influence on renal blood flow a. sympathetic vasoconstrictors: very effective b. adrenal medulla: reinforces direct sympathetic constriction Note 1: The above contribute to the reduction of renal blood flow in stress Note 2: Although the nerves innervating the kidney aid in regulation of renal blood flow and renal transport, they are not essential for normal renal function Note 3: At sufficiently low systemic arterial pressure, renal blood flow can be reduced to levels compromising renal function and even kidney survival
6 page 6 GLOMERULAR FILTRATION A. Role: formation of the initial fluid entering the nephron B. Composition of the glomerular filtrate: ultrafiltrate of plasma, due to size-selective filtration: nonselectively permeable to small particles but not very permeable to larger particles, such as blood cells and plasma proteins C. Mechanism: passive filtration 1. Forces: hydrostatic pressure determined by renal arterial and venous pressures, and by vasomotor state of afferent and efferent arterioles; osmotic pressure determined by plasma protein concentration Because of the resistance of the efferent arterioles, the hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries is higher than in most other capillaries and the hydrostatic pressure difference forcing fluid out of the capillaries is greater than the osmotic pressure difference attracting fluid back into the capillaries, or ΔP > Δπ Renal Artery afferent arteriole P = 50 mmhg π = 25 mmhg P = 48 π = 31 glomerular capillary GLOMERULAR FILTRATION P = 17 mmhg π = 0 mmhg proximal tubule peritubular capillary P = 10 mmhg efferent arteriole D. Glomerular Filtration Rate 1. Normal value: ml/min (for 70 kg human)
7 page 7 PROXIMAL TUBULE TRANSPORT A. Role: Initial adjustment of tubular fluid by reabsorption (main mechanism) and by secretion Reabsorption: Transport from tubular lumen to peritubular capillary blood Secretion: Transport from peritubular capillary blood into the tubular lumen B. Active Reabsorption (direct active transport and cotransport secondary active transport, symport) 1. Based on Na + active transport (actually Na-K-ATPase) pump at the interstitial (baso-lateral) cell membrane (leading to low intracellular Na + ), and carrier-mediated cotransport at the luminal (apical) membrane powered by the Na + luminal-intracellular concentration gradient 2. Substances actively reabsorbed compared with the amount filtered; reabsorbed mainly by the transcellular pathway (through cells) Sodium ion Glucose Amino acids Plasma proteins about 70% (60-80%, including passive component) complete; cotransported with sodium complete; cotransported with sodium complete (only small amount filtered) C. Passive Reabsorption: due to concentrating effect of active reabsorption followed by water reabsorption Chloride ion Bicarbonate ion Potassium ion Urea Water paracellular variable (depends in part on H + secretion) most or all about 40% (because of limited permeability) about 70% (60-80%) (due to osmotic effect of particle reabsorption plus tubule-peritubular capillary pressure difference)
8 page 8 PROXIMAL TUBULE TRANSPORT (continued) C. Passive Reabsorption (continued) Mechanism: Active particle reabsorption (particularly Na + ) creates a small osmotic gradient between the luminal fluid and the spaces between tubule cells on the interstitial surface. The osmotic gradient causes water to be reabsorbed because the proximal tubule is very permeable to water. The water reabsorption concentrates the remaining dissolved substances (including Na + ), and, if they are readily permeable, the resulting concentration gradient leads to their reabsorption at about the same rate as water. Note: The above mechanism maintains proximal tubule fluid approximately iso-osmotic with plasma D. Active Secretion 1. Mechanism: cotransport with Na + ion reabsorption (antiport) 2. Substances secreted, e.g. Exogenous (introduced from outside the body) Para-aminohippurate (PAH) Certain pharmacological agents (e.g. penicillin) Endogenous (produced within the body) Hydrogen ion (Na + antiport) E. No Transport (neither reabsorption nor secretion) 1. Not actively transported and tubule impermeable to diffusion Creatinine (endogenous protein metabolism product) Note: Creatinine clearance can be used as an index of glomerular function
9 page 9 PROXIMAL TUBULE TRANSPORT (continued) Summary: Entering the proximal tubule at a rate of about 120 ml/min is an ultrafiltrate of blood plasma. As a direct or indirect consequence of active transport, about 70% of the amount filtered is reabsorbed and returned to the body by way of the peritubular capillaries and renal veins. Since the proximal tubule is quite permeable to water, the tubular fluid remains iso-osmotic to plasma, but its composition is changed (e.g. no glucose, higher urea and creatinine concentrations, about the same sodium and chloride concentrations). The remaining fluid leaves the proximal tubule and enters the loop of Henle at a rate of about ml/min. F. Tubular Transport Maximum [T m ]: For many substances transported by carriers (active transport or facilitated diffusion), there exists some maximum rate for their transport; this is termed their tubular transport maximum or T m Examples: Glucosuria in diabetes mellitus Albuminurea in nephritis LOOP OF HENLE (& INITIAL DISTAL TUBULE) TRANSPORT A. Role: establishes an appropriate osmotic environment for the adjustment of fluid balance B. Active Reabsorption Sodium ion Chloride ion about 75% of amount entering loop about 70% of amount entering C. Passive Reabsorption Water about 25% of amount entering D. No Transport Creatinine
10 page 10 LOOP OF HENLE TRANSPORT (continued) Summary: Because the reabsorption of sodium and chloride (the major dissolved substances) is much more rapid than the reabsorption of water, the tubular fluid becomes quite hypo-osmotic (to about one-third the osmolality of plasma). Thus, a hypo-osmotic fluid leaves the loop of Henle (and enters the distal tubule) at the rate of about 20 ml/min. COLLECTING TUBULES/DUCT TRANSPORT A. Role: Final adjustment of the fluid to be excreted in order to maintain homeostasis B. Reabsorption (variable) 1. Active transport Na + Cl - osmotic and electrolyte balance osmotic and electrolyte balance 2. Passive electrochemical diffusion or osmosis urea H 2 O body fluid balance osmotic and body fluid balance 3. Associated with renal metabolism HCO 3 - acid-base balance C. Secretion (variable) 1. Active transport K + H + electrolyte balance acid-base balance 2. Associated with renal metabolism NH 4 + acid-base balance D. No Transport 1. Tubule impermeable creatinine Summary: leaving the collecting duct (to be excreted as urine) is a fluid of varying composition, varying osmolality (hyper-, hypo-, or iso-osmotic), varying ph, and varying volume (0.2 to 20 ml/min), as required to satisfy homeostasis.
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION
 LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science
 Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Chapter 26: The Urinary System
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
RENAL WATER REGULATION page 1
 page 1 INTRODUCTION TO WATER EXCRETION A. Role of the Kidney: to adjust urine formation rate and urine concentration to maintain 1. body fluid osmolar concentration 2. body fluid volume 3. intravascular
page 1 INTRODUCTION TO WATER EXCRETION A. Role of the Kidney: to adjust urine formation rate and urine concentration to maintain 1. body fluid osmolar concentration 2. body fluid volume 3. intravascular
Select the one that is the best answer:
 MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Body Fluids. Physiology of Fluid. Body Fluids, Kidneys & Renal Physiology
 Pc Remember arterioles have more smooth muscle So SNS effects are greater on arterioles than on venules Net effects: SNS P c (vasoconstriction > venoconstriction) SNS P c (vasodilation > venodilation)
Pc Remember arterioles have more smooth muscle So SNS effects are greater on arterioles than on venules Net effects: SNS P c (vasoconstriction > venoconstriction) SNS P c (vasodilation > venodilation)
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
CHAPTER 20: URINARY SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
Urinary System. And Adrenal Function
 Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 15. The Urinary System. Slides 15.1 15.20. Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II
 Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II I. Effects of blood volume on the filtration fraction (FF) {Altered Volume Effects in syllabus A. Under normal conditions, ~20% of renal plasma flow becomes
Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II I. Effects of blood volume on the filtration fraction (FF) {Altered Volume Effects in syllabus A. Under normal conditions, ~20% of renal plasma flow becomes
Kidney Structure and Function.
 Kidney Structure and Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this section, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of the kidney; 2. understand the vascular organisation of the kidneys;
Kidney Structure and Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this section, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of the kidney; 2. understand the vascular organisation of the kidneys;
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - PART 1 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 273 5 th NOVEMBER 2012 Dr Matthew Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Dr Jennifer Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Correspondence to: mgwinnutt@doctors.org.uk
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - PART 1 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 273 5 th NOVEMBER 2012 Dr Matthew Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Dr Jennifer Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Correspondence to: mgwinnutt@doctors.org.uk
Components. Urinary System. Formation of Urine. Functions of Kidney. Pathway of Urine. Kidney. Major functions of the kidneys include:
 Components Urinary System To Accompany: Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Components Urinary System To Accompany: Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function
 Objectives 1. Understand the roles of the kidney 2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function 3. Begin to appreciate the inter-dependence of regulatory mechanisms
Objectives 1. Understand the roles of the kidney 2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function 3. Begin to appreciate the inter-dependence of regulatory mechanisms
Kidneys, Nephrons, and Urine Production
 Valerie ovelace Kidneys, Nephrons, and rine Production Part of the urinary system, our kidneys are vital organs that serve to remove waste from the bloodstream through ultrafiltration and the formation
Valerie ovelace Kidneys, Nephrons, and rine Production Part of the urinary system, our kidneys are vital organs that serve to remove waste from the bloodstream through ultrafiltration and the formation
Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus!
 Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Urinary System Components:! -Kidneys! -Ureters! -Urinary Bladder!! -Urethra!
Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Urinary System Components:! -Kidneys! -Ureters! -Urinary Bladder!! -Urethra!
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal
 Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases
 Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function
 Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function I. Functions of the kidney A. Maintaining homeostasis of a large number of solutes and water is the main job of the kidney. Total body contents
Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function I. Functions of the kidney A. Maintaining homeostasis of a large number of solutes and water is the main job of the kidney. Total body contents
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 3)
 Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 3) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 27. Effect of Hypoventilation Now let's look at how the
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 3) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 27. Effect of Hypoventilation Now let's look at how the
Chapter 23. Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration
 Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
Renal Blood Flow GFR. Glomerulus Fluid Flow and Forces. Renal Blood Flow (cont d)
 GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
Water Homeostasis. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Acid-Base Balance and Renal Acid Excretion
 AcidBase Balance and Renal Acid Excretion Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Cite the basic principles of acidbase physiology. 2. Understand the bicarbonatecarbon dioxide
AcidBase Balance and Renal Acid Excretion Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Cite the basic principles of acidbase physiology. 2. Understand the bicarbonatecarbon dioxide
UNIT 11 - URINARY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 11 - URINARY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 11.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM A. Regulate the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. B. Excretes
UNIT 11 - URINARY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 11.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM A. Regulate the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. B. Excretes
23. The Urinary System Text The McGraw Hill Companies, 2003 CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 The kidneys (green), ureters, and urinary bladder (red) of a healthy person (colorized X ray) The Urinary System CHAPTER OUTLINE Functions of the Urinary System 880 Functions of the Kidneys
CHAPTER 23 The kidneys (green), ureters, and urinary bladder (red) of a healthy person (colorized X ray) The Urinary System CHAPTER OUTLINE Functions of the Urinary System 880 Functions of the Kidneys
THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM 2012
 THE URINARY SYSTEM KIDNEYS A. Location: a. under the back muscles b. behind the parietal peritoneum c. just above the waistline d. right kidney a little lower than the left B. internal structure a. cortex:
THE URINARY SYSTEM KIDNEYS A. Location: a. under the back muscles b. behind the parietal peritoneum c. just above the waistline d. right kidney a little lower than the left B. internal structure a. cortex:
Quiz Urinary System. 1. The kidneys help regulate blood volume. help control blood pressure. help control ph. All of the above are correct.
 Quiz Urinary System 1. The kidneys help regulate blood volume. help control blood pressure. help control ph. All of the above are correct. 2. The location of the kidneys in relationship to the peritoneal
Quiz Urinary System 1. The kidneys help regulate blood volume. help control blood pressure. help control ph. All of the above are correct. 2. The location of the kidneys in relationship to the peritoneal
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Dr. Johnson PA Renal Winter 2010
 1 Renal Control of Acid/Base Balance Dr. Johnson PA Renal Winter 2010 Acid/Base refers to anything having to do with the concentrations of H + ions in aqueous solutions. In medical physiology, we are concerned
1 Renal Control of Acid/Base Balance Dr. Johnson PA Renal Winter 2010 Acid/Base refers to anything having to do with the concentrations of H + ions in aqueous solutions. In medical physiology, we are concerned
CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM. At the end of this chapter, student will be able to:
 CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM At the end of this chapter, student will be able to: a) Describe the location and general function of each organ of the urinary system. b) Name the parts of a nephron and the
CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM At the end of this chapter, student will be able to: a) Describe the location and general function of each organ of the urinary system. b) Name the parts of a nephron and the
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS (Continued)
 ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS (Continued) Osmolarity Osmotic pressure is an important biologic parameter which involves diffusion of solutes or the transfer of fluids through semi permeable membranes. Per US Pharmacopeia,
ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS (Continued) Osmolarity Osmotic pressure is an important biologic parameter which involves diffusion of solutes or the transfer of fluids through semi permeable membranes. Per US Pharmacopeia,
AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR
 AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR Renal Anatomy Renal Artery & Veins 6 cm 3cm Cortex 11cm Pelvis of the ureter Capsule Ureter To the bladder Medulla Medulary Pyramid Renal Anatomy and Physiology
AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR Renal Anatomy Renal Artery & Veins 6 cm 3cm Cortex 11cm Pelvis of the ureter Capsule Ureter To the bladder Medulla Medulary Pyramid Renal Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar (v.khullar@imperial.ac.uk)
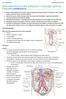 Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar (v.khullar@imperial.ac.uk) 1. Draw a simple diagram of the urinary system including the following: kidney, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder,
Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar (v.khullar@imperial.ac.uk) 1. Draw a simple diagram of the urinary system including the following: kidney, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder,
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney --Overview of Kidney Function a. Regulation of blood ionic composition b. Regulation of blood ph and osmolarity c. Regulate blood glucose level (gluconeogenesis) d.
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney --Overview of Kidney Function a. Regulation of blood ionic composition b. Regulation of blood ph and osmolarity c. Regulate blood glucose level (gluconeogenesis) d.
Drug Excretion. Renal Drug Clearance. Drug Clearance and Half-Life. Glomerular Filtration II. Glomerular Filtration I. Drug Excretion and Clearance
 t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
Renal Acid/Base. Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 H+ Balance... 2
 Renal Acid/Base By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 H+ Balance... 2 Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 Role of Kidneys in Acid- Base Homeostasis... 3 Renal H+ Secretion... 3 Proximal
Renal Acid/Base By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 H+ Balance... 2 Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 Role of Kidneys in Acid- Base Homeostasis... 3 Renal H+ Secretion... 3 Proximal
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Excretory Physiology
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
The kidneys play a dominant role in regulating the composition
 PART VI RENAL PHYSIOLOGY AND BODY FLUIDS C H A P T E R 22 Kidney Function George A. Tanner, Ph.D. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon mastering the material in this chapter you should be able to: Summarize the functions
PART VI RENAL PHYSIOLOGY AND BODY FLUIDS C H A P T E R 22 Kidney Function George A. Tanner, Ph.D. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon mastering the material in this chapter you should be able to: Summarize the functions
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology
 Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology 1 Kidney Anatomy and Function (Lecture 1) 2 Functions of Kidney A) Regulation of water B) Regulation of electrolytes C) Acid-base
Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology 1 Kidney Anatomy and Function (Lecture 1) 2 Functions of Kidney A) Regulation of water B) Regulation of electrolytes C) Acid-base
Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus
 Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus In order to workout this problem, study pages 240 6, 249 51, 318 9, 532 3 and 886 7 of the Pathophysiology, 5 th Edition. (This problem was based on
Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus In order to workout this problem, study pages 240 6, 249 51, 318 9, 532 3 and 886 7 of the Pathophysiology, 5 th Edition. (This problem was based on
The Urinary System. Anatomy of Urinary System. Urine production and elimination are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis
 The Urinary System Urine production and elimination are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis all body systems are directly or indirectly affected by kidney function eg. composition
The Urinary System Urine production and elimination are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis all body systems are directly or indirectly affected by kidney function eg. composition
The Urinary System Urine (pp. 984 985)
 Kidney Anatomy (pp. 961 969) Location and External Anatomy (pp. 961 962) Internal Anatomy (pp. 962 963) Blood and Nerve Supply (pp. 963 964) Nephrons (pp. 964 969) Kidney Physiology: Mechanisms of Urine
Kidney Anatomy (pp. 961 969) Location and External Anatomy (pp. 961 962) Internal Anatomy (pp. 962 963) Blood and Nerve Supply (pp. 963 964) Nephrons (pp. 964 969) Kidney Physiology: Mechanisms of Urine
Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap
 Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap 1. The body strives for electrical neutrality. a. Cations = Anions b. One of the cations is very special, H +, and its concentration is monitored and regulated very
Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap 1. The body strives for electrical neutrality. a. Cations = Anions b. One of the cations is very special, H +, and its concentration is monitored and regulated very
The first vertebrates evolved in seawater, and the physiology
 58 Maintaining the Internal Environment Concept Outline 58.1 The regulatory systems of the body maintain homeostasis. The Need to Maintain Homeostasis. Regulatory mechanisms maintain homeostasis through
58 Maintaining the Internal Environment Concept Outline 58.1 The regulatory systems of the body maintain homeostasis. The Need to Maintain Homeostasis. Regulatory mechanisms maintain homeostasis through
Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia
 Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia Case Presentation: History 62 y/o male is admitted to the hospital with a 3 month history of excessive urination (polyuria) and excess water intake up to
Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia Case Presentation: History 62 y/o male is admitted to the hospital with a 3 month history of excessive urination (polyuria) and excess water intake up to
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 4)
 Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 4) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 5. The newly formed bicarbonate moves into the plasma.
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 4) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 5. The newly formed bicarbonate moves into the plasma.
The Kidneys: Structure, Function, Disorders
 The Kidneys: Structure, Function, Disorders by John H. Dirckx, M.D. Everyone knows that the heart, the lungs, and the brain are vital organs that is, that their absence or destruction is incompatible with
The Kidneys: Structure, Function, Disorders by John H. Dirckx, M.D. Everyone knows that the heart, the lungs, and the brain are vital organs that is, that their absence or destruction is incompatible with
Fluid, Electrolyte & ph Balance
 , Electrolyte & ph Balance / Electrolyte / AcidBase Balance Body s: Cell function depends not only on continuous nutrient supply / waste removal, but also on the physical / chemical homeostasis of surrounding
, Electrolyte & ph Balance / Electrolyte / AcidBase Balance Body s: Cell function depends not only on continuous nutrient supply / waste removal, but also on the physical / chemical homeostasis of surrounding
This article reviews the role of the kidneys in the regulation of acid-base balance. It
 RENAL REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE Bruce M. Koeppen Departments of Medicine and Physiology, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, Connecticut 06030 This article reviews the role
RENAL REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE Bruce M. Koeppen Departments of Medicine and Physiology, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, Connecticut 06030 This article reviews the role
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
ACID-BASE BALANCE AND ACID-BASE DISORDERS. I. Concept of Balance A. Determination of Acid-Base status 1. Specimens used - what they represent
 ACID-BASE BALANCE AND ACID-BASE DISORDERS I. Concept of Balance A. Determination of Acid-Base status 1. Specimens used - what they represent II. Electrolyte Composition of Body Fluids A. Extracellular
ACID-BASE BALANCE AND ACID-BASE DISORDERS I. Concept of Balance A. Determination of Acid-Base status 1. Specimens used - what they represent II. Electrolyte Composition of Body Fluids A. Extracellular
FIGURE 2.18. A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged) and hydrophilic (attracted to water).
 PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. The plasma membrane is the outermost part of a cell. 2. The main component of the plasma membrane is phospholipids. FIGURE 2.18 A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged)
PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. The plasma membrane is the outermost part of a cell. 2. The main component of the plasma membrane is phospholipids. FIGURE 2.18 A. The phosphate end of the molecule is polar (charged)
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology)
 Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology) ١ University/ Academy: Al-Azhar University Faculty/ Institute: Faculty of Medicine (Assuit) Department: physiology Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology)
Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology) ١ University/ Academy: Al-Azhar University Faculty/ Institute: Faculty of Medicine (Assuit) Department: physiology Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology)
REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE
 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 1 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE The kidney is the primary organ that maintains the total volume, ph, and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid within
REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 1 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE The kidney is the primary organ that maintains the total volume, ph, and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid within
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
References below to Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 9th Edition, 1996 are denoted as G&H.
 Osmolarity References below to Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 9th Edition, 1996 are denoted as G&H. The osmolarity of body fluids is an important part of many physiological responses.
Osmolarity References below to Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 9th Edition, 1996 are denoted as G&H. The osmolarity of body fluids is an important part of many physiological responses.
2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC
 Renal Function Tests WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed December, 2015, Expires December, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Renal Function Tests WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed December, 2015, Expires December, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance
 Distribution of Body Fluids Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Total body fluids=60% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Comp 20% of Total body wt. Interstitial= 15% of total body wt. Intravascular=5%
Distribution of Body Fluids Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Total body fluids=60% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Comp 20% of Total body wt. Interstitial= 15% of total body wt. Intravascular=5%
Total body water ~(60% of body mass): Intracellular fluid ~2/3 or ~65% Extracellular fluid ~1/3 or ~35% fluid. Interstitial.
 http://www.bristol.ac.uk/phys-pharm/teaching/staffteaching/sergeykasparov.htmlpharm/teaching/staffteaching/sergeykasparov.html Physiology of the Cell Membrane Membrane proteins and their roles (channels,
http://www.bristol.ac.uk/phys-pharm/teaching/staffteaching/sergeykasparov.htmlpharm/teaching/staffteaching/sergeykasparov.html Physiology of the Cell Membrane Membrane proteins and their roles (channels,
Week 30. Water Balance and Minerals
 Week 30 Water Balance and Minerals Water: more vital to life than food involved in almost every body function is not stored--excreted daily largest single constituent of the human body, averaging 60% of
Week 30 Water Balance and Minerals Water: more vital to life than food involved in almost every body function is not stored--excreted daily largest single constituent of the human body, averaging 60% of
Modes of Membrane Transport
 Modes of Membrane Transport Transmembrane Transport movement of small substances through a cellular membrane (plasma, ER, mitochondrial..) ions, fatty acids, H 2 O, monosaccharides, steroids, amino acids
Modes of Membrane Transport Transmembrane Transport movement of small substances through a cellular membrane (plasma, ER, mitochondrial..) ions, fatty acids, H 2 O, monosaccharides, steroids, amino acids
KIDNEY Locate the following structures on the sheep kidney and human kidney models:
 Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Syre-base regulering og bikarbonat
 Syrebase regulering og bikarbonat Peter Bie Institut for Molekylær Medicin Syddansk Universitet, Odense The (only) example of acidbase metabolism in normal man H + 80 Nonorganic acids 80 NH 3 Organic ions
Syrebase regulering og bikarbonat Peter Bie Institut for Molekylær Medicin Syddansk Universitet, Odense The (only) example of acidbase metabolism in normal man H + 80 Nonorganic acids 80 NH 3 Organic ions
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer. α-helix transmembrane domain. Multiple transmembrane helices in one polypeptide
 Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer α-helix transmembrane domain Hydrophobic R groups of a.a. interact with fatty acid chains Multiple transmembrane helices in one polypeptide Polar a.a. Hydrophilic
Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer α-helix transmembrane domain Hydrophobic R groups of a.a. interact with fatty acid chains Multiple transmembrane helices in one polypeptide Polar a.a. Hydrophilic
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Acute Renal Failure. usually a consequence.
 Acute Renal Failure usually a consequence www.philippelefevre.com Definitions Pathogenisis Classification ICU Incidence/ Significance Treatments Prerenal Azotaemia Blood Pressure Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors
Acute Renal Failure usually a consequence www.philippelefevre.com Definitions Pathogenisis Classification ICU Incidence/ Significance Treatments Prerenal Azotaemia Blood Pressure Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors
Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes
 : 204 : Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes 27 Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes We can live without food for several days but we cannot live without breathing
: 204 : Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes 27 Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes We can live without food for several days but we cannot live without breathing
DIALYSIS COMPACT. The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney.
 DIALYSIS COMPACT The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney. Content 3 Editorial 4 What do healthy kidneys accomplish? 5 What causes kidney disease? 6 What effects does kidney disease have?
DIALYSIS COMPACT The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney. Content 3 Editorial 4 What do healthy kidneys accomplish? 5 What causes kidney disease? 6 What effects does kidney disease have?
ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE. MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011
 ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011 ACID- BASE BALANCE Ions balance themselves like a see-saw. Solutions turn into acids when concentration of hydrogen ions rises
ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011 ACID- BASE BALANCE Ions balance themselves like a see-saw. Solutions turn into acids when concentration of hydrogen ions rises
Metabolic alkalosis. ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc
 Metabolic alkalosis ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Case History 28-year-old male Discovered by roommate at home in bewildering state During transport by EMS possible tonicclonic seizure Arrival in
Metabolic alkalosis ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Case History 28-year-old male Discovered by roommate at home in bewildering state During transport by EMS possible tonicclonic seizure Arrival in
Cell Membrane Structure (and How to Get Through One)
 Cell Membrane Structure (and How to Get Through One) A cell s membrane is a wall of sorts that defines the boundaries of a cell. The membrane provides protection and structure for the cell and acts as
Cell Membrane Structure (and How to Get Through One) A cell s membrane is a wall of sorts that defines the boundaries of a cell. The membrane provides protection and structure for the cell and acts as
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
Dehydration & Overhydration. Waseem Jerjes
 Dehydration & Overhydration Waseem Jerjes Dehydration 3 Major Types Isotonic - Fluid has the same osmolarity as plasma Hypotonic -Fluid has fewer solutes than plasma Hypertonic-Fluid has more solutes than
Dehydration & Overhydration Waseem Jerjes Dehydration 3 Major Types Isotonic - Fluid has the same osmolarity as plasma Hypotonic -Fluid has fewer solutes than plasma Hypertonic-Fluid has more solutes than
Absorption of Drugs. Transport of a drug from the GI tract
 Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯
 The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
Compound extracted from plant Aristolochia. Nephrotoxin and carcinogen. Page 2
 Mariana Babayeva MD, PhD Touro College of Pharmacy, New York, NY, USA Page 1 Compound extracted from plant Aristolochia Nephrotoxin and carcinogen Page 2 AA-I is an organic anion eliminated by the kidney
Mariana Babayeva MD, PhD Touro College of Pharmacy, New York, NY, USA Page 1 Compound extracted from plant Aristolochia Nephrotoxin and carcinogen Page 2 AA-I is an organic anion eliminated by the kidney
Sodium. 1 Name and description of analyte. 1.1 Name of analyte Sodium (serum, plasma, whole blood and urine)
 Sodium 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Sodium (serum, plasma, whole blood and urine) 1.2 Alternative names: none Chemical symbol: Na (from the Latin, Natrium) 1.3 NLMC code: to follow
Sodium 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Sodium (serum, plasma, whole blood and urine) 1.2 Alternative names: none Chemical symbol: Na (from the Latin, Natrium) 1.3 NLMC code: to follow
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Interpretation Of Renal Function Tests and The Renal Effects of Lithium. John Collins (April 2014)
 Interpretation Of Renal Function Tests and The Renal Effects of Lithium John Collins (April 2014) Causes of Kidney disease Diabetes Glomerulonephritis Genetic disorders- Polycystic kidney disease Causes
Interpretation Of Renal Function Tests and The Renal Effects of Lithium John Collins (April 2014) Causes of Kidney disease Diabetes Glomerulonephritis Genetic disorders- Polycystic kidney disease Causes
THE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION AND THE URINARY SYSTEM. 156 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics
 56 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics The Urinary System The urinary system consists of the kidneys, where urine production occurs, and the conducting system that transports and stores urine
56 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics The Urinary System The urinary system consists of the kidneys, where urine production occurs, and the conducting system that transports and stores urine
Oedema: causes, physiology and nursing management
 CONTINUING PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT By reading this article and writing a practice profile, you can gain a certificate of learning. You have up to a year to send in your practice profile. Guidelines on
CONTINUING PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT By reading this article and writing a practice profile, you can gain a certificate of learning. You have up to a year to send in your practice profile. Guidelines on
MEMBRANE FUNCTION CELLS AND OSMOSIS
 CELLS AND OSMOSIS MEMBRANE FUNCTION Consider placing a cell in a beaker of pure water (Fig. 1). The cell contains a water solution with many different kinds of dissolved molecules and ions so that it is
CELLS AND OSMOSIS MEMBRANE FUNCTION Consider placing a cell in a beaker of pure water (Fig. 1). The cell contains a water solution with many different kinds of dissolved molecules and ions so that it is
4. Biology of the Cell
 4. Biology of the Cell Our primary focus in this chapter will be the plasma membrane and movement of materials across the plasma membrane. You should already be familiar with the basic structures and roles
4. Biology of the Cell Our primary focus in this chapter will be the plasma membrane and movement of materials across the plasma membrane. You should already be familiar with the basic structures and roles
PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement)
 1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
Intravenous Fluid Selection
 BENNMC03_0131186116.qxd 3/9/05 18:24 Page 20 seema Seema-3:Desktop Folder:PQ731: CHAPTER 3 Intravenous Fluid Selection LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and
BENNMC03_0131186116.qxd 3/9/05 18:24 Page 20 seema Seema-3:Desktop Folder:PQ731: CHAPTER 3 Intravenous Fluid Selection LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and
