Acute Renal Failure. usually a consequence.
|
|
|
- Beverley Barber
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acute Renal Failure usually a consequence
2 Definitions Pathogenisis Classification ICU Incidence/ Significance Treatments
3 Prerenal Azotaemia Blood Pressure Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors RBF GRF Intrarenal Baroreceptors Sympathetic Drive afferent vasodilatation autoregulation NaCl delivery to Macula Densa Renin
4 Prerenal Azotaemia Blood Pressure Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors RBF GRF Intrarenal Baroreceptors Sympathetic Drive afferent vasodilatation autoregulation GFR = permeability x surface area x net filtration pressure NaCl delivery Plasma to Urea & Creatinine GFR Macula Densa Renin
5 Prerenal Azotaemia Blood Pressure Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors RBF GRF Intrarenal Baroreceptors Sympathetic Drive afferent vasodilatation autoregulation NaCl delivery to Macula Densa Renin
6 angiotensinogen angiotensin I ACE Renin angiotensin II ADH & ACTH vasoconstriction aldosterone noradrenalin reuptake
7 angiotensinogen angiotensin I ACE Renin angiotensin II ADH & ACTH vasoconstriction aldosterone noradrenalin reuptake Salt Retention
8 Prerenal Azotaemia Prerenal Azotaemia Urine Osmolality (mosm/kg) >500 Urine Sodium (mmol/l) <20 Urine/ Plasma Creatinine ratio >40 FENa <1% FEUrea <35% Urinary Sediment occasional hyaline or fine granular casts
9 Pathogenesis: Vascular Factors Cortex 70% O2 requirement 90% Blood supply Medulla 30% O2 requirement 10% Blood supply
10 Pathogenesis: Vascular Factors Cortex 70% O2 requirement 90% Blood supply Renal Blood Flow Oxygen Demand Medulla 30% O2 requirement 10% Blood supply
11 Pathogenesis: Vascular Factors Cortex 70% O2 requirement 90% Blood supply Renal Blood Flow Oxygen Demand Medulla 30% O2 requirement 10% Blood supply Ischaemia
12 Pathogenesis: Vascular Factors Cortex 70% O2 requirement 90% Blood supply Renal Blood Flow Oxygen Demand Medulla 30% O2 requirement 10% Blood supply Ischaemia Intracellular Calcium Loss of Autoregulation
13 Pathogenisis: Vascular Factors Blood Pressure Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors RBF GRF Intrarenal Baroreceptors Sympathetic Drive afferent vasodilatation autoregulation NaCl delivery to Macula Densa Renin
14 Pathogenisis: Vascular Factors Blood Pressure Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors RBF GRF Intrarenal Baroreceptors Sympathetic Drive afferent vasoconstriction NaCl delivery to Macula Densa Renin
15 Acute Renal Failure Prerenal Azotaemia Urine Osmolality (mosm/kg) >500 Urine Sodium (mmol/l) <20 Urine/ Plasma Creatinine ratio >40 FENa <1% FEUrea <35% Urinary Sediment occasional hyaline or fine granular casts
16 Acute Renal Failure Prerenal Azotaemia Acute Renal failure Urine Osmolality (mosm/kg) >500 <400 Urine Sodium (mmol/l) <20 >40 Urine/ Plasma Creatinine ratio >40 <40 FENa <1% >2% FEUrea <35% >35% Urinary Sediment occasional hyaline or fine granular casts tubular cells, coarse granular casts
17 Pathogenesis: Tubular Factors Na/K ATPase
18 Pathogenesis: Tubular Factors Loss of Brush Border Loss of Polarity Na/K ATPase
19 Pathogenesis: Tubular Factors Loss of Brush Border Loss of Polarity Na/K ATPase
20 Pathogenesis: Tubular Factors Sloughing of Viable Epithelial Cells Necrosis Na/K ATPase
21 Pathogenesis: Tubular Factors Sloughing of Viable Epithelial Cells Necrosis Inflammatory Infiltration Na/K ATPase
22 Pathogenesis: Tubular Factors Kidney stem cells Adjacent tubule cells Haematopoietic cells Na/K ATPase
23 Pathogenesis: Tubular Factors Na/K ATPase
24 Pathogenesis: Summary Initiation Prerenal azotaemia Loss of autoregulation Intracellular calcium ATD Depletion Oxidative injury Extension Loss of tubular cell polarity Cell necrosis Medullary congestion GFR Inflammatory infiltration Maintenance Tubular histology is rebuilt by: Adjacent tubule cells Kidney stem cells Haematopoietic cells Repair Polarity and function restored
25 Pathogenesis: Summary Initiation Prerenal azotaemia Loss of autoregulation Intracellular calcium ATD Depletion Oxidative injury Extension Loss of tubular cell polarity Cell necrosis Medullary congestion GFR Inflammatory infiltration Maintenance Tubular histology is rebuilt by: Adjacent tubule cells Kidney stem cells Haematopoietic cells Repair Polarity and function restored
26 Pathogenesis: Summary Initiation Prerenal azotaemia Loss of autoregulation Intracellular calcium ATD Depletion Oxidative injury Extension Loss of tubular cell polarity Cell necrosis Medullary congestion GFR Inflammatory infiltration Maintenance Tubular histology is rebuilt by: Adjacent tubule cells Kidney stem cells Haematopoietic cells Repair Polarity and function restored
27 Pathogenesis: Summary Initiation Prerenal azotaemia Loss of autoregulation Intracellular calcium ATD Depletion Oxidative injury Extension Loss of tubular cell polarity Cell necrosis Medullary congestion GFR Inflammatory infiltration Maintenance Tubular histology is rebuilt by: Adjacent tubule cells Kidney stem cells Haematopoietic cells Repair Polarity and function restored
28 Pathogenesis: Tubular Factors Extension Phase Maintenance Phase
29 RIFLE the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative
30 RIFLE the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Risk Injury Indicator Classes Failure
31 RIFLE the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Risk Injury Indicator Classes Failure Loss End-stage Kidney Disease Outcome Classes Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P, the ADQI workgroup: Acute renal failure definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 2004, 8:R204-R212
32 RIFLE: Classification GFR (Serum Creatinine) Urine Output (ml/kg/hr) Risk x 1.5 < 0.5 for 6 hours Injury 6.1% < 0.5 for 12 hours Failure 4.4% < 0.3 for 24 hours or anuria for 12 hours Loss End-stage Complete loss of kidney disease > 4 weeks Complete loss of kidney disease > 3 months
33 RIFLE: In Practice n = 5383 patients E A Hoste, G Clermont, A Kersten et al: RIFLE critereria for acute kidney injury. Crit Care 2006, 10:R73 Pittsburg University Hospital 2006 At Admission Ever Mortality (HR) No ARF 78% 33% Risk 8% 12% 1.0 ( ) Injury 7% 27% 1.4 ( ) Failure 7% 28% 2.7 ( )
34 RIFLE: In Practice n = 5383 patients E A Hoste, G Clermont, A Kersten et al: RIFLE critereria for acute kidney injury. Crit Care 2006, 10:R73 Pittsburg University Hospital 2006 At Admission Ever Mortality (HR) No ARF 78% 33% Risk 8% 12% 1.0 ( ) 52% Injury 7% 27% 1.4 ( ) Failure 7% 28% 2.7 ( )
35 Preventions Treatments Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Ca Channel Blockers N-Acetylcysteine Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Dopamine/ Fenoldopam Dialysis Mode Dialysis Dosing Theophyllines
36 Prevention & Treatment: Frusemide Inhibits Na/K/Cl channel in ascending Loop-of-Henley Reduced intracellular substrate for Na/K ATPase Reduced energy consumption in the critical outer medulla (by 45% in-vitro) Wash out tubular debris
37 Prevention & Treatment: Frusemide 9 RCT n = 849 K M Ho, D J Sheridan: Meta-analysis of frusemide to prevent or treat acute renal failre. BMJ 2006, doi: /bmj c In or at risk of ARF Heterogeneous selection criteria Many methodological problems Ototoxic
38 Prevention & Treatment: Frusemide Renal Replacement Therapy Mortality Prevention Treatment
39 Prevention: Ca Channel Blockers Kribben, A, et al. Evidence for role of cytosolic free calcium in hypoxia-induced proximal tubule injury. J. Clin. Invest. 1994;93: Untreated Ca Blockade
40 Prevention: Ca Channel Blockers n = 210 Better serum creatinine at 3 months and 12 months post for patients receiving live or cadaveric kidney transplant V Riemsdijk, et al. Isradipine results in a beter renal function after kidney transplant. Transplantation. 2000;70: Poor quality evidence. Adverse effects not reported. Other, trials (cumulatively larger) limited to cadaveric transplants have failed to find a benefit
41 Treatment: Dopamine/ Fenoldopam Based on the vasomotor nephropathy model Correct aberrant vascular responses and improve renal blood supply Good in-vitro evidence to show improved RBF & GFR
42 Treatment: Dopamine/ Fenoldopam 58 RCT n = 2149 Kellum J A, Decker J M: The use of dopamine in acute renal failure: a meta-analysis. Crit Care Med 2001;29: No difference from placebo in mortality or renal replacement therapy This review did not list adverse effects but we know dopamine can cause: Extravasation necrosis Arythmias Headaches
43 Treatment: Dialysis Dose The biggest RCT n = 425 Ronco C, Bellomo R, Homel et al. Effects of different doses in continious veno-veno heamofiltration on outcomes of renal failure. Lancet 200;356:26-30 CVVHF 20 / 30 / 45 (ml/kg/hour) Low dose substantially inferior to higher two cohorts Three-way comparison: RR = 1.88 ( ) NNT = 7 (4-16)
44 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Ca Channel Blockers Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Dopamine Dialysis Mode Dialysis Dosing N-Acetylcysteine Theophyllines
45 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Ca Channel Blockers N-Acetylcysteine Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Dopamine Dialysis Mode Dialysis Dosing Theophyllines
46 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Ca Channel Blockers N-Acetylcysteine Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Dopamine Dialysis Mode Dialysis Dosing Theophyllines
47 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Ca Channel Blockers N-Acetylcysteine Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Dopamine Dialysis Mode Dialysis Dosing Theophyllines
48 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Ca Channel Blockers N-Acetylcysteine Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Dopamine Dialysis Mode Dialysis Dosing Theophyllines
49 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Ca Channel Blockers N-Acetylcysteine Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Dopamine Dialysis Mode Dialysis Dosing Theophyllines
50 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Ca Channel Blockers N-Acetylcysteine Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Dopamine Dialysis Mode Dialysis Dosing Theophyllines
51 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Osmotic Diuretics Dopamine Dialysis Mode Ca Channel Blockers Dialysis Dosing High dose N-Acetylcysteine Theophyllines
52 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Osmotic Diuretics Dopamine Dialysis Mode Ca Channel Blockers Dialysis Dosing High dose N-Acetylcysteine Theophyllines
53 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Osmotic Diuretics Dopamine Dialysis Mode Ca Channel Blockers Dialysis Dosing High dose N-Acetylcysteine Theophyllines
54 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Osmotic Diuretics Dopamine Dialysis Mode Ca Channel Blockers Dialysis Dosing High dose N-Acetylcysteine Theophyllines
55 Interventions: Summary Prevention Treatment Cause Prevention Loop Diuretics Loop Diuretics Natriuretic Peptides Osmotic Diuretics Dopamine Dialysis Mode Ca Channel Blockers Dialysis Dosing High dose N-Acetylcysteine Theophyllines
56 Questions
57 Key points RIFLE is the future of ARF research Preventing the causes of ARF is our best strategy Frusemide for fluid management only
Renal Blood Flow GFR. Glomerulus Fluid Flow and Forces. Renal Blood Flow (cont d)
 GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION
 LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
Select the one that is the best answer:
 MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
Body Fluids. Physiology of Fluid. Body Fluids, Kidneys & Renal Physiology
 Pc Remember arterioles have more smooth muscle So SNS effects are greater on arterioles than on venules Net effects: SNS P c (vasoconstriction > venoconstriction) SNS P c (vasodilation > venodilation)
Pc Remember arterioles have more smooth muscle So SNS effects are greater on arterioles than on venules Net effects: SNS P c (vasoconstriction > venoconstriction) SNS P c (vasodilation > venodilation)
Chapter 23. Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration
 Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
Chapter 26: The Urinary System
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II
 Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II I. Effects of blood volume on the filtration fraction (FF) {Altered Volume Effects in syllabus A. Under normal conditions, ~20% of renal plasma flow becomes
Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II I. Effects of blood volume on the filtration fraction (FF) {Altered Volume Effects in syllabus A. Under normal conditions, ~20% of renal plasma flow becomes
Urinary System. And Adrenal Function
 Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email [email protected]
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - PART 1 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 273 5 th NOVEMBER 2012 Dr Matthew Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Dr Jennifer Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Correspondence to: [email protected]
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - PART 1 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 273 5 th NOVEMBER 2012 Dr Matthew Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Dr Jennifer Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Correspondence to: [email protected]
April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science
 Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
RENAL WATER REGULATION page 1
 page 1 INTRODUCTION TO WATER EXCRETION A. Role of the Kidney: to adjust urine formation rate and urine concentration to maintain 1. body fluid osmolar concentration 2. body fluid volume 3. intravascular
page 1 INTRODUCTION TO WATER EXCRETION A. Role of the Kidney: to adjust urine formation rate and urine concentration to maintain 1. body fluid osmolar concentration 2. body fluid volume 3. intravascular
Water Homeostasis. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Grading of acute kidney injury (2013)
 Acute kidney disease represents a spectrum of disease associated with a sudden onset of renal parenchymal injury most typically characterized by generalized failure of the kidneys to meet the excretory,
Acute kidney disease represents a spectrum of disease associated with a sudden onset of renal parenchymal injury most typically characterized by generalized failure of the kidneys to meet the excretory,
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function
 Objectives 1. Understand the roles of the kidney 2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function 3. Begin to appreciate the inter-dependence of regulatory mechanisms
Objectives 1. Understand the roles of the kidney 2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function 3. Begin to appreciate the inter-dependence of regulatory mechanisms
Nefropatia de Contraste
 Nefropatia de Contraste H. Luz Rodrigues Serviço de Nefrologia e Transplantação Instituto de Farmacologia e Neurociências Contrast-induced nephropathy Agenda Pathogenesis Clinical features Prevention Postulated
Nefropatia de Contraste H. Luz Rodrigues Serviço de Nefrologia e Transplantação Instituto de Farmacologia e Neurociências Contrast-induced nephropathy Agenda Pathogenesis Clinical features Prevention Postulated
CHAPTER 20: URINARY SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
Kidney Structure and Function.
 Kidney Structure and Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this section, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of the kidney; 2. understand the vascular organisation of the kidneys;
Kidney Structure and Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this section, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of the kidney; 2. understand the vascular organisation of the kidneys;
Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus
 Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus In order to workout this problem, study pages 240 6, 249 51, 318 9, 532 3 and 886 7 of the Pathophysiology, 5 th Edition. (This problem was based on
Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus In order to workout this problem, study pages 240 6, 249 51, 318 9, 532 3 and 886 7 of the Pathophysiology, 5 th Edition. (This problem was based on
Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia
 Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia Case Presentation: History 62 y/o male is admitted to the hospital with a 3 month history of excessive urination (polyuria) and excess water intake up to
Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia Case Presentation: History 62 y/o male is admitted to the hospital with a 3 month history of excessive urination (polyuria) and excess water intake up to
Components. Urinary System. Formation of Urine. Functions of Kidney. Pathway of Urine. Kidney. Major functions of the kidneys include:
 Components Urinary System To Accompany: Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Components Urinary System To Accompany: Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Excretory Physiology
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Renal syndromes leading to abnormal kidney function:
 Renal syndromes leading to abnormal kidney function: An abnormality in kidney function can be detected by the following: 1) changes in serum creatinine concentration, reflecting changes in GFR 2) abnormalities
Renal syndromes leading to abnormal kidney function: An abnormality in kidney function can be detected by the following: 1) changes in serum creatinine concentration, reflecting changes in GFR 2) abnormalities
HYPERTENSION ASSOCIATED WITH RENAL DISEASES
 RENAL DISEASE v Patients with renal insufficiency should be encouraged to reduce dietary salt and protein intake. v Target blood pressure is less than 135-130/85 mmhg. If patients have urinary protein
RENAL DISEASE v Patients with renal insufficiency should be encouraged to reduce dietary salt and protein intake. v Target blood pressure is less than 135-130/85 mmhg. If patients have urinary protein
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal
 Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function
 Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function I. Functions of the kidney A. Maintaining homeostasis of a large number of solutes and water is the main job of the kidney. Total body contents
Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function I. Functions of the kidney A. Maintaining homeostasis of a large number of solutes and water is the main job of the kidney. Total body contents
Approach to the Patient with Acute Renal Failure. Michael Ornes Abbott Northwestern Hospital
 Approach to the Patient with Acute Renal Failure Michael Ornes Abbott Northwestern Hospital Definition Abrupt decrease in glomerular filtration rate Accumulation of urea and other metabolic byproducts
Approach to the Patient with Acute Renal Failure Michael Ornes Abbott Northwestern Hospital Definition Abrupt decrease in glomerular filtration rate Accumulation of urea and other metabolic byproducts
Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: Pathophysiology and Preventive Strategies
 Feature Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: Pathophysiology and Preventive Strategies Ann L. Jorgensen, MS, APN-BC, PCCN Contrast-induced nephropathy is the third most common cause of hospitalacquired renal
Feature Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: Pathophysiology and Preventive Strategies Ann L. Jorgensen, MS, APN-BC, PCCN Contrast-induced nephropathy is the third most common cause of hospitalacquired renal
Hypertension and Heart Failure Medications. Dr William Dooley
 Hypertension and Heart Failure Medications Dr William Dooley Plan Heart Failure Acute vs. chronic Mx Hypertension Common drugs used Method of action Choice of medications Heart Failure Aims; Short term:
Hypertension and Heart Failure Medications Dr William Dooley Plan Heart Failure Acute vs. chronic Mx Hypertension Common drugs used Method of action Choice of medications Heart Failure Aims; Short term:
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results
 Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR
 AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR Renal Anatomy Renal Artery & Veins 6 cm 3cm Cortex 11cm Pelvis of the ureter Capsule Ureter To the bladder Medulla Medulary Pyramid Renal Anatomy and Physiology
AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR Renal Anatomy Renal Artery & Veins 6 cm 3cm Cortex 11cm Pelvis of the ureter Capsule Ureter To the bladder Medulla Medulary Pyramid Renal Anatomy and Physiology
Update in Contrast Induced Nephropathy
 Update in Contrast Induced Nephropathy Yves Pirson Service de Néphrologie, Clin. Univ. St-Luc - UCL A 76-year-old man with - type 2 diabetes - CKD (ser. creat.: 1.8 mg/dl; GFR: 32) presents with angina
Update in Contrast Induced Nephropathy Yves Pirson Service de Néphrologie, Clin. Univ. St-Luc - UCL A 76-year-old man with - type 2 diabetes - CKD (ser. creat.: 1.8 mg/dl; GFR: 32) presents with angina
There has been an increase in
 Acute Kidney Injury: An Overview Of Pathophysiology and Treatments Continuing Nursing Education Kristina M. Yaklin There has been an increase in the prevalence of acute kidney injury (AKI) over the past
Acute Kidney Injury: An Overview Of Pathophysiology and Treatments Continuing Nursing Education Kristina M. Yaklin There has been an increase in the prevalence of acute kidney injury (AKI) over the past
REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE
 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 1 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE The kidney is the primary organ that maintains the total volume, ph, and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid within
REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 1 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE The kidney is the primary organ that maintains the total volume, ph, and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid within
Prevalence and risk factor of chronic kidney disease in elderly diabetic patients in Korea 성애병원 내과 김정한
 Prevalence and risk factor of chronic kidney disease in elderly diabetic patients in Korea 성애병원 내과 김정한 Introduction CKD의 정의와 egfr의 측정 CKD의 risk factor와 mechanism 한국의 CKD prevalence 와 prognosis CKD의 치료와
Prevalence and risk factor of chronic kidney disease in elderly diabetic patients in Korea 성애병원 내과 김정한 Introduction CKD의 정의와 egfr의 측정 CKD의 risk factor와 mechanism 한국의 CKD prevalence 와 prognosis CKD의 치료와
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 15. The Urinary System. Slides 15.1 15.20. Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Canine Hypoadrenocorticism. Diagnosis and Treatment
 Diagnosis and Treatment Adrenal Physiology The adrenal gland is a two-part structure located on the cranial pole of each kidney. Essential for life Produces hormones Epinephrine Estrogen Testosterone Cortisol
Diagnosis and Treatment Adrenal Physiology The adrenal gland is a two-part structure located on the cranial pole of each kidney. Essential for life Produces hormones Epinephrine Estrogen Testosterone Cortisol
嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯
 The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 嘉 義 長 庚 醫 院 藥 劑 科 Speaker : 翁 玟 雯 Diabetes Mellitus : A group of diseases characterized
PU/PD- Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Approach. Polyuria/Polydipsia PU/PD. Michael Geist, DVM, DACVIM VCA- Animal Specialty Group San Diego, Ca
 PU/PD- Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Approach Michael Geist, DVM, DACVIM VCA- Animal Specialty Group San Diego, Ca Polyuria/Polydipsia Drinking too much? >100ml/kg/day Water intake is variable Have owners
PU/PD- Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Approach Michael Geist, DVM, DACVIM VCA- Animal Specialty Group San Diego, Ca Polyuria/Polydipsia Drinking too much? >100ml/kg/day Water intake is variable Have owners
Hypertension and Diabetes
 Hypertension and Diabetes C.W. Spellman, D.O., Ph.D., FACOI Professor & Associate Dean Research Dir. Center Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders Texas Tech University Health Science Center Midland-Odessa, Texas
Hypertension and Diabetes C.W. Spellman, D.O., Ph.D., FACOI Professor & Associate Dean Research Dir. Center Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders Texas Tech University Health Science Center Midland-Odessa, Texas
Mechanism for Dehydration Associated Kidney Disease
 Mechanism for Dehydration Associated Kidney Disease Richard J Johnson, University of Colorado A sugarcane worker dying from kidney failure Dr Johnson has received funding from Danone Research Chronic Kidney
Mechanism for Dehydration Associated Kidney Disease Richard J Johnson, University of Colorado A sugarcane worker dying from kidney failure Dr Johnson has received funding from Danone Research Chronic Kidney
American Thoracic Society Documents
 American Thoracic Society Documents An Official ATS/ERS/ESICM/SCCM/SRLF Statement: Prevention and Management of Acute Renal Failure in the ICU Patient An International Consensus Conference in Intensive
American Thoracic Society Documents An Official ATS/ERS/ESICM/SCCM/SRLF Statement: Prevention and Management of Acute Renal Failure in the ICU Patient An International Consensus Conference in Intensive
Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology
 Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology 1 Kidney Anatomy and Function (Lecture 1) 2 Functions of Kidney A) Regulation of water B) Regulation of electrolytes C) Acid-base
Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology 1 Kidney Anatomy and Function (Lecture 1) 2 Functions of Kidney A) Regulation of water B) Regulation of electrolytes C) Acid-base
Inpatient Heart Failure Management: Risks & Benefits
 Inpatient Heart Failure Management: Risks & Benefits Dr. Kenneth L. Baughman Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Advanced Heart Disease Section Brigham & Women's Hospital Harvard Medical
Inpatient Heart Failure Management: Risks & Benefits Dr. Kenneth L. Baughman Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Advanced Heart Disease Section Brigham & Women's Hospital Harvard Medical
High Blood Pressure and Kidney Disease
 High Blood Pressure and Kidney Disease National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The kidneys play a key
High Blood Pressure and Kidney Disease National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The kidneys play a key
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy. Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS History of the CRRT program 1988 Open heart program Active transplant program Deep dissatisfaction with peritoneal dialysis in hemodynamically
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS History of the CRRT program 1988 Open heart program Active transplant program Deep dissatisfaction with peritoneal dialysis in hemodynamically
Nierfunctiemeting en follow-up van chronisch nierlijden
 Nierfunctiemeting en follow-up van chronisch nierlijden 12 Jan 2016 Patrick Peeters, M.D. Dept Nephrology Ghent University Hospital Plan of presentation 1/ Renal function determination: Measured GFR Estimated
Nierfunctiemeting en follow-up van chronisch nierlijden 12 Jan 2016 Patrick Peeters, M.D. Dept Nephrology Ghent University Hospital Plan of presentation 1/ Renal function determination: Measured GFR Estimated
Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop: Stimulus. Production Cell. Hormone. Target Cell. Target Cell Action
 Hormonal Cycles Directions: a. Click the Contents button. b. Open the Endocrine System File. c. Click Animations. d. Click Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop:
Hormonal Cycles Directions: a. Click the Contents button. b. Open the Endocrine System File. c. Click Animations. d. Click Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop:
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases
 Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Acid-Base Disorders. Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS. Objectives. Diagnostic Considerations. Step 1: Primary Disorder. Formulae. Step 2: Compensation
 Objectives Diagnostic approach to acid base disorders Common clinical examples of acidoses and alkaloses Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan 1 2 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph,
Objectives Diagnostic approach to acid base disorders Common clinical examples of acidoses and alkaloses Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan 1 2 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph,
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus!
 Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Urinary System Components:! -Kidneys! -Ureters! -Urinary Bladder!! -Urethra!
Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Urinary System Components:! -Kidneys! -Ureters! -Urinary Bladder!! -Urethra!
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working
 GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
CASE A1 Hypoglycemia in an Elderly T2DM Patient with Heart Failure
 Hypoglycemia in an Elderly T2DM Patient with Heart Failure 1 I would like to introduce you to Sophie, an elderly patient with long-standing type 2 diabetes, who has a history of heart failure, a common
Hypoglycemia in an Elderly T2DM Patient with Heart Failure 1 I would like to introduce you to Sophie, an elderly patient with long-standing type 2 diabetes, who has a history of heart failure, a common
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Septic Shock: Pharmacologic Agents for Hemodynamic Support. Nathan E Cope, PharmD PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident
 Septic Shock: Pharmacologic Agents for Hemodynamic Support Nathan E Cope, PharmD PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident Objectives Define septic shock and briefly review pathophysiology Outline receptor
Septic Shock: Pharmacologic Agents for Hemodynamic Support Nathan E Cope, PharmD PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident Objectives Define septic shock and briefly review pathophysiology Outline receptor
Prediction of Kidney Disease Progression in Patients with Diabetes
 Prediction of Kidney Disease Progression in Patients with Diabetes John Arthur, MD, PhD Medical University of South Carolina SEKDC Meeting September 8, 2012 Objectives Understand the importance of predicting
Prediction of Kidney Disease Progression in Patients with Diabetes John Arthur, MD, PhD Medical University of South Carolina SEKDC Meeting September 8, 2012 Objectives Understand the importance of predicting
IM 655 Nephrology Clerkship. Selective/Elective Clerkship Rotation Syllabus
 IM 655 Nephrology Clerkship Selective/Elective Clerkship Rotation Syllabus Osteopathic Medical Specialties Mary Hughes DO Chairperson, Instructor of Record Mary Hughes DO [email protected] (100% for CLIFMS
IM 655 Nephrology Clerkship Selective/Elective Clerkship Rotation Syllabus Osteopathic Medical Specialties Mary Hughes DO Chairperson, Instructor of Record Mary Hughes DO [email protected] (100% for CLIFMS
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney --Overview of Kidney Function a. Regulation of blood ionic composition b. Regulation of blood ph and osmolarity c. Regulate blood glucose level (gluconeogenesis) d.
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney --Overview of Kidney Function a. Regulation of blood ionic composition b. Regulation of blood ph and osmolarity c. Regulate blood glucose level (gluconeogenesis) d.
Intravenous Fluids: Composition & Uses. Srinidhi Jayaram, PGY1
 Intravenous Fluids: Composition & Uses Srinidhi Jayaram, PGY1 Body Fluid Compartments Total Body Water (TBW): 50-70% of total body wt. Avg. is greater for males. Decreases with age. Highest in newborn,
Intravenous Fluids: Composition & Uses Srinidhi Jayaram, PGY1 Body Fluid Compartments Total Body Water (TBW): 50-70% of total body wt. Avg. is greater for males. Decreases with age. Highest in newborn,
The Urinary System Urine (pp. 984 985)
 Kidney Anatomy (pp. 961 969) Location and External Anatomy (pp. 961 962) Internal Anatomy (pp. 962 963) Blood and Nerve Supply (pp. 963 964) Nephrons (pp. 964 969) Kidney Physiology: Mechanisms of Urine
Kidney Anatomy (pp. 961 969) Location and External Anatomy (pp. 961 962) Internal Anatomy (pp. 962 963) Blood and Nerve Supply (pp. 963 964) Nephrons (pp. 964 969) Kidney Physiology: Mechanisms of Urine
Advantages and disadvantages of CRRT in ARF patients. Norbert Lameire Renal Division University Hospital Ghent, Belgium
 Advantages and disadvantages of CRRT in ARF patients Norbert Lameire Renal Division University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Alexandria, 17/2/2005 Indications for RRT in critically ill ARF patients Renal Replacement
Advantages and disadvantages of CRRT in ARF patients Norbert Lameire Renal Division University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Alexandria, 17/2/2005 Indications for RRT in critically ill ARF patients Renal Replacement
Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know
 Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make hormones your body needs for some important functions. When kidney failure
Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make hormones your body needs for some important functions. When kidney failure
Acid-Base Disorders. Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS
 Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS 1 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph, pco 2, HCO 3 Chem-7 panel: anion gap Step 1: Acidemia/alkalemia (Primary disorder) Step 2: Compensation
Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS 1 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph, pco 2, HCO 3 Chem-7 panel: anion gap Step 1: Acidemia/alkalemia (Primary disorder) Step 2: Compensation
Diabetes and the Kidneys
 Diabetes and the Kidneys Aim(s) and objective(s) This guideline focuses on the detection, prevention, and management of kidney disease in people with diabetes. The management of end-stage renal disease
Diabetes and the Kidneys Aim(s) and objective(s) This guideline focuses on the detection, prevention, and management of kidney disease in people with diabetes. The management of end-stage renal disease
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys
 High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys About 65 million Americans have high blood pressure, but as many as one third or three in 10 don't even know it. There are usually no signs or symptoms that your blood
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys About 65 million Americans have high blood pressure, but as many as one third or three in 10 don't even know it. There are usually no signs or symptoms that your blood
Hydration Protocol for Cisplatin Chemotherapy
 Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Version: 1.3 CSPM2 Hydration Protocol for Cisplatin Chemotherapy Date to be reviewed: July 2018 No of pages: 9 Author(s): Tracy Parry-Jones Author(s) title: Lead Cancer
Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Version: 1.3 CSPM2 Hydration Protocol for Cisplatin Chemotherapy Date to be reviewed: July 2018 No of pages: 9 Author(s): Tracy Parry-Jones Author(s) title: Lead Cancer
ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS (Continued)
 ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS (Continued) Osmolarity Osmotic pressure is an important biologic parameter which involves diffusion of solutes or the transfer of fluids through semi permeable membranes. Per US Pharmacopeia,
ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS (Continued) Osmolarity Osmotic pressure is an important biologic parameter which involves diffusion of solutes or the transfer of fluids through semi permeable membranes. Per US Pharmacopeia,
ACID-BASE BALANCE AND ACID-BASE DISORDERS. I. Concept of Balance A. Determination of Acid-Base status 1. Specimens used - what they represent
 ACID-BASE BALANCE AND ACID-BASE DISORDERS I. Concept of Balance A. Determination of Acid-Base status 1. Specimens used - what they represent II. Electrolyte Composition of Body Fluids A. Extracellular
ACID-BASE BALANCE AND ACID-BASE DISORDERS I. Concept of Balance A. Determination of Acid-Base status 1. Specimens used - what they represent II. Electrolyte Composition of Body Fluids A. Extracellular
Protocol for the safe administration of iodinated contrast media in diagnostic radiology
 Protocol for the safe administration of iodinated contrast media in diagnostic radiology Protocol statement: This protocol applies to all staff within Radiology Departments at Heart of England NHS Foundation
Protocol for the safe administration of iodinated contrast media in diagnostic radiology Protocol statement: This protocol applies to all staff within Radiology Departments at Heart of England NHS Foundation
CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM. At the end of this chapter, student will be able to:
 CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM At the end of this chapter, student will be able to: a) Describe the location and general function of each organ of the urinary system. b) Name the parts of a nephron and the
CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM At the end of this chapter, student will be able to: a) Describe the location and general function of each organ of the urinary system. b) Name the parts of a nephron and the
Emergency Fluid Therapy in Companion Animals
 Emergency Fluid Therapy in Companion Animals Paul Pitney BVSc [email protected] The administration of appropriate types and quantities of intravenous fluids is the cornerstone of emergency therapy
Emergency Fluid Therapy in Companion Animals Paul Pitney BVSc [email protected] The administration of appropriate types and quantities of intravenous fluids is the cornerstone of emergency therapy
Milwaukee School of Engineering [email protected]. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
The kidneys play a dominant role in regulating the composition
 PART VI RENAL PHYSIOLOGY AND BODY FLUIDS C H A P T E R 22 Kidney Function George A. Tanner, Ph.D. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon mastering the material in this chapter you should be able to: Summarize the functions
PART VI RENAL PHYSIOLOGY AND BODY FLUIDS C H A P T E R 22 Kidney Function George A. Tanner, Ph.D. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon mastering the material in this chapter you should be able to: Summarize the functions
Renovascular Hypertension
 Renovascular Hypertension Philip Stockwell, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Warren Alpert School of Medicine Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider September 28, 201 Renovascular Hypertension
Renovascular Hypertension Philip Stockwell, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Warren Alpert School of Medicine Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider September 28, 201 Renovascular Hypertension
Renal Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Renal Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 6th Collaborative DiGP/HSE/UCC Conference 25 th September 2013 Dr. Eoin O Sullivan Consultant Endocrinologist Bon Secours Hospital Cork Case 69 year old woman
Renal Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 6th Collaborative DiGP/HSE/UCC Conference 25 th September 2013 Dr. Eoin O Sullivan Consultant Endocrinologist Bon Secours Hospital Cork Case 69 year old woman
Aus der Medizinischen Klinik mit Schwerpunkt Kardiologie, Campus Virchow-Klinikum der Medizinischen Fakultät der Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin
 Aus der Medizinischen Klinik mit Schwerpunkt Kardiologie, Campus Virchow-Klinikum der Medizinischen Fakultät der Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin DISSERTATION Risk of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy (CIN)
Aus der Medizinischen Klinik mit Schwerpunkt Kardiologie, Campus Virchow-Klinikum der Medizinischen Fakultät der Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin DISSERTATION Risk of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy (CIN)
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. Hyperkalaemia
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Hyperkalaemia Purpose of Guideline Dealing with adult patients with Hyperkalaemia in the community Definition Serum potassium normal range is 3.5 5.3
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Hyperkalaemia Purpose of Guideline Dealing with adult patients with Hyperkalaemia in the community Definition Serum potassium normal range is 3.5 5.3
Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar ([email protected])
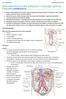 Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar ([email protected]) 1. Draw a simple diagram of the urinary system including the following: kidney, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder,
Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar ([email protected]) 1. Draw a simple diagram of the urinary system including the following: kidney, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder,
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
STAGES OF SHOCK. IRREVERSIBLE SHOCK Heart deteriorates until it can no longer pump and death occurs.
 STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
PROCEEDINGS DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY: DETECTION AND TREATMENT OF RENAL DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES* Jiten Vora, MA, MD, FRCP ABSTRACT
 DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY: DETECTION AND TREATMENT OF RENAL DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES* Jiten Vora, MA, MD, FRCP ABSTRACT Diabetic nephropathy affects people with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus.
DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY: DETECTION AND TREATMENT OF RENAL DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES* Jiten Vora, MA, MD, FRCP ABSTRACT Diabetic nephropathy affects people with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus.
NEPHROLOGY COMMON CLINICAL PRESENTATIONS AND CARDINAL MANIFESTATIONS OF RENAL DISEASES-
 NEPHOLOGY OON LINIAL PESENTATIONS AND ADINAL ANIFESTATIONS OF ENAL DISEASES- INITIAL EVALUATION AND DEISION-AKING SKILLS GOAL: The residents will learn the evaluation, diagnosis, and management of patients
NEPHOLOGY OON LINIAL PESENTATIONS AND ADINAL ANIFESTATIONS OF ENAL DISEASES- INITIAL EVALUATION AND DEISION-AKING SKILLS GOAL: The residents will learn the evaluation, diagnosis, and management of patients
Renal Function Tests. Carmella L. D Addezio, DO, MS, FACOI, LTC, USAF, MC
 Renal Function Tests Carmella L. D Addezio, DO, MS, FACOI, LTC, USAF, MC Goals and objectives At the end of this discussion you will be able to state: What test you should use to screen a patient for renal
Renal Function Tests Carmella L. D Addezio, DO, MS, FACOI, LTC, USAF, MC Goals and objectives At the end of this discussion you will be able to state: What test you should use to screen a patient for renal
Kidneys, Nephrons, and Urine Production
 Valerie ovelace Kidneys, Nephrons, and rine Production Part of the urinary system, our kidneys are vital organs that serve to remove waste from the bloodstream through ultrafiltration and the formation
Valerie ovelace Kidneys, Nephrons, and rine Production Part of the urinary system, our kidneys are vital organs that serve to remove waste from the bloodstream through ultrafiltration and the formation
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE MANAGEMENT GUIDE
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Outline I. Introduction II. Identifying Members with Kidney Disease III. Clinical Guidelines for Kidney Disease A. Chronic Kidney Disease B. End Stage Renal Disease
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Outline I. Introduction II. Identifying Members with Kidney Disease III. Clinical Guidelines for Kidney Disease A. Chronic Kidney Disease B. End Stage Renal Disease
3. Tunica adventitia is the outermost layer; it is composed of loosely woven connective tissue infiltrated by nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics
 Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. AKI guidelines for primary care
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH AKI DETECTED IN PRIMARY CARE...2 FLOW DIAGRAM: POST AKI MANAGEMENT
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH AKI DETECTED IN PRIMARY CARE...2 FLOW DIAGRAM: POST AKI MANAGEMENT
