AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR
|
|
|
- Jeremy Shelton
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR
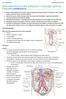
2 Renal Anatomy Renal Artery & Veins 6 cm 3cm Cortex 11cm Pelvis of the ureter Capsule Ureter To the bladder Medulla Medulary Pyramid
3 Renal Anatomy and Physiology pair of fist-sized organs located on either side of the spinal column just behind the lower abdomen (L1-3). Consists of an outer layer (renal cortex) and an inner region (renal medulla). The functional unit is the nephron; 10 6 nephrons/kidney.
4 The Nephron Afferent arteriole Glomerulus Bowman s capsule Proximal tubule Distal tubule Collecting duct Renal artery Vasa Recta Henle s Loop
5 KIDNEY: Blood flow 1 Inter-lobar artery 2 Arcuate artery 3 Renal artery 1 Inter-lobular artery 4
6 KIDNEY: Blood flow 4 Venous drainage Inter-lobar vein 11 Renal vein 12 Arcuate vein 10 Inter-lobular vein 9
7 FILTRATION BARRIER Fenestrated endothelium Basal lamina The charged proteoglycans of the BL help control what passes through Capsular space Capillary lumen Podocytes with Filtration slits between feet Capsular space Fenestration Basal lamina Filtration slit closed by a diaphragm
8 Why Test Renal Function? To identify renal dysfunction. To diagnose renal disease. To monitor disease progress. To monitor response to treatment. To assess changes in function that may impact on therapy (e.g.digoxin, chemotherapy).
9 Renal Functions Production of urine Elimination of metabolic end products (Urea/Creatinine) Elimination of foreign materials (Drugs) Control of volume & composition of ECF Water and electrolyte balance Acid/Base status Endocrine Functions Vit D, Epo, Renin
10 Biochemical Tests of Renal Function Urinalysis Appearance Specific gravity and osmolality ph Glucose Protein Urinary sediments? Measurement of GFR Clearance tests Plasma creatinine Tubular function tests
11 Determination of Clearance Clearance = (U xv)/p Where U is the urinary concentration of substance x V is the rate of urine formation (ml/min) P is the plasma concentration of substance x Units = volume/unit time (ml/min) If clearance = GFR then substance x properties: - freely filtered by glomerulus glomerulus = sole route of excretion from the body (no tubular secretion or reabsorbtion) Non-toxic and easily measurable
12 1-2%/day of muscle creatine converted to creatinine Amount produced relates to muscle mass Freely filtered at the glomerulus Some tubular excretion.
13 Plasma Creatinine Concentration Difficulties: - Concentration depends on balance between input and output. Production determined by muscle mass which is related to age, sex and weight. High between subject variability but low within subject. Concentration inversely related to GFR. Small changes in creatinine within and around the reference limits = large changes in GFR. Reference limits can be misleading
14 Relationship between Serum Creatinine Concentration and Creatinine Clearance Serum Creatinine (µmol/l) Creatinine Clearance (ml/min) ULN
15 Effect of Muscle Mass on Serum Creatinine Creatinine Input Normal Muscle Mass Normal Muscle Mass Increased Muscle Mass Reduced Muscle Mass Plasma Pool Content Output Kidney Normal Kidneys Diseased Kidneys Normal Kidneys Diseased Kidneys
16 Measurement of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) GFR is essential to renal function Most frequently performed test of renal function. Measurement is based on concept of clearance: - The determination of the volume of plasma from which a substance is removed by glomerular filtration during it s passage through the kidney
17 Acute Renal Failure Metabolic features: - Retention of: - Urea & creatinine Na& water potassium with hyperkalaemia Acid with metabolic acidosis Classification of Causes: Pre-renal reduced perfusion Intrinsic Renal vascular inflammation infiltration toxicity Post-renal obstruction
18 Pre-renal versus intrinsic ARF Test Result Pre-renal Renal Urea & Creatinine Disproportionate rise in Urea Tend to rise together Protein in urine Uncommon Present on dipstick testing
19 What are the functions of the kidneys? Regulate body fluid osmolality and volume Regulate electrolyte balance Regulate acid-base balance Excrete metabolic products and foreign substances Produce and excrete hormones Gluconeogenic
20
21
22 Glomerular filtration Vascular space 2,000 Liters per day (25% of cardiac output) Glomerlular capillary membrane Mean capillary blood pressure = 50 mm Hg BC pressure = 10 mm Hg Onc. pressure = 30 mm Hg Bowman s space 200 Liters per day Net hydrostatic = 10 mm Hg GFR 110 ml/min
23 Dynamics? 200 liters of filtrate enter the nephrons/day 1-2 liters of urine produced filtrate (99+ %) is reabsorbed. Reabsorption active or passive occurs in virtually all segments of the nephron.
24 What makes it into the glomerular filtrate? Freely filtered H 2 O Na +, K +, Cl -, HCO 3-, Ca ++, Mg +, PO 4, etc. Glucose Urea Creatinine Insulin Less freely filtered β 2 - microglobulin RBP α 1 - microglobulin Albumin Not usually filtered Immunoglobulins Ferritin Cells
25 Functions of renal tubules Selective reabsorbtion or excretion of water and various ions to maintain constancy of the body electrolyte composition. Active reabsorption of filtered compounds, such as glucose and amino acids Acquired and inherited disorders of tubular mechanisms lead to characteristic syndromes (Fanconi, RTA)
26 Reabsorption from glomerular filtrate % Reabsorbed Water 99.2 Sodium 99.6 Potassium 92.9 Chloride 99.5 Bicarbonate 99.9 Glucose 100 Albumin Urea Creatinine 0 (or negative)
27 Tubular Reabsorbtion and Secretion of Organic Substances Active Glucose Amino acids Proteins (pinocytosis) 3 secretory systems ; functionally identified: - organic acids (PAH, penicillin) Strong organic bases (TEA) (EDTA)
28 JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS Renal corpuscle Reninsecreting JG cells 3 2 Mesangium Renal corpuscle Afferent arteriole Proxima l tubule Interstitiu m Distal tubule ~ Distal tubule ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Thin segment Collecting duct ~ ~ ~ ~ Arched collecting tubule ~ Vasa recta Flow & NaCl-sensing Macula densa Efferent arteriole 1 ~
29 JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS 2 Reninsecreting JG cells Afferent arteriole Vascular smooth muscle cells High luminal flow results in VSMC Vasoconstriction NaCl Distal tubule for single-nephron tubuloglomerular feedback to relate glomerular flow to distal flow rate Mesangium Renal corpuscle Flow & NaCl-sensing Macula densa Efferent arteriole
30 JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS 3 Efferent arteriole Reninsecreting JG cells Afferent arteriole The renin-secreting JG cells are modified arteriolar smooth muscle cells. More can be recruited as needed. Vascular smooth muscle cells Mesangium Renal corpuscle NaCl Distal tubule
31 JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS 4 Reninsecreting JG cells Afferent arteriole Vascular smooth muscle cells Distal tubule Low distal NaCl causes JGmediated renin release & subsequent effects via angiotensin and aldosterone NaCl Mesangium Renal corpuscle Efferent arteriole Flow & NaCl-sensing Macula densa
32 JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS 5 Vascular smooth muscle cells Reninsecreting JG cells Afferent arteriole Renin Low distal NaCl causes JG-mediated renin release & subsequent effects via angiotensin and aldosterone Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I Converting enzyme NaCl Angiotensin II Renal corpuscle Efferent arteriole Aldosterone
33
34 SOME RENAL DISEASES GLOMERULONEPHRITIS e.g., mesangial-cell reaction TUBULAR epithelial NEPHROTOXICITY from aminoglycosides & heavy metals Proximal tubule Interstitiu m FIBROSIS RENAL ISCHEMIA Renal corpuscle ~ Distal tubule ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Thin segment Collecting duct ~ ~ ~ ~ Arched collecting tubule ~ Vasa recta ~ DIABETES INSIPIDUS pituitary or nephrogenic
35 Osmotic pressure Vascular Extravascular CRRT Hydrostatic pressure Oncotic pressure Volume
36 Osmotic pressure Vascular Hypovolemia CRRT Extravascular Oncotic pressure Hydrostatic pressure Consequences depend on: duration permeability(ies) rate Volume
37 Danger : Oxygen delivery impairment 1) DO2 = CO x SaO2 x Hb x ) CO = HR x SV 3) SV = function (ventricular preload) Franck Starling law
38 Cardiac Preload - Franck Starling law Ventricular stroke volume No preload dependence Preload dependence Ventricular preload
39 Relation between vascular volume and ventricular function Osmotic pressure Ventricular stroke volume Volume 3 Ventricular preload MAP = SV x HR x SVR
40 Definition of Terms SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration CAVH - Continuous Arteriovenous Hemofiltration CAVH-D - Continuous Arteriovenous Hemofiltration with Dialysis CVVH - Continuous Venovenous Hemofiltration CVVH-D - Continuous Venovenous Hemofiltration with Dialysis
41 Indications for Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Remove excess fluid because of fluid overload Clinical need to administer fluid to someone who is oliguric Nutrition solution Antibiotics Vasoactive substances Blood products Other parenteral medications
42 Basic Principles Blood passes down one side of a highly permeable membrane Water and solute pass across the membrane Solutes up to 20,000 daltons Drugs & electrolytes Infuse replacement solution with physiologic concentrations of electrolytes
43 Anatomy of a Hemofilter blood in dialysate out Cross Section hollow fiber membra dialysate in blood out Outside the Fiber (effluent) Inside the Fiber (blood)
44 Basic Principles Hemofiltration Convection based on a pressure gradient Transmembrane pressure gradient Dialysis Difference between plasma oncotic pressure and hydrostatic pressure Diffusion based on a concentration gradient
45 CVVH Continuous Veno-Venous Hemofiltration to waste Blood In (from patient) Repl. Solution Blood Out (to patient) LOW PRESS HIGH PRESS (Convection)
46 CVVH Continuous VV Hemofiltration Primary therapeutic goal: Convective solute removal Management of intravascular volume Blood Flow rate = ml/min UF rate ranges 6-50 L/24 h (> 500 ml/h) Requires replacement solution to drive convection No dialysate
47 CVVHDF Continuous Veno-Venous Hemodiafiltration Dialysate Solution to waste Blood In (from patient) Repl. Solution Blood Out (to patient) LOW PRESS LOW CONC HIGH PRESS HIGH CONC (Convection) (Diffusion)
48 CVVHDF Continuous VV Hemodiafiltration Primary therapeutic goal: Solute removal by diffusion and convection Management of intravascular volume Blood Flow rate = ml/min Combines CVVH and CVVHD therapies UF rate ranges L/24h (> 500 ml/h) Dialysate Flow rate = ml/min (~1-3 L/h) Uses both dialysate (1 L/h) and replacement fluid (500 ml/h)
49 Continuous veno-venous hemofiltration (CVVH) allows removal of solutes and modification of the volume and composition of the extracellular fluid to occur evenly over time. introduction
50 hemofiltration A small filter that is highly permeable to water and small solutes, but impermeable to plasma proteins and the formed elements of the blood, is placed in an extracorporeal circuit. As the blood perfuses the 'hemofilter' an ultrafiltrate of plasma is removed in a manner analogous to glomerular filtration.
51 CVVH 1. near-complete control of the rate of fluid removal (i.e. the ultrafiltration rate) 2. precision and stability 3. electrolytes or any formed element of the circulation, including platelets or red or white blood cells, be removed or added independently of changes in the volume of total body water.
52 ultrafiltration Filtration across an ultrafiltration membrane is convective, similar to that found in the glomerulus of the kidney.
53 convection convection a solute molecule is swept through a membrane by a moving stream of ultrafiltrate, a process that is also called 'solvent drag.' hemofiltration during hemofiltration no dialysate is used, and diffusive transport cannot occur. Solute transfer is entirely dependent on convective transport, making hemofiltration relatively inefficient at solute removal.
54 hemodialysis Hemodialysis allows the removal of water and solutes by diffusion across a concentration gradient.
55 diffusion diffusion solute molecules are transferred across the membrane in the direction of the lower solute concentration at a rate inversely proportional to molecular weight. hemodialysis during hemodialysis, solute movement across the dialysis membrane from blood to dialysate is primarily the result of diffusive transport.
56 biocompatibility Various synthetic materials are used in hemofiltration membranes: polysulfone polyacrylonitrile polyamide all of which are extremely biocompatible. Consequently, complement activation and leukopenia, both of which are common in hemodialysis, occur infrequently during hemofiltration.
57 hemofiltration membrane Hemodialysis membranes contain long, tortuous interconnecting channels that result in high resistance to fluid flow. The hemofiltration membrane consists of relatively straight channels of ever-increasing diameter that offer little resistance to fluid flow. phosphate bicarbonate interleukin-1 interleukin-6 endotoxin vancomycin heparin pesticides ammonia
58 hemofiltration membrane Hemofilters allow easy transfer of solutes of less than 100 daltons (e.g. urea, creatinine, uric acid, sodium, potassium, ionized calcium and almost all drugs not bound to plasma proteins). All CVVH hemofilters are impermeable to albumin and other solutes of greater than 50,000 daltons. phosphate bicarbonate ionized Ca++ interleukin-6 endotoxin vancomycin heparin pesticides ammonia albumin protein-bound medications platelets
59 sluggishness A filtration rate of more than 25-30% greatly increases blood viscosity within the circuit, risking clot and malfunction.
60 pre-dilution Sludging problems are reduced, but the efficiency of ultrafiltration is compromised, as the ultrafiltrate now contains a portion of the replacement fluid.
61 experimental: high flow High-volume CVVH might improve hemodynamics, increase organ blood flow, and decreased blood lactate and nitrite/nitrate concentrations.
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION
 LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
CHAPTER 20: URINARY SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
Select the one that is the best answer:
 MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
Chapter 23. Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration
 Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
Chapter 26: The Urinary System
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
Body Fluids. Physiology of Fluid. Body Fluids, Kidneys & Renal Physiology
 Pc Remember arterioles have more smooth muscle So SNS effects are greater on arterioles than on venules Net effects: SNS P c (vasoconstriction > venoconstriction) SNS P c (vasodilation > venodilation)
Pc Remember arterioles have more smooth muscle So SNS effects are greater on arterioles than on venules Net effects: SNS P c (vasoconstriction > venoconstriction) SNS P c (vasodilation > venodilation)
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases
 Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - PART 1 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 273 5 th NOVEMBER 2012 Dr Matthew Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Dr Jennifer Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Correspondence to: mgwinnutt@doctors.org.uk
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - PART 1 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 273 5 th NOVEMBER 2012 Dr Matthew Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Dr Jennifer Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Correspondence to: mgwinnutt@doctors.org.uk
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal
 Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Urinary System. And Adrenal Function
 Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science
 Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function
 Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function I. Functions of the kidney A. Maintaining homeostasis of a large number of solutes and water is the main job of the kidney. Total body contents
Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function I. Functions of the kidney A. Maintaining homeostasis of a large number of solutes and water is the main job of the kidney. Total body contents
Components. Urinary System. Formation of Urine. Functions of Kidney. Pathway of Urine. Kidney. Major functions of the kidneys include:
 Components Urinary System To Accompany: Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Components Urinary System To Accompany: Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Kidney Structure and Function.
 Kidney Structure and Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this section, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of the kidney; 2. understand the vascular organisation of the kidneys;
Kidney Structure and Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this section, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of the kidney; 2. understand the vascular organisation of the kidneys;
Renal Blood Flow GFR. Glomerulus Fluid Flow and Forces. Renal Blood Flow (cont d)
 GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 15. The Urinary System. Slides 15.1 15.20. Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Water Homeostasis. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy. Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS History of the CRRT program 1988 Open heart program Active transplant program Deep dissatisfaction with peritoneal dialysis in hemodynamically
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS History of the CRRT program 1988 Open heart program Active transplant program Deep dissatisfaction with peritoneal dialysis in hemodynamically
2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function
 Objectives 1. Understand the roles of the kidney 2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function 3. Begin to appreciate the inter-dependence of regulatory mechanisms
Objectives 1. Understand the roles of the kidney 2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function 3. Begin to appreciate the inter-dependence of regulatory mechanisms
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Excretory Physiology
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Kidneys, Nephrons, and Urine Production
 Valerie ovelace Kidneys, Nephrons, and rine Production Part of the urinary system, our kidneys are vital organs that serve to remove waste from the bloodstream through ultrafiltration and the formation
Valerie ovelace Kidneys, Nephrons, and rine Production Part of the urinary system, our kidneys are vital organs that serve to remove waste from the bloodstream through ultrafiltration and the formation
The kidneys play a dominant role in regulating the composition
 PART VI RENAL PHYSIOLOGY AND BODY FLUIDS C H A P T E R 22 Kidney Function George A. Tanner, Ph.D. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon mastering the material in this chapter you should be able to: Summarize the functions
PART VI RENAL PHYSIOLOGY AND BODY FLUIDS C H A P T E R 22 Kidney Function George A. Tanner, Ph.D. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon mastering the material in this chapter you should be able to: Summarize the functions
Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II
 Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II I. Effects of blood volume on the filtration fraction (FF) {Altered Volume Effects in syllabus A. Under normal conditions, ~20% of renal plasma flow becomes
Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II I. Effects of blood volume on the filtration fraction (FF) {Altered Volume Effects in syllabus A. Under normal conditions, ~20% of renal plasma flow becomes
RENAL WATER REGULATION page 1
 page 1 INTRODUCTION TO WATER EXCRETION A. Role of the Kidney: to adjust urine formation rate and urine concentration to maintain 1. body fluid osmolar concentration 2. body fluid volume 3. intravascular
page 1 INTRODUCTION TO WATER EXCRETION A. Role of the Kidney: to adjust urine formation rate and urine concentration to maintain 1. body fluid osmolar concentration 2. body fluid volume 3. intravascular
Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus!
 Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Urinary System Components:! -Kidneys! -Ureters! -Urinary Bladder!! -Urethra!
Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Urinary System Components:! -Kidneys! -Ureters! -Urinary Bladder!! -Urethra!
CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM. At the end of this chapter, student will be able to:
 CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM At the end of this chapter, student will be able to: a) Describe the location and general function of each organ of the urinary system. b) Name the parts of a nephron and the
CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM At the end of this chapter, student will be able to: a) Describe the location and general function of each organ of the urinary system. b) Name the parts of a nephron and the
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Questions and Answers for Health Care Providers: Renal Dosing and Administration Recommendations for Peramivir IV
 Questions and Answers for Health Care Providers: Renal Dosing and Administration Recommendations for Peramivir IV The purpose of this document is to provide additional clarification to the existing information
Questions and Answers for Health Care Providers: Renal Dosing and Administration Recommendations for Peramivir IV The purpose of this document is to provide additional clarification to the existing information
Drug Excretion. Renal Drug Clearance. Drug Clearance and Half-Life. Glomerular Filtration II. Glomerular Filtration I. Drug Excretion and Clearance
 t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
Dr. Johnson PA Renal Winter 2010
 1 Renal Control of Acid/Base Balance Dr. Johnson PA Renal Winter 2010 Acid/Base refers to anything having to do with the concentrations of H + ions in aqueous solutions. In medical physiology, we are concerned
1 Renal Control of Acid/Base Balance Dr. Johnson PA Renal Winter 2010 Acid/Base refers to anything having to do with the concentrations of H + ions in aqueous solutions. In medical physiology, we are concerned
23. The Urinary System Text The McGraw Hill Companies, 2003 CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 The kidneys (green), ureters, and urinary bladder (red) of a healthy person (colorized X ray) The Urinary System CHAPTER OUTLINE Functions of the Urinary System 880 Functions of the Kidneys
CHAPTER 23 The kidneys (green), ureters, and urinary bladder (red) of a healthy person (colorized X ray) The Urinary System CHAPTER OUTLINE Functions of the Urinary System 880 Functions of the Kidneys
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
THE PRISMAFLEX SYSTEM
 THE PRISMAFLEX SYSTEM The Prismaflex Control Unit is intended for: Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) for patients weighing 20 kilograms or more with acute renal failure and/or fluid overload.
THE PRISMAFLEX SYSTEM The Prismaflex Control Unit is intended for: Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) for patients weighing 20 kilograms or more with acute renal failure and/or fluid overload.
The PRISMAFLEX System. Making possible personal.
 The PRISMAFLEX System Making possible personal. TPE on the PRISMAFLEX System The PRISMAFLEX System can help you meet the demands of multiple therapies with a versatile platform that can be customized to
The PRISMAFLEX System Making possible personal. TPE on the PRISMAFLEX System The PRISMAFLEX System can help you meet the demands of multiple therapies with a versatile platform that can be customized to
PRISMAFLEX CRRT SYSTEM
 THE PRISMAFLEX CRRT SYSTEM Recover. patients benefit There s a simple reason why the Prismaflex system is used more than any other Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) It s a complete system with
THE PRISMAFLEX CRRT SYSTEM Recover. patients benefit There s a simple reason why the Prismaflex system is used more than any other Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) It s a complete system with
Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology
 Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology 1 Kidney Anatomy and Function (Lecture 1) 2 Functions of Kidney A) Regulation of water B) Regulation of electrolytes C) Acid-base
Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology 1 Kidney Anatomy and Function (Lecture 1) 2 Functions of Kidney A) Regulation of water B) Regulation of electrolytes C) Acid-base
UNIT 11 - URINARY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 11 - URINARY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 11.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM A. Regulate the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. B. Excretes
UNIT 11 - URINARY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 11.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM A. Regulate the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. B. Excretes
The Urinary System Urine (pp. 984 985)
 Kidney Anatomy (pp. 961 969) Location and External Anatomy (pp. 961 962) Internal Anatomy (pp. 962 963) Blood and Nerve Supply (pp. 963 964) Nephrons (pp. 964 969) Kidney Physiology: Mechanisms of Urine
Kidney Anatomy (pp. 961 969) Location and External Anatomy (pp. 961 962) Internal Anatomy (pp. 962 963) Blood and Nerve Supply (pp. 963 964) Nephrons (pp. 964 969) Kidney Physiology: Mechanisms of Urine
DIALYSIS COMPACT. The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney.
 DIALYSIS COMPACT The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney. Content 3 Editorial 4 What do healthy kidneys accomplish? 5 What causes kidney disease? 6 What effects does kidney disease have?
DIALYSIS COMPACT The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney. Content 3 Editorial 4 What do healthy kidneys accomplish? 5 What causes kidney disease? 6 What effects does kidney disease have?
Acute Renal Failure. usually a consequence.
 Acute Renal Failure usually a consequence www.philippelefevre.com Definitions Pathogenisis Classification ICU Incidence/ Significance Treatments Prerenal Azotaemia Blood Pressure Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors
Acute Renal Failure usually a consequence www.philippelefevre.com Definitions Pathogenisis Classification ICU Incidence/ Significance Treatments Prerenal Azotaemia Blood Pressure Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors
Acid-Base Balance and Renal Acid Excretion
 AcidBase Balance and Renal Acid Excretion Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Cite the basic principles of acidbase physiology. 2. Understand the bicarbonatecarbon dioxide
AcidBase Balance and Renal Acid Excretion Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Cite the basic principles of acidbase physiology. 2. Understand the bicarbonatecarbon dioxide
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 3)
 Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 3) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 27. Effect of Hypoventilation Now let's look at how the
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 3) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 27. Effect of Hypoventilation Now let's look at how the
Ultrafiltration Devices
 6 21 CFR 876.5820, Hemodialysis system and accessories. 7 21 CFR 876.5860, High permeability hemodialysis system. 10 21 CFR 876.5540, Blood access device and accessories. 8 21 CFR 876.5540, Blood access
6 21 CFR 876.5820, Hemodialysis system and accessories. 7 21 CFR 876.5860, High permeability hemodialysis system. 10 21 CFR 876.5540, Blood access device and accessories. 8 21 CFR 876.5540, Blood access
ACID-BASE BALANCE AND ACID-BASE DISORDERS. I. Concept of Balance A. Determination of Acid-Base status 1. Specimens used - what they represent
 ACID-BASE BALANCE AND ACID-BASE DISORDERS I. Concept of Balance A. Determination of Acid-Base status 1. Specimens used - what they represent II. Electrolyte Composition of Body Fluids A. Extracellular
ACID-BASE BALANCE AND ACID-BASE DISORDERS I. Concept of Balance A. Determination of Acid-Base status 1. Specimens used - what they represent II. Electrolyte Composition of Body Fluids A. Extracellular
Milwaukee School of Engineering Gerrits@msoe.edu. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Fluid, Electrolyte & ph Balance
 , Electrolyte & ph Balance / Electrolyte / AcidBase Balance Body s: Cell function depends not only on continuous nutrient supply / waste removal, but also on the physical / chemical homeostasis of surrounding
, Electrolyte & ph Balance / Electrolyte / AcidBase Balance Body s: Cell function depends not only on continuous nutrient supply / waste removal, but also on the physical / chemical homeostasis of surrounding
Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap
 Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap 1. The body strives for electrical neutrality. a. Cations = Anions b. One of the cations is very special, H +, and its concentration is monitored and regulated very
Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap 1. The body strives for electrical neutrality. a. Cations = Anions b. One of the cations is very special, H +, and its concentration is monitored and regulated very
Quiz Urinary System. 1. The kidneys help regulate blood volume. help control blood pressure. help control ph. All of the above are correct.
 Quiz Urinary System 1. The kidneys help regulate blood volume. help control blood pressure. help control ph. All of the above are correct. 2. The location of the kidneys in relationship to the peritoneal
Quiz Urinary System 1. The kidneys help regulate blood volume. help control blood pressure. help control ph. All of the above are correct. 2. The location of the kidneys in relationship to the peritoneal
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney --Overview of Kidney Function a. Regulation of blood ionic composition b. Regulation of blood ph and osmolarity c. Regulate blood glucose level (gluconeogenesis) d.
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney --Overview of Kidney Function a. Regulation of blood ionic composition b. Regulation of blood ph and osmolarity c. Regulate blood glucose level (gluconeogenesis) d.
Replacement post-filter (ml/hr) Blood flow (ml/min) Dialysate (ml/hr) Weight (kg)
 404FM.1 CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY (CRRT) USING CITRATE Target Audience: Hospital only ICU (Based on Gambro and Kalmar Hospital protocols) CRRT using regional citrate anticoagulation This is
404FM.1 CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY (CRRT) USING CITRATE Target Audience: Hospital only ICU (Based on Gambro and Kalmar Hospital protocols) CRRT using regional citrate anticoagulation This is
Acid-Base Disorders. Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS. Objectives. Diagnostic Considerations. Step 1: Primary Disorder. Formulae. Step 2: Compensation
 Objectives Diagnostic approach to acid base disorders Common clinical examples of acidoses and alkaloses Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan 1 2 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph,
Objectives Diagnostic approach to acid base disorders Common clinical examples of acidoses and alkaloses Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan 1 2 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph,
Renal syndromes leading to abnormal kidney function:
 Renal syndromes leading to abnormal kidney function: An abnormality in kidney function can be detected by the following: 1) changes in serum creatinine concentration, reflecting changes in GFR 2) abnormalities
Renal syndromes leading to abnormal kidney function: An abnormality in kidney function can be detected by the following: 1) changes in serum creatinine concentration, reflecting changes in GFR 2) abnormalities
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Renal Acid/Base. Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 H+ Balance... 2
 Renal Acid/Base By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 H+ Balance... 2 Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 Role of Kidneys in Acid- Base Homeostasis... 3 Renal H+ Secretion... 3 Proximal
Renal Acid/Base By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 H+ Balance... 2 Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 Role of Kidneys in Acid- Base Homeostasis... 3 Renal H+ Secretion... 3 Proximal
ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS (Continued)
 ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS (Continued) Osmolarity Osmotic pressure is an important biologic parameter which involves diffusion of solutes or the transfer of fluids through semi permeable membranes. Per US Pharmacopeia,
ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS (Continued) Osmolarity Osmotic pressure is an important biologic parameter which involves diffusion of solutes or the transfer of fluids through semi permeable membranes. Per US Pharmacopeia,
Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology)
 Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology) ١ University/ Academy: Al-Azhar University Faculty/ Institute: Faculty of Medicine (Assuit) Department: physiology Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology)
Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology) ١ University/ Academy: Al-Azhar University Faculty/ Institute: Faculty of Medicine (Assuit) Department: physiology Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology)
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM 2012
 THE URINARY SYSTEM KIDNEYS A. Location: a. under the back muscles b. behind the parietal peritoneum c. just above the waistline d. right kidney a little lower than the left B. internal structure a. cortex:
THE URINARY SYSTEM KIDNEYS A. Location: a. under the back muscles b. behind the parietal peritoneum c. just above the waistline d. right kidney a little lower than the left B. internal structure a. cortex:
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
Compound extracted from plant Aristolochia. Nephrotoxin and carcinogen. Page 2
 Mariana Babayeva MD, PhD Touro College of Pharmacy, New York, NY, USA Page 1 Compound extracted from plant Aristolochia Nephrotoxin and carcinogen Page 2 AA-I is an organic anion eliminated by the kidney
Mariana Babayeva MD, PhD Touro College of Pharmacy, New York, NY, USA Page 1 Compound extracted from plant Aristolochia Nephrotoxin and carcinogen Page 2 AA-I is an organic anion eliminated by the kidney
Metabolic alkalosis. ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc
 Metabolic alkalosis ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Case History 28-year-old male Discovered by roommate at home in bewildering state During transport by EMS possible tonicclonic seizure Arrival in
Metabolic alkalosis ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Case History 28-year-old male Discovered by roommate at home in bewildering state During transport by EMS possible tonicclonic seizure Arrival in
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar (v.khullar@imperial.ac.uk)
 Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar (v.khullar@imperial.ac.uk) 1. Draw a simple diagram of the urinary system including the following: kidney, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder,
Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar (v.khullar@imperial.ac.uk) 1. Draw a simple diagram of the urinary system including the following: kidney, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder,
Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus
 Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus In order to workout this problem, study pages 240 6, 249 51, 318 9, 532 3 and 886 7 of the Pathophysiology, 5 th Edition. (This problem was based on
Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus In order to workout this problem, study pages 240 6, 249 51, 318 9, 532 3 and 886 7 of the Pathophysiology, 5 th Edition. (This problem was based on
STAGES OF SHOCK. IRREVERSIBLE SHOCK Heart deteriorates until it can no longer pump and death occurs.
 STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
The Urinary System. Anatomy of Urinary System. Urine production and elimination are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis
 The Urinary System Urine production and elimination are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis all body systems are directly or indirectly affected by kidney function eg. composition
The Urinary System Urine production and elimination are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis all body systems are directly or indirectly affected by kidney function eg. composition
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Nursing 113. Pharmacology Principles
 Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
GCE. Biology. Mark Scheme for June 2011. Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy. Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Mark Scheme for June 2011 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Biology Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Mark Scheme for June 2011 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
The Kidneys: Structure, Function, Disorders
 The Kidneys: Structure, Function, Disorders by John H. Dirckx, M.D. Everyone knows that the heart, the lungs, and the brain are vital organs that is, that their absence or destruction is incompatible with
The Kidneys: Structure, Function, Disorders by John H. Dirckx, M.D. Everyone knows that the heart, the lungs, and the brain are vital organs that is, that their absence or destruction is incompatible with
MANITOBA NEPHROLOGY NURSING COURSE
 MANITOBA NEPHROLOGY NURSING COURSE Introduction to the Manitoba Renal Program 3 The Renal Education Department 6 WRHA Renal Education Department 6 Site Educators 7 Philosophy Statement of MRP Education
MANITOBA NEPHROLOGY NURSING COURSE Introduction to the Manitoba Renal Program 3 The Renal Education Department 6 WRHA Renal Education Department 6 Site Educators 7 Philosophy Statement of MRP Education
Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia
 Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia Case Presentation: History 62 y/o male is admitted to the hospital with a 3 month history of excessive urination (polyuria) and excess water intake up to
Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia Case Presentation: History 62 y/o male is admitted to the hospital with a 3 month history of excessive urination (polyuria) and excess water intake up to
ASN Dialysis Advisory Group ASN DIALYSIS CURRICULUM
 ASN Dialysis Advisory Group ASN DIALYSIS CURRICULUM 0 ASN Dialysis Curriculum Dialysis Circuit Review Bessie A. Young, MD, MPH, FACP Associate Professor, University of Washington Director Home Dialysis,
ASN Dialysis Advisory Group ASN DIALYSIS CURRICULUM 0 ASN Dialysis Curriculum Dialysis Circuit Review Bessie A. Young, MD, MPH, FACP Associate Professor, University of Washington Director Home Dialysis,
PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement)
 1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE
 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 1 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE The kidney is the primary organ that maintains the total volume, ph, and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid within
REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 1 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE The kidney is the primary organ that maintains the total volume, ph, and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid within
Liver Function Tests. Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB
 Liver Function Tests Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB Introduction Case presentation What is the liver? Overview of tests used to measure liver function RJ 10 month old European girl
Liver Function Tests Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB Introduction Case presentation What is the liver? Overview of tests used to measure liver function RJ 10 month old European girl
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Intravenous Fluid Selection
 BENNMC03_0131186116.qxd 3/9/05 18:24 Page 20 seema Seema-3:Desktop Folder:PQ731: CHAPTER 3 Intravenous Fluid Selection LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and
BENNMC03_0131186116.qxd 3/9/05 18:24 Page 20 seema Seema-3:Desktop Folder:PQ731: CHAPTER 3 Intravenous Fluid Selection LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 4)
 Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 4) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 5. The newly formed bicarbonate moves into the plasma.
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 4) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 5. The newly formed bicarbonate moves into the plasma.
Your Kidneys: Master Chemists of the Body
 Your Kidneys: Master Chemists of the Body www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
Your Kidneys: Master Chemists of the Body www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
Approach to the Patient with Acute Renal Failure. Michael Ornes Abbott Northwestern Hospital
 Approach to the Patient with Acute Renal Failure Michael Ornes Abbott Northwestern Hospital Definition Abrupt decrease in glomerular filtration rate Accumulation of urea and other metabolic byproducts
Approach to the Patient with Acute Renal Failure Michael Ornes Abbott Northwestern Hospital Definition Abrupt decrease in glomerular filtration rate Accumulation of urea and other metabolic byproducts
3. Tunica adventitia is the outermost layer; it is composed of loosely woven connective tissue infiltrated by nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics
 Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Automation: Introduction. Urine Automation. published by Bayer. Unit 3. Chemical Examination of Urine
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 7, Automation, Function Tests, and Calculi Automation: Introduction Advantages Saves time Allows for standardization of procedures
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 7, Automation, Function Tests, and Calculi Automation: Introduction Advantages Saves time Allows for standardization of procedures
Week 30. Water Balance and Minerals
 Week 30 Water Balance and Minerals Water: more vital to life than food involved in almost every body function is not stored--excreted daily largest single constituent of the human body, averaging 60% of
Week 30 Water Balance and Minerals Water: more vital to life than food involved in almost every body function is not stored--excreted daily largest single constituent of the human body, averaging 60% of
Advantages and disadvantages of CRRT in ARF patients. Norbert Lameire Renal Division University Hospital Ghent, Belgium
 Advantages and disadvantages of CRRT in ARF patients Norbert Lameire Renal Division University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Alexandria, 17/2/2005 Indications for RRT in critically ill ARF patients Renal Replacement
Advantages and disadvantages of CRRT in ARF patients Norbert Lameire Renal Division University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Alexandria, 17/2/2005 Indications for RRT in critically ill ARF patients Renal Replacement
Objectives. Functions of the kidney. Renal failure. Categories of AKI. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) RENAL FAILURE: AN UPDATE FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
 RENAL FAILURE: AN UPDATE FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS Tamara Kear, PhD, RN Assistant Professor of Nursing Villanova University Objectives Review normal kidney function. Define the pathophysiology of acute
RENAL FAILURE: AN UPDATE FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS Tamara Kear, PhD, RN Assistant Professor of Nursing Villanova University Objectives Review normal kidney function. Define the pathophysiology of acute
Advanced Subsidiary GCE Biology
 Advanced Subsidiary GCE Biology Unit F214 - Communication, Homeostasis and Energy - High banded OCR has produced these candidate style answers to support teachers in interpreting the assessment criteria
Advanced Subsidiary GCE Biology Unit F214 - Communication, Homeostasis and Energy - High banded OCR has produced these candidate style answers to support teachers in interpreting the assessment criteria
Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes
 Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance
 Distribution of Body Fluids Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Total body fluids=60% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Comp 20% of Total body wt. Interstitial= 15% of total body wt. Intravascular=5%
Distribution of Body Fluids Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Total body fluids=60% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Comp 20% of Total body wt. Interstitial= 15% of total body wt. Intravascular=5%
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Hemodialysis remains the major modality of renal replacement
 High-Efficiency and High-Flux Hemodialysis Sivasankaran Ambalavanan Gary Rabetoy Alfred K. Cheung Hemodialysis remains the major modality of renal replacement therapy in the United States. Since the 1970s
High-Efficiency and High-Flux Hemodialysis Sivasankaran Ambalavanan Gary Rabetoy Alfred K. Cheung Hemodialysis remains the major modality of renal replacement therapy in the United States. Since the 1970s
Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know
 Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make hormones your body needs for some important functions. When kidney failure
Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make hormones your body needs for some important functions. When kidney failure
