Power System Series Resonance Studies by Modified Admittance Scan
|
|
|
- Grant Woods
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Power System Series Resonance Studies by Modified Admittance Scan Felix O. Kalunta, MNSE, Frank N. Okafor, FNSE, Member, IEEE, Osita U. Omeje Abstract This paper presents a modified method of formulating the loop admittance matrix which is deployed to identify the series resonant frequencies in large electrical networks involving numerous shunt capacitances. Three matrices were assembled from the network R, L and C elements and later synthesized to obtain the network loop admittance matrix. Its application to a sample network has shown the practicability and effectiveness of this method. This paper also seeks to demonstrate the impact of certain factors like cable capacitance and skin effect on the value of resonant frequencies. Index Terms Harmonic Resonance, Loop Admittance Matrix, Power Quality and Series Resonance. I. INTRODUCTION The application of capacitor banks in the power industry has yielded some utility benefits such as power factor correction, voltage support and release of system capacity. However, their interaction with system inductive supply circuit [1, 2] causes power quality problems by way of amplifying high order harmonics. These could lead to overheating, failure of the capacitor banks themselves or blowing of power transformer units resulting in constant interruption in production schedules. Another concern is that the broadband spectrum emitted in the process could result in emission limits being exceeded for non-characteristic harmonics and for inter-harmonics. The challenge is how to theoretically predict the resonant frequencies based on which appropriate mitigation measures can be included at the planning stage or the magnitude of amplified currents for the power equipment to be de-rated in order to withstand this exigency. There is also the need to indicate which of the system component is under the threat of series resonance [3]. The papers [4 5] describes the use of frequency scan technique to detect the possible resonant frequencies in the electrical network while [5, 6] presented a harmonic resonance mode assessment based on the analysis of eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the system bus impedance matrix. Further details of modal analysis in the study of resonance are treated in the technical literature [9-11]. Felix O. Kalunta is currently pursuing his Ph.D degree with the Department of Electrical/Electronic Engineering, University of Lagos, Nigeria. He is on study leave from Federal Institute of industrial Research Lagos, Nigeria ( [email protected]). Osita U. Omeje is currently pursuing his Ph.D degree with the Department of Electrical/Electronic Engineering, University of Lagos, Nigeria ( [email protected]) Frank N. Okafor is a professor with the Electrical/Electronic Engineering Department, University of Lagos, Nigeria. ( [email protected]). These methods are primarily suitable for parallel resonance problem with little adaptation to the analysis of series resonance. The reason lies in the close relationship between loop impedance and the occurrence of series resonance. An attempt to apply the modal analysis to series resonance problem was also made [8] but yielded an incomplete solution. A dummy branch method was later incorporated into the modal analysis but the approach seems more like a short circuit study which does not reflect the actual series resonance scenario. The loop admittance scan technique is an adaptation of frequency scan for locating the resonance peaks in a series resonance problem. Calculations are performed to determine the loop admittance matrix of the concerned network, while the driving point admittances are the determinants of the resonant frequencies. The complexities involved in the calculation of the loop admittance matrix for large power networks especially when cable capacitance is involved have necessitated the need for a modified admittance scan. In such cases, matrix of network elements R, L and C are easily assembled by computer programming and later synthesized to form a loop impedance matrix. This is the approach adopted in this paper. The formation of dummy loops in the calculation of the network matrices is applied in order to account for the shunt capacitances without altering the network topology. Other factors that affect resonance characteristics like skin effect of cables are also investigated in this paper. This study will account for skin effect by calculating the resistance R of the cable at various discrete frequencies using an equation that varies according to cable type [11]. R = R 1 ( h ), where h (1) where R 1 is the resistance of the cable at the fundamental frequency and h is the harmonic order. II. MODAL ANALYSIS APPLIED TO SERIES RESONANCE The determination of series resonant frequencies is based on mesh analysis at each harmonic frequency h in per unit. Resonance mode analysis in this case is based on the fact that the loop impedance matrix of a power network becomes singular at resonant frequencies. This requires the calculation of the eigenvalues of the system as well as their sensitivities to changes in system parameters. Imagine that a system experiences resonance at frequency h according to the frequency scan analysis. It implies that some elements of the loop current vector have large values at h. This in turn implies that the inverse of the [Z h ] matrix has large elements. This phenomenon is primarily caused by the fact that one of the eigen-values of the Z matrix is close to zero. In fact, if the system had no damping, the Z matrix would become singular due to one of its eigenvalues becoming zero. The above reasoning leads us to believe that the characteristics of the smallest eigenvalue of the [Z h ] matrix could contain useful information about the cause of the harmonic
2 resonance. The above analysis can be formally stated as follows: [V] h = [Z loop ] h [I loop ] h The current vector for each harmonic order is as follows [I loop ] h = [Z loop ] h [V] h, h = 1, 2, 3 n (2) Where[Z loop ] h, is the loop impedance matrix [V] h is the harmonic loop voltage vector. As usual, the loop impedance matrix can be decomposed into the following form: [Z] = [L][D][T] is the eigen-decomposition of the [Z] matrix at frequency h. [L] and [T] are the left and right eigenvector matrices of [Z] [D] - diagonal eigenvalue matrix of Z. T= L is due to the fact that Y is symmetric. Equation (2) now becomes [I]=[L][D] [T] [V] (3) If [T][V] and [T][I] are defined as the modal voltage and current vectors respectively. It can be seen that admittance scan equation has been transformed into the following form: J 1 λ 1 V m1 J [ 2 λ ] = 2 V [ m2 ] (4) J n [ λ n ] V mn This can be abbreviated as, [J k ] h = [λ k ] h [V mk ] h (5) The inverse of the eigen value, λ k, has the unit of admittance and is named modal admittance. One can easily see that if λ 1 = or is very small, a small applied mode 1 voltage will lead to a large mode 1 current. On the other hand, the other modal currents will not be affected since they have no 'coupling' with mode 1 voltage. In other words, one can easily identify the 'locations' of resonance frequencies in the modal domain. After identifying the critical mode of resonance, it is possible to find the 'participation' of each loop in the resonance. This can be done using the well-known participation factor theory described in [1]. III. FORMULATION OF LOOP ADMITTANCE SCAN The admittance scan is a series resonance counterpart of the bus impedance scan. The scan is performed in one network mesh at a time. A sinusoidal voltage of unit amplitude V = 1, and of certain harmonic frequency is inserted into this mesh and the corresponding loop current is calculated. The process is repeated for other harmonic frequencies in per unit. For the purpose of illustration, consider a radial network in fig. 1 containing capacitor banks with a non-linear load connected to bus J through a transformer and a long cable. The network is partitioned along the point of common coupling between the consumer distribution network and public utility supply as in fig. 2. The consumer side of the network is modeled at each harmonic frequency h, and the system supply side is reduced to its Thevenin equivalent also at each harmonic frequency. There are two buses where voltage amplification could be excited by parallel resonance and also three meshes or loops where current amplification can occur by series resonance. Fig. 1: A simple consumer premises supplied from the public utility network Fig. 2: The equivalent circuit model of the 2 bus consumer network The application of loop analysis to fig. 2 produces the following equation, [V] h = [Z loop ] h [I loop ] h The current vector at each harmonic frequency, h is as follows [I loop ] h = [Z loop ] h [V] h, h = 1, 2, 3 n (6) The matrix [Z loop ] h is known as the loop impedance matrix. The inverse of the loop impedance matrix is known as loop admittance matrix, Y loop Y loop = [Z loop ] (7) This matrix is the counterpart of bus impedance matrix and is therefore useful in the determination of the frequencies at which harmonic series resonance occurs. Equation (6) can now be written as loop I 1 [ I 2 ] I 3 loop Y 11 Y 12 Y 13 = [ Y 21 Y 22 Y 23 ] Y 31 Y 32 Y 33 V 1 [ V 2 ] (8) V 3 For the purpose of resonance analysis, only the driving point admittances Y l kk are required. l Therefore Y kk = [ I k ], k j V k V j = [I loop ] h k = [Y loop ] h h kk [V loop ] k, V j = k j ---- (9) Suppose V k = 1p. u for all h =1, 2, 3 n [I loop ] h h k = [Y loop ] kk (1) A graph of [I loop ] k against h is equivalent to a graph of [Y loop ] kk against h. Therefore, driving point admittance versus frequency plot is obtained for each mesh in the network. Therefore, driving point admittance versus frequency plot is obtained for each mesh in the network. This technique when applied for the determination of series resonant frequencies in power networks can be referred to as admittance scan. The off diagonal or transfer admittances could be considered in the admittance scan when dealing
3 with many harmonic sources applied simultaneously at different network meshes. The current change in the k-th mesh due to the insertion of unit harmonic voltages in meshes k, i and j is stated as C p = the inverse shunt capacitance at p-th dummy loop. I k = Y kk + Y ki + Y kj (11) IV. MODIFICATION OF NETWORK MATRICES TO ACCOUNT FOR THE SHUNT CAPACITANCES Procedure: 1. The three (n n) network matrices are assembled as usual in the absence of the shunt capacitances. These are designated as R old, L old and G old respectively. Fig 3: Equivalent circuit diagram showing two dummy loops for shunt capacitors C 1 and C 2 2. All parallel connection of capacitances can be combined together by summation. 3. Dummy loops m in number are created at each node where the shunt capacitances exist such that the total number of loops becomes(n + m), see fig 3. The dummy loops are assigned loop numbers n + 1, n + 2, n + m 4. Extra rows and columns corresponding to the number of the created dummy loops are added to each of the three network matrices to form a partitioned matrix as shown, R new = [ R old A ] (12) A Q L new = [ L old B ] (13) B H G new = [ G old U ] (14) U V 5. The dummy loops are eliminated using the kron reduction formular, R new = R old AQA T, L new = L old BHB T and G new = G old UVU T 6. The matrix of network elements R, L and G are finally synthesized according to equation (15) to obtain the loop impedance matrix. This is repeated for each harmonic frequency, h. [Z loop ] = [R new ] + jω 1 h[l new ] j[g new ]/ω 1 h - (15) Where L n n loop inductance matrix R n n loop resistance matrix G n n loop inverse capacitance matrix ω 1 fundamental frequency in rad/s For a dummy loop p created between two actual loops i and j A ip = A pi = R sp, A jp = A pj = R sp, Q pp = R sp, elsewhere the entries are zero. Similarly, B ip = B pi = L sp, B jp = B pj = L sp, H pp = L sp and V pp = C p, elsewhere the entries are zero. Where R sp = the total resistance in the branch common to loops i, j and p L sp = the total inductance in the branch common to loops i, j and p Fig. 4: The sequential process of carrying out an admittance scan based on the creation of dummy loops The updated matrices obtained from application of the above procedure to fig. 3 are, R Loop = L Loop = G Loop = [ [ R 11 R 21 R 31 R s1 L 11 L 21 L 31 G 11 G 21 G 31 [ R 12 R 22 R 32 R s1 L 12 L 22 L 32 G 12 G 22 G 32 R 11 R 23 R 33 G 11 G 23 G 33 L 11 L 23 L 33 R s1 R s1 R s1 C 1 ] C 2 ] (16) L s2 L s2 L s2 ] (17) (18)
4 Modal Impedance (pu) Impedance (pu) Admittance (pu) Modal Admittance (pu) Equation (15) is then applied after the process of eliminating the dummy loops, [Z loop ] = [R new ] + jω 1 h[l new ] j[g new ]/ω 1 h 12 1 Loop1 Loop2 Loop3 Y loop = [Z loop ] new (19) 8 6 The entire process of carrying out an admittance scan based on the creation of dummy loops is described in the flow chart in fig. 4. The modified admittance scan and modal loop analysis has been applied to the equivalent circuit shown in fig.2, and the results are displayed in Fig. 7 and 8 respectively. With the circuit, series resonance result could be compared to that of parallel resonance solved by frequency scan and Resonance Mode Analysis (see fig. 5 and 6) Fig. 7: Results of modal Loop analysis on test system bus1 bus2 bus Loop1 Loop2 Loop Fig 5: Bus Impedance Scan Results of the test system Fig. 8: Loop Admittance Scan results of the test system bus1 bus2 bus3 V. APPLICATION TO A DISTRIBUTION NETWORK The network diagram in fig.9 represents an 11kV underground radial distribution network which feeds nine load centers containing two major harmonic sources and four capacitor banks. It is an expansion of the distribution network used as case study in Reference [7]. The load centers are connected by 35mm 2 x 3, 11kV underground cables whose parameters are as follows, Fig. 6: Results of bus Resonance mode analysis (RMA) The results indicate that the modified loop admittance scan compares favourably to its counterparts: modal-loop analysis and bus impedance scan. The key resonance modes according to the results displayed in Fig. 5 8 occur at frequencies (pu) = 4, 17 and 27. The modal admittance scan (fig.7) produces only one resonance peak for each mesh whereas about three peaks are captured in each mesh in the results of modified loop admittance scan. This achievement is because the network topological structure was not altered in the process of applying the proposed technique in localizing the series resonant frequencies. Resistance/ph/km =.243Ω, Inductance/ph/km = 5.23 x 1-4 H Capacitance/ph/km = x 1-8 F The frequency response characteristics resulting from application of modified loop admittance scan across the entire distribution network are shown in fig
5 Fig. 12: Frequency response considering the effect of cable capacitance Fig. 9: Diagram showing the 11kV radial distribution network in a consumer premises Fig.13: Frequency response considering cable capacitance and skin effect The results indicate the occurrence of series resonance peaks at the various meshes M1 M9 as indicated. Fig 1: Frequency response neglecting the effect of cable capacitance and skin effect In figure 1 where the effects of cable capacitance and skin effect are neglected, the resonant frequencies in per unit are h = 6, 7, 14 and 15. In figure 11 where the effect of aggregate harmonic sources is considered, the resonant frequencies are the same as in fig. 1. In figure 12 where only the effect of cable capacitance is considered, the resonance frequencies in per unit are h = 6, 7 and 14. In figure 13 where the effects of cable capacitance and skin effect are considered, the resonance frequencies in per unit are h = 6, 7 and 14. Fig 11: Frequency response for aggregate sources neglecting the effect of cable capacitance and skin effect Comparison between figures 1-13 indicates that cable capacitance contributes immensely to the shifting of the resonant frequencies in M3 M6 while the skin effect only reduces the magnitude of loop admittance and widens the frequency curve. Since resistance instead of inductance or capacitance (that is the main contributors to system resonance) varies according to the skin effect, consequently, considering the skin effect in the calculations does not shift the resonant frequencies. However, the increased resistance could dampen the admittance peaks at resonance points thereby decreasing the branch currents. Skin effect also
6 increases the bandwidth of resonance. This implies the greater chance of current amplification occurring within the neighbourhood of the resonant peaks. Comparison between fig. 1 and 11 indicates that the application of many harmonic frequency sources only impacts on the magnitude of the driving point admittances and therefore is of no consequence to this study which is focused on the resonant frequencies. VI. CONCLUSION The modified loop admittance scan proves to be an acceptable method for capturing all the dominant frequencies involved in series resonance without any restriction to the utilized frequency step. The application of a single unit voltage is sufficient in the definition of admittance scan. Specific achievements are recorded in this study: the determination of series resonant frequencies by the application of loop admittance matrix, the use of matrix partitioning to treat independently the connection of shunt capacitors and the contribution of skin effect as well as cable capacitance on these results. It is noted that skin effect does not contribute to the shifting of resonant frequencies but only cable capacitance. Hence, in the calculation of the resonance peaks, the contribution of skin effect can be neglected. However, skin effect makes a significant contribution to the value of branch currents which necessitates its consideration. Conference on Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IET 211), Faculty of Engineering, University of Lagos, Nigeria, 8th 1th August 211, pp [8] H. Zhou, Y. Wu, S. Lou and X. Xiong, Power System Series Harmonic Resonance Assessment based on Improved Modal Analysis, Journal Of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Istanbul University, 27, vol.7, No.2, pp [9] C. Yang, K. Liu and Q. Zhang, An Improved Modal Analysis Method for Harmonic Resonance Analysis, IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT 28), ISBN: , Chengdu, China, 28, pp.1 5. [1] K. Md Hasan, K. Rauma et al, Harmonic Resonance Study for Wind Power Plant, International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 12), Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 8th to 3th March 212. [11] K. Nisak, K. Rauma et al, An Overview of Harmonic Analysis and Resonances of a Large Wind Power Plant, Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 211), 7 1 November, 211. VII. REFERENCES [1] Z. Huang, Y. Cui and W. Xu, "Application of Modal Sensitivity for Power System Harmonic Resonance Analysis", IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, vol. 22, 27, pp [2] J. Li, N. Samaan and S. Williams, "Modeling of Large Wind Farm Systems for Dynamic and Harmonics Analysis", Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition, T&D, IEEE/PES, 28, pp [3] C. Chien and R. Bucknall, "Harmonic Calculations of Proximity Effect on Impedance Characteristics in Subsea Power Transmission Cables", IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, ISSN: , vol. 24, October 29, pp [4] H. K. Lukasz, J. Hjerrild and C. L. Bak, Wind Farm Structures: Impact on Harmonic Emission and Grid Interaction, European Wind Energy Conference 21, Warsaw, Poland, 21. [5] R. Zheng and M. Bollen, Harmonic Resonances Due to a Grid-Connected Wind Farm, In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power (ICHQP 21), Bergamo, Italy, September 21, pp [6] J. Arrillaga and W. Neville, Power System Harmonics, ISBN: , West Sussex: Wiley & Sons, 23. [7] F. O. Kalunta and F. N. Okafor, Harmonic Analysis of Power Networks Supplying Nonlinear Loads, International
A Direct Numerical Method for Observability Analysis
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL 15, NO 2, MAY 2000 625 A Direct Numerical Method for Observability Analysis Bei Gou and Ali Abur, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract This paper presents an algebraic method
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL 15, NO 2, MAY 2000 625 A Direct Numerical Method for Observability Analysis Bei Gou and Ali Abur, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract This paper presents an algebraic method
Power System review W I L L I A M V. T O R R E A P R I L 1 0, 2 0 1 3
 Power System review W I L L I A M V. T O R R E A P R I L 1 0, 2 0 1 3 Basics of Power systems Network topology Transmission and Distribution Load and Resource Balance Economic Dispatch Steady State System
Power System review W I L L I A M V. T O R R E A P R I L 1 0, 2 0 1 3 Basics of Power systems Network topology Transmission and Distribution Load and Resource Balance Economic Dispatch Steady State System
Sensitivity Analysis of Waveform Distortion Assessment for Wind Plants
 Sensitivity Analysis of Waveform Distortion Assessment for Wind Plants Mariana B. Pereira 1, Einar V. Larsen 2, Sebastian A. Achilles 3 Energy Consulting General Electric 1 Av. Magalhães de Castro 4800,
Sensitivity Analysis of Waveform Distortion Assessment for Wind Plants Mariana B. Pereira 1, Einar V. Larsen 2, Sebastian A. Achilles 3 Energy Consulting General Electric 1 Av. Magalhães de Castro 4800,
Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models
 EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Current, Voltage, Impedance Ohm
EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Current, Voltage, Impedance Ohm
Typical Data Requirements Data Required for Power System Evaluation
 Summary 66 Carey Road Queensbury, NY 12804 Ph: (518) 792-4776 Fax: (518) 792-5767 www.nepsi.com [email protected] Harmonic Filter & Power Capacitor Bank Application Studies This document describes NEPSI
Summary 66 Carey Road Queensbury, NY 12804 Ph: (518) 792-4776 Fax: (518) 792-5767 www.nepsi.com [email protected] Harmonic Filter & Power Capacitor Bank Application Studies This document describes NEPSI
Bandwidth analysis of multimode fiber passive optical networks (PONs)
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 2, 2009 Bandwidth analysis of multimode fiber passive optical networks (PONs) GRZEGORZ STEPNIAK *, LUKASZ MAKSYMIUK, JERZY SIUZDAK Institute of Telecommunications, Warsaw
Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 2, 2009 Bandwidth analysis of multimode fiber passive optical networks (PONs) GRZEGORZ STEPNIAK *, LUKASZ MAKSYMIUK, JERZY SIUZDAK Institute of Telecommunications, Warsaw
HARMONIC DISTORTION IN THE ELECTRIC SUPPLY SYSTEM
 Technical Note No.3 March 2000 HARMONIC DISTORTION IN THE ELECTRIC SUPPLY SYSTEM This Technical Note discusses harmonic distortion, its causes and adverse effects, what levels are unacceptable and how
Technical Note No.3 March 2000 HARMONIC DISTORTION IN THE ELECTRIC SUPPLY SYSTEM This Technical Note discusses harmonic distortion, its causes and adverse effects, what levels are unacceptable and how
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy Grid Integration. Jian Sun, Professor and Director Department of ECSE & Center for Future Energy Systems
 Smart Grid and Renewable Energy Grid Integration Jian Sun, Professor and Director Department of ECSE & Center for Future Energy Systems 1 How Smart Can We Make This Grid? 2 Smart Grid Drivers Need to Use
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy Grid Integration Jian Sun, Professor and Director Department of ECSE & Center for Future Energy Systems 1 How Smart Can We Make This Grid? 2 Smart Grid Drivers Need to Use
Positive Feedback and Oscillators
 Physics 3330 Experiment #6 Fall 1999 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
Physics 3330 Experiment #6 Fall 1999 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
INTRODUCTION TO HARMONIC ASSESSMENT IN POWER SYSTEMS
 INTRODUCTION TO HARMONIC ASSESSMENT IN POWER SYSTEMS LIST OF CONTENT 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 2. HARMONIC VOLTAGE ASSESSMENT REQUIREMENT IN THE UK... 2 3. THE ASSESSMENT... 2 3.1. SYSTEM MODELLING...3 3.2.
INTRODUCTION TO HARMONIC ASSESSMENT IN POWER SYSTEMS LIST OF CONTENT 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 2. HARMONIC VOLTAGE ASSESSMENT REQUIREMENT IN THE UK... 2 3. THE ASSESSMENT... 2 3.1. SYSTEM MODELLING...3 3.2.
POWER SYSTEM HARMONICS. A Reference Guide to Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures AN ALLEN-BRADLEY SERIES OF ISSUES AND ANSWERS
 A Reference Guide to Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures AN ALLEN-BRADLEY SERIES OF ISSUES AND ANSWERS By: Robert G. Ellis, P. Eng., Rockwell Automation Medium Voltage Business CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...
A Reference Guide to Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures AN ALLEN-BRADLEY SERIES OF ISSUES AND ANSWERS By: Robert G. Ellis, P. Eng., Rockwell Automation Medium Voltage Business CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...
EMTP STUDIES PERFORMED TO INSERT LONG AC CABLES IN THE FRENCH GRID
 Tension (kv) Impedance (Ohms) EMTP STUDIES PERFORMED TO INSERT LONG AC CABLES IN THE FRENCH GRID frequency (Hz) Simon DESCHANVRES Yannick VERNAY RTE, CNER, Substations Department t (ms) EMTP-RV Users Group
Tension (kv) Impedance (Ohms) EMTP STUDIES PERFORMED TO INSERT LONG AC CABLES IN THE FRENCH GRID frequency (Hz) Simon DESCHANVRES Yannick VERNAY RTE, CNER, Substations Department t (ms) EMTP-RV Users Group
IMPROVED NETWORK PARAMETER ERROR IDENTIFICATION USING MULTIPLE MEASUREMENT SCANS
 IMPROVED NETWORK PARAMETER ERROR IDENTIFICATION USING MULTIPLE MEASUREMENT SCANS Liuxi Zhang and Ali Abur Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University Boston, MA, USA [email protected]
IMPROVED NETWORK PARAMETER ERROR IDENTIFICATION USING MULTIPLE MEASUREMENT SCANS Liuxi Zhang and Ali Abur Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University Boston, MA, USA [email protected]
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 3. Symmetrical Components & Faults Calculations
 SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 3 3.0 Introduction Fortescue's work proves that an unbalanced system of 'n' related phasors can be resolved into 'n' systems of balanced phasors called the
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 3 3.0 Introduction Fortescue's work proves that an unbalanced system of 'n' related phasors can be resolved into 'n' systems of balanced phasors called the
MINISTERIE VAN ECONOMISCHE ZAKEN GENERAL COST COMPARISON BETWEEN UNDERGROUND CABLES AND O.H. LINE SYSTEMS FOR H.V. TRANSMISSION
 MINISTERIE VAN ECONOMISCHE ZAKEN GENERAL COST COMPARISON BETWEEN UNDERGROUND CABLES AND O.H. LINE SYSTEMS FOR H.V. TRANSMISSION REPORT ON NETWORK RELIABILITY ASPECTS OF THE CHOICE LINE VERSUS CABLE FOR
MINISTERIE VAN ECONOMISCHE ZAKEN GENERAL COST COMPARISON BETWEEN UNDERGROUND CABLES AND O.H. LINE SYSTEMS FOR H.V. TRANSMISSION REPORT ON NETWORK RELIABILITY ASPECTS OF THE CHOICE LINE VERSUS CABLE FOR
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Terms and definitions
 .1 Introduction An important step in the procedure for solving any circuit problem consists first in selecting a number of independent branch currents as (known as loop currents or mesh currents) variables,
.1 Introduction An important step in the procedure for solving any circuit problem consists first in selecting a number of independent branch currents as (known as loop currents or mesh currents) variables,
A bidirectional DC-DC converter for renewable energy systems
 BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES Vol. 57, No. 4, 2009 A bidirectional DC-DC converter for renewable energy systems S. JALBRZYKOWSKI, and T. CITKO Faculty of Electrical Engineering,
BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES Vol. 57, No. 4, 2009 A bidirectional DC-DC converter for renewable energy systems S. JALBRZYKOWSKI, and T. CITKO Faculty of Electrical Engineering,
Impact of electric vehicles on the IEEE 34 node distribution infrastructure
 International Journal of Smart Grid and Clean Energy Impact of electric vehicles on the IEEE 34 node distribution infrastructure Zeming Jiang *, Laith Shalalfeh, Mohammed J. Beshir a Department of Electrical
International Journal of Smart Grid and Clean Energy Impact of electric vehicles on the IEEE 34 node distribution infrastructure Zeming Jiang *, Laith Shalalfeh, Mohammed J. Beshir a Department of Electrical
Nonlinear Iterative Partial Least Squares Method
 Numerical Methods for Determining Principal Component Analysis Abstract Factors Béchu, S., Richard-Plouet, M., Fernandez, V., Walton, J., and Fairley, N. (2016) Developments in numerical treatments for
Numerical Methods for Determining Principal Component Analysis Abstract Factors Béchu, S., Richard-Plouet, M., Fernandez, V., Walton, J., and Fairley, N. (2016) Developments in numerical treatments for
Electrical Resonance
 Electrical Resonance (R-L-C series circuit) APPARATUS 1. R-L-C Circuit board 2. Signal generator 3. Oscilloscope Tektronix TDS1002 with two sets of leads (see Introduction to the Oscilloscope ) INTRODUCTION
Electrical Resonance (R-L-C series circuit) APPARATUS 1. R-L-C Circuit board 2. Signal generator 3. Oscilloscope Tektronix TDS1002 with two sets of leads (see Introduction to the Oscilloscope ) INTRODUCTION
zcable Model for Frequency Dependent Modelling of Cable Transmission Systems
 zcable Model for Frequency Dependent Modelling of Cable Transmission Systems T. C. Yu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia 356 Main Mall, Vancouver, B.C., Canada
zcable Model for Frequency Dependent Modelling of Cable Transmission Systems T. C. Yu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia 356 Main Mall, Vancouver, B.C., Canada
Voltage Stability Improvement using Static Var Compensator in Power Systems
 Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 14, January-June 2009 p. 167-172 Voltage Stability Improvement using Static Var Compensator in Power Systems Department of Electrical/Computer Engineering,
Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 14, January-June 2009 p. 167-172 Voltage Stability Improvement using Static Var Compensator in Power Systems Department of Electrical/Computer Engineering,
Analyses of delivery reliability in electrical power systems
 Risk, Reliability and Societal Safety Aven & Vinnem (eds) 2007 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-0-415-44786-7 Analyses of delivery reliability in electrical power systems T. Digernes MathConsult,
Risk, Reliability and Societal Safety Aven & Vinnem (eds) 2007 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-0-415-44786-7 Analyses of delivery reliability in electrical power systems T. Digernes MathConsult,
Introduction to PowerWorld Simulator: Interface and Common Tools
 Introduction to PowerWorld Simulator: Interface and Common Tools 2001 South First Street Champaign, Illinois 61820 +1 (217) 384.6330 [email protected] http://www.powerworld.com Fault Analysis Analysis
Introduction to PowerWorld Simulator: Interface and Common Tools 2001 South First Street Champaign, Illinois 61820 +1 (217) 384.6330 [email protected] http://www.powerworld.com Fault Analysis Analysis
Control Strategy for Three Phase Shunt Active Power Filter with Minimum Current Measurements
 International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE) Vol.1, No.1, September 2011, pp. 31~ 42 ISSN: 2088-8708 31 Control Strategy for Three Phase Shunt Active Power Filter with Minimum Current
International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE) Vol.1, No.1, September 2011, pp. 31~ 42 ISSN: 2088-8708 31 Control Strategy for Three Phase Shunt Active Power Filter with Minimum Current
The design and performance of Static Var Compensators for particle accelerators
 CERN-ACC-2015-0104 [email protected] The design and performance of Static Var Compensators for particle accelerators Karsten Kahle, Francisco R. Blánquez, Charles-Mathieu Genton CERN, Geneva, Switzerland,
CERN-ACC-2015-0104 [email protected] The design and performance of Static Var Compensators for particle accelerators Karsten Kahle, Francisco R. Blánquez, Charles-Mathieu Genton CERN, Geneva, Switzerland,
Impedance Matching and Matching Networks. Valentin Todorow, December, 2009
 Impedance Matching and Matching Networks Valentin Todorow, December, 2009 RF for Plasma Processing - Definition of RF What is RF? The IEEE Standard Dictionary of Electrical and Electronics Terms defines
Impedance Matching and Matching Networks Valentin Todorow, December, 2009 RF for Plasma Processing - Definition of RF What is RF? The IEEE Standard Dictionary of Electrical and Electronics Terms defines
Introduction. Harmonics and IEEE 519 Page 1 of 19
 Introduction In an ideal power system, the voltage supplied to customer equipment, and the resulting load current are perfect sine waves. In practice, however, conditions are never ideal, so these waveforms
Introduction In an ideal power system, the voltage supplied to customer equipment, and the resulting load current are perfect sine waves. In practice, however, conditions are never ideal, so these waveforms
Hybrid Power System with A Two-Input Power Converter
 Hybrid Power System with A Two-Input Power Converter Y. L. Juan and H. Y. Yang Department of Electrical Engineering National Changhua University of Education Jin-De Campus, Address: No.1, Jin-De Road,
Hybrid Power System with A Two-Input Power Converter Y. L. Juan and H. Y. Yang Department of Electrical Engineering National Changhua University of Education Jin-De Campus, Address: No.1, Jin-De Road,
SOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS
 SOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS Linear systems Ax = b occur widely in applied mathematics They occur as direct formulations of real world problems; but more often, they occur as a part of the numerical analysis
SOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS Linear systems Ax = b occur widely in applied mathematics They occur as direct formulations of real world problems; but more often, they occur as a part of the numerical analysis
Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups
 Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited [email protected] www.syscompdesign.com April 30, 2011 Introduction The CircuitGear
Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited [email protected] www.syscompdesign.com April 30, 2011 Introduction The CircuitGear
Fault Analysis I13-1. 2008 PowerWorld Corporation
 Fault Analysis Analysis of power system parameters resulting from a ground or line to line fault somewhere in the system Simulator contains a tool for analyzing faults in an automatic fashion Can perform
Fault Analysis Analysis of power system parameters resulting from a ground or line to line fault somewhere in the system Simulator contains a tool for analyzing faults in an automatic fashion Can perform
COMPARISON OF THE FACTS EQUIPMENT OPERATION IN TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
 COMPARISON OF THE FACTS EQUIPMENT OPERATION IN TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS Afshin LASHKAR ARA Azad University of Dezfoul - Iran [email protected] Seyed Ali NABAVI NIAKI University of Mazandaran
COMPARISON OF THE FACTS EQUIPMENT OPERATION IN TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS Afshin LASHKAR ARA Azad University of Dezfoul - Iran [email protected] Seyed Ali NABAVI NIAKI University of Mazandaran
RLC Resonant Circuits
 C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
Product Data Bulletin
 Product Data Bulletin Power System Harmonics Causes and Effects of Variable Frequency Drives Relative to the IEEE 519-1992 Standard Raleigh, NC, U.S.A. INTRODUCTION This document describes power system
Product Data Bulletin Power System Harmonics Causes and Effects of Variable Frequency Drives Relative to the IEEE 519-1992 Standard Raleigh, NC, U.S.A. INTRODUCTION This document describes power system
Measurement, Modeling and Simulation of Capacitor Bank Switching Transients
 Measurement, Modeling and Simulation of Capacitor Bank Switching Transients Mirza Softić*, Amir Tokić**, Ivo Uglešić*** *Kreka - Dubrave e, Dubrave, Bosnia and Herzegovina (e-mail: [email protected]).
Measurement, Modeling and Simulation of Capacitor Bank Switching Transients Mirza Softić*, Amir Tokić**, Ivo Uglešić*** *Kreka - Dubrave e, Dubrave, Bosnia and Herzegovina (e-mail: [email protected]).
Circuits 1 M H Miller
 Introduction to Graph Theory Introduction These notes are primarily a digression to provide general background remarks. The subject is an efficient procedure for the determination of voltages and currents
Introduction to Graph Theory Introduction These notes are primarily a digression to provide general background remarks. The subject is an efficient procedure for the determination of voltages and currents
1 Introduction. 2 The Symmetrical Component Transformation. J.L. Kirtley Jr.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.06 Introduction to Power Systems Class Notes Chapter 4 Introduction To Symmetrical Components J.L. Kirtley
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.06 Introduction to Power Systems Class Notes Chapter 4 Introduction To Symmetrical Components J.L. Kirtley
BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS. December 2011
 AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
Fast analytical techniques for electrical and electronic circuits. Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology
 Fast analytical techniques for electrical and electronic circuits Vatché Vorpérian Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology PUBLISHED BY THE PRESS SYNDICATE OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
Fast analytical techniques for electrical and electronic circuits Vatché Vorpérian Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology PUBLISHED BY THE PRESS SYNDICATE OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
RLC Series Resonance
 RLC Series Resonance 11EM Object: The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study resonance in a resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) circuit by examining the current through the circuit as a function
RLC Series Resonance 11EM Object: The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study resonance in a resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) circuit by examining the current through the circuit as a function
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 10 / HIGH SPEED BUILDING BLOCKS / PAPER 10.5
 ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 10 / HIGH SPEED BUILDING BLOCKS / PAPER 10.5 10.5 Broadband ESD Protection Circuits in CMOS Technology Sherif Galal, Behzad Razavi Electrical Engineering Department, University of
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 10 / HIGH SPEED BUILDING BLOCKS / PAPER 10.5 10.5 Broadband ESD Protection Circuits in CMOS Technology Sherif Galal, Behzad Razavi Electrical Engineering Department, University of
LAB1 INTRODUCTION TO PSS/E EE 461 Power Systems Colorado State University
 LAB1 INTRODUCTION TO PSS/E EE 461 Power Systems Colorado State University PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to introduce PSS/E. This lab will introduce the following aspects of PSS/E: Introduction to
LAB1 INTRODUCTION TO PSS/E EE 461 Power Systems Colorado State University PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to introduce PSS/E. This lab will introduce the following aspects of PSS/E: Introduction to
Analysis of Common-Collector Colpitts Oscillator
 Analysis of Common-Collector Colpitts Oscillator H R Pota May 20, 2005 Introduction Murphy s rule when paraphrased for oscillators reads [], Amplifiers will oscillate but oscillators won t. As we all know,
Analysis of Common-Collector Colpitts Oscillator H R Pota May 20, 2005 Introduction Murphy s rule when paraphrased for oscillators reads [], Amplifiers will oscillate but oscillators won t. As we all know,
Impedance Matching of Filters with the MSA Sam Wetterlin 2/11/11
 Impedance Matching of Filters with the MSA Sam Wetterlin 2/11/11 Introduction The purpose of this document is to illustrate the process for impedance matching of filters using the MSA software. For example,
Impedance Matching of Filters with the MSA Sam Wetterlin 2/11/11 Introduction The purpose of this document is to illustrate the process for impedance matching of filters using the MSA software. For example,
Dynamics of Offshore Wind Turbines
 Proceedings of the Twenty-first (2011) International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference Maui, Hawaii, USA, June 19-24, 2011 Copyright 2011 by the International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers
Proceedings of the Twenty-first (2011) International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference Maui, Hawaii, USA, June 19-24, 2011 Copyright 2011 by the International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers
Three phase circuits
 Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO)
 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO) Copyright 2008 Caribbean
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL REPORT ON CANDIDATES WORK IN THE CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION MAY/JUNE 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO) Copyright 2008 Caribbean
SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS
 Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
METHODOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS OF DRIVE SYSTEM SIMULATION, WHEN COUPLING FINITE ELEMENT MACHINE MODELS WITH THE CIRCUIT SIMULATOR MODELS OF CONVERTERS.
 SEDM 24 June 16th - 18th, CPRI (Italy) METHODOLOGICL CONSIDERTIONS OF DRIVE SYSTEM SIMULTION, WHEN COUPLING FINITE ELEMENT MCHINE MODELS WITH THE CIRCUIT SIMULTOR MODELS OF CONVERTERS. Áron Szûcs BB Electrical
SEDM 24 June 16th - 18th, CPRI (Italy) METHODOLOGICL CONSIDERTIONS OF DRIVE SYSTEM SIMULTION, WHEN COUPLING FINITE ELEMENT MCHINE MODELS WITH THE CIRCUIT SIMULTOR MODELS OF CONVERTERS. Áron Szûcs BB Electrical
A Fuzzy Based Solution for Improving Power Quality in Electric Railway Networks
 A Fuzzy Based Solution for Improving Power Quality in Electric Railway Networks Mohammad Ali Sandidzadeh School of Railway Engineering, Iran University of Science & Technology, Tehran, Iran Tel: 98-21-7749-1030
A Fuzzy Based Solution for Improving Power Quality in Electric Railway Networks Mohammad Ali Sandidzadeh School of Railway Engineering, Iran University of Science & Technology, Tehran, Iran Tel: 98-21-7749-1030
Introduction to the Smith Chart for the MSA Sam Wetterlin 10/12/09 Z +
 Introduction to the Smith Chart for the MSA Sam Wetterlin 10/12/09 Quick Review of Reflection Coefficient The Smith chart is a method of graphing reflection coefficients and impedance, and is often useful
Introduction to the Smith Chart for the MSA Sam Wetterlin 10/12/09 Quick Review of Reflection Coefficient The Smith chart is a method of graphing reflection coefficients and impedance, and is often useful
Simulation of Cable Overloading Problem on a University Distribution System
 Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 6 (2013), pp. 765-770 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Simulation of Cable Overloading
Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 6 (2013), pp. 765-770 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Simulation of Cable Overloading
Line Reactors and AC Drives
 Line Reactors and AC Drives Rockwell Automation Mequon Wisconsin Quite often, line and load reactors are installed on AC drives without a solid understanding of why or what the positive and negative consequences
Line Reactors and AC Drives Rockwell Automation Mequon Wisconsin Quite often, line and load reactors are installed on AC drives without a solid understanding of why or what the positive and negative consequences
SURVEY OF HARMONIC DISTORTION IN LV AND MV NETWORKS: RESULTS AND CORRECTIVE STRATEGIES
 SURVEY OF HARMONIC DISTORTION IN LV AND MV NETWORKS: RESULTS AND CORRECTIVE STRATEGIES E Bompard*, E Carpaneto*, R Napoli*, P Ribaldone**, C Vercellino** * Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica Industriale,
SURVEY OF HARMONIC DISTORTION IN LV AND MV NETWORKS: RESULTS AND CORRECTIVE STRATEGIES E Bompard*, E Carpaneto*, R Napoli*, P Ribaldone**, C Vercellino** * Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica Industriale,
Considering the effects of UPS operation with leading power factor loads
 Considering the effects of UPS operation with leading power factor loads Over the past five years, a new generation of data processing and communications equipment has become prevalent in modern data centers
Considering the effects of UPS operation with leading power factor loads Over the past five years, a new generation of data processing and communications equipment has become prevalent in modern data centers
Telecommunication Line Protectors
 TN CR 0025 Telecommunication Line s 1.1 The nature of telecom surges The telecom services considered in this report are transported on twisted pair. Each service has two wires, or lines, sometimes called
TN CR 0025 Telecommunication Line s 1.1 The nature of telecom surges The telecom services considered in this report are transported on twisted pair. Each service has two wires, or lines, sometimes called
A COMPARISON ON PERFORMANCE OF TCSC/SSSC FOR A RADIAL SYSTEM
 IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN(E): 31-8843; ISSN(P): 347-4599 Vol. 3, Issue 9, Sep 015, 7-18 Impact Journals A COMPARISON ON PERFORMANCE OF TCSC/SSSC
IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN(E): 31-8843; ISSN(P): 347-4599 Vol. 3, Issue 9, Sep 015, 7-18 Impact Journals A COMPARISON ON PERFORMANCE OF TCSC/SSSC
An extended EMC study of an electrical powertrain for transportation systems
 European Association for the Development of Renewable Energies, Environment and Power Quality (EA4EPQ) International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 12) Santiago de Compostela
European Association for the Development of Renewable Energies, Environment and Power Quality (EA4EPQ) International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 12) Santiago de Compostela
Control Strategies of the Doubly Fed Induction Machine for Wind Energy Generation Applications
 Control Strategies of the Doubly Fed Induction Machine for Wind Energy Generation Applications AUTHORS Dr. Gonzalo Abad, The University of Mondragon, SPAIN. Dr. Miguel Ángel Rodríguez, Ingeteam Transmission
Control Strategies of the Doubly Fed Induction Machine for Wind Energy Generation Applications AUTHORS Dr. Gonzalo Abad, The University of Mondragon, SPAIN. Dr. Miguel Ángel Rodríguez, Ingeteam Transmission
EMI and t Layout Fundamentals for Switched-Mode Circuits
 v sg (t) (t) DT s V pp = n - 1 2 V pp V g n V T s t EE core insulation primary return secondary return Supplementary notes on EMI and t Layout Fundamentals for Switched-Mode Circuits secondary primary
v sg (t) (t) DT s V pp = n - 1 2 V pp V g n V T s t EE core insulation primary return secondary return Supplementary notes on EMI and t Layout Fundamentals for Switched-Mode Circuits secondary primary
Frequency-dependent underground cable model for electromagnetic transient simulation
 Frequency-dependent underground cable model for electromagnetic transient simulation Vasco José Realista Medeiros Soeiro Abstract A computation method for transients in a three-phase underground power-transmission
Frequency-dependent underground cable model for electromagnetic transient simulation Vasco José Realista Medeiros Soeiro Abstract A computation method for transients in a three-phase underground power-transmission
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits
 Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits The configuration of circuit elements clearly affects the behaviour of a circuit. Resistors connected in series or in parallel are very common in a circuit and act
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits The configuration of circuit elements clearly affects the behaviour of a circuit. Resistors connected in series or in parallel are very common in a circuit and act
Design of Four Input Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Application
 Design of Four Input Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Application A.Thiyagarajan Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Karpagam Institute of Technology
Design of Four Input Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Application A.Thiyagarajan Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Karpagam Institute of Technology
Variable Frequency Drives - a Comparison of VSI versus LCI Systems
 Variable Frequency Drives - a Comparison of VSI versus LCI Systems Introduction TMEIC is a leader in the innovative design and manufacture of large ac variable f requency drive systems. TMEIC has been
Variable Frequency Drives - a Comparison of VSI versus LCI Systems Introduction TMEIC is a leader in the innovative design and manufacture of large ac variable f requency drive systems. TMEIC has been
Simulation and Design of Printed Circuit Boards Utilizing Novel Embedded Capacitance Material
 Simulation and Design of Printed Circuit Boards Utilizing Novel Embedded Capacitance Material Yu Xuequan, Yan Hang, Zhang Gezi, Wang Haisan Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd Lujiazui Subpark, Pudong Software
Simulation and Design of Printed Circuit Boards Utilizing Novel Embedded Capacitance Material Yu Xuequan, Yan Hang, Zhang Gezi, Wang Haisan Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd Lujiazui Subpark, Pudong Software
Drivetech, Inc. Innovations in Motor Control, Drives, and Power Electronics
 Drivetech, Inc. Innovations in Motor Control, Drives, and Power Electronics Dal Y. Ohm, Ph.D. - President 25492 Carrington Drive, South Riding, Virginia 20152 Ph: (703) 327-2797 Fax: (703) 327-2747 [email protected]
Drivetech, Inc. Innovations in Motor Control, Drives, and Power Electronics Dal Y. Ohm, Ph.D. - President 25492 Carrington Drive, South Riding, Virginia 20152 Ph: (703) 327-2797 Fax: (703) 327-2747 [email protected]
Survey of Harmonics Measurements in Electrical Distribution System of a Technical Institution
 Survey of Harmonics Measurements in Electrical Distribution System of a Technical Institution Nandita Dey, Dr.A.K.Chakraborty Lecturer, Electrical Engineering Department, Tripura University Suryamaninagar
Survey of Harmonics Measurements in Electrical Distribution System of a Technical Institution Nandita Dey, Dr.A.K.Chakraborty Lecturer, Electrical Engineering Department, Tripura University Suryamaninagar
High Voltage Transient Analysis
 High Voltage Transient Analysis 4. Surges on Transmission Lines Due to a variety of reasons, such as a direct stroke of lightning on the line, or by indirect strokes, or by switching operations or by faults,
High Voltage Transient Analysis 4. Surges on Transmission Lines Due to a variety of reasons, such as a direct stroke of lightning on the line, or by indirect strokes, or by switching operations or by faults,
Transmission Line Transformers
 Radio Frequency Circuit Design. W. Alan Davis, Krishna Agarwal Copyright 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Print ISBN 0-471-35052-4 Electronic ISBN 0-471-20068-9 CHAPTER SIX Transmission Line Transformers 6.1
Radio Frequency Circuit Design. W. Alan Davis, Krishna Agarwal Copyright 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Print ISBN 0-471-35052-4 Electronic ISBN 0-471-20068-9 CHAPTER SIX Transmission Line Transformers 6.1
Lecture 24: Oscillators. Clapp Oscillator. VFO Startup
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 24 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 24: Oscillators. Clapp Oscillator. VFO Startup Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic output voltages, such as sinusoids. They accomplish this feat
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 24 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 24: Oscillators. Clapp Oscillator. VFO Startup Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic output voltages, such as sinusoids. They accomplish this feat
Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive
 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-237, Volume-1, Issue-5, November 211 Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive Bal Mukund Sharma, A.
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-237, Volume-1, Issue-5, November 211 Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive Bal Mukund Sharma, A.
Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques
 Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques 1 x 1 Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques Allan Huynh, Magnus Karlsson and Shaofang Gong Linköping University Sweden 1. Introduction Differential
Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques 1 x 1 Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques Allan Huynh, Magnus Karlsson and Shaofang Gong Linköping University Sweden 1. Introduction Differential
Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment
 Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
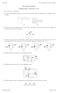 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Simulation and Analysis of Parameter Identification Techniques for Induction Motor Drive
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 7, Number 10 (2014), pp. 1027-1035 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Simulation and
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 7, Number 10 (2014), pp. 1027-1035 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Simulation and
Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies
 Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Analysis of Broadband Slot Cut Semi-Circular Microstrip Antennas
 Analysis of Broadband Slot Cut Semi-Circular Microstrip Antennas Amit A. Deshmukh EXTC, DJSCOE Vile Parle (W), Mumbai, India Ankita R. Jain EXTC, DJSCOE Vile Parle (W), Mumbai, India Apurva A. Joshi EXTC,
Analysis of Broadband Slot Cut Semi-Circular Microstrip Antennas Amit A. Deshmukh EXTC, DJSCOE Vile Parle (W), Mumbai, India Ankita R. Jain EXTC, DJSCOE Vile Parle (W), Mumbai, India Apurva A. Joshi EXTC,
Agilent AN 154 S-Parameter Design Application Note
 Agilent AN 154 S-Parameter Design Application Note Introduction The need for new high-frequency, solid-state circuit design techniques has been recognized both by microwave engineers and circuit designers.
Agilent AN 154 S-Parameter Design Application Note Introduction The need for new high-frequency, solid-state circuit design techniques has been recognized both by microwave engineers and circuit designers.
Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods
 Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods We have seen that using Kirchhoff s laws and Ohm s law we can analyze any circuit to determine the operating conditions (the currents and voltages). The
Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods We have seen that using Kirchhoff s laws and Ohm s law we can analyze any circuit to determine the operating conditions (the currents and voltages). The
MEASUREMENT SET-UP FOR TRAPS
 Completed on 26th of June, 2012 MEASUREMENT SET-UP FOR TRAPS AUTHOR: IW2FND Attolini Lucio Via XXV Aprile, 52/B 26037 San Giovanni in Croce (CR) - Italy [email protected] Trappole_01_EN 1 1 DESCRIPTION...3
Completed on 26th of June, 2012 MEASUREMENT SET-UP FOR TRAPS AUTHOR: IW2FND Attolini Lucio Via XXV Aprile, 52/B 26037 San Giovanni in Croce (CR) - Italy [email protected] Trappole_01_EN 1 1 DESCRIPTION...3
by the matrix A results in a vector which is a reflection of the given
 Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors Example Suppose Then So, geometrically, multiplying a vector in by the matrix A results in a vector which is a reflection of the given vector about the y-axis We observe that
Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors Example Suppose Then So, geometrically, multiplying a vector in by the matrix A results in a vector which is a reflection of the given vector about the y-axis We observe that
Electrical engineering education in the field of electric circuits theory at AGH University of Science and Technology in Kraków
 st World Conference on Technology and Engineering Education WIETE Kraków, Poland, 4-7 September Electrical engineering education in the field of electric circuits theory at AGH University of Science and
st World Conference on Technology and Engineering Education WIETE Kraków, Poland, 4-7 September Electrical engineering education in the field of electric circuits theory at AGH University of Science and
PIEZO FILTERS INTRODUCTION
 For more than two decades, ceramic filter technology has been instrumental in the proliferation of solid state electronics. A view of the future reveals that even greater expectations will be placed on
For more than two decades, ceramic filter technology has been instrumental in the proliferation of solid state electronics. A view of the future reveals that even greater expectations will be placed on
Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement. 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits. Experiment no 1
 Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
MOBILE SYSTEM FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HIGH VOLTAGE CABLES (132KV/220KV) VLF-200 HVCD
 MOBILE SYSTEM FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HIGH VOLTAGE CABLES (132KV/220KV) VLF-200 HVCD VERY LOW FREQUENCY (VLF) - PARTIAL DISCHARGES AND TANGENT DELTA HV/EHV POWER CABLES DIAGNOSTIC AND ON-SITE FIELD TESTING WITH
MOBILE SYSTEM FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HIGH VOLTAGE CABLES (132KV/220KV) VLF-200 HVCD VERY LOW FREQUENCY (VLF) - PARTIAL DISCHARGES AND TANGENT DELTA HV/EHV POWER CABLES DIAGNOSTIC AND ON-SITE FIELD TESTING WITH
Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation
 Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation To be performed during Week 9 (Oct. 20-24) and Week 10 (Oct. 27-31) Due Week 11 (Nov. 3-7) 1 Pre-Lab This Pre-Lab should be completed before attending your regular
Laboratory 4: Feedback and Compensation To be performed during Week 9 (Oct. 20-24) and Week 10 (Oct. 27-31) Due Week 11 (Nov. 3-7) 1 Pre-Lab This Pre-Lab should be completed before attending your regular
ε: Voltage output of Signal Generator (also called the Source voltage or Applied
 Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
AN-837 APPLICATION NOTE
 APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 916 Norwood, MA 262-916, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.47 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com DDS-Based Clock Jitter Performance vs. DAC Reconstruction Filter Performance
APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 916 Norwood, MA 262-916, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.47 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com DDS-Based Clock Jitter Performance vs. DAC Reconstruction Filter Performance
Lecture 7 Circuit analysis via Laplace transform
 S. Boyd EE12 Lecture 7 Circuit analysis via Laplace transform analysis of general LRC circuits impedance and admittance descriptions natural and forced response circuit analysis with impedances natural
S. Boyd EE12 Lecture 7 Circuit analysis via Laplace transform analysis of general LRC circuits impedance and admittance descriptions natural and forced response circuit analysis with impedances natural
S-DOMAIN ANALYSIS: POLES, ZEROS, AND BODE PLOTS
 S-DOMAIN ANAYSIS: POES, ZEROS, AND BODE POTS The main objectiveis to find amplifier voltage gain as a transfer function of the complex frequency s. In this s-domain analysis a capacitance С is replaced
S-DOMAIN ANAYSIS: POES, ZEROS, AND BODE POTS The main objectiveis to find amplifier voltage gain as a transfer function of the complex frequency s. In this s-domain analysis a capacitance С is replaced
WHY DIFFERENTIAL? instruments connected to the circuit under test and results in V COMMON.
 WHY DIFFERENTIAL? Voltage, The Difference Whether aware of it or not, a person using an oscilloscope to make any voltage measurement is actually making a differential voltage measurement. By definition,
WHY DIFFERENTIAL? Voltage, The Difference Whether aware of it or not, a person using an oscilloscope to make any voltage measurement is actually making a differential voltage measurement. By definition,
Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
30. Bode Plots. Introduction
 0. Bode Plots Introduction Each of the circuits in this problem set is represented by a magnitude Bode plot. The network function provides a connection between the Bode plot and the circuit. To solve these
0. Bode Plots Introduction Each of the circuits in this problem set is represented by a magnitude Bode plot. The network function provides a connection between the Bode plot and the circuit. To solve these
A Low Cost Power Quality and Energy Savings Laboratory for Undergraduate Education and Research
 Session #3133 A Low Cost Power Quality and Energy Savings Laboratory for Undergraduate Education and Research Abdullatif Bagegni, Vance Poteat Merrimack College Abstract This paper describes the design
Session #3133 A Low Cost Power Quality and Energy Savings Laboratory for Undergraduate Education and Research Abdullatif Bagegni, Vance Poteat Merrimack College Abstract This paper describes the design
