Heterochromia of the iris in rabbits belonging to the Dutch breed.
|
|
|
- MargaretMargaret Norris
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
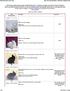
1 Heterochromia of the iris in rabbits belonging to the Dutch breed. Kimberly Butler, Beth DeGeorge, Gabriela Dunn, Julie VanGyzen, Michel Gruaz, Arie van Praag and Esther van Praag Pigmentation of the iris can present anomalies in Dutch rabbits. It may be sectorial heterochromia within one iris, complete heterochromia of the iris between one eye and the other, or ocular albinism with a blue iris in both eyes. Dutch rabbits, also known as Hollander or Brabander, belong to a very old breed and have been represented on antique etchings of the 16 th century already. Its name refers to the Dutch province of Holland in the Netherlands. Indeed, it seems Figure 1: Family of Dutch rabbits with the characteristic bicolor black and white markings and sharp and even edges between the colored and white areas. Photo: Arie Van Praag
2 the underneath of the rabbit s belly (Figures 1, 2). Their size is smaller too. Hair color in rabbits Figure 2 : Young Harlequin or Tri-color Dutch rabbit with three different colors of fur. Photo: Arie Van Praag Hair growth is accompanied by the expression of the dark brown eumelanin and the yellow phaeomelanin pigments. The presence, absence, or variations in the combination of these pigments is determined genetically. The distribution of pigment density in the hair shaft will affect the intensity of the color. In long haired breeds, e.g., the Angora rabbit, the pigment granules are spread along a greater distance, causing the color to appear diluted, whereas in breeds with short hair such as the Rex rabbit, the granules are closer to each other and the color becomes more intense. The absence of any pigments causes albinism. Albino rabbits typically have a pale skin, white fur, and pink eyes. Figure 3: Young male New-Zealand rabbit with an entirely white fur and pinkish eyes. Photo: Arie Van Praag Several hair coloration patterns are found in rabbits: - Agouti. It is a multi-band arrangement of colors along the hair. Along the coloring of wild rabbits there are several variations such as brown-grey (Figures 10, 11), or gray as in Chinchilla rabbits. that it originates from this region even though rabbits showing a coat with Dutch markings were found more generally in the Netherlands, in Northern Belgium and in England. Even so, it was in England that the Dutch rabbit was selected for its beautiful coat and its distinctive markings in order to obtain animals presenting fully symmetric colored markings. The edges between colored and white areas should be as even and sharp as possible (Figures 1, 2). The colored parts on the body include the ears, neck, sides of the head (cheeks and eyes) and the rear end, according to a straight line running behind the shoulders to - Self-color. Each hair has one single color. The main pigment is eumelanin. - Multicolor. Areas of hairs with an eumelanin dominance alternate with areas of hair with phaeomelanin dominance or unpigmented hair. - Albino. Albino rabbits have a very lightly colored skin, a white fur and pinkish eyes due to the transparency of the blood vessels. In most rabbit breeds, genes controlling the color of the fur have undergone extensive manipulation by breeders in order to produce breed-specific colors or to achieve: info@medirabbit.com Page 2 /13
3 - Markings, areas with more or less large areas of white depigmented hair that form plaques or spots. It can be differentiated in large areas on the body as observed on the Dutch rabbit, or spotted as seen in the spotted rabbit or the Hotot rabbit. - Patterning, genes expressing the eumelanin pigment are sensitive to temperature and the pigment is only synthetized under specific temperature conditions, as seen on the Himalayan or Russian rabbits, or the Sable dwarf. - Shading, it includes a pointed coat and a partial discoloration over the body, except limbs, as observed in the Sable Netherland or Siamese Dwarf. - Silver, these rabbits are born all black. A more or less important depigmentation of the hair tips leads to the silver effect, as seen on the Argenté de Champagne. Heterozygous Du/du rabbits have a colored fur on most parts of their body, with one or few white markings, e.g., a few white hairs at the extremity of a limb, a nail, or tip of the nose. Only homozygous du/du rabbits will get the typical coat of Dutch rabbits with white markings/areas of white fur. The colored fur is gradually invaded by fully depigmented hairs on more or less extensive areas of the body. These white Genetics of the Dutch coat Genetics of fur color is complex in rabbits. Part of the genes deals with the color of the hair shaft and the distribution of pigments along the shaft, or their absence. Other genes control the distribution of the colored areas or albino/white on the body. Finally a gene pool regulates the intensity of certain colors. Ten loci determine the appearance of the fur: A, B, C, D, E, En, Du, Si, V, and W. Each one may have several dominant or recessive genes. The coat of the Dutch rabbit is determined by the gene "Du" = Dutch. A homozygous Du/Du rabbit has a uniform coloration of its fur, without white hairs or a white nail. Figure 4: Young male Dutch rabbits showing the classical white and black markings. Breeders have introduces other color variations such as chocolate. Photos: Arie Van Praag info@medirabbit.com Page 3 /13
4 markings appear on the head, neck, upper trunk, upper limbs, and evolve independently from each other. The expression of the "Du" gene does, however, not explain the variation in the degree of white marking on the body of Dutch rabbits, neither the appearance of newborn with Dutch marking in breeds whose ancestors are Dutch rabbits. This is, for instance, observed in litters of the Hotot rabbit, a "black rabbit with a huge white marking covering the whole body" except around the eyes (Figure 5 A, B). There is usually one or more newborn with an incomplete marking of the coat. Sometimes one descendant presents an almost perfect Dutch coat (Figure 5 B). Nowadays, it is suggested that the Dutch rabbit as well as breeds selected from the former carry the dominant "Hol" gene and many modifying polygenes or modifiers that influence the white marking and, consequently, the color of the eyes. The effect of one single polygene has little effect. It is the sum of polygenes that will greatly influence the degree of white marking on the body of the animal and eye color. Consequently, it is interesting to note how genetics leads to numerous differences in coat and eye color. The expression of some polygenes leads to the presence of a few white hairs in the fur. All intermediaries are possible, with sporadic cases of rabbits with blue eyes. The ultimate stage of white marking is a rabbit with white fur and blue eyes. A Dutch with blue eyes B Figure 5: A: Young Hotot rabbits of a same nest, presenting varying degrees of white marking of their coat. B: Hotot rabbit referred to as a wrong Dutch as he presents the typical marking of the Dutch breed. Photos : Michel Gruaz The iris is a component of the uveal tissue of the eye, which acts as a diaphragm of the eye. Its anterior part also determines the color to eyes. The color of the iris, such as we perceive it, depends on three factors: - Density of cells producing the melanin pigment, the melanocytes. - Density of melanin pigments in the anterior layer and posterior epithelium of the iris. - Density and structure of the collagen fibers in the anterior layer and the stroma of the iris. The density of pigmented cells and info@medirabbit.com Page 4 /13
5 melanin pigment varies greatly in brown or blue irises, less dense in the latter. The distribution of pigment cells within the iris is also different. In a blue iris, the melanin pigment is mainly found in the posterior epithelium, a bit in the stroma while the anterior layers have none and are translucent. The blue or brown color of the iris is also determined by the refractive index of light in the iris, compared to the surrounding environment. In the case of blue eyes, light is little absorbed. Light waves are reflected to the outside environment or scatter throughout the structures of the eye. The structure of the anterior layer of the iris and the absence of melanin pigment favor the passage of short blue waves, which allows: - Transmission of light waves deeper into the eye, to the pigmented cells of the posterior epithelium. - Diffusion through reflection of an intense blue light. The microscopic size of the different structures of the iris causes, in addition, a greater diffusion of short-wave light (blue) than long-wave light (red). The iris color is thus perceived as blue. Figure 6: Dutch rabbit with a different pigmentation within the same iris. Photos: Kimberly Butler When pigmented cells are present in the anterior layer and posterior epithelium of the iris, part of the light is absorbed. The ratio of the reflected and scattered light results in the info@medirabbit.com Page 5 /13
6 gray, light brown or dark brown colors of the iris. In the case of an iris with sectoral color variations, differences in blue and brown colors are caused by variations in the size of the different structures of the iris and/or changes in the density of pigmentation between the blue and brown parts of the iris. In albino rabbits, the absence of melanin pigments in the anterior layer and posterior iris epithelium allows a full penetration of light without it being absorbed. Therefore the color of the iris of the eye is pink to purplish. These rabbits are usually photophobic. In conclusion, rabbits with a colored coat have brown or gray eyes while those with a very white fur or albino have light blue or pinkish eye irises. Dutch rabbits can, however, sometimes, be born with blue irises in both eyes, a difference of color within the same iris or a difference of color of the iris of one eye compared to the other (Figures 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10). This phenomenon is also observed in rabbit breeds that have been selected from very marked (very white) Dutch rabbits like the Polish or Vienna White rabbits, both born with blue eyes (Figures 13, 14). Geneticists concluded that there was a sudden mutation of the recessive gene with complete penetrance v", which is responsible for the Figure 7: Rabbits belonging to other breeds may also have a sectorial heterochromia of the iris. Here a lop rabbit with a very white fur and a possible spotted origin. Photos : Julie VanGyzen info@medirabbit.com Page 6 /13
7 Figure 8: Another Dutch rabbit avec small depigmented areas in the irises of both eyes. Photos: Maria- Gabriella Atzori Page 7 /13
8 Figure 9: Lateral view of a Dutch rabbit with heterochromia between the iris of one eye and the other : brown and normal on his right side and blue on his left side. Photos : Beth DeGeorge info@medirabbit.com Page 8 /13
9 Figure 10: Rabbits with a different pattern of fur coloration may also be affected by sectorial heterochromia of the iris. It includes rabbits with the agouti pattern, similar to that of wild rabbits, but also rabbits belonging to the Chinchilla breed. Photos : Gabriela Dunn white fur/blue eyes in homozygous v/v animals. This model of mutation does, however, not consider that: - Dutch rabbits may have one or both blue eyes (Figures 9, 12). info@medirabbit.com Page 9 /13
10 - Breeds that descend from the Dutch rabbit are the result of a slow and precise selection from the Dutch rabbit. In extreme cases, the following types were obtained: - Rabbit with a fully white coat and preservation of the pigmentation of the iris, as observed in Hotot rabbits (Figure 5). - Rabbits with an entirely white and depigmentation of the iris, or white with blue eyes like the Vienna White rabbit or the Polish dwarf rabbit (Figures 13, 14). There is, thus, a correlation between the degree of white marking of the coat and the appearance of blue eyes in rabbit belonging to the Dutch breed. Various hypotheses have been proposed. The most likely one remains that suggested by Searle in 1968: the existence of a recessive du gene is accompanied by a certain number of polygenes modifying the marking that are expressed under certain conditions only. Heterochromia of the iris Heterochromia is defined as variations of color within areas of a same iris (sectorial heterochromia or heterochromia iridum) (Figures 6, 7, 8, 10, 11) or a difference of color of the iris of one eye, compared to the other eye (heterochromia iridis) (Figure 9). In the Dutch rabbit, the observed types of iris heterochromia have no clinical importance and do not seem to be associated to other ocular anomalies. These include a Figure 11 : Heterochromia of the iris in both eyes in a lop rabbit with agouti fur. Photos : Nancy Ainsworth info@medirabbit.com Page 10 /13
11 hypoplasia of the iris, a colobome of the iris, or a displacement of the central position of the pupil (corectopia). The latter has been observed in a Vienna White rabbit (Figure 13). A higher incidence of neurological issues such as epileptic crisis/seizures has been observed in white rabbits with blue eyes that were selected from the Dutch rabbit (Figures 13, 14). Causes are idiopathic, but visual or auditory stimuli may become triggering factors. Those attacks last a few minutes and present different phases. Iris heterochromia is also observed in other rabbit breeds, in particular Chinchilla or Hotot rabbits. These rabbits often have a white nail or few white hairs. This anomaly can also be observed in lop rabbits with a very white fur (Figure 7). In cats and few dog breeds, there is an association between blue eyes and congenital deafness. This association could not be established in Dutch rabbits and rabbits with white fur and blue eyes. Histology of blue eyes Histological analyses of blue eye show that there is a depigmentation of the mesodermal sheet of the iris, while the anterior sheets that developed from the ectoderm are pigmented. In a 6 months old rabbit with Dutch markings and heterochrome eyes, the blue eye showed hypochromia on the front part of the back of the eye (fundus). It is accompanied by a reduced pigmentation in the retinal epithelium and the choroid, in comparison with the normal pigmented brown eye. A Figure 12: Young Dutch rabbit with a reduced pigmentation of both eyes, with blue brilliant irises. Photo: Michel Gruaz info@medirabbit.com Page 11 /13
12 Figure 13: Displacement of the central position of the pupil (corectopia) in a Vienna white rabbit, a breed that has been selected from the Dutch rabbit. Photo: Michel Gruaz decrease of the amount of pigmented cells was, however observed in the stroma of the iris in both eyes. Acknowledgements Many thanks to Tal Saarony (USA), to Janet Geren (USA) and to a person who wishes to Figure 14: Rabbits with a white fur, light colored skin and blue eyes are sensitive to visual and auditory stimuli. They can lead to seizures. Here a dwarf rabbit. Photos: Arie van Praag info@medirabbit.com Page 12 /13
13 MediRabbit.com is funded solely by the generosity of donors. Every donation, no matter what the size, is appreciated and will aid in the continuing research of medical care and health of rabbits. Thank you remain anonymous for his help to find rabbits with heterochrome eyes. References Arnold J. Les modèles de pigmentation chez le lapin. Dans : PARCOURS ANIMALIER, Escapades zootechniques, Cheminement cuniculicole. ion/arnold/chapitre-05.pdf Boucher S. Nouvelle données sur les lapins blancs aux yeux bleus. Goin J. Ophtalmologie des NAC : Principales affections oculaires chez le lapin. Le Point Vétérinaire 2015;359: _4591 Miklos Botha M, Petrescu-Mag V, Hettig A. Genetic disorders in domestic rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). International Journal of the Bioflux Society. Rabbit Genetics 2014; 4:7-47. Reiswig R. Rabbit Eye Color Examples. Rennie IG. Don't it make my blue eyes brown: heterochromia and other abnormalities of the iris. Eye (Lond). 2012;26(1): Searle A.G., 1968; Comparative genetics of coat colour in mammals, Logos press Academic press, London, 308p. Toyoguchi M. Cheng L, Freeman WR. Heterochromia in rabbit - Heterochromia in a Dutch pigmented rabbit. International Journal of Ophthalmology 2007; 7(4): Hinkle A. Color Genetics of the Dwarf Hotot. American Dwarf Hotot Specialty Club Guidebook. 2011; info@medirabbit.com Page 13 /13
Genetics for the Novice
 Genetics for the Novice by Carol Barbee Wait! Don't leave yet. I know that for many breeders any article with the word genetics in the title causes an immediate negative reaction. Either they quickly turn
Genetics for the Novice by Carol Barbee Wait! Don't leave yet. I know that for many breeders any article with the word genetics in the title causes an immediate negative reaction. Either they quickly turn
ARBA Official Breed ID Guide RABBIT. Breed Showroom Variety Four or Six Class Registration Variety
 AMERICAN RABBIT BREEDERS ASSOCIATION Devoted to the Interest of Raising for Fancy and Commercial Parent Body of All Chartered Local and Specialty Clubs / One National Judging and Registration System PO
AMERICAN RABBIT BREEDERS ASSOCIATION Devoted to the Interest of Raising for Fancy and Commercial Parent Body of All Chartered Local and Specialty Clubs / One National Judging and Registration System PO
Cat Coat Color, Pattern and Genetics
 Sonja Prohaska Computational EvoDevo University of Leipzig May 18, 2015 Cat Coat Color, Pattern and Genetics How Hair Gets Color melanoblasts derive from neural crest dorso-ventral migration (back to belly)
Sonja Prohaska Computational EvoDevo University of Leipzig May 18, 2015 Cat Coat Color, Pattern and Genetics How Hair Gets Color melanoblasts derive from neural crest dorso-ventral migration (back to belly)
RABBITS. Board Members in Charge William B. Tolle and Marshall Coyle. Patricia Byerley - Superintendent
 RABBITS Board Members in Charge William B. Tolle and Marshall Coyle Patricia Byerley - Superintendent ENTRY DEADLINE: JULY 18 LOCATION PAVILION ARRIVAL OF RABBITS Wednesday, August 17-10:00 a.m. to 9:00
RABBITS Board Members in Charge William B. Tolle and Marshall Coyle Patricia Byerley - Superintendent ENTRY DEADLINE: JULY 18 LOCATION PAVILION ARRIVAL OF RABBITS Wednesday, August 17-10:00 a.m. to 9:00
Heredity. Sarah crosses a homozygous white flower and a homozygous purple flower. The cross results in all purple flowers.
 Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
UNDERSTANDING THE BASIC GENETICS OF CAT COLORS
 UNDERSTANDING THE BASIC GENETICS OF CAT COLORS Photographs copyright by Chanan, Larry Johnson, Mark McCullough, and Paradox What colors do you find on cats? There are two basic colors of cats, black and
UNDERSTANDING THE BASIC GENETICS OF CAT COLORS Photographs copyright by Chanan, Larry Johnson, Mark McCullough, and Paradox What colors do you find on cats? There are two basic colors of cats, black and
Helen Geeson BSc PGCE. Background
 The Genetics of Dachshund Coats and Colours Helen Geeson Sc PGCE ackground Dogs have 39 pairs of Chromosomes (one from each parent). Chromosomes are long chains of genes which are the coded instructions
The Genetics of Dachshund Coats and Colours Helen Geeson Sc PGCE ackground Dogs have 39 pairs of Chromosomes (one from each parent). Chromosomes are long chains of genes which are the coded instructions
The Genetics of Breed Color In The American Pit Bull Terrier by Amy Greenwood Burford B.S.
 The Genetics of Breed Color In The American Pit Bull Terrier by Amy Greenwood Burford B.S. One of my responsibilities as a member of the staff of the American Dog Breeders Association is to be the color
The Genetics of Breed Color In The American Pit Bull Terrier by Amy Greenwood Burford B.S. One of my responsibilities as a member of the staff of the American Dog Breeders Association is to be the color
Screening for Progressive Retinal Atrophy in Tibetan Terriers
 Screening for Progressive Retinal Atrophy in Tibetan Terriers What is PRA? Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) is the name given to a group of conditions that are inherited and result in a progressive loss
Screening for Progressive Retinal Atrophy in Tibetan Terriers What is PRA? Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) is the name given to a group of conditions that are inherited and result in a progressive loss
A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes.
 1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
Species Horse Module - Colors
 Species Horse Module - Colors Learning Objectives Beginner Identify the following coat colors of the horse: Bay, Black, Brown, Chestnut. Targeting Life Skills Beginner Learning to Learn Intermediate Decision
Species Horse Module - Colors Learning Objectives Beginner Identify the following coat colors of the horse: Bay, Black, Brown, Chestnut. Targeting Life Skills Beginner Learning to Learn Intermediate Decision
Baby Lab. Class Copy. Introduction
 Class Copy Baby Lab Introduction The traits on the following pages are believed to be inherited in the explained manner. Most of the traits, however, in this activity were created to illustrate how human
Class Copy Baby Lab Introduction The traits on the following pages are believed to be inherited in the explained manner. Most of the traits, however, in this activity were created to illustrate how human
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles. Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully
 Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele.
 Genetics Problems Name ANSWER KEY Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele. 1. What would be the genotype
Genetics Problems Name ANSWER KEY Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele. 1. What would be the genotype
CAT IDENTIFICATION Solid Coat Colors Eye Coloration Brown Hazel Gold Green Blue
 CAT IDENTIFICATION Solid Coat Colors Black (pictured) or Blue with white roots. Eye Coloration Brown Hazel Gold Green Blue Tabby Coat Markings Tabby M All tabbies have distinctive M on forehead. Mackeral
CAT IDENTIFICATION Solid Coat Colors Black (pictured) or Blue with white roots. Eye Coloration Brown Hazel Gold Green Blue Tabby Coat Markings Tabby M All tabbies have distinctive M on forehead. Mackeral
1 of 9 12/03/2010 11:10 pm
 1 of 9 12/03/2010 11:10 pm Welcome! Here you will see the many varieties in Netherland Dwarfs there are. Along with a descriptions, faults, and DQ's. To get more information purchase a Netherland Dwarf
1 of 9 12/03/2010 11:10 pm Welcome! Here you will see the many varieties in Netherland Dwarfs there are. Along with a descriptions, faults, and DQ's. To get more information purchase a Netherland Dwarf
COLOR ON, COLOR OFF. Without thinking about it, we use. Young. Naturalists. By SUSAN KANEKO BINKLEY THERE S MORE TO ALBINISM THAN MEETS THE EYE.
 Young Naturalists Without thinking about it, we use color to recognize things in nature. A male cardinal is red. A deer turns By SUSAN KANEKO BINKLEY COLOR ON, COLOR OFF ALBINO SQUIRREL BY DOMINIQUE BRAUD,
Young Naturalists Without thinking about it, we use color to recognize things in nature. A male cardinal is red. A deer turns By SUSAN KANEKO BINKLEY COLOR ON, COLOR OFF ALBINO SQUIRREL BY DOMINIQUE BRAUD,
Inheritance of the colour of eyes in humans and the distribution of this characteristic in a given population.
 EXTENDED ESSAY BIOLOGY Inheritance of the colour of eyes in humans and the distribution of this characteristic in a given population. MAY 2015 WORD COUNT: 3 532 Abstract The aim of this investigation is
EXTENDED ESSAY BIOLOGY Inheritance of the colour of eyes in humans and the distribution of this characteristic in a given population. MAY 2015 WORD COUNT: 3 532 Abstract The aim of this investigation is
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
about Why You Should Know Melanoma
 about Why You Should Know Melanoma Why You Should Know about Melanoma Each year, more than 3 million Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer. This is the most common form of cancer. Of these, more than
about Why You Should Know Melanoma Why You Should Know about Melanoma Each year, more than 3 million Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer. This is the most common form of cancer. Of these, more than
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance
 Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
CHEM 107. Hair handout. Basic Structure of Hair. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05
 CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot
 Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
LABRADOR RETRIEVER. FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 12.01.
 12.01.2011/EN FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) FCI-Standard N 122 LABRADOR RETRIEVER M.Davidson, illustr. NKU Picture Library
12.01.2011/EN FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) FCI-Standard N 122 LABRADOR RETRIEVER M.Davidson, illustr. NKU Picture Library
Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Heredity Grade Ten
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
of the ocular fundus in dogs
 N ormal variation of the ocular fundus in dogs G.H.R.R. Janssens (1) S U M M A R Y The fundus is the part of the posterior eye segment that can be seen when using an ophthalmoscope. The different visible
N ormal variation of the ocular fundus in dogs G.H.R.R. Janssens (1) S U M M A R Y The fundus is the part of the posterior eye segment that can be seen when using an ophthalmoscope. The different visible
CALCASIEU 4-H RABBIT SHOWMANSHIP STUDY GUIDE. Rabbit Terms
 CALCASIEU 4-H RABBIT SHOWMANSHIP STUDY GUIDE NEW STUDY GUIIDE MATERIALS!! The Showmanship contest will consist of 4 parts. A Written Exam, Parts I.D., Breed I.D, and a Skills Test. Written Test Test questions
CALCASIEU 4-H RABBIT SHOWMANSHIP STUDY GUIDE NEW STUDY GUIIDE MATERIALS!! The Showmanship contest will consist of 4 parts. A Written Exam, Parts I.D., Breed I.D, and a Skills Test. Written Test Test questions
Variations on a Human Face Lab
 Variations on a Human Face Lab Introduction: Have you ever wondered why everybody has a different appearance even if they are closely related? It is because of the large variety or characteristics that
Variations on a Human Face Lab Introduction: Have you ever wondered why everybody has a different appearance even if they are closely related? It is because of the large variety or characteristics that
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Problems
 Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Problems 1. The frequency of two alleles in a gene pool is 0.19 (A) and 0.81(a). Assume that the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. (a) Calculate the percentage of
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Problems 1. The frequency of two alleles in a gene pool is 0.19 (A) and 0.81(a). Assume that the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. (a) Calculate the percentage of
ALBINISM. Other Common Names. Causes/Etiology. Incidence. Characteristics. Hypopigmentation
 ALBINISM Other Common Names Hypopigmentation Causes/Etiology Incidence Most types of albinism are inherited when a child receives the albinism gene from both parents. There is an exception with one type
ALBINISM Other Common Names Hypopigmentation Causes/Etiology Incidence Most types of albinism are inherited when a child receives the albinism gene from both parents. There is an exception with one type
Inheritance of Color And The Polled Trait Dr. R. R. Schalles, Dept. of Animal Sciences and Industry Kansas State University
 Inheritance of Color And The Polled Trait Dr. R. R. Schalles, Dept. of Animal Sciences and Industry Kansas State University Introduction All functions of an animal are controlled by the enzymes (and other
Inheritance of Color And The Polled Trait Dr. R. R. Schalles, Dept. of Animal Sciences and Industry Kansas State University Introduction All functions of an animal are controlled by the enzymes (and other
JACK RUSSELL TERRIER
 05.12.2012 / EN FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) FCI-Standard N 345 JACK RUSSELL TERRIER SMOOTH COATED VARIETY BROKEN COATED
05.12.2012 / EN FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) FCI-Standard N 345 JACK RUSSELL TERRIER SMOOTH COATED VARIETY BROKEN COATED
Cat caryotype (38 chromosomes)
 CAT GENETICS Cat caryotype (38 chromosomes) D Dense pigment d dilute pigment L short hair dominant l long hair monohybrid dihybrid Cat Genetics and Mosaicism The Calico phenotype reflects transcriptional
CAT GENETICS Cat caryotype (38 chromosomes) D Dense pigment d dilute pigment L short hair dominant l long hair monohybrid dihybrid Cat Genetics and Mosaicism The Calico phenotype reflects transcriptional
Genetics 1. Defective enzyme that does not make melanin. Very pale skin and hair color (albino)
 Genetics 1 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents. Parents and their children tend to have similar appearance because children inherit genes from their parents and these genes influence
Genetics 1 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents. Parents and their children tend to have similar appearance because children inherit genes from their parents and these genes influence
NFRS Standards of Excellence As of January 2015
 NFRS Standards of Excellence As of January 1 Genetics: Full genetic formulae not given, only the salient loci. Where unrecognised loci are given, this has been indicated with an *. Variety Standard Class
NFRS Standards of Excellence As of January 1 Genetics: Full genetic formulae not given, only the salient loci. Where unrecognised loci are given, this has been indicated with an *. Variety Standard Class
Name: 4. A typical phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross is a) 9:1 b) 3:4 c) 9:3:3:1 d) 1:2:1:2:1 e) 6:3:3:6
 Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
7A The Origin of Modern Genetics
 Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
Breeds of Swine. Berkshire. Chester White
 Breeds of Swine Picture Provided by Prairie State Berkshire The Berkshire breed has long been known for its efficiency in gaining weight. Berkshire hogs have possessed their excellent carcass quality since
Breeds of Swine Picture Provided by Prairie State Berkshire The Berkshire breed has long been known for its efficiency in gaining weight. Berkshire hogs have possessed their excellent carcass quality since
DNA Determines Your Appearance!
 DNA Determines Your Appearance! Summary DNA contains all the information needed to build your body. Did you know that your DNA determines things such as your eye color, hair color, height, and even the
DNA Determines Your Appearance! Summary DNA contains all the information needed to build your body. Did you know that your DNA determines things such as your eye color, hair color, height, and even the
CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Hair & Fiber. (Unit 5)
 37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
Coat Color Mutations, Animals
 1 Coat Color Mutations, Animals Coat Color Mutations, Animals G S Barsh Copyright ß 2001 Academic Press doi: 10.1006/rwgn.2001.0234 Barsh, G S Department of Pediatrics, University of Stanford, School of
1 Coat Color Mutations, Animals Coat Color Mutations, Animals G S Barsh Copyright ß 2001 Academic Press doi: 10.1006/rwgn.2001.0234 Barsh, G S Department of Pediatrics, University of Stanford, School of
Ringneck Doves. A Handbook of Care & Breeding
 Ringneck Doves A Handbook of Care & Breeding With over 100 Full Color Photos, Including Examples and Descriptions of 33 Different Colors and Varieties. K. Wade Oliver Table of Contents Introduction, 4
Ringneck Doves A Handbook of Care & Breeding With over 100 Full Color Photos, Including Examples and Descriptions of 33 Different Colors and Varieties. K. Wade Oliver Table of Contents Introduction, 4
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
ILLUSTRATED STANDARD. for the CHINESE SHAR-PEI GENERAL INFORMATION:
 ILLUSTRATED STANDARD for the CHINESE SHAR-PEI GENERAL INFORMATION: An alert, compact dog of medium size and substance; square in profile, close-coupled; the well proportioned head slightly, but not overly
ILLUSTRATED STANDARD for the CHINESE SHAR-PEI GENERAL INFORMATION: An alert, compact dog of medium size and substance; square in profile, close-coupled; the well proportioned head slightly, but not overly
FCI-Standard N 105 / 29. 03. 2006 /GB FRENCH WATER DOG. (Barbet)
 FCI-Standard N 105 / 29. 03. 2006 /GB FRENCH WATER DOG (Barbet) 2 TRANSLATION : Jennifer Mulholland. ORIGIN : France DATE OF PUBLICATION OF ORIGINAL VALID STANDARD : 21.02.2006. UTILIZATION: Water dog
FCI-Standard N 105 / 29. 03. 2006 /GB FRENCH WATER DOG (Barbet) 2 TRANSLATION : Jennifer Mulholland. ORIGIN : France DATE OF PUBLICATION OF ORIGINAL VALID STANDARD : 21.02.2006. UTILIZATION: Water dog
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES
 SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
HUMAN SKIN COLOR: EVIDENCE FOR SELECTION
 OVERVIEW HUMAN SKIN COLOR: EVIDENCE FOR SELECTION This activity supports the viewing of the short film The Biology of Skin Color. Students watch the film in segments and use real data to propose hypotheses,
OVERVIEW HUMAN SKIN COLOR: EVIDENCE FOR SELECTION This activity supports the viewing of the short film The Biology of Skin Color. Students watch the film in segments and use real data to propose hypotheses,
Junior s Family Tree Inherited Traits of Animals
 Junior s Family Tree Inherited Traits of Animals Objectives 1. Students will understand genetic make-up is received from both parents and is expressed by traits that can be predicted. 2. Students will
Junior s Family Tree Inherited Traits of Animals Objectives 1. Students will understand genetic make-up is received from both parents and is expressed by traits that can be predicted. 2. Students will
1. Three-Color Light. Introduction to Three-Color Light. Chapter 1. Adding Color Pigments. Difference Between Pigments and Light. Adding Color Light
 1. Three-Color Light Chapter 1 Introduction to Three-Color Light Many of us were taught at a young age that the primary colors are red, yellow, and blue. Our early experiences with color mixing were blending
1. Three-Color Light Chapter 1 Introduction to Three-Color Light Many of us were taught at a young age that the primary colors are red, yellow, and blue. Our early experiences with color mixing were blending
SCOTTISH TERRIER. FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 10.01.
 FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 10.01.2011/EN FCI-Standard N 73 SCOTTISH TERRIER M.Davidson, illustr. NKU Picture Library
FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 10.01.2011/EN FCI-Standard N 73 SCOTTISH TERRIER M.Davidson, illustr. NKU Picture Library
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions
 Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
Causes of Birth Defects
 Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
CCpp X ccpp. CcPp X CcPp. CP Cp cp cp. Purple. White. Purple CcPp. Purple Ccpp White. White. Summary: 9/16 purple, 7/16 white
 P F 1 CCpp X ccpp Cp Cp CcPp X CcPp F 2 CP Cp cp cp CP Cp cp cp CCPP CCPp CcPP CcPp CCPp CCpp CcPp Ccpp CcPP CcPp ccpp ccpp Summary: 9/16 purple, 7/16 white CcPp Ccpp ccpp ccpp AABB X aabb P AB ab Gametes
P F 1 CCpp X ccpp Cp Cp CcPp X CcPp F 2 CP Cp cp cp CP Cp cp cp CCPP CCPp CcPP CcPp CCPp CCpp CcPp Ccpp CcPP CcPp ccpp ccpp Summary: 9/16 purple, 7/16 white CcPp Ccpp ccpp ccpp AABB X aabb P AB ab Gametes
Melanoma The Skin Understanding Cancer
 Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
SIHHHDS303A. Hair colour. Skilling people for the industry
 SIHHHDS303A Hair colour Skilling people for the industry SIHHHDS303A Hair colour Skilling people for the industry Hair colour all theory and preparation for real skills transfer from mannequin activities
SIHHHDS303A Hair colour Skilling people for the industry SIHHHDS303A Hair colour Skilling people for the industry Hair colour all theory and preparation for real skills transfer from mannequin activities
Can receive blood from: * I A I A and I A i o Type A Yes No A or AB A or O I B I B and I B i o Type B No Yes B or AB B or O
 Genetics of the ABO Blood Groups written by J. D. Hendrix Learning Objectives Upon completing the exercise, each student should be able: to explain the concept of blood group antigens; to list the genotypes
Genetics of the ABO Blood Groups written by J. D. Hendrix Learning Objectives Upon completing the exercise, each student should be able: to explain the concept of blood group antigens; to list the genotypes
Painting A Face in Oils
 Painting A Face in Oils Ebook Guide to Painting a Face. HOW TO PAINT A FACE IN OILS Welcome to 2PaintMiniatures.com tutorial on Painting a Face in Oils. Please make sure you are connected to the Internet
Painting A Face in Oils Ebook Guide to Painting a Face. HOW TO PAINT A FACE IN OILS Welcome to 2PaintMiniatures.com tutorial on Painting a Face in Oils. Please make sure you are connected to the Internet
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009
 MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
Table of Contents. 10 Drawing Portraits: Fundamentals. Introduction and how this book is organized 13
 10 Drawing Portraits: Fundamentals Table of Contents Introduction and how this book is organized 13 Section One: 15 Drawing fundamentals for the new artist. 15 Some introductory words for the newbie artist
10 Drawing Portraits: Fundamentals Table of Contents Introduction and how this book is organized 13 Section One: 15 Drawing fundamentals for the new artist. 15 Some introductory words for the newbie artist
BioBoot Camp Genetics
 BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
Genetics with a Smile
 Teacher Notes Materials Needed: Two coins (penny, poker chip, etc.) per student - One marked F for female and one marked M for male Copies of student worksheets - Genetics with a Smile, Smiley Face Traits,
Teacher Notes Materials Needed: Two coins (penny, poker chip, etc.) per student - One marked F for female and one marked M for male Copies of student worksheets - Genetics with a Smile, Smiley Face Traits,
BASIC CONCEPTS OF HAIR PHYSIOLOGY AND COSMETIC HAIR DYES
 Staple here TECHNICAL MANUAL BASIC CONCEPTS OF HAIR PHYSIOLOGY AND COSMETIC HAIR DYES COVER PAGE MACRO-STRUCTURE OF THE HAIR The hair is formed by the shaft and the piliferous bulb. The visible part of
Staple here TECHNICAL MANUAL BASIC CONCEPTS OF HAIR PHYSIOLOGY AND COSMETIC HAIR DYES COVER PAGE MACRO-STRUCTURE OF THE HAIR The hair is formed by the shaft and the piliferous bulb. The visible part of
Basics of Marker Assisted Selection
 asics of Marker ssisted Selection Chapter 15 asics of Marker ssisted Selection Julius van der Werf, Department of nimal Science rian Kinghorn, Twynam Chair of nimal reeding Technologies University of New
asics of Marker ssisted Selection Chapter 15 asics of Marker ssisted Selection Julius van der Werf, Department of nimal Science rian Kinghorn, Twynam Chair of nimal reeding Technologies University of New
Pink & White Gel Tip Overlay Rules, Judges Instructions & Criteria Student Division Competition Rules
 Competition Rules 1. Total time allowed 3 hours (180 minutes) 2. These are traditional square style competition nails. 3. The nails must be applied with Tips and Gel overlay 4. The competitor must apply
Competition Rules 1. Total time allowed 3 hours (180 minutes) 2. These are traditional square style competition nails. 3. The nails must be applied with Tips and Gel overlay 4. The competitor must apply
Color Lift. for Correction/Camouflage. Correction and Camouflage are used for hiding minor errors and mistakes including:
 Color Lift for Correction/Camouflage Correction and Camouflage are used for hiding minor errors and mistakes including: Minor control loss Nitpicky alterations Shape Change Last minute mind changes Final
Color Lift for Correction/Camouflage Correction and Camouflage are used for hiding minor errors and mistakes including: Minor control loss Nitpicky alterations Shape Change Last minute mind changes Final
Mendelian Genetics in Drosophila
 Mendelian Genetics in Drosophila Lab objectives: 1) To familiarize you with an important research model organism,! Drosophila melanogaster. 2) Introduce you to normal "wild type" and various mutant phenotypes.
Mendelian Genetics in Drosophila Lab objectives: 1) To familiarize you with an important research model organism,! Drosophila melanogaster. 2) Introduce you to normal "wild type" and various mutant phenotypes.
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Chapter 32: An Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Name Period Concept 32.1 Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers 1. Like the fungi, animals are multicellular heterotrophs. How do they feed?
Name Period Concept 32.1 Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers 1. Like the fungi, animals are multicellular heterotrophs. How do they feed?
Science In Action 8 Unit C - Light and Optical Systems. 1.1 The Challenge of light
 1.1 The Challenge of light 1. Pythagoras' thoughts about light were proven wrong because it was impossible to see A. the light beams B. dark objects C. in the dark D. shiny objects 2. Sir Isaac Newton
1.1 The Challenge of light 1. Pythagoras' thoughts about light were proven wrong because it was impossible to see A. the light beams B. dark objects C. in the dark D. shiny objects 2. Sir Isaac Newton
PROFESSIONAL HAIR COLOR BASIC HAIR COLOR THEORY
 PROFESSIONAL HAIR COLOR BASIC HAIR COLOR THEORY BASIC COLOR THEORY When Coloring the hair, remember the rules of complementarities Red is opposite Green Blue is opposite Orange Yellow is opposite Violet
PROFESSIONAL HAIR COLOR BASIC HAIR COLOR THEORY BASIC COLOR THEORY When Coloring the hair, remember the rules of complementarities Red is opposite Green Blue is opposite Orange Yellow is opposite Violet
GENETIC CROSSES. Monohybrid Crosses
 GENETIC CROSSES Monohybrid Crosses Objectives Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype Explain the difference between homozygous and heterozygous Explain how probability is used to predict
GENETIC CROSSES Monohybrid Crosses Objectives Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype Explain the difference between homozygous and heterozygous Explain how probability is used to predict
B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses
 B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 55 Q. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released
B2 5 Inheritrance Genetic Crosses 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 55 Q. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released
Inside Hair: A Closer Look at Color and Shape
 Inside Hair: A Closer Look at Color and Shape For the past decade women and men alike have had chemical treatments preformed on their hair. Consumers spend millions of dollars on hair care products such
Inside Hair: A Closer Look at Color and Shape For the past decade women and men alike have had chemical treatments preformed on their hair. Consumers spend millions of dollars on hair care products such
Color Vision Defects - Color Blindness
 Color Vision Defects - Color Blindness Introduction A color vision defect causes a person to see colors differently than most people. Color vision defects are sometimes called color blindness. There are
Color Vision Defects - Color Blindness Introduction A color vision defect causes a person to see colors differently than most people. Color vision defects are sometimes called color blindness. There are
Color Filters and Light
 activity 4 Color Filters and Light OBJECTIVES Students add to their understanding of subtractive color mixing by investigating the effect of filters on the color of light. The students shine white light
activity 4 Color Filters and Light OBJECTIVES Students add to their understanding of subtractive color mixing by investigating the effect of filters on the color of light. The students shine white light
Coat Patterns that Include White (C-1 Standard) 1. Paint or Pinto Color Patterns
 Coat Patterns that Include White (C-1 Standard) 1. Paint or Pinto Color Patterns Reference: American Paint Horse Association s Guide to Coat Color Genetics: http://press.apha.com/pdfs/guidebooks/colorgenguide.pdf
Coat Patterns that Include White (C-1 Standard) 1. Paint or Pinto Color Patterns Reference: American Paint Horse Association s Guide to Coat Color Genetics: http://press.apha.com/pdfs/guidebooks/colorgenguide.pdf
New Methods for Guidance of Light-Based Treatments Using Objective Melanin Measurements
 New Methods for Guidance of Light-Based Treatments Using Objective Melanin Measurements Sean Doherty, MD, 1 Richard Cohen, PhD, 2 Felicia Whitney, RN, 2 Oksana Bradley, MD, 2 (Ukraine) Brooke Seckel, MD
New Methods for Guidance of Light-Based Treatments Using Objective Melanin Measurements Sean Doherty, MD, 1 Richard Cohen, PhD, 2 Felicia Whitney, RN, 2 Oksana Bradley, MD, 2 (Ukraine) Brooke Seckel, MD
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
Just About Everything You Need to Know About Champagne Colored Horses Carolyn Shepard
 Just About Everything You Need to Know About Champagne Colored Horses Carolyn Shepard A Brief History The champagne dilution appears to be a recent phenomenon. While we have seen pale skinned horses in
Just About Everything You Need to Know About Champagne Colored Horses Carolyn Shepard A Brief History The champagne dilution appears to be a recent phenomenon. While we have seen pale skinned horses in
FINNISH SPITZ. FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) 27.05.
 27.05.2015/ EN FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) FCI-Standard N 49 FINNISH SPITZ (Suomenpystykorva) 2 TRANSLATION: Finnish
27.05.2015/ EN FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) FCI-Standard N 49 FINNISH SPITZ (Suomenpystykorva) 2 TRANSLATION: Finnish
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs
 Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Explaining Ellipse I 2 PL
 Explaining Ellipse I 2 PL CLINICALLY PROVEN SAFE AND EFFECTIVE Ellipse I 2 PL stands for Ellipse secondgeneration Intense Pulsed Light The Ellipse I 2 PL system is used for the treatment of a wide range
Explaining Ellipse I 2 PL CLINICALLY PROVEN SAFE AND EFFECTIVE Ellipse I 2 PL stands for Ellipse secondgeneration Intense Pulsed Light The Ellipse I 2 PL system is used for the treatment of a wide range
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Hair. *credit to Anthony and Patti Bertino for image. Dec 2 8:10 PM
 Hair *credit to Anthony and Patti Bertino for image Dec 2 8:10 PM 1 Essential Question: How can hair be used to solve a crime? Dec 2 8:12 PM 2 History of hair evidence criminal evidence in 1800's 1883
Hair *credit to Anthony and Patti Bertino for image Dec 2 8:10 PM 1 Essential Question: How can hair be used to solve a crime? Dec 2 8:12 PM 2 History of hair evidence criminal evidence in 1800's 1883
CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE
 SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
Hair Analysis 2005, 2004, 2003, 2001, 1999 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved.
 Hair Analysis 2005, 2004, 2003, 2001, 1999 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Hair can be important physical evidence at a crime scene. Hair normally falls from the body over the course of a day. It
Hair Analysis 2005, 2004, 2003, 2001, 1999 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Hair can be important physical evidence at a crime scene. Hair normally falls from the body over the course of a day. It
Chapter 3 The Study of Hair By the end of the chapter you will be able to:
 Chapter 3 The Study of Hair By the end of the chapter you will be able to: identify the various parts of a hair describe variations in the structure of the medulla, cortex, and cuticle distinguish between
Chapter 3 The Study of Hair By the end of the chapter you will be able to: identify the various parts of a hair describe variations in the structure of the medulla, cortex, and cuticle distinguish between
Color and Light. DELTA SCIENCE READER Overview... 125 Before Reading... 126 Guide the Reading... 127 After Reading... 133
 Color and Light T ABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT DELTA SCIENCE MODULES Program Introduction................... iii Teacher s Guide..................... iv Delta Science Readers............... vi Equipment and
Color and Light T ABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT DELTA SCIENCE MODULES Program Introduction................... iii Teacher s Guide..................... iv Delta Science Readers............... vi Equipment and
The Genetics of Drosophila melanogaster
 The Genetics of Drosophila melanogaster Thomas Hunt Morgan, a geneticist who worked in the early part of the twentieth century, pioneered the use of the common fruit fly as a model organism for genetic
The Genetics of Drosophila melanogaster Thomas Hunt Morgan, a geneticist who worked in the early part of the twentieth century, pioneered the use of the common fruit fly as a model organism for genetic
PICCOLO LEVRIERO ITALIANO
 17.12.2015/EN FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) (VALID FROM 01/01/2016) FCI-Standard N 200 PICCOLO LEVRIERO ITALIANO (Italian
17.12.2015/EN FEDERATION CYNOLOGIQUE INTERNATIONALE (AISBL) SECRETARIAT GENERAL: 13, Place Albert 1 er B 6530 Thuin (Belgique) (VALID FROM 01/01/2016) FCI-Standard N 200 PICCOLO LEVRIERO ITALIANO (Italian
Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
 Name: Date: Period: Incomplete Dominance and Codominance 1. In Japanese four o'clock plants red (R) color is incompletely dominant over white (r) flowers, and the heterozygous condition (Rr) results in
Name: Date: Period: Incomplete Dominance and Codominance 1. In Japanese four o'clock plants red (R) color is incompletely dominant over white (r) flowers, and the heterozygous condition (Rr) results in
Skin cancer Patient information
 Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
 no!no! Thermicon: A Novel, Home-based Hair Removal Device Dr. Mira Barki Yavne, Israel Introduction Lasers and intense pulsed light sources have become a popular method for long-term removal of unwanted
no!no! Thermicon: A Novel, Home-based Hair Removal Device Dr. Mira Barki Yavne, Israel Introduction Lasers and intense pulsed light sources have become a popular method for long-term removal of unwanted
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
