APPENDIX 5. Newfoundland Ecoregions. i) Western Newfoundland Ecoregion
|
|
|
- Julius McLaughlin
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 APPENDIX 5 ECOREGION DESCRIPTIONS O F NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR
2 Newfoundland Ecoregions i) Western Newfoundland Ecoregion This ecoregion is characterized by a humid climate with a relatively long frost-free period. It contains some of the most favourable sites for forest growth in the province. The Dryopteris- Hylocomium-Balsam Fir forest is the dominate forest type of this ecoregion. The absence of prolonged dry periods has excluded fires from all but the most coarse-textured soils. Consequently, balsam fir rather than black spruce is the dominant forest cover. On flat coastal areas, extensive plateau bogs occur, while slope fens and alder swamps are the dominant wetland types on nutrient rich slopes and valleys. Serpentine and limestone barrens are common on exposed ultramafic (serpentine) and calcareous (limestone and dolomite) bedrock. APPENDIX 5 ii) Central Newfoundland Ecoregion Central Newfoundland has the most continental climate of any part of insular Newfoundland. It has the highest summer temperatures and the lowest winter temperatures. Because of warm summers and high evapo-transpiration rate, soils in the northern part of this ecoregion exhibit actual soil-moisture deficiency. The Hylocomium-Balsam Fir forest type is characteristic of this area. Forest fires have played a more important role in this ecoregion's natural history than in other regions. Thus, much of the Balsam Fir-Feathermoss forest types have been converted to black spruce and some of the richer site types are dominated by white birch and aspen. In areas that have been burned repeatedly, dwarf shrub (Kalmia) barrens have replaced forest stands. Raised bogs are the characteristic wetland type. iii) Northshore Ecoregion This ecoregion represents a narrow coastal zone km wide extending from Bonavista Bay to the Baie Verte Peninsula. Black spruce and balsam fir form a continuous forest, except where crowberry barrens dominate coastal headlands. The vegetation season is shorter and cooler than in central Newfoundland, but the frost-free period is several weeks longer (W.J. Meades and Moores, 1989). The summers are relatively dry and warm and soil moisture deficiencies may occur. Like the Central Newfoundland Ecoregion, encroachment of ericaceous shrubs on dry nutrient-poor sites after cutting and fire is a serious silvicultural problem. iv) Northern Peninsula Ecoregion This ecoregion differs from most other forested parts of the island by the shortness of the vegetation season: days compared to days for other areas (W.J. Meades and Moores, 1989). The frost-free period is similar to other areas and somewhat longer than central Newfoundland. Soils are comparable to those of western Newfoundland, with limestone underlying most of the region. Acidic rock is more common on the eastern side of the peninsula. Balsam fir is the dominant tree in forest stands, except at high elevations on the eastern side of the peninsula, where it is replaced by black spruce. There is very little fire history in this ecoregion. Limestone barrens are common along the west coast, with dwarf shrub and crowberry barrens on the east coast. Plateau bogs cover extensive areas of the coastal lowlands. 99
3 APPENDIX 5 v) Avalon Forest Ecoregion This ecoregion represents a sheltered outlier within the more open and exposed Maritime Barrens Ecoregion. Pure stands of balsam fir with a significant mixture of white and yellow birch dominate this region. The Avalon Forest Ecoregion has been spared the ravages of fire that decimated the forests in the surrounding landscape, converting them to open heathland. The very moist climate and ribbed moraine topography give this small (500km2) ecoregion its uniqueness. Raised bogs occur between moraines. The excessive frequency of fog is clearly evidenced by the abundance of pendant, arboreal lichens hanging from the branches of balsam fir. vi) Maritime Barrens Ecoregion The Maritime Barrens Ecoregion extends from the east to the west coast of Newfoundland along the south-central portion of the Island. This ecoregion has the coldest summers, with frequent fog and strong winds. Winters are relatively mild, with intermittent snow cover, particularly near the coastline. The landscape pattern usually consists of stunted balsam fir broken by extensive open Kalmia barren, which developed because of indiscriminate burning by European settlers. Good forest growth is restricted to the long slopes of a few protected valleys. Slope and basin bogs are the most common wetland type. vii) Eastern Hyper-Oceanic Barrens Ecoregion The main portion of this ecoregion occurs on the extreme south coast of the Avalon and Burin Peninsulas, with two additional areas on the northeast coast near Bay de Verte and Cape Freels. Although this ecoregion is no more than 200m in elevation, the extreme oceanic climate prevents the development of forest other than balsam fir krummholz. Moss (Rhacomitrium) and crowberry (Empetrum) barrens in this area have a close affinity to oceanic parts of northern Scotland and southern Norway (W.J. Meades, 1983). Blanket bogs are characteristic of this ecoregion and cover extensive areas. viii) Long Range Mountain Ecoregion This ecoregion encompasses the mountainous areas above the tree-line on the Long Range Mountains. Trees occur only as krummholz (i.e., stunted forest) which is usually dominated by eastern larch and black spruce; however, sheltered valleys may contain small patches of forest. The vegetation is primarily alpine barren, dominated by Arctic-alpine plants, or crowberry barren. Shallow ribbed fens and slope bogs often cover extensive areas. ix) Strait of Belle Isle Ecoregion This region is dominated by an almost treeless tundra-like vegetation. White spruce and balsam fir occur as krummholz, interspersed with Arctic-alpine plants. The soils are generally very shallow and outcrops of calcareous bedrock are common throughout. Numerous endemic and rare species occur in the limestone barrens which are characteristic of this ecoregion. Wet depressions are vegetated by rich fens. 100
4 Labrador Ecoregions i) Low Arctic Tundra - Cape Chidley This ecoregion is located on the northern tip of Labrador. A flat coastal plain dominates the area near Ungava Bay, while the southern portion contains low, steep-sided hills. It has the driest climate in Labrador and a growing season of less than sixty days. The dominant vegetation is tundra (alpine barren, dominated by rock and open ground with patches of mosses and lichens). Coastal headlands and ledges often support moss (Rhacomitrium) barren, while sporadic snowbed communities (sedge meadows) occur in late melting zabois. There are no tall shrubs or trees, and no true peatlands exist; however, marshes can occur along river valleys. APPENDIX 5 ii) Low Arctic-Alpine - Torngat The Torngat mountains and intervening fjords dominate this ecoregion. The upper walls of the fjords are nearly vertical rock faces, while lower slopes are covered with scree. Valley floors usually consist of outwash terraces. The climatic gradient is great, due to the wide elevation range. The climate is similar to the Low Arctic Tundra - Cape Chidley ecoregion, but with a longer growing season (60 to 80 days). The dominant vegetation is alpine heath, with sedge meadows (snowbed communities), fed by seepage from late melting snow patches. Trees are absent from this region also. iii) High Subarctic Tundra - Kingurutik/Fraser The George River Plateau makes up the main (northern) portion of this ecoregion. Various mountainous outliers, including the Benedict Mountains, Wine River Mountains, Mealy Mountains, and the McPhadyen Plateau also belong to this region. Summers are short and cool, with a growing season of 80 to 120 days; winters are long, severe, and very cold. The upland vegetation is similar to the Low Arctic Tundra - Torngat ecoregion; however, the valleys support tree growth. Closed black spruce forests (with some larch) occur on lower valley slopes. River terraces support open spruce forests with a lichen dominated understory. Shallow fens with frozen peat occupy small depressions in plateau surfaces. iv) Coastal Barrens - Okak/Battle Harbour This ecoregion extends from Napaktok Bay south to the Strait of Belle Isle. Much of the coast is characterized by long, sheltered inlets. The summers are cool to warm and the growing season is 100 to 120 days. The winters are cold. Empetrum barren is the dominate vegetation type, with forest occurring in sheltered valleys. Most mid and lower slopes support a continuous spruce forest with a moss understory. Repeated fires have changed many forested areas to dwarf shrub barrens. Plateau bogs with frozen peat (palsas) and salt marshes on marine terraces are characteristic of the valleys in this ecoregion. v) Mid Subarctic Forest - Michikamau This ecoregion encompasses the upland plateaus of central and western Labrador. Eskers and drumlin ridges are characteristic. This region has a very continental, subarctic climate with cool, short summers and long, severe, cold winters. The growing season is 100 to 120 days. Black 101
5 APPENDIX 5 spruce is the dominant trees species, except in the most northern areas, where white spruce dominates. Trembling aspen reaches its northern limit here and the only native population of jack pine occurs in this ecoregion. Open lichen woodlands are characteristic of this ecoregion. Extensive ribbed fen-string bog complexes, bordered by black spruce-sphagnum forest stands, dominate areas with little relief. vi) High Boreal Forest - Lake Melville This ecoregion encompasses the Churchill River Valley and the coastal plain surrounding Lake Melville. River terraces are composed of coarse-textured, alluvial soils, and uplands have shallow, well-drained soils. This region has the most favourable climate in Labrador. Summers are cool and winters cold. The growing season is 120 to 140 days. The forests are closedcanopied and highly productive. Richer slopes are dominated by balsam fir, white birch, and trembling aspen. Black spruce is present in most stands, but only dominates in upland areas and lichen woodlands, which occupy river terraces. Ribbed fens occur in upland depressions; plateau bogs occur on coastal plains. vii) Mid Boreal Forest - Paradise River This undulating, bedrock controlled landscape of southeastern Labrador has many rock outcrops and supports fairly productive, closed-crown forests. The climate is considered boreal and is moister and cooler than the Lake Melville area. Summers are cool to warm and winters are short and cold. The growing season is 120 to 140 days. Black spruce and balsam fir are the most common tree species, but hardwoods are commonly encountered. Raised bogs are characteristic of valleys in the area. viii) Low Subarctic Forest - Mecatina River The main portion of this ecoregion is located in southern Labrador, with two separate areas to the north of Lake Melville and the Red Wine Mountains. Broad river valleys and rolling hills covered by shallow till, drumlins, and eskers are characteristic of the region. Summers are cool and winters are long. The growing season is 120 to 140 days. Somewhat open black spruce forests are the dominant vegetation, with crown densities greater than 75% on better sites. String bog-ribbed fen complexes cover extensive areas throughout the region. ix) String Bog - Eagle River Plateau The Eagle River Plateau comprises most of this ecoregion. This upland plateau is composed of extensive string bogs with numerous open pools surrounded by fen vegetation. Bog hummocks are dominated by scrub spruce, Labrador tea, and feathermoss. The peatland expanses are occasionally interrupted by only a few conspicuous eskers, which support open, lichen woodland. Alder thickets are common along river banks. x) Forteau Barrens This ecoregion is located at the southeasternmost tip of Labrador, adjacent to the Strait of Belle Isle. Low hills are covered with scrub spruce, crowberry barren, and slope bogs. Strong winds and frequent storms occur because of the ecoregion's proximity to the Strait of Belle Isle. The 102
6 growing season is 100 to 120 days. Tree growth is limited by a combination of wind, wet soils, and a history of repeated burns. Black spruce and larch can reach 10 to 12m only along rivers, where soils are better drained. APPENDIX 5 103
Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms
 Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms Definitions Climate is the average weather of a place over many years Geographers discuss five broad types of climates Moderate, dry, tropical, continental, polar Vegetation:
Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms Definitions Climate is the average weather of a place over many years Geographers discuss five broad types of climates Moderate, dry, tropical, continental, polar Vegetation:
6.4 Taigas and Tundras
 6.4 Taigas and Tundras In this section, you will learn about the largest and coldest biomes on Earth. The taiga is the largest land biome and the tundra is the coldest. The taiga The largest land biome
6.4 Taigas and Tundras In this section, you will learn about the largest and coldest biomes on Earth. The taiga is the largest land biome and the tundra is the coldest. The taiga The largest land biome
Bioregional Conservation Status for each BioEVC
 Bridgewater 3 Damp Sands Herb-rich Woodland Vulnerable Bridgewater 9 Coastal Saltmarsh Vulnerable Bridgewater 10 Estuarine Wetland Endangered Bridgewater 23 Herb-rich Foothill Forest Vulnerable Bridgewater
Bridgewater 3 Damp Sands Herb-rich Woodland Vulnerable Bridgewater 9 Coastal Saltmarsh Vulnerable Bridgewater 10 Estuarine Wetland Endangered Bridgewater 23 Herb-rich Foothill Forest Vulnerable Bridgewater
Although greatly MOUNTAINS AND SEA BRITISH COLUMBIA S AWIDE RANGE OF. Environment. Old Forests. Plants. Animals
 BRITISH COLUMBIA is Canada s westernmost province. From island-dotted Pacific coast to spectacular Rocky Mountain peak, and from hot dry grassland to moist and majestic coastal forest, British Columbia
BRITISH COLUMBIA is Canada s westernmost province. From island-dotted Pacific coast to spectacular Rocky Mountain peak, and from hot dry grassland to moist and majestic coastal forest, British Columbia
THE ECOSYSTEM - Biomes
 Biomes The Ecosystem - Biomes Side 2 THE ECOSYSTEM - Biomes By the end of this topic you should be able to:- SYLLABUS STATEMENT ASSESSMENT STATEMENT CHECK NOTES 2.4 BIOMES 2.4.1 Define the term biome.
Biomes The Ecosystem - Biomes Side 2 THE ECOSYSTEM - Biomes By the end of this topic you should be able to:- SYLLABUS STATEMENT ASSESSMENT STATEMENT CHECK NOTES 2.4 BIOMES 2.4.1 Define the term biome.
Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
 Benchmark Identify physical & human characteristics of places, regions in North America. Grade Level Indicator Describe, compare landforms, climates, population, vegetation, economic characteristics of
Benchmark Identify physical & human characteristics of places, regions in North America. Grade Level Indicator Describe, compare landforms, climates, population, vegetation, economic characteristics of
NATURAL RESOURCES & NATURAL FEATURES
 A3 NATURAL RESOURCES & NATURAL FEATURES INTRODUCTION This chapter will discuss the topography, geology, soils, and other natural features found in Casco Township. The identification of the natural features
A3 NATURAL RESOURCES & NATURAL FEATURES INTRODUCTION This chapter will discuss the topography, geology, soils, and other natural features found in Casco Township. The identification of the natural features
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Before You Read Before you read the chapter, respond to these statements. 1. Write an A if you agree with the statement. 2. Write a D if you disagree with the statement.
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Before You Read Before you read the chapter, respond to these statements. 1. Write an A if you agree with the statement. 2. Write a D if you disagree with the statement.
Environmentally Significant Areas of Alberta. Volume 3. Prepared by: Sweetgrass Consultants Ltd. Calgary, AB. for:
 Environmentally Significant Areas of Alberta Volume 3 Prepared by: Calgary, AB for: Resource Data Division Alberta Environmental Protection Edmonton, Alberta March 1997 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Large portions
Environmentally Significant Areas of Alberta Volume 3 Prepared by: Calgary, AB for: Resource Data Division Alberta Environmental Protection Edmonton, Alberta March 1997 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Large portions
EcoInformatics International Inc.
 1 von 10 03.08.2010 14:25 EcoInformatics International Inc. Home Services - solutions Projects Concepts Tools Links Contact EXPLORING BEAVER HABITAT AND DISTRIBUTION WITH GOOGLE EARTH: THE LONGEST BEAVER
1 von 10 03.08.2010 14:25 EcoInformatics International Inc. Home Services - solutions Projects Concepts Tools Links Contact EXPLORING BEAVER HABITAT AND DISTRIBUTION WITH GOOGLE EARTH: THE LONGEST BEAVER
Deserts, Wind Erosion and Deposition
 Deserts, Wind Erosion and Deposition By definition, a desert has less than 10 in (25 cm) of precipitation per year. Deserts occur at 30 o and 60 o in regions of descending air. Deserts can be hot or cold.
Deserts, Wind Erosion and Deposition By definition, a desert has less than 10 in (25 cm) of precipitation per year. Deserts occur at 30 o and 60 o in regions of descending air. Deserts can be hot or cold.
4. Which choice below lists the biomes in order from lowest precipitation amounts to highest precipitation amounts?
 Ecosystems and Biomes 1. All of the living organisms in a forest plus their environment is an example of A. a biome. B. a community. C. a population. D. an ecosystem. 2. Which of the following best describes
Ecosystems and Biomes 1. All of the living organisms in a forest plus their environment is an example of A. a biome. B. a community. C. a population. D. an ecosystem. 2. Which of the following best describes
APPENDIX D. EXAMPLES OF OTHER FORMATION-LEVEL CLASSIFICATIONS
 APPENDIX D. EXAMPLES OF OTHER FORMATION-LEVEL CLASSIFICATIONS Main World Terrestrial Biome Types (Box and Fujiwara 2005, Table 4.4,) The authors provide 18 major biome types recognized by most modern treatments
APPENDIX D. EXAMPLES OF OTHER FORMATION-LEVEL CLASSIFICATIONS Main World Terrestrial Biome Types (Box and Fujiwara 2005, Table 4.4,) The authors provide 18 major biome types recognized by most modern treatments
Glacier Erosion Notes
 Name Date ES per Mr. Landsman Glacier Erosion Notes Erosion: the of weathered material. Glacier: A large mass of ice and snow that exists year-round and moves under the influence of. Evidence for Glacier
Name Date ES per Mr. Landsman Glacier Erosion Notes Erosion: the of weathered material. Glacier: A large mass of ice and snow that exists year-round and moves under the influence of. Evidence for Glacier
LEARNING THE LANDFORMS Grade Level: Third Presented by: Elizabeth Turcott, Endeavor Charter Academy, Springfield, Michigan Length of Unit: 14 lessons
 LEARNING THE LANDFORMS Grade Level: Third Presented by: Elizabeth Turcott, Endeavor Charter Academy, Springfield, Michigan Length of Unit: 14 lessons I. ABSTRACT This unit develops an understanding of
LEARNING THE LANDFORMS Grade Level: Third Presented by: Elizabeth Turcott, Endeavor Charter Academy, Springfield, Michigan Length of Unit: 14 lessons I. ABSTRACT This unit develops an understanding of
WEATHERING, EROSION, AND DEPOSITION PRACTICE TEST. Which graph best shows the relative stream velocities across the stream from A to B?
 NAME DATE WEATHERING, EROSION, AND DEPOSITION PRACTICE TEST 1. The diagram below shows a meandering stream. Measurements of stream velocity were taken along straight line AB. Which graph best shows the
NAME DATE WEATHERING, EROSION, AND DEPOSITION PRACTICE TEST 1. The diagram below shows a meandering stream. Measurements of stream velocity were taken along straight line AB. Which graph best shows the
6. NATURAL AREAS FIRE MANAGEMENT
 6. NATURAL AREAS FIRE MANAGEMENT 6-1 Wildfire management is an important component of managing and maintaining County natural areas. The natural areas are woven into the community fabric and are a part
6. NATURAL AREAS FIRE MANAGEMENT 6-1 Wildfire management is an important component of managing and maintaining County natural areas. The natural areas are woven into the community fabric and are a part
Key Idea 2: Ecosystems
 Key Idea 2: Ecosystems Ecosystems An ecosystem is a living community of plants and animals sharing an environment with non-living elements such as climate and soil. An example of a small scale ecosystem
Key Idea 2: Ecosystems Ecosystems An ecosystem is a living community of plants and animals sharing an environment with non-living elements such as climate and soil. An example of a small scale ecosystem
1. Incredible India. Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India
 1. Incredible India Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India The DCSF supported Action plan for Geography is delivered
1. Incredible India Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India The DCSF supported Action plan for Geography is delivered
DESCRIBING DESERT, TAIGA, AND TUNDRA BIOMES
 Lesson B5 1 DESCRIBING DESERT, TAIGA, AND TUNDRA BIOMES Unit B. Science and Technology in Wildlife Management Problem Area 5. Desert, Taiga, and Tundra Biomes National Academic Standard. NS.9-12.1 Science
Lesson B5 1 DESCRIBING DESERT, TAIGA, AND TUNDRA BIOMES Unit B. Science and Technology in Wildlife Management Problem Area 5. Desert, Taiga, and Tundra Biomes National Academic Standard. NS.9-12.1 Science
Assessing Ecological Restoration Potentials of Wisconsin (U.S.A.) Using Historical Landscape Reconstructions
 Assessing Ecological Restoration Potentials of Wisconsin (U.S.A.) Using Historical Landscape Reconstructions Janine Bolliger, 1,2,3 Lisa A. Schulte, 2,4 Sean N. Burrows, 2 Theodore A. Sickley, 2 and David
Assessing Ecological Restoration Potentials of Wisconsin (U.S.A.) Using Historical Landscape Reconstructions Janine Bolliger, 1,2,3 Lisa A. Schulte, 2,4 Sean N. Burrows, 2 Theodore A. Sickley, 2 and David
Natural Resources and Landscape Survey
 Landscape Info Property Name Address Information Contact Person Relationship to Landscape Email address Phone / Fax Website Address Landscape Type (private/muni/resort, etc.) Former Land Use (if known)
Landscape Info Property Name Address Information Contact Person Relationship to Landscape Email address Phone / Fax Website Address Landscape Type (private/muni/resort, etc.) Former Land Use (if known)
Name Date Hour. Plants grow in layers. The canopy receives about 95% of the sunlight leaving little sun for the forest floor.
 Name Date Hour Directions: You are to complete the table by using your environmental text book and the example given here. You want to locate all the abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) factors in
Name Date Hour Directions: You are to complete the table by using your environmental text book and the example given here. You want to locate all the abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) factors in
4.2 Buena Vista Creek Watershed
 Buena Vista Creek Watershed 4.2 Buena Vista Creek Watershed Watershed Overview The Buena Vista Creek Watershed is the fourth-largest system within the Carlsbad Hydrologic Unit. The watershed extends approximately
Buena Vista Creek Watershed 4.2 Buena Vista Creek Watershed Watershed Overview The Buena Vista Creek Watershed is the fourth-largest system within the Carlsbad Hydrologic Unit. The watershed extends approximately
The Climate of Oregon Climate Zone 2 Willamette Valley
 /05 E-55 No. ci oi Unbound issue e2_, Does not circulate Special Report 914 May 1993 The Climate of Oregon Climate Zone 2 Property of OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY Library Serials Corvallis, OR 97331-4503 Agricultural
/05 E-55 No. ci oi Unbound issue e2_, Does not circulate Special Report 914 May 1993 The Climate of Oregon Climate Zone 2 Property of OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY Library Serials Corvallis, OR 97331-4503 Agricultural
defined largely by regional variations in climate
 1 Physical Environment: Climate and Biomes EVPP 110 Lecture Instructor: Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 Climate and Biomes Ecosystem concept physical and biological components of environment are considered as single,
1 Physical Environment: Climate and Biomes EVPP 110 Lecture Instructor: Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 Climate and Biomes Ecosystem concept physical and biological components of environment are considered as single,
2. The map below shows high-pressure and low-pressure weather systems in the United States.
 1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
Plants, like all other living organisms have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food),
 LEARNING FROM LEAVES: A LOOK AT LEAF SIZE Grades 3 6 I. Introduction Plants, like all other living organisms have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food), water, space in which to live, air, and optimal
LEARNING FROM LEAVES: A LOOK AT LEAF SIZE Grades 3 6 I. Introduction Plants, like all other living organisms have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food), water, space in which to live, air, and optimal
Chapter 18 Introduction to. A f r i c a
 Chapter 18 Introduction to A f r i c a Ch. 18:1 Landforms & Resources 1. Africa s shape & landforms are the result of its location in the southern part of the ancient supercontinent of. Pangaea Over thousands
Chapter 18 Introduction to A f r i c a Ch. 18:1 Landforms & Resources 1. Africa s shape & landforms are the result of its location in the southern part of the ancient supercontinent of. Pangaea Over thousands
NATURAL REGIONS OF KENTUCKY
 NATURAL WONDERS As you travel around Kentucky taking pictures, you are excited by what you see. Kentucky offers diverse and amazing sights. The Six Regions In the West, you see the Mississippi River, the
NATURAL WONDERS As you travel around Kentucky taking pictures, you are excited by what you see. Kentucky offers diverse and amazing sights. The Six Regions In the West, you see the Mississippi River, the
6. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below, which shows the average monthly temperature of two cities A and B.
 1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
Biomes An Overview of Ecology Biomes Freshwater Biomes
 Biomes An Overview of Ecology Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their environments. Ecology can be divided into four increasingly comprehensive levels: Organismal
Biomes An Overview of Ecology Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their environments. Ecology can be divided into four increasingly comprehensive levels: Organismal
Water & Climate Review
 Water & Climate Review 1. The cross section below shows the direction of air flowing over a mountain. Points A and B are at the same elevation on opposite sides of the mountain. 4. The graph below shows
Water & Climate Review 1. The cross section below shows the direction of air flowing over a mountain. Points A and B are at the same elevation on opposite sides of the mountain. 4. The graph below shows
Aquatic Biomes, Continued
 Aquatic Biomes, Continued Introduction Extent of Marine biomes Issues & challenges Factors influencing distribution Dynamics in time & space Depth Tour of marine biomes Issues (by biome) Freshwater biomes
Aquatic Biomes, Continued Introduction Extent of Marine biomes Issues & challenges Factors influencing distribution Dynamics in time & space Depth Tour of marine biomes Issues (by biome) Freshwater biomes
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best answers each question Part B: Matching 1
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best answers each question Part B: Matching 1
The Ice Age By: Sue Peterson
 www.k5learning.com Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific
www.k5learning.com Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific
Monsoon Variability and Extreme Weather Events
 Monsoon Variability and Extreme Weather Events M Rajeevan National Climate Centre India Meteorological Department Pune 411 005 rajeevan@imdpune.gov.in Outline of the presentation Monsoon rainfall Variability
Monsoon Variability and Extreme Weather Events M Rajeevan National Climate Centre India Meteorological Department Pune 411 005 rajeevan@imdpune.gov.in Outline of the presentation Monsoon rainfall Variability
Geography affects climate.
 KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment
 Wildfires Risk Assessment This plan is an update of the 2004 City of Redmond Hazard Mitigation Plan (HMP). Although it is an update, this document has been redesigned so that it looks, feels, and reads
Wildfires Risk Assessment This plan is an update of the 2004 City of Redmond Hazard Mitigation Plan (HMP). Although it is an update, this document has been redesigned so that it looks, feels, and reads
Marchand Provincial Park. Draft Management Plan
 Marchand Provincial Park Draft Management Plan Marchand Provincial Park Draft Management Plan Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Park History... 3 3. Park Attributes... 4 3.1 Natural... 4 3.2 Recreational...
Marchand Provincial Park Draft Management Plan Marchand Provincial Park Draft Management Plan Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Park History... 3 3. Park Attributes... 4 3.1 Natural... 4 3.2 Recreational...
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource
 Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
Tree Height-Age Correlation within Varying Elevations
 Tree Height-Age Correlation within Varying Elevations Marissa Padgett Norwood High School Telluride Institute Bridal Veil Living Classroom Fall 2011 !" Abstract: The science of tree morphology and understanding
Tree Height-Age Correlation within Varying Elevations Marissa Padgett Norwood High School Telluride Institute Bridal Veil Living Classroom Fall 2011 !" Abstract: The science of tree morphology and understanding
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist. Introduction. Climatic controls
 Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
4.0 Discuss some effects of disturbances on the forest.
 4.0 Discuss some effects of disturbances on the forest. 4.1 Describe common disturbances that occur in the Boreal forest. Disturbances are normal to the life of the forest. Forests are very resilient (able
4.0 Discuss some effects of disturbances on the forest. 4.1 Describe common disturbances that occur in the Boreal forest. Disturbances are normal to the life of the forest. Forests are very resilient (able
Global Water Resources
 Global Water Resources Highlights from assessment activities over the past two decades, which are used to establish present and future water trends, reveal that: 1. Freshwater resources are unevenly distributed,
Global Water Resources Highlights from assessment activities over the past two decades, which are used to establish present and future water trends, reveal that: 1. Freshwater resources are unevenly distributed,
Climate Change on the Prairie:
 Climate Change on the Prairie: A Basic Guide to Climate Change in the High Plains Region - UPDATE Global Climate Change Why does the climate change? The Earth s climate has changed throughout history and
Climate Change on the Prairie: A Basic Guide to Climate Change in the High Plains Region - UPDATE Global Climate Change Why does the climate change? The Earth s climate has changed throughout history and
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures. Seasons & Sun's Distance. Solstice & Equinox. Seasons & Solar Intensity
 Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
Flame Spread Performance of Wood Products
 Flame Spread Performance of Wood Products Wood and wood-based products are widely used in interior wall, ceiling, and floor surfaces in all types of buildings. Appearance, acoustical qualities, and interior
Flame Spread Performance of Wood Products Wood and wood-based products are widely used in interior wall, ceiling, and floor surfaces in all types of buildings. Appearance, acoustical qualities, and interior
The concepts developed in this standard include the following: Oceans cover about 70% of the surface of the Earth.
 Name Date Grade 5 SOL 5.6 Review Oceans Made by SOLpass - www.solpass.org solpass100@comcast.net Reproduction is permitted for SOLpass subscribers only. The concepts developed in this standard include
Name Date Grade 5 SOL 5.6 Review Oceans Made by SOLpass - www.solpass.org solpass100@comcast.net Reproduction is permitted for SOLpass subscribers only. The concepts developed in this standard include
Storms Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Life Cycle Of A Plant Population
 Life Cycle Of A Plant Population Seed Rain n=3 Growth And Mortality n=7 Seedling Cohort n=22 Environmental Sieve Seed Bank n=5 Copyright G. Bonan 22 Suvivorship Of Seedlings In A Northern Hardwood Forest
Life Cycle Of A Plant Population Seed Rain n=3 Growth And Mortality n=7 Seedling Cohort n=22 Environmental Sieve Seed Bank n=5 Copyright G. Bonan 22 Suvivorship Of Seedlings In A Northern Hardwood Forest
NALCOR ENERGY LABRADOR ISLAND TRANSMISSION LINK ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT. Chapter 4 Effects of the Environment on the Project
 NALCOR ENERGY LABRADOR ISLAND TRANSMISSION LINK ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT Chapter 4 Effects of the Environment on the Project Chapter 4 Effects of the Environment on the Project TABLE OF CONTENTS
NALCOR ENERGY LABRADOR ISLAND TRANSMISSION LINK ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT Chapter 4 Effects of the Environment on the Project Chapter 4 Effects of the Environment on the Project TABLE OF CONTENTS
WONDERFUL, WATERFUL WETLANDS
 WONDERFUL, WATERFUL WETLANDS OBJECTIVES The student will do the following: 1. List characteristics of wetlands. SUBJECTS: Science, Language Arts TIME: 60 minutes 2. Describe the functions of a wetland.
WONDERFUL, WATERFUL WETLANDS OBJECTIVES The student will do the following: 1. List characteristics of wetlands. SUBJECTS: Science, Language Arts TIME: 60 minutes 2. Describe the functions of a wetland.
Facts on Arctic Climate Change
 Facts on Arctic Climate Change A Summary of the Arctic Climate Impact Assessment ARCTIC CLIMATE CHANGE will not only affect local people and ecosystems but also the rest of the world, because the Arctic
Facts on Arctic Climate Change A Summary of the Arctic Climate Impact Assessment ARCTIC CLIMATE CHANGE will not only affect local people and ecosystems but also the rest of the world, because the Arctic
CLIMATE OF RWANDA. Overview. Linked to other lessons
 Geography S6 GENERAL PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF RWANDA Lesson 75 Developed by (Niwagaba Innocent) Subtopic Climate and factors influencing it in Rwanda Specific Objectives The learners must be able to: Describe
Geography S6 GENERAL PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF RWANDA Lesson 75 Developed by (Niwagaba Innocent) Subtopic Climate and factors influencing it in Rwanda Specific Objectives The learners must be able to: Describe
CROSSING THE OSLOFJORD - AN EARLY STRATEGIC ANALYSIS - Technical challenges and consideration of Feasible solutions
 CROSSING THE OSLOFJORD - AN EARLY STRATEGIC ANALYSIS - Technical challenges and consideration of Feasible solutions Ove Solheim MSc - Norwegian Public Roads Administration ABSTRACT Feasibility studies
CROSSING THE OSLOFJORD - AN EARLY STRATEGIC ANALYSIS - Technical challenges and consideration of Feasible solutions Ove Solheim MSc - Norwegian Public Roads Administration ABSTRACT Feasibility studies
Michigan Wetlands. Department of Environmental Quality
 Department of Environmental Quality Wetlands are a significant component of Michigan s landscape, covering roughly 5.5 million acres, or 15 percent of the land area of the state. This represents about
Department of Environmental Quality Wetlands are a significant component of Michigan s landscape, covering roughly 5.5 million acres, or 15 percent of the land area of the state. This represents about
CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate
 Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
CHAPTER 5 Lectures 10 & 11 Air Temperature and Air Temperature Cycles
 CHAPTER 5 Lectures 10 & 11 Air Temperature and Air Temperature Cycles I. Air Temperature: Five important factors influence air temperature: A. Insolation B. Latitude C. Surface types D. Coastal vs. interior
CHAPTER 5 Lectures 10 & 11 Air Temperature and Air Temperature Cycles I. Air Temperature: Five important factors influence air temperature: A. Insolation B. Latitude C. Surface types D. Coastal vs. interior
How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form?
 298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
taiga Encyclopedic Entry boreal forest
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry taiga boreal
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 7) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry taiga boreal
Woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou) in the Far North of Ontario: Background information in support of land use planning
 Woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou) in the Far North of Ontario: Background information in support of land use planning The Far North Caribou Project (FNCP) was initiated in 2008 to support land
Woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou) in the Far North of Ontario: Background information in support of land use planning The Far North Caribou Project (FNCP) was initiated in 2008 to support land
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Echo Sounding Record. Measuring Bathymetry. CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE
 7 WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1. Why weather changes so frequently? Ans. All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The movement of the
7 WEATHER, CLIMATE AND ADAPTATIONS OF ANIMALS TO CLIMATE TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q.1. Why weather changes so frequently? Ans. All changes in the weather are caused by the sun. The movement of the
Earth Science. River Systems and Landforms GEOGRAPHY 1710. The Hydrologic Cycle. Introduction. Running Water. Chapter 14.
 Earth Science GEOGRAPHY 1710 River Systems and Landforms DAVID R. SALLEE Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Chapter 14 Introduction Rivers and streams are dynamic systems that continually adjust
Earth Science GEOGRAPHY 1710 River Systems and Landforms DAVID R. SALLEE Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Chapter 14 Introduction Rivers and streams are dynamic systems that continually adjust
2013 Annual Climate Summary for the Southeast United States
 Months of heavy rain forced the U.S. Army Corp of Engineers to open the spillways at Lake Hartwell, located at the headwaters of the Savannah River along the South Carolina-Georgia border, on July 9,.
Months of heavy rain forced the U.S. Army Corp of Engineers to open the spillways at Lake Hartwell, located at the headwaters of the Savannah River along the South Carolina-Georgia border, on July 9,.
Deciduous Forest. Courtesy of Wayne Herron and Cindy Brady, U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service
 Deciduous Forest INTRODUCTION Temperate deciduous forests are found in middle latitudes with temperate climates. Deciduous means that the trees in this forest change with the seasons. In fall, the leaves
Deciduous Forest INTRODUCTION Temperate deciduous forests are found in middle latitudes with temperate climates. Deciduous means that the trees in this forest change with the seasons. In fall, the leaves
The Effect of Climate Change and Land Use on Biodiversity. Bruce C. Forbes Research Professor Arctic Centre University of Lapland Rovaniemi, Finland
 The Effect of Climate Change and Land Use on Biodiversity Bruce C. Forbes Research Professor Arctic Centre University of Lapland Rovaniemi, Finland Finland Northern portions of the Barents Euro-Arctic
The Effect of Climate Change and Land Use on Biodiversity Bruce C. Forbes Research Professor Arctic Centre University of Lapland Rovaniemi, Finland Finland Northern portions of the Barents Euro-Arctic
Higher Geography Biosphere Vegetation Succession: Sand Dunes
 Higher Geography Biosphere Vegetation Succession: Sand Dunes A PowerPoint resource to accompany the posters available at: http://www.macaulay.ac.uk/soilposters/education_vegetation_6v2.pdf http://www.macaulay.ac.uk/soilposters/education_vegetation_7v2.pdf
Higher Geography Biosphere Vegetation Succession: Sand Dunes A PowerPoint resource to accompany the posters available at: http://www.macaulay.ac.uk/soilposters/education_vegetation_6v2.pdf http://www.macaulay.ac.uk/soilposters/education_vegetation_7v2.pdf
8.5 Comparing Canadian Climates (Lab)
 These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
STATEMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS AND NOTES IN SUPPORT OF DEVELOPMENT APPLICATION
 CITY COUNCIL PROPOSED NEW RESIDENCE AT LOT XX, DP:55555 XXX Anon Drive, Somewhere FOR X. & Y Anonymous STATEMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS AND NOTES IN SUPPORT OF DEVELOPMENT APPLICATION Angela Elliss Design
CITY COUNCIL PROPOSED NEW RESIDENCE AT LOT XX, DP:55555 XXX Anon Drive, Somewhere FOR X. & Y Anonymous STATEMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS AND NOTES IN SUPPORT OF DEVELOPMENT APPLICATION Angela Elliss Design
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS THINGS
 CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
WILLOCHRA BASIN GROUNDWATER STATUS REPORT 2009-10
 WILLOCHRA BASIN GROUNDWATER STATUS REPORT 2009-10 SUMMARY 2009-10 The Willochra Basin is situated in the southern Flinders Ranges in the Mid-North of South Australia, approximately 50 km east of Port Augusta
WILLOCHRA BASIN GROUNDWATER STATUS REPORT 2009-10 SUMMARY 2009-10 The Willochra Basin is situated in the southern Flinders Ranges in the Mid-North of South Australia, approximately 50 km east of Port Augusta
Igneous rocks formed when hot molten material (magma) cools and hardens (crystallizes).
 Objectives You will learn about how the land of North Dakota was formed. Introduction North Dakota is a wonderful place to live. Have you ever though about how it was formed? To answer that question, you
Objectives You will learn about how the land of North Dakota was formed. Introduction North Dakota is a wonderful place to live. Have you ever though about how it was formed? To answer that question, you
Physiography, Geography and Climate of Latin America (Lecture 3)
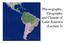 Physiography, Geography and Climate of Latin America (Lecture 3) Natural Landmarks in Latin America World's longest and second highest mountain range, and the world's highest active volcanoes. Biggest
Physiography, Geography and Climate of Latin America (Lecture 3) Natural Landmarks in Latin America World's longest and second highest mountain range, and the world's highest active volcanoes. Biggest
weather information management system / remote automated weather station
 weather information management system / remote automated weather station (wims/raws) OpERATIONS GUIDE wyoming blm June 2010 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES... A. District Manager...
weather information management system / remote automated weather station (wims/raws) OpERATIONS GUIDE wyoming blm June 2010 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES... A. District Manager...
Rapid Assessment Reference Condition Model
 R1ASPN Rapid Assessment Reference Condition Model The Rapid Assessment is a component of the LANDFIRE project. Reference condition models for the Rapid Assessment were created through a series of expert
R1ASPN Rapid Assessment Reference Condition Model The Rapid Assessment is a component of the LANDFIRE project. Reference condition models for the Rapid Assessment were created through a series of expert
Recognizing Wetlands. For additional information contact your local U.S. Army Corps of Engineers office. Pitcher plant.
 US Army Corps of Engineers For additional information contact your local U.S. Army Corps of Engineers office. 1998 Edition Recognizing Wetlands Pitcher plant The information presented here will help you
US Army Corps of Engineers For additional information contact your local U.S. Army Corps of Engineers office. 1998 Edition Recognizing Wetlands Pitcher plant The information presented here will help you
WEATHERING, EROSION, and DEPOSITION REVIEW
 WEATHERING, EROSION, and DEPOSITION REVIEW Weathering: The breaking up of rock from large particles to smaller particles. a) This Increases surface area of the rock which speeds the rate of chemical weathering.
WEATHERING, EROSION, and DEPOSITION REVIEW Weathering: The breaking up of rock from large particles to smaller particles. a) This Increases surface area of the rock which speeds the rate of chemical weathering.
8/18/2014. Chapter 9: Erosion and Deposition. Section 1 (Changing Earth s Surface) 8 th Grade. Weathering
 Section 1 (Changing Earth s Surface) Weathering the chemical and physical processes that break down rock at Earth s surface Chapter 9: Erosion and Deposition 8 th Grade Mechanical weathering when rock
Section 1 (Changing Earth s Surface) Weathering the chemical and physical processes that break down rock at Earth s surface Chapter 9: Erosion and Deposition 8 th Grade Mechanical weathering when rock
Description of Simandou Archaeological Potential Model. 13A.1 Overview
 13A Description of Simandou Archaeological Potential Model 13A.1 Overview The most accurate and reliable way of establishing archaeological baseline conditions in an area is by conventional methods of
13A Description of Simandou Archaeological Potential Model 13A.1 Overview The most accurate and reliable way of establishing archaeological baseline conditions in an area is by conventional methods of
T5.1 THE DYNAMICS OF NOVA SCOTIA S CLIMATE
 PAGE 94... T5.1 THE DYNAMICS OF NOVA SCOTIA S CLIMATE T5.1 The Dynamics of The main features of climate are ample and reliable precipitation, a fairly wide but not extreme temperature range, a late and
PAGE 94... T5.1 THE DYNAMICS OF NOVA SCOTIA S CLIMATE T5.1 The Dynamics of The main features of climate are ample and reliable precipitation, a fairly wide but not extreme temperature range, a late and
Drought in the Czech Republic in 2015 A preliminary summary
 Drought in the Czech Republic in 2015 A preliminary summary October 2015, Prague DISCLAIMER All data used in this preliminary report are operational and might be a subject of change during quality control.
Drought in the Czech Republic in 2015 A preliminary summary October 2015, Prague DISCLAIMER All data used in this preliminary report are operational and might be a subject of change during quality control.
Text and photos: Juha Siekkinen, Life+ Return of Rural Wetlands Cover drawing: Jari Kostet Maps and aerial photos: National Land Survey of Finland
 Life+ Return of Rural Wetlands Pikku Nuoluanjärvi Wetlands, Liminka Text and photos: Juha Siekkinen, Life+ Return of Rural Wetlands Cover drawing: Jari Kostet Maps and aerial photos: National Land Survey
Life+ Return of Rural Wetlands Pikku Nuoluanjärvi Wetlands, Liminka Text and photos: Juha Siekkinen, Life+ Return of Rural Wetlands Cover drawing: Jari Kostet Maps and aerial photos: National Land Survey
Region of Georgia : Mountains
 Region of Georgia : Mountains Northern most region of GA Cold weather in the winter Brasstown Bald is the highest point in Georgia Lots of creeks and streams High above sea level Poor soil for farming
Region of Georgia : Mountains Northern most region of GA Cold weather in the winter Brasstown Bald is the highest point in Georgia Lots of creeks and streams High above sea level Poor soil for farming
SLOPE AND TOPOGRAPHY
 SLOPE AND TOPOGRAPHY What are Slope and Topography? Slope and topography describe the shape and relief of the land. Topography is a measurement of elevation, and slope is the percent change in that elevation
SLOPE AND TOPOGRAPHY What are Slope and Topography? Slope and topography describe the shape and relief of the land. Topography is a measurement of elevation, and slope is the percent change in that elevation
Climate Change: A Local Focus on a Global Issue Newfoundland and Labrador Curriculum Links 2010-2011
 Climate Change: A Local Focus on a Global Issue Newfoundland and Labrador Curriculum Links 2010-2011 HEALTH Kindergarten: Grade 1: Grade 2: Know that litter can spoil the environment. Grade 3: Grade 4:
Climate Change: A Local Focus on a Global Issue Newfoundland and Labrador Curriculum Links 2010-2011 HEALTH Kindergarten: Grade 1: Grade 2: Know that litter can spoil the environment. Grade 3: Grade 4:
Beasley Lake Watershed National Sedimentation Laboratory Water Quality & Ecology Research Unit USDA ARS Oxford, Mississippi
 Beasley Lake Watershed National Sedimentation Laboratory Water Quality & Ecology Research Unit USDA ARS Oxford, Mississippi M. A. Locke, S. S. Knight, C. M. Cooper, S. Smith, Jr., M. T. Moore, F. D. Shields,
Beasley Lake Watershed National Sedimentation Laboratory Water Quality & Ecology Research Unit USDA ARS Oxford, Mississippi M. A. Locke, S. S. Knight, C. M. Cooper, S. Smith, Jr., M. T. Moore, F. D. Shields,
Comparison of Satellite Imagery and Conventional Aerial Photography in Evaluating a Large Forest Fire
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs LARS Symposia Laboratory for Applications of Remote Sensing --98 Comparison of Satellite Imagery and Conventional Aerial Photography in Evaluating a Large Forest Fire G.
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs LARS Symposia Laboratory for Applications of Remote Sensing --98 Comparison of Satellite Imagery and Conventional Aerial Photography in Evaluating a Large Forest Fire G.
Appendix A: Affordable Housing Site Inventory
 Appendix A: Affordable Housing Site Inventory Following is a brief summary of the various sites considered for the Affordable Housing Project. Each site is provided with a photo when available and a concise
Appendix A: Affordable Housing Site Inventory Following is a brief summary of the various sites considered for the Affordable Housing Project. Each site is provided with a photo when available and a concise
LESSON PLAN UNIT: THE EARTH S CLIMATES SESSIONS: 6. Ana Fructuoso Sánchez. Social Sciences teacher. Bilingual group. 1º ESO. IES El Palmar. Murcia.
 LESSON PLAN UNIT: THE EARTH S CLIMATES SESSIONS: 6 Ana Fructuoso Sánchez teacher. Bilingual group. 1º ESO IES El Palmar. Murcia. INTRODUCTION: In this unit we are going to analyze the layers of the atmosphere
LESSON PLAN UNIT: THE EARTH S CLIMATES SESSIONS: 6 Ana Fructuoso Sánchez teacher. Bilingual group. 1º ESO IES El Palmar. Murcia. INTRODUCTION: In this unit we are going to analyze the layers of the atmosphere
Identification and Prevention of Frost or Freeze Damage By Linda Reddick, Kingman Area Master Gardener
 KINGMAN IS GROWING! COLUMN Identification and Prevention of Frost or Freeze Damage By Linda Reddick, Kingman Area Master Gardener Again this year we have been experiencing some very cold weather, with
KINGMAN IS GROWING! COLUMN Identification and Prevention of Frost or Freeze Damage By Linda Reddick, Kingman Area Master Gardener Again this year we have been experiencing some very cold weather, with
What Causes Climate? Use Target Reading Skills
 Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Using LIDAR to monitor beach changes: Goochs Beach, Kennebunk, Maine
 Geologic Site of the Month February, 2010 Using LIDAR to monitor beach changes: Goochs Beach, Kennebunk, Maine 43 o 20 51.31 N, 70 o 28 54.18 W Text by Peter Slovinsky, Department of Agriculture, Conservation
Geologic Site of the Month February, 2010 Using LIDAR to monitor beach changes: Goochs Beach, Kennebunk, Maine 43 o 20 51.31 N, 70 o 28 54.18 W Text by Peter Slovinsky, Department of Agriculture, Conservation
ENVIRONMENTAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: CLIMATE SYSTEM Vol. II - Low-Latitude Climate Zones and Climate Types - E.I. Khlebnikova
 LOW-LATITUDE CLIMATE ZONES AND CLIMATE TYPES E.I. Khlebnikova Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Keywords: equatorial continental climate, ITCZ, subequatorial continental (equatorial
LOW-LATITUDE CLIMATE ZONES AND CLIMATE TYPES E.I. Khlebnikova Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Keywords: equatorial continental climate, ITCZ, subequatorial continental (equatorial
Forest Management Guidelines for the Protection of Four-toed and Spotted Salamander Populations Carol Hall & Bruce Carlson May 2004
 Forest Management Guidelines for the Protection of Four-toed and Spotted Salamander Populations Carol Hall & Bruce Carlson May 2004 Salamander Natural History Four-toed Salamanders: The Four-toed Salamander,
Forest Management Guidelines for the Protection of Four-toed and Spotted Salamander Populations Carol Hall & Bruce Carlson May 2004 Salamander Natural History Four-toed Salamanders: The Four-toed Salamander,
JUNIPER TREE NURSERY. Growing The Future Forest Today. A Promise We ve Been Keeping Since 1957.
 JUNIPER TREE NURSERY Growing The Future Forest Today. A Promise We ve Been Keeping Since 1957. JUNIPER TREE NURSERY J.D. Irving, Limited has had an active tree growing program since 1957 as part of our
JUNIPER TREE NURSERY Growing The Future Forest Today. A Promise We ve Been Keeping Since 1957. JUNIPER TREE NURSERY J.D. Irving, Limited has had an active tree growing program since 1957 as part of our
Chapter 3: Climate and Climate Change Answers
 Chapter 3: Climate and Climate Change Answers Section A: Climate 1. (a) Explain what each of the following means: (4 x 1 mark) (i) climate the average weather of an area over a 25 30 year period (ii) maritime
Chapter 3: Climate and Climate Change Answers Section A: Climate 1. (a) Explain what each of the following means: (4 x 1 mark) (i) climate the average weather of an area over a 25 30 year period (ii) maritime
High Elevation Rock Outcrops Southern Blue Ridge Mountains
 High Elevation Rock Outcrops Southern Blue Ridge Mountains High elevation rock outcrops are quite limited across the North Carolina landscape, however they are quite variable in terms of both geological
High Elevation Rock Outcrops Southern Blue Ridge Mountains High elevation rock outcrops are quite limited across the North Carolina landscape, however they are quite variable in terms of both geological
