F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Alkanes.
|
|
|
- Thomasina Gallagher
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Alkanes. 1. Kerosene is used as a fuel for aeroplane engines. Kerosene is obtained from crude oil. Name the process used to obtain kerosene from crude oil and explain why the process works [Total 2 marks] 2. Some of the hydrocarbons in kerosene have the formula C 10 H 22. What is the name of the straight chain hydrocarbon with the formula C 10 H 22? Draw the skeletal formula of one branched chain isomer with the formula C 10 H 22. (iii) Explain why the straight chain isomer of C 10 H 22 has a higher boiling point than any of its branched chain structural isomers. Plymstock School 1
2 (iv) Explain why the straight chain isomer of C 10 H 22 is converted by the petroleum industry into its branched chain isomers. [Total 5 marks] 3. Kerosene is used as a fuel for aeroplane engines. When kerosene burns in an aeroplane engine very little carbon monoxide, CO, is formed but a significant amount of nitrogen monoxide, NO, is formed. Construct the equation to show the complete combustion of C 10 H 22. Suggest, with the aid of an equation, how NO is formed within an aeroplane engine. [Total 3 marks] 4. A reaction mechanism shows the individual steps that take place during a reaction. Methane reacts with bromine in the presence of ultraviolet radiation to form several products. Two of these products are bromomethane and hydrogen bromide. Write an equation for the reaction between methane and bromine to make bromomethane and hydrogen bromide. Plymstock School 2
3 Name one other bromine-containing organic product which is formed when methane reacts with bromine. (iii) The mechanism for this reaction is called radical substitution. Describe the mechanism for the radical substitution of methane by bromine to make bromomethane. Use the mechanism to suggest why a small amount of ethane is also formed. In your answer, you should organise your answer and use the correct technical terms. [7] [Total 9 marks] Plymstock School 3
4 5. Alkenes are a very useful series of hydrocarbons used widely in synthesis. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. What is the name of the process used to convert long chain alkanes into more useful shorter chain alkenes?... [Total 1 mark] 6. Carbon monoxide, CO, is formed during the incomplete combustion of octane. Write an equation for the incomplete combustion of octane, forming carbon monoxide and water. Why does incomplete combustion sometimes take place? [Total 2 marks] 7. Oil companies process hydrocarbons, such as octane, into branched and cyclic hydrocarbons that promote efficient combustion in petrol. Draw the skeletal formulae of a branched hydrocarbon and a cyclic hydrocarbon, each containing eight carbon atoms. [Total 2 marks] Plymstock School 4
5 8. Catalysts are increasingly being used in chemical processes. A catalyst speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the overall reaction. A catalyst provides an alternative reaction route with a lower activation energy. Chlorine radicals, Cl, catalyse some reactions. Choose a reaction that you have studied that is catalysed by chlorine radicals. Write down an equation for the overall reaction and show how chlorine radicals are not consumed by the overall reaction. [3] Using the axes below, sketch an enthalpy profile diagram for an exothermic reaction to show how a catalyst provides an alternative reaction route with a lower activation energy. Include on your diagram labels for: enthalpy change, H; activation energy for the catalysed route, E c ; activation energy for the uncatalysed route, E a. enthalpy reactants progress of reaction [3] Plymstock School 5
6 9. The table below lists the boiling points of some alkanes. alkane number of carbon atoms molecular formula boiling point / C butane 4 C 4 H 10 0 pentane 5 C 5 H hexane 6 C 6 H heptane 7 C 7 H octane 8 C 8 H 18 nonane 9 C 9 H decane 10 C 10 H Predict the boiling point of octane. State and explain the trend in the boiling points of these alkanes. [Total 3 marks] 10. Long chain alkanes, such as nonane, are cracked into shorter chain alkanes and alkenes. Write a balanced equation for the cracking of nonane into heptane and ethene.... [Total 1 mark] Plymstock School 6
7 11. Straight chain alkanes such as heptane, C 7 H 16, are processed into branched-chain alkanes and cyclic compounds. These products are required to make petrol burn better in car engines than when using unbranched alkanes. Draw the skeletal formula of a branched structural isomer of heptane and state its name. skeletal formula: name:... Write a balanced equation to show the formation of the cyclic compound methylcyclohexane from heptane. [Total 4 marks] 12. Butane, C 4 H 10, reacts with chlorine to produce a chloroalkane with molecular formula C 4 H 9 Cl. The reaction is initiated by the formation of chlorine radicals from chlorine. What is meant by the term radical? State the conditions necessary to bring about the formation of the chlorine free radicals from Cl 2. Plymstock School 7
8 (iii) State the type of bond fission involved in the formation of the chlorine radicals. (iv) The chlorine radicals react with butane in several steps to produce C 4 H 9 Cl. Write equations for the two propagation steps. [Total 5 marks] 13. Crude oil is first separated by fractional distillation. The fractions can then be refined further by cracking, reforming and isomerisation. The reaction sequence below shows the production of heptane, C 7 H 16, from fractional distillation of crude oil, followed by cracking, reforming and isomerisation. cracking propene + A crude oil fractional distillation heptane reforming methylcyclohexane + B isomerisation branched alkanes (a) What is meant by the term fractional distillation? (b) The cracking of heptane produces propene and A. Write a balanced equation for this cracking of heptane. Plymstock School 8
9 (c) The reforming of heptane produces methylcyclohexane and B. Show the structural formula of methylcyclohexane. Write a balanced equation for this reforming. (d) The isomerisation of heptane produces seven branched alkanes, five of which are shown below. 2,3-dimethylpentane 2,4-dimethylpentane 2,2,3-trimethylbutane 2,4-dimethylpentane compound C Plymstock School 9
10 Name compound C. (iii) In the boxes above, draw skeletal formulae for the other two branched alkanes formed by isomerisation of heptane. Predict which of 2-methylhexane, 2,3-dimethylpentane and 2,2,3-trimethylbutane has the lowest boiling point. (iv) Explain why 2-methylhexane, 2,3-dimethylpentane and 2,2,3-trimethylbutane have different boiling points. [Total 10 marks] 14. Butane, C 4 H 10, under certain conditions, reacts with Cl 2 to form a mixture of chlorinated products. One possible product is C 4 H 9 Cl. C 4 H 10 + Cl 2 C 4 H 9 Cl + HCl (a) State the conditions. Write equations to show the mechanism of this reaction. initiation... propagation... [3] Plymstock School 10
11 (iii) Write one equation for a reaction that would terminate this mechanism. (iv) State the type of bond fission involved in the initiation step.... (b) One other possible product of the reaction between butane and chlorine is compound J, C 4 H 8 Cl l2, shown below. compound J H Cl H H H C C C C H H H Cl H Name compound J. Draw the skeletal formula of compound J. (iii) In addition to compound J, suggest one other possible structural isomer of C 4 H 8 Cl 2 that could have been formed in this reaction. [Total 9 marks] 15. In this question, one mark is available for the quality of use and organisation of scientific terms. Describe, with the aid of a suitable diagram, the formation of the π-bond in propene. State the shape, and an approximate value for the bond angles, around each carbon atom in propene. Describe, with the aid of a suitable example, why some alkenes show cis-trans isomerism. [9] Quality of Written Communication [Total 10 marks] Plymstock School 11
12 16. Hexane reacts with Br 2 in the presence of ultraviolet light. C 6 H 14 + Br 2 C 6 H 13 Br + HBr State the type of reaction. Identify the three possible structural isomers of the product, C 6 H 13 Br, that could be formed from this reaction with hexane. [3] [Total 4 marks] 17. In this question, one mark is available for the quality of spelling, punctuation and grammar. The fractions from crude oil can be processed by cracking, reforming and isomerisation. Outline these processes with the aid of suitable equations. State clearly the industrial importance of the products formed in each process. [8] Quality of Written Communication [Total 9 marks] Plymstock School 12
13 18. (a) Cyclohexane can be converted into cyclohexene via a three-stage synthesis. OH stage 1 Cl 2 compound A stage 2 stage 3 cyclohexane cyclohexanol cyclohexene In stage 1, cyclohexane reacts with chlorine to form the organic product, compound A. Show the structure of compound A. Stage 3 involves the dehydration of an alcohol. State a suitable reagent for dehydrating an alcohol. (iii) Write a balanced equation for the dehydration of cyclohexanol, C 6 H 11 OH. (b) The reaction in stage 1 is difficult to control. One other possible chlorinated product is 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane.This is shown below. Plymstock School 13
14 Cl stage 1 Cl 2 stage 2 stage 3 compound B compound C and D Cl cyclohexane 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane 1,4-Dichlorocyclohexane reacts in the same way as compound A in stages 2 and 3. Suggest the structure of compound B. Two cyclic alkenes, C and D are formed in stage 3. C and D are structural isomers. Suggest the structures of C and D. [Total 6 marks] 19. Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons. Initial separation is achieved by fractional distillation. The separate fractions are then further refined to produce hydrocarbons such as decane. (a) State what is meant by the term hydrocarbon. Plymstock School 14
15 A molecule of decane contains ten carbon atoms. State the molecular formula of decane. (iii) Deduce the empirical formula of decane.... (b) Dodecane, C 12 H 26, is a straight chain alkane that reacts with chlorine to produce a compound with molecular formula C 12 H 25 Cl. C 12 H 26 + Cl 2 C 12 H 25 Cl + HCl The reaction is initiated by the formation of chlorine free radicals from chlorine. What is meant by the term free radical? State the conditions necessary to bring about the formation of the chlorine free radicals from Cl 2. (iii) State the type of bond fission involved in the formation of the chlorine free radicals. (iv) The chlorine free radicals react with dodecane to produce C 12 H 25 Cl. Write equations for the two propagation steps involved. (v) How many different structural isomers can be formed when chlorine reacts with dodecane to form C 12 H 25 Cl? answer... Plymstock School 15
16 (c) Dodecane, C 12 H 26, can be cracked into ethene and a straight chain alkane such that the molar ratio ethene: straight chain alkane is 2 : 1. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. Name the straight chain alkane formed. (d) Straight chain alkanes such as heptane, C 7 H 16, can be isomerised into branched chain alkanes and reformed into cyclic compounds. Using skeletal formulae, write an equation to show the isomerisation of heptane into 2,2,3-trimethylbutane. Write a balanced equation to show the reforming of heptane into methylcyclohexane. [Total 16 marks] Plymstock School 16
17 20. The graph below shows the boiling points of some alkanes boiling point /K number of carbon atoms in a molecule of the alkane (a) Draw a smooth curve through the points on the graph and estimate the boiling points of octane C 8 H 18, hexadecane, C 16 H 34. (b) State how decane, C 10 H 22, can be separated from a mixture of the alkanes. (c) Isomerisation of hexane, C 6 H 14, produces a mixture of structural isomers, three of which are shown in the boxes below. Draw, using skeletal formulae, two other structural isomers of hexane. isomer A isomer B isomer C Plymstock School 17
18 Name isomer B.... (iii) Isomers A, B and C have different boiling points. In the boxes below, list the isomers A, B and C in order of their boiling points. lowest boiling point highest boiling point (iv) Explain the order given in (c) (iii). (d) Hexane can be reformed to produce cyclohexane as one of the products. (iii) Draw the structural formula of cyclohexane. Write a balanced equation for the reforming of hexane into cyclohexane. Suggest one reason why oil companies reform alkanes such as hexane. (e) Oxygen-containing compounds can be added to improve the efficiency and performance of fuels. In Formula One racing cars, it is common practice to add oxygen-containing compounds, such as 2-methylpropan-2-ol, (CH 3 ) 3 COH. The amount of oxygen-containing compounds added is strictly controlled by the Federation Internationale de l Automobile, FIA. Calculate the percentage by mass of oxygen in (CH 3 ) 3 COH. Give your answer to three significant figures. answer Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of (CH 3 ) 3 COH. [Total 16 marks] Plymstock School 18
19 21. Cyclohexane, C 6 H 12, reacts with chlorine to produce chlorocyclohexane, C 6 H 11 Cl. C 6 H 12 + Cl 2 C 6 H 11 Cl + HCl The mechanism for this reaction is a free radical substitution. Write an equation to show the initiation step. State the conditions necessary for the initiation step. (iii) The reaction continues by two propagation steps resulting in the formation of chlorocyclohexane, C 6 H 11 Cl. Write equations for these two propagation steps. step 1... step 2... (iv) State what happens to the free radicals in the termination steps. 22. In this question, one mark is available for the quality of use and organisation of scientific terms. Different cars require different grades of petrol. The first stage in the production of petrol in an oil refinery is to fractionate the crude oil. After that, refineries carry out further processes. Outline, with the aid of equations, three of these processes in the production of petrol. Explain why, in the long term, ethanol could replace oil-based fuels. [Total 5 marks] Write an equation for the combustion of ethanol. [10] Quality of Written Communication [Total 11 marks] Plymstock School 19
20 23. The table below lists the boiling points of some alkanes. alkane number of carbon atoms molecular formula boiling point / C butane 4 C 4 H 10 0 pentane 5 C 5 H hexane 6 69 heptane 7 C 7 H octane 8 C 8 H 18 nonane 9 C 9 H decane 10 C 10 H (a) What is the molecular formula of hexane?... (b) State the trend in the boiling points of the alkanes. Explain the trend in the boiling points of the alkanes. (iii) Predict the boiling point of octane.... C [Total 4 marks] 24. Long chain alkanes, such as nonane, can be cracked into shorter chain alkanes and alkenes. Write a balanced equation for the cracking of nonane into heptane and ethene. Plymstock School 20
21 Much of the ethene is then converted into ethanol. Write a balanced equation for the conversion of ethene into ethanol. State the essential conditions. equation... conditions... [Total 4 marks] 25. (a) Heptane can be isomerised to produce branched chain alkanes such as 2-methylhexane or 2,3-dimethylpentane. The equation below shows the isomerisation of heptane into 2-methylhexane. Using skeletal formulae, complete the balanced equation for the isomerisation of heptane into 2,3-dimethylpentane. The boiling point of 2,3-dimethylpentane is 84 C. Predict the boiling point of 2-methylhexane.... C (b) Heptane can be reformed to produce methylcyclohexane which is a cycloalkane. Write a balanced equation to show the reforming of heptane to obtain methylcyclohexane Plymstock School 21
22 (c) State why branched chain alkanes and cycloalkanes are more useful than straight chain alkanes. [Total 5 marks] 26. Propane, C 3 H 8, is used in the reaction sequence shown below. A B reaction 1 reaction 2 H 3 C CH 2 CH 3 H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 Cl H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 OH C /uv light aqueous OH / heat l 2 reaction 3 ethanolic OH / heat E polymerisation H 3 C CH CH 2 reaction 4 H 3 C OH CH CH 3 C D (a) The reaction sequence shows several important reaction mechanisms. Select from reactions 1 to 4, the reaction that shows free radical substitution, reaction... electrophilic addition, reaction... (iii) elimination, reaction... (b) In reaction 2, the aqueous OH acts as a nucleophile. State what is meant by the term nucleophile. Complete, with the aid of curly arrows, the mechanism involved in reaction 2. Show any relevant dipoles. H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 Cl H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 OH +... OH [4] Plymstock School 22
23 (c) Compounds B and D are structural isomers of each other. State what is meant by the term structural isomers. Draw the skeletal formulae of compounds B and D. Compound B Compound D (d) Compound C can be polymerised to form compound E. State the type of polymerisation.... Name compound E.... (iii) Draw a section of compound E. Show two repeat units. [Total 15 marks] Plymstock School 23
24 27. Isomer L, C 5 H 10, reacts with Cl 2 in the presence of UV light to produce the organic product C 5 H g Cl. The reaction takes place in three stages: initiation, propagation and termination. The reaction is initiated by the fission of Cl 2. State the type of fission involved. Write an equation to illustrate the fission of Cl 2 in. (iii) The fission of Cl 2 leads to a chain reaction involving two propagation steps. Complete the equations for the two propagation steps. C 5 H C 5 H C 5 H [Total 4 marks] Plymstock School 24
25 28. In this question, one mark is available for the quality of written communication. Alkanes can be separated from crude oil because they have different boiling points. The table below shows the boiling points of some alkanes. alkane boiling point/ C M r ethane propane butane 0 58 pentane methylbutane ,2-dimethylpropane Explain the variation in boiling points of the alkanes shown. Explain why, in industry, alkanes such as octane are processed by isomerisation. [5] [3] Illustrate your answers by referring to suitable examples. Write equations where appropriate. Quality of Written Communication [Total 9 marks] Plymstock School 25
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols
 F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3. Copyright 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 1: Organic Compounds 1.1-1
 Section 1.1: Alkanes Mini Investigation: Arranging Carbon Atoms, page 10 A. Three different molecules of C 5 H 12 are possible. B. Five arrangements are possible for C 6 H 14, as predicted: H 3 C CH 2
Section 1.1: Alkanes Mini Investigation: Arranging Carbon Atoms, page 10 A. Three different molecules of C 5 H 12 are possible. B. Five arrangements are possible for C 6 H 14, as predicted: H 3 C CH 2
Page 1. 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? (1) 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? (1) (2) (2) (3) (3) (4) (4)
 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
Alkanes. Chapter 1.1
 Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I
 Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I 1. (a) What do you understand by the following terms : (i) Organic chemistry (ii) Organic compounds (iii) Catenation? [3] (b) Why are there very large number of organic
Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I 1. (a) What do you understand by the following terms : (i) Organic chemistry (ii) Organic compounds (iii) Catenation? [3] (b) Why are there very large number of organic
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 9701/02 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 9701/02 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN
GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS
 Name: GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This paper consists of: a question paper of 7 pages a data and formula booklet
Name: GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This paper consists of: a question paper of 7 pages a data and formula booklet
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 81 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon with the exception of simple compounds e.g. carbonates (CO 3 2- ), carbon dioxide
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 81 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon with the exception of simple compounds e.g. carbonates (CO 3 2- ), carbon dioxide
CHM220 Addition lab. Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes*
 CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
Calculating the Degrees of Unsaturation From a Compound s Molecular Formula
 Calculating the Degrees of Unsaturation From a Compound s Molecular Formula Alkanes have the molecular formula C n. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons because each member of the family has the maximum
Calculating the Degrees of Unsaturation From a Compound s Molecular Formula Alkanes have the molecular formula C n. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons because each member of the family has the maximum
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS IN THREE DIMENSIONS
 (adapted from Blackburn et al., Laboratory Manual to Accompany World of hemistry, 2 nd ed., (1996) Saunders ollege Publishing: Fort Worth) Purpose: To become familiar with organic molecules in three dimensions
(adapted from Blackburn et al., Laboratory Manual to Accompany World of hemistry, 2 nd ed., (1996) Saunders ollege Publishing: Fort Worth) Purpose: To become familiar with organic molecules in three dimensions
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models
 Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
e. What are the compositions and uses of fractions of crude oil? f. How are further fractions lubricationg oils and waxes obtained?
 CRUDE OIL AND ITS COMPOSITION 1. Use a textbook to answer the following questions: a. How was crude oil formed? b. What is crude oil chemically? c. How can the components of crude oil be separated? d.
CRUDE OIL AND ITS COMPOSITION 1. Use a textbook to answer the following questions: a. How was crude oil formed? b. What is crude oil chemically? c. How can the components of crude oil be separated? d.
Unit Vocabulary: o Organic Acid o Alcohol. o Ester o Ether. o Amine o Aldehyde
 Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
CHEM 203 Exam 1. KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHEM 203 Exam 1 KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. _D C 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both
CHEM 203 Exam 1 KEY Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. _D C 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both
Chapter 1: Moles and equations. Learning outcomes. you should be able to:
 Chapter 1: Moles and equations 1 Learning outcomes you should be able to: define and use the terms: relative atomic mass, isotopic mass and formula mass based on the 12 C scale perform calculations, including
Chapter 1: Moles and equations 1 Learning outcomes you should be able to: define and use the terms: relative atomic mass, isotopic mass and formula mass based on the 12 C scale perform calculations, including
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Specimen Paper. Chemistry 1F. Time allowed! 60 minutes
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number Specimen Paper For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Question 1 Mark Science
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number Specimen Paper For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Question 1 Mark Science
Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know: -What occurs -Why and
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know: -What occurs -Why and
*0500/402* 0500/402. CHEMISTRY STANDARD GRADE Credit Level. Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre
 FOR OFFIIL USE 0500/402 NTIONL QULIFITIONS 2009 MONDY, MY 0.50 M 2.20 PM Total HEMISTRY STNDRD GRDE redit Level Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre Town Forename(s)
FOR OFFIIL USE 0500/402 NTIONL QULIFITIONS 2009 MONDY, MY 0.50 M 2.20 PM Total HEMISTRY STNDRD GRDE redit Level Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre Town Forename(s)
Stoichiometry. Lecture Examples Answer Key
 Stoichiometry Lecture Examples Answer Key Ex. 1 Balance the following chemical equations: 3 NaBr + 1 H 3 PO 4 3 HBr + 1 Na 3 PO 4 2 C 3 H 5 N 3 O 9 6 CO 2 + 3 N 2 + 5 H 2 O + 9 O 2 2 Ca(OH) 2 + 2 SO 2
Stoichiometry Lecture Examples Answer Key Ex. 1 Balance the following chemical equations: 3 NaBr + 1 H 3 PO 4 3 HBr + 1 Na 3 PO 4 2 C 3 H 5 N 3 O 9 6 CO 2 + 3 N 2 + 5 H 2 O + 9 O 2 2 Ca(OH) 2 + 2 SO 2
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 2015. M33 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 CHEMISTRY ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 16 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions
2015. M33 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 CHEMISTRY ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 16 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11. PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2
 MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 0620/03 Paper 3 Theory (Core) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 1 hour
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 0620/03 Paper 3 Theory (Core) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 1 hour
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (separate award)
 EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (separate award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles in each of the three states of matter:
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (separate award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles in each of the three states of matter:
Chapter 4. Chemical Energy
 hapter 4 hemical Energy Perhaps the most convenient form in which to store energy is chemical energy. The foods we eat, combined with the oxygen we breathe, store energy that our bodies extract and convert
hapter 4 hemical Energy Perhaps the most convenient form in which to store energy is chemical energy. The foods we eat, combined with the oxygen we breathe, store energy that our bodies extract and convert
20.2 Chemical Equations
 All of the chemical changes you observed in the last Investigation were the result of chemical reactions. A chemical reaction involves a rearrangement of atoms in one or more reactants to form one or more
All of the chemical changes you observed in the last Investigation were the result of chemical reactions. A chemical reaction involves a rearrangement of atoms in one or more reactants to form one or more
Summer Holidays Questions
 Summer Holidays Questions Chapter 1 1) Barium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. The initial concentration of the 1 st solution its 0.1M and the volume is 100ml. The initial concentration of the
Summer Holidays Questions Chapter 1 1) Barium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. The initial concentration of the 1 st solution its 0.1M and the volume is 100ml. The initial concentration of the
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models
 EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry)
 Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
ORGANIC CHEM I Practice Questions for Ch. 4
 ORGANIC CHEM I Practice Questions for Ch. 4 1) Write an equation to describe the initiation step in the chlorination of methane. 2) Reaction intermediates that have unpaired electrons are called. 3) When
ORGANIC CHEM I Practice Questions for Ch. 4 1) Write an equation to describe the initiation step in the chlorination of methane. 2) Reaction intermediates that have unpaired electrons are called. 3) When
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
How To Calculate Mass In Chemical Reactions
 We have used the mole concept to calculate mass relationships in chemical formulas Molar mass of ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH)? Molar mass = 2 x 12.011 + 6 x 1.008 + 1 x15.999 = 46.069 g/mol Mass percentage of
We have used the mole concept to calculate mass relationships in chemical formulas Molar mass of ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH)? Molar mass = 2 x 12.011 + 6 x 1.008 + 1 x15.999 = 46.069 g/mol Mass percentage of
GCE. Chemistry A. Mark Scheme for June 2012. Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F322: Chains, Energy and Resources. Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Chemistry A Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Mark Scheme for June 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
GCE Chemistry A Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Mark Scheme for June 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
IB Chemistry. DP Chemistry Review
 DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum
 Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum Unit 5 Organic Chemistry General Outcomes Students will: 1. explore organic compounds as a common form of matter
Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum Unit 5 Organic Chemistry General Outcomes Students will: 1. explore organic compounds as a common form of matter
GCSE Chemistry Quiz Chemical Reactions
 GCSE Chemistry Quiz Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process where the molecular structure changes. Chemical reactions are all around us. We can see many reactions such as fireworks and explosions.
GCSE Chemistry Quiz Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process where the molecular structure changes. Chemical reactions are all around us. We can see many reactions such as fireworks and explosions.
Austin Peay State University Department of Chemistry CHEM 1021 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
Worksheets for Organic Chemistry
 Worksheets for Organic Chemistry Worksheet 1 Alkanes Question 1. Provide IUPAC names for the following structures a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) Chemistry of Natural Substances Organic Chemistry Worksheets 1
Worksheets for Organic Chemistry Worksheet 1 Alkanes Question 1. Provide IUPAC names for the following structures a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) Chemistry of Natural Substances Organic Chemistry Worksheets 1
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 CHEMISTRY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 19 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 CHEMISTRY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 19 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 13_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In organic chemistry, the term unsaturated means a molecule A) which contains one or more
Ch 13_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In organic chemistry, the term unsaturated means a molecule A) which contains one or more
Stoichiometry. What is the atomic mass for carbon? For zinc?
 Stoichiometry Atomic Mass (atomic weight) Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams We use atomic mass units an atomic mass unit (AMU) is one twelfth the mass of the catbon-12
Stoichiometry Atomic Mass (atomic weight) Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams We use atomic mass units an atomic mass unit (AMU) is one twelfth the mass of the catbon-12
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry
 Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Basic definitions for organic chemistry
 rganic Chemistry - Introduction F 1 Basic definitions for organic chemistry Scope rganic chemistry is a vast subject so is split it into small sections for study. This is done by studying compounds which
rganic Chemistry - Introduction F 1 Basic definitions for organic chemistry Scope rganic chemistry is a vast subject so is split it into small sections for study. This is done by studying compounds which
Unit 2 Review: Answers: Review for Organic Chemistry Unit Test
 Unit 2 Review: Answers: Review for Organic Chemistry Unit Test 2. Write the IUPAC names for the following organic molecules: a) acetone: propanone d) acetylene: ethyne b) acetic acid: ethanoic acid e)
Unit 2 Review: Answers: Review for Organic Chemistry Unit Test 2. Write the IUPAC names for the following organic molecules: a) acetone: propanone d) acetylene: ethyne b) acetic acid: ethanoic acid e)
Unit 2: Quantities in Chemistry
 Mass, Moles, & Molar Mass Relative quantities of isotopes in a natural occurring element (%) E.g. Carbon has 2 isotopes C-12 and C-13. Of Carbon s two isotopes, there is 98.9% C-12 and 11.1% C-13. Find
Mass, Moles, & Molar Mass Relative quantities of isotopes in a natural occurring element (%) E.g. Carbon has 2 isotopes C-12 and C-13. Of Carbon s two isotopes, there is 98.9% C-12 and 11.1% C-13. Find
The energy level diagram for this reaction is shown below.
 Q. Methanol can be made when methane reacts with oxygen. (a) The energy level diagram for this reaction is shown below. (i) What is the energy change represented by A? () (ii) Use the energy level diagram
Q. Methanol can be made when methane reacts with oxygen. (a) The energy level diagram for this reaction is shown below. (i) What is the energy change represented by A? () (ii) Use the energy level diagram
Calculating Atoms, Ions, or Molecules Using Moles
 TEKS REVIEW 8B Calculating Atoms, Ions, or Molecules Using Moles TEKS 8B READINESS Use the mole concept to calculate the number of atoms, ions, or molecules in a sample TEKS_TXT of material. Vocabulary
TEKS REVIEW 8B Calculating Atoms, Ions, or Molecules Using Moles TEKS 8B READINESS Use the mole concept to calculate the number of atoms, ions, or molecules in a sample TEKS_TXT of material. Vocabulary
IB Chemistry 1 Mole. One atom of C-12 has a mass of 12 amu. One mole of C-12 has a mass of 12 g. Grams we can use more easily.
 The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Paper 2 (7404/2): Organic and Physical Chemistry Mark scheme
 AQA Qualifications AS hemistry Paper 2 (7404/2): Organic and Physical hemistry Mark scheme 7404 Specimen paper Version 0.5 MARK SEME AS hemistry Specimen paper 2 Question Marking guidance Mark AO omments
AQA Qualifications AS hemistry Paper 2 (7404/2): Organic and Physical hemistry Mark scheme 7404 Specimen paper Version 0.5 MARK SEME AS hemistry Specimen paper 2 Question Marking guidance Mark AO omments
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of carbon based compounds. The structural and genetic materials of living organisms are organic compounds. Many of the substances
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of carbon based compounds. The structural and genetic materials of living organisms are organic compounds. Many of the substances
CHEMICAL FORMULA COEFFICIENTS AND SUBSCRIPTS. Chapter 3: Molecular analysis 3O 2 2O 3
 Chapter 3: Molecular analysis Read: BLB 3.3 3.5 H W : BLB 3:21a, c, e, f, 25, 29, 37,49, 51, 53 Supplemental 3:1 8 CHEMICAL FORMULA Formula that gives the TOTAL number of elements in a molecule or formula
Chapter 3: Molecular analysis Read: BLB 3.3 3.5 H W : BLB 3:21a, c, e, f, 25, 29, 37,49, 51, 53 Supplemental 3:1 8 CHEMICAL FORMULA Formula that gives the TOTAL number of elements in a molecule or formula
Name Date Class STOICHIOMETRY. SECTION 12.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358)
 Name Date Class 1 STOICHIOMETRY SECTION 1.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358) This section explains how to calculate the amount of reactants required or product formed in a nonchemical process.
Name Date Class 1 STOICHIOMETRY SECTION 1.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358) This section explains how to calculate the amount of reactants required or product formed in a nonchemical process.
COMBUSTION. In order to operate a heat engine we need a hot source together with a cold sink
 COMBUSTION In order to operate a heat engine we need a hot source together with a cold sink Occasionally these occur together in nature eg:- geothermal sites or solar powered engines, but usually the heat
COMBUSTION In order to operate a heat engine we need a hot source together with a cold sink Occasionally these occur together in nature eg:- geothermal sites or solar powered engines, but usually the heat
Molecular Formula Determination
 Molecular Formula Determination Classical Approach Qualitative elemental analysis Quantitative elemental analysis Determination of empirical formula Molecular weight determination Molecular formula determination
Molecular Formula Determination Classical Approach Qualitative elemental analysis Quantitative elemental analysis Determination of empirical formula Molecular weight determination Molecular formula determination
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION. 37 74 20 40 60 80 m/e
 CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
These instructions are for a classroom activity which supports OCR A Level Chemistry A.
 Lesson Element Keyword activities Instructions for teachers These instructions are for a classroom activity which supports OCR A Level Chemistry A. Just a minute! To run this activity you will need a set
Lesson Element Keyword activities Instructions for teachers These instructions are for a classroom activity which supports OCR A Level Chemistry A. Just a minute! To run this activity you will need a set
Chemical Reactions Practice Test
 Chemical Reactions Practice Test Chapter 2 Name Date Hour _ Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The only sure evidence for a chemical reaction
Chemical Reactions Practice Test Chapter 2 Name Date Hour _ Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The only sure evidence for a chemical reaction
Unit 5 Practice Test. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Unit 5 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The internal energy of a system is always increased by. A) adding
Name: Class: Date: Unit 5 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The internal energy of a system is always increased by. A) adding
IUPAC System of Nomenclature
 IUPAC System of Nomenclature The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is composed of chemists representing the national chemical societies of several countries. ne committee of the
IUPAC System of Nomenclature The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is composed of chemists representing the national chemical societies of several countries. ne committee of the
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies
 Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the following ionic compounds in order of increasing lattice energy: NaF, CsI, and CaO. Analyze: From the formulas
Sample Exercise 8.1 Magnitudes of Lattice Energies Without consulting Table 8.2, arrange the following ionic compounds in order of increasing lattice energy: NaF, CsI, and CaO. Analyze: From the formulas
In the box below, draw the Lewis electron-dot structure for the compound formed from magnesium and oxygen. [Include any charges or partial charges.
 Name: 1) Which molecule is nonpolar and has a symmetrical shape? A) NH3 B) H2O C) HCl D) CH4 7222-1 - Page 1 2) When ammonium chloride crystals are dissolved in water, the temperature of the water decreases.
Name: 1) Which molecule is nonpolar and has a symmetrical shape? A) NH3 B) H2O C) HCl D) CH4 7222-1 - Page 1 2) When ammonium chloride crystals are dissolved in water, the temperature of the water decreases.
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3)
 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3) Chemical Compounds 1. Classification of Elements and Compounds Types of Pure Substances (Figure 3.4) Elements -- made up of only one type of atom
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3) Chemical Compounds 1. Classification of Elements and Compounds Types of Pure Substances (Figure 3.4) Elements -- made up of only one type of atom
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
 Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
Chemical Calculations: Formula Masses, Moles, and Chemical Equations
 Chemical Calculations: Formula Masses, Moles, and Chemical Equations Atomic Mass & Formula Mass Recall from Chapter Three that the average mass of an atom of a given element can be found on the periodic
Chemical Calculations: Formula Masses, Moles, and Chemical Equations Atomic Mass & Formula Mass Recall from Chapter Three that the average mass of an atom of a given element can be found on the periodic
Chemistry 1110 Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature
 hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
The Mole and Molar Mass
 The Mole and Molar Mass 1 Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. Molar mass is numerically equal to atomic mass, molecular mass, or formula mass. However the units of molar mass are g/mol.
The Mole and Molar Mass 1 Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. Molar mass is numerically equal to atomic mass, molecular mass, or formula mass. However the units of molar mass are g/mol.
AP Chemistry 2010 Scoring Guidelines Form B
 AP Chemistry 2010 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to college success and opportunity. Founded
AP Chemistry 2010 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to college success and opportunity. Founded
Sample Exercise 3.1 Interpreting and Balancing Chemical Equations
 Sample Exercise 3.1 Interpreting and Balancing Chemical Equations The following diagram represents a chemical reaction in which the red spheres are oxygen atoms and the blue spheres are nitrogen atoms.
Sample Exercise 3.1 Interpreting and Balancing Chemical Equations The following diagram represents a chemical reaction in which the red spheres are oxygen atoms and the blue spheres are nitrogen atoms.
States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS]
![States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS] States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS]](/thumbs/40/21739317.jpg) OpenStax-CNX module: m38210 1 States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS] Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m38210 1 States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS] Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual
 Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
GCE AS and A Level. Chemistry. AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards. Unit 2: Specimen mark scheme. Version 1.1
 GCE AS and A Level Chemistry AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards Unit 2: Specimen mark scheme Version 1.1 Version 1.1: 07/07 abc General Certificate of Education Chemistry 2420 CHEM2 Chemistry
GCE AS and A Level Chemistry AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards Unit 2: Specimen mark scheme Version 1.1 Version 1.1: 07/07 abc General Certificate of Education Chemistry 2420 CHEM2 Chemistry
Lecture 10 Solving Material Balances Problems Involving Reactive Processes
 CHE 31. INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERING CALCULATIONS Lecture 10 Solving Material Balances Problems Involving Reactive Processes Material Balances on Reactive Processes Material balances on processes
CHE 31. INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERING CALCULATIONS Lecture 10 Solving Material Balances Problems Involving Reactive Processes Material Balances on Reactive Processes Material balances on processes
Chem 31 Fall 2002. Chapter 3. Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations. Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
 Chem 31 Fall 2002 Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Write Equation in Words -you cannot write an equation unless you
Chem 31 Fall 2002 Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Write Equation in Words -you cannot write an equation unless you
Chemistry Grade 11 Year and weekly plan 2015
 Chemistry Grade 11 Year and weekly plan 2015 TERM1 Content Curriculum Statement Teaching Method Atomic combinations: molecular structure chemical bond (is seen as the net electrostatic force two atoms
Chemistry Grade 11 Year and weekly plan 2015 TERM1 Content Curriculum Statement Teaching Method Atomic combinations: molecular structure chemical bond (is seen as the net electrostatic force two atoms
Chapter 15 Radical Reactions. Radicals are reactive species with a single unpaired electron, formed by
 Chapter 15 Radical Reactions Radicals are reactive species with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond; a radical contains an atom that does not have an octet of electrons,
Chapter 15 Radical Reactions Radicals are reactive species with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond; a radical contains an atom that does not have an octet of electrons,
83 to 87% carbon 11-15% hydrogen 0.1-7% sulphur 0.06-1.5% oxygen 0.1-0.5% nitrogen
 Petroleum chemistry rude is the name for a liquid mixture of different hydrocarbon connections found in the earth. Petroleum, strictly speaking is crude oil, but it is used to describe all kinds of hydrocarbons.
Petroleum chemistry rude is the name for a liquid mixture of different hydrocarbon connections found in the earth. Petroleum, strictly speaking is crude oil, but it is used to describe all kinds of hydrocarbons.
Chemical formulae are used as shorthand to indicate how many atoms of one element combine with another element to form a compound.
 29 Chemical Formulae Chemical formulae are used as shorthand to indicate how many atoms of one element combine with another element to form a compound. C 2 H 6, 2 atoms of carbon combine with 6 atoms of
29 Chemical Formulae Chemical formulae are used as shorthand to indicate how many atoms of one element combine with another element to form a compound. C 2 H 6, 2 atoms of carbon combine with 6 atoms of
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
 Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Bomb Calorimetry. Electrical leads. Stirrer
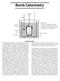 Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Answers Outline I. Molar Mass and Moles A. Calculations of Molar Masses
 Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Answers Outline I. Molar Mass and Moles A. Calculations of Molar Masses B. Calculations of moles C. Calculations of number of atoms from moles/molar masses 1. Avagadro
Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Answers Outline I. Molar Mass and Moles A. Calculations of Molar Masses B. Calculations of moles C. Calculations of number of atoms from moles/molar masses 1. Avagadro
MOLAR MASS AND MOLECULAR WEIGHT Themolar mass of a molecule is the sum of the atomic weights of all atoms in the molecule. Molar Mass.
 Counting Atoms Mg burns in air (O 2 ) to produce white magnesium oxide, MgO. How can we figure out how much oxide is produced from a given mass of Mg? PROBLEM: If If 0.200 g of Mg is is burned, how much
Counting Atoms Mg burns in air (O 2 ) to produce white magnesium oxide, MgO. How can we figure out how much oxide is produced from a given mass of Mg? PROBLEM: If If 0.200 g of Mg is is burned, how much
Electrophilic Addition Reactions
 Electrophilic Addition Reactions Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reactions that allow the interconversion of C=C and C C into a range of important functional groups. Conceptually,
Electrophilic Addition Reactions Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reactions that allow the interconversion of C=C and C C into a range of important functional groups. Conceptually,
Chapter 3. Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry. Lecture Presentation. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided. Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work you do not want to be marked.
 GCSE CHEMISTRY Higher Tier Chemistry 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed). Instructions Answer all
GCSE CHEMISTRY Higher Tier Chemistry 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed). Instructions Answer all
Amount of Substance. http://www.avogadro.co.uk/definitions/elemcompmix.htm
 Page 1 of 14 Amount of Substance Key terms in this chapter are: Element Compound Mixture Atom Molecule Ion Relative Atomic Mass Avogadro constant Mole Isotope Relative Isotopic Mass Relative Molecular
Page 1 of 14 Amount of Substance Key terms in this chapter are: Element Compound Mixture Atom Molecule Ion Relative Atomic Mass Avogadro constant Mole Isotope Relative Isotopic Mass Relative Molecular
Coal-To-Gas & Coal-To-Liquids
 Located in the Energy Center at Discovery Park, Purdue University Coal-To-Gas & Coal-To-Liquids CCTR Basic Facts File #3 Brian H. Bowen, Marty W. Irwin The Energy Center at Discovery Park Purdue University
Located in the Energy Center at Discovery Park, Purdue University Coal-To-Gas & Coal-To-Liquids CCTR Basic Facts File #3 Brian H. Bowen, Marty W. Irwin The Energy Center at Discovery Park Purdue University
Question (3): What are the different types of covalent bonds found in carbons compounds? Briefly explain with examples.
 CLASS: X NCERT (CBSE) Chemistry: For Class 10 Page : 1 Question (1): What is organic chemistry? Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds of living matter i.e., plants and animals (CO 2, carbonates,
CLASS: X NCERT (CBSE) Chemistry: For Class 10 Page : 1 Question (1): What is organic chemistry? Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds of living matter i.e., plants and animals (CO 2, carbonates,
F321 MOLES. Example If 1 atom has a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g 1 mole of atoms will have a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g x 6.02 x 10 23 = 7.
 Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Atomic mass is the mass of an atom in atomic mass units (amu)
 Micro World atoms & molecules Laboratory scale measurements Atomic mass is the mass of an atom in atomic mass units (amu) By definition: 1 atom 12 C weighs 12 amu On this scale 1 H = 1.008 amu 16 O = 16.00
Micro World atoms & molecules Laboratory scale measurements Atomic mass is the mass of an atom in atomic mass units (amu) By definition: 1 atom 12 C weighs 12 amu On this scale 1 H = 1.008 amu 16 O = 16.00
87 16 70 20 58 24 44 32 35 40 29 48 (a) graph Y versus X (b) graph Y versus 1/X
 HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
Lecture 5, The Mole. What is a mole?
 Lecture 5, The Mole What is a mole? Moles Atomic mass unit and the mole amu definition: 12 C = 12 amu. The atomic mass unit is defined this way. 1 amu = 1.6605 x 10-24 g How many 12 C atoms weigh 12 g?
Lecture 5, The Mole What is a mole? Moles Atomic mass unit and the mole amu definition: 12 C = 12 amu. The atomic mass unit is defined this way. 1 amu = 1.6605 x 10-24 g How many 12 C atoms weigh 12 g?
Final. Mark Scheme CH1HP. Science A / Chemistry. (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit 1: Chemistry 1
 02.3 General Certificate of Secondary Education January 203 Science A / Chemistry CHHP (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit : Chemistry Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
02.3 General Certificate of Secondary Education January 203 Science A / Chemistry CHHP (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit : Chemistry Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to a benzene ring.
 Chapter : rganic Compounds with xygen Alcohols, Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a benzene ring.
Chapter : rganic Compounds with xygen Alcohols, Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a benzene ring.
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
 Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
Chapter Three: STOICHIOMETRY
 p70 Chapter Three: STOICHIOMETRY Contents p76 Stoichiometry - The study of quantities of materials consumed and produced in chemical reactions. p70 3-1 Counting by Weighing 3-2 Atomic Masses p78 Mass Mass
p70 Chapter Three: STOICHIOMETRY Contents p76 Stoichiometry - The study of quantities of materials consumed and produced in chemical reactions. p70 3-1 Counting by Weighing 3-2 Atomic Masses p78 Mass Mass
