Intensity and Damage Assessment of the 2007 Tocopilla Earthquake, Chile.
|
|
|
- Hubert Wilcox
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intensity and Damage Assessment of the 2007 Tocopilla Earthquake, Chile. Maximiliano Astroza I., a), Jorge Omerovic P. b), Rodrigo Astroza E. c), Juan Music T. b), Rodolfo Saragoni H. a), Ingrid Alvarez A. b), Alex Covarrubias A. b), Eduardo Morales P. b), Sergio Vladilo V. b), Orlando Rabello G. b). (a) University of Chile, Department of Civil Engineering. (b) Northern Catholic University, Department of Civil Engineering. (c) University of Los Andes, Faculty of Engineering.. This report presents the findings of the reconnaissance team from three Chilean universities that conducted site visits to approximately 20 towns in the earthquake zone shortly after the event. The focus was primarily on damage to dwellings and lifelines, geotechnical effects and the calculation of intensities. Introduction At 12:0 a.m. local time on November 1 th, 2007, a Ms 7. (M W 7.7) earthquake struck the northern coast of Chile, about 1 km north-east of the city of Mejillones (60 km from Antofagasta). Twenty six aftershocks with a magnitude greater than.0 were recorded during the first fifteen days after the earthquake. There were two fatalities and at least people injured. The damage zone extended from the Guatacondo gorge to the city of Antofagasta. The region is part of the Atacama desert and, since the middle of the nineteenth century, it has been inhabited mainly by workers in the nitrate mines. Today, only 8% of the regional population lives in the interior towns. In the last fifty years, there has been significant migration to the coastal cities of Tocopilla, Mejillones and Antofagasta. Much of the damage occurred in Tocopilla, a city of 2,000 inhabitants and the most populated city in the area affected by the earthquake. The buildings which sustained more damage were one story self-construction dwellings. Hospitals, schools, and other public buildings sustained moderate to severe damage. Some of these buildings had been previously damaged in the earthquake of December 1967 (Ms=7.3). Highways and urban roads suffered slight damage due to landslides and rock falls. Geology Located between latitudes 21º and 2º South in northern Chile, the damaged region has four main morphostructures with north-south orientation. These are the Cordillera de Los Andes, the Precordillera, the Central Valley and the Coastal Cordillera (see Figure 1). Most of the
2 towns surveyed during the visits are located on quaternary-aged alluvial and fluvial deposits on the Coast and the Central Valley. The Central Valley is a N-S trending elongated basin with a mean altitude of 1,300 m. Here the superficial deposits are fluvial silty sands with gravel and alluvial deposits of fine soils interbedded with thin coarse-grained soil layers. Figure 1 - Geological map (Modified from SERNAGEOMIN, 2003) Tectonics/Strong Ground Motion The Tocopilla earthquake was the result of the subduction of the Nazca plate under the South American continental plate. This plate interaction generates significant seismic activity along the coasts of Peru and Chile. The earthquake was an interplate event and occurred to the north of the 199 Antofagasta earthquake rupture area. The region is a highly active subduction zone where many large subduction interplate earthquakes have occurred during the last century (Comte and Pardo, 1991). The earthquake had a moment magnitude (Mw) of 7.7 (NEIC), and the hypocenter was located at S and W, at a depth of 39 km (Barrientos, 2007). Fault rupture propagated to the south from the hypocenter between Tocopilla and Mejillones and is approximately 100 km in length. The locations of the aftershock hypocenters match this fault plane (Barrientos, 2007). The cities most affected lie within the ground surface projection of the fault plane.
3 The earthquake was recorded at several strong motion stations in a variety of geologic site conditions. The station s hypocentral distance D H and horizontal and vertical recorded peak ground accelerations (PGA) are shown in Table 1. The ratio of vertical (VPGA) to horizontal PGA (HPGA) ranges from approximately 0.2 (Copiapó) to 1.0 (Tocopilla-Gobernacion), making the seismic code (INN, 1996) ratio (VPGA=2/3 HPGA) inaccurate in this case. It was observed that the degree of seismic wave amplifications was affected by the site soil condition (i.e., rock at Tocopilla-SQM and stiff soil at Tocopilla Gobernación). Table 1 Peak ground accelerations of the Tocopilla Earthquake, November 2007 (Boroschek et al. 2008). Station D H [km] HPGA [g] VPGA [g] Calama Mejillones Punta Patache Pica Antofagasta Iquique - Hospital Iquique - Esc. Pub. Chipana Tocopilla - SQM Tocopilla - Gobernación Tocopilla - Consultorio San Pedro de Atacama Baquedano Alto Hospicio Calama Copiapó The acceleration records from the stations closest to the epicenter (Tocopilla and Mejillones) are shown in Figure 2. Two phases of strong motion are apparent, corresponding to slip along two asperities in the finite fault solution (Zeng et al., 2007; Salden, 2007). Notwithstanding the large peak acceleration, damage to the buildings where the ground motion record was registered was minimal in Mejillones and Tocopilla-SQM and moderate in Tocopilla Gobernación. Figure 3 shows the post earthquake condition of the buildings. Figures a, b and c show the spectral acceleration responses of these records, for a damping ratio of %, indicating that rigid structures were likely to be the most damaged by this earthquake. All the strong motion records have long duration, about 1 seconds, with a strong motion phase of 20 sec (Boroschek et al., 2007).
4 a) Mejillones Station
5 b) Tocopilla-Gobernación Station c) Tocopilla-SQM Station Figure 2 - Acceleration time history at Tocopilla and Mejillones stations (Boroschek et al. 2008).
6 Accelerograph location in the Mejillones Health Center. View of undamaged health center in Mejillones where the accelerograph is located. View of the Gobernacion buildings in Tocopilla where the accelerograp is located Moderate damage in short columns of the Gobernacion building. View of some buildings near the accelerograph location on rock in Tocopilla. View of undamaged thermoelectrical plant near the station located on rock in Tocopilla. Figure 3 Condition of buildings where ground motion records were obtained.
7 Figure a Spectral acceleration response, % damping. Mejillones Station. Figure b Spectral acceleration response, % damping. Tocopilla-Gobernacion Station.
8 Figure c Spectral acceleration response, % damping. Tocopilla-SQM Station (Boroschek et al., 2007). In order to verify the kindness of the attenuation relationship proposed for Chilean interplate subduction earthquakes (Ruiz and Saragoni, 200), in the Figure can observed that the November 2007 Tocopilla peak ground accelerations are reasonably well represented by the Ruiz-Saragoni attenuation relationship for stiff soil and Ms = 7.. Figura Comparison of recorded peak ground aceleration data and the attenuation relationship proposed for stiff soil for Chilean interplate subduction earthquakes (Ruiz and Saragoni, 200)
9 Geotechnical Aspects Serious geotechnical hazards were not found although some landslides and pavement cracking were observed (see Figures 6 and 7). The landslides occured in road cuttings and natural slopes and caused the closure of Highway 1 between Tocopilla and Iquique (see Figure 8). No sand boils or other signs of soil liquefaction were observed near the coast. Figure 6 Landslide and pavement cracking on Highway 1. Figure 7 Landslide at Hornitos beach
10 Figure 8 Landslide at La Paragua, Highway 1 between Tocopilla and Iquique (20 km from Tocopilla). The hillside residential area of Tocopilla, located on the eastern side of the city, experienced some slope failures during the earthquake. Construction and retaining wall in the area have been carried out by homeowners cutting into the hillside and using the resulting material as fill. In some places the retaining wall had failed with the soil mass sliding downwards a short distance. Significant damage to structures due to slope and retaining wall deformations was observed along the hillside. Figure 9 shows some of these failures. Figure 9 - Damage to the hillside residential area of Tocopilla. Types of Construction and Damage Most of the dwellings in the area are one story buildings. The dwellings over years old are made of adobe and wooden frame with adobe or low quality concrete infill. Newer constructions are of reinforced or confined masonry (see Figure 10).
11 a). House made of adobe in Sierra Gorda b) Wooden frame with adobe infill in Quillagua. c) Wooden frame with low quality concrete infill in Maria Elena. d) Confined masonry house in Mejillones Figure 10. Types of construction:(a) Adobe, (b, c) Infilled wooden frame, and (d) Structural masonry. Adobe: Adobe units are made with low plasticity fine silts. Although no reinforcement is included, few buildings made of adobe collapsed in the epicentral zone. This type of construction is more common in central Chile. Wood frame with adobe infill: In this type of construction void spaces between wooden frames are filled with vertically aligned adobe units covered with mud plaster. Moderate damage to stucco or fallen adobe units was observed. Most of this construction is found in towns near Highway. Wood frame with low quality concrete infill: In this case, wooden frames are filled with low quality concrete reinforced with a wire mesh, see Figure 11. Generally, the quality of the connections is good and the seismic perfomance is satisfactory. Fine vertical and diagonal cracks in the contact between the frame and the concrete were observed. This type of construction is found in Mejillones and Tocopilla, as well as the nitrate towns of Maria Elena and Pedro Valdivia.
12 Wire mesh reinforcement Connection between wooden elements Figure 11 Details of a house made with wooden frames with low quality concrete infill. The seismic performance of this type of self-construction dwellings is poor because the resisting elements (vertical and horizontal) are not assembled adequately. Masonry: When properly designed and built, masonry walls of concrete block resisted the earthquake with little or no damage. However, the observed behavior was less satisfactory when the quality of the construction procedure and materials was poor, or the reinforcement detailing inadequate. (a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 12. Observed damage: (a) Adobe house in Maria Elena, (b) Wooden frame with adobe infill in Baquedano, (c) Self-construction wooden frame with low quality concrete infill in Tocopilla and (d) Masonry in Maria Elena.
13 Lifelines Water In general, lifelines sustained relatively little damage with the exception of the water system in Tocopilla. The water for the city comes from the Topater Plant in Calama, through a 133 km long steel pipeline. The pipeline is divided into three sections separated by storage tanks, terminating in a tank located in the north of the city. Damage occurred in the connections and the longitudinal welds in the steel surface pipeline and in the pipe that connects the Esmeralda regulation storage tank with the valve chamber. The steel surface pipeline was also damaged by landslides. Additionally, connections in the asbestos-cement (AC) pipeline which crosses the town were damaged interrupting the water supply for two days. The Baquedano water treatment plant suffered minor damage to the filter tank anchor bolts (see Figure 13). There was no interruption of the water supply for this town. Sewerage Figure 13 - Damage to filter tank at Baquedano The sewerage system of Mejillones suffered minor damage to the main sewer, the treatment plant and the surge chamber of the submarine outfall sewer. The damage was concentrated near the coast and it was caused by settlement in the saturated sand filling (see Figure 1).
14 Treatment plant and surge chamber of outfall sewer. Settlements of main sewer sections. Figure 1 - Damage to sewerage system in Mejillones. The sewerage system of Tocopilla was undamaged, but sewage could not flow into it after the earthquake because the entrance had been blocked by debris. Seismic Intensities Intensity values are determined by visual inspection based on the distribution of damage in different types of structures, classified according to vulnerability (see Table 2). To determine the intensities, the European Scale of Intensities (MSK) was used. This scale is based on the damage distribution for each vulnerability class and was adapted to the Chilean dwellings by Monge and Astroza (1989) as shown in Table 3. Vulnerability Class A B C Table 2. Vulnerability class Type of Structure Adobe and Self-construction. Unreinforced masonry. Braced wooden frame infills with adobe or low quality concrete ( Palo Ahogado ). Reinforced and confined concrete block masonry. Table 3. Intensity degree based on damage distribution according to MSK (Monge and Astroza 1989). Intensity Class A Class B Class C Value % Damage Grade % Damage Grade % Damage Grade
15 Damage grades for different types of building are given in Tables and. Both table are the product of the study carried out by Monge and Astroza in 1989 to determine intensity values based on the performance of dwellings made of adobe and diagonally braced wooden frames with adobe infills. These structures were the most damaged during the Tocopilla earthquake. Table. Description of damage to adobe or masonry buildings Damage Description Grade 0 No damage. 1 Fine cracks in stucco. 2 Fine cracks in walls. Horizontal cracks in chimneys, tanks, pediments, cornices. Vertical cracks at intersection of walls. 3 Large and deep cracks in walls. Inclination or falling of chimneys, pediments, cornices. Vertical cracks in walls at intersections and some lean out-of-plumb. Diagonal cracks on walls are larger than 3 mm. Partial collapse or total failure of a wall. Total collapse. Table. Description of damage for buildings with infill braced wooden frame Damage Description Grade 0 No damage. 1 Fine vertical and diagonal cracks on plaster. Vertical and diagonal cracks in the contact between braced wooden frame elements and infill. 2 Plaster falling. 3 Infill falling. Partial or total collapse of a braced wooden frame.
16 Figure 1 and Table 6 summarize the estimated intensities for the towns visited and the resulting isoseismal map when the soil local condition corresponds to stiff soil, soil type II according the Chilean Seismic Code classification (INN, 1996). Much of the damage was concentrated between Quillagua and Antofagasta in the north-south direction, and as far as Sierra Gorda to the east. The earthquake severely affected the city of Tocopilla and to a lesser extent the city of Mejillones. Maximum intensities of VII (MSK), in the north-south direction, were observed along the coast immediately above the activated fault segment. The same distribution pattern is observed for lower intensity values. Table 6. Estimated intensities, I MSK Place Intensity Place Intensity Quillagua 6. Sierra Gorda.0 Oficina Buena 6.0 Baquedano 6.0 Esperanza Tocopilla 7.0 Antofagasta 6.0 María Elena 7.0 Iquique.0 Pedro de Valdivia 6.0 Alto Hospicio.0 Gatico (1) 6. Calama.0 Cobija (1) 6. Taltal.0 Hornitos 6. Valparaíso 2.0 Mejillones 6. Viña del mar 2.0 Chacabuco 6.0 Santiago 2.0 (1) On rock.
17 Figure 1 Isoseismal map of the Tocopilla Earthquake, November 1 th, 2007 when the soil local condition corresponds to soil type II according the Chilean Seismic Code classification (INN, 1996). The variation in the intensity value (up ± 0. degree) in some sectors of Mejillones and Tocopilla can be explained by local soil conditions. The intensity value increases on recent
18 alluvial deposits or uncontrolled fills confined by retaining walls, as shown by the effects on dwellings built on hillsides discussed earlier. On the other hand the intensity decreases on rock, as can be seen from the intensities in Cobija, Gatico and the south zone of Tocopilla (see Table 6). To evaluate the impact of this moderate thrust earthquake on regional seismic hazard, the intensity values of the Tocopilla Earthquake, December 20 th, 1967 (Ms=7.3), values obtained from the Chilean Seismological Service, and Tocopilla Earthquake, November 1 th, 2007 (Ms=7.), values give in Table 6, are compared in Figure 16 with the intensity attenuation relationship for Chilean earthquakes (Barrientos, 1980). Figure 16 shows that the estimated intensities of the Tocopilla 1967 and 2007 earthquakes are similar and that Barrientos equation predicts intensity values greater than those estimated. Figura 16 Comparison of 2007 and 1967 Tocopilla Earthquake intensity data with intensity attenuation relationship proposed by Barrientos (Ms=7.). Comments The November 1 th, 2007 Mw=7.7 event was a moderate interplate earthquake and its fault slip was localized at a depth between 30 and 0 km. Most of the early aftershocks were located towards the southern end of the rupture zone.
19 Self-construction dwellings must be avoided in regions where this type of earthquake occurs since the assembly of the resisting elements (vertical an horizontal) is generally inadequate and they suffer sever damage, increasing the risk of injury. Well constructed confined concrete block masonry for low-cost dwellings is an efficient construction system to reduce earthquake damage. Damage increases dramatically when dwellings are located on recent alluvial deposits and uncontrolled fills in hillside residential areas. Acknowledgments The site visits were financed by the MAR-VASTO BID/IADB Project, the Faculty of Engineering of the University of Los Andes, the Office of Research and Graduate Studies and the Faculty of Construction and Architecture of Northern Catholic University. The authors thank the collaboration of CODELCO-División Chuquicamata and the Maria Elena and Sierra Gorda Municipalities, and professors Esther Norton P. Patricio Tapia G. and Ricardo Herrera M. for their comments. References Barrientos S., (2007), Informe del sismo del 1 de Noviembre del 2007, Servicio Sismológico, Departamento de Geofísica, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile. Barrientos S., (1980), Regionalización sísmica de Chile MSc. Thesis, Geophysics Dept., University of Chile, Santiago, Chile. Boroschek R., D. Comte, P.Soto, R. León, (2007). Terremoto Norte Chile, 1 Noviembre de 2007 M=7.7, Informe Preliminar N, Departamento de Ingeniería Civil y Departamento de Geofísica, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas y Matemáticas, Universidad de Chile, Noviembre, Santiago, Chile. Boroschek, R., Comte, D., Soto, P., León, R., (2008). Eventos Registrados Año Informe RENADIC 08/0, Departamento de Ingeniería Civil y Departamento de Geofísica, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas y Matemáticas, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile. Comte D. y M. Pardo, (1991), Reappraisal of great historical earthquakes in the Northern Chile and Southern Peru seismic gaps, Natural Hazards : 23-. INN, (1996), Norma NCh33.Of96 Diseño Sísmico de Edificios, Instituto Nacional de Normalización, Santiago, Chile. Monge, J. and Astroza, M., (1989), Metodología para determinar el grado de intensidad a partir de los daños, V Jornadas Chilenas de Sismología e Ingeniería Antisísmica, Vol. 1, Santiago, Chile, August, 7-11, pp NEIC, (2008), U.S.Geological Survey Earthquake Database, National Earthquake Information Center, USA.
20 Ruiz, S. y Saragoni, R. (200). Fórmulas de atenuación para la subducción de Chile considerando los dos mecanismos de sismogénesis y los efectos del suelo. IX Jornadas Chilenas de Sismología e Ingeniería Antisísmica, Concepción, Chile. Paper Nº A SERNAGEOMIN, (2003), Mapa Geológico de Chile, Versión Digital-Base Geológica 1: , Gobierno de Chile, Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería, Publicación Geológica Digital N, Santiago, Chile. Salden, A. (2007). Preliminary result 11/1/2007 (mw 7.7), Tocopilla earthquake, Chile. Report by Tectonics Observatory California Institute of Technology ( Zeng, Y.; Hayes, G., Ji, C. (2007). Finite Fault Model, in Preliminary Earthquake Report, United States Geological Survey (earthquake.usgs.gov).
KCC Event Brief: 2014 La Habra Earthquake
 KAREN CLARK & COMPANY KCC Event Brief: 2014 La Habra Earthquake June 2014 2 COPLEY PLACE BOSTON, MA 02116 T: 617.423.2800 F: 617.423.2808 Overview On Friday, March 28, 2014 at 9:09pm, a magnitude 5.1 earthquake
KAREN CLARK & COMPANY KCC Event Brief: 2014 La Habra Earthquake June 2014 2 COPLEY PLACE BOSTON, MA 02116 T: 617.423.2800 F: 617.423.2808 Overview On Friday, March 28, 2014 at 9:09pm, a magnitude 5.1 earthquake
Chincha and Cañete, Peru, Based
 Reconstruction of Ica, Pisco, Chincha and Cañete, Peru, Based on Updated Hazard Maps Julio Kuroiwa Professor emeritus National University of Engineering and UNDP Reconstruction Program/Sustainable Cities.
Reconstruction of Ica, Pisco, Chincha and Cañete, Peru, Based on Updated Hazard Maps Julio Kuroiwa Professor emeritus National University of Engineering and UNDP Reconstruction Program/Sustainable Cities.
REPAIR AND SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF HOSPITAL AND SCHOOL BUILDINGS IN PERU
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2000 REPAIR AND SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF HOSPITAL AND SCHOOL BUILDINGS IN PERU Alejandro MUÑOZ 1, Daniel
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2000 REPAIR AND SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF HOSPITAL AND SCHOOL BUILDINGS IN PERU Alejandro MUÑOZ 1, Daniel
Expected Performance Rating System
 Expected Performance Rating System In researching seismic rating systems to determine how to best classify the facilities within the Portland Public School system, we searched out what was used by other
Expected Performance Rating System In researching seismic rating systems to determine how to best classify the facilities within the Portland Public School system, we searched out what was used by other
A Preliminary Report The May 19, 2011 Simav, Turkey Earthquake
 A Preliminary Report The May 19, 2011 Simav, Turkey Earthquake Ömer AYDAN Tokai University, Shizuoka, Japan Visiting Professor, İstanbul Technical University Halil KUMSAR Pamukkale University May 24, 2011
A Preliminary Report The May 19, 2011 Simav, Turkey Earthquake Ömer AYDAN Tokai University, Shizuoka, Japan Visiting Professor, İstanbul Technical University Halil KUMSAR Pamukkale University May 24, 2011
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
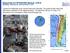 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
Using Remotely Sensed Data From ASTER to Look Impact of Recent Earth Quakes in Gujarat, India.
 Using Remotely Sensed Data From ASTER to Look Impact of Recent Earth Quakes in Gujarat, India. A major earth quake occurred in Gujarat, India on January 26,2000. (Origin time 03:16 GMT, Location 23.399N
Using Remotely Sensed Data From ASTER to Look Impact of Recent Earth Quakes in Gujarat, India. A major earth quake occurred in Gujarat, India on January 26,2000. (Origin time 03:16 GMT, Location 23.399N
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE
 EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
Development of Guidance Information for the Repair and Rebuilding of Houses Following the Canterbury Earthquake Series
 Development of Guidance Information for the Repair and Rebuilding of Houses Following the Canterbury Earthquake Series Graeme J Beattie (1) 1. Principal Structural Engineer, BRANZ Ltd, Private Bag 50908,
Development of Guidance Information for the Repair and Rebuilding of Houses Following the Canterbury Earthquake Series Graeme J Beattie (1) 1. Principal Structural Engineer, BRANZ Ltd, Private Bag 50908,
Recent Earthquakes: Implications for U.S. Water Utilities [Project #4408]
![Recent Earthquakes: Implications for U.S. Water Utilities [Project #4408] Recent Earthquakes: Implications for U.S. Water Utilities [Project #4408]](/thumbs/25/5582528.jpg) Recent Earthquakes: Implications for U.S. Water Utilities [Project #4408] ORDER NUMBER: 4408 DATE AVAILABLE: July 2012 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS: John Eidinger and Craig A. Davis PROJECT PURPOSE: The purpose
Recent Earthquakes: Implications for U.S. Water Utilities [Project #4408] ORDER NUMBER: 4408 DATE AVAILABLE: July 2012 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS: John Eidinger and Craig A. Davis PROJECT PURPOSE: The purpose
RESEARCH ON GEOTECHNICAL EARTHQUAKE IN THE HUMAN SETTLEMENT OF LIMA-PERU RICARDO PALMA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
 RICARDO PALMA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING CIVIL ENGINEERING RESEARCH INSTITITUTE RESEARCH ON GEOTECHNICAL EARTHQUAKE IN THE HUMAN SETTLEMENT OF LIMA-PERU RESEARCH ON GEOTECHNICAL EARTHQUAKE IN THE
RICARDO PALMA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING CIVIL ENGINEERING RESEARCH INSTITITUTE RESEARCH ON GEOTECHNICAL EARTHQUAKE IN THE HUMAN SETTLEMENT OF LIMA-PERU RESEARCH ON GEOTECHNICAL EARTHQUAKE IN THE
GEOTECHNICAL ISSUES OF LANDSLIDES CHARACTERISTICS MECHANISMS PREPARDNESS: BEFORE, DURING AND AFTER A LANDSLIDE QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSIONS
 GEOTECHNICAL ISSUES OF LANDSLIDES CHARACTERISTICS MECHANISMS PREPARDNESS: BEFORE, DURING AND AFTER A LANDSLIDE QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSIONS Huge landslide Leyte, Phillipines, 1998 2000 casulties Small debris
GEOTECHNICAL ISSUES OF LANDSLIDES CHARACTERISTICS MECHANISMS PREPARDNESS: BEFORE, DURING AND AFTER A LANDSLIDE QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSIONS Huge landslide Leyte, Phillipines, 1998 2000 casulties Small debris
Important Points: Timing: Timing Evaluation Methodology Example Immediate First announcement of building damage
 3.3. Evaluation of Building Foundation Damage Basic Terminology: Damage: Destruction, deformation, inclination and settlement of a building foundation caused by an earthquake. Damage grade: Degree of danger
3.3. Evaluation of Building Foundation Damage Basic Terminology: Damage: Destruction, deformation, inclination and settlement of a building foundation caused by an earthquake. Damage grade: Degree of danger
4 EFFECTS OF SURFACE FAULT RUPTURE ON INFRASTRUCTURE
 4 EFFECTS OF SURFACE FAULT RUPTURE ON INFRASTRUCTURE 4.1 Introduction The preliminary reconnaissance efforts performed by GEER on August 24, 2014 (the day of the M6 South Napa earthquake) noted significant
4 EFFECTS OF SURFACE FAULT RUPTURE ON INFRASTRUCTURE 4.1 Introduction The preliminary reconnaissance efforts performed by GEER on August 24, 2014 (the day of the M6 South Napa earthquake) noted significant
Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction. 2nd Edition
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2171210/ Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction. 2nd Edition Description: Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction,
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2171210/ Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction. 2nd Edition Description: Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction,
ASSESSMENT AND RETROFITTING OF EXISTING RC BUILDINGS IN VIETNAM IN TERMS OF EARTHQUAKE RESISTANCES
 GEM-SEA Workshop on Seismic Vulnerability of Buildings Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 1 st July 2013 ASSESSMENT AND RETROFITTING OF EXISTING RC BUILDINGS IN VIETNAM IN TERMS OF EARTHQUAKE
GEM-SEA Workshop on Seismic Vulnerability of Buildings Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 1 st July 2013 ASSESSMENT AND RETROFITTING OF EXISTING RC BUILDINGS IN VIETNAM IN TERMS OF EARTHQUAKE
Page & Turnbull imagining change in historic environments through design, research, and technology
 DCI+SDE STRUCTURAL EVALUATIONS OFFICE BUILDING, TOOL SHED & WATER TANK, AND BLACKSMITH & MACHINE SHOP BUILDINGS SAN FRANCISCO, CALIFORNIA [14290] PRIMARY PROJECT CONTACT: H. Ruth Todd, FAIA, AICP, LEED
DCI+SDE STRUCTURAL EVALUATIONS OFFICE BUILDING, TOOL SHED & WATER TANK, AND BLACKSMITH & MACHINE SHOP BUILDINGS SAN FRANCISCO, CALIFORNIA [14290] PRIMARY PROJECT CONTACT: H. Ruth Todd, FAIA, AICP, LEED
6 RETROFITTING POST & PIER HOUSES
 Retrofitting Post & Pier Houses 71 6 RETROFITTING POST & PIER HOUSES by James E. Russell, P.E. 72 Retrofitting Post & Pier Houses Retrofitting Post & Pier Houses 73 RETROFITTING POST AND PIER HOUSES This
Retrofitting Post & Pier Houses 71 6 RETROFITTING POST & PIER HOUSES by James E. Russell, P.E. 72 Retrofitting Post & Pier Houses Retrofitting Post & Pier Houses 73 RETROFITTING POST AND PIER HOUSES This
SEISMIC DAMAGE ESTIMATION PROCEDURE FOR WATER SUPPLY PIPELINES
 SEISMIC DAMAGE ESTIMATION PROCEDURE FOR WATER SUPPLY PIPELINES Ryoji ISOYAMA 1, Eisuke ISHIDA 2, Kiyoji YUNE 3 And Toru SHIROZU 4 SUMMARY This paper presents a practical procedure for estimating damage
SEISMIC DAMAGE ESTIMATION PROCEDURE FOR WATER SUPPLY PIPELINES Ryoji ISOYAMA 1, Eisuke ISHIDA 2, Kiyoji YUNE 3 And Toru SHIROZU 4 SUMMARY This paper presents a practical procedure for estimating damage
POST-EVENT DATA COLLECTION USING MOBILE GIS/GPS AND DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC EVALUATION TECHNIQUE FOR DAMAGE
 POST-EVENT DATA COLLECTION USING MOBILE GIS/GPS AND DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC EVALUATION TECHNIQUE FOR DAMAGE Satoshi IWAI 1 And Hiroyuki KAMEDA 2 SUMMARY This paper presents mobile system for post-event
POST-EVENT DATA COLLECTION USING MOBILE GIS/GPS AND DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC EVALUATION TECHNIQUE FOR DAMAGE Satoshi IWAI 1 And Hiroyuki KAMEDA 2 SUMMARY This paper presents mobile system for post-event
Prepared For San Francisco Community College District 33 Gough Street San Francisco, California 94103. Prepared By
 Project Structural Conditions Survey and Seismic Vulnerability Assessment For SFCC Civic Center Campus 750 Eddy Street San Francisco, California 94109 Prepared For San Francisco Community College District
Project Structural Conditions Survey and Seismic Vulnerability Assessment For SFCC Civic Center Campus 750 Eddy Street San Francisco, California 94109 Prepared For San Francisco Community College District
REPAIR AND RETROFIT OF BRIDGES DAMAGED BY THE 2010 CHILE MAULE EARTHQUAKE
 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan REPAIR AND RETROFIT OF BRIDGES DAMAGED BY THE 2010 CHILE
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 2012, Tokyo, Japan REPAIR AND RETROFIT OF BRIDGES DAMAGED BY THE 2010 CHILE
Foundations 65 5 FOUNDATIONS. by Richard Chylinski, FAIA and Timothy P. McCormick, P.E. Seismic Retrofit Training
 Foundations 65 5 FOUNDATIONS by Richard Chylinski, FAIA and Timothy P. McCormick, P.E. 66 Foundations Foundations 67 FOUNDATIONS Let's assume that the retrofit has been done correctly from the roofline
Foundations 65 5 FOUNDATIONS by Richard Chylinski, FAIA and Timothy P. McCormick, P.E. 66 Foundations Foundations 67 FOUNDATIONS Let's assume that the retrofit has been done correctly from the roofline
Earthquakes. Earthquakes: Big Ideas. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
ENGINEERING-BASED EARTHQUAKE RISK MANAGEMENT
 ENGINEERING-BASED EARTHQUAKE RISK MANAGEMENT MRP Engineering Newsletter February 2012 The world recently experienced several major earthquakes, which caused severe local impacts and major worldwide repercussions.
ENGINEERING-BASED EARTHQUAKE RISK MANAGEMENT MRP Engineering Newsletter February 2012 The world recently experienced several major earthquakes, which caused severe local impacts and major worldwide repercussions.
RAILROAD DAMAGE FROM THE OCTOBER 16, 1999 HECTOR MINE EARTHQUAKE
 RAILROAD DAMAGE FROM THE OCTOBER 16, 1999 HECTOR MINE EARTHQUAKE By: William G. Byers, P.E. Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway 4515 Kansas Avenue Kansas City, Kansas 66106 Phone (913) 551-4070 Fax
RAILROAD DAMAGE FROM THE OCTOBER 16, 1999 HECTOR MINE EARTHQUAKE By: William G. Byers, P.E. Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway 4515 Kansas Avenue Kansas City, Kansas 66106 Phone (913) 551-4070 Fax
Chapter. Earthquake Damage: Types, Process, Categories
 3 Chapter Earthquake Damage: Types, Process, Categories Earthquakes leave behind a trail of damage and destruction. People s lives are affected by the loss of loved ones, destruction of property, economic
3 Chapter Earthquake Damage: Types, Process, Categories Earthquakes leave behind a trail of damage and destruction. People s lives are affected by the loss of loved ones, destruction of property, economic
The earthquake source
 Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
SECTION 7 Engineered Buildings Field Investigation
 SECTION 7 Engineered Buildings Field Investigation Types of Data to Be Collected and Recorded A field investigator looking at engineered buildings is expected to assess the type of damage to buildings.
SECTION 7 Engineered Buildings Field Investigation Types of Data to Be Collected and Recorded A field investigator looking at engineered buildings is expected to assess the type of damage to buildings.
PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel
 PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel Avigdor Rutenberg and Robert Levy Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel Avi Shapira International
PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel Avigdor Rutenberg and Robert Levy Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel Avi Shapira International
Chapter 3 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION FEATURES IMPORTANT TO SEISMIC PERFORMANCE
 Chapter 3 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION FEATURES IMPORTANT TO SEISMIC PERFORMANCE To satisfy the performance goals of the NEHRP Recommended Seismic Provisions, a number of characteristics are important to the
Chapter 3 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION FEATURES IMPORTANT TO SEISMIC PERFORMANCE To satisfy the performance goals of the NEHRP Recommended Seismic Provisions, a number of characteristics are important to the
STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT REPORT BOLINAS MARINE STATION - BOLINAS, CALIFORNIA
 STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT REPORT BOLINAS MARINE STATION - BOLINAS, CALIFORNIA College of Marin c/o Swinerton Management & Consulting P.O. Box 144003 835 College Avenue, Building MS-3 Kentfield, California
STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT REPORT BOLINAS MARINE STATION - BOLINAS, CALIFORNIA College of Marin c/o Swinerton Management & Consulting P.O. Box 144003 835 College Avenue, Building MS-3 Kentfield, California
Settlement of Precast Culverts Under High Fills; The Influence of Construction Sequence and Structural Effects of Longitudinal Strains
 Settlement of Precast Culverts Under High Fills; The Influence of Construction Sequence and Structural Effects of Longitudinal Strains Doug Jenkins 1, Chris Lawson 2 1 Interactive Design Services, 2 Reinforced
Settlement of Precast Culverts Under High Fills; The Influence of Construction Sequence and Structural Effects of Longitudinal Strains Doug Jenkins 1, Chris Lawson 2 1 Interactive Design Services, 2 Reinforced
Miss S. S. Nibhorkar 1 1 M. E (Structure) Scholar,
 Volume, Special Issue, ICSTSD Behaviour of Steel Bracing as a Global Retrofitting Technique Miss S. S. Nibhorkar M. E (Structure) Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering
Volume, Special Issue, ICSTSD Behaviour of Steel Bracing as a Global Retrofitting Technique Miss S. S. Nibhorkar M. E (Structure) Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering
Earthquake Hazards and Risks
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Using GIS for Assessing Earthquake Hazards of San Francisco Bay, California, USA
 Using GIS for Assessing Earthquake Hazards of San Francisco Bay, California, USA Marzieh Zeinali Department of Resource Analysis, Saint Mary s University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55404 Keywords: San
Using GIS for Assessing Earthquake Hazards of San Francisco Bay, California, USA Marzieh Zeinali Department of Resource Analysis, Saint Mary s University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55404 Keywords: San
Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF STRUCTURES
 SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF STRUCTURES RANJITH DISSANAYAKE DEPT. OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF PERADENIYA, SRI LANKA ABSTRACT Many existing reinforced concrete structures in present
SEISMIC RETROFITTING OF STRUCTURES RANJITH DISSANAYAKE DEPT. OF CIVIL ENGINEERING, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING, UNIVERSITY OF PERADENIYA, SRI LANKA ABSTRACT Many existing reinforced concrete structures in present
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES
 DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
Seismic Risk Prioritization of RC Public Buildings
 Seismic Risk Prioritization of RC Public Buildings In Turkey H. Sucuoğlu & A. Yakut Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey J. Kubin & A. Özmen Prota Inc, Ankara, Turkey SUMMARY Over the past
Seismic Risk Prioritization of RC Public Buildings In Turkey H. Sucuoğlu & A. Yakut Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey J. Kubin & A. Özmen Prota Inc, Ankara, Turkey SUMMARY Over the past
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
 Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Post Earthquake Quick Damage Inspection of Buildings in Nepal
 Post Earthquake Quick Damage Inspection of Buildings in Nepal Collaborative Research and Development (R&D) Project for Disaster Mitigation in Earthquake Prone Areas in Asia (Sep 27, 2007) Presented By
Post Earthquake Quick Damage Inspection of Buildings in Nepal Collaborative Research and Development (R&D) Project for Disaster Mitigation in Earthquake Prone Areas in Asia (Sep 27, 2007) Presented By
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q.
 Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
DAMAGE TO WOOD BUILDINGS DURING THE GREAT TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE PART2- DAMAGE DUE TO GROUND MOTION
 DAMAGE TO WOOD BUILDINGS DURING THE GREAT TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE PART2- DAMAGE DUE TO GROUND MOTION Naohito Kawai 1, Hiroshi Isoda 2, Takahiro Tsuchimoto 3, Mikio Koshihara 4 ABSTRACT: The damage to wood buildings
DAMAGE TO WOOD BUILDINGS DURING THE GREAT TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE PART2- DAMAGE DUE TO GROUND MOTION Naohito Kawai 1, Hiroshi Isoda 2, Takahiro Tsuchimoto 3, Mikio Koshihara 4 ABSTRACT: The damage to wood buildings
4.6 GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS
 4.6 GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS This Section describes the current conditions relating to the geologic and seismic characteristics of the City of Cypress. This Section concludes with an analysis of geologic
4.6 GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS This Section describes the current conditions relating to the geologic and seismic characteristics of the City of Cypress. This Section concludes with an analysis of geologic
WILLOCHRA BASIN GROUNDWATER STATUS REPORT 2009-10
 WILLOCHRA BASIN GROUNDWATER STATUS REPORT 2009-10 SUMMARY 2009-10 The Willochra Basin is situated in the southern Flinders Ranges in the Mid-North of South Australia, approximately 50 km east of Port Augusta
WILLOCHRA BASIN GROUNDWATER STATUS REPORT 2009-10 SUMMARY 2009-10 The Willochra Basin is situated in the southern Flinders Ranges in the Mid-North of South Australia, approximately 50 km east of Port Augusta
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Five reasons buildings fail in an earthquake and how to avoid them
 Five reasons buildings fail in an earthquake and how to avoid them by Jeff White, AIA Published in Healthcare Design magazine There s a saying among seismologists: Earthquakes don t kill people. Buildings
Five reasons buildings fail in an earthquake and how to avoid them by Jeff White, AIA Published in Healthcare Design magazine There s a saying among seismologists: Earthquakes don t kill people. Buildings
Disaster Management Cycle
 GIS TOOL FOR CALCULATING REPAIR COST OF BUILDINGS DUE TO EARTHQUAKE EFFECTS (CCRE CISMID) Miguel Estrada Carlos Zavala Fernando Lazares Jorge Morales Japan Peru Center for Earthquake Engineering Research
GIS TOOL FOR CALCULATING REPAIR COST OF BUILDINGS DUE TO EARTHQUAKE EFFECTS (CCRE CISMID) Miguel Estrada Carlos Zavala Fernando Lazares Jorge Morales Japan Peru Center for Earthquake Engineering Research
CONTRASTING DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS OF DUCTILE STRUCTURES FROM TOHOKU SUBDUCTION TO CRUSTAL EARTHQUAKE RECORDS. Peter Dusicka 1 and Sarah Knoles 2
 CONTRASTING DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS OF DUCTILE STRUCTURES FROM TOHOKU SUBDUCTION TO CRUSTAL EARTHQUAKE RECORDS Abstract Peter Dusicka 1 and Sarah Knoles 2 With the impending Cascadia subduction zone event
CONTRASTING DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS OF DUCTILE STRUCTURES FROM TOHOKU SUBDUCTION TO CRUSTAL EARTHQUAKE RECORDS Abstract Peter Dusicka 1 and Sarah Knoles 2 With the impending Cascadia subduction zone event
Structural Failures Cost Lives and Time
 Structural Failures Cost Lives and Time Recent failures of storage bins, silos and other structures highlight the need to increase awareness of hazards associated with these structures. Since 2010, one
Structural Failures Cost Lives and Time Recent failures of storage bins, silos and other structures highlight the need to increase awareness of hazards associated with these structures. Since 2010, one
Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra
 Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: pb65@gmx.net
Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: pb65@gmx.net
 13º Encontro Sociedade Brasileira de Geofísica 2013 Rio de Janeiro, 26-29 29 August Earthquake Mitigation in the Lisbon and Lower Tagus Valley area, Portugal 1 J. Carvalho, R. Dias, C. Pinto, T. Cunha,
13º Encontro Sociedade Brasileira de Geofísica 2013 Rio de Janeiro, 26-29 29 August Earthquake Mitigation in the Lisbon and Lower Tagus Valley area, Portugal 1 J. Carvalho, R. Dias, C. Pinto, T. Cunha,
SEISMIC DESIGN OF HIGHWAY BRIDGES
 Journal of Japan Association for Earthquake Engineering, Vol.4, No.3 (Special Issue), 2004 SEISMIC DESIGN OF HIGHWAY BRIDGES Kazuhiko KAWASHIMA 1 and Shigeki UNJOH 2 1 Member of JAEE, Professor, Department
Journal of Japan Association for Earthquake Engineering, Vol.4, No.3 (Special Issue), 2004 SEISMIC DESIGN OF HIGHWAY BRIDGES Kazuhiko KAWASHIMA 1 and Shigeki UNJOH 2 1 Member of JAEE, Professor, Department
Date, Time and Place: Presented by: Presented to: 22 August 2013, 0900 hrs, Pier 1 The Embarcadero, San Francisco
 Date, Time and Place: 22 August 2013, 0900 hrs, Pier 1 The Embarcadero, San Francisco Presented by: Nick Rogers, Mike Jacka, Kate Williams, Sjoerd van Ballegooy and Rick Wentz, Tonkin & Taylor International
Date, Time and Place: 22 August 2013, 0900 hrs, Pier 1 The Embarcadero, San Francisco Presented by: Nick Rogers, Mike Jacka, Kate Williams, Sjoerd van Ballegooy and Rick Wentz, Tonkin & Taylor International
Predicting Seismic Vulnerable Zones using GIS. Outline of the presentation. Objectives. Risk Mapping Overview Factor Maps. Three levels of Zonation
 Predicting Seismic Vulnerable Zones using GIS by K.S.A. Dinesh Kumar Research Scholar, Anna University & Lecturer in Civil Engineering Dept. National Institute of Technical Teachers Training & Research
Predicting Seismic Vulnerable Zones using GIS by K.S.A. Dinesh Kumar Research Scholar, Anna University & Lecturer in Civil Engineering Dept. National Institute of Technical Teachers Training & Research
A Report on Post-Earthquake Rapid Visual Damage Assessment of Buildings Of Tribhuvan International Airport
 A Report on Post-Earthquake Rapid Visual Damage Assessment of Buildings Of Tribhuvan International Airport Prepared By: Civil Engineering Division Tribhuvan International Airport Civil Aviation Office
A Report on Post-Earthquake Rapid Visual Damage Assessment of Buildings Of Tribhuvan International Airport Prepared By: Civil Engineering Division Tribhuvan International Airport Civil Aviation Office
Sewers Float and other aspects of Sewer Performance in Earthquakes
 Sewers Float and other aspects of Sewer Performance in Earthquakes Presented by Donald Ballantyne, PE Niigata Japan, 1964 Overview Introduction Earthquake Hazards Historic Damage Seattle 1965 Loma Prieta
Sewers Float and other aspects of Sewer Performance in Earthquakes Presented by Donald Ballantyne, PE Niigata Japan, 1964 Overview Introduction Earthquake Hazards Historic Damage Seattle 1965 Loma Prieta
THE NEW BRAZILIAN STANDARD FOR SEISMIC DESIGN
 ABSTRACT : THE NEW BRAZILIAN STANDARD FOR SEISMIC DESIGN Sergio Hampshire C. Santos 1 and Silvio de Souza Lima 1 1 Professor, Polytechnic School, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
ABSTRACT : THE NEW BRAZILIAN STANDARD FOR SEISMIC DESIGN Sergio Hampshire C. Santos 1 and Silvio de Souza Lima 1 1 Professor, Polytechnic School, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Seismic Risk Assessment Procedures for a System consisting of Distributed Facilities -Part three- Insurance Portfolio Analysis
 Seismic Risk Assessment Procedures for a System consisting of Distributed Facilities -Part three- Insurance Portfolio Analysis M. Achiwa & M. Sato Yasuda Risk Engineering Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan M. Mizutani
Seismic Risk Assessment Procedures for a System consisting of Distributed Facilities -Part three- Insurance Portfolio Analysis M. Achiwa & M. Sato Yasuda Risk Engineering Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan M. Mizutani
Tunnelling & Underground. Specialists
 Tunnelling & Underground Specialists Mined Tunnels Excavation at Ayer Rajah Avenue, Singapore Introduction Amberg & TTI Engineering Pte Ltd (AETTI) was established in Singapore in 2002 by Amberg Engineering
Tunnelling & Underground Specialists Mined Tunnels Excavation at Ayer Rajah Avenue, Singapore Introduction Amberg & TTI Engineering Pte Ltd (AETTI) was established in Singapore in 2002 by Amberg Engineering
Personal Information. Professional Education
 Jose Antonio Flores Ruiz Structural Engineer Personal Information Telephone + (52) 1 322 108 41 12 e mail Place of birth Toluca, Mexico Date of birth October 6th 1978 Marital Status Married Nationality
Jose Antonio Flores Ruiz Structural Engineer Personal Information Telephone + (52) 1 322 108 41 12 e mail Place of birth Toluca, Mexico Date of birth October 6th 1978 Marital Status Married Nationality
BEHAVIOR OF WELDED T-STUBS SUBJECTED TO TENSILE LOADS
 BEHAVIOR OF WELDED T-STUBS SUBJECTED TO TENSILE LOADS R.A. Herrera 1, G. Desjouis 2, G. Gomez 2, M. Sarrazin 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Chile, Santiago, Chile 2
BEHAVIOR OF WELDED T-STUBS SUBJECTED TO TENSILE LOADS R.A. Herrera 1, G. Desjouis 2, G. Gomez 2, M. Sarrazin 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Chile, Santiago, Chile 2
Part 1 - How Much Danger is Your Home or Business In? Where do you live?
 Earthquake Insurance and San Diego County Residents Part 1 - How much danger is your home in? Where do you live? Part 2 - What do San Diego County residents have to know about Earthquake Insurance Policies,
Earthquake Insurance and San Diego County Residents Part 1 - How much danger is your home in? Where do you live? Part 2 - What do San Diego County residents have to know about Earthquake Insurance Policies,
Preliminary damage survey report on 2015 Nepal Gorkha Earthquake
 Tokyo, 13 May 2015 Preliminary damage survey report on 2015 Nepal Gorkha Earthquake Pokhrel R.M., Chiaro G., Kiyota T., Katagiri T. Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo, Japan Goda K. Bristol
Tokyo, 13 May 2015 Preliminary damage survey report on 2015 Nepal Gorkha Earthquake Pokhrel R.M., Chiaro G., Kiyota T., Katagiri T. Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo, Japan Goda K. Bristol
FOUNDATION TECHNICAL CATEGORY 3 (TC3) AUGUST 2012
 FOUNDATION TECHNICAL CATEGORY 3 (TC3) AUGUST 2012 Building and Housing has published technical guidance for foundation repairs and reconstruction for residential properties in green zone Foundation Technical
FOUNDATION TECHNICAL CATEGORY 3 (TC3) AUGUST 2012 Building and Housing has published technical guidance for foundation repairs and reconstruction for residential properties in green zone Foundation Technical
NONLINEAR BEHAVIOR AND FRAGILITY ASSESSMENT OF MULTI-STORY CONFINED MASONRY WALLS UNDER CYCLIC LOADS
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 216, pp. 113-127, Article ID: IJCIET_7_1_1 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=1
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 1, Jan-Feb 216, pp. 113-127, Article ID: IJCIET_7_1_1 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=1
THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY
 Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Nuevas tendencias de la Minería Subterránea profunda Planeación, operación y estabilización del macizo rocoso
 Nuevas tendencias de la Minería Subterránea profunda Planeación, operación y estabilización del macizo rocoso By Ernesto Villaescusa, PhD Chair in Rock Mechanics WA School of Mines, CRC Mining & Curtin
Nuevas tendencias de la Minería Subterránea profunda Planeación, operación y estabilización del macizo rocoso By Ernesto Villaescusa, PhD Chair in Rock Mechanics WA School of Mines, CRC Mining & Curtin
Strong earthquakes in seismic regions are inevitable! Build your house safely to avoid future disaster!
 Central Asia Earthquake Safety Initiative SEISMIC SAFETY FOR ADOBE HOMES: what everyone should know Seismic Damage to Adobe Homes Central Asia is known for periodic large earthquakes. Strong earthquakes
Central Asia Earthquake Safety Initiative SEISMIC SAFETY FOR ADOBE HOMES: what everyone should know Seismic Damage to Adobe Homes Central Asia is known for periodic large earthquakes. Strong earthquakes
SAP REPORT. Safety Assessment Program VOLUNTEER REPORT FROM THE FIELD. April 9-12, 2010 Calexico, California
 SAP REPORT Safety Assessment Program VOLUNTEER REPORT FROM THE FIELD April 9-12, 2010 Calexico, California by Robert Thiele, Architect, A.I.A. SAP Volunteer 63577 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY AIA San Diego Members
SAP REPORT Safety Assessment Program VOLUNTEER REPORT FROM THE FIELD April 9-12, 2010 Calexico, California by Robert Thiele, Architect, A.I.A. SAP Volunteer 63577 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY AIA San Diego Members
Critical Facility Round Table
 Critical Facility Round Table October 16, 2003 San Francisco Seismic Risk for Data Centers David Bonneville Senior Principal Degenkolb Engineers San Francisco, California Presentation Outline Seismic Risk
Critical Facility Round Table October 16, 2003 San Francisco Seismic Risk for Data Centers David Bonneville Senior Principal Degenkolb Engineers San Francisco, California Presentation Outline Seismic Risk
Current Status of Seismic Retrofitting Technology
 CONTENTS Current Status of Seismic Retrofitting Technology Damages of Past Earthquakes Seismic Diagnosis Method Building Control Section Urban Building Division Bureau of Urban Development, TMG Seismic
CONTENTS Current Status of Seismic Retrofitting Technology Damages of Past Earthquakes Seismic Diagnosis Method Building Control Section Urban Building Division Bureau of Urban Development, TMG Seismic
Methods for Seismic Retrofitting of Structures
 Methods for Seismic Retrofitting of Structures Retrofitting of existing structures with insufficient seismic resistance accounts for a major portion of the total cost of hazard mitigation. Thus, it is
Methods for Seismic Retrofitting of Structures Retrofitting of existing structures with insufficient seismic resistance accounts for a major portion of the total cost of hazard mitigation. Thus, it is
June 2007 CHAPTER 7 - CULVERTS 7.0 CHAPTER 7 - CULVERTS 7.1 GENERAL
 7.0 7.1 GENERAL For the purpose of this manual, culverts are defined as structures that are completely surrounded by soil and located below the surface of the roadway parallel to the general direction
7.0 7.1 GENERAL For the purpose of this manual, culverts are defined as structures that are completely surrounded by soil and located below the surface of the roadway parallel to the general direction
PCI Reconnaissance Team Report. Preview of PCI s Japan Earthquake Reconnaissance Team Report
 Photo: Joseph R. Maffei PCI Reconnaissance Team Report Preview of PCI s Japan Earthquake Reconnaissance Team Report Richard Sause, Robert Frosch, S. K. Ghosh, Jason Lien, Clay Naito, Larbi Sennour, and
Photo: Joseph R. Maffei PCI Reconnaissance Team Report Preview of PCI s Japan Earthquake Reconnaissance Team Report Richard Sause, Robert Frosch, S. K. Ghosh, Jason Lien, Clay Naito, Larbi Sennour, and
SMIP2000 Seminar Proceedings COSMOS VIRTUAL STRONG MOTION DATA CENTER. Ralph Archuleta
 COSMOS VIRTUAL STRONG MOTION DATA CENTER Ralph Archuleta Institute for Crustal Studies & Department of Geological Sciences University of California, Santa Barbara ABSTRACT The COSMOS virtual data center
COSMOS VIRTUAL STRONG MOTION DATA CENTER Ralph Archuleta Institute for Crustal Studies & Department of Geological Sciences University of California, Santa Barbara ABSTRACT The COSMOS virtual data center
Strengthening of Brick Masonry Walls against Earthquake Loading
 International Journal of Advanced Structures and Geotechnical Engineering ISSN 2319-5347, Vol. 01, No. 01, July 2012 Strengthening of Brick Masonry Walls against Earthquake ing KHAN SHAHZADA, MUHAMMAD
International Journal of Advanced Structures and Geotechnical Engineering ISSN 2319-5347, Vol. 01, No. 01, July 2012 Strengthening of Brick Masonry Walls against Earthquake ing KHAN SHAHZADA, MUHAMMAD
Jackson Gulch Outlet Canal Rehabilitation Project
 Jackson Gulch Outlet Canal Rehabilitation Project Preliminary Budgetary Estimate for Rehabilitation February 2004 Prepared for the Mancos Water Conservancy District Jackson Gulch Reservoir 42888 County
Jackson Gulch Outlet Canal Rehabilitation Project Preliminary Budgetary Estimate for Rehabilitation February 2004 Prepared for the Mancos Water Conservancy District Jackson Gulch Reservoir 42888 County
Development of Seismic-induced Fire Risk Assessment Method for a Building
 Development of Seismic-induced Fire Risk Assessment Method for a Building AI SEKIZAWA National Research Institute of Fire and Disaster 3-14-1, Nakahara, Mitaka, Tokyo 181-8633, Japan sekizawa@fri.go.jp
Development of Seismic-induced Fire Risk Assessment Method for a Building AI SEKIZAWA National Research Institute of Fire and Disaster 3-14-1, Nakahara, Mitaka, Tokyo 181-8633, Japan sekizawa@fri.go.jp
Overview. NRC Regulations for Seismic. Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station. NRC History. How we Regulate
 Overview 1. NRC History and Overview NRC Regulations for Seismic Analysis and Design Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station Christie Hale Megan Williams 2. Regulations for Seismic Hazards 3.
Overview 1. NRC History and Overview NRC Regulations for Seismic Analysis and Design Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station Christie Hale Megan Williams 2. Regulations for Seismic Hazards 3.
Magnitude 7.2 GUERRERO, MEXICO
 A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
SEISMIC RETROFITTING STRATEGIES FOR BRIDGES IN MODERATE EARTHQUAKE REGIONS
 SEISMIC RETROFITTING STRATEGIES FOR BRIDGES IN MODERATE EARTHQUAKE REGIONS ABSTRACT Ayaz H. Malik, P.E. Project Engineer New York State Department of Transportation Certain parts of the United States have
SEISMIC RETROFITTING STRATEGIES FOR BRIDGES IN MODERATE EARTHQUAKE REGIONS ABSTRACT Ayaz H. Malik, P.E. Project Engineer New York State Department of Transportation Certain parts of the United States have
Residential Seismic Strengthening
 CITY OF PORTLAND, OREGON BUREAU OF DEVELOPMENT SERVICES 1900 SW 4th Avenue, Portland, Oregon 97201 (503) 823-7300 www.portlandoregon.gov/bds Residential Seismic Strengthening Methods to Reduce Potential
CITY OF PORTLAND, OREGON BUREAU OF DEVELOPMENT SERVICES 1900 SW 4th Avenue, Portland, Oregon 97201 (503) 823-7300 www.portlandoregon.gov/bds Residential Seismic Strengthening Methods to Reduce Potential
Seismic Analysis and Design of Steel Liquid Storage Tanks
 Vol. 1, 005 CSA Academic Perspective 0 Seismic Analysis and Design of Steel Liquid Storage Tanks Lisa Yunxia Wang California State Polytechnic University Pomona ABSTRACT Practicing engineers face many
Vol. 1, 005 CSA Academic Perspective 0 Seismic Analysis and Design of Steel Liquid Storage Tanks Lisa Yunxia Wang California State Polytechnic University Pomona ABSTRACT Practicing engineers face many
SEISMIC ANALYSIS AND RETROFITTING OF R.C.C STRUCTURE
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biology Engineering Science and Technology (IJARBEST) Vol., Issue, April 1 SEISMIC ANALYSIS AND RETROFITTING OF R.C.C STRUCTURE M.R.NAVANEETHA KRISHNAN 1,
International Journal of Advanced Research in Biology Engineering Science and Technology (IJARBEST) Vol., Issue, April 1 SEISMIC ANALYSIS AND RETROFITTING OF R.C.C STRUCTURE M.R.NAVANEETHA KRISHNAN 1,
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy
 February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION KARISMA BENCHMARK
 CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION KARISMA BENCHMARK Presented by F. Wang (CEA, France), CLUB CAST3M 2013 28/11/2013 5 DÉCEMBRE 2013 CEA 10 AVRIL 2012 PAGE 1 CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SSI
CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION KARISMA BENCHMARK Presented by F. Wang (CEA, France), CLUB CAST3M 2013 28/11/2013 5 DÉCEMBRE 2013 CEA 10 AVRIL 2012 PAGE 1 CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SSI
METHODS FOR ACHIEVEMENT UNIFORM STRESSES DISTRIBUTION UNDER THE FOUNDATION
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 45-66, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 45-66, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
Parametric Analysis of School Classroom Typologies' Energy Performance
 PLEA2013-29th Conference, Sustainable Architecture for a Renewable Future, Munich, Germany 10-12 September 2013 Parametric Analysis of School Classroom Typologies' Energy Performance MAUREEN TREBILCOCK
PLEA2013-29th Conference, Sustainable Architecture for a Renewable Future, Munich, Germany 10-12 September 2013 Parametric Analysis of School Classroom Typologies' Energy Performance MAUREEN TREBILCOCK
3. Observed Damage in Railway Viaducts
 Structural Damage of Tohoku Shinkansen Viaducts by the Off the Pacific Tohoku Earthquake First Report on March 16, 2011 Dr. Yoshikazu Takahashi, Associate Professor Disaster Prevention Research Institute,
Structural Damage of Tohoku Shinkansen Viaducts by the Off the Pacific Tohoku Earthquake First Report on March 16, 2011 Dr. Yoshikazu Takahashi, Associate Professor Disaster Prevention Research Institute,
Chapter. Restoration of Damaged Structures
 5 Chapter Restoration of Damaged Structures Bringing back a damaged structure to its pre-earthquake state and original strength is called restoration. This is the first step of building rehabilitation.
5 Chapter Restoration of Damaged Structures Bringing back a damaged structure to its pre-earthquake state and original strength is called restoration. This is the first step of building rehabilitation.
World Housing Encyclopedia Report
 World Housing Encyclopedia Report Country: Chile Housing Type: Concrete frame and shear wall building Contributors: Ofelia Moroni Cristian Gómez Primary Reviewer: Sergio Alcocer Created on: 6/5/2002 Last
World Housing Encyclopedia Report Country: Chile Housing Type: Concrete frame and shear wall building Contributors: Ofelia Moroni Cristian Gómez Primary Reviewer: Sergio Alcocer Created on: 6/5/2002 Last
Module 7 (Lecture 24 to 28) RETAINING WALLS
 Module 7 (Lecture 24 to 28) RETAINING WALLS Topics 24.1 INTRODUCTION 24.2 GRAVITY AND CANTILEVER WALLS 24.3 PROPORTIONING RETAINING WALLS 24.4 APPLICATION OF LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE THEORIES TO DESIGN 24.5
Module 7 (Lecture 24 to 28) RETAINING WALLS Topics 24.1 INTRODUCTION 24.2 GRAVITY AND CANTILEVER WALLS 24.3 PROPORTIONING RETAINING WALLS 24.4 APPLICATION OF LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE THEORIES TO DESIGN 24.5
How To Repair A House After An Earthquake
 REHABILITATION Anti-seismic construction handbook Arch. Wilfredo Carazas Aedo Arch. Alba Rivero Olmos CRATerre-EAG PRELUDE Earthquakes have a considerable effect on adobe houses built with a large number
REHABILITATION Anti-seismic construction handbook Arch. Wilfredo Carazas Aedo Arch. Alba Rivero Olmos CRATerre-EAG PRELUDE Earthquakes have a considerable effect on adobe houses built with a large number
HOMEOWNER S GUIDE. to LANDSLIDES. and MITIGATION RECOGNITION, PREVENTION, CONTROL, Compiled by Dr. Scott F. Burns Tessa M. Harden Carin J.
 HOMEOWNER S GUIDE to LANDSLIDES RECOGNITION, PREVENTION, CONTROL, and MITIGATION Compiled by Dr. Scott F. Burns Tessa M. Harden Carin J. Andrew Federal Emergency Management Agency Region 10 If you are
HOMEOWNER S GUIDE to LANDSLIDES RECOGNITION, PREVENTION, CONTROL, and MITIGATION Compiled by Dr. Scott F. Burns Tessa M. Harden Carin J. Andrew Federal Emergency Management Agency Region 10 If you are
NATIONAL CIVIL PROTECTION SYSTEM ONEMI. Evolution Current Development Future Challenges
 NATIONAL CIVIL PROTECTION SYSTEM ONEMI Evolution Current Development Future Challenges CHILE 1 A nation exposed to all kind of hazards Volcanic Eruptions Wild Fires Tidal waves/ Tsunamis Quakes/ Earthquakes
NATIONAL CIVIL PROTECTION SYSTEM ONEMI Evolution Current Development Future Challenges CHILE 1 A nation exposed to all kind of hazards Volcanic Eruptions Wild Fires Tidal waves/ Tsunamis Quakes/ Earthquakes
ICOLD POSITION PAPER ON DAM SAFETY AND EARTHQUAKES
 ICOLD POSITION PAPER ON DAM SAFETY AND EARTHQUAKES August 2012 Dam Safety and Earthquakes Position Paper of International Commission on Large Dams (ICOLD) Prepared by ICOLD Committee on Seismic Aspects
ICOLD POSITION PAPER ON DAM SAFETY AND EARTHQUAKES August 2012 Dam Safety and Earthquakes Position Paper of International Commission on Large Dams (ICOLD) Prepared by ICOLD Committee on Seismic Aspects
Report on. Wind Resistance of Signs supported by. Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC) Pillars
 Report on Wind Resistance of Signs supported by Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC) Pillars Prepared for US Sign and Fabrication Corporation January, 2006 SUMMARY This study found the attachment of
Report on Wind Resistance of Signs supported by Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC) Pillars Prepared for US Sign and Fabrication Corporation January, 2006 SUMMARY This study found the attachment of
