River Valley Civilizations
|
|
|
- Elinor Johns
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 W Egyptian wood carving 60 W E 60 0 E Equator River Valley Civilizations 0 Prime Meridian UNIT 0 18 Blue Nile hippopotamus 5000 B.C. Groups of people begin migrating B.C. Sumeria established 2600 B.C. Old Kingdom begins in Egypt 2300 B.C. Sargon I establishes world s first empire
2 TM Compare and Contrast Study Foldable Make this foldable to help you compare and contrast the river valley civilizations that developed in the Middle East, South Asia, and China. Step 1 Fold a sheet of paper in half from side to side. Step 2 Turn the paper and fold it into thirds. the unit, write notes under each appropriate tab of your foldable. Keep in mind that you are trying to compare these civilizations. Fold it so the left edge is about 12 inch from the right edge. Step 3 Unfold and cut the top layer only along both folds. This will make three tabs. Reading and Writing As you read Step 4 Label as shown. Mesopotamia Egypt Eastern River Valleys RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS PRIMARY SOURCES Library See pages for another primary source reading to accompany Unit 2. Read The Epic of Gilgamesh from the World History Primary Source Document Library CD-ROM. es Journal Not re than ily life like mo a d s a w t a h W ils go? Note deta 5,000 years a u read. about it as yo 1800 B.C. Hammurabi establishes Babylonian Empire 1766 B.C. Shang Dynasty begins in China 1600 B.C. New Kingdom begins in Egypt 53
3 CHAPTER 3 Mesopotamia 3500 B.C B.C. Sumerian man and woman Gold Sumerian warrior s helmet 3500 B.C. Sumeria established B.C. Sargon I creates the world s first empire UNIT 2 RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS 1800 B.C. Hammurabi conquers Akkad and Sumer 1700 B.C. Tales of Gilgamesh started
4 Chapter Focus Read to Discover How religion, family life, and government influenced the civilization of Sumer. Why Hammurabi and his reforms were important. How the developments of Mesopotamia contributed to other civilizations. Chapter Overview Visit the Human Heritage Web site at humanheritage.glencoe.com and click on Chapter 3 Chapter Overviews to preview this chapter. Terms to Learn city-state artisans ziggurat cuneiform scribe priest-kings empire culture reform reign People to Know Gilgamesh Sargon I Hammurabi Places to Locate Mesopotamia Sumer Ur Babylon Why It s Important The earliest known civilizations developed along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, which begin in the mountains of eastern Turkey. The twin rivers each flow more than 1,000 miles, or 1,600 kilometers, southeast across a great plain in an area known as the Middle East. Then, the waters join and empty into the Persian Gulf. Today, the land between the two rivers is part of the country of Iraq. In ancient times, the area was called Mesopotamia (mes uh puh tay me uh), the land between the rivers. Around 4000 B.C., groups of people began migrating, or moving, into Mesopotamia. They developed so many new ideas that the area has been called the cradle of civilization. The influence of Mesopotamia left a lasting impact on the ancient world. SECTION 1 The Rise of Sumer The people who settled in southern Mesopotamia about 3500 B.C. were a short, stocky, black-haired people called Sumerians (sū mer ē uhnz). Their area of Mesopotamia was known as Sumer (sū mŭhr). CHAPTER 3 MESOPOTAMIA 55
5 Student Web Activity Visit the Human Heritage Web site at humanheritage.glencoe.com and click on Chapter 3 Student Web Activities to find out more about the Sumerian civilization. Sumerian civilization is the earliest known on Earth. For the first time, people began to control their physical environment. The Sumerians knew they had to control the twin rivers. The rivers flooded each spring. When the waters went down, natural levees (lev ēz), or raised areas of soil, remained behind. The Sumerians built the levees even higher and used them to keep back the floodwaters. During summer when the land became dry, they poked holes in the levees. The river water that ran through the holes made channels in the soil. The Sumerians made the channels larger until they became canals. They used the water in the canals to irrigate their crops. The chief crop of the Sumerians was barley. The Sumerians also grew wheat, sesame, flax, fruit trees, date palms, and many different kinds of vegetables. A system of irrigation canals took much planning. People had to learn to work together. In time, they became more organized. They set up governments to make laws so they would know what was expected of them. As the population grew, they began to build cities. There was no building stone and little timber in Sumer. The Sumerians had to find other materials to use for their houses and public buildings. They mixed mud from the river with crushed reeds to make bricks. They left the bricks out in the sun to bake and then used them to build their cities. One of the great cities of Official Seals Around 3500 to 3400 B.C., officials in Mesopotamia started using cylinder seals (below) to mark goods and verify documents written in cuneiform on clay. Today governments around the world continue to use seals to mark documents such as the passports carried by United States citizens (right). Why do you think governments stamp important documents with seals? 56 UNIT 2 RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS
6 Sumer was Ur (uhr). The Sumerians were the first city-builders in this area of the world. City-States Each Sumerian city was considered a state in itself, with its own god and government. Each city-state was made up of the city and the farmland around it. Each city was surrounded by a wall of sun-dried brick. The wall had bronze gates that were opened during the day and closed at night to keep out lions and bandits. Narrow, winding streets led from the gates to the center of the city. Near the center were the houses of the upper class priests and merchants. These houses were two stories high with wooden balconies. The balconies looked out over courtyards around which the living quarters were built. The courtyards provided light and air for rooms. Outside walls were windowless to keep out heat from the sun and smells of the streets. Behind the houses of the rich were the houses of the middle class government officials, shopkeepers, and artisans (art uh zuhnz), or skilled workers. These houses also were built around open courtyards but were only one story high. Farther out were the houses of the lower class farmers, unskilled workers, and people who made their living by fishing. The Sumerians were very proud of their cities. Often, one city-state would go to war with another city-state. They fought over boundary lines and to prove which city-state was stronger. Religious and Family Life At the center of each Sumerian city was a temple, called a ziggurat (zig uh rat). The word ziggurat means mountain of god or hill of heaven. Each ziggurat was made up of a series of square levels. Each level was smaller than the one below it. Great stairways led to the top of a ziggurat, which was believed to be the home of the city s chief god. Only priests could enter the home of the god. Around the ziggurat were courts. The courts and the ziggurat were the center of Sumerian life. Artisans worked there. Children went to school there. Farmers, artisans, and traders stored their goods there. The poor were fed there. All great events were celebrated in this area. The Sumerians believed that all the forces of nature, such as wind, rain, and flood, were alive. Because they could not control these forces, they viewed them as gods. In all, there were more than 3,000 Sumerian gods. The Sumerians believed that at first there were only male gods. Then female gods appeared. The male gods found they had to work very hard to please the female gods. The male gods decided that they needed servants to do their work. So, from the mud of the rivers, they made humans who would be their servants. The Sumerians believed that they were on Earth only to What areas made up each Sumerian city-state? What are artisans? What was the purpose of a ziggurat? CHAPTER 3 MESOPOTAMIA 57
7 SUMERIAN PRAYING STATUES To honor their gods, Sumerians left statues of themselves within their temple. These statues, standing with their hands clasped, were meant to offer prayers when the people were not present. In how many gods did the Sumerians believe? What was cuneiform? What were some of the places a scribe might work? 58 serve the gods. If the gods were unhappy with them, their crops would not grow and they would not live happy lives. Therefore, the goal of each Sumerian was to please the gods. Only priests, however, could know the will of the gods. This made Sumerian priests very powerful. For example, all land was owned by a city s god. But priests controlled and administered the land in the god s name. The priests also ran schools. Schools were only for the sons of the rich. Poorer boys worked in the fields or learned a trade. Schools were made up of rooms off the temple courtyards. They were known as tablet houses because their main purpose was to teach students how to write. Students sat in rows on brick benches. They wrote with sharp-ended reeds on clay tablets about the size of a postcard. Sumerian writing was called cuneiform (kyu n e uh form). It was made up of hundreds of markings shaped like wedges. Writing developed because people had to keep track of business deals. When people lived in villages, they knew everyone and could remember what goods they exchanged with whom. When cities arose, there were too many people and goods to remember. At first, the Sumerians used pictures to represent objects. Later, they used pictures to represent ideas. Still later, they used pictures to represent syllables. When a student graduated from school, he became a scribe, or writer. He worked for the temple, the palace, the government, or the army. Some scribes went to work for a merchant or set up their own businesses as public writers. UNIT 2 RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS
8 Although only Sumerian males went to school, women did have rights. They could buy and sell property. They could run businesses and own and sell enslaved persons. Although a woman handled her husband s affairs when he was away, the husband was the head of a household. He could divorce his wife by saying, You re not my wife. If he needed money, he had the right to sell or rent his wife and children as enslaved persons for up to three years. He also arranged the marriages of his children. Children were expected to support their parents when the parents became old and were also expected to obey older family members. All family members were to obey the gods and the priests. Priests and Kings At first, Sumerian priests were also kings of city-states. One of the most famous priest-kings was Gilgamesh (gil ga mesh) of Uruk (u ru k). Tales told about Gilgamesh made him seem more like a god than a person. One tale, written about 1700 B.C., is the oldest known story in the world. In the story, Gilgamesh and his friend Enkidu (en ki du ) travel the world performing great acts of courage. When Enkidu dies, Gilgamesh searches for a way to live forever. He learns that only the gods can live forever. Part of the Gilgamesh story tells of a great flood that covered the whole world. The account of the flood is very much like the biblical story of Noah and the ark. The Sumerian priest-kings received advice from an assembly made up of free men. When war broke out with another citystate, the assembly would choose one of its members to serve as military leader until the war was over. As time went on, these leaders stayed in charge even after peace returned. By about 3000 B.C., they took the place of priests as permanent kings. At the same time, kingship became hereditary (huh red uh ter e ), or passed down from parent to child. Section 1 Assessment 1. Define: city-state, artisans, ziggurat, cuneiform, scribe, priest-kings. 2. How did the Sumerians gain control of the twin rivers? 3. What was the center of Sumerian life? Cuneiform Today only about 250 people know how to read the more than 1 million cuneiform signs that make up the written Sumerian language. To change this, a team of language experts at the University of Pennsylvania is working on an 18-volume Sumerian dictionary. The team expects the work to be done sometime in the 2000s. Who was one of the most famous Sumerian priestkings? time of Sumer to the lives of women in the modern world? Graphic Organizer Activity 5. Draw a diagram like this one, and use it to show accomplishments of the Sumerians. Critical Thinking 4. Making Comparisons How would you compare the lives of women in the Accomplishments CHAPTER 3 MESOPOTAMIA 59
9 Distinguishing Fact From Opinion Suppose a friend says, "Our school s basketball team is awesome. That s a fact." Actually, it is not a fact; it is an opinion. Are you able to tell the difference? Learning the Skill A fact answers a specific question such as: What happened? Who did it? When and where did it happen? Why did it happen? Statements of fact can be checked for accuracy and proven. If your friend had said, "We have the highest-ranking team in the state," that could be a fact. We can look up the rankings of state teams and determine whether the statement is a fact. An opinion, on the other hand, expresses beliefs, feelings, and judgments. Although it may reflect someone s thoughts, we cannot prove or disprove it. An opinion often begins with phrases such as I believe, I think, probably, it seems to me, or in my opinion. It often contains words such as might, could, should, and ought, and superlatives such as best, worst, and greatest. Judgment words that express approval or disapproval such as good, bad, poor, and satisfactory also usually indicate an opinion. To distinguish between facts and opinions, ask yourself these questions: 60 Does this statement give specific information about an event? Can I check the accuracy of this statement? Does this statement express someone s feelings, beliefs, or judgment? Does it include phrases such as I believe, superlatives, or judgment words? Skill Practice Read each numbered statement. Then tell whether each is a fact or an opinion, and explain how you arrived at your answer. 1. Sumerian civilization is the earliest known on Earth. 2. The greatest accomplishment of the Sumerians was their system of irrigation. 3. A temple called a ziggurat formed the center of Sumerian life. 4. Women in Sumeria had terrible lives. 5. The priest-kings were better rulers than the military leaders who came into power. Glencoe s Skillbuilder Interactive Workbook CD-ROM, Level 1, provides instruction and practice in key social studies skills.
10 SECTION 2 Later Mesopotamian Empires About 2400 B.C., the power of Sumer started to fade. New civilizations began to develop in Mesopotamia as conquerors moved in from nearby areas. Sargon I Sargon I (sar gon) was a ruler from an area in northern Mesopotamia known as Akkad (ak ad). About 2300 B.C., he moved his armies south and began to conquer the citystates of Sumer one by one. He united the conquered city-states with Akkad and became known as king of Sumer and Akkad. Thus, Sargon I created the world s first empire (em pı r), or group of states under one ruler. He extended this empire to include all of Mesopotamia. Under Sargon I, Akkadian became the language of the people. Sumerian was used only for religious purposes. The Akkadians, however, worshiped the Sumerian gods. They also wrote their language in Sumerian cuneiform. Sargon I ruled his empire for more than 50 years. Shortly after his death, the empire fell. Hammurabi of Babylon Following the death of Sargon I, the separate city-states again rose to power. Then, about 1800 B.C., a new group of people called Amorites (am uh rı ts) entered the Tigris-Euphrates valley and built cities of their own. One of these cities was Babylon (bab uh luhn). The king of Babylon, Hammurabi (ham uh rob e ), conquered Akkad and Sumer and became ruler of a great new empire. The people of Babylon took as their own many parts of the culture, or way of life, of the people they had conquered. For example, they took over the language of the city-states. They also worshiped the same Sumerian gods that the Akkadians had worshiped, but they gave those gods Babylonian names. Hammurabi was a great conqueror. He extended his rule to the Mediterranean Sea. As ruler, he brought about many changes. He improved irrigation systems by building and repairing canals. He changed religion by raising the god of Babylon above all other gods. When the people began to worship this god as well as their own local god, they became more united. Hammurabi also reorganized the tax system and began a government housing program. The reform, or improvement, for which Hammurabi became best known was a code of law. Each city-state had its own code. Hammurabi took what he believed were the best laws from each code. He put these together and then issued one code by which everyone in the empire was to live. Hammurabi wanted to make sure that his code was carried out fairly and justly. To do this, he How did Sargon I build his empire? From what culture did the people of Babylon borrow? For what reform is Hammurabi best known? Hammurabi C.1750 B.C. Babylonian King Hammurabi built an empire that stretched north from the Persian Gulf through the Tigris and Euphrates valleys and west to the Mediterranean Sea. He turned Babylon into one of the most powerful capitals of the ancient world. CHAPTER 3 MESOPOTAMIA 61
11 Identifying Physical Features Different physical features making up Earth s surface are often shown on maps. They include landforms, such as mountains, hills, plateaus, and plains. Physical features also include bodies of water, such as oceans, seas, lakes, and rivers. Most maps use black boundary lines and color to point out water and land areas. Blue is generally used to show the size and shape of large bodies of water. For example, notice the Mediterranean Sea located west of Syria on the map below. Rivers, such as the Nile River in Egypt, are often shown by black lines. To distinguish rivers from boundaries, which are also shown by black lines, rivers are usually labeled. Maps in this textbook use earth tone colors to point out land areas. Mountains are shown by shades of black. For example, there are mountains located where the Euphrates River begins but not where the river empties into the Persian Gulf. Look at the map below, and answer the following questions. Map Practice 1. In addition to the Mediterranean, what seas are shown? 2. Besides the Nile, what rivers are shown? 3. How can you tell that the Persian Gulf coastline has changed over the years? Mesopotamia Glencoe s Skillbuilder Interactive Workbook CDROM, Level 1, provides instruction and practice in key social studies skills. 62
12 appointed royal judges. Judges who were not honest and witnesses who did not tell the truth were punished. Hammurabi s code covered almost everything in daily life. A person was believed innocent until proven guilty. Once proven guilty, a person was punished. Punishments ranged from fines to death. There were no prison sentences. Members of the upper class generally were punished more severely than members of the middle or lower classes. During Hammurabi s rule, Babylon became an important trade center. Babylonians exchanged their surplus, or extra, products for money or for goods. People from other parts of the world came to trade, some from as far away as India and China. These traders paid gold and silver for the goods made by Babylonians. Hammurabi ruled for more than 40 years. His reign (ra n), or period of power, is known as the Golden Age of Babylon. After his death, however, the Babylonian Empire declined, and Mesopotamia was again divided into a number of small city-states. Sculpture of a Sumerian Chariot What did people call the reign of Hammurabi? Section 2 Assessment Graphic Organizer Activity 1. Define: empire, culture, reform, reign. 2. What happened to Sumer under Sargon I s rule? 3. How did Hammurabi come to power? 5. Draw a diagram like this one, and use it to show key events in the life of Hammurabi. Critical Thinking 4. Using Reasoned Judgment What do you think Hammurabi would say about the court system in the United States today? SECTION 3 Contributions From the beginnings of Sumer until the death of Hammurabi, the influence of Mesopotamia on other civilizations was felt in many ways. Inventions, customs, and ideas of the Sumerian and Babylonian cultures were copied and improved upon by other peoples. The Sumerians developed the earliest known civilization in the world. Mesopotamia has been called the cradle of civilization. The oldest written records known are Sumerian. The Sumerians were the first people to write down their laws. Sumerian cuneiform became the model for other people s writing. The Sumerians also invented many things such as the wheel, which helped transportation. Another was the plow, which made CHAPTER 3 MESOPOTAMIA 63
13 it possible for farmers to grow more food with less effort. Still another was the sailboat, which replaced muscle power with wind power. The people of Mesopotamia developed a 12-month calendar based on the cycles of the moon. The calendar marked the times for religious festivals and planting. From Mesopotamia also came contributions in the field of mathematics. The people developed a number system based on 60. From that came the 60-minute hour, 60-second minute, and 360-degree circle. The people of Mesopotamia also used a clock that was operated by controlled drops of water. Section 3 Assessment 1. Why was Mesopotamia called the cradle of civilization? 2. What did the people of Mesopotamia contribute to the field of mathematics? Critical Thinking 3. Determining Cause and Effect How have inventions by the people of Mesopotamia helped shape presentday life? Graphic Organizer Activity 4. Draw a diagram like this one, and use it to show facts that support this statement: Mesopotamia was the cradle of civilization. Cradle of Civilization Fact Fact Fact Fact Chapter Summary & Study Guide 1. Civilization began in an area known as Mesopotamia, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. 2. Sumer was the first known civilization in the world. 3. Sumerian civilization consisted of a series of city-states, the most important of which was Ur. 4. Each Sumerian city-state had its own chief god and government. 5. Sargon I of Akkad created the world s first empire in 2300 B.C. 6. About 1800 B.C., Hammurabi conquered Akkad and Sumer and established the Babylonian Empire. 7. Hammurabi unified the Babylonian Empire by setting up a single code of law and by raising the god of Babylon above all others. 8. Major contributions of the Mesopotamian civilizations include writing, the wheel, the plow, the sailboat, and a number system based on 60. Self-Check Quiz Visit the Human Heritage Web site at humanheritage. glencoe.com and click on Chapter 3 Self-Check Quiz to assess your understanding of this chapter. 64 UNIT 2 RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS
14 CHAPTER 3 Assessment Using Key Terms Graphic Organizer Activity Imagine that you are a visitor to ancient Mesopotamia. Use the following words in a letter home in which you describe what you have seen and experienced during your visit. History Create a chart like this one, and use it to write newspaper headlines that tell the importance of each date to the history of Mesopotamia. artisans ziggurat reform reign culture priest-kings cuneiform empire scribe city-state Understanding Main Ideas 1. Why were the twin rivers important to Sumerian life? 2. Why was the ziggurat important to the Sumerians? 3. Who was Gilgamesh, and why was he important? 4. What did Sargon I accomplish? 5. What trading system did the people of Babylonia use? 6. What changes did Hammurabi bring to Mesopotamia? 7. What happened to people who broke Hammurabi s laws? 8. Why was the sailboat an important invention? Critical Thinking 1. In what ways do you think your school is similar to or different from the schools in Sumeria? 2. What do you think would have happened to Sumer if it had suffered ten years of drought? How would the kingdom be affected? 3. Why do you think religion played such an important part in Sumerian life? Date Headline 3500 B.C B.C B.C B.C. Geography in History Human Systems Babylon became a major trading center. Refer to the map on page 62 and imagine that you are King Hammurabi. You must select the location for another settlement that you hope will also become a trading center. Where would you locate this settlement? Explain. rnal u o J r You Using ay you m ils rly y deta n a e r a e in ea daily Comp ed about lif r of you ing ot n s il e a v t a e h with d raph explain ia r e m g er Su a para ilar and diff e it r W life. re sim plaining that a x s g in th were e u ved in o y if who li e n ent as o e to som them B.C
Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and
 Mesopotamia Review Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. This curving strip
Mesopotamia Review Mesopotamia is the first known civilization. Mesopotamia means land between two rivers. This civilization began on the plains between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. This curving strip
The Rise of Civilizations
 Page 1 of 6 The Rise of Civilizations Thousands of years ago, several societies in different parts of the world changed from hunting and gathering to farming. Some began to produce surpluses of food. Those
Page 1 of 6 The Rise of Civilizations Thousands of years ago, several societies in different parts of the world changed from hunting and gathering to farming. Some began to produce surpluses of food. Those
Teacher s Masters California Education and the Environment Initiative. History-Social Science Standards 6.2.6. and 6.2.8. Egypt and Kush: A Tale of
 6 Teacher s Masters California Education and the Environment Initiative History-Social Science Standards 6.2.6. and 6.2.8. Egypt and Kush: A Tale of Two Kingdoms California Education and the Environment
6 Teacher s Masters California Education and the Environment Initiative History-Social Science Standards 6.2.6. and 6.2.8. Egypt and Kush: A Tale of Two Kingdoms California Education and the Environment
Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack
 Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack This pack includes the following lessons: Locating Egypt The River Nile Archeology Hieroglyphics Pharaohs Every effort has been made to seek permission for the
Year 2 History: Ancient Egypt Resource Pack This pack includes the following lessons: Locating Egypt The River Nile Archeology Hieroglyphics Pharaohs Every effort has been made to seek permission for the
Fry Phrases Set 1. TeacherHelpForParents.com help for all areas of your child s education
 Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
PUSD High Frequency Word List
 PUSD High Frequency Word List For Reading and Spelling Grades K-5 High Frequency or instant words are important because: 1. You can t read a sentence or a paragraph without knowing at least the most common.
PUSD High Frequency Word List For Reading and Spelling Grades K-5 High Frequency or instant words are important because: 1. You can t read a sentence or a paragraph without knowing at least the most common.
Ancient India Lesson 2
 Name: Date: Ancient India Lesson 2 Early Indian Civilization Over 1,000 miles separate the Indus River valley from Iraq, the region once known as Mesopotamia. This distance did not keep people from traveling
Name: Date: Ancient India Lesson 2 Early Indian Civilization Over 1,000 miles separate the Indus River valley from Iraq, the region once known as Mesopotamia. This distance did not keep people from traveling
Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt
 Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt MAIN IDEAS Economics Egyptians developed a complex society with many different jobs and social roles. Science and Technology Egyptians made advances in calendars, geometry,
Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt MAIN IDEAS Economics Egyptians developed a complex society with many different jobs and social roles. Science and Technology Egyptians made advances in calendars, geometry,
Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK #
 Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK # H0MEWORK # I THE RIVER NILE The river Nile is one of the world's great rivers. It begins its long journey in Africa, as two
Woolooware High School YEAR 7 EGYPT HOMEWORK NAME: CLASS: TEACHER: HOMEWORK # H0MEWORK # I THE RIVER NILE The river Nile is one of the world's great rivers. It begins its long journey in Africa, as two
Ancient China. Vocabulary. 15. Terracotta Army collection of seven thousand life-sized sculptures made from pottery in the tomb of Shi Huangdi
 Ancient China 1. Analects the collected sayings and teachings of Confucius 2. Bronze Age (3300 1200 B.C.) time when people made weapons and tools from bronze 3. calligraphy artistic form of ancient Chinese
Ancient China 1. Analects the collected sayings and teachings of Confucius 2. Bronze Age (3300 1200 B.C.) time when people made weapons and tools from bronze 3. calligraphy artistic form of ancient Chinese
Sumerian Civilization
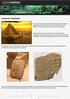 Sumerian Civilization In the south eastern region of Mesopotamia between the mighty Euphrates and Tigris Rivers lay the ruins of the Sumerian City- States. The history of the Sumerians is shrouded in mystery.
Sumerian Civilization In the south eastern region of Mesopotamia between the mighty Euphrates and Tigris Rivers lay the ruins of the Sumerian City- States. The history of the Sumerians is shrouded in mystery.
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties
 Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Note Taking Study Guide CIVILIZATIONS OF MESOAMERICA
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide CIVILIZATIONS OF MESOAMERICA Focus Question: What factors encouraged the rise of powerful civilizations in Mesoamerica? A. As you read People Settle in the Americas, complete
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide CIVILIZATIONS OF MESOAMERICA Focus Question: What factors encouraged the rise of powerful civilizations in Mesoamerica? A. As you read People Settle in the Americas, complete
Jainism Jainism also began in India; religion teaches ahimsa nonviolence - Jains believe all living things have souls and should not be hurt
 Lesson 3 Buddhism and India s Golden Age MAIN IDEAS Belief System A teacher called the Buddha developed a new religion that focused on helping people to escape suffering. Government The Maurya rulers united
Lesson 3 Buddhism and India s Golden Age MAIN IDEAS Belief System A teacher called the Buddha developed a new religion that focused on helping people to escape suffering. Government The Maurya rulers united
KS2: Baghdad AD 900 (6 lessons)
 KS2: Baghdad AD 900 (6 lessons) Contents Include: An Introduction to Mesopotamia Building Baghdad The House of Wisdom The Mongol Attack on Baghdad in 1258 This pack of lessons has been designed for Key
KS2: Baghdad AD 900 (6 lessons) Contents Include: An Introduction to Mesopotamia Building Baghdad The House of Wisdom The Mongol Attack on Baghdad in 1258 This pack of lessons has been designed for Key
Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet
 Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet Your group will research Ancient Egyptian culture focusing on the Government of Ancient Egypt. Assign jobs to group members. Everyone must have a job. Research
Government of Ancient Egypt Question Packet Your group will research Ancient Egyptian culture focusing on the Government of Ancient Egypt. Assign jobs to group members. Everyone must have a job. Research
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L
 7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the soil was rich and easy to farm. It is there that the world
7 URUK CIVILIZATION 950L URUK THE WORLD S FIRST BIG CITY By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the soil was rich and easy to farm. It is there that the world
Second Grade Ancient Greece Assessment
 Second Grade Ancient Greece Assessment 1a. Which letter is labeling the Mediterranean Sea: A or B? A B 1b. Which body of water is labeled with an A? A 1c. Label the Mediterranean Sea. Then, answer the
Second Grade Ancient Greece Assessment 1a. Which letter is labeling the Mediterranean Sea: A or B? A B 1b. Which body of water is labeled with an A? A 1c. Label the Mediterranean Sea. Then, answer the
Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks
 Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
CH10 Practice Test 2015
 Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
Egypt. The Old Kingdom
 Egypt The Old Kingdom Vocabulary: Narmer (Menes)- King that united Upper and Lower Egypt Old Kingdom Began around 2600BC, rise of Egyptian cities as centers for religion and government Artisans- someone
Egypt The Old Kingdom Vocabulary: Narmer (Menes)- King that united Upper and Lower Egypt Old Kingdom Began around 2600BC, rise of Egyptian cities as centers for religion and government Artisans- someone
The Neolithic Revolution
 The Neolithic Revolution The archaeologist took out his small brush and carefully removed the remaining dirt from the fragment of human skull. To help him reconstruct the life of the ancient human, he
The Neolithic Revolution The archaeologist took out his small brush and carefully removed the remaining dirt from the fragment of human skull. To help him reconstruct the life of the ancient human, he
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia
 Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period of almost 1800 years. This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period of almost 1800 years. This timeline shows four empires that ruled Mesopotamia during a period
C-14: God Created the World and People Spoiled It
 Title: GOD CREATED THE WORLD AND PEOPLE SPOILED IT Theme / Bible Basis: Review of Genesis 1-11 Bible Reading: Psalm 148, NLT Introduction: In our recent messages, we have read together from several stories
Title: GOD CREATED THE WORLD AND PEOPLE SPOILED IT Theme / Bible Basis: Review of Genesis 1-11 Bible Reading: Psalm 148, NLT Introduction: In our recent messages, we have read together from several stories
AFRICAN KINGDOMS. Ghana. Around AD 800 the rulers of many farming villages united to create the kingdom of Ghana.
 AFRICAN KINGDOMS In Africa, towns soon became part of an important trade network. Gold and salt were the most important products traded. People needed salt in their diets to prevent dehydration. There
AFRICAN KINGDOMS In Africa, towns soon became part of an important trade network. Gold and salt were the most important products traded. People needed salt in their diets to prevent dehydration. There
West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society
 West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society Bantu Migration Around 1500 BCE farmers of the Niger and Benue River valleys in West Africa began migrating south and east, bringing with them their
West Africa: Bantu Migration and the Stainless Society Bantu Migration Around 1500 BCE farmers of the Niger and Benue River valleys in West Africa began migrating south and east, bringing with them their
LESSON TITLE: A Story about Investing. THEME: We should share the love of Jesus! SCRIPTURE: Luke 19:11-27 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF:
 Devotion NT258 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: A Story about Investing THEME: We should share the love of Jesus! SCRIPTURE: Luke 19:11-27 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids!
Devotion NT258 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: A Story about Investing THEME: We should share the love of Jesus! SCRIPTURE: Luke 19:11-27 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids!
Ancient China. Military Stamp/Seal. The Qin and Han Dynasties
 Ancient China The Qin and Han Dynasties Military Stamp/Seal http://history.cultural-china.com/chinawh/images/exbig_images/c03bc44c62df55844b6ebc96427e0f5f.jpg Qin Shi Huangdi 246BCE - Warring States Period
Ancient China The Qin and Han Dynasties Military Stamp/Seal http://history.cultural-china.com/chinawh/images/exbig_images/c03bc44c62df55844b6ebc96427e0f5f.jpg Qin Shi Huangdi 246BCE - Warring States Period
Joseph Helps Pharaoh
 Genesis 41 14 So Pharaoh sent for Joseph, and he was quickly brought from the dungeon. When he had shaved and changed his clothes, he came before Pharaoh. 15 Pharaoh said to Joseph, I had a dream, and
Genesis 41 14 So Pharaoh sent for Joseph, and he was quickly brought from the dungeon. When he had shaved and changed his clothes, he came before Pharaoh. 15 Pharaoh said to Joseph, I had a dream, and
September 15th TEACHER BIBLE STUDY. The Northern Kingdom Was Destroyed
 Big Picture Question: Why did God scatter His people? God s people sinned against Him. Bible Passage: 2 Kings 17:1-23 Christ Connection: The prophets called God s people to repentance as Christ calls people
Big Picture Question: Why did God scatter His people? God s people sinned against Him. Bible Passage: 2 Kings 17:1-23 Christ Connection: The prophets called God s people to repentance as Christ calls people
Lesson 35. The Tabernacle. Exodus 25 26. God lives among his people
 Gospel Story Curriculum (OT) PRESCHOOL Lesson 35 The Tabernacle Exodus 25 26 Bible Truth God lives among his people l e s s o n snapshot 1. Opening Activity and Introduction.... 5 min Supplies: Nine sheets
Gospel Story Curriculum (OT) PRESCHOOL Lesson 35 The Tabernacle Exodus 25 26 Bible Truth God lives among his people l e s s o n snapshot 1. Opening Activity and Introduction.... 5 min Supplies: Nine sheets
Ancient Egypt Handouts
 Ancient Egypt Handouts Map of Egypt Lower Egypt Upper Egypt Ancient Egypt 1 Map of Egypt-Answer Sheet 30ºE 40ºE 50ºN Mediterranean Sea 40ºN Africa Alexandria Rosetta Giza Memphis Sinai Pen. Middle East
Ancient Egypt Handouts Map of Egypt Lower Egypt Upper Egypt Ancient Egypt 1 Map of Egypt-Answer Sheet 30ºE 40ºE 50ºN Mediterranean Sea 40ºN Africa Alexandria Rosetta Giza Memphis Sinai Pen. Middle East
Name Class Date. Ancient China Section 4
 Name Class Date Ancient China Section 4 MAIN IDEAS 1. Han dynasty government was based on the ideas of Confucius. 2. Family life was supported and strengthened in Han China. 3. The Han made many achievements
Name Class Date Ancient China Section 4 MAIN IDEAS 1. Han dynasty government was based on the ideas of Confucius. 2. Family life was supported and strengthened in Han China. 3. The Han made many achievements
DRAW CONCLUSIONS As you read, draw conclusions about the importance of the Nile River to life in Egypt. Focus Skill
 Lesson 1 PAGES 116 121 OBJECTIVES Evaluate the impact of the Nile River on life in ancient Egypt. Analyze the relationship between nature and the religion of the ancient Egyptians. Examine how the peoples
Lesson 1 PAGES 116 121 OBJECTIVES Evaluate the impact of the Nile River on life in ancient Egypt. Analyze the relationship between nature and the religion of the ancient Egyptians. Examine how the peoples
Ancient China: The Qin and Han Dynasties**
 Name Period Date Ancient China: The Qin and Han Dynasties** 246BCE - Warring States Period Zhou Dynasty has almost no power in China Qin Shi Huangdi comes to power in 246BCE as king of state of Qin Conquers
Name Period Date Ancient China: The Qin and Han Dynasties** 246BCE - Warring States Period Zhou Dynasty has almost no power in China Qin Shi Huangdi comes to power in 246BCE as king of state of Qin Conquers
12. Choose You This Day
 RWS #106, Our Mighty God... 12. Choose You This Day Joshua 23-24 Joshua was a good example. He put God first in his life. When Joshua died at the age of 110, he was called the servant of the Lord (Joshua
RWS #106, Our Mighty God... 12. Choose You This Day Joshua 23-24 Joshua was a good example. He put God first in his life. When Joshua died at the age of 110, he was called the servant of the Lord (Joshua
7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR?
 7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR? In this three-part video David Christian explains how the rise of agriculture led to the formation of the world s first large-scale civilizations. Fueled by
7 WHERE AND WHY DID THE FIRST CITIES APPEAR? In this three-part video David Christian explains how the rise of agriculture led to the formation of the world s first large-scale civilizations. Fueled by
NATURAL REGIONS OF KENTUCKY
 NATURAL WONDERS As you travel around Kentucky taking pictures, you are excited by what you see. Kentucky offers diverse and amazing sights. The Six Regions In the West, you see the Mississippi River, the
NATURAL WONDERS As you travel around Kentucky taking pictures, you are excited by what you see. Kentucky offers diverse and amazing sights. The Six Regions In the West, you see the Mississippi River, the
Theme: The deliverance of the Israelites from Egypt demonstrates God s power
 Title: THE LIBERATING POWER AND LOVE OF GOD Theme: The deliverance of the Israelites from Egypt demonstrates God s power Bible Basis: Genesis 15:13-15 CEV; Exodus 1-12* Introduction: We have been learning
Title: THE LIBERATING POWER AND LOVE OF GOD Theme: The deliverance of the Israelites from Egypt demonstrates God s power Bible Basis: Genesis 15:13-15 CEV; Exodus 1-12* Introduction: We have been learning
Devotion NT347 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Hall of Faith. THEME: God wants us to trust Him. SCRIPTURE: Hebrews 11:1-40
 Devotion NT347 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Hall of Faith THEME: God wants us to trust Him. SCRIPTURE: Hebrews 11:1-40 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids! This is a
Devotion NT347 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Hall of Faith THEME: God wants us to trust Him. SCRIPTURE: Hebrews 11:1-40 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids! This is a
The Interconnectedness of Ancient Peoples Map Study Janet Cuenca Parkway Northeast Middle School St. Louis County, Missouri
 The Interconnectedness of Ancient Peoples Map Study Janet Cuenca Parkway Northeast Middle School St. Louis County, Missouri Level: Grade 7 Length of Unit: Intermittent days throughout the school year,
The Interconnectedness of Ancient Peoples Map Study Janet Cuenca Parkway Northeast Middle School St. Louis County, Missouri Level: Grade 7 Length of Unit: Intermittent days throughout the school year,
- 7. Oracle bones were used a. to practice written Chinese. b. to try to predict the future. p Ch 14 Ancient China section 1
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A p Ch 14 Ancient China section 1 Multiple Choice Identzh the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. - I. Before the Shang kingdom arose, Chinese civilization
Name: Class: Date: ID: A p Ch 14 Ancient China section 1 Multiple Choice Identzh the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. - I. Before the Shang kingdom arose, Chinese civilization
Four Early River Valley Civilizations. Egyptian Civilization - Nile River
 Four Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River I. GEOGRAPHY A. The Nile Egypt on the Nile 1. Egypt s settlements
Four Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River Early River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Civilization - Nile River I. GEOGRAPHY A. The Nile Egypt on the Nile 1. Egypt s settlements
BEFORE THE ROOSTER CROWS
 BOOK 3, PART I, LESSON 5 BEFORE THE ROOSTER CROWS THE BIBLE: Luke 22:54-62 THEME: We remember that Jesus taught about love and showed love in everything he did. During Lent and Easter we remember and celebrate
BOOK 3, PART I, LESSON 5 BEFORE THE ROOSTER CROWS THE BIBLE: Luke 22:54-62 THEME: We remember that Jesus taught about love and showed love in everything he did. During Lent and Easter we remember and celebrate
BmLE LESSON # 22 1. was able to tell us the meaning of our dreams, and the dreams came true!
 BmLE LESSON 1. Genesis 40 Do you have many cows near your home? Do you sometimes go for a drive and see cows in a field? Do you know what cows eat? They eat grass and grain like wheat and barley. One day
BmLE LESSON 1. Genesis 40 Do you have many cows near your home? Do you sometimes go for a drive and see cows in a field? Do you know what cows eat? They eat grass and grain like wheat and barley. One day
AP World History Class Notes, Bentley Brief Edition Ch 1 The Foundations of Complex Societies September 14, 2010
 This first chapter of Traditions and Encounters sets the stage for the drama of world history by tracing the development of humans from their earliest appearance on earth through the rise of important
This first chapter of Traditions and Encounters sets the stage for the drama of world history by tracing the development of humans from their earliest appearance on earth through the rise of important
Lesson 35. The Tabernacle. Exodus 25 27. God lives among his people
 Gospel Story Curriculum (OT) lower Lower elementary Lesson 35 The Tabernacle Exodus 25 27 Bible Truth God lives among his people l e s s o n snapshot 1. Opening review.... 5 min Use last week s lesson
Gospel Story Curriculum (OT) lower Lower elementary Lesson 35 The Tabernacle Exodus 25 27 Bible Truth God lives among his people l e s s o n snapshot 1. Opening review.... 5 min Use last week s lesson
Period #1: Technological and Environmental Transformations, c. 8,000 B.C.E. - 600 B.C.E. Study Guide by Key Concepts
 Note: the question numbers are my own customization, and do NOT reflect official College Board designation. Ask yourself the question in the left column. Your answer should come close to the middle column.
Note: the question numbers are my own customization, and do NOT reflect official College Board designation. Ask yourself the question in the left column. Your answer should come close to the middle column.
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao
 Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Egypt and China. Ancient Worlds: VMFA Resources
 VMFA Resources Ancient Worlds: Pre- and Post-Visit Activities VIRGINIA MUSEUM OF FINE ARTS Egypt and China Grade 2 Based on images of two works of art from VMFA s collection, these activities will provide
VMFA Resources Ancient Worlds: Pre- and Post-Visit Activities VIRGINIA MUSEUM OF FINE ARTS Egypt and China Grade 2 Based on images of two works of art from VMFA s collection, these activities will provide
GOD GAVE HIS CHILDREN A PATH THROUGH THE SEA (A.2.Spring.7)
 GOD GAVE HIS CHILDREN A PATH THROUGH THE SEA (A.2.Spring.7) Biblical Reference Exodus 14 Key Verse 1 Peter 7:5 Key Concept God opens doors that lead me to Him Educational Objectives At the end of the class
GOD GAVE HIS CHILDREN A PATH THROUGH THE SEA (A.2.Spring.7) Biblical Reference Exodus 14 Key Verse 1 Peter 7:5 Key Concept God opens doors that lead me to Him Educational Objectives At the end of the class
WILL WE BE MARRIED IN THE LIFE AFTER DEATH?
 Explanatory Notes: WILL WE BE MARRIED IN THE LIFE AFTER DEATH? Series title: Topic: Marriage in heaven / heaven as a marriage Table of Contents: Message 1: What is the Life after Death Like? p. 1 Message
Explanatory Notes: WILL WE BE MARRIED IN THE LIFE AFTER DEATH? Series title: Topic: Marriage in heaven / heaven as a marriage Table of Contents: Message 1: What is the Life after Death Like? p. 1 Message
Crossing the Red Sea
 Unit 4: Lesson 3 Please note that these files are subject to copyright, and each Sunday School must own a copy of the Teaching Little Ones: Introducing the Bible CD-ROM in order to use these files. Please
Unit 4: Lesson 3 Please note that these files are subject to copyright, and each Sunday School must own a copy of the Teaching Little Ones: Introducing the Bible CD-ROM in order to use these files. Please
Bible for Children. presents THE MAN OF FIRE
 Bible for Children presents THE MAN OF FIRE Written by: Edward Hughes Illustrated by: Lazarus Adapted by: E. Frischbutter Produced by: Bible for Children www.m1914.org 2007 Bible for Children, Inc. License:
Bible for Children presents THE MAN OF FIRE Written by: Edward Hughes Illustrated by: Lazarus Adapted by: E. Frischbutter Produced by: Bible for Children www.m1914.org 2007 Bible for Children, Inc. License:
The Greeks 500 300 BC. Greek City States Early Greek sates called polis Usually built around a market or fortified hill top called an acropolis
 The Greeks 500 300 BC Greek City States Early Greek sates called polis Usually built around a market or fortified hill top called an acropolis Greek City-State Political Monarch - ruled by a single person
The Greeks 500 300 BC Greek City States Early Greek sates called polis Usually built around a market or fortified hill top called an acropolis Greek City-State Political Monarch - ruled by a single person
THEME: Jesus knows all about us and He loves us.
 Devotion NT224 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Woman at the Well THEME: Jesus knows all about us and He loves us. SCRIPTURE: John 4:1-42 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids!
Devotion NT224 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Woman at the Well THEME: Jesus knows all about us and He loves us. SCRIPTURE: John 4:1-42 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids!
Students will: Explain how ancient Egypt was united. Analyze the workings of government and the importance of religion in Egypt.
 Ancient Egypt Unit Name: Lisa Nash Grade Level: 6 Lesson Topic: The Kingdoms of Egypt Day 02, 03, & 04 of 14 Teacher s Initials: Date: November 10, 11, & 12, 2003 Instructional Goals Students will: Explain
Ancient Egypt Unit Name: Lisa Nash Grade Level: 6 Lesson Topic: The Kingdoms of Egypt Day 02, 03, & 04 of 14 Teacher s Initials: Date: November 10, 11, & 12, 2003 Instructional Goals Students will: Explain
Old Testament. Part One. Created for use with young, unchurched learners Adaptable for all ages including adults
 Old Testament Part One Created for use with young, unchurched learners Adaptable for all ages including adults Mission Arlington Mission Metroplex Curriculum Lesson 17 Page 1 M ISSION ARLINGTON MISSION
Old Testament Part One Created for use with young, unchurched learners Adaptable for all ages including adults Mission Arlington Mission Metroplex Curriculum Lesson 17 Page 1 M ISSION ARLINGTON MISSION
Joseph and the Coat of Many Colors
 Joseph and the Coat of Many Colors Teacher Pep Talk: Joseph was called a dreamer by his brothers. But are you really a dreamer just because God chooses to speak to you in a dream? Joseph s brothers hated
Joseph and the Coat of Many Colors Teacher Pep Talk: Joseph was called a dreamer by his brothers. But are you really a dreamer just because God chooses to speak to you in a dream? Joseph s brothers hated
CHRISTIAN STEWARDSHIP FOR YOUNG PEOPLE Curriculum Outline. Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 The Beginning Elias Helps a A Poor Jars of Oil
 CHRISTIAN STEWARDSHIP FOR YOUNG PEOPLE Curriculum Outline Session Title* Scripture Reference** Learning Objective*** Bible Verse To Remember Activities Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 The Beginning
CHRISTIAN STEWARDSHIP FOR YOUNG PEOPLE Curriculum Outline Session Title* Scripture Reference** Learning Objective*** Bible Verse To Remember Activities Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 The Beginning
Moses and Pharaoh (The Ten Plagues)
 Moses and Pharaoh (The Ten Plagues) Teacher Pep Talk: Stubborn Pharaoh was stubborn. In fact, he was SO stubborn that, after he hardened his heart so many times, God finally hardened it for him. God had
Moses and Pharaoh (The Ten Plagues) Teacher Pep Talk: Stubborn Pharaoh was stubborn. In fact, he was SO stubborn that, after he hardened his heart so many times, God finally hardened it for him. God had
STANDARD 3.1 Greece & Rome. STANDARD 3.2 - Mali
 2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Social Studies Standards Condensed format created by SOLpass. www.solpass.org Key: red text highlights NEW (2008 revision) content; crossout indicates content cut
2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Social Studies Standards Condensed format created by SOLpass. www.solpass.org Key: red text highlights NEW (2008 revision) content; crossout indicates content cut
Chapter 18 Introduction to. A f r i c a
 Chapter 18 Introduction to A f r i c a Ch. 18:1 Landforms & Resources 1. Africa s shape & landforms are the result of its location in the southern part of the ancient supercontinent of. Pangaea Over thousands
Chapter 18 Introduction to A f r i c a Ch. 18:1 Landforms & Resources 1. Africa s shape & landforms are the result of its location in the southern part of the ancient supercontinent of. Pangaea Over thousands
From c. A.D. 45- A.D. 116, a woman named Ban Zhao served as the imperial historian.
 The Han Dynasty A Time of Great Achievement From Chaos and Disunity to Stability and Great Works With the fall of the Qin Dynasty, China was plunged into chaos and fighting. In time, a farmer-turned soldier,
The Han Dynasty A Time of Great Achievement From Chaos and Disunity to Stability and Great Works With the fall of the Qin Dynasty, China was plunged into chaos and fighting. In time, a farmer-turned soldier,
Section #7: NOAH: A MAN OF FAITH
 21 Discussion Guide Section #7: NOAH: A MAN OF FAITH 1. How did Noah show his faith in God? 2. How specific were the instructions God gave? 3. Describe the size of the ark. Read to the Group: Since the
21 Discussion Guide Section #7: NOAH: A MAN OF FAITH 1. How did Noah show his faith in God? 2. How specific were the instructions God gave? 3. Describe the size of the ark. Read to the Group: Since the
Phillis Wheatley, 1753-1784: Early African- American Poet
 17 December 2011 voaspecialenglish.com Phillis Wheatley, 1753-1784: Early African- American Poet A rare signed edition of Phillis Wheatley s poetry from 1773 (Download an MP3 of this story at voaspecialenglish.com)
17 December 2011 voaspecialenglish.com Phillis Wheatley, 1753-1784: Early African- American Poet A rare signed edition of Phillis Wheatley s poetry from 1773 (Download an MP3 of this story at voaspecialenglish.com)
Ancient Greece: Teacher s Guide
 Ancient Greece: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Curriculum Focus: Ancient History Lesson Duration: 2 or 3 class periods Program Description Warring city-states flourished into centers of culture 2,500
Ancient Greece: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Curriculum Focus: Ancient History Lesson Duration: 2 or 3 class periods Program Description Warring city-states flourished into centers of culture 2,500
3. The Buddha followed some Hindu ideas and changed others, but he did not consider himself to be a god.
 True / False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Like the ancient Greeks, Indian astronomers proposed the theory that the Earth was round and revolved around the sun. 2. During his time
True / False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Like the ancient Greeks, Indian astronomers proposed the theory that the Earth was round and revolved around the sun. 2. During his time
Wise Men from Afar. Coloring page for each child. Glue, gold glitter, and newspaper. Costumes for skit (Optional) See skit for costume ideas.
 Wise Men from Afar Teacher Pep Talk: Say you are a wise man. You study the stars. In addition you have a working knowledge of mathematics and have read the ancient Hebrew scriptures. You know that one
Wise Men from Afar Teacher Pep Talk: Say you are a wise man. You study the stars. In addition you have a working knowledge of mathematics and have read the ancient Hebrew scriptures. You know that one
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Lesson title: Reflections of Ancient Greece Grade level: 5-6, with an adaptation for older students Subject area: Ancient History Duration: Two or three class periods Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
Lesson title: Reflections of Ancient Greece Grade level: 5-6, with an adaptation for older students Subject area: Ancient History Duration: Two or three class periods Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
The Empty Tomb. (Easter Sunday)
 The Empty Tomb! (Easter Sunday) Teacher Pep Talk: Congratulations! You get to teach children the greatest Bible story of all: The Resurrection of Jesus Christ! EASTER!! There is no greater story of God
The Empty Tomb! (Easter Sunday) Teacher Pep Talk: Congratulations! You get to teach children the greatest Bible story of all: The Resurrection of Jesus Christ! EASTER!! There is no greater story of God
Ghana: A West African Trading Empire
 Ghana: A West African Trading Empire The kingdom of Ghana lasted from 500 C.E. to the 11 th century C.E. The kingdom arose from the Sahel of Africa and spread to the valley between the Senegal and Niger
Ghana: A West African Trading Empire The kingdom of Ghana lasted from 500 C.E. to the 11 th century C.E. The kingdom arose from the Sahel of Africa and spread to the valley between the Senegal and Niger
Parable of The Prodigal Son
 Parable of The Prodigal Son Teacher Pep Talk: Children need to know that they are loved unconditionally. In fact, we all need to know it! In the Parable of the Prodigal Son, Jesus assures us that God will
Parable of The Prodigal Son Teacher Pep Talk: Children need to know that they are loved unconditionally. In fact, we all need to know it! In the Parable of the Prodigal Son, Jesus assures us that God will
In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
 Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
Name: Date: Period: Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1 - Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the African kingdom of Kush. Kush was located on the Nile River, to the south of Egypt.
Rosa Parks. Stop and think: Have you ever been fed up with a situation? What did you do? How did things change?
 Rosa Parks l Reading Comprehension l 1 Read the paragraphs. Stop and think as you read. Stop and Think Good readers are active readers. Good readers stop and think about what they are reading. Active reading
Rosa Parks l Reading Comprehension l 1 Read the paragraphs. Stop and think as you read. Stop and Think Good readers are active readers. Good readers stop and think about what they are reading. Active reading
Guided Reading Level Ī - -
 A Friend to the Pilgrims Guided Reading Level Ī - - No part of this publication may be reproduced in whole or in part, or stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic,
A Friend to the Pilgrims Guided Reading Level Ī - - No part of this publication may be reproduced in whole or in part, or stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic,
Africa Before the Slave Trade
 Africa Before the Slave Trade Overview of African Kingdoms Ghana and Songhai Ghana (Wagadu) is the earliest known empire of the western Sudan, came into the history books around the eighth century but
Africa Before the Slave Trade Overview of African Kingdoms Ghana and Songhai Ghana (Wagadu) is the earliest known empire of the western Sudan, came into the history books around the eighth century but
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE.
 SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
SSWH3 THE STUDENT WILL EXAMINE THE POLITICAL, PHILOSOPHICAL, AND CULTURAL INTERACTION OF CLASSICAL MEDITERRANEAN SOCIETIES FROM 700 BCE TO 400 CE. A. COMPARE THE ORIGINS AND STRUCTURE OF THE GREEK POLIS,
CHINA OVERVIEW: A BRIEF HISTORY OF CHINESE DYNASTIES. Student Handouts, Inc.
 CHINA OVERVIEW: A BRIEF HISTORY OF CHINESE DYNASTIES Student Handouts, Inc. GEOGRAPHY OF CHINA Larger than the United States Climate varies North Temperate and cold South Subtropical Erosion Floods and
CHINA OVERVIEW: A BRIEF HISTORY OF CHINESE DYNASTIES Student Handouts, Inc. GEOGRAPHY OF CHINA Larger than the United States Climate varies North Temperate and cold South Subtropical Erosion Floods and
Mansa Musa s Pilgrimage Grade Seven
 Ohio Standards Connection: Geography Benchmark A Identify on a map the location of major physical and human features of each continent. Indicator 2 On a map, identify places related to the historical events
Ohio Standards Connection: Geography Benchmark A Identify on a map the location of major physical and human features of each continent. Indicator 2 On a map, identify places related to the historical events
the call of moses after before
 the call of moses after before The Moses Series Day 1: The Call of Moses Sketchboard title: "God chose a leader" Text: Exodus 1-4 Introduction: Have you ever been asked to do something you didn't want
the call of moses after before The Moses Series Day 1: The Call of Moses Sketchboard title: "God chose a leader" Text: Exodus 1-4 Introduction: Have you ever been asked to do something you didn't want
The Early Church Peter Preaches After Denying
 The Early Church Peter Preaches After Denying Lesson 1 LESSON OVERVIEW Key Point: Jesus makes a difference in people s lives. Repeat this phrase throughout the lesson. Bible Story: Mark 14:66-72 Challenge
The Early Church Peter Preaches After Denying Lesson 1 LESSON OVERVIEW Key Point: Jesus makes a difference in people s lives. Repeat this phrase throughout the lesson. Bible Story: Mark 14:66-72 Challenge
Bible for Children. presents JOSHUA TAKES CHARGE
 Bible for Children presents JOSHUA TAKES CHARGE Written by: Edward Hughes Illustrated by: Janie Forest Adapted by: Ruth Klassen Produced by: Bible for Children www.m1914.org 2007 Bible for Children, Inc.
Bible for Children presents JOSHUA TAKES CHARGE Written by: Edward Hughes Illustrated by: Janie Forest Adapted by: Ruth Klassen Produced by: Bible for Children www.m1914.org 2007 Bible for Children, Inc.
Mesopotamia. The 'Ram in a Thicket' From Ur, southern Iraq, 2600-2400 BC. Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2
 The 'Ram in a Thicket' From Ur, southern Iraq, 2600-2400 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities
The 'Ram in a Thicket' From Ur, southern Iraq, 2600-2400 BC Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2 Contents Before your visit Background information Resources Gallery information Preliminary activities
The Golden Calf. Pre-Session Warm Up. Opening Prayer. Memory Verse. Lesson. Moses Lesson #13 Page 69
 Pre-Session Warm Up The Golden Calf (Exodus 19-32) Imagine being invited to visit a king in his palace. How would you act? Would you run into the throne room, laughing and talking? Would you ignore the
Pre-Session Warm Up The Golden Calf (Exodus 19-32) Imagine being invited to visit a king in his palace. How would you act? Would you run into the throne room, laughing and talking? Would you ignore the
Currency and Exchange Rates
 Grade Five Currency and Exchange Rates Overview Students share the book The Story of Money, by Betsy Maestro, to learn about exchange and barter, the functions of money, currency, and spending money. Students
Grade Five Currency and Exchange Rates Overview Students share the book The Story of Money, by Betsy Maestro, to learn about exchange and barter, the functions of money, currency, and spending money. Students
HEAVEN, GOD S BEAUTIFUL HOME
 Bible for Children presents HEAVEN, GOD S BEAUTIFUL HOME Written by: E. Duncan Hughes Illustrated by: Lazarus Adapted by: Sarah S. Produced by: Bible for Children www.m1914.org BFC PO Box 3 Winnipeg, MB
Bible for Children presents HEAVEN, GOD S BEAUTIFUL HOME Written by: E. Duncan Hughes Illustrated by: Lazarus Adapted by: Sarah S. Produced by: Bible for Children www.m1914.org BFC PO Box 3 Winnipeg, MB
The Ten Commandments
 The Ten Commandments Teacher Pep Talk: God had miraculously led His people (the Israelites) out of Egypt and safely through the Red Sea. Now at long last the Israelites had arrived at the mountain of God.
The Ten Commandments Teacher Pep Talk: God had miraculously led His people (the Israelites) out of Egypt and safely through the Red Sea. Now at long last the Israelites had arrived at the mountain of God.
TEST BOOK AND ANSWER KEY
 The Story of the World TEST BOOK AND ANSWER KEY Volume 1: Ancient Times Peace Hill Press Charles City, Virginia www.peacehillpress.com How to Use These Tests and Answer Key These Tests and their accompanying
The Story of the World TEST BOOK AND ANSWER KEY Volume 1: Ancient Times Peace Hill Press Charles City, Virginia www.peacehillpress.com How to Use These Tests and Answer Key These Tests and their accompanying
Benchmark C Describe the characteristics of feudal societies and the transition to the Renaissance and Reformation in Europe.
 Feudalism in Japan and Europe Connection: History Benchmark C Describe the characteristics of feudal societies and the transition to the Renaissance and Reformation in Europe. Indicator 3 Describe the
Feudalism in Japan and Europe Connection: History Benchmark C Describe the characteristics of feudal societies and the transition to the Renaissance and Reformation in Europe. Indicator 3 Describe the
LESSON TITLE: Jesus Heals Blind Bartimaeus
 Devotion NT257 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: Jesus Heals Blind Bartimaeus THEME: Jesus always has time for us! SCRIPTURE: Mark 10:46-52 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids!
Devotion NT257 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: Jesus Heals Blind Bartimaeus THEME: Jesus always has time for us! SCRIPTURE: Mark 10:46-52 Dear Parents Welcome to Bible Time for Kids!
Wall of China Project
 Target Age: K-3 rd Grades Wall of China Project Skills Used Following directions, introduction to fractions, measuring with a ruler using half-inches, 2-D to 3-D concept transfer, creative interpretation,
Target Age: K-3 rd Grades Wall of China Project Skills Used Following directions, introduction to fractions, measuring with a ruler using half-inches, 2-D to 3-D concept transfer, creative interpretation,
THE FORGIVING FATHER
 BOOK 1, PART 3, LESSON 4 THE FORGIVING FATHER THE BIBLE: Luke 15:11-32 THEME: We can discover what Jesus wants us to do and be by hearing the parables Jesus told. PREPARING FOR THE LESSON MAIN IDEA: Jesus
BOOK 1, PART 3, LESSON 4 THE FORGIVING FATHER THE BIBLE: Luke 15:11-32 THEME: We can discover what Jesus wants us to do and be by hearing the parables Jesus told. PREPARING FOR THE LESSON MAIN IDEA: Jesus
THE JOURNEY TO JERUSALEM
 BOOK 3, PART 1, LESSON 1 THE JOURNEY TO JERUSALEM THE BIBLE: Luke 19:29-40 THEME: We remember that Jesus taught about love and showed love in everything he did. During Lent and Easter, we remember and
BOOK 3, PART 1, LESSON 1 THE JOURNEY TO JERUSALEM THE BIBLE: Luke 19:29-40 THEME: We remember that Jesus taught about love and showed love in everything he did. During Lent and Easter, we remember and
Bible for Children. presents WISE KING SOLOMON
 Bible for Children presents WISE KING SOLOMON Written by: Edward Hughes Illustrated by: Lazarus Adapted by: Ruth Klassen Produced by: Bible for Children www.m1914.org 2007 Bible for Children, Inc. License:
Bible for Children presents WISE KING SOLOMON Written by: Edward Hughes Illustrated by: Lazarus Adapted by: Ruth Klassen Produced by: Bible for Children www.m1914.org 2007 Bible for Children, Inc. License:
The Fruit of the Spirit is Love
 The Fruit of the Spirit is Love Pre-Session Warm Up (Galatians 5:22-23) Today we are going to learn more about the fruit of the Spirit called, Love. What do you think of when you hear the word love? A
The Fruit of the Spirit is Love Pre-Session Warm Up (Galatians 5:22-23) Today we are going to learn more about the fruit of the Spirit called, Love. What do you think of when you hear the word love? A
Soul-Winning Commitment Day. Sunday School/ Small Group Lessons. Soul-Winning. Commitment Day
 Sunday School/ Small Group Lessons Soul-Winning Commitment Day Purpose of Lesson: This guide is for the purpose of preparing older children through adult Sunday school members to understand the importance
Sunday School/ Small Group Lessons Soul-Winning Commitment Day Purpose of Lesson: This guide is for the purpose of preparing older children through adult Sunday school members to understand the importance
GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE - PAGE 1 of 19 THIS IS GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE CHARACTERISTICS (ELEMENTS) OF CIVILIZATIONS
 GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE - PAGE 1 of 19 THIS IS GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE THE TOPICS OF STUDY IN THIS PACKET ARE: THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION CHARACTERISTICS (ELEMENTS) OF
GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE - PAGE 1 of 19 THIS IS GLOBAL REGENTS REVIEW PACKET NUMBER THREE THE TOPICS OF STUDY IN THIS PACKET ARE: THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION CHARACTERISTICS (ELEMENTS) OF
THEME: Jesus sent the Holy Spirit to indwell and empower us.
 Devotion NT285 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Day of Pentecost THEME: Jesus sent the Holy Spirit to indwell and empower us. Dear Parents SCRIPTURE: Acts 2:1-41 Dear Parents, Welcome
Devotion NT285 CHILDREN S DEVOTIONS FOR THE WEEK OF: LESSON TITLE: The Day of Pentecost THEME: Jesus sent the Holy Spirit to indwell and empower us. Dear Parents SCRIPTURE: Acts 2:1-41 Dear Parents, Welcome
