Interactive Notebook Packet. Resources for a Middle School Math Notebook. Recommended Shrink to % on Xerox Machine
|
|
|
- Wesley Sparks
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Interactive Notebook Packet Resources for a Middle School Math Notebook Compiled and Created by Lauren Kubin Recommended Shrink to % on Xerox Machine
2 Math Interactive Notebook Resources Table of Contents Original New Title and Notes Page # Page # 1 Fold and Glue to front cover to create a Pocket 2 Cover Sheet First and Last Name Class Period Teacher School Year Commonly Used Websites and Login Information 3 I What is the Math Interactive Notebook? 4 II Right Side versus Left Side 5 III Notebook Grading Rubric 6 IV Cornell Notes How-To and Tips 7 V Blooms Taxonomy and Costa s Level of Questioning Verbs 8 VI Blooms Taxonomy and Costa s Level of Questioning Sentence Stems 9 VII UPS check 10 VIII Operation Key Words and Symbols 11 IX Place Value Chart and Griddable 12 X 13 XI Table of Contents 14 XII Table of Contents continued 15 XIII Table of Contents continued 16 XIV Table of Contents continued 17 XV Table of Contents continued 18 XVI Table of Contents continued 19 XVII Table of Contents continued 20 XVIII Table of Contents continued 21 XIX Table of Contents continued 22 XX Table of Contents continued 23 XXI Table of Contents continued 24 XXII Table of Contents continued 25 XXIII Table of Contents continued 26 XXIV Table of Contents continued 27 XXV Table of Contents continued 28 1 (Begin Class Notebook of Notetaking) Created by Lauren Kubin
3 Math Interactive Notebook For the entire school year, we will be using an Interactive Notebook. The interactive notebook is more than a notebook in which to take notes. It is a way of collecting and processing information. It will replace your math textbook. The Interactive Notebook uses a right side and left side to help you organize your learning. The right page includes traditional class assignments: notes, worksheets, etc. The left side is a place for you to process that information. Purpose: focus on today s activity Examples: pre-test, quick-write, demonstration, T-chart Purpose: reflect or apply today s activity Examples: content or lab questions, quick-write, summary, diagram, graph Interactive Cafe Purpose: information from today s activity (learning) Examples: textbook or lecture notes, vocabulary, lab procedure & data, worksheet, concept map Implementation Notebooks can be kept in your binder or stored in the classroom. Bring it to class every day. It will not be in your best interest to lose it. Number the pages sequentially. Do not remove any pages. Both right and left pages should be numbered. It is important that all of us have the same information on the same page. The first pages are reserved for a table of contents, and instructions. Other information will be included as appendices. Use color to help organize your information. Handouts, foldables and other papers should be glued or taped in place. No staples. You will need other supplies: markers, glue stick, tape, ruler, pencils, colored pencils Notebooks will be graded weekly using self, peer and teacher checklists. Compiled and Created by Lauren Kubin
4 Interactive Notebooks are characterized by RIGHT SIDE Input and LEFT SIDE Output! Left Side Characteristics Colorful, creative, unique to student, demonstrates understanding, entered on even numbered pages, date and subject title at top of each page Right Side Characteristics Content and concepts of curriculum, notes in Cornell style, teacher or text driven, entered on odd numbered pages, date and subject title at top of page Left Side Examples Poems Vocabulary Cartoons Word Puzzles Analogies Graphics Sketches Practice problems or examples Paraphrases Pictures Articles Lyrics to a song Web information Memory tips and techniques Brainstorming Concept maps/flow charts Study plan Reflections Goal setting Communication with parent/teacher Right Side Examples Lecture Notes Daily and homework assignments Tests Quizzes Lab activities Hand outs Vocabulary Assignments Focus or warm-up activities Foldables Pre-lab notes Book notes Graphic organizers Film notes An Interactive Notebook gives students a place to: Set Goals Plan Study Strategies Document Learning Track Success
5 Output Excellent All work is: Finished Thoughtful Making connections Clear Creative Interactive Notebook Rubric Satisfactory Majority of work is: Finished Thoughtful Making connections Clear Creative Need Improvement Some work is: Finished Thoughtful Making connections Clear Creative Weak Little/No work is: Finished Thoughtful Making connections Clear Creative Points Input All work is: Finished Thoughtful Thorough Consistently done with good effort Majority of work is: Finished Thoughtful Thorough Consistently done with good effort Some work is: Finished Thoughtful Thorough Consistently done with good effort Little/No work is: Finished Thoughtful Thorough Consistently done with good effort Points Organization and Neatness Pages are numbered Table of Contents complete with titles Work is neat and legible Contents is organized and in its proper place Less than 4 items are missing. Five to Eight items are missing. Nine or more items are missing. Points Teacher Comments: Score: Rubric Points: 50 = %
6 Student Handout/Display Master 1.1b Taking Cornell Notes Some Tips Level 2: sort, infer, analyze, sequence, organize, solve, explain, compare, contrast, classify, isolate, characterize, make analogies. Level 3: conclude, criticize, reorganize, justify, judge, estimate, predict, speculate, make a model, extrapolate, apply a principle, interpret, hypothesize, if/then Topic Note-taking Strategies Name: Class: Period: Date: Study/Review Questions How can you use the speaker s style to identify important points? How can you keep-up with the speaker? Become familiar with the speaker s style. Listen for important points that might be emphasized when the speaker: Pauses or slows down Repeats a point Modulates the volume of her/his voice Uses introductory phrases (e.g., The four main points are or Note the relationship ) Writes on the board Gestures or uses visual aids Write only the important ideas such as name, examples, terms, definitions, effects, evaluations, cross references: make it brief, but clear. Use abbreviations for familiar words. Speaker says: An altitude of a triangle is the perpendicular segment from a vertex to the opposite side or the line that contains the opposite side. An altitude can lie inside, on, or outside the triangle. Notes say: Altitude of is from vertex to opp side or line containg opp side. Can be inside, on or outside How should you use your notes to review? Use notes to review: Develop study questions and identify the main ideas. Fill in details for clarity. Look up and add to the definitions of new words/terminology. Identify information that is unclear and/or questions that need to be answered; write and mark them so they can be easily found; get answers to the questions from other students and/or the speaker. Add symbols to highlight important ideas and key words. Delete irrelevant information. Review the overall organization of the material: add symbols to make the organization clear or rewrite for clarity as needed. Write a summary of the significant ideas. Connections, Summary, Reflection, Analysis: Three important note-taking strategies are reviewed in the notes. Identifying important points and main ideas, using abbreviations to paraphrase information provided during the class and the use of notes for review are outlined. The important cues in identifying main points and the use of questions to help with review are particularly helpful strategies as is the writing of summaries. 4 The Write Path I: Mathematics Student Guide
7 penthouse A Three Story Intellect! The Student will Knowledge (Remembering) Learn specific facts, ideas, vocabulary; remembering/recalling information or specific facts. BLOOM S TAXONOMY and Costa s Levels of Questioning Comprehension (Understanding) Ability to grasp the meaning of material; communicate knowledge; understanding information without relating it to other material. Application (Applying) Ability to use learned material in new and concrete situations; use learned knowledge and interpret previous situations. ground floor Analysis (Analyzing) Ability to break down material into its component parts and perceive interrelationships. basement Synthesis (Creating) Ability to put parts together to form a new whole; use elements in new patterns and relationships. Evaluation (Evaluating) Ability to judge the value of material (statement, novel, poem, report, etc.) for a given purpose; judgment is based on given criteria. Introduction of knowledge Level One the basement Practice knowledge learned Level Two the ground floor Demonstrates mastery of knowledge learned Level Three the penthouse By doing the following collect, copy, define, describe, examine, find, group, identify, indicate, label, list, locate, match, name, omit, observe, point, provide, quote, read, recall, recite, recognize, repeat, reproduce, say, select, sort, spell, state, tabulate, tell, touch, underline, who, when, where, what alter, associate calculate, categorize, change, communicate, convert, distinguish, expand, explain, inform, name alternatives, outline, paraphrase, rearrange, reconstruct, relate, restate (own words), summarize, tell the meaning of, translate, understand, verbalize, write By doing the following acquire, adopt, apply, assemble, capitalize, construct, consume, demonstrate, develop, discuss, experiment, formulate, manipulate, organize, relate, report, search, show, solve novel problems, tell consequences, try, use, utilize analyze, arrange, break down, categorize, classify, compare, contrast, deduce, determine, diagram, differentiate, discuss causes, dissect, distinguish, give reasons, order, separate, sequence, survey, take apart, test for, why By doing the following alter, build, combine, compose, construct, create, develop, estimate, form a new, generate, hypothesize, imagine, improve, infer, invent, modify, plan, predict, produce, propose, reorganize, rewrite, revise, simplify, synthesize appraise, argue, assess, challenge, choose, conclude, criticize, critique, debate, decide, defend, discriminate, discuss, document, draw conclusions, editorialize, evaluate, grade, interpret, judge, justify, prioritize, rank, rate, recommend, reject, support, validate, weigh Compiled and Created by Lauren Kubin
8 Knowledge Level 1A (Remembering) Comprehension Level 1B (Understanding) Application Level 2A (Applying) Analysis Level 2B (Analyzing) Synthesis Level 3A (Creating) Evaluation Level 3B (Evaluating) Skills Demonstrated: Skills Demonstrated: Skills Demonstrated: Skills Demonstrated: Skills Demonstrated: Skills Demonstrated: Observation and recall of information Knowledge of dates, events, places Knowledge of major ideas Master of subject matter Understanding information Grasp meaning Translate knowledge into new context Interpret facts, compare, contrast Order, group, infer causes Predict consequences Use information Use methods, concepts, theories in new situations Solve problems using required skills or knowledge Seeing patterns Organization of parts Recognition of hidden meanings Identification of components Use old ideas to create new ones Generalize from given facts Relate knowledge from several areas Predict, draw conclusions Compare and discriminate between ideas Assess value of theories, presentations Make choices based on reasoned argument What is? How is? Where is? When did happen? How did? Why did? How would you describe? When did? Can you recall? How would you show? Can you select? Who were the main...? Can you list three? Which one? Who was? How would you classify the type of? How would you compare/contrast? Will you state or interpret in your own words? How would you rephrase the meaning? What facts or ideas show? What is the main idea of? Which statements support? Can you explain what is happening what is meant? What can you say about? Which is the best answer? How would you summarize? How would you use? What examples can you find to? How would you solve using what you have learned? How would you organize to show? How would you show your understanding? What approach would you use to? How would you apply what you learned to develop? What other way would you plan to? What would result if? Can you make use of the facts to? What elements would you choose to change? What facts would you select to show? What questions would you ask in an interview with? What are the parts of? How is related to? Why do you think? What is the theme? What motive is there? Can you list the parts? What inference can you make? What conclusions can you draw? How would you classify? How would you categorize? Can you identify the different parts? What evidence can you find? What is the relationship between? Can you make a distinction between? What is the function of? What ideas justify? How would you estimate the results for? What facts can you compile? Can you construct a model that would change? Can you think of an original way for the? Do you agree with the actions? with the outcomes.? What is your opinion of? How would you prove? Disprove? Can you assess the value or importance of? Would it be better if? Why did they (the character) choose? What would you recommend? How would you rate the? What would you cite to defend the actions? How would you evaluate? How could you determine? What choice would you have? Do you agree with the actions? With the outcomes? What is your opinion of? How would you prove? Disprove? Can you assess the value or importance of? Would it be better if? Why did they (the character) choose? What would you recommend? How would you evaluate? How could you determine? What choice would you have made? What would you select? How would you prioritize? What judgment would you make about? Based on what you know, how would you explain? What information would you use to support the view? How would you justify? What data was used to make the conclusion? Why was it better that? How would you prioritize the facts? How would you compare the ideas? Compiled and Created by Lauren Kubin
9 Steps I must follow on EVERY WORD PROBLEM UPS 1. Read the problem, sentence by sentence. 2. Write what you know and what you need to know from the word problem. (UNDERSTAND) Take apart each sentence and write only what is important to know and what you need to know. (WIK/WINK) 3. Write a plan of action to solve the problem. (PLAN) What type of question is it? What TEKS are involved? What are the steps you are going to use to solve the problem? 4. Solve the problem using your plan. (SOLVE) 5. Check: Is your answer Reasonable? ( ) Justify and Explain your answer in complete sentences. TEKS: 6.1 B Adopted 2012 by TEA Created by Miss Lauren Kubin
10 Common Operation Key Words Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division 1. Sum 2. Altogether 3. More 4. Combined 5. Increase 6. Plus 7. Total 8. Both 9. In all 10. Received 1. Difference 2. Remains 3. How much more 4. Take away 5. Less than 6. Remainder 7. Fewer 8. Decrease 9. Minus 1. Multiply by 2. Twice 3. Product 4. Most 5. Each 6. Total Equally 2. Split 3. Each 4. Goes into 5. Cut into 6. Quotient Deposit 12. Gone up 13. Wins 14. Gain 15. Rises Withdraws 11. Looses 12. A loss of 13. Spent Symbol (s) Symbol (s) Symbol (s) Symbol (s) + X ab 2(3) or 4*6 or / Created by Lauren Kubin
11 Integer (Positive or Negative) Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones Decimal Tenths Hundredths Created by Lauren Kubin
12 Table of Contents Date Left Side Page # Date Right Side Page # Created by Lauren Kubin
13 Name: Multiplication Table Super Teacher Worksheets -
14 STAAR GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS REFERENCE MATERIALS STAAR State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness AREA Triangle A = 1 h 2 b Rectangle or parallelogram A = bh Trapezoid A = 1 (b + b h VOLUME Rectangular prism V = Bh ) 0 Inches
15 STAAR GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS REFERENCE MATERIALS Centimeters LENGTH Customary Metric 1 mile (mi) = 1,760 yards (yd) 1 kilometer (km) = 1,000 meters (m) 1 yard (yd) = 3 feet (ft) 1 meter (m) = 100 centimeters (cm) 1 foot (ft) = 12 inches (in.) 1 centimeter (cm) = 10 millimeters (mm) VOLUME AND CAPACITY Customary Metric 1 gallon (gal) = 4 quarts (qt) 1 liter (L) = 1,000 milliliters (ml) 1 quart (qt) = 2 pints (pt) 1 pint (pt) = 2 cups (c) 1 cup (c) = 8 fluid ounces (fl oz) WEIGHT AND MASS Customary Metric 1 ton (T) = 2,000 pounds (lb) 1 kilogram (kg) = 1,000 grams (g) 1 pound (lb) = 16 ounces (oz) 1 gram (g) = 1,000 milligrams (mg)
16 facebook Status Updates Mother s name, Phone number, and Occupation. Father s name, Phone number and Occupation. Guardian s name, Phone number and Occupation. Last year I went to school at... Friends (76) See All I live in a house with... First Name My favorite thing to do in my free time is... Last Name When I grow up, I want to... Name I Go By My Birthday Favorite Book Favorite Subject Favorite Teacher Favorite Food Best Friends Favorite Sport 6th Grade Math Teacher The clubs/sports I want to participate in are... 3 things that you should know about me are... My address is... Do you have a computer at home? Do you have access to the internet at home? Math is... I learn best from teachers that... I struggle to learn from teachers that... This year in math, I hope to...
17 Interactive Notebook and Parent Communication Math Student: Each 6 weeks, schedule a time to meet with your parent or significant adult. Show them your INB and let them know what is going on in class. Write down a few comments made. Dear Parent or Significant Adult, Your student is keeping an Interactive Notebook in Mathematics. Please look through it and respond to the following questions. Thank you for supporting our science program. 1) The work I found most interesting was.. because. 2) What does the notebook tell you about your student s learning habits? 3) Do you have any comments, questions, or concerns? Print Name Signature Student s Name Date
Converting Units of Measure Measurement
 Converting Units of Measure Measurement Outcome (lesson objective) Given a unit of measurement, students will be able to convert it to other units of measurement and will be able to use it to solve contextual
Converting Units of Measure Measurement Outcome (lesson objective) Given a unit of measurement, students will be able to convert it to other units of measurement and will be able to use it to solve contextual
Exhibit memory of previously-learned materials by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. Key Words
 The Six Levels of Questioning Level 1 Knowledge Exhibit memory of previously-learned materials by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. who what why when where which omit choose find how
The Six Levels of Questioning Level 1 Knowledge Exhibit memory of previously-learned materials by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. who what why when where which omit choose find how
Measurement. Customary Units of Measure
 Chapter 7 Measurement There are two main systems for measuring distance, weight, and liquid capacity. The United States and parts of the former British Empire use customary, or standard, units of measure.
Chapter 7 Measurement There are two main systems for measuring distance, weight, and liquid capacity. The United States and parts of the former British Empire use customary, or standard, units of measure.
Bloom s Taxonomy. List the main characteristics of one of the main characters in a WANTED poster.
 Bloom s Taxonomy Bloom s Taxonomy provides an important framework for teachers to use to focus on higher order thinking. By providing a hierarchy of levels, this taxonomy can assist teachers in designing
Bloom s Taxonomy Bloom s Taxonomy provides an important framework for teachers to use to focus on higher order thinking. By providing a hierarchy of levels, this taxonomy can assist teachers in designing
Writing learning objectives
 Writing learning objectives This material was excerpted and adapted from the following web site: http://www.utexas.edu/academic/diia/assessment/iar/students/plan/objectives/ What is a learning objective?
Writing learning objectives This material was excerpted and adapted from the following web site: http://www.utexas.edu/academic/diia/assessment/iar/students/plan/objectives/ What is a learning objective?
Objective To introduce a formula to calculate the area. Family Letters. Assessment Management
 Area of a Circle Objective To introduce a formula to calculate the area of a circle. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game Family Letters Assessment
Area of a Circle Objective To introduce a formula to calculate the area of a circle. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit Algorithms Practice EM Facts Workshop Game Family Letters Assessment
MEASUREMENTS. U.S. CUSTOMARY SYSTEM OF MEASUREMENT LENGTH The standard U.S. Customary System units of length are inch, foot, yard, and mile.
 MEASUREMENTS A measurement includes a number and a unit. 3 feet 7 minutes 12 gallons Standard units of measurement have been established to simplify trade and commerce. TIME Equivalences between units
MEASUREMENTS A measurement includes a number and a unit. 3 feet 7 minutes 12 gallons Standard units of measurement have been established to simplify trade and commerce. TIME Equivalences between units
Scope and Sequence KA KB 1A 1B 2A 2B 3A 3B 4A 4B 5A 5B 6A 6B
 Scope and Sequence Earlybird Kindergarten, Standards Edition Primary Mathematics, Standards Edition Copyright 2008 [SingaporeMath.com Inc.] The check mark indicates where the topic is first introduced
Scope and Sequence Earlybird Kindergarten, Standards Edition Primary Mathematics, Standards Edition Copyright 2008 [SingaporeMath.com Inc.] The check mark indicates where the topic is first introduced
Conversion Formulas and Tables
 Conversion Formulas and Tables Metric to English, Introduction Most of the world, with the exception of the USA, uses the metric system of measurements exclusively. In the USA there are many people that
Conversion Formulas and Tables Metric to English, Introduction Most of the world, with the exception of the USA, uses the metric system of measurements exclusively. In the USA there are many people that
Music Makers. paper clips
 Fifth Grade Science Design Brief Music Makers Background: We know that sound is a form of energy produced and transmitted by vibrating matter and that pitch is determined by the frequency of a vibrating
Fifth Grade Science Design Brief Music Makers Background: We know that sound is a form of energy produced and transmitted by vibrating matter and that pitch is determined by the frequency of a vibrating
Measurement: Converting Distances
 Measurement: Converting Distances Measuring Distances Measuring distances is done by measuring length. You may use a different system to measure length differently than other places in the world. This
Measurement: Converting Distances Measuring Distances Measuring distances is done by measuring length. You may use a different system to measure length differently than other places in the world. This
REVIEW SHEETS INTRODUCTORY PHYSICAL SCIENCE MATH 52
 REVIEW SHEETS INTRODUCTORY PHYSICAL SCIENCE MATH 52 A Summary of Concepts Needed to be Successful in Mathematics The following sheets list the key concepts which are taught in the specified math course.
REVIEW SHEETS INTRODUCTORY PHYSICAL SCIENCE MATH 52 A Summary of Concepts Needed to be Successful in Mathematics The following sheets list the key concepts which are taught in the specified math course.
Healthcare Math: Using the Metric System
 Healthcare Math: Using the Metric System Industry: Healthcare Content Area: Mathematics Core Topics: Using the metric system, converting measurements within and between the metric and US customary systems,
Healthcare Math: Using the Metric System Industry: Healthcare Content Area: Mathematics Core Topics: Using the metric system, converting measurements within and between the metric and US customary systems,
Alignment of Taxonomies
 Alignment of Taxonomies Bloom s Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain Bloom s Taxonomy Cognitive Domain Revised Cognitive Demand Mathematics Cognitive Demand English Language Arts Webb s Depth of Knowledge Knowledge
Alignment of Taxonomies Bloom s Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain Bloom s Taxonomy Cognitive Domain Revised Cognitive Demand Mathematics Cognitive Demand English Language Arts Webb s Depth of Knowledge Knowledge
TAXONOMY OF EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (Excerpts from Linn and Miller Measurement and Assessment in Teaching, 9 th ed)
 TAXONOMY OF EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (Excerpts from Linn and Miller Measurement and Assessment in Teaching, 9 th ed) Table 1 Major categories in the cognitive domain of the taxonomy of educational objectives
TAXONOMY OF EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (Excerpts from Linn and Miller Measurement and Assessment in Teaching, 9 th ed) Table 1 Major categories in the cognitive domain of the taxonomy of educational objectives
MEASUREMENT. Historical records indicate that the first units of length were based on people s hands, feet and arms. The measurements were:
 MEASUREMENT Introduction: People created systems of measurement to address practical problems such as finding the distance between two places, finding the length, width or height of a building, finding
MEASUREMENT Introduction: People created systems of measurement to address practical problems such as finding the distance between two places, finding the length, width or height of a building, finding
Quarter One: August-October
 Quarter One: August-October (Chapters 1 3, 5-6, 10) August - December Quarterly Addition facts with sums through 20 General Math Content 1. Write sums through 20. 1. Choose and enter the appropriate answer.
Quarter One: August-October (Chapters 1 3, 5-6, 10) August - December Quarterly Addition facts with sums through 20 General Math Content 1. Write sums through 20. 1. Choose and enter the appropriate answer.
Handout Unit Conversions (Dimensional Analysis)
 Handout Unit Conversions (Dimensional Analysis) The Metric System had its beginnings back in 670 by a mathematician called Gabriel Mouton. The modern version, (since 960) is correctly called "International
Handout Unit Conversions (Dimensional Analysis) The Metric System had its beginnings back in 670 by a mathematician called Gabriel Mouton. The modern version, (since 960) is correctly called "International
High Flying Balloons
 Second Grade Science Design Brief High Flying Balloons Background: In our study of science we have been investigating the three stages of matter: solids, liquids and gases. You will use your knowledge
Second Grade Science Design Brief High Flying Balloons Background: In our study of science we have been investigating the three stages of matter: solids, liquids and gases. You will use your knowledge
Resources for Writing Program Learning Outcomes
 Resources for Writing Program Learning Outcomes Supplementary Materials for Writing and Revising Learning Outcomes Workshop Presented Jointly by TLA and Student Affairs LEVEL OF SPECIFICITY AND REACH Learning
Resources for Writing Program Learning Outcomes Supplementary Materials for Writing and Revising Learning Outcomes Workshop Presented Jointly by TLA and Student Affairs LEVEL OF SPECIFICITY AND REACH Learning
Fourth Grade Math Standards and "I Can Statements"
 Fourth Grade Math Standards and "I Can Statements" Standard - CC.4.OA.1 Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 x 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and
Fourth Grade Math Standards and "I Can Statements" Standard - CC.4.OA.1 Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 x 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and
Webb s Depth of Knowledge Guide
 Webb Webb s Depth of Knowledge Guide Career and Technical Education Definitions 2009 1 H T T P : / / WWW. MDE. K 12.MS. US H T T P : / / R E D E S I G N. R C U. M S S T A T E. EDU 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview...
Webb Webb s Depth of Knowledge Guide Career and Technical Education Definitions 2009 1 H T T P : / / WWW. MDE. K 12.MS. US H T T P : / / R E D E S I G N. R C U. M S S T A T E. EDU 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview...
Cognitive Domain (Bloom)
 Bloom s Taxonomy So what exactly is this thing called Bloom s Taxonomy, and why do education people keep talking about it? Well, Bloom was the head of a group in the 1950 s and 1960 s that created the
Bloom s Taxonomy So what exactly is this thing called Bloom s Taxonomy, and why do education people keep talking about it? Well, Bloom was the head of a group in the 1950 s and 1960 s that created the
Fractional Part of a Set
 Addition and Subtraction Basic Facts... Subtraction Basic Facts... Order in Addition...7 Adding Three Numbers...8 Inverses: Addition and Subtraction... Problem Solving: Two-Step Problems... 0 Multiplication
Addition and Subtraction Basic Facts... Subtraction Basic Facts... Order in Addition...7 Adding Three Numbers...8 Inverses: Addition and Subtraction... Problem Solving: Two-Step Problems... 0 Multiplication
Subject: Math Grade Level: 5 Topic: The Metric System Time Allotment: 45 minutes Teaching Date: Day 1
 Subject: Math Grade Level: 5 Topic: The Metric System Time Allotment: 45 minutes Teaching Date: Day 1 I. (A) Goal(s): For student to gain conceptual understanding of the metric system and how to convert
Subject: Math Grade Level: 5 Topic: The Metric System Time Allotment: 45 minutes Teaching Date: Day 1 I. (A) Goal(s): For student to gain conceptual understanding of the metric system and how to convert
5. Formally register for INS299 for the number of semester hours indicated on your contract.
 HONORS INDEPENDENT STUDY GUIDELINES: According to the Lake Land College catalog course description, independent study is designed to permit the student to pursue a course of study not typically available
HONORS INDEPENDENT STUDY GUIDELINES: According to the Lake Land College catalog course description, independent study is designed to permit the student to pursue a course of study not typically available
BPS Math Year at a Glance (Adapted from A Story Of Units Curriculum Maps in Mathematics K-5) 1
 Grade 4 Key Areas of Focus for Grades 3-5: Multiplication and division of whole numbers and fractions-concepts, skills and problem solving Expected Fluency: Add and subtract within 1,000,000 Module M1:
Grade 4 Key Areas of Focus for Grades 3-5: Multiplication and division of whole numbers and fractions-concepts, skills and problem solving Expected Fluency: Add and subtract within 1,000,000 Module M1:
To Multiply Decimals
 4.3 Multiplying Decimals 4.3 OBJECTIVES 1. Multiply two or more decimals 2. Use multiplication of decimals to solve application problems 3. Multiply a decimal by a power of ten 4. Use multiplication by
4.3 Multiplying Decimals 4.3 OBJECTIVES 1. Multiply two or more decimals 2. Use multiplication of decimals to solve application problems 3. Multiply a decimal by a power of ten 4. Use multiplication by
Build a Bridge. Based on the book
 Fifth Grade English Design Brief Build a Bridge Based on the book Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson Background: You have just completed reading the book Bridge to Terabithia. Jess has asked for
Fifth Grade English Design Brief Build a Bridge Based on the book Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson Background: You have just completed reading the book Bridge to Terabithia. Jess has asked for
Lesson 18 Pythagorean Triples & Special Right Triangles
 Student Name: Date: Contact Person Name: Phone Number: Teas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills Eit Level Math Review Lesson 18 Pythagorean Triples & Special Right Triangles TAKS Objective 6 Demonstrate
Student Name: Date: Contact Person Name: Phone Number: Teas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills Eit Level Math Review Lesson 18 Pythagorean Triples & Special Right Triangles TAKS Objective 6 Demonstrate
Charlesworth School Year Group Maths Targets
 Charlesworth School Year Group Maths Targets Year One Maths Target Sheet Key Statement KS1 Maths Targets (Expected) These skills must be secure to move beyond expected. I can compare, describe and solve
Charlesworth School Year Group Maths Targets Year One Maths Target Sheet Key Statement KS1 Maths Targets (Expected) These skills must be secure to move beyond expected. I can compare, describe and solve
TEKS TAKS 2010 STAAR RELEASED ITEM STAAR MODIFIED RELEASED ITEM
 7 th Grade Math TAKS-STAAR-STAAR-M Comparison Spacing has been deleted and graphics minimized to fit table. (1) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student represents and uses numbers in
7 th Grade Math TAKS-STAAR-STAAR-M Comparison Spacing has been deleted and graphics minimized to fit table. (1) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student represents and uses numbers in
Revision Notes Adult Numeracy Level 2
 Revision Notes Adult Numeracy Level 2 Place Value The use of place value from earlier levels applies but is extended to all sizes of numbers. The values of columns are: Millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands
Revision Notes Adult Numeracy Level 2 Place Value The use of place value from earlier levels applies but is extended to all sizes of numbers. The values of columns are: Millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands
Math - 5th Grade. two digit by one digit multiplication fact families subtraction with regrouping
 Number and Operations Understand division of whole numbers N.MR.05.01 N.MR.05.02 N.MR.05.03 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with and without remainders; relate division to and to repeated
Number and Operations Understand division of whole numbers N.MR.05.01 N.MR.05.02 N.MR.05.03 Understand the meaning of division of whole numbers with and without remainders; relate division to and to repeated
DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS #2
 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS #2 Area is measured in square units, such as square feet or square centimeters. These units can be abbreviated as ft 2 (square feet) and cm 2 (square centimeters). For example, we
DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS #2 Area is measured in square units, such as square feet or square centimeters. These units can be abbreviated as ft 2 (square feet) and cm 2 (square centimeters). For example, we
Grade 6 Mathematics Assessment. Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 Grade 6 Mathematics Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Grade 6 Mathematics Assessment Mathematical Process Standards These student expectations will not be listed under a separate
Grade 6 Mathematics Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Grade 6 Mathematics Assessment Mathematical Process Standards These student expectations will not be listed under a separate
Appendix C: Conversions and Calculations
 Appendix C: Conversions and Calculations Effective application of pesticides depends on many factors. One of the more important is to correctly calculate the amount of material needed. Unless you have
Appendix C: Conversions and Calculations Effective application of pesticides depends on many factors. One of the more important is to correctly calculate the amount of material needed. Unless you have
Writing Goals and Objectives If you re not sure where you are going, you re liable to end up some place else. ~ Robert Mager, 1997
 Writing Goals and Objectives If you re not sure where you are going, you re liable to end up some place else. ~ Robert Mager, 1997 Instructional goals and objectives are the heart of instruction. When
Writing Goals and Objectives If you re not sure where you are going, you re liable to end up some place else. ~ Robert Mager, 1997 Instructional goals and objectives are the heart of instruction. When
Prealgebra Textbook. Chapter 6 Odd Solutions
 Prealgebra Textbook Second Edition Chapter 6 Odd Solutions Department of Mathematics College of the Redwoods 2012-2013 Copyright All parts of this prealgebra textbook are copyrighted c 2009 in the name
Prealgebra Textbook Second Edition Chapter 6 Odd Solutions Department of Mathematics College of the Redwoods 2012-2013 Copyright All parts of this prealgebra textbook are copyrighted c 2009 in the name
HFCC Math Lab General Math Topics -1. Metric System: Shortcut Conversions of Units within the Metric System
 HFCC Math Lab General Math Topics - Metric System: Shortcut Conversions of Units within the Metric System In this handout, we will work with three basic units of measure in the metric system: meter: gram:
HFCC Math Lab General Math Topics - Metric System: Shortcut Conversions of Units within the Metric System In this handout, we will work with three basic units of measure in the metric system: meter: gram:
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide Grade 5 2012 2013. First Nine Weeks
 First Nine Weeks s The value of a digit is based on its place value. What changes the value of a digit? 5.NBT.1 RECOGNIZE that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much
First Nine Weeks s The value of a digit is based on its place value. What changes the value of a digit? 5.NBT.1 RECOGNIZE that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much
Writing Learning Objectives
 Writing Learning Objectives Faculty Development Program Office of Medical Education Boston University School of Medicine All Rights Reserved 2004 No copying or duplication of this presentation without
Writing Learning Objectives Faculty Development Program Office of Medical Education Boston University School of Medicine All Rights Reserved 2004 No copying or duplication of this presentation without
Accommodated Lesson Plan on Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination for Diego
 Accommodated Lesson Plan on Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination for Diego Courtney O Donovan Class: Algebra 1 Day #: 6-7 Grade: 8th Number of Students: 25 Date: May 12-13, 2011 Goal: Students will
Accommodated Lesson Plan on Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination for Diego Courtney O Donovan Class: Algebra 1 Day #: 6-7 Grade: 8th Number of Students: 25 Date: May 12-13, 2011 Goal: Students will
Exploring Animal Environments
 Third Grade Science Design Brief Exploring Animal Environments forest - desert - grassland rainforest - marshland - swamp - pond - river - ocean - stream Background: In our studies of science, we have
Third Grade Science Design Brief Exploring Animal Environments forest - desert - grassland rainforest - marshland - swamp - pond - river - ocean - stream Background: In our studies of science, we have
How do you compare numbers? On a number line, larger numbers are to the right and smaller numbers are to the left.
 The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of pre-algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in algebra 1. Number Basics
The verbal answers to all of the following questions should be memorized before completion of pre-algebra. Answers that are not memorized will hinder your ability to succeed in algebra 1. Number Basics
Form: Filled in table. Method: Peer assessment. Tool: Checklist. Form: Completed table. Method: Peer assessment. Tool: Checklist
 Lesson Plan English First Additional Language Grade 5 Content in context: Text from other Learning Area - Whether Los and ASs Learning Activities Details of Assessment Barriers to Learning LO 1 Listening
Lesson Plan English First Additional Language Grade 5 Content in context: Text from other Learning Area - Whether Los and ASs Learning Activities Details of Assessment Barriers to Learning LO 1 Listening
Quick Reference ebook
 This file is distributed FREE OF CHARGE by the publisher Quick Reference Handbooks and the author. Quick Reference ebook Click on Contents or Index in the left panel to locate a topic. The math facts listed
This file is distributed FREE OF CHARGE by the publisher Quick Reference Handbooks and the author. Quick Reference ebook Click on Contents or Index in the left panel to locate a topic. The math facts listed
Unit Conversions. Ben Logan <ben.logan@gmail.com> Feb 10, 2005
 Unit Conversions Ben Logan Feb 0, 2005 Abstract Conversion between different units of measurement is one of the first concepts covered at the start of a course in chemistry or physics.
Unit Conversions Ben Logan Feb 0, 2005 Abstract Conversion between different units of measurement is one of the first concepts covered at the start of a course in chemistry or physics.
Indicator 2: Use a variety of algebraic concepts and methods to solve equations and inequalities.
 3 rd Grade Math Learning Targets Algebra: Indicator 1: Use procedures to transform algebraic expressions. 3.A.1.1. Students are able to explain the relationship between repeated addition and multiplication.
3 rd Grade Math Learning Targets Algebra: Indicator 1: Use procedures to transform algebraic expressions. 3.A.1.1. Students are able to explain the relationship between repeated addition and multiplication.
Writing Student Learning Outcomes for an Academic Program
 Writing Student Learning Outcomes for an Academic Program Student learning outcomes (SLOs) are statements of the knowledge, skills, competencies, or attitudes that students are expected to gain through
Writing Student Learning Outcomes for an Academic Program Student learning outcomes (SLOs) are statements of the knowledge, skills, competencies, or attitudes that students are expected to gain through
2006 Core Knowledge National Conference, Measurement, 4 th Grade 1
 Measurement Grade Level or Special Area: Grade 4 Mathematics Written by: Caroline Ruppert Tuiolosega, Aurora Academy Charter School, Aurora, Colorado Length of Unit: Seven lessons; eight one-hour days
Measurement Grade Level or Special Area: Grade 4 Mathematics Written by: Caroline Ruppert Tuiolosega, Aurora Academy Charter School, Aurora, Colorado Length of Unit: Seven lessons; eight one-hour days
4 Mathematics Curriculum
 New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E GRADE 4 MODULE 1 Topic F Addition and Subtraction Word Problems 4.OA.3, 4.NBT.1, 4.NBT.2, 4.NBT.4 Focus Standard: 4.OA.3 Solve multistep word
New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E GRADE 4 MODULE 1 Topic F Addition and Subtraction Word Problems 4.OA.3, 4.NBT.1, 4.NBT.2, 4.NBT.4 Focus Standard: 4.OA.3 Solve multistep word
Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, and Trapezoids (pages 314 318)
 Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, and Trapezoids (pages 34 38) Any side of a parallelogram or triangle can be used as a base. The altitude of a parallelogram is a line segment perpendicular to the base
Area of Parallelograms, Triangles, and Trapezoids (pages 34 38) Any side of a parallelogram or triangle can be used as a base. The altitude of a parallelogram is a line segment perpendicular to the base
Revised Bloom s Taxonomy
 Revised Bloom s Taxonomy Revised Bloom s Taxonomy (RBT) employs the use of 25 verbs that create collegial understanding of student behavior and learning outcome. Bloom s Revised Taxonomy Taxonomy of Cognitive
Revised Bloom s Taxonomy Revised Bloom s Taxonomy (RBT) employs the use of 25 verbs that create collegial understanding of student behavior and learning outcome. Bloom s Revised Taxonomy Taxonomy of Cognitive
ALGEBRA I (Common Core) Thursday, January 28, 2016 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only
 ALGEBRA I (COMMON CORE) The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION ALGEBRA I (Common Core) Thursday, January 28, 2016 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: The
ALGEBRA I (COMMON CORE) The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION ALGEBRA I (Common Core) Thursday, January 28, 2016 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: The
6 Week Strategic Onboarding Program:
 6 Week Strategic Onboarding Program: Creating a Culture of Learning to Increase Success for Financial Services First Timers Matt Ragan- GMAC Mortgage The New Hire Process A successful New Hire On-boarding
6 Week Strategic Onboarding Program: Creating a Culture of Learning to Increase Success for Financial Services First Timers Matt Ragan- GMAC Mortgage The New Hire Process A successful New Hire On-boarding
MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116
 MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116 STANDARDS 5.MD.C.4 Goals Students will find the number of cubes in a rectangular stack and develop the formula length width height for the number of cubes in a stack.
MD5-26 Stacking Blocks Pages 115 116 STANDARDS 5.MD.C.4 Goals Students will find the number of cubes in a rectangular stack and develop the formula length width height for the number of cubes in a stack.
Differentiated Instruction
 Differentiated Instruction In any classroom, students will have a range of abilities, needs and interests. Differentiated instruction is any instructional strategy that recognizes and supports individual
Differentiated Instruction In any classroom, students will have a range of abilities, needs and interests. Differentiated instruction is any instructional strategy that recognizes and supports individual
Glencoe. correlated to SOUTH CAROLINA MATH CURRICULUM STANDARDS GRADE 6 3-3, 5-8 8-4, 8-7 1-6, 4-9
 Glencoe correlated to SOUTH CAROLINA MATH CURRICULUM STANDARDS GRADE 6 STANDARDS 6-8 Number and Operations (NO) Standard I. Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers,
Glencoe correlated to SOUTH CAROLINA MATH CURRICULUM STANDARDS GRADE 6 STANDARDS 6-8 Number and Operations (NO) Standard I. Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers,
MOUNTAIN VIEW COLLEGE CORE CURRICULUM EVALUATION COMMITTEE STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES COURSE LEVEL VICTOR J. SOTO INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGNER PREPARED BY
 1 MOUNTAIN VIEW COLLEGE CORE CURRICULUM EVALUATION COMMITTEE WRITING INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES COURSE LEVEL PREPARED BY VICTOR J. SOTO INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGNER 2 WRITING INSTRUCTIONAL
1 MOUNTAIN VIEW COLLEGE CORE CURRICULUM EVALUATION COMMITTEE WRITING INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES COURSE LEVEL PREPARED BY VICTOR J. SOTO INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGNER 2 WRITING INSTRUCTIONAL
Industrial Engineering Definition of Tuning
 Industrial Engineering Definition of Tuning Tuning is a faculty-led pilot project designed to define what students must know, understand, and be able to demonstrate after completing a degree in a specific
Industrial Engineering Definition of Tuning Tuning is a faculty-led pilot project designed to define what students must know, understand, and be able to demonstrate after completing a degree in a specific
Grade 4 Mathematics Measurement: Lesson 1
 Grade 4 Mathematics Measurement: Lesson 1 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and all information outside
Grade 4 Mathematics Measurement: Lesson 1 Read aloud to the students the material that is printed in boldface type inside the boxes. Information in regular type inside the boxes and all information outside
SAMPLE TEST MATHEMATICS. 2007 Oregon Content Standards Grades 3-8 GRADE 5
 SAMPLE TEST MATHEMATICS GRADE 5 2007 Oregon Content Standards Grades 3-8 It is the policy of the State Board of Education and a priority of the that there will be no discrimination or harassment on the
SAMPLE TEST MATHEMATICS GRADE 5 2007 Oregon Content Standards Grades 3-8 It is the policy of the State Board of Education and a priority of the that there will be no discrimination or harassment on the
Minnesota Academic Standards
 A Correlation of to the Minnesota Academic Standards Grades K-6 G/M-204 Introduction This document demonstrates the high degree of success students will achieve when using Scott Foresman Addison Wesley
A Correlation of to the Minnesota Academic Standards Grades K-6 G/M-204 Introduction This document demonstrates the high degree of success students will achieve when using Scott Foresman Addison Wesley
Higher order questions encourages higher order thinking Based on Bloom s Taxonomy
 Higher order questions encourages higher order thinking Based on Bloom s Taxonomy Knowledge What happened after...? How many...? Who was it that...? Can you name the...? Describe what happened at...? Who
Higher order questions encourages higher order thinking Based on Bloom s Taxonomy Knowledge What happened after...? How many...? Who was it that...? Can you name the...? Describe what happened at...? Who
One basic concept in math is that if we multiply a number by 1, the result is equal to the original number. For example,
 MA 35 Lecture - Introduction to Unit Conversions Tuesday, March 24, 205. Objectives: Introduce the concept of doing algebra on units. One basic concept in math is that if we multiply a number by, the result
MA 35 Lecture - Introduction to Unit Conversions Tuesday, March 24, 205. Objectives: Introduce the concept of doing algebra on units. One basic concept in math is that if we multiply a number by, the result
GRADE 7. Mathematics. Administered April 2013 RELEASED
 GRADE 7 Mathematics Administered April 03 RELEASED Copyright 03, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited without express written permission
GRADE 7 Mathematics Administered April 03 RELEASED Copyright 03, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited without express written permission
Grade 8 FCAT 2.0 Mathematics Sample Questions
 Grade FCAT. Mathematics Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT. tests. By using these materials, students will become
Grade FCAT. Mathematics Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT. tests. By using these materials, students will become
GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS CORE 1 VIRGINIA STANDARDS OF LEARNING. Spring 2006 Released Test. Property of the Virginia Department of Education
 VIRGINIA STANDARDS OF LEARNING Spring 2006 Released Test GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS CORE 1 Property of the Virginia Department of Education 2006 by the Commonwealth of Virginia, Department of Education, P.O.
VIRGINIA STANDARDS OF LEARNING Spring 2006 Released Test GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS CORE 1 Property of the Virginia Department of Education 2006 by the Commonwealth of Virginia, Department of Education, P.O.
Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for Four Content Areas Norman L. Webb March 28, 2002. Reading (based on Wixson, 1999)
 Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for Four Content Areas Norman L. Webb March 28, 2002 Language Arts Levels of Depth of Knowledge Interpreting and assigning depth-of-knowledge levels to both objectives within
Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for Four Content Areas Norman L. Webb March 28, 2002 Language Arts Levels of Depth of Knowledge Interpreting and assigning depth-of-knowledge levels to both objectives within
SAMPLE TEST MATHEMATICS. 2009 Oregon Content Standards High School HIGH SCHOOL
 SAMPLE TEST MATHEMATICS HIGH SCHOOL 2009 Oregon Content Standards High School It is the policy of the State Board of Education and a priority of the that there will be no discrimination or harassment on
SAMPLE TEST MATHEMATICS HIGH SCHOOL 2009 Oregon Content Standards High School It is the policy of the State Board of Education and a priority of the that there will be no discrimination or harassment on
FCAT FLORIDA COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT TEST. Mathematics Reference Sheets. Copyright Statement for this Assessment and Evaluation Services Publication
 FCAT FLORIDA COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT TEST Mathematics Reference Sheets Copyright Statement for this Assessment and Evaluation Services Publication Authorization for reproduction of this document is hereby
FCAT FLORIDA COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT TEST Mathematics Reference Sheets Copyright Statement for this Assessment and Evaluation Services Publication Authorization for reproduction of this document is hereby
Math Mammoth End-of-the-Year Test, Grade 6, Answer Key
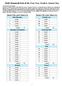 Math Mammoth End-of-the-Year Test, Grade 6, Answer Key Instructions to the teacher: In order to continue with the Math Mammoth Grade 7 Complete Worktext, I recommend that the student score a minimum of
Math Mammoth End-of-the-Year Test, Grade 6, Answer Key Instructions to the teacher: In order to continue with the Math Mammoth Grade 7 Complete Worktext, I recommend that the student score a minimum of
Open-Ended Problem-Solving Projections
 MATHEMATICS Open-Ended Problem-Solving Projections Organized by TEKS Categories TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 GRADE 7 PROJECTION MASTERS for PROBLEM-SOLVING OVERVIEW The Projection Masters for Problem-Solving
MATHEMATICS Open-Ended Problem-Solving Projections Organized by TEKS Categories TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 GRADE 7 PROJECTION MASTERS for PROBLEM-SOLVING OVERVIEW The Projection Masters for Problem-Solving
Grade 6 FCAT 2.0 Mathematics Sample Questions
 Grade FCAT. Mathematics Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT. tests. By using these materials, students will become
Grade FCAT. Mathematics Sample Questions The intent of these sample test materials is to orient teachers and students to the types of questions on FCAT. tests. By using these materials, students will become
Science Grade 06 Unit 05 Exemplar Lesson 01: Advantages and Disadvantages of Energy Resources
 Grade 06 Unit 05 Exemplar Lesson 01: Advantages and Disadvantages of Energy Resources This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit. Districts are encouraged to
Grade 06 Unit 05 Exemplar Lesson 01: Advantages and Disadvantages of Energy Resources This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with this unit. Districts are encouraged to
LECTURE AND NOTE TAKING
 LECTURE AND NOTE TAKING Goals of Note Taking Taking notes helps with classroom concentration, test preparation and for clues as to what the instructor feels is most important. Prepare to take effective
LECTURE AND NOTE TAKING Goals of Note Taking Taking notes helps with classroom concentration, test preparation and for clues as to what the instructor feels is most important. Prepare to take effective
Commutative Property Grade One
 Ohio Standards Connection Patterns, Functions and Algebra Benchmark E Solve open sentences and explain strategies. Indicator 4 Solve open sentences by representing an expression in more than one way using
Ohio Standards Connection Patterns, Functions and Algebra Benchmark E Solve open sentences and explain strategies. Indicator 4 Solve open sentences by representing an expression in more than one way using
TIPS FOR WRITING LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 TIPS FOR WRITING LEARNING OBJECTIVES N ational ACEP receives numerous requests from chapters for assistance on how to write good learning objectives. The information presented in this section has been
TIPS FOR WRITING LEARNING OBJECTIVES N ational ACEP receives numerous requests from chapters for assistance on how to write good learning objectives. The information presented in this section has been
Don t worry! There is no right or wrong answer.be honest so that I can figure out the best way to help you next year!
 AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment 2016-2017 Mrs. Carlson, rcarlson@g.aledoisd.org Welcome to AP Environmental Science! This class is highly intensive, with a lot of material that needs to be covered.
AP Environmental Science Summer Assignment 2016-2017 Mrs. Carlson, rcarlson@g.aledoisd.org Welcome to AP Environmental Science! This class is highly intensive, with a lot of material that needs to be covered.
Solving Equations With Fractional Coefficients
 Solving Equations With Fractional Coefficients Some equations include a variable with a fractional coefficient. Solve this kind of equation by multiplying both sides of the equation by the reciprocal of
Solving Equations With Fractional Coefficients Some equations include a variable with a fractional coefficient. Solve this kind of equation by multiplying both sides of the equation by the reciprocal of
The Virginia Company of London Wants You!
 The Virginia Company of London Wants You! Background: The Virginia Company of London has hired you to recruit new settlers to travel to Jamestown. You will need to have a good working knowledge about why
The Virginia Company of London Wants You! Background: The Virginia Company of London has hired you to recruit new settlers to travel to Jamestown. You will need to have a good working knowledge about why
numerical place value additional topics rounding off numbers power of numbers negative numbers addition with materials fundamentals
 Math Scope & Sequence fundamentals number sense and numeration of the decimal system Count to 10 by units Associate number to numeral (1-10) KN 1 KN 1 KN 2 KN 2 Identify odd and even numbers/numerals and
Math Scope & Sequence fundamentals number sense and numeration of the decimal system Count to 10 by units Associate number to numeral (1-10) KN 1 KN 1 KN 2 KN 2 Identify odd and even numbers/numerals and
ESL I English as a Second Language I Curriculum
 ESL I English as a Second Language I Curriculum ESL Curriculum alignment with NJ English Language Proficiency Standards (Incorporating NJCCCS and WIDA Standards) Revised November, 2011 The ESL program
ESL I English as a Second Language I Curriculum ESL Curriculum alignment with NJ English Language Proficiency Standards (Incorporating NJCCCS and WIDA Standards) Revised November, 2011 The ESL program
Mathematics Scope and Sequence, K-8
 Standard 1: Number and Operation Goal 1.1: Understands and uses numbers (number sense) Mathematics Scope and Sequence, K-8 Grade Counting Read, Write, Order, Compare Place Value Money Number Theory K Count
Standard 1: Number and Operation Goal 1.1: Understands and uses numbers (number sense) Mathematics Scope and Sequence, K-8 Grade Counting Read, Write, Order, Compare Place Value Money Number Theory K Count
5 Mathematics Curriculum
 New York State Common Core 5 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E GRADE 5 MODULE 1 Topic B Decimal Fractions and Place Value Patterns 5.NBT.3 Focus Standard: 5.NBT.3 Read, write, and compare decimals to thousandths.
New York State Common Core 5 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E GRADE 5 MODULE 1 Topic B Decimal Fractions and Place Value Patterns 5.NBT.3 Focus Standard: 5.NBT.3 Read, write, and compare decimals to thousandths.
Quickwrite Questions: How did you learn the skill of note taking? How did this skill contribute to your success?
 Quickwrite Questions: How did you learn the skill of note taking? How did this skill contribute to your success? Cornell note taking stimulates critical thinking skills. Note taking helps students remember
Quickwrite Questions: How did you learn the skill of note taking? How did this skill contribute to your success? Cornell note taking stimulates critical thinking skills. Note taking helps students remember
ALGEBRA I (Common Core) Wednesday, August 13, 2014 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only
 ALGEBRA I (COMMON CORE) The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION ALGEBRA I (Common Core) Wednesday, August 13, 2014 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: The
ALGEBRA I (COMMON CORE) The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION ALGEBRA I (Common Core) Wednesday, August 13, 2014 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: The
Chapter 2 Measurement and Problem Solving
 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Measurement and Problem Solving Graph of global Temperature rise in 20 th Century. Cover page Opposite page 11. Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Measurement and Problem Solving Graph of global Temperature rise in 20 th Century. Cover page Opposite page 11. Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community
CHAPTER 4 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS
 CHAPTER 4 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 1. DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS Dimensional analysis, which is also known as the factor label method or unit conversion method, is an extremely important tool in the field of chemistry.
CHAPTER 4 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 1. DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS Dimensional analysis, which is also known as the factor label method or unit conversion method, is an extremely important tool in the field of chemistry.
Units of Measurement: A. The Imperial System
 Units of Measurement: A. The Imperial System Canada uses the metric system most of the time! However, there are still places and occasions where the imperial system of measurement is used. People often
Units of Measurement: A. The Imperial System Canada uses the metric system most of the time! However, there are still places and occasions where the imperial system of measurement is used. People often
HSU Division of Enrollment Management and Student Affairs. Assessment Workbook
 HSU Division of Enrollment Management and Student Affairs Assessment Workbook Contents Introduction..... 3 Mission Statements...... 4 Goals......5 Outcomes.6 Program Outcomes Learning Outcomes Methods
HSU Division of Enrollment Management and Student Affairs Assessment Workbook Contents Introduction..... 3 Mission Statements...... 4 Goals......5 Outcomes.6 Program Outcomes Learning Outcomes Methods
Problem of the Month: Perfect Pair
 Problem of the Month: The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common Core State Standards:
Problem of the Month: The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common Core State Standards:
Geometry Unit 6 Areas and Perimeters
 Geometry Unit 6 Areas and Perimeters Name Lesson 8.1: Areas of Rectangle (and Square) and Parallelograms How do we measure areas? Area is measured in square units. The type of the square unit you choose
Geometry Unit 6 Areas and Perimeters Name Lesson 8.1: Areas of Rectangle (and Square) and Parallelograms How do we measure areas? Area is measured in square units. The type of the square unit you choose
1) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-1) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-1)(2) =
 Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
Solve addition and subtraction word problems, and add and subtract within 10, e.g., by using objects or drawings to represent the problem.
 Solve addition and subtraction word problems, and add and subtract within 10, e.g., by using objects or drawings to represent the problem. Solve word problems that call for addition of three whole numbers
Solve addition and subtraction word problems, and add and subtract within 10, e.g., by using objects or drawings to represent the problem. Solve word problems that call for addition of three whole numbers
Essential Question: Why does what we measure influence how we measure?
 Core Content: 5.MD.1 Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system (e.g., convert 5 cm to 0.05 m), and use these conversions in solving multi-step, real world
Core Content: 5.MD.1 Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system (e.g., convert 5 cm to 0.05 m), and use these conversions in solving multi-step, real world
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3-5 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS
 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3-5 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS Compiled by Dewey Gottlieb, Hawaii Department of Education June 2010 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS 3-5 DOMAIN PROGRESSIONS Compiled by Dewey Gottlieb, Hawaii Department of Education June 2010 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving
