WHI - Volume 8, Section 4 - Outcome Classifications: Cancer Outcomes Page 4-1 SECTION 4 OUTCOME CLASSIFICATIONS: CANCER OUTCOMES
|
|
|
- Gillian Morris
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WHI - Volume 8, Section 4 - Outcome Classifications: Cancer Outcomes Page 4-1 SECTION 4 OUTCOME CLASSIFICATIONS: CANCER OUTCOMES INTRODUCTION Breast and colorectal cancers are primary outcomes of the Dietary Modification (DM) trial and secondary outcomes of the Calcium and Vitamin D (CaD) trial. Endometrial, ovarian and other cancers are secondary outcomes of all three clinical trial interventions. R:\DOC\MAN\CUR\MOP\VOL8\4.DOC WHI MANUALS: VOLUME 8 - OUTCOMES VER. 1: 08/15/97
2 WHI - Volume 8, Section 4 - Outcome Classifications: Cancer Outcomes Page Cancer Outcomes - Overview The following incident cancer diagnoses will be monitored during the Women's Health Initiative (WHI): Breast cancer Endometrial cancer Ovarian cancer Colon cancer Rectal cancer Other cancers (exclusive of non-melanoma skin cancer) All WHI participants (Clinical Trial [CT] and Observational Study [OS]) will be asked to self-report any physician diagnosis of new cancer, a malignant tumor, or growth of any type. Clinical Trial participants complete a Form 33 - Medical History Update at each semi-annual contact; OS participants complete this form annually. For each self-report of a new cancer diagnosis in CT or OS participants, the following data sources are to be requested by the CC: pathology/cytology report hospital Face Sheet with ICD-9-CM codes operative report hospital discharge summary outpatient, day surgery, or short stay recode In addition, for the five major cancer outcomes, copies of the following are to be requested by the CC: history and physical oncology consult/treatment summary radiology report (diagnostic) tumor registry abstract estrogen and progesterone receptor assay report (for breast cancer only) TNM staging form. Referred to as the five major cancers for WHI. For the five major cancers, the above documentation is required for a new diagnosis of primary breast, endometrial, ovarian, colon or rectal cancer in CT and OS participants. Appendix is not included as a sub-site for colon. It is coded independently as other cancer (see Appendix C, Coding Reference). CCs are responsible for documenting the occurrence of cancer, the primary site, including the 2-digit ICD-0-2 code, date of diagnosis, whether the cancer was pathologically confirmed, and the type of reporting source. When requested by the CCC, CCs will forward all documents relevant to the cancer diagnosis (including Form Report of Cancer Outcome) to the CCC for centralized review. The Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center (FHCRC) Cancer Surveillance System (CSS) staff will code site, date of diagnosis, confirmation, laterality, and source, as well as anatomic sub-site, tumor morphology, and stage of disease at diagnosis. Cancer cases where the CSS staff cannot assign a final diagnosis will be forwarded to the CSS reference pathologist for the definitive diagnoses. If CSS requires further documentation or information in order to code a specific cancer case, a query will be sent to the CC for response. For all hospitalized cancer occurrences, Form Report of Hospitalization Diagnosis should also be completed. R:\DOC\MAN\CUR\VOL8\4.DOC WHI MANUALS: VOLUME 8 - OUTCOMES VER. 1: 09/01/99
3 WHI - Volume 8, Section 4 - Outcome Classifications: Cancer Outcomes Page 4-3 For all other cancers (i.e., other than the five major cancer outcomes of interest to WHI), the CCs will be responsible for documenting the occurrence of a cancer in CT and OS participants, the primary site, date of diagnosis, whether the cancer was pathologically confirmed, and the type of reporting source. These data will be recorded by the CCs, and a copy of the pathology report and other relevant documents will be included in the adjudicator case packet and filed in the participant s outcomes file First vs. Recurrent Disease Only information on newly diagnosed incident cancers is of interest to WHI. Information on recurrent disease or metastasis from a previously diagnosed cancer(s) is not collected. A cancer metastases from a primary cancer site that has already been adjudicated would not require adjudication. However, a second primary cancer would require local and central adjudication, as this would be considered a new cancer, and not a metastasis. For example, a second cancer in the breast (even if the same breast) would be considered a new primary, unless stated to be recurrent or metastatic (i.e., Form 125 Summary of hospitalization Diagnoses). Subsequent (recurrent) cancer requiring hospitalization will be documented as are other hospitalization s, and adjudicated as such locally and will not require the extensive documentation that is required for the first occurrence Occurrence (Definition) Cancer is defined as a physician diagnosis of any primary malignant tumor. Invasive and in situ cancers of all histologic subtypes will be included, as well as borderline malignant ovarian tumors. The definition of cancer and procedures for defining and coding a new primary tumor will be based on those utilized by the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program (The SEER Program Code Manual, June 1992). Both pathologically (biopsy-proven) confirmed and not pathologically confirmed tumors will be recorded. A. Pathologically confirmed: is defined as a pathology report that clearly states the diagnosis in specific terms that are synonymous with cancer (e.g., malignancy, malignant tumor, malignant neoplasm, carcinoma, CA, or a specific histology that defines malignant tumor morphology). Ambiguous terms "probable, suspect, suspicious, compatible with, most likely, and consistent with" cancer ARE considered to be diagnostic of cancer. Ambiguous terms "questionable, possible, suggests, worrisome, and equivocal" ARE NOT considered to be diagnostic of cancer. The term "neoplasm" or "tumor" alone does not constitute a cancer diagnosis; the word "malignant" usually precedes these terms to indicate a diagnosis of cancer except for cancers with specific terms (e.g., Burkitt's lymphoma, Hodgkin's disease, hepatoma, etc.). B. Not pathologically confirmed: a physician diagnosis of cancer based on direct visual observation, radiography, positive laboratory test/marker study or clinical examination only Primary Site/Histology (ICD-0-2 Codes) The CC Physician Adjudicator should determine whether the cancer site is primary or secondary and which site would be the most definitive one. The WHI identifies "cases" of cancer according to the primary site. If the site of origin cannot be determined exactly, it may be possible to use the NOS category of an organ system or the Ill-Defined Sites. Form 122 Report of Cancer Outcome lists cancers by site. The CC Physician Adjudicator checks the appropriate box for the primary site. The codes listed beside tumor site correspond to the ICD-0-2-coding LC system. If the primary site cannot be determined, check box 00 and write in the cancer site. Then, use Appendix C Cancer coding reference (alphabetical index) to identify the appropriate ICD-0-2-code and document this on Form 122. For example: A case pathology report states the primary site is "breast" carcinoma. This site is looked up in the Alphabetic Index, and is found to be 50. In coding, the two-character code, '50' will be recorded.
4 WHI - Volume 8, Section 4 - Outcome Classifications: Cancer Outcomes Page 4-4 In addition to the ICD-0-2 codes on Form 122 Report of Cancer, the ICD-9-CM code from the woman's cancer diagnosis on the hospital Face Sheet is to be recorded on Form Summary of Hospitalization Diagnosis. (See Appendix C for detailed lists of ICD-9-CM codes.) Date of Diagnosis The date of diagnosis of the cancer will be defined according to the method of confirmation (see Section Confirmation). The following rules apply: a. Microscopically-confirmed cancer -- the date of diagnosis is the date the tissue, that resulted in the positive pathology (histology), was removed. For microscopic confirmation based on a positive cytology report (no positive histology), the date of diagnosis will be the date the sample that resulted in the positive cytology was taken. b. Not microscopically-confirmed cancer -- the date of diagnosis will be the date of first hospitalization for the cancer. If no hospitalization, the date of diagnoses will be (ordered hierarchically) the date of a positive laboratory test or marker study, the date of a positive radiography or other imaging technique study, the date of direct visualization of the cancer by the physician, or, lastly, the date the physician made the clinical diagnosis (in the absence of any of the above). c. Autopsy-only cancer - date of diagnosis is the date of death. d. Death certificate-only cancer - date of diagnosis is the date of death. e. Self-report only cancer - date of diagnosis is the date reported by the participant Tumor Behavior The usual behavior codes are listed in both the numeric and alphabetic indices of ICD-0-2, following the histology code. The following codes are used for defining tumor behavior: 0 = benign 1 = uncertain whether benign or malignant; borderline malignancy; low malignant potential; indeterminate malignancy. 2 = carcinoma in situ; intraepithelial; non-infiltrating; non-invasive; Bowen s disease; CINIII; Clark s level 1 for melanoma; confined to epithelium; intraductal; intraepidermal NOS; lobular neoplasia; no stromal invasion; VAINIII; VIN III. 3 = malignant (invasive), primary site Confirmation Diagnostic confirmation indicates whether AT ANY TIME there was microscopic confirmation of the morphology of the cancer. Data on confirmation will be sought for each cancer that is self-reported by WHI participants, but will be limited to cancers occurring after enrollment in WHI (i.e., during follow-up). The confirmation recorded on Form 122 Report of Cancer indicates not only the fact of microscopic confirmation, but the nature of the BEST evidence available. Thus, the codes are in a priority series with code '1' (one) taking precedence.
5 WHI - Volume 8, Section 4 - Outcome Classifications: Cancer Outcomes Page 4-5 Specifics: Code: Microscopically confirmed Code 1 - Positive histology (pathology), primary site: Microscopic diagnosis based upon tissue specimens from biopsy, frozen section, surgery, autopsy, or dilatation and curettage (D & C). Positive hematologic findings relative to leukemia are also included. Bone marrow specimens (including bone marrow aspiration biopsies) are also coded as '1'. Code 2 - Positive exfoliative cytology, no positive histology: Cytologic diagnosis based on microscopic examination of cells as contrasted with tissues. Included are smears from sputum, bronchial brushings, bronchial washings, tracheal washings, breast secretions, gastric fluid, spinal fluid, peritoneal fluid, pleural fluid, endometrial aspiration, urinary sediment, cervical and vaginal smears. Also included are diagnoses based upon paraffin block specimens from concentrated spinal, pleural, or peritoneal fluid. Code 3 - Positive histology (pathology), distant metastatic site only: Microscopic diagnosis based upon a tissue specimen from a metastatic site only (code to 1 if histologic confirmation is also done on the primary site or a regional site). Code 4 - Positive microscopic confirmation, method not specified: Diagnosis stated to be microscopically-confirmed, but with no detailed information on method. Code 5: Not Microscopically confirmed Code 5 - Positive laboratory test/marker study: Clinical diagnosis of cancer based on certain laboratory tests or marker studies which are clinically diagnostic for cancer. Examples are the presence of alpha fetoprotein for liver cancer and an abnormal electrophoretic spike for multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Code 6 - Direct visualization without microscopic confirmation: Visualization includes diagnosis made at surgical exploration or by use of the various endoscopes (including colposcope, mediastinoscope, peritoneoscope). However, use this code only if such visualization is not supplemented by positive histology or positive cytology reports. Also use this code when gross autopsy findings are the only positive information. Code 7 Positive laboratory test/marker study: Cases with diagnostic radiology for which there is neither a positive histology nor a positive cytology report. "Other imaging techniques" include procedures such as ultrasound, computerized (axial) tomography (CT or CAT scans), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Code 8 Clinical diagnosis only (other than 5, 6, or 7): Cases diagnosed by clinical methods not mentioned above and for which there were no positive microscopic findings. Code: Confirmation Unknown: Code 9 Unknown whether or not microscopically-confirmed: Cases for which it is unknown whether or not they have been microscopically confirmed. Also included are all "self-report only" and "death certificate only" cancers Reporting Source This data item provides information to help assess the completeness and reliability of the data in other fields; to indicate the number of patients who were not hospitalized as inpatients or outpatients for their cancers; and to identify the cases diagnosed by autopsy or death certificate only. The code should be based on all source documents used to prepare Form Report of Cancer Outcome, rather than only the source of the original diagnosis, and should be assigned hierarchically in the order shown.
6 WHI - Volume 8, Section 4 - Outcome Classifications: Cancer Outcomes Page 4-6 Code:. 1 Hospital inpatient (with or without any of the following) 2 Hospital outpatient/radiation or chemotherapy facility, surgical center, or clinic - includes outpatient services of HMO's and large multi-specialty physician group practices where at a minimum the reports from multiple physicians and laboratories are filed in a single medical record for the patient. 3 Laboratory only (hospital or private) 4 Physician's office/private medical practitioner (LMD) 5 Nursing/convalescent home/hospice 6 Autopsy only - means that the cancer was not diagnosed even as a clinical diagnosis while the patient was alive. If the patient was an inpatient with another admitting diagnosis and an autopsy disclosed the cancer for the first time, code '6' is proper. Autopsy findings take precedence over death certificate information (i.e., code '6' takes precedence over code '7'). However, a clinical diagnosis of cancer at any of the sources coded '1'-'5' has priority over confirmation at autopsy. 7 Death certificate only (including Coroners' case) - used only when "follow-back" activities have produced no other medical reports--the death certificate is truly the only source of information. Often a case is reported first via the death certificate, but later action yields previously - missing or additional medical reports. Such additional reports take precedence
7 WHI - Volume 8, Section 4 - Outcome Classifications: Cancer Outcomes Section 4 Outcome Classifications: Cancer Outcomes Table of Contents Contents Page INTRODUCTION Cancer Outcomes - Overview First vs. Recurrent Disease Occurrence (Definition) Primary Site/Histology (ICD-0-2 Codes) Date of Diagnosis Tumor Behavior Confirmation Reporting Source R:\DOC\MAN\CUR\VOL8\4.DOC WHI MANUALS: VOLUME 8 - OUTCOMES VER. 1: 09/01/99
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
General Rules SEER Summary Stage 2000. Objectives. What is Staging? 5/8/2014
 General Rules SEER Summary Stage 2000 Linda Mulvihill Public Health Advisor NCRA Annual Meeting May 2014 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention
General Rules SEER Summary Stage 2000 Linda Mulvihill Public Health Advisor NCRA Annual Meeting May 2014 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion Division of Cancer Prevention
Chapter 13. The hospital-based cancer registry
 Chapter 13. The hospital-based cancer registry J.L. Young California Tumor Registry, 1812 14th Street, Suite 200, Sacramento, CA 95814, USA Introduction The purposes of a hospital-based cancer registry
Chapter 13. The hospital-based cancer registry J.L. Young California Tumor Registry, 1812 14th Street, Suite 200, Sacramento, CA 95814, USA Introduction The purposes of a hospital-based cancer registry
The Ontario Cancer Registry moves to the 21 st Century
 The Ontario Cancer Registry moves to the 21 st Century Rebuilding the OCR Public Health Ontario Grand Rounds Oct. 14, 2014 Diane Nishri, MSc Mary Jane King, MPH, CTR Outline 1. What is the Ontario Cancer
The Ontario Cancer Registry moves to the 21 st Century Rebuilding the OCR Public Health Ontario Grand Rounds Oct. 14, 2014 Diane Nishri, MSc Mary Jane King, MPH, CTR Outline 1. What is the Ontario Cancer
An Introduction to the. cancer registry. instructor s guide
 An Introduction to the cancer registry instructor s guide National Cancer Registrars Association Education Foundation 1340 Braddock Place, Suite 203 Alexandria, Virginia 22314 (703) 299-6640 www.ncraeducationfoundation.org
An Introduction to the cancer registry instructor s guide National Cancer Registrars Association Education Foundation 1340 Braddock Place, Suite 203 Alexandria, Virginia 22314 (703) 299-6640 www.ncraeducationfoundation.org
NEOPLASMS C00 D49. Presented by Jan Halloran CCS
 NEOPLASMS C00 D49 Presented by Jan Halloran CCS 1 INTRODUCTION A neoplasm is a new or abnormal growth. In the ICD-10-CM classification system, neoplastic disease is classified in categories C00 through
NEOPLASMS C00 D49 Presented by Jan Halloran CCS 1 INTRODUCTION A neoplasm is a new or abnormal growth. In the ICD-10-CM classification system, neoplastic disease is classified in categories C00 through
CHAPTER 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014. 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc.
 Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion. Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain
 Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
GENERAL CODING. When you review old cases that were coded to unknown, make corrections based on guidelines in effect at the time of diagnosis.
 GENERAL CODING When you review old cases that were coded to unknown, make corrections based on guidelines in effect at the time of diagnosis. Exception: You must review and revise EOD coding for prostate
GENERAL CODING When you review old cases that were coded to unknown, make corrections based on guidelines in effect at the time of diagnosis. Exception: You must review and revise EOD coding for prostate
How To Treat A Uterine Sarcoma
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory
 The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory Dr Edward Sheffield Christmas Select 74 Meeting, Queen s Hotel Cheltenham, 3 rd December 2014 Agenda Overview of the pathology of cancer How specimens
The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory Dr Edward Sheffield Christmas Select 74 Meeting, Queen s Hotel Cheltenham, 3 rd December 2014 Agenda Overview of the pathology of cancer How specimens
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Breast cancer Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Breast cancer 2 Clinical background 2 Who
Employee Critical Illness Option
 ECIO Employee Critical Illness Option Financial Protection for the Unexpected Includes Cancer Benefit First Occurrence Additional Occurrence Reoccurrence Spouse Coverage Available Child Coverage at No
ECIO Employee Critical Illness Option Financial Protection for the Unexpected Includes Cancer Benefit First Occurrence Additional Occurrence Reoccurrence Spouse Coverage Available Child Coverage at No
METROPOLITAN LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY NEW YORK, NEW YORK
 METROPOLITAN LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY NEW YORK, NEW YORK POLICYHOLDER: Your Employer Group Policy Form No: GPNP14-CI (Referred to as the Group Policy ) Certificate Form No: GCERT14-CI (Referred to as the
METROPOLITAN LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY NEW YORK, NEW YORK POLICYHOLDER: Your Employer Group Policy Form No: GPNP14-CI (Referred to as the Group Policy ) Certificate Form No: GCERT14-CI (Referred to as the
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Cancer doesn t care but we do. 2010 Cancer Annual Report
 Cancer doesn t care but we do. 2010 Cancer Annual Report The Cancer Committee of CHRISTUS St. Patrick Hospital is proud to present its 2010 Annual Report. The Community Hospital Comprehensive Cancer Program
Cancer doesn t care but we do. 2010 Cancer Annual Report The Cancer Committee of CHRISTUS St. Patrick Hospital is proud to present its 2010 Annual Report. The Community Hospital Comprehensive Cancer Program
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer
 Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination
 Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Oncology. Objectives. Cancer Nomenclature. Cancer is a disease of the cell Cancer develops when certain cells begin to grow out of control
 Oncology Objectives Describe the etiology and pathophysiological mechanisms of cancer Discuss medical and family history findings relevant to cancer Identify general signs and symptoms associated with
Oncology Objectives Describe the etiology and pathophysiological mechanisms of cancer Discuss medical and family history findings relevant to cancer Identify general signs and symptoms associated with
Post-PET Restaging Cancer Form National Oncologic PET Registry
 Post-PET Restaging Cancer Form National Oncologic PET Registry Facility ID #: Registry Case Number: Patient Name: Your patient had a PET scan on: mm/dd/yyyy. The PET scan was done for restaging of (cancer
Post-PET Restaging Cancer Form National Oncologic PET Registry Facility ID #: Registry Case Number: Patient Name: Your patient had a PET scan on: mm/dd/yyyy. The PET scan was done for restaging of (cancer
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY
 PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
why? 75 percent The percentage of healthy individuals over age 40 who will become critically ill at some time in the future. 3
 Elite coverage can help protect your savings. USAble Life s 1 coverage helps protect your family from the financial impact that can occur as the result of a heart attack, stroke or even cancer by providing
Elite coverage can help protect your savings. USAble Life s 1 coverage helps protect your family from the financial impact that can occur as the result of a heart attack, stroke or even cancer by providing
How CanCer becomes critical in the claims
 How CanCer becomes critical in the claims arena Cancer is a disease in which cells in your body grow in an uncontrolled way and form a lump called a tumour. In a healthy individual cells grow and reproduce
How CanCer becomes critical in the claims arena Cancer is a disease in which cells in your body grow in an uncontrolled way and form a lump called a tumour. In a healthy individual cells grow and reproduce
Multiple Primary and Histology Coding Rules
 Multiple Primary and Histology Coding Rules January 10, 2008 National Cancer Institute Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program Bethesda, MD PLEASE NOTE This PDF of the 2007 Multiple Primaries
Multiple Primary and Histology Coding Rules January 10, 2008 National Cancer Institute Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program Bethesda, MD PLEASE NOTE This PDF of the 2007 Multiple Primaries
Tumour Markers. What are Tumour Markers? How Are Tumour Markers Used?
 Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
Dr. Anthony C.H. YING What are? Tumour markers are substances that can be found in the body when cancer is present. They are usually found in the blood or urine. They can be products of cancer cells or
Breast Cancer Follow-Up
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Follow-Up Breast Cancer Follow-Up Version 2002: Thomssen / Scharl Version 2003 2009: Bauerfeind / Bischoff /
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Follow-Up Breast Cancer Follow-Up Version 2002: Thomssen / Scharl Version 2003 2009: Bauerfeind / Bischoff /
The Ontario Cancer Registry and its Data Quality. Diane Nishri Senior Research Associate, Surveillance February, 2011
 The Ontario Cancer Registry and its Data Quality Diane Nishri Senior Research Associate, Surveillance February, 2011 Objectives Become familiar with cancer registration in Ontario, including issues related
The Ontario Cancer Registry and its Data Quality Diane Nishri Senior Research Associate, Surveillance February, 2011 Objectives Become familiar with cancer registration in Ontario, including issues related
Directly Coded Summary Stage Is Back
 Directly Coded Summary Stage Is Back Donna M. Hansen, CTR Auditor & Training Coordinator California Cancer Registry June 30, 2015 1 Outline What is SEER Summary Stage 2000 (SS2000)? Summary Stage Housekeeping
Directly Coded Summary Stage Is Back Donna M. Hansen, CTR Auditor & Training Coordinator California Cancer Registry June 30, 2015 1 Outline What is SEER Summary Stage 2000 (SS2000)? Summary Stage Housekeeping
4/15/2013. bi/o carcin/ chem/o immun/o onc/o radi/o sarc/o. anabrachydysectoendoneo- -ectomy -genesis -oma -plasia -sarcoma
 Chapter Sixteen Oncology bi/o carcin/ chem/o immun/o onc/o radi/o sarc/o Combining Forms Prefixes and Suffixes Carcinogenesis anabrachydysectoendoneo- -ectomy -genesis -oma -plasia -sarcoma Causes of cancer
Chapter Sixteen Oncology bi/o carcin/ chem/o immun/o onc/o radi/o sarc/o Combining Forms Prefixes and Suffixes Carcinogenesis anabrachydysectoendoneo- -ectomy -genesis -oma -plasia -sarcoma Causes of cancer
2011 Radiology Diagnosis Coding Update Questions and Answers
 2011 Radiology Diagnosis Coding Update Questions and Answers How can we subscribe to the Coding Clinic for ICD-9 guidelines and updates? The American Hospital Association publishes this quarterly newsletter.
2011 Radiology Diagnosis Coding Update Questions and Answers How can we subscribe to the Coding Clinic for ICD-9 guidelines and updates? The American Hospital Association publishes this quarterly newsletter.
Lung cancer is not just one disease. There are two main types of lung cancer:
 1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
COLONIAL LIFE & ACCIDENT INSURANCE COMPANY P.O. Box 1365, Columbia, South Carolina 29202 1-800-325-4368
 COLONIAL LIFE & ACCIDENT INSURANCE COMPANY P.O. Box 1365, Columbia, South Carolina 29202 1-800-325-4368 SPECIFIED DISEASE COVERAGE OUTLINE OF COVERAGE (Applicable to Policy Form C1000-CA) 'THIS POLICY
COLONIAL LIFE & ACCIDENT INSURANCE COMPANY P.O. Box 1365, Columbia, South Carolina 29202 1-800-325-4368 SPECIFIED DISEASE COVERAGE OUTLINE OF COVERAGE (Applicable to Policy Form C1000-CA) 'THIS POLICY
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Ovarian Cancer. in Georgia, 1999-2003. Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health
 Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
Ovarian Cancer in Georgia, 1999-23 Georgia Department of Human Resources Division of Public Health Acknowledgments Georgia Department of Human Resources......B. J. Walker, Commissioner Division of Public
Effective For Cases Diagnosed January 1, 2015 and Later
 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL FOR REPORTING FACILITIES May 2015 Effective For Cases Diagnosed January 1, 2015 and Later Indiana State Cancer Registry Indiana State Department of Health 2 North Meridian Street,
POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL FOR REPORTING FACILITIES May 2015 Effective For Cases Diagnosed January 1, 2015 and Later Indiana State Cancer Registry Indiana State Department of Health 2 North Meridian Street,
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
.org. Metastatic Bone Disease. Description
 Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
HAVE YOU BEEN NEWLY DIAGNOSED with DCIS?
 HAVE YOU BEEN NEWLY DIAGNOSED with DCIS? Jen D. Mother and volunteer. Diagnosed with DCIS breast cancer in 2012. An educational guide prepared by Genomic Health This guide is designed to educate women
HAVE YOU BEEN NEWLY DIAGNOSED with DCIS? Jen D. Mother and volunteer. Diagnosed with DCIS breast cancer in 2012. An educational guide prepared by Genomic Health This guide is designed to educate women
Provider Reimbursement for Women's Cancer Screening Program
 Reimbursement Schedule July 1, 2015 June 30, 2016 Office Visits - Established Patients Office Visit / Minimal / no physician 99211 $ 16.70 Office Visit / Problem focused History / exam 99212 $ 36.46 Preventive
Reimbursement Schedule July 1, 2015 June 30, 2016 Office Visits - Established Patients Office Visit / Minimal / no physician 99211 $ 16.70 Office Visit / Problem focused History / exam 99212 $ 36.46 Preventive
Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Oral Lesions Causing Pain
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Oral Lesions Causing Pain John D. McDowell, DDS, MS University of Colorado School of Dentistry Chair, Oral Diagnosis, Medicine and Radiology Director, Oral Medicine and
Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Oral Lesions Causing Pain John D. McDowell, DDS, MS University of Colorado School of Dentistry Chair, Oral Diagnosis, Medicine and Radiology Director, Oral Medicine and
DELRAY MEDICAL CENTER. Cancer Program Annual Report
 DELRAY MEDICAL CENTER Cancer Program Annual Report Cancer Statistical Data From 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chairman s Report....3 Tumor Registry Statistical Report Summary...4-11 Lung Study.12-17 Definitions
DELRAY MEDICAL CENTER Cancer Program Annual Report Cancer Statistical Data From 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chairman s Report....3 Tumor Registry Statistical Report Summary...4-11 Lung Study.12-17 Definitions
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES. Personal General Insurance (4 th Edition) Date Of Issue: 1 October 2014
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Personal General Insurance (4 th Edition) Date Of Issue: 1 October 2014 The following amendments have NOT been incorporated in the Study Guide. They should be marked up in the Study
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Personal General Insurance (4 th Edition) Date Of Issue: 1 October 2014 The following amendments have NOT been incorporated in the Study Guide. They should be marked up in the Study
Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer
 A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer
 Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up
 Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up What is a Pap Smear? A Pap smear (also known as the Pap test) is a medical procedure in which a sample of cells from a woman's cervix (the end of the
Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up What is a Pap Smear? A Pap smear (also known as the Pap test) is a medical procedure in which a sample of cells from a woman's cervix (the end of the
Policy Wording. Together, all the way.
 Cancer cover Policy Wording Together, all the way. Cancer Cover Insurance Policy Wording 1. Introducing your Policy 2. What is Cancer Cover Insurance? 3. About your Policy 4. Some terms defined 5. What
Cancer cover Policy Wording Together, all the way. Cancer Cover Insurance Policy Wording 1. Introducing your Policy 2. What is Cancer Cover Insurance? 3. About your Policy 4. Some terms defined 5. What
Breast Imaging Made Brief and Simple. Jane Clayton MD Associate Professor Department of Radiology LSUHSC New Orleans, LA
 Breast Imaging Made Brief and Simple Jane Clayton MD Associate Professor Department of Radiology LSUHSC New Orleans, LA What women are referred for breast imaging? Two groups of women are referred for
Breast Imaging Made Brief and Simple Jane Clayton MD Associate Professor Department of Radiology LSUHSC New Orleans, LA What women are referred for breast imaging? Two groups of women are referred for
Dictionary of SEER*Stat Variables November 2011 Submission (released April 2012) http://seer.cancer.gov/data/seerstat/nov2011/ 1 of 18
 November 2011 Data Submission Item # refers to the item - see http://www.naaccr.org/standardsandregistryoperations/volumeii.aspx CS= Collaborative Staging SSF = Site-specific Factor Field Item # Description
November 2011 Data Submission Item # refers to the item - see http://www.naaccr.org/standardsandregistryoperations/volumeii.aspx CS= Collaborative Staging SSF = Site-specific Factor Field Item # Description
Number. Source: Vital Records, M CDPH
 Epidemiology of Cancer in Department of Public Health Revised April 212 Introduction The general public is very concerned about cancer in the community. Many residents believe that cancer rates are high
Epidemiology of Cancer in Department of Public Health Revised April 212 Introduction The general public is very concerned about cancer in the community. Many residents believe that cancer rates are high
FRIEND TO FRIEND CPT CODES 2015 2016. Diagnostic digital breast tomosynthesis, unilateral (list separately in addition to code for primary procedure)
 FRIEND TO FRIEND CPT CODES 2015 2016 CPT CODE SERVICE DESCRIPTION FEE EFFECTIVE G0101 Screening pelvic examination $36.69 01 Jan 16 G0202 Mammography, screening, digital, bilateral (2 view film study of
FRIEND TO FRIEND CPT CODES 2015 2016 CPT CODE SERVICE DESCRIPTION FEE EFFECTIVE G0101 Screening pelvic examination $36.69 01 Jan 16 G0202 Mammography, screening, digital, bilateral (2 view film study of
Cancer treatment. TOP EUROPEAN CANCER EXPERTISE The path to recovery
 Cancer treatment TOP EUROPEAN CANCER EXPERTISE The path to recovery 0% LAND OF HIGH QUALITY HEALTHCARE Located in Finland, a land of high quality healthcare, Helsinki University Hospital is regarded as
Cancer treatment TOP EUROPEAN CANCER EXPERTISE The path to recovery 0% LAND OF HIGH QUALITY HEALTHCARE Located in Finland, a land of high quality healthcare, Helsinki University Hospital is regarded as
Benign (beh-nine): Not cancerous. Benign tumors may grow larger but do not spread to other parts of the body.
 Cancer Glossary Source: National Cancer Institute: What You Need to Know About Cancer Adenoma (ad-in-oh-ma): A noncancerous tumor. Adjuvant therapy (AD-joo-vant): Treatment given after the primary treatment
Cancer Glossary Source: National Cancer Institute: What You Need to Know About Cancer Adenoma (ad-in-oh-ma): A noncancerous tumor. Adjuvant therapy (AD-joo-vant): Treatment given after the primary treatment
Mammograms & Breast Health. An Information Guide for Women U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Mammograms & Breast Health An Information Guide for Women This booklet was developed by the Centers for Disease Control
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Mammograms & Breast Health An Information Guide for Women This booklet was developed by the Centers for Disease Control
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass. Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic. Secondary / adaptation due to other cause.
 Disorders of Growth Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic Secondary / adaptation due to other cause. Neoplastic. Primary growth abnormality. Non-Neoplastic
Disorders of Growth Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic Secondary / adaptation due to other cause. Neoplastic. Primary growth abnormality. Non-Neoplastic
Nicole Kounalakis, MD
 Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Management Nicole Kounalakis, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Goal of Breast Evaluation The goal of breast evaluation is to classify findings as: normal physiologic variations
Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Management Nicole Kounalakis, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Goal of Breast Evaluation The goal of breast evaluation is to classify findings as: normal physiologic variations
Group Critical Illness Insurance Provides lump-sum cash benefits that can help with daily expenses
 What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS Benefit coverage for A Plus Benefits
What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS Benefit coverage for A Plus Benefits
Fact sheet 10. Borderline ovarian tumours. The difficult cases. What is borderline ovarian cancer (BOC)?
 For this reason, some doctors prefer the term borderline ovarian tumour rather than borderline ovarian cancer. Fact sheet 10 Borderline ovarian tumours We, Ovacome, are a support network for people affected
For this reason, some doctors prefer the term borderline ovarian tumour rather than borderline ovarian cancer. Fact sheet 10 Borderline ovarian tumours We, Ovacome, are a support network for people affected
Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report
 Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report Abstract Ovarian cancer is a very common cancer among women. It is an extremely diverse disease requiring several treatment options. Occasionally ovarian cancer is diagnosed
Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report Abstract Ovarian cancer is a very common cancer among women. It is an extremely diverse disease requiring several treatment options. Occasionally ovarian cancer is diagnosed
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Explanation of your PAP smear
 Explanation of your PAP smear Approximately 5-10% of PAP smears in the United States are judged to be abnormal. Too often, the woman who receives this news worries that she already has, or will develop,
Explanation of your PAP smear Approximately 5-10% of PAP smears in the United States are judged to be abnormal. Too often, the woman who receives this news worries that she already has, or will develop,
COLONIAL LIFE & ACCIDENT INSURANCE COMPANY 1200 Colonial Life Boulevard, P. O. Box 1365 Columbia, South Carolina 29202 (800) 325-4368
 COLONIAL LIFE & ACCIDENT INSURANCE COMPANY 1200 Colonial Life Boulevard, P. O. Box 1365 Columbia, South Carolina 29202 (800) 325-4368 GROUP SPECIFIED DISEASE INSURANCE Outline of Coverage (Applicable to
COLONIAL LIFE & ACCIDENT INSURANCE COMPANY 1200 Colonial Life Boulevard, P. O. Box 1365 Columbia, South Carolina 29202 (800) 325-4368 GROUP SPECIFIED DISEASE INSURANCE Outline of Coverage (Applicable to
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Cancer Registry Checklist
 BookI SEER PROGRAM SELF INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL FOR CANCER REGISTRARS Book 1: Objectives and Functions of Cancer Registries Hospital and Central (Population-Based) Third Edition Revised by: Evelyn M. Shambaugh,
BookI SEER PROGRAM SELF INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL FOR CANCER REGISTRARS Book 1: Objectives and Functions of Cancer Registries Hospital and Central (Population-Based) Third Edition Revised by: Evelyn M. Shambaugh,
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients
 Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. Colorectal Cancer Care Map
The effect of the introduction of ICD-10 on cancer mortality trends in England and Wales
 The effect of the introduction of ICD-10 on cancer mortality trends in Anita Brock, Clare Griffiths and Cleo Rooney, Offi ce for INTRODUCTION From January 2001 deaths in have been coded to the Tenth Revision
The effect of the introduction of ICD-10 on cancer mortality trends in Anita Brock, Clare Griffiths and Cleo Rooney, Offi ce for INTRODUCTION From January 2001 deaths in have been coded to the Tenth Revision
Breast Cancer. CSC Cancer Experience Registry Member, breast cancer
 ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
Table 16a Multiple Myeloma Average Annual Number of Cancer Cases and Age-Adjusted Incidence Rates* for 2002-2006
 Multiple Myeloma Figure 16 Definition: Multiple myeloma forms in plasma cells that are normally found in the bone marrow. 1 The plasma cells grow out of control and form tumors (plasmacytoma) or crowd
Multiple Myeloma Figure 16 Definition: Multiple myeloma forms in plasma cells that are normally found in the bone marrow. 1 The plasma cells grow out of control and form tumors (plasmacytoma) or crowd
Understanding Metastatic Disease
 Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Understanding Metastatic Disease Metastatic disease or metastases are phrases that mean the same as Secondary cancer. This means that the cancer
Pleural and Pericardial fluids a one year analysis
 Pleural and Pericardial fluids a one year analysis Dr Olafsdottir Dr J Williams Department of Cytology, Llandough Hospital Contents Background Standards Aims/Questions Investigation group Results Conclusions
Pleural and Pericardial fluids a one year analysis Dr Olafsdottir Dr J Williams Department of Cytology, Llandough Hospital Contents Background Standards Aims/Questions Investigation group Results Conclusions
Live carefree knowing our coverage will be there to help during a critical illness.
 GROUP solutions Live carefree knowing our coverage will be there to help during a critical illness. GVCIP1 critical illness insurance t h e r i g h t c o v e r a g e y o u r f u t u r e g r e a t c h o
GROUP solutions Live carefree knowing our coverage will be there to help during a critical illness. GVCIP1 critical illness insurance t h e r i g h t c o v e r a g e y o u r f u t u r e g r e a t c h o
Group Critical Illness Insurance
 What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS HOME RESCRIPTIONS Group
What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS HOME RESCRIPTIONS Group
Carcinoma of the vagina is a relatively uncommon disease, affecting only about 2,000 women in
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
Cancer 1000 Level 2 Benefit Chart and Outline of Coverage
 Cancer 1000 Level 2 Benefit Chart and Outline of Coverage We will pay benefits if certain routine cancer screening tests are performed or if cancer is diagnosed after the waiting period and while your
Cancer 1000 Level 2 Benefit Chart and Outline of Coverage We will pay benefits if certain routine cancer screening tests are performed or if cancer is diagnosed after the waiting period and while your
COLONIAL LIFE & ACCIDENT INSURANCE COMPANY P.O. Box 1365, Columbia, South Carolina 29202 1-800-325-4368
 COLONIAL LIFE & ACCIDENT INSURANCE COMPANY P.O. Box 1365, Columbia, South Carolina 29202 1-800-325-4368 SPECIFIED DISEASE COVERAGE OUTLINE OF COVERAGE (Applicable to Policy Form C1000-PA-R) THIS POLICY
COLONIAL LIFE & ACCIDENT INSURANCE COMPANY P.O. Box 1365, Columbia, South Carolina 29202 1-800-325-4368 SPECIFIED DISEASE COVERAGE OUTLINE OF COVERAGE (Applicable to Policy Form C1000-PA-R) THIS POLICY
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules KIDNEY. FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM MPH Kidney Site Specific Coding Rules
 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules KIDNEY 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways to view the Multiple l Primary/Histology
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules KIDNEY 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways to view the Multiple l Primary/Histology
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Group Critical Illness Insurance Provides lump-sum cash benefits that can help with daily expenses
 What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS Benefit coverage for Catholic
What can living with a critical illness mean to you? Daily out-of-pocket expenses for fighting the disease while still paying your bills! GROCERIES CAR HOME PRESCRIPTIONS Benefit coverage for Catholic
Areola: The area of dark-colored skin on the breast that surrounds the nipple.
 Glossary of Terms Adenocarcinoma: Cancer arising in gland-forming tissue; the medical term meaning related to a gland is adeno ; breast lobules and ducts are types of glands. Adjuvant: Treatment given
Glossary of Terms Adenocarcinoma: Cancer arising in gland-forming tissue; the medical term meaning related to a gland is adeno ; breast lobules and ducts are types of glands. Adjuvant: Treatment given
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
D. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 ACR BI-RADS ATLAS D. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Under MQSA, is it necessary to include a numeric assessment code (i.e., 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6) in addition to the assessment category in all mammography
ACR BI-RADS ATLAS D. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Under MQSA, is it necessary to include a numeric assessment code (i.e., 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6) in addition to the assessment category in all mammography
The Lewin Group undertook the following steps to identify the guidelines relevant to the 11 targeted procedures:
 Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
chapter 5. Quality control at the population-based cancer registry
 chapter 5. Quality control at the population-based cancer registry All cancer registries should be able to give some objective indication of the quality of the data that they have collected. The methods
chapter 5. Quality control at the population-based cancer registry All cancer registries should be able to give some objective indication of the quality of the data that they have collected. The methods
Cancer is the leading cause of death for Canadians aged 35 to 64 and is also the leading cause of critical illness claims in Canada.
 Underwriting cancer In this issue of the Decision, we provide an overview of Canadian cancer statistics and the information we use to make an underwriting decision. The next few issues will deal with specific
Underwriting cancer In this issue of the Decision, we provide an overview of Canadian cancer statistics and the information we use to make an underwriting decision. The next few issues will deal with specific
Chapter 6. Items of patient information which may be collected by registries
 Chapter 6. Items of patient information which may be collected by registries Queensland Institute of Medical Research, Bramston Terrace, Herston, Brisbane, QLD 4006, Australia The information needed by
Chapter 6. Items of patient information which may be collected by registries Queensland Institute of Medical Research, Bramston Terrace, Herston, Brisbane, QLD 4006, Australia The information needed by
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
Total Cost of Cancer Care by Site of Service: Physician Office vs Outpatient Hospital
 Total Cost of Cancer Care by Site of Service: Physician Office vs Outpatient Hospital Prepared by Avalere Health, LLC Page 2 Executive Summary Avalere Health analyzed three years of commercial health plan
Total Cost of Cancer Care by Site of Service: Physician Office vs Outpatient Hospital Prepared by Avalere Health, LLC Page 2 Executive Summary Avalere Health analyzed three years of commercial health plan
SEER PROGRAM CODING AND STAGING MANUAL 2013
 SEER PROGRAM CODING AND STAGING MANUAL 2013 SURVEILLANCE SYSTEMS BRANCH SURVEILLANCE RESEARCH PROGRAM DIVISION OF CANCER CONTROL AND POPULATION SCIENCES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICE
SEER PROGRAM CODING AND STAGING MANUAL 2013 SURVEILLANCE SYSTEMS BRANCH SURVEILLANCE RESEARCH PROGRAM DIVISION OF CANCER CONTROL AND POPULATION SCIENCES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICE
Polyps. Hyperplasias. CAP 2011: Course AP104. The High Risk Benign Endometrium. Mutter and Nucci 1
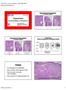 Course AP104 Endometrial Hyperplasia A morphologic Definition Hyperplasias Hormonal Effect or Precancer? George L. Mutter, MD Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA Endometrial
Course AP104 Endometrial Hyperplasia A morphologic Definition Hyperplasias Hormonal Effect or Precancer? George L. Mutter, MD Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA Endometrial
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER
 dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Medicare Part B. Mammograms - Updated Billing Guide for Screening and Diagnostic Tests
 Mammograms - Updated Billing Guide for Screening and Diagnostic Tests This article from Medicare B News Issue 223 dated October 21, 2005 is being updated and reprinted to ensure that the Noridian Administrative
Mammograms - Updated Billing Guide for Screening and Diagnostic Tests This article from Medicare B News Issue 223 dated October 21, 2005 is being updated and reprinted to ensure that the Noridian Administrative
CARDCARE PROTECTOR CERTIFICATE OF INSURANCE
 CARDCARE PROTECTOR CERTIFICATE OF INSURANCE DBS Bank Ltd ( DBS ) is the master policyholder under Group Policy No. MD00000002 (the Policy ), underwritten by Manulife (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. (the Insurer
CARDCARE PROTECTOR CERTIFICATE OF INSURANCE DBS Bank Ltd ( DBS ) is the master policyholder under Group Policy No. MD00000002 (the Policy ), underwritten by Manulife (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. (the Insurer
