The future HR roles of Shared Service Centres
|
|
|
- Oliver Fields
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The future HR roles of Shared Service Centres Author: Ward Uijlenberg University of Twente P.O. Box 217, 7500AE Enschede The Netherlands ABSTRACT Human Resource Shared Service Centres (HR SSC s) are becoming increasingly important for organisations by centralising activities to achieve economies of scale, while leaving decision-making to line-management. There are already theories describing the HR roles that SSC s fulfil today, but information about the future is scarce. Therefore we studied the HR roles of Shared Service Centres within five years by conducting a Delphi study among Dutch SSC managers. Using institutional theory we tried to find if SSC s will adapt the same HR roles within five years, but we could not find significant proof of this. Using theories from Ulrich D. and Storey J. we found that SSC s within five years will fulfil an Administrative Expert role in combination with the Handmaiden or Advisor role, dependent on their long-term view. Supervisors: J.G. Meijerink and H.J.M. Ruël Keywords Shared Service Centre, future, HR roles, Ulrich, Storey, institutional theory, Delphi study Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page. To copy otherwise, or republish, to post on servers or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission and/or a fee. 5 th IBA Bachelor Thesis Conference, July 2 nd, 2015, Enschede, The Netherlands. Copyright 2015, University of Twente, The Faculty of Behavioural, Management and Social sciences.
2 Introduction Over the years companies have centralised more and more Human Resource activities in Shared service centres (SSC). These centres use the advantages of centralising and decentralising activities while minimizing their drawbacks, by creating economies of scale to reduce costs and improve efficiency, while leaving the day-to-day decision making to line management. (Quinn, Cooke and Kris, 2000; Farndale, 2009; Janssen and Joha, 2006). SSC s are departments within organisations and provide services to other departments (Strikwerda, 2004). Which role the SSC fulfils for this department is based on expected behaviour from the department or business unit. This expectation of behaviour brings us to HR roles. HR roles are defined as expectations from business units and employees to the responsibilities of SSC managers. The responsibilities in this study are the tasks whereby an HR SSC provides value for the organisation. The theory about HR roles with the most citations is the Human Resource Champions theory from Ulrich (1997). He determined four roles for personnel management bases on the distinction between process/people and strategic/operational for facilitating services to employees or business units. This theory from Ulrich is based on Storey s (1992) four roles of personnel management. Storey made a distinction between interventionary/non-interventionary and strategic/tactical view to fulfil HR roles. These roles will be further explained in the theory section and help us to explain which HR roles SSC s fulfil at this point in time. However the goal for this study is to find if, and how, these roles will develop within five years. Meijerink et al. (2013) and Ulrich and Brockbank (2005) already proved there has been a change in HR SSC activities, and the related HR role, before and this makes it presumable this will happen again. Meijerink et al. (2013) found that SSC s made a shift from just transactional services, like payroll administration and information on labour regulations to a combination of transactional and transformational activities, e.g. change management and strategic HRM (Farndale et al., 2009; Meijerink et al., 2013). Ulrich and Brockbank (2005) confirm this by arguing that transactional activities are more outsourced or addressed by employee self-service (Ulrich et al., 2008). According to the institutional theory from Dimaggio and Powell (1983), there is also a possibility that there will be a universal HR role for SSC s. They argue that there are three institutional mechanisms (coercive, mimetic and normative mechanisms) that influence decision-making in organisations. According to them these mechanisms are the reason organisations will get more alike over time. We focus on a SSC manager perspective, because there are the experts on how these centres operate, while they work in a SSC on a daily basis. For the SSC manger it is interesting to know the results of future HR roles, because it gives them knowledge about SSC s in other organisations. This leads to an advantage, because (from an classical economic perspective) organisations always try to improve efficiency and reduce costs. With this study they get to know how other organisations operate with their SSC and use this information to improve their own centre. They can use this knowledge to better estimate the role changes in the next five years. This is important, because they have to train their employees to be ready for the upcoming HR role change. Researchers, on the other hand, want to know how new theories work in order to explain future developments. They need to know from which theoretical perspective new phenomena need to be approached. Previous studies have shown the current expected behaviour from SSC s and with this information researchers can explain how these expectations lead to HR roles. But in order to explain how these roles will develop in the next five years further research has to be done into future expected behaviour of SSC s. To do this we will answer the following research question: Which HR roles will Shared Service Centres fulfil in the next five years from a SSC manager perspective? Theory Over the years much research have been done into the topic of Human Resource roles and Shared Service Centres. In this section we will further elaborate the concept of Shared Service Centres and point out a few theories that have proven to be relevant for the HR sector and useful for this study. Shared Service Centres The rise of Shared Service Centres started several years ago to deal with the uncertainty whether to centralise or decentralise HRM tasks (Quinn, Cooke and Kris, 2000; Farndale et al, 2009). The distinctive feature of Shared Service Centres is that it uses the advantages of both centralising and decentralising, while minimizing their drawbacks (Farndale, 2009; Janssen and Joha, 2006). With a SSC it might look like there is only a centralisation of tasks, but according to Ulrich (1995: 14) and Redman et al. (2007) this is not the case. They argue that centralised organisations are above the business units, because their role involves governance and control, but with shared service centres the business units are able to choose which services they acquire and at what price (Redman et al., 2007). Ulrich (1995: 14) complements this view by arguing that with an SSC the actual service provision is centralised, but it is not centralised in the sense that it is corporately determined because the business units maintain in control, or more succinctly the user is the chooser (Maatman et al, 2010). The local business units can choose which services they use from the SSC and which they carry out themselves. The benefit of this is that centralisation reduces costs, but the business units still remain in control of the decisions that are best for the organisation. Examples of services that can be shared in a SSC are training methods, selection procedures and payroll administration (Farndale et al, 2009). HR roles and their classification In 1992 Story came up with his Four roles of personnel managers (Story, 1992). He made a distinction between interventionary/non-interventionary and strategic/tactical managers and this led to the four personnel roles showed in figure 1. Advisors are the internal consultants of an organisation (Storey, 1992, p.168). Their job is to offer their expertise in HR services (e.g. training and selection of employees) to the line managers of the firm. However the line managers are still responsible for the decision which trainings will be offered and to whom. Therefore the advisors can best be seen as consultants i.e. allowing other employees to use your knowledge, with the main task to advise the line managers in doing their job (Storey, 1992, p.170). Handmaidens are HR managers (in this study SSC s) that offer supportive services, e.g. administration, to the organisation on a predominantly customer led basis (Storey, 1992, p.168). They are just as Advisors non-interventionary, i.e. they don t make the actual decision, but focus more on short-term goals. This places Handmaidens on the bottom right corner of figure 1, being tactical and non-interventionary. In practise this means they have less complex en more repetitive tasks than Advisors. They also differentiate from Advisors in sense that
3 Handmaidens are more focussed on the demands from business units in the services they provide (Storey, 1992, p.168). This means they only do the tasks line managers ask them to do. This responsiveness to customer requirements often results from a period of organisational changes and reorganisations (Storey, 1992, p.172), which happened when the SSC was introduced. Regulators are the managers who make sure employees behave as they are supposed to. They can do this by formulating rules ranging from personnel procedure to agreements with labour unions. They are interventionary, because they make sure the employees work as their job description says, but are rarely concerned with the overall business strategy (Storey, 1992, p.175). I.e. other HR experts, or top-level management, working for the same organisation define the business strategy and Regulators make sure the employees follow the rules and procedures to execute this strategy. This role works as a supervisor for employees and needs to be decentralised in order to do this on a day-to-day basis (Storey, 1992, p.175). A SSC is not physically present to supervise the employees, so this role might not fit a SSC. The last personnel specialist type named by Storey (1992) is the Change Maker category. The integration of the different aspects of resourcing, planning, appraising, rewarding and developing; and the further integration of all of this into the business plan are the characteristic features of this type of personnel approach (Storey, 1992, p.180). They make an interventionary and strategic contribution to the organisation. This role is seen as interventionary, because it contributes to organisational change for different HR functions like appraising and training. It is also seen as strategic, because they integrate HR activities into the business plan and this is a long-term goal. We speak of a long-term goal, if the activities have duration of more than half a year. As found by Farndale et al. (2009) and Meijerink et al. (2013) SSC s typically consists of transactional activities such as payroll, personnel administration, benefits management and employee records, traditional activities (recruitment, selection, training and performance management) and transformational activities focused on change management, knowledge management and strategic HRM. When comparing the definition of Storey s four personnel roles with the typical SSC activities found by Farndale et al. (2009) and Meijerink et al. (2013) a SSC nowadays best fits the Advisor role, but also has some characteristics of the Change Maker role. As Storey (1992, p.168) describes Advisors act as internal consultants for the firm and provide their expertise on HR services to the line managers of the firm. Traditional activities like recruitment and training are good examples of activities where SSC s can advise on. In recent years there have been a shift towards more change management and strategic HRM (Meijerink et al. 2013). These services better fit the description of the Change Maker role, because it focuses on strategy and has a more interventionary approach to HR. Figure 1: Story s four roles of personnel management (Caldwell, 2003) A few years later, in 1997, Ulrich wrote a book named Human Resource Champions in which he described four HR roles. These roles are the Strategic Partner, Administrative Expert, Employee Champion and Change Agent (Ulrich, 1997). The Strategic Partner role focuses on aligning the HR practises with the business strategy (Ulrich, 1997, p.26). This helps the business to better execute its business strategy in three ways. First the business can adapt to change because the time from conception to execution of the strategy is shortened. Second, the business can better meet customer demands because its customer service strategies have been translated into specific policies and practices, Third, the firm can achieve financial performance through its more effective execution of strategy (Ulrich, 1997, p.26). Ulrich (1997, p.26) also states that there is almost in any organisation a strategy and thus the need for strategic partners. Because SSC s are more concerned with company wide integration and long-term goals than business units they could fulfil the Strategic Partner role. A Shared Service Centre with an Administrative Expert role facilitates administrative services for the organisation. Examples of administrative services are registration of employees, training application and vacation requests. SSC s with an Administrative Expert role are constantly seeking to achieve administrative efficiency. As Ulrich (1997, p.28) describes this can be done in two ways. First by optimizing HR efficiency, for example standardising registration systems, or cutting the time to find new employees by optimizing solicitation procedures. Another way to improve overall business efficiency is by hiring, training and rewarding managers who increase productivity and reduce waste (Ulrich, 1997, p.28). HR professionals with an Administrative Expert role are thus constantly optimising processes in the organisation to improve efficiency and cut costs. Standardising processes for rewarding, promoting, staffing, and training and thereby creating economies of scale could achieve this (Ulrich, 1997, p.28). This role suits a SSC well, because one of its distinctive features is to create economies of scale. Because of its standardised nature and time intensity administrative services could very well be used for this. The role of an Employee Champion is to link the employees performance to organisational success. As Ulrich (1997, p.29) described Employee contribution is essential to any business, not only for its own sake (the social desirability of committed employees), but also because it affects a business s ability to change, meet customer expectations, and increase financial performance (Ulrich, 1997, p.29). Because the employees are the people who need to deliver the performance for the organisation it is very important to stimulate them to do the right job. Employee motivation can be achieved by giving attention to them end letting the employees feel connected to the organisation. It is also important to create a work environment they feel comfortable in, to improve their performance (Ulrich, 1997, p.29). The Employee Champion is responsible for creating this environment and motivates the employee in doing their job. The fourth and last role described by Ulrich is the Change Agent role. In this role the HR professional delivers organisational transformation and change, by respectively watching over the culture of the organisation and identifying and implementing the organisational change (Ulrich, 1997, p.30). Transformation refers to fundamental cultural changes within the organisation. Organisational Change has to do with an organisations ability to implement changes that reduce cycle time and improve efficiency in all organisational activities 3
4 (Ulrich, 1997, p.30). Because people are naturally resistant to change the Change Agents have to be careful how they implement the transformation or change. They need to respect the history of the organisation, their norms and values, while focussing on the future goals. (Ulrich, 1997, p.31) As described before in the section determining the current HR role of SSC s, using Storey s four roles of personnel management, Farndale et al. (2009) and Meijerink et al. (2013) found that a SSC typically performs three types of activities: transactional activities (such as payroll, personnel administration, benefits management and employee records), traditional activities (recruitment, selection, training and performance management) and transformational activities (change management, knowledge management and strategic HRM). This is of course a very broad definition and therefore many roles could be assigned to these activities. However by combining this definition with findings of Meijerink et al. (2013) who argue that SSC s now fulfil a combination of both transactional and transformational activities, we conclude that the HR SSC fulfils two roles, the Administrative Expert and Strategic Partner role. Examples of transactional activities are record keeping and administrative tasks and therefore best fit the Administrative Expert role as described by Ulrich (1997, p.28). According to Ulrich (1997, p.28) this role delivers the administrative infrastructure for an organisation and standardises processes to achieve economies of scale. The other role is connected to the transformational activities and is the Strategic Partner role. This is a more strategic role and focuses on aligning the HR practises with the business strategy (Ulrich, 1997, p.26). As Caldwell (2003) described in his article about the changing roles of personnel managers, neither model (Ulrich nor Storey) can adequately accommodate the emergent tensions between competing role demands, ever-increasing managerial expectations of performance and new challenges to professional expertise, all of which are likely to intensify in the future (Caldwell, 2003, p.1). This suggests HR managers will have to deal with more demands for HR services and improved performance in the future. Since there is a continuing increase in centralizing HR practices in SSC s these centres will face the same demands for improved performance. It is not stated which changes Caldwell (2003) suspects, but with more demands and therefore more services it is likely the roles will be more complex. This is in line with the expectations from Ulrich and Brockbank (2005), who argue that there will be a shift to more strategic, transformational, activities and that transactional activities will be outsourced. (Ulrich et al. 2008) They did not study Shared Service Centres, but since both, managers and SSC s, fulfil HR practises we assume the results from Ulrich et al. (2008) are interchangeable. With this said there is a possibility the current HR roles as determined by Storey and Ulrich will change to more strategic roles. Further research will have to prove if this is true. Hypothesis 1: Within five years HR SSC roles will shift to more strategic roles. Institutional theory As described in the introduction, another phenomenon we want to study is if the HR roles will get more alike over time. The institutional theory by Dimaggio and Powell (1983) argues this is the case for organisations, but we want to find out if it also applies to HR roles of SSC s. Several researchers like Caldwell (2003), Dimaggio and Powell (1983) have argued that organisations will get more alike over time. The concept that best captures the process of homogenisation is isomorphism. Isomorphism is a constraining process that, say Dimaggio and Powell (1983), forces one unit in a population to resemble other units that face the same set of environmental conditions (Paauwe and Boselie, 2003, p.5). This concept captures the challenges SSC managers have to deal with. To deal with the uncertainty of which HR role SSC s will fulfil within five years they resemble other SSC s. HR SSC s are especially prone to institutional pressures, because they have to deal with the relatively new concept of shared services. According to Dimaggio and Powell (1983), there are three institutional mechanisms that influence decision making in organisations. Coercive mechanisms have to do with legislation that organisations have to abide. This could be a governmental rule from the country where the company is located in, or socially accepted rules they have to live by (Dimaggio and Powell, 1983). Over time there will be more and more rules and as a result of this a SSC can only act within certain boundaries. Each SSC has to respect these rules and in the long term they will therefore get more alike. Mimetic mechanisms describe the response to imitate competitors to deal with uncertainty (Dimaggio and Powell, 1983). When organisations have to deal with uncertainty they may benchmark themselves to successful organisations to see how they use HR roles and imitate them (Paauwe and Boselie, 2003). Since Shared Service Centres are a relatively new phenomenon there is more likeliness for uncertainty. For example, which services to provide in the centre or where to locate it. Following the theory from Paauwe and Boselie (2003) all the SSC s will benchmark to the best centre, imitate them and therefore adopt the same HR role in the long term. The third institutional mechanism is the normative mechanism, which argues that organisations get more the same because managers get the same information about new trends and innovations (Dimaggio and Powell, 1983). This could be from scientific magazines like The International Journal of HRM, information lectures or from consultants. Dimaggio and Powell, (1983) found that, because HR managers from SSC access the same information about new trends and innovations on SSC expected behaviour they will get more alike over time. This theory leads to the following hypothesis for SSC roles within five years. Hypothesis 2: Within five years HR SSC roles will get more alike. Methodology The challenging part of this study is that we do research into the future of SSC roles and so far there is no evidence how this will look like. Literature has not proven it and therefore we need to look at other research methods. Because of its use of experts opinions to find consensus about the unknown future, a Delphi study is a good research method for this study. Its multi stage process and use of expert opinions to find consensus distinguishes it from other research methods. A Delphi study normally consists of four rounds where respondents are asked to answer mail-distributed questionnaires anonymously (Cookson, 1986, p.5). The type of Delphi study we use here is slightly different from normal and is called the Policy Delphi. It is different, because this Delphi type not only seeks consensus but also stimulates divergent responses, which is useful when exploring multiple alternatives like future SSC roles (Boberg and Morris-Khoo, 1992). The first step is to ask SSC managers to give their opinion about the responsibilities and task they expect their SSC to have within the next five years. We ask SSC managers because they are the experts in the field of 4
5 SSC s. They work in these centres every day and know the ins and outs. If they want to share their knowledge on this subject with us, this will be very useful for our research. In the followup we ask them to rank the opinions of other experts and score the most likely outcomes. The outcomes will show the most likely responsibilities and tasks of SSC s within five years and with this information we can determine which HR role fits best to this expectation. Our Delphi study consists of two rounds. But first we need to select the HR experts based on predetermined criteria. Criteria for this study are that the experts work in a SSC and know how these centres operate. We selected eleven SSC managers to participate in this study from different organisations and sectors in the Netherlands. Next is the divergent phase, which consist of asking SSC manager s open questions about the responsibilities and tasks of their centre. The goal for this phase is to generate possible responsibilities and services that can later be used as indicators for the HR role of SSC s. Asking open questions that allow participants freedom in their responses will do this. In these questions they are encouraged to donate as many opinions as possible so as to maximize the chance of covering the most important opinions and issues (Hasson F., Keeney S. & McKenna H., 2000, p.1011). During the first round of the Delphi study the following questions will be asked: Welke verantwoordelijkheden verwacht u dat uw HR SSC over vijf jaar zal hebben? Welke taken verwacht u dat uw HR SSC over vijf jaar uit zal voeren om van waarde te zijn voor {naam organisatie}? We chose to ask these questions as it gives us a good view of the responsibilities and tasks SSC managers think their centre will fulfil within five years. The next step is analysing the experts opinions and coding them into specific categories using existing literature on HR roles from Ulrich (1997) and Storey (1992). We also check the responses for duplicates so the answers are all unique. The results of the coding are showed in table 1 and 2. To ensure inter-coder reliability we asked two of our colleagues how they would decode our responses and check whether we could find inter-coder reliability between the responsibilities/tasks and the corresponding HR role. The results of this were 80% reliability between our colleagues and this is seen as sufficient. Responsibility Verantwoordelijkheid voor HR administratieve taken. Verantwoordelijkheid voor het toegankelijk maken van betrouwbare management informatie, met voorspellende waarde naar de toekomst, basis & high-end (talentmanagement) via IT technologieën Verantwoordelijk voor het afstemmen van de HR dienstverlening op behoefte van de gebruiker (line management) Verantwoordelijk voor het leveren van HR expertise aan line management Role Administrative Expert. Strategic partner Employee Champion Advisors Langere openingstijden voor de HR afdeling en meer gebruiksgemak voor employees m.b.t. contact opnemen. Ontzorgen van leidinggevende zonder verantwoordelijkheid over te nemen Verantwoordelijk voor functioneel beheer van alle HR systemen. Verantwoordelijk voor het beheren van Employee Self Service en Management Self Service. Employee Champion Handmaidens Handmaidens Handmaidens Table 1: Coding of question one of the first Delphi round results. Task Het monitoren van werknemers in HR processen Volledige digitalisering van administraties Het verwerken van alle administratie tot en met de payroll Het beheren van HR Analytics en op basis daarvan adviseren Helpdesk functie of eerste aanspreekpunt voor leidinggevenden en medewerkers op HR gebied Het beheren van HR gegevens Role Regulators Administrative Expert Administrative Expert Advisors Handmaidens Administrative Expert Het beheer en onderhoud van Handmaidens het intranet Adviseren van leidinggevenden Advisors op basis van aanwezige informatie. Table 2: Coding of the second question of Delphi round one. When this is done the results from round one will be ed to the SSC managers again. In the second round of the Delphi study we asked the respondents to rank the answers found in the first round. Every number could hereby only be used once and the highest scoring number would be the task or responsibility that HR SSC s will most likely fulfil within five years. With this method we can see which task and responsibility will be most likely to be fulfilled by the SSC as this has the highest score. To answer our hypothesis we also need to find the level of consensus between the respondents. To do this we will analyse how often each number is answered at each category. The next step is to calculate how often this number is answered out of the total responses for this category. This results in a percentage. When two categories next to each other combined score more than 51% of the answers, there is consensus about this category. This is a norm used in most Delphi studies according to Loughlin K. & Moore L. (1979). With this method we can confirm of reject our hypotheses. The numbers that respondents could score ranged from 1 to 7 on the first question and 1 to 8 in the second question. With the first question the numbers 1-3 would mean the respondents do not think it is likely that these responsibilities will be fulfilled by the SSC in the future, number 4 is intermediate and numbers 5-7 would mean the respondents think it is likely that these responsibilities will be fulfilled by SSC s in the future. With the second question we did the same, but since this question had eight 5
6 possible answers 1-3 were defined as not likely, 4-5 as intermediate and 6-8 as likely tasks to be fulfilled by the SSC in the future. First round findings In this section we present the findings from the first round of the Delphi study. As described before there were two rounds of this study. The first round is the divergent round, whereby respondents were encouraged to answer the open questions as detailed as possible. This has led to several tasks and responsibilities HR SSC experts think their SSC will fulfil within five years. One of the findings that stood out was that seven out of ten respondents expected their SSC to fulfil administrative or transactional activities within five years. These tasks and responsibilities are characteristics of the Administrative Expert role as described in the theory section. This finding also complements the statement that SSC s will get more alike over time, but further conclusions about the hypothesis will be done in the discussion section. According to the responses the SSC s will also adapt to the needs of the users. By the users we mean the line-managers and employees of the organisation. Longer opening hours, one stop shopping and a wider range of services (Personal communication, 24 June 2015) The employees and linemanagers make contact with the SSC and they help them with their questions. This is primarily customer led, since they need to make contact with the SSC. Another finding is that the managers also expect their SSC to be responsible for managing the E-HRM systems. This includes keeping the system up and running, but also checking the data for possible flaws. This supports the experts predictions for more Employee Self Service (ESS) and Management Self Service (MSS). A good E-HRM system that allows employees and managers to check for vacation days, salary, insight in strategic data for their department and organisation etc. supports the implementation of ESS and MSS. These systems support employees and line-managers in doing their job. They can access this information on demand when they want to. These services accommodate to the needs of employees and managers, and motivate them to do a good job and contribute to organisational success. Although a detailed reflection of the hypotheses will be given in the discussion section the first round of the Delphi study already shows a conformation for a shift to more strategic roles within five years. Further implementation of ESS and MSS brings HR responsibilities more to line-management. The SSC can therefore take the role of a strategic business partner (Personal communication, 24 June 2015). With only four out of ten respondents mentioning the increase in strategic responsibilities for their SSC, this might not be the strongest confirmation, but the second round will provide more information and allow us to check the validity. The most striking result from the first round of the Delphi study is however that there is not just one role, but in most of the cases a combination of roles, dependent on the layout of the organisation and level op responsibility of the linemanagement. Based on the literature review we expected the SSC s just to fulfil one role, but this seems not to be true. From the responses we see multiple roles applicable to the responsibilities and tasks SSC managers think their SSC will have within five years. From the findings up to this point we can conclude that most (7/10) SSC s within five years will fulfil an Administrative Expert role. Hereby consists the possibility for an additional role. This addition can be various roles dependent on the layout of the organisation and the level of responsibility for the linemanagement. Organisations with a non-interventionary SSC are more likely to adopt a Handmaiden role, but interventionary and more strategic organisations will tend more to an additional Strategic Partner role in order to wider their range of activities. Second round findings In this section we will present the findings of the second round of the Delphi study. In this round we asked the respondents to rank the answers found in the first round. Every number could hereby only be used once and the highest scoring number would be the task or responsibility that HR SSC s will most likely fulfil within five years. The results of this study are presented in table 3 and 4 Table 3: Het results of the question Welke verantwoordelijkheden verwacht u dat uw HR SSC over vijf jaar zal hebben? For the first question that asked about responsibilities the responsibilities they expected their SSC to fulfil within five years, there was just one question where the respondents couldn t find consensus in. Only on the question about longer opening hours respondents disagreed too much to find consensus. This means that in the other questions there were always two numbers next to each other that made more than 51% of the answers. The responsibilities that the HR experts agreed on fulfilling within five years are responsibilities for administrative HR activities (question 1) and the responsibilities for delivering HR expertise to line-managers (question 4). Looking at the coding showed in table 1 this would mean that SSC s fulfil respectively the Administrative Expert and Advisor role within five years. Table 4: The results of the question Welke taken verwacht u dat uw HR SSC over vijf jaar uit zal voeren om van waarde te zijn voor {naam organisatie}? For the second question that asked HR experts about the tasks they expected their SSC to fulfil within five years, the answers were more dispersed than the first question. Consensus was found on only half of the categories. Full consensus (numbers 6-8) was only found on SSC s fulfilling the task of a helpdesk function and first point of contact for line-managers and employees. Using the coding we did in table 1 this results to a Handmaiden role. The category that involved digitalising administrations scored consensus on place 5-6 which is not very strong, but worth mentioning. This task belongs to the Administrative Expert role as can seen in table 1. As shown in table 1&2 the highest percentage of consensus over two scores in this study is only 66,6%. This means that the HR experts asked to participate in this study have not a high level of consensus about the responsibilities and tasks SSC s will fulfil within five years. This suggests that organisations will not get more alike over time. 6
7 Discussion In this section we will discuss if the hypotheses can be confirmed or rejected based on our study results. We also discuss what these results mean for further research and what this implicates for organisation. In the first hypothesis we expected the HR SSC to fulfil more strategic roles within five years. But analysing the results from Delphi study, we have to reject this hypothesis. In the first round of the Delphi study there were only four out of ten respondents who said their SSC would fulfil responsibilities and tasks related to a more strategic HR role. We already mentioned this was not a very strong conformation, but the results of the second round also suggest the rejection of this hypothesis. Four categories from round one were assigned to a role concerned with strategy. This was one time the Strategic Partner from Ulrich role and three times the Advisor role from Storey. Only in the category delivering HR expertise to line-management there was 55,5% consensus among the respondents. In the other categories there was no consensus, or even consensus that this role would not be fulfilled by the SSC within five years, so there is very little conformation of our hypothesis. The not very convincing results from round one and two of our Delphi study, combined with the fact that there are already some transformational/strategic activities performed by the SSC s nowadays (Meijerink et al., 2013) and that it is therefore not more than now, has led us to reject this hypothesis. The second hypothesis we tested in this study is if organisations, and therefore HR roles, will get more alike within five years. As stated in the theory section this would be the case according to Dimaggio and Powell (1983). However on the basis of our study results we have to reject this hypothesis. In the results section we already described that the highest percentage of agreement on two scores combined was only 66,6%, and although we say this is enough for reaching consensus, it not very high. Table 3 and 4 also show that the results are very dispersed and that it is hard to confirm the hypothesis that SSC s will fulfil the same role over time. The only finding that confirms our hypothesis is that the first round results showed that 7/10 respondents thought their SSC would fulfil and Administrative Expert role within five years. In the second round however, the HR experts reached 55,5% agreement about this finding, so we say they found consensus and that SSC s will fulfil this role within five years, but it is not a strong conformation. Although we do not know for sure, we think both the rejections of our hypotheses have to do with how we measured the results of the second round. Our method limited respondents to use each number only once and this obligated them do make a distinction. There is a possibility that they thought more responsibilities and tasks will be fulfilled by the SSC in the future, but they did not have this choice to answer this in the survey. If we would have let them score each category on how likely they think this will happen in the future on a five or seven point scale, we could have analysed responsibilities and tasks individually and we think there might be more consensus among respondents this way. Theoretical implication And important part is what these findings mean for other researchers and companies. Where do they need to do more research in, and which adaptions do companies need to make to deal with future HR SSC roles? To start from the researchers perspective, this study has shown that there is little consensus on which HR roles SSC s will fulfil in the future. Due to our limited time we did not study which variables caused the lack of consensus. There could be multiple factors that influence this outcome, but as said we did not study this. Because we did not find consensus on country level, further research have to study the SSC s on a smaller organisational level to find the differences that caused us not to find consensus. Our study showed very dispersed answers and this means that the SSC s we studied are very different from each other and they cannot reach consensus about the future role SSC s will fulfil. For organisations our findings mean they have to invest in database and ICT facilities. The Administrative Expert role facilitates administrative services for the organisation and tries to maximize efficiency (Ulrich, 1997). In order to fulfil this role to its potential SSC s need to have access to online databases and ICT facilities to do their job. Also the Advisor role uses strategic HR information to deliver their HR expertise to line managers (Storey, 1992). To do this they need the facilities to access this information as efficiently as possible. Another role we found was the Handmaiden role. This role is noninterventionary and offers customer led services to the organisation (Storey, 1992). As can be seen in table 1 and 2 responsibilities and task of Handmaidens involve helpdesk functions and managing HR systems to improve ESS and MSS. For both of these services Handmaidens rely on ICT facilities. This, combined with the importance for the other roles, ICT and databases can be seen as the most important requirement for an SSC. Conclusion The research question we tried to answer in this paper is: Which HR roles will shared service centres fulfil in the next five years from a SSC manager perspective? The answer to this is that there is no universal role that all the SSC s will fulfil. The results from the Delphi study have shown that SSC s will most likely fulfil the Administrative Expert role as described by Ulrich (1997) in combination with other roles. We think the SSC will in most of the organisations fulfil the A.E. role, because the first round of the Delphi study showed that seven out of ten experts thought their SSC would fulfil this role within five years and the finding that experts reached consensus in round two on multiple responsibilities and tasks that characterise this role. The results however also show that there are other roles that can be performed by the SSC alongside the Administrative Expert role that was mentioned before. Results from the first round of the study showed responsibilities and tasks related to the Strategic Partner, Employee Champion, Advisors, Handmaiden and Regulator role. This however, does not say anything about the likeliness of actually happening of these roles. Therefore we studied in the second round of the Delphi study if there can be found consensus, which reached by more than 51% agreement among respondents (Loughlin K. & Moore L., 1979), about the existence of these roles within five years. Results showed that respondents found consensus on the Advisor and Handmaiden role, next to the Administrative Expert. The Advisor role will be fulfilled by SSC s that are more long-term/strategic focussed and the Handmaiden role by SSC s that are more shortterm/tactical oriented (Storey, 1992). Therefore we can conclude that SSC s in five years will fulfil the Administrative Expert role and that is the possibility for an additional Handmaiden or Advisor role, dependent on the longterm view of an SSC. 7
8 Limitations and suggestions for further research Naturally this research has several limitations. First there is the problem with the small sample size. We conducted the Delphi study with only eleven SSC s and since not every respondent filled the questions in the right way there were only nine left in round two. As can be seen in the findings section the results are quite dispersed and the SSC managers have different opinions. For a better validity of this study there should have been more respondents. With more respondents the results would better represent the opinion of all the SSC s and be better generalizable to other SSC s. Another limitation of our study is the small number of Delphi rounds. According to Cookson (1986, p.5) a Delphi study normally consists of four rounds with different rounds of follow-up questions. Due to time limitation we did only two rounds of this study type. One round of questions and one round of scoring the answers to find consensus among the SSC experts. Because of this we could not ask all of the questions we wanted to ask, to achieve the best possible outcome. When the responses of the first round came back we wanted to ask some respondents for future elaboration of their answers, but this was not possible. For this reason some answers are a bit vague and not as reliable as we hoped. The third limitation of this study is that our study only involved Dutch SSC s. Findings from this study might therefore not be generalizable to other countries, because of other legal regulations or cultural differences. The final en largest limitation of our study is the method we used to find consensus among HR experts in this study. We already mentioned this in the discussion section, but because we asked the respondents to ranking the responsibilities and tasks, we could not analyse the likeliness of them becoming reality individually. Because of our dispersed responses, we think respondents might be limited by having to make a choice, while there might be two responsibilities or task equally likely to be fulfilled in the future. We think this limited our chances to find consensus and we would suggest using a five-point scale for each category in further research. Future research could study if the size of the organisation has influence on the role of the SSC. Large companies like Coca Cola have multiple SSC s not only for Human Resources, but for example also for the Finance department (novinite.com, 2013). There is not yet studied how these centres operate together and what this means for the roles of these centres, so this could be an interesting topic. Another suggestion for further research is if there is a difference in between different sectors of the market. Based on the responses of the Delphi study we expect a difference between market sectors. It was clear that not every SSC was as developed as the others and we think this might have to do with different market sectors and their culture to change or the usefulness of a SSC for their sector. Acknowledgements We would like to thank dr. J.G. Meijerink for his supervision of this research paper and expertise that helped to improve this article. We would also like to thank dr. H.J.M. Ruël for his second supervision and feedback. The final appreciation goes out to my colleagues A.M.L. Buningh and J.J.G. Hooge Venterink for comments that improved this paper. Appendix Second round questions. De volgende vragen gaan over de toekomstige rol van uw HR SSC. Een rol wordt hierbij gezien als de verwachting die de klanten en gebruikers van uw SSC hebben. Hieronder zijn zeven mogelijke verantwoordelijkheden van een HR SSC beschreven. Wilt u deze verantwoordelijkheden rangschikken van 1 t/m 7. Hierbij kunt u het cijfer 7 geven aan de verantwoordelijkheid die uw SSC over 5 jaar het meest waarschijnlijk heeft en het cijfer 1 aan de verantwoordelijkheid die uw SSC over 5 jaar het minst waarschijnlijk heeft. Elk cijfer mag hierbij 1 keer gebruikt worden, om zo tot een rangschikking van 1 t/m 7 te komen. Verantwoordelijkheid Verantwoordelijkheid voor HR administratieve taken. Bijvoorbeeld: correcte salarisverwerking, personeelsadministratie, inclusief digitaal personeelsdossier, subsidieprocessen, wagenparkbeheer, arbeidsongeschiktheid, Opleiding en Ontwikkeling. Verantwoordelijkheid voor het toegankelijk maken van betrouwbare management informatie. Verantwoordelijkheid voor het afstemmen van de HR dienstverlening op behoefte van de gebruiker. Verantwoordelijk voor het leveren van expertise aan lijnmanagers/leidinggevende. Langere openingstijden voor het HR SSC en vergroten gebruiksgemak voor medewerkers. Bijvoorbeeld: One stop shopping en Call me back. Ontzorgen van leidinggevenden zonder verantwoordelijkheid over te nemen. Verantwoordelijkheid voor functioneel beheer van alle HR systemen. Ranking 8
9 Hieronder zijn acht mogelijke taken van een HR SSC beschreven. Wilt u deze mogelijke taken rangschikken van 1 t/m 8. Hierbij kunt u het cijfer 8 geven aan de taak die uw SSC over 5 jaar het meest waarschijnlijk heeft en het cijfer 1 aan de taak die uw SSC over 5 jaar het minst waarschijnlijk heeft. Elk cijfer mag hierbij 1 keer gebruikt worden, om zo tot een rangschikking van 1 t/m 8 te komen. Hasson F., Keeney S. & McKenna H. (2000). Research guidelines for the Delphi survey technique. Journal of Advanced Nursing 32(4) Janssen, M., and Joha, A. (2006), Motives for Establishing Shared Service Centers in Public Administrations, International Journal of Information Management, 26, Taak Het monitoren van werknemers in HR processen. Volledige digitalisering van administraties. Het verwerken van alle administratie tot en met de payroll. Het beheren van HR Analytics en op basis daarvan adviseren. Helpdesk functie of eerste aanspreekpunt voor leidinggevenden en medewerkers op HR gebied. Het beheren van HR gegevens. Het beheer en onderhoud van het intranet. Adviseren van leidinggevenden op basis van aanwezige informatie. Ranking Loughlin K. & Moore L. (1979) Using Delphi to achieve congruent objectives and activities in a pediatrics department. Journal of Medical Education 54, 101±106. Maatman, M., Bondarouk, T.V. and Looise, J.C. (2010) Conceptualising the capabilities and value creation of HRM shared services models, Human Resource Management Review, Vol. 20, No. 4, pp Meijerink, J.G. and Bondarouk, T. (2013) Exploring the central characteristics of HR shared services: evidence from a critical case study in the Netherlands, International Journal of Human Resource Management, Vol. 24, No. 3, pp Meijerink, J., Bondarouk, T. & Maatman, M. (2013b). Exploring and comparing HR shared services in subsidiaries of multinational corporations and indigenous organizations in the Netherlands: a strategic response analysis. European Journal International Management, 7(4), Novinite.com. (2013). Coca-Cola Opens Finance Shared Service Center in Sofia. Obtained on 18, June, 2015, Cola+Opens+Finance+Shared+Service+Center+in+Sofia Paauwe, J. and Boselie, P. Challenging strategic HRM and the relevance of the institutional setting, Erasmus University, Rotterdam Human Resource Management Journal, Vol 13 No 3, 2003, pages Quinn, B., Cooke, R., and Kris, A. (2000), Shared Services: Mining for Corporate Gold, Harlow: Pearson Education. References Boberg, A.L., Morris-Khoo, S.A., (1992), The Delphi method: a review of methodology and an application in the evaluation of a higher education program, The Canadian journal of program evolution, p27-39 Caldwell, R. (2003). The Changing Roles of Personnel Managers: Old Ambiguities, New Uncertainties. London: Blackwell Publishing Ltd. Cookson, P.S. (1986) Charting the unknown: Delphi and Policy Delphi strategies for international cooperation, International Journal of lifelong education, 5, 3-13 Dimaggio, P.J. and W.W. Powell (1983) The iron cage revisited: institutional isomorphism and collective rationality in organizational fields, American Sociological Review, 48, p Farndale, E., Paauwe, J., & Hoeksema, L. (2009). In-sourcing HR: Shared service centres in the Netherlands. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 20(3), Redman, T., Snape, E., Wass, J., & Hamilton, P. (2007). Evaluating the human resource shared services model: evidence from the NHS. International Journal of Human Resource Management, 18(8), Storey, J. (1992). Developments in the Management of Human Resources. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. Strikwerda, J. (2004), Shared Service Center: van kosten besparing naar waardecreatie, Assen: Koninklijke Van Gorcum. Ulrich, D. (1995). Shared services: From Vogue to value. Human Resource Planning, 18(3), Ulrich, D. (1997). Human Resource Champions. Boston: Harvard University Press. Ulrich, D., & Brockbank, W. (2005). The HR value proposition. Boston: Harvard Business School Press. Ulrich, D., Younger, J. & Brockbank, W. (2008), The twentyfirst-century HR organization. Human Resource Management, 47(4),
WHEN DO HR DELIVERY CHANNELS PROVIDE THE HIGHEST HR SERVICE VALUE? AN INTEGRATED ANALYSIS USING RESOURCE-
 WHEN DO HR DELIVERY CHANNELS PROVIDE THE HIGHEST HR SERVICE VALUE? AN INTEGRATED ANALYSIS USING RESOURCE- BASED VIEW, TRANSACTION COST ECONOMICS, AND RESOURCE-DEPENDENCE PERSPECTIVES MASTER THESIS BUSINESS
WHEN DO HR DELIVERY CHANNELS PROVIDE THE HIGHEST HR SERVICE VALUE? AN INTEGRATED ANALYSIS USING RESOURCE- BASED VIEW, TRANSACTION COST ECONOMICS, AND RESOURCE-DEPENDENCE PERSPECTIVES MASTER THESIS BUSINESS
Edward Wong Sek Khin 1, Mehdi Poorangi 2, Ahmad Zahiruddin 3 E-HRM AND E-RECRUITMENT FOR SMES: MALAYSIAN PERSPECTIVE
 376 НОВИНИ ЗАРУБІЖНОЇ НАУКИ Edward Wong Sek Khin 1, Mehdi Poorangi 2, Ahmad Zahiruddin 3 E-HRM AND E-RECRUITMENT FOR SMES: MALAYSIAN PERSPECTIVE The purpose of this study is the analysis of possibilities
376 НОВИНИ ЗАРУБІЖНОЇ НАУКИ Edward Wong Sek Khin 1, Mehdi Poorangi 2, Ahmad Zahiruddin 3 E-HRM AND E-RECRUITMENT FOR SMES: MALAYSIAN PERSPECTIVE The purpose of this study is the analysis of possibilities
HUMAN RESOURCE. SHARED SERVICES MOTIVATIONS, TYPES and IMPACTS. By Whitney Winspear 38 HR ECHO
 HUMAN RESOURCE SHARED SERVICES MOTIVATIONS, TYPES and IMPACTS By Whitney Winspear This article is printed with permission from Monash University Copyright and all Intellectual property are reserved for
HUMAN RESOURCE SHARED SERVICES MOTIVATIONS, TYPES and IMPACTS By Whitney Winspear This article is printed with permission from Monash University Copyright and all Intellectual property are reserved for
HRQM AND COLLIDING GYROSCOPES AN ALTERNATIVE WAY OF LOOKING AT VALUE CREATION IN ORGANIZATIONS
 HRQM AND COLLIDING GYROSCOPES AN ALTERNATIVE WAY OF LOOKING AT VALUE CREATION IN ORGANIZATIONS Study stream Human resource and Quality management JOOP VINKE Arnhem Business School Arnhem, HAN University
HRQM AND COLLIDING GYROSCOPES AN ALTERNATIVE WAY OF LOOKING AT VALUE CREATION IN ORGANIZATIONS Study stream Human resource and Quality management JOOP VINKE Arnhem Business School Arnhem, HAN University
PH.D THESIS ON A STUDY ON THE STRATEGIC ROLE OF HR IN IT INDUSTRY WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO SELECT IT / ITES ORGANIZATIONS IN PUNE CITY
 ABSTRACT OF PH.D THESIS ON A STUDY ON THE STRATEGIC ROLE OF HR IN IT INDUSTRY WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO SELECT IT / ITES ORGANIZATIONS IN PUNE CITY SUBMITTED TO THE UNIVERSITY OF PUNE FOR THE AWARD OF
ABSTRACT OF PH.D THESIS ON A STUDY ON THE STRATEGIC ROLE OF HR IN IT INDUSTRY WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO SELECT IT / ITES ORGANIZATIONS IN PUNE CITY SUBMITTED TO THE UNIVERSITY OF PUNE FOR THE AWARD OF
HR PLANNING STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK PRESENTATION BURGERS PARK - PTA 23 JANUARY 2008
 HR PLANNING STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK PRESENTATION BURGERS PARK - PTA 23 JANUARY 2008 1 OVERVIEW OF THE PRESENTATION Purpose and objectives of the strategic framework HR Planning in the global context HR Planning
HR PLANNING STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK PRESENTATION BURGERS PARK - PTA 23 JANUARY 2008 1 OVERVIEW OF THE PRESENTATION Purpose and objectives of the strategic framework HR Planning in the global context HR Planning
The future demand for Human Resource professionals in light of some structural changes
 The future demand for Human Resource professionals in light of some structural changes Master Thesis Human Resource Studies University of Tilburg, Faculty of Social Sciences October, 2009 Marieke Kaptein
The future demand for Human Resource professionals in light of some structural changes Master Thesis Human Resource Studies University of Tilburg, Faculty of Social Sciences October, 2009 Marieke Kaptein
How to manage Business Apps - Case for a Mobile Access Strategy -
 How to manage Business Apps - Case for a Mobile Access Strategy - Hans Heising, Product Manager Gábor Vida, Manager Software Development RAM Mobile Data 2011 Content Introduction 2 Bring your own device
How to manage Business Apps - Case for a Mobile Access Strategy - Hans Heising, Product Manager Gábor Vida, Manager Software Development RAM Mobile Data 2011 Content Introduction 2 Bring your own device
Oversight Management: een zinvolle aanvulling!
 Oversight Management: een zinvolle aanvulling! Houfhoff Pension Fund Academy Christiaan Tromp info@fiduciaryservices.eu April 2012 1 Agenda The Fiduciary Management promise The evolution of Pension Fund
Oversight Management: een zinvolle aanvulling! Houfhoff Pension Fund Academy Christiaan Tromp info@fiduciaryservices.eu April 2012 1 Agenda The Fiduciary Management promise The evolution of Pension Fund
Page 1. Worldwide. Case problem: Learning objectives:
 Student Self-administered case study Introducing HRM Case duration (Min): 45-60 Human Resource Management (HRM) Introducing HRM Worldwide Case summary: This case introduces some of the essential elements
Student Self-administered case study Introducing HRM Case duration (Min): 45-60 Human Resource Management (HRM) Introducing HRM Worldwide Case summary: This case introduces some of the essential elements
UvA college Governance and Portfolio Management
 UvA college Han Verniers Principal Consultant Han.Verniers@LogicaCMG.com Programma Governance IT Governance, wat is dat? Governance: structuren, processen, instrumenten Portfolio Management Portfolio Management,
UvA college Han Verniers Principal Consultant Han.Verniers@LogicaCMG.com Programma Governance IT Governance, wat is dat? Governance: structuren, processen, instrumenten Portfolio Management Portfolio Management,
Center for Effective Organizations
 Center for Effective Organizations HR METRICS AND ANALYTICS USES AND IMPACTS CEO PUBLICATION G 04-8 (460) EDWARD E. LAWLER III ALEC LEVENSON JOHN BOUDREAU Center for Effective Organizations Marshall School
Center for Effective Organizations HR METRICS AND ANALYTICS USES AND IMPACTS CEO PUBLICATION G 04-8 (460) EDWARD E. LAWLER III ALEC LEVENSON JOHN BOUDREAU Center for Effective Organizations Marshall School
ADAPTATION OF EMPLOYEES IN THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS IMPORTANCE IN TERMS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 114 Management and Economics ADAPTATION OF EMPLOYEES IN THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS IMPORTANCE IN TERMS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Jaroslav NEKORANEC Jaroslav.Nekoranec@aos.sk Lenka NAGYOVÁ lenka.nagyova@mil.sk
114 Management and Economics ADAPTATION OF EMPLOYEES IN THE ORGANIZATION AND ITS IMPORTANCE IN TERMS OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Jaroslav NEKORANEC Jaroslav.Nekoranec@aos.sk Lenka NAGYOVÁ lenka.nagyova@mil.sk
IT Works check. December 12th, 2012
 IT Works check December 12th, 2012 RESOC RESOC-SERR Gent en rondom Gent RESOC Gent en rondom Gent = Committee for regional social-economic consultation Representatives of: City of Ghent + 9 municipalities
IT Works check December 12th, 2012 RESOC RESOC-SERR Gent en rondom Gent RESOC Gent en rondom Gent = Committee for regional social-economic consultation Representatives of: City of Ghent + 9 municipalities
BANK OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA POSITION DESCRIPTION MANAGER LIBRARY UNIT, ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT
 BANK OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA POSITION DESCRIPTION MANAGER LIBRARY UNIT, ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT This Position Description outlines the role, skills, relationships, authorities and accountabilities. The position
BANK OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA POSITION DESCRIPTION MANAGER LIBRARY UNIT, ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT This Position Description outlines the role, skills, relationships, authorities and accountabilities. The position
The Effect of Information Technology (IT) Support on Innovations Concepts: A study of Textile Sector in Pakistan
 The Effect of Information Technology (IT) Support on Innovations Concepts: A study of Textile Sector in Pakistan Abstract Muhammad Mohsin MBA (Quality Management), Govt College University Faisalabad, Pakistan
The Effect of Information Technology (IT) Support on Innovations Concepts: A study of Textile Sector in Pakistan Abstract Muhammad Mohsin MBA (Quality Management), Govt College University Faisalabad, Pakistan
Human Resource Management. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, June 2011
 Human Resource Management From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, June 2011 Human Resource Management (HRM, HR) is the management of an organization's employees.[1] This includes employment and arbitration
Human Resource Management From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, June 2011 Human Resource Management (HRM, HR) is the management of an organization's employees.[1] This includes employment and arbitration
Organizational Design Toolkit
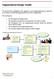 Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Beyond Shared Savings
 Beyond Shared Savings A multilevel analysis of the perceived value of HR shared services Jeroen Meijerink Beyond Shared Savings aim to create value. Although several studies uncovered the value potential
Beyond Shared Savings A multilevel analysis of the perceived value of HR shared services Jeroen Meijerink Beyond Shared Savings aim to create value. Although several studies uncovered the value potential
Changing culture the experience of TU Delft Library
 Abstract: Changing culture the experience of TU Delft Library Ellen van der Sar / Maria Heijne Delft University of Technology Library When seeking to introduce change into an organisation, it is usually
Abstract: Changing culture the experience of TU Delft Library Ellen van der Sar / Maria Heijne Delft University of Technology Library When seeking to introduce change into an organisation, it is usually
THE ROLE AND IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATIONAL TECHNOLOGIES IN ENSURING THE SUCCESS OF HRM ACTIVITIES
 THE ROLE AND IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATIONAL TECHNOLOGIES IN ENSURING THE SUCCESS OF HRM ACTIVITIES ADELA SUZANA ARTENE TIBISCUS UNIVERSITY OF TIMISOARA, FACULTY OF ECONOMICS WEST UNIVERSITY OF TIMISOARA,
THE ROLE AND IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATIONAL TECHNOLOGIES IN ENSURING THE SUCCESS OF HRM ACTIVITIES ADELA SUZANA ARTENE TIBISCUS UNIVERSITY OF TIMISOARA, FACULTY OF ECONOMICS WEST UNIVERSITY OF TIMISOARA,
THEORETICAL APPROACHES TO EMPLOYEE APPRAISAL METHODS
 THEORETICAL APPROACHES TO EMPLOYEE APPRAISAL METHODS Andrea Šalková Abstract: Performance appraisal is the most important process of HR management in an organization. Regular employee appraisal can reveal
THEORETICAL APPROACHES TO EMPLOYEE APPRAISAL METHODS Andrea Šalková Abstract: Performance appraisal is the most important process of HR management in an organization. Regular employee appraisal can reveal
Course Author: Dr. Monica Belcourt, School of Human Resource Management, York University; Ron Alexandrowich and Mark Podolsky
 Strategic Human Resources Planning Course Author: Dr. Monica Belcourt, School of Human Resource Management, York University; Ron Alexandrowich and Mark Podolsky Description: The course provides students
Strategic Human Resources Planning Course Author: Dr. Monica Belcourt, School of Human Resource Management, York University; Ron Alexandrowich and Mark Podolsky Description: The course provides students
RISK BASED INTERNAL AUDIT
 RISK BASED INTERNAL AUDIT COURSE OBJECTIVE The objective of this course is to clarify the principles of Internal Audit along with the Audit process and arm internal auditors with a good knowledge of risk
RISK BASED INTERNAL AUDIT COURSE OBJECTIVE The objective of this course is to clarify the principles of Internal Audit along with the Audit process and arm internal auditors with a good knowledge of risk
Information Security Governance
 Information Security Governance Aart Bitter Aart.Bitter@information-security-governance.com Agenda Governance & Compliance Information Security Governance Aanpak om information security governance in organisaties
Information Security Governance Aart Bitter Aart.Bitter@information-security-governance.com Agenda Governance & Compliance Information Security Governance Aanpak om information security governance in organisaties
ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
 Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
Exploring Strategic Change
 Julia Balogun, Veronica Hope Hailey, Gerry Johnson, Kevan Scholes FT Prentice Hall 2003 ISBN: 0273683276, 280 pages Theme of the Book The book links into (and develops further) the ideas on strategic change
Julia Balogun, Veronica Hope Hailey, Gerry Johnson, Kevan Scholes FT Prentice Hall 2003 ISBN: 0273683276, 280 pages Theme of the Book The book links into (and develops further) the ideas on strategic change
Assuring the Cloud. Hans Bootsma Deloitte Risk Services hbootsma@deloitte.nl +31 (0)6 1098 0182
 Assuring the Cloud Hans Bootsma Deloitte Risk Services hbootsma@deloitte.nl +31 (0)6 1098 0182 Need for Assurance in Cloud Computing Demand Fast go to market Support innovation Lower costs Access everywhere
Assuring the Cloud Hans Bootsma Deloitte Risk Services hbootsma@deloitte.nl +31 (0)6 1098 0182 Need for Assurance in Cloud Computing Demand Fast go to market Support innovation Lower costs Access everywhere
Voorbeeld. Preview ISO 10018 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Quality management Guidelines on people involvement and competence
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10018 First edition 2012-09-01 Quality management Guidelines on people involvement and competence Dit document mag slechts op een stand-alone PC worden geinstalleerd. Gebruik
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10018 First edition 2012-09-01 Quality management Guidelines on people involvement and competence Dit document mag slechts op een stand-alone PC worden geinstalleerd. Gebruik
IJMIE Volume 2, Issue 7 ISSN: 2249-0558
 A STUDY ON THE PRESENT AND EMERGING TRENDS IN E-HRM AND HRIS IN THE HINDU C.M.Sudha Arogya Mary* B.Sc,MBA,MHRM,MSW,M.Phil,(Ph.D) B. Kunthala Nayagi** B.Sc., (MBA) ABSTRACT The project was conducted to
A STUDY ON THE PRESENT AND EMERGING TRENDS IN E-HRM AND HRIS IN THE HINDU C.M.Sudha Arogya Mary* B.Sc,MBA,MHRM,MSW,M.Phil,(Ph.D) B. Kunthala Nayagi** B.Sc., (MBA) ABSTRACT The project was conducted to
6 Essential Characteristics of a PLC (adapted from Learning by Doing)
 6 Essential Characteristics of a PLC (adapted from Learning by Doing) 1. Shared mission, vision, values, goals Educators in a PLC benefit from clarity regarding their shared purpose, a common understanding
6 Essential Characteristics of a PLC (adapted from Learning by Doing) 1. Shared mission, vision, values, goals Educators in a PLC benefit from clarity regarding their shared purpose, a common understanding
THE EMOTIONAL VALUE OF PAID FOR MAGAZINES. Intomart GfK 2013 Emotionele Waarde Betaald vs. Gratis Tijdschrift April 2013 1
 THE EMOTIONAL VALUE OF PAID FOR MAGAZINES Intomart GfK 2013 Emotionele Waarde Betaald vs. Gratis Tijdschrift April 2013 1 CONTENT 1. CONCLUSIONS 2. RESULTS Reading behaviour Appreciation Engagement Advertising
THE EMOTIONAL VALUE OF PAID FOR MAGAZINES Intomart GfK 2013 Emotionele Waarde Betaald vs. Gratis Tijdschrift April 2013 1 CONTENT 1. CONCLUSIONS 2. RESULTS Reading behaviour Appreciation Engagement Advertising
NECESSITY TO EVALUATE HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT IN COMPANIES OF LATVIA
 NECESSITY TO EVALUATE HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT IN COMPANIES OF LATVIA Līga Peiseniece 1, Tatjana Volkova 2 1 BA School of Business and Finance, Latvia, liga.peiseniece@ba.lv 2 BA School of Business and
NECESSITY TO EVALUATE HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT IN COMPANIES OF LATVIA Līga Peiseniece 1, Tatjana Volkova 2 1 BA School of Business and Finance, Latvia, liga.peiseniece@ba.lv 2 BA School of Business and
Impact of Information Technology in Human Resources Management
 Global Journal of Business Management and Information Technology. ISSN 2278-3679 Volume 4, Number 1 (2014), pp. 33-41 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Impact of Information Technology
Global Journal of Business Management and Information Technology. ISSN 2278-3679 Volume 4, Number 1 (2014), pp. 33-41 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Impact of Information Technology
GMP-Z Annex 15: Kwalificatie en validatie
 -Z Annex 15: Kwalificatie en validatie item Gewijzigd richtsnoer -Z Toelichting Principle 1. This Annex describes the principles of qualification and validation which are applicable to the manufacture
-Z Annex 15: Kwalificatie en validatie item Gewijzigd richtsnoer -Z Toelichting Principle 1. This Annex describes the principles of qualification and validation which are applicable to the manufacture
Full-time MSc in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
 Full-time MSc in Logistics and Supply Chain Management Course structure and content 2016-2017 The course has been developed to produce expert logistics and supply chain professionals who can take the skills
Full-time MSc in Logistics and Supply Chain Management Course structure and content 2016-2017 The course has been developed to produce expert logistics and supply chain professionals who can take the skills
Bachelor of Public Administration Curriculum
 2010 Bachelor of Public Administration Curriculum From the beginning of the academic year 2010 1 Contents Preamble 1. Aims and scope of the degree programme 1.1. Aims 1.2. ECTS credits 1.3. Titles 1.4.
2010 Bachelor of Public Administration Curriculum From the beginning of the academic year 2010 1 Contents Preamble 1. Aims and scope of the degree programme 1.1. Aims 1.2. ECTS credits 1.3. Titles 1.4.
Spread. B&R Beurs. March 2010
 B&R Beurs March 2010 Spread Find out about the latest investment proposals of B&R's investment groups. Check the agenda, and the upcoming activities we organized for you! B&R Beurs Website: www.bnrbeurs.nl
B&R Beurs March 2010 Spread Find out about the latest investment proposals of B&R's investment groups. Check the agenda, and the upcoming activities we organized for you! B&R Beurs Website: www.bnrbeurs.nl
HR Transformation The evolution of the HR model. Philip Rice PA Consulting May 2013
 HR Transformation The evolution of the HR model Philip Rice PA Consulting May 2013 Agenda 1. Background and the drive to transformation 2. Understanding the model and how to get it to work 3. Where to
HR Transformation The evolution of the HR model Philip Rice PA Consulting May 2013 Agenda 1. Background and the drive to transformation 2. Understanding the model and how to get it to work 3. Where to
Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA)
 Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA) Chief Manager - HR Development and Performance Management Job details Reference Number: KRA/HR02/14 Job Title: Chief Manager - HR Development and Performance Management Supervisor:
Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA) Chief Manager - HR Development and Performance Management Job details Reference Number: KRA/HR02/14 Job Title: Chief Manager - HR Development and Performance Management Supervisor:
The Future is Now: HR Competencies for High Performance
 The RBL White Paper Series The Future is Now: HR Competencies for High Performance WAYNE BROCKBANK, DAVE ULRICH, JON YOUNGER, AND MIKE ULRICH The Future is Now: HR Competencies for High Performance * Wayne
The RBL White Paper Series The Future is Now: HR Competencies for High Performance WAYNE BROCKBANK, DAVE ULRICH, JON YOUNGER, AND MIKE ULRICH The Future is Now: HR Competencies for High Performance * Wayne
SAFETY CULTURE: A GLOBAL APPROACH, SUPPORTED BY THE HIERARCHY
 SAFETY CULTURE: A GLOBAL APPROACH, SUPPORTED BY THE HIERARCHY 1. Organisations involved 2. Description of the case 2.1. Introduction The American multinational Avery Dennison is active in publishing in
SAFETY CULTURE: A GLOBAL APPROACH, SUPPORTED BY THE HIERARCHY 1. Organisations involved 2. Description of the case 2.1. Introduction The American multinational Avery Dennison is active in publishing in
CIPD Employee engagement
 CIPD Employee engagement See www.cipd.co.uk for further details January 2007 This factsheet gives introductory guidance. It: considers what is meant by employee engagement and why organisations are interested
CIPD Employee engagement See www.cipd.co.uk for further details January 2007 This factsheet gives introductory guidance. It: considers what is meant by employee engagement and why organisations are interested
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement
 Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
Research Scientist I. Chemical Sciences Epidemiology/Biostatistics Microbiological Sciences Physical/Engineering Sciences Social/Behavioral Sciences
 Research Scientist I Under the supervision of senior scientific research personnel, incumbents at this level plan, organize, and carry out scientific research studies of limited scientific scope and complexity.
Research Scientist I Under the supervision of senior scientific research personnel, incumbents at this level plan, organize, and carry out scientific research studies of limited scientific scope and complexity.
Risks are Key, Processes Follow. Michiel Schuijt Chief Risk Officer, Mn Services
 Risks are Key, Processes Follow Michiel Schuijt Chief Risk Officer, Mn Services Mn Services & Our Risk Management Philosophy 8 June 2011 ProcessWorld 2011 2 Pension Companies in the Netherlands APG Groep
Risks are Key, Processes Follow Michiel Schuijt Chief Risk Officer, Mn Services Mn Services & Our Risk Management Philosophy 8 June 2011 ProcessWorld 2011 2 Pension Companies in the Netherlands APG Groep
Leverage energy efficiency potentials with the principals of Industry 4.0 Background and experiences out of the application in a family-owned company
 Leverage energy efficiency potentials with the principals of Industry 4.0 Background and experiences out of the application in a family-owned company Charles Preeker, Weidmüller Amersfoort IE MotorenEvent
Leverage energy efficiency potentials with the principals of Industry 4.0 Background and experiences out of the application in a family-owned company Charles Preeker, Weidmüller Amersfoort IE MotorenEvent
ABN AMRO Bank N.V. The Royal Bank of Scotland N.V. ABN AMRO Holding N.V. RBS Holdings N.V. ABN AMRO Bank N.V.
 Op 6 februari 2010 is de naam ABN AMRO Bank N.V. (geregistreerd bij de Kamer van Koophandel onder nummer 33002587) gewijzigd in The Royal Bank of Scotland N.V. Op 1 april 2010 is de naam van ABN AMRO Holding
Op 6 februari 2010 is de naam ABN AMRO Bank N.V. (geregistreerd bij de Kamer van Koophandel onder nummer 33002587) gewijzigd in The Royal Bank of Scotland N.V. Op 1 april 2010 is de naam van ABN AMRO Holding
HRM. The importance of HRM. Why Human Resource Management (HRM) is important for organizations today to make
 HRM The importance of HRM Why Human Resource Management (HRM) is important for organizations today to make their Human Resource into a competitive advantage Mr. CHUOP Theot Therith (2009), MBA, BIT, DPA
HRM The importance of HRM Why Human Resource Management (HRM) is important for organizations today to make their Human Resource into a competitive advantage Mr. CHUOP Theot Therith (2009), MBA, BIT, DPA
Operational Improvement Using specialist skills in specific functional areas to enhance your own capabilities
 Page 1 of 10 About FMEA We are a network of diverse, practical and experienced senior business consultants who have worked in small and world renowned Consultancy Organisations. We believe in working co
Page 1 of 10 About FMEA We are a network of diverse, practical and experienced senior business consultants who have worked in small and world renowned Consultancy Organisations. We believe in working co
Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises. [Writer Name] [Institute Name]
![Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises. [Writer Name] [Institute Name] Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises. [Writer Name] [Institute Name]](/thumbs/22/1512415.jpg) 1 Paper: Dissertation Proposal Style: Harvard Pages: 7 Sources: 8 Level: Masters Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises [Writer Name] [Institute Name] 2 Human Resource Management in Multinational
1 Paper: Dissertation Proposal Style: Harvard Pages: 7 Sources: 8 Level: Masters Human Resource Management in Multinational Enterprises [Writer Name] [Institute Name] 2 Human Resource Management in Multinational
Organisation Profiling and the Adoption of ICT: e-commerce in the UK Construction Industry
 Organisation Profiling and the Adoption of ICT: e-commerce in the UK Construction Industry Martin Jackson and Andy Sloane University of Wolverhampton, UK A.Sloane@wlv.ac.uk M.Jackson3@wlv.ac.uk Abstract:
Organisation Profiling and the Adoption of ICT: e-commerce in the UK Construction Industry Martin Jackson and Andy Sloane University of Wolverhampton, UK A.Sloane@wlv.ac.uk M.Jackson3@wlv.ac.uk Abstract:
Writing a degree project at Lund University student perspectives
 1 Writing a degree project at Lund University student perspectives Summary This report summarises the results of a survey that focused on the students experiences of writing a degree project at Lund University.
1 Writing a degree project at Lund University student perspectives Summary This report summarises the results of a survey that focused on the students experiences of writing a degree project at Lund University.
ARHINFUL LORETTA ABA A (844974) SAM PETRA MENSIMAA (844794) AHMED SK ASHIF (843888)
 GROUP MEMBERS ARHINFUL LORETTA ABA A (844974) SAM PETRA MENSIMAA (844794) AHMED SK ASHIF (843888) P W 1 THE HRM BUSINESS MODEL OF ENTERPRISE LIFE ASSURANCE COMPANY GHANA (ELAC) CONTENT ENTERPRISE LIFE
GROUP MEMBERS ARHINFUL LORETTA ABA A (844974) SAM PETRA MENSIMAA (844794) AHMED SK ASHIF (843888) P W 1 THE HRM BUSINESS MODEL OF ENTERPRISE LIFE ASSURANCE COMPANY GHANA (ELAC) CONTENT ENTERPRISE LIFE
SUBJECT LINES DONE RIGHT (ENGELSTALIG)
 SUBJECT LINES DONE RIGHT (ENGELSTALIG) Pagina 1 van 6 An email s subject line is like a first impression. It is one of the first things a recipiënt sees when they glance at their inbox and a determining
SUBJECT LINES DONE RIGHT (ENGELSTALIG) Pagina 1 van 6 An email s subject line is like a first impression. It is one of the first things a recipiënt sees when they glance at their inbox and a determining
Building HR Capabilities. Through the Employee Survey Process
 Building Capabilities Through the Employee Survey Process Survey results are only data unless you have the capabilities to analyze, interpret, understand and act on them. Your organization may conduct
Building Capabilities Through the Employee Survey Process Survey results are only data unless you have the capabilities to analyze, interpret, understand and act on them. Your organization may conduct
Turku School of Economics: Strategy for 2010 2015
 Turku School of Economics: Strategy for 2010 2015 Appendix A TURKU SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS STRATEGY FOR 2010 2015 1 The strategic position of the Turku School of Economics... 1 1.1 Operating environment...
Turku School of Economics: Strategy for 2010 2015 Appendix A TURKU SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS STRATEGY FOR 2010 2015 1 The strategic position of the Turku School of Economics... 1 1.1 Operating environment...
Shell Mentoring Toolkit
 Shell Mentoring Toolkit A reference document for mentors and mentees Human Resources LEARNING 25/07/2007 Copyright: Shell International Ltd 2006 CONTENTS What is Mentoring? 4 The Mentor s Role The Role
Shell Mentoring Toolkit A reference document for mentors and mentees Human Resources LEARNING 25/07/2007 Copyright: Shell International Ltd 2006 CONTENTS What is Mentoring? 4 The Mentor s Role The Role
Citrix Access Gateway: Implementing Enterprise Edition Feature 9.0
 coursemonstercom/uk Citrix Access Gateway: Implementing Enterprise Edition Feature 90 View training dates» Overview Nederlands Deze cursus behandelt informatie die beheerders en andere IT-professionals
coursemonstercom/uk Citrix Access Gateway: Implementing Enterprise Edition Feature 90 View training dates» Overview Nederlands Deze cursus behandelt informatie die beheerders en andere IT-professionals
Strategic HR Partner Assessment (SHRPA) Feedback Results
 Strategic HR Partner Assessment (SHRPA) Feedback Results January 04 Copyright 997-04 Assessment Plus, Inc. Introduction This report is divided into four sections: Part I, The SHRPA TM Model, explains how
Strategic HR Partner Assessment (SHRPA) Feedback Results January 04 Copyright 997-04 Assessment Plus, Inc. Introduction This report is divided into four sections: Part I, The SHRPA TM Model, explains how
A9. What is the total number of employees worldwide including Denmark by headcount?
 SURVEY OF EMPLOYMENT PRACTICES OF MULTINATIONAL COMPANIES OPERATING IN DENMARK Home-based English version Please select a language: SECTION A: INTRODUCTION English... 1 Danish... 2 First page: EMPLOYMENT
SURVEY OF EMPLOYMENT PRACTICES OF MULTINATIONAL COMPANIES OPERATING IN DENMARK Home-based English version Please select a language: SECTION A: INTRODUCTION English... 1 Danish... 2 First page: EMPLOYMENT
University Mission. Strategic Plan. Organisation Structure. Jobs
 Introduction The main purpose of any job description is to outline the main duties and responsibilities that are involved in a particular job. Additional information is often requested in order that one
Introduction The main purpose of any job description is to outline the main duties and responsibilities that are involved in a particular job. Additional information is often requested in order that one
Financial Services Purchasing Forum Best practice SRM the supplier s view
 Financial Services Purchasing Forum Best practice SRM the supplier s view 23 June 2008 Peter Fawcett, Director, Financial Services www.alsbridge.eu Contents SRM : Market trends and challenges The supplier
Financial Services Purchasing Forum Best practice SRM the supplier s view 23 June 2008 Peter Fawcett, Director, Financial Services www.alsbridge.eu Contents SRM : Market trends and challenges The supplier
Patient participation is limited. Background. More information is no solution PATIENT CHECKS HOSPITAL?
 PATIENT CHECKS HOSPITAL? Dirk de Korne PhD MSc - José Rekko RN - Lara Vankan MSc Fatma Unal RN - Claudia van Gaalen MSc - Koen van Overdam MD FEBOpht - Francis Hiddema MD 29 th ISQua-2489, Geneva - October
PATIENT CHECKS HOSPITAL? Dirk de Korne PhD MSc - José Rekko RN - Lara Vankan MSc Fatma Unal RN - Claudia van Gaalen MSc - Koen van Overdam MD FEBOpht - Francis Hiddema MD 29 th ISQua-2489, Geneva - October
Role of Training & Development in an Organizational Development
 International Journal of Management and International Business Studies. ISSN 2277-3177 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 213-220 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Role of Training &
International Journal of Management and International Business Studies. ISSN 2277-3177 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 213-220 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Role of Training &
Strategic time tracking
 Strategic time tracking Manage your time and stay ahead! When time is money... Eliminate the guesswork and generate better results This whitepaper details how to fully optimise your business activities
Strategic time tracking Manage your time and stay ahead! When time is money... Eliminate the guesswork and generate better results This whitepaper details how to fully optimise your business activities
Use Your Master s Thesis Supervisor
 Use Your Master s Thesis Supervisor This booklet was prepared in dialogue with the heads of studies at the faculty, and it was approved by the dean of the faculty. Thus, this leaflet expresses the faculty
Use Your Master s Thesis Supervisor This booklet was prepared in dialogue with the heads of studies at the faculty, and it was approved by the dean of the faculty. Thus, this leaflet expresses the faculty
Human Capital Advantage for Business What is the value of ADP ihcm for HR Directors?
 Human Capital Advantage for Business What is the value of ADP ihcm for HR Directors? HR.Payroll.Benefits. ADP ihcm: Rethink Human Capital Management The need for HR to be a true business partner has never
Human Capital Advantage for Business What is the value of ADP ihcm for HR Directors? HR.Payroll.Benefits. ADP ihcm: Rethink Human Capital Management The need for HR to be a true business partner has never
Appendix 2: Intended learning outcomes of the Bachelor IBA
 Appendix 2: Intended learning outcomes of the Bachelor IBA Intended international & intercultural learning outcomes are presented in bold. Content related aspects Have knowledge of business administrative
Appendix 2: Intended learning outcomes of the Bachelor IBA Intended international & intercultural learning outcomes are presented in bold. Content related aspects Have knowledge of business administrative
HRM Opinion Leaders: Big challenges in a changing world
 HRM Opinion Leaders: Big challenges in a changing world Introduction Monizze has conducted several interviews of top HRM managers from various sectors, whether profit or not, in the course of 2012: Mobistar,
HRM Opinion Leaders: Big challenges in a changing world Introduction Monizze has conducted several interviews of top HRM managers from various sectors, whether profit or not, in the course of 2012: Mobistar,
HKIHRM HR PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS MODEL
 HKIHRM HR PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS MODEL Creating Values For You and For Organisations Setting Standards Recognising s ABOUT HKIHRM The Hong Kong Institute of Human Resource Management (HKIHRM) is the leading
HKIHRM HR PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS MODEL Creating Values For You and For Organisations Setting Standards Recognising s ABOUT HKIHRM The Hong Kong Institute of Human Resource Management (HKIHRM) is the leading
University of Twente. Faculty of Mathematical Sciences. Design and performance evaluation of agile manufacturing systems. Memorandum No.
 Faculty of Mathematical Sciences Ø University of Twente The Netherlands P.O. Box 217 7500 AE Enschede The Netherlands Phone: +31-53-4893400 Fax: +31-53-4893114 Email: memo@math.utwente.nl www.math.utwente.nl/publications
Faculty of Mathematical Sciences Ø University of Twente The Netherlands P.O. Box 217 7500 AE Enschede The Netherlands Phone: +31-53-4893400 Fax: +31-53-4893114 Email: memo@math.utwente.nl www.math.utwente.nl/publications
Human Resources Organizational Development and Design
 Human Resources Organizational Development and Design Job Evaluation: A guide to the UCT system and process Issue 3: August 2015 A. What is Job Evaluation? Job evaluation is the rating of jobs according
Human Resources Organizational Development and Design Job Evaluation: A guide to the UCT system and process Issue 3: August 2015 A. What is Job Evaluation? Job evaluation is the rating of jobs according
HR Transformation and Future of HR Brussel, 25 april 2013 Material part 1/2
 HR Transformation and Future of HR Brussel, 25 april 2013 Material part 1/2 Doelstellingen Ideeën uitwisselen over hoe een HR transformatie te starten Ervaringen delen over hoe HR toegevoegde waarde kan
HR Transformation and Future of HR Brussel, 25 april 2013 Material part 1/2 Doelstellingen Ideeën uitwisselen over hoe een HR transformatie te starten Ervaringen delen over hoe HR toegevoegde waarde kan
Martine de Bruijne, Cordula Wagner Safety 4 Patients www.onderzoekpatientveiligheid.nl
 Patient safety and patient outcomes Martine de Bruijne, Cordula Wagner Safety 4 Patients www.onderzoekpatientveiligheid.nl TRIP symposium, 19 maart 2013 Safety 4 patients www.onderzoekpatientveiligheid.nl
Patient safety and patient outcomes Martine de Bruijne, Cordula Wagner Safety 4 Patients www.onderzoekpatientveiligheid.nl TRIP symposium, 19 maart 2013 Safety 4 patients www.onderzoekpatientveiligheid.nl
Dutch Mortgage Market Pricing On the NMa report. Marco Haan University of Groningen November 18, 2011
 Dutch Mortgage Market Pricing On the NMa report Marco Haan University of Groningen November 18, 2011 Introductory remarks My comments are complementary: I do not focus so much on this market as such, more
Dutch Mortgage Market Pricing On the NMa report Marco Haan University of Groningen November 18, 2011 Introductory remarks My comments are complementary: I do not focus so much on this market as such, more
Ethical Conduct in Youth Work
 Ethical Conduct in Youth Work a statement of values and principles from The National Youth Agency Reprinted December 2004 Eastgate House, 19 23 Humberstone Road, Leicester LE5 3GJ. Tel: 0116 242 7350.
Ethical Conduct in Youth Work a statement of values and principles from The National Youth Agency Reprinted December 2004 Eastgate House, 19 23 Humberstone Road, Leicester LE5 3GJ. Tel: 0116 242 7350.
1. CORPORATE SUPPORT SERVICES DEPARTMENT - HUMAN RESOURCES DIVISION
 1. CORPORATE SUPPORT SERVICES DEPARTMENT - HUMAN RESOURCES DIVISION (i) CHIEF MANAGER - COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS, AND HR ADMINISTRATION (Grade KRA 7 ) JOB DESCRIPTION FORM Date: Kenya Revenue Authority
1. CORPORATE SUPPORT SERVICES DEPARTMENT - HUMAN RESOURCES DIVISION (i) CHIEF MANAGER - COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS, AND HR ADMINISTRATION (Grade KRA 7 ) JOB DESCRIPTION FORM Date: Kenya Revenue Authority
International Human Resource Management (IHRM) Nature and concepts of IHRM
 International Human Resource Management (IHRM) Dr. Shyamal Gomes Chapter 2: Nature and concepts of IHRM Introduction: The advent of the era of liberalization and globalization along with the advancements
International Human Resource Management (IHRM) Dr. Shyamal Gomes Chapter 2: Nature and concepts of IHRM Introduction: The advent of the era of liberalization and globalization along with the advancements
Science teachers pedagogical studies in Finland
 1 Science teachers pedagogical studies in Finland Jari Lavonen Summary An overview of planning, organising and evaluating of science teachers pedagogical studies in Finland is given. Examples are from
1 Science teachers pedagogical studies in Finland Jari Lavonen Summary An overview of planning, organising and evaluating of science teachers pedagogical studies in Finland is given. Examples are from
Human Resource Assistant Payroll Practitioner
 Human Resource Assistant Payroll Practitioner PROGRAM OBJECTIVES Rapid workforce change makes responsible and responsive human resources service delivery and management one of the most pressing and critical
Human Resource Assistant Payroll Practitioner PROGRAM OBJECTIVES Rapid workforce change makes responsible and responsive human resources service delivery and management one of the most pressing and critical
HR Function Optimization
 HR Function Optimization People & Change Advisory Services kpmg.com/in Unlocking the value of human capital Human Resources function is now recognized as a strategic enabler, aimed at delivering sustainable
HR Function Optimization People & Change Advisory Services kpmg.com/in Unlocking the value of human capital Human Resources function is now recognized as a strategic enabler, aimed at delivering sustainable
Keywords- Talent Management, retain, Talent Management a part of an organizational structure.
 Talent Management Nitesh Jaiswal Student PGDM MIT-school of business Pune. Abstract Despite of being of significance importance till today organizations are not approachable to Talent Management, they
Talent Management Nitesh Jaiswal Student PGDM MIT-school of business Pune. Abstract Despite of being of significance importance till today organizations are not approachable to Talent Management, they
SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP. Undergraduate Prospectus Bachelor of Management Studies
 SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP Undergraduate Prospectus Bachelor of Management Studies 1 CONTACT INFORMATION: Vivek Ahuja Manager Undergraduate Programs School of Management and Entrepreneurship
SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP Undergraduate Prospectus Bachelor of Management Studies 1 CONTACT INFORMATION: Vivek Ahuja Manager Undergraduate Programs School of Management and Entrepreneurship
MA Degree Plan in Business Administration (Thesis Track)
 MA Degree Plan in Business Administration (Thesis Track) Plan Number 2012 T I. GENERAL RULES and CONDITIONS: 1. This plan conforms to the valid regulations of the programs of graduate studies. Areas of
MA Degree Plan in Business Administration (Thesis Track) Plan Number 2012 T I. GENERAL RULES and CONDITIONS: 1. This plan conforms to the valid regulations of the programs of graduate studies. Areas of
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT MASTER COURSES 2015-2016 HRM MASTER COURSES 1 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT MASTER PROFILE The business community has come to understand that success relies on careful Human Resource
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT MASTER COURSES 2015-2016 HRM MASTER COURSES 1 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT MASTER PROFILE The business community has come to understand that success relies on careful Human Resource
Uw partner in system management oplossingen
 Uw partner in system management oplossingen User Centric IT Bring your Own - Corporate Owned Onderzoek Forrester Welke applicatie gebruik je het meest op mobiele devices? Email 76% SMS 67% IM / Chat 48%
Uw partner in system management oplossingen User Centric IT Bring your Own - Corporate Owned Onderzoek Forrester Welke applicatie gebruik je het meest op mobiele devices? Email 76% SMS 67% IM / Chat 48%
The state of DIY. Mix Express DIY event Maarssen 14 mei 2014
 The state of DIY!! Mix Express DIY event Maarssen 14 mei 2014 Inleiding Mix press DIY sessie Maarssen 14 mei 2014 Deze presentatie is gemaakt voor het Mix DIY congres en gebaseerd op onze analyse van de
The state of DIY!! Mix Express DIY event Maarssen 14 mei 2014 Inleiding Mix press DIY sessie Maarssen 14 mei 2014 Deze presentatie is gemaakt voor het Mix DIY congres en gebaseerd op onze analyse van de
ACM Courses. Management and Organization Department. Ramon V. del Rosario College of Business. De La Salle University.
 ACM Courses Management and Organization Department Ramon V. del Rosario College of Business De La Salle University 2011 ACM-P003-4 Page 0 1.0 COURSE OVERVIEW 1.1 Human Resources Management. The heart of
ACM Courses Management and Organization Department Ramon V. del Rosario College of Business De La Salle University 2011 ACM-P003-4 Page 0 1.0 COURSE OVERVIEW 1.1 Human Resources Management. The heart of
2009 Talent Management Factbook
 2009 Talent Management Factbook Executive Summary Karen O Leonard Principal Analyst May 2009 BERSIN & ASSOCIATES RESEARCH REPORT V.2.0 2009 Talent Management Factbook: Executive Summary i The Bersin &
2009 Talent Management Factbook Executive Summary Karen O Leonard Principal Analyst May 2009 BERSIN & ASSOCIATES RESEARCH REPORT V.2.0 2009 Talent Management Factbook: Executive Summary i The Bersin &
Making the move to HR business partnering really work
 Bath Consultancy Group www.bathconsultancygroup.com Making the move to HR business partnering really work Bath Consultancy Group 11 Kelso Place, Upper Bristol Road, Bath BA1 3AU Main Office: +44 (0)1225
Bath Consultancy Group www.bathconsultancygroup.com Making the move to HR business partnering really work Bath Consultancy Group 11 Kelso Place, Upper Bristol Road, Bath BA1 3AU Main Office: +44 (0)1225
Revised Body of Knowledge And Required Professional Capabilities (RPCs)
 Revised Body of Knowledge And Required Professional Capabilities (RPCs) PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE Strategic contribution to organizational success RPC:1 Contributes to the development of the organization s
Revised Body of Knowledge And Required Professional Capabilities (RPCs) PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE Strategic contribution to organizational success RPC:1 Contributes to the development of the organization s
The European Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning (EQF)
 European Qualifications Framework The European Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning (EQF) Europe Direct is a service to help you find answers to your questions about the European Union Freephone
European Qualifications Framework The European Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning (EQF) Europe Direct is a service to help you find answers to your questions about the European Union Freephone
Code Banken. 9 september 2010
 Code Banken 9 september 2010 The original Dutch text will be binding and shall prevail in case of any variance between the Dutch text and the English translation. 1/17 PREAMBLE The Banking Code (Code Banken)
Code Banken 9 september 2010 The original Dutch text will be binding and shall prevail in case of any variance between the Dutch text and the English translation. 1/17 PREAMBLE The Banking Code (Code Banken)
What can Office 365 do for your organization? Cor Kroon
 What can Office 365 do for your organization? Cor Kroon Ciber Knowledge Carrousel 2013 What can Office 365 do for your Organization? Cor Kroon Business Analyst / Senior Microsoft Professional cor.kroon@ciber.nl
What can Office 365 do for your organization? Cor Kroon Ciber Knowledge Carrousel 2013 What can Office 365 do for your Organization? Cor Kroon Business Analyst / Senior Microsoft Professional cor.kroon@ciber.nl
Human Resources Systems Advisor (Partners) Job Profile
 Human Resources Systems Advisor (Partners) Job Profile About the HCPC The Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) is the regulator of 16 different health and care professions. We were set up to protect
Human Resources Systems Advisor (Partners) Job Profile About the HCPC The Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) is the regulator of 16 different health and care professions. We were set up to protect
