DDR2SOFT DDR2 Memory Controller VHDL SOURCE CODE OVERVIEW
|
|
|
- Shawn Simmons
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
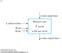
1 Overview The DDR2SOFT is a generic DDR2 memory controller core (including the VHDL source code) designed to interface DDR2 memory modules and memory ICs with low-cost FPGAs. This generic code does not use any hardware-based memory controller block (MCB). It is therefore slower but free of keyt MCB constraints (data bus width, number of instantiations). In particular, this component allows Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGAs to interface with 64-bit wide DDR2 DIMM/SODIMM, for streaming throughputs up to 16 Gbps. The binary (.ngc) component is free for use on ComBlock FPGA development platforms. The VHDL source code is sold separately. The component s very efficient implementation makes it suitable for multiple instantiations within a small FPGA. The object-oriented code structure provides two levels of abstraction: - The DDR2 core controller makes many low-level tasks invisible to the user: refresh, initialization and most timing. Its simple interface accepts burst read and burst write commands. - The DDR2 wrapper provides another layer of abstraction by optimizing memory access for maximum throughput or minimum latency. Users can interface with their own clock, different than the DDR2 controller clock. Key features include: Concurrent read/write at the user interface. Independent clocking for user data and DDR2. Optimized for efficient data streaming: DDR2SOFT DDR2 Memory Controller VHDL SOURCE CODE OVERVIEW o Address auto-increment o Start/Stop address boundaries o Continuous/Single-shot modes Compliant with DDR2 SDRAM standard JESD79-2F (Nov. 2009) Support for low-power self-refresh mode. Automatic banks management (multiple banks can be opened simultaneously). Automatic calibration to cancel the round-trip delay FPGA SDRAM FPGA and sample the read data at the center of the eye diagram. Block Diagram to/from User Elastic Buffer Elastic Buffer Speed Intelligent Scheduler SDRAM Write SDRAM Read Configuration & Status DDR2 wrapper simple burst read/ burst write interface MSS A Flower Hill Way Gaithersburg, Maryland U.S.A. Telephone: (240) Facsimile: (240) MSS 2010 Issued 9/22/2010 DDR2 Core Controller to/from DDR2 SDRAM FPGA Clock (max) Read/Write streaming throughput Spartan MHz = 260 MTransfers/s 16-bit IC: 4 Gbit/s 8/16/32/64 DDR2 SDRAM Interface 64-bit SODIMM 16 Gbits/s
2 Target Hardware The code is written in generic VHDL so that it can be ported to a variety of FPGAs. The code was developed and tested on a Xilinx Spartan-6 XC6SLX FPGA. It can be easily ported to any Xilinx Virtex-5, Virtex-6, Spartan-6 FPGAs and other FPGAs capable of running at or above the minimum DDR2 clock frequency of 125 MHz. Please note that the target FPGA must be capable of - Creating programmable input delays at the SDRAM interface. - Generating a low-jitter SDRAM clock using a true PLL (DCM are not recommended), or using an external lowjitter clock. Device Utilization Summary Device: Xilinx Spartan-6, Core DDR2 SDRAM controller only FPGA resources 16-bit DDR2 data width LUTs Flip Flops (in slices) RAMB16BWERs 0 0 DSP48A1s 0 0 GCLKs 4 4 DCMs bit DDR2 DIMM /SODIMM data width Device: Xilinx Spartan-6, Complete controller, including wrapper. FPGA resources 16-bit DDR2 data width Flip Flops LUTs RAMB16BWERs 2 8 DSP48A1s 0 0 GCLKs 2 2 DCMs bit DDR2 DIMM/SODIMM data width Core Controller Interface USER INTERFACE CLK_DDR2_REF ASYNC_RESET CLOCKS CLK_DDR2G_OUT DATA_IN(127/63/31/15:0) DATA_IN_CTS WRITE DATA DATA_OUT(127/63/31/15:0) READ DATA_OUT_EN DATA START_ADDR(31:0) CONTROLs TRANSACTION_REQ(1:0) TRANSACTION_REQ_NO(3:0) TRANSACTION_REQ_ACQ SELF_REFRESH_REQ SDRAM_READY NSDRAM_BYTES CONFIG ADDRESS_MAP CLOCK_CYCLES (Presynthesis) DDR2_CLK_FREQ RTDELAY_COARSE DDR2 INTERFACE SDRAM_DQ(63/31/15/7:0) SDRAM_DQS_P(7/3/1/0:0) SDRAM_DQS_N(7/3/1/0:0) SDRAM_ODT(1:0) SDRAM_CK0_P SDRAM_CK0_N SDRAM_CKE0 SDRAM_CK1_P SDRAM_CK1_N SDRAM_CKE1 SDRAM_CASN SDRAM_RASN SDRAM_WEN SDRAM_S0N SDRAM_S1N SDRAM_DM(7/3/1/0:0) SDRAM_A(15:0) SDRAM_BA(2:0) On the controller DDR2 interface side, all signals connect directly to the external DDR2 SDRAM. The controller user interface side comprises four signal groups: (a) Clocks: The user sets the DDR2 SDRAM speed by providing a reference frequency as CLK_DDR2_REF. The controller internally generates a global clock CLK_DDR2G_OUT for use by the user code. (b) Controls for the two elementary transactions: burst read and burst write. Each burst comprises 4 words, the word size being determined by the DDR2 SDRAM data width (8/16/32 or 64 bits). User data is transferred two-words at a time to match the DDR2 SDRAM throughput. (c) Configuration parameters are set at the time of VHDL synthesis (i.e. cannot be modified at run-time). All user-side signals are clock synchronous with the user-selected clock CLK_DDR2G_OUT. The best way to generate the DDR2 SDRAM reference clock is by using a PLL as illustrated in the clkgen_pll.vhd example. 2
3 Core Controller Transactions Burst Read The user declares its intent to read a 4-word burst by simultaneously (a) Changing the transaction request number TRANSACTION_REQ_NO (b) Setting the transaction request to burst read TRANSACTION_REQ = 01 (c) Setting the burst start address START_ADDR, expressed as integer multiple of words, not bytes. The controller will send a 1-CLK wide pulse acknowledgement TRANSACTION_REQ_ACK as soon as it can process the transaction request. The acknowledgement indicates that this transaction was accepted and processing has just started. The user can now send the next request (even while the current transaction is in progress). Note: When possible, the controller will send the acknowledgement pulse very quickly, within the same clock period as the user request. CLK TRANSACTION_REQ_NO TRANSACTION_REQ START_ADDR TRANSACTION_REQ_ACQ CLK XX Request is latched in at the rising edge of CLK. Can be changed thereafter. N N + 1 XX 01 addr Transaction request acknowledgement can be immediate Burst Read Request Read data words Wi/Wi+1 at the rising edge of CLK when DATA_OUT_EN = '1' DATA_OUT W0/W1 W2/W3 DATA_OUT_EN Data latency from the request ack TRANSACTION_REQ_ACQ is fixed but depends on hardware Burst Read Data following request The 4 words read from the SDRAM are returned, packed two words at a time in DATA_OUT while DATA_OUT_EN = 1. Burst Write The user declares its intent to write a 4-word burst by simultaneously (a) Changing the transaction request number TRANSACTION_REQ_NO (b) Setting the transaction request to burst write TRANSACTION_REQ = 10 (c) Setting the burst start address START_ADDR, expressed as integer multiple of words, not bytes. The controller will send a 1-CLK wide pulse acknowledgement TRANSACTION_REQ_ACK as soon as it can process the transaction request. The acknowledgement indicates that this transaction was accepted and processing has just started. Following the transaction acknowledgement, the controller will tell the user when to provide the data by setting DATA_IN_CTS to 1 exactly two clocks before the data is due at the DATA_IN input. IMPORTANT: input data must be provided exactly at the right time: 2 CLKs after the DATA_IN_CTS pulse. This interface is perfect for interfacing with an external dual-port block RAM (since it takes up to 2 CLKs to read data from a RAMB). The user must pack DATA_IN with two words at a time. Request is latched in at the rising edge of CLK. Can be changed thereafter. CLK TRANSACTION_REQ_NO TRANSACTION_REQ START_ADDR TRANSACTION_REQ_ACQ CLK N N + 1 XX XX 10 addr Transaction request acknowledgement can be immediate Burst Write Request Write data words Wi/Wi+1 at the rising edge of CLK two clocks after DATA_IN_CTS DATA_IN W0/W1 W2/W3 DATA_IN_CTS Data latency from the request ack TRANSACTION_REQ_ACQ is fixed but depends on hardware 3
4 Configuration The user can set the following controls at run-time: DDR2 Controller Description Configuration SELF_REFRESH_REQ 1 = User requests the controller to enter the Self refresh mode to reduce power consumption. The SDRAM data is retained. This low-power mode is typically used for long-term idle periods (for example when the memory is in standby mode). Exiting from this mode takes 200 CLKs. 0 = Normal mode. Read and Write is allowed. The user can set the following controls prior to synthesis in the generic section of the DDR2 component instantiation. Physical Configuration NSDRAM _BYTES ADDRESS _MAP Description DDR2 interface data width, expressed in bytes. Also defines the user interface data width (which is always twice as large). 1 = 8-bit word (IC) 2 = 16-bit word (IC, e.g. COM-1600) 4 = 32-bit word (ICs or partial DIMM/SODIMM) 8 = 64-bit word (DIMM/SODIMM, e.g. COM-1500) The logical to physical address mapping can vary depending on the hardware. See the DDR2 SDRAM hardware specifications. The most common mappings are described below: 00000: 1Gb x8 IC, column A[9:0], 8 banks BA[2:0], 1 rank S[1:0], row A[13:0] 00001: 1Gb x16 IC, column A[9:0], 8 banks BA[2:0], 1 rank S[1:0], row A[12:0] 00010: 2Gb x8 IC, column A[9:0], 8 banks BA[2:0], 1 rank S[1:0], row A[14:0] 00011: 2Gb x16 IC, column A[9:0], 8 banks BA[2:0], 1 rank S[1:0], row A[13:0] 0xxxx: other ICs, reserved for future use 10000: 1GB DIMM/SODIMM, column A[9:0], 8 banks BA[2:0], 2 CLOCK _CYCLES RTDELAY _COARSE ranks S[1:0], row A[12:0] 10001: 2GB DIMM/SODIMM, column A[9:0], 8 banks BA[2:0], 2 ranks S[1:0], row A[13:0] 10010: 4GB DIMM/SODIMM, column A[9:0], 8 banks BA[2:0], 2 ranks S[1:0], row A[14:0] 1xxxx: other DIMM/SODIMMs, reserved for future use CL - trcd - trp (CAS latency) - (RAS-CAS-Delay time) - (RAS precharge time) See DDR2 SDRAM hardware specifications. 3 = DDR = DDR = DDR = DDR2-800 Round-trip delay in the path FPGA -> SDRAM -> FPGA, rounded up to the nearest integer multiple of clock periods. Example Spartan MHz: Output delay for SDRAM_CKx: 9ns Input delay for SDRAM_DQSy: 4ns RTDELAY_COARSE = 13ns*2*125MHz = 3.25 rounded up to 4. In addition, less frequently used timing parameters can be customized as VHDL constants in the --// TIMERS section of the source code instead of using the default worst case. For example, the refresh to command timer trfc can be shortened in the case of smaller memories. Another example is the adjusting of the periodic refresh time trefi for extended temperature (85-95C) operation. The list of customizable timers, using the JEDEC standard notation, is as follows: trfc, trefi, twr Other DDR2 configuration parameters are fixed in the source code: Normal mode Burst length BL = 4 ODT enabled, 75 Ohm Rtt DQS# enable RDQS disable Output buffer enabled Optional duty cycle corrector disabled OCD calibration is not used 4
5 Wrapper Interface Exclusions This software does not support the following features: - Serial Presence-Detect (best handled by a microprocessor) Software Licensing The DDR2SOFT is supplied under the following key licensing terms: 1. A nonexclusive, nontransferable license to use the VHDL source code internally, and 2. An unlimited, royalty-free, nonexclusive transferable license to make and use products incorporating the licensed materials, solely in bitstream format, on a worldwide basis. The complete VHDL/IP Software License Agreement can be downloaded from Reference documents [1] DDR2 SDRAM Specification, JEDEC Standard No. 79-2F [2] ComBlock COM-1600 FPGA + ARM + USB2.0+ DDR2 + NAND development platform [3] COM-1600 development platform schematics 5
6 Configuration Management The current software revision is 1. [a] VHDL source code in directory DDR2_rev\src [b] Xilinx ISE project files DDR2_rev\DDR2_ISE114.xise DDR2_rev\DDR2_ISE122.xise [c].ucf constraint file DDR2_rev\src\DDR2.ucf [d] VHDL testbenches in directory DDR2_rev\sim [e].ngc binary for use in conjunction with the COM-1600 module DDR2_rev\bin\DDR2.ngc Xilinx-specific code The VHDL source code is written in generic VHDL with few Xilinx primitives. No Xilinx CORE is used. The Xilinx primitives are: - IBUF - IBUFG - BUFG (global clocks) - IDDR2 - ODDR2 - IODELAY2 to delay the read data and data strobe - IOBUFDS differential input/output buffer - Dual-port RAM block: RAMB16BWERs Top-Level VHDL hierarchy where rev is the current revision number. VHDL development environment The VHDL software was developed using the following development environment: (a) Xilinx ISE 11.4 with XST as synthesis tool (b) Xilinx ISE 12.2 with XST as synthesis tool (c) Xilinx ISE Isim as VHDL simulation tool Important: The FPGA SDRAM interface is timecritical. It is therefore important to ask the tools (Synthesis, Map) to pack the flip-flops in IOBs. Ready-to-use Hardware The binary component (.ngc) is freely available for use on the following ComBlock hardware modules: COM-1600 FPGA + ARM + DDR2 + NAND + USB2 development platform COM-1500 FPGA + DDR2 SODIMM socket + ARM + NAND + USB2 development platform See the following code templates: TBD The schematics are available in this CD. The design consists primarily of two components: - A core controller component (DDR2_SDRAM_CONTROLLER.vhd) and - A wrapper (DDR2_WRAPPER.vhd) The code is stored with one, and only one, component per file. The core component DDR2_SDRAM_CONTROLLER.vhd operates at the DDR2 SDRAM clock. It performs the SDRAM power-up initialization, refresh, low-power selfrefresh mode, round-trip delay fine calibration, active banks/rows management and burst read/write transactions. The user can request a burst read or a burst write transaction. All transactions transfer exactly 4 * NSDRAM_BYTES bytes. The core component s usage is described in the operation section above. An optional wrapper (DDR2_WRAPPER.vhd) comprises the transmit and receive elastic buffers, user-clock to memory-clock domains translation, read/write sequencing and data segmentation into bursts. DDR2_SDRAM_CONTROLLER_TEST.vhd is an optional component aimed at hardware verification such as board post-assembly tests. The components 6
7 writes and reads-back pseudo-random data at addresses within the specified address range. Additional components are used for simulation purposes: tbddr2_sdram_controller_test.v hd is a simulation testbench for the test component. It simulates propagation delay between external SDRAM and FPGA. DDR2_MODULE.v is a SODIMM Verilog simulation module (from Micron). Verilog define statements at the top of file help select the memory type. Calibration The FPGA - DDR2 SDRAM interface timing can quite challenging at higher clock speeds. The core controller code is written with two timing principles: (a) FPGA to DDR2 SDRAM direction: signals and synchronous clocks propagate in the same direction, with little timing variation through the IOBs. No problem is expected here. (b) DDR2 SDRAM to FPGA direction: the controller automatically calibrates out the round-trip delays so as to sample the input signals in the FPGA at the optimum time. The automatic calibration is only capable of performing fine delay compensation in the range 0 to ½ clock period. It is up to the user to specify the coarse delay RTDELAY_COARSE, expressed as an integer number of ½ clock periods rounded up. Since the signal round-trip delay (FPGA->SDRAM->FPGA) is designdependent, the user must find out the round-trip delay for its design. The fine delay (fraction of a ½ clock period) is removed automatically by the built-in calibration circuit. Calibration is triggered automatically at power up or after reset. Once the calibration is complete, the controller will set the SDRAM_READY flag high. The controller ignores user-generated Read/Write transaction requests issued before the SDRAM is ready. 7
8 Machine The DDR2 memory controller state machine is described by the SDL flowchart below: 0 idle DDR2 Power-up and Initialization (1/3) 3 Reset EMRS EMR(2) start clock 1 200us 4 tmrd EMRS EMR(3) NOP +CKE high tmrd 400ns 5 2 EMRS EMR(1) Enable DLL PRE ALL tmrd trp 6 3 8
9 6 DDR2 Power-up and Initialization (2/3) 9 MRS DLL reset REF second refresh tmrd Timer2 200 CLKs trfc 7 10 PRE ALL Precharge all MRS initialize device operation without DLL reset trp tmrd 8 11 Timer2 both and Timer2 expired REF first refresh EMRS EMR(1) set OCD calibration default trfc tmrd
10 12 DDR2 Power-up and Initialization (3/3) EMRS EMR(1) set OCD calibration default tmrd 13 Timer2 trefi 16 DDR2 SDRAM is now ready for normal operation 10
11 16 DDR2 controller ready Refresh Power-Down Read/Write Timer2 Refresh has priority over read/write PD=1 user requests power-down user requests a burst read or write PRE ALL precharge all PRE ALL all banks idle 26 trp trp Timer2 trefi ODT OFF Timer2 taofd REF 22 trfc Timer2 both timers expired 18 REF + turn CKE off = self refresh minimum Self refresh duration tcke
12 DDR2 Refresh / Read / Write / Power-Down (2/3) Exit Self-Refresh PD=0 user-directed exit from power-down / self refresh CKE = 1 re-enable CKE txsrd clear Timer2 to force a refresh ASAP (better safe)
13 DDR2 Burst Read / Write, Banks management (3/3) 26 (a) n bank open? y (b) n row active? (c) y a burst read/write ACT Activate PRE close bank row R/W? trcd trp READ WRITE 27 CL ACT Activate trcd user requests a burst read before previous read transaction is complete 28 Burst read transaction is complete. All data read prior to next command. a 13
14 Simulations All simulations below are conducted in the following environment: DDR2-400, 200 MHz clock, burst length = 4 Auto-Refresh Timer 2 schedules a refresh cycle once every trefi = 7.8us. Refresh transaction details 14
15 Burst read 4 successive burst read requests, burst length = 4, CL = 3 Burst read, DDR2 SDRAM side Burst read, user side. Burst write 4 successive burst write requests, burst length = 4, CL = 3 Burst write, DDR2 SDRAM side 15
16 Burst write, user side ComBlock Compatibility List FPGA development platform COM-1600 FPGA + ARM + DDR2 + USB2 + NAND development platform COM-1500 FPGA + DDR2 SODIMM socket + ARM + USB2 + NAND development platform ComBlock Ordering Information DDR2SOFT DDR2 MEMORY CONTROLLER, VHDL SOURCE CODE Contact Information MSS A Flower Hill Way Gaithersburg, Maryland U.S.A. Telephone: (240) Facsimile: (240) [email protected] 16
3.11.5.5 DDR2 Specific SDRAM Functions
 JEDEC Standard No. 2-C Page..5.5..5.5 DDR2 Specific SDRAM Functions DDR2 SDRAM EMRS2 and EMRS For DDR2 SDRAMs, both bits BA and BA must be decoded for Mode/Extended Mode Register Set commands. Users must
JEDEC Standard No. 2-C Page..5.5..5.5 DDR2 Specific SDRAM Functions DDR2 SDRAM EMRS2 and EMRS For DDR2 SDRAMs, both bits BA and BA must be decoded for Mode/Extended Mode Register Set commands. Users must
Technical Note DDR2 Offers New Features and Functionality
 Technical Note DDR2 Offers New Features and Functionality TN-47-2 DDR2 Offers New Features/Functionality Introduction Introduction DDR2 SDRAM introduces features and functions that go beyond the DDR SDRAM
Technical Note DDR2 Offers New Features and Functionality TN-47-2 DDR2 Offers New Features/Functionality Introduction Introduction DDR2 SDRAM introduces features and functions that go beyond the DDR SDRAM
ADQYF1A08. DDR2-1066G(CL6) 240-Pin O.C. U-DIMM 1GB (128M x 64-bits)
 General Description ADQYF1A08 DDR2-1066G(CL6) 240-Pin O.C. U-DIMM 1GB (128M x 64-bits) The ADATA s ADQYF1A08 is a 128Mx64 bits 1GB DDR2-1066(CL6) SDRAM over clocking memory module, The SPD is programmed
General Description ADQYF1A08 DDR2-1066G(CL6) 240-Pin O.C. U-DIMM 1GB (128M x 64-bits) The ADATA s ADQYF1A08 is a 128Mx64 bits 1GB DDR2-1066(CL6) SDRAM over clocking memory module, The SPD is programmed
Features. DDR SODIMM Product Datasheet. Rev. 1.0 Oct. 2011
 Features 200pin, unbuffered small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-2100, PC-2700, PC3-3200 Single or Dual rank 256MB(32Megx64), 512MB (64Meg x 64), 1GB(128 Meg x
Features 200pin, unbuffered small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-2100, PC-2700, PC3-3200 Single or Dual rank 256MB(32Megx64), 512MB (64Meg x 64), 1GB(128 Meg x
Table 1: Address Table
 DDR SDRAM DIMM D32PB12C 512MB D32PB1GJ 1GB For the latest data sheet, please visit the Super Talent Electronics web site: www.supertalentmemory.com Features 184-pin, dual in-line memory module (DIMM) Fast
DDR SDRAM DIMM D32PB12C 512MB D32PB1GJ 1GB For the latest data sheet, please visit the Super Talent Electronics web site: www.supertalentmemory.com Features 184-pin, dual in-line memory module (DIMM) Fast
Address Summary Table: 128MB 256MB 512MB 1GB 2GB Module
 12MB - WD1SN12X0 256MB - WD1SN256X0 512MB - WD1SN512X0 1GB - WD1SN01GX0 2GB - WD1SN02GS0 (Stacked) Features: 200-pin Unbuffered Non-ECC DDR SDRAM SODIMM for DDR-266, DDR-333, DDR-400 JEDEC standard VDD=2.5V
12MB - WD1SN12X0 256MB - WD1SN256X0 512MB - WD1SN512X0 1GB - WD1SN01GX0 2GB - WD1SN02GS0 (Stacked) Features: 200-pin Unbuffered Non-ECC DDR SDRAM SODIMM for DDR-266, DDR-333, DDR-400 JEDEC standard VDD=2.5V
Technical Note. Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM. Introduction. Initializing DDR SDRAM
 TN-46-8: Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM Introduction Technical Note Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM Introduction The double data rate DDR synchronous dynamic random access memory SDRAM device
TN-46-8: Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM Introduction Technical Note Initialization Sequence for DDR SDRAM Introduction The double data rate DDR synchronous dynamic random access memory SDRAM device
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864H 1GB MT16HTF25664H 2GB
 Features DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864H 1GB MT16HTF25664H 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM)
Features DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864H 1GB MT16HTF25664H 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM)
GR2DR4B-EXXX/YYY/LP 1GB & 2GB DDR2 REGISTERED DIMMs (LOW PROFILE)
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The Gigaram is a 128M/256M bit x 72 DDDR2 SDRAM high density JEDEC standard ECC Registered memory module. The Gigaram consists of eighteen CMOS 128MX4 DDR2 for 1GB and thirty-six CMOS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The Gigaram is a 128M/256M bit x 72 DDDR2 SDRAM high density JEDEC standard ECC Registered memory module. The Gigaram consists of eighteen CMOS 128MX4 DDR2 for 1GB and thirty-six CMOS
USB - FPGA MODULE (PRELIMINARY)
 DLP-HS-FPGA LEAD-FREE USB - FPGA MODULE (PRELIMINARY) APPLICATIONS: - Rapid Prototyping - Educational Tool - Industrial / Process Control - Data Acquisition / Processing - Embedded Processor FEATURES:
DLP-HS-FPGA LEAD-FREE USB - FPGA MODULE (PRELIMINARY) APPLICATIONS: - Rapid Prototyping - Educational Tool - Industrial / Process Control - Data Acquisition / Processing - Embedded Processor FEATURES:
are un-buffered 200-Pin Double Data Rate (DDR) Synchronous DRAM Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module (SO-DIMM). All devices
 PC2700 200 pin Unbuffered DDR SO-DIMM Based on DDR333 512Mb bit B Die device Features 200-Pin Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module (SO-DIMM) Unbuffered DDR SO-DIMM based on 110nm 512M bit die B device,
PC2700 200 pin Unbuffered DDR SO-DIMM Based on DDR333 512Mb bit B Die device Features 200-Pin Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module (SO-DIMM) Unbuffered DDR SO-DIMM based on 110nm 512M bit die B device,
DDR SDRAM SODIMM. MT9VDDT1672H 128MB 1 MT9VDDT3272H 256MB MT9VDDT6472H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.
 Features DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT9VDDT1672H 128MB 1 MT9VDDT3272H 256MB MT9VDDT6472H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory
Features DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT9VDDT1672H 128MB 1 MT9VDDT3272H 256MB MT9VDDT6472H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory
User s Manual HOW TO USE DDR SDRAM
 User s Manual HOW TO USE DDR SDRAM Document No. E0234E30 (Ver.3.0) Date Published April 2002 (K) Japan URL: http://www.elpida.com Elpida Memory, Inc. 2002 INTRODUCTION This manual is intended for users
User s Manual HOW TO USE DDR SDRAM Document No. E0234E30 (Ver.3.0) Date Published April 2002 (K) Japan URL: http://www.elpida.com Elpida Memory, Inc. 2002 INTRODUCTION This manual is intended for users
V58C2512(804/404/164)SB HIGH PERFORMANCE 512 Mbit DDR SDRAM 4 BANKS X 16Mbit X 8 (804) 4 BANKS X 32Mbit X 4 (404) 4 BANKS X 8Mbit X 16 (164)
 V58C2512804/404/164SB HIGH PERFORMAE 512 Mbit DDR SDRAM 4 BANKS X 16Mbit X 8 804 4 BANKS X 32Mbit X 4 404 4 BANKS X 8Mbit X 16 164 5 6 75 DDR400 DDR333 DDR266 Clock Cycle Time t CK2.5 6ns 6ns 7.5ns Clock
V58C2512804/404/164SB HIGH PERFORMAE 512 Mbit DDR SDRAM 4 BANKS X 16Mbit X 8 804 4 BANKS X 32Mbit X 4 404 4 BANKS X 8Mbit X 16 164 5 6 75 DDR400 DDR333 DDR266 Clock Cycle Time t CK2.5 6ns 6ns 7.5ns Clock
Technical Note. Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA. Overview. TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview
 Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF3264HD 256MB MT8HTF6464HD 512MB MT8HTF12864HD 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.
 DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF3264HD 256MB MT8HTF6464HD 512MB MT8HTF12864HD 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR): 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF3264HD 256MB MT8HTF6464HD 512MB MT8HTF12864HD 1GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR): 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features
DDR SDRAM SODIMM. MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 1 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com
 SODIMM MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 1 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
SODIMM MT8VDDT3264H 256MB 1 MT8VDDT6464H 512MB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 256MB, 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB
 DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB, 2GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT16VDDT6464A 512MB MT16VDDT12864A 1GB MT16VDDT25664A 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 512MB, 1GB, 2GB (x64, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF6464HDZ 512MB MT8HTF12864HDZ 1GB. Features. 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM. Features
 DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF6464HDZ 5MB MT8HTF864HDZ GB 5MB, GB (x64, DR) 00-Pin DDR SODIMM Features Features 00-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-300, PC-400,
DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF6464HDZ 5MB MT8HTF864HDZ GB 5MB, GB (x64, DR) 00-Pin DDR SODIMM Features Features 00-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC-300, PC-400,
LogiCORE IP AXI Performance Monitor v2.00.a
 LogiCORE IP AXI Performance Monitor v2.00.a Product Guide Table of Contents IP Facts Chapter 1: Overview Target Technology................................................................. 9 Applications......................................................................
LogiCORE IP AXI Performance Monitor v2.00.a Product Guide Table of Contents IP Facts Chapter 1: Overview Target Technology................................................................. 9 Applications......................................................................
Modeling Latches and Flip-flops
 Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT4HTF6464HZ 512MB. Features. 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM. Features. Figure 1: 200-Pin SODIMM (MO-224 R/C C)
 DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT4HTF6464HZ 512MB 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-3200, PC2-4200, PC2-5300,
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT4HTF6464HZ 512MB 512MB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-3200, PC2-4200, PC2-5300,
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices. Chapter 10 Counters. Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies
 ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT16HTF12864HZ 1GB MT16HTF25664HZ 2GB MT16HTF51264HZ 4GB. Features. 1GB, 2GB, 4GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM.
 DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT6HTF864HZ GB MT6HTF5664HZ GB MT6HTF564HZ 4GB GB, GB, 4GB (x64, DR) 00-Pin DDR SDRAM SODIMM Features Features 00-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer
DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT6HTF864HZ GB MT6HTF5664HZ GB MT6HTF564HZ 4GB GB, GB, 4GB (x64, DR) 00-Pin DDR SDRAM SODIMM Features Features 00-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer
1.55V DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM
 1.55V DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM MT18RTF25672FDZ 2GB 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered DIMM (FBDIMM) Very low-power DDR2 operation Component configuration: 256 Meg
1.55V DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM MT18RTF25672FDZ 2GB 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered DIMM (FBDIMM) Very low-power DDR2 operation Component configuration: 256 Meg
DDR2 Device Operations & Timing Diagram DDR2 SDRAM. Device Operations & Timing Diagram
 DDR2 SDRAM Device Operations & Timing Diagram 1 Contents 1. Functional Description 1.1 Simplified State Diagram 1.2 Basic Function & Operation of DDR2 SDRAM 1.2.1 Power up and Initialization 1.2.2 Programming
DDR2 SDRAM Device Operations & Timing Diagram 1 Contents 1. Functional Description 1.1 Simplified State Diagram 1.2 Basic Function & Operation of DDR2 SDRAM 1.2.1 Power up and Initialization 1.2.2 Programming
DDR3 SDRAM UDIMM MT8JTF12864A 1GB MT8JTF25664A 2GB
 DDR3 SDRAM UDIMM MT8JTF12864A 1GB MT8JTF25664A 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x64, SR) 240-Pin DDR3 SDRAM UDIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features DDR3 functionality
DDR3 SDRAM UDIMM MT8JTF12864A 1GB MT8JTF25664A 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x64, SR) 240-Pin DDR3 SDRAM UDIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features DDR3 functionality
DDR SDRAM SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB
 SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR SODIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
SODIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x64, DR) 200-Pin DDR SODIMM Features For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com Features 200-pin, small-outline dual
DDR2 SDRAM UDIMM MT18HTF6472AY 512MB MT18HTF12872AY 1GB MT18HTF25672AY 2GB MT18HTF51272AY 4GB. Features
 DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT8HTF647AY 5MB MT8HTF87AY GB MT8HTF567AY GB MT8HTF57AY 4GB 5MB, GB, GB, 4GB (x7, DR) 40-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features Features 40-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module Fast data transfer
DDR SDRAM UDIMM MT8HTF647AY 5MB MT8HTF87AY GB MT8HTF567AY GB MT8HTF57AY 4GB 5MB, GB, GB, 4GB (x7, DR) 40-Pin DDR SDRAM UDIMM Features Features 40-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module Fast data transfer
JEDEC STANDARD DDR2 SDRAM SPECIFICATION JESD79-2B. (Revision of JESD79-2A) JEDEC SOLID STATE TECHNOLOGY ASSOCIATION. January 2005
 JEDEC STANDARD DDR2 SDRAM SPECIFICATION JESD79-2B (Revision of JESD79-2A) January 2005 JEDEC SOLID STATE TECHNOLOGY ASSOCIATION NOTICE JEDEC standards and publications contain material that has been prepared,
JEDEC STANDARD DDR2 SDRAM SPECIFICATION JESD79-2B (Revision of JESD79-2A) January 2005 JEDEC SOLID STATE TECHNOLOGY ASSOCIATION NOTICE JEDEC standards and publications contain material that has been prepared,
Note: Data Rate (MT/s) CL = 3 CL = 4 CL = 5 CL = 6. t RCD (ns) t RP (ns) t RC (ns) t RFC (ns)
 TwinDie DDR2 SDRAM MT47H512M4 32 Meg x 4 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks MT47H256M8 16 Meg x 8 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks 2Gb: x4, x8 TwinDie DDR2 SDRAM Features Features Uses two 1Gb Micron die Two ranks (includes dual
TwinDie DDR2 SDRAM MT47H512M4 32 Meg x 4 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks MT47H256M8 16 Meg x 8 x 8 Banks x 2 Ranks 2Gb: x4, x8 TwinDie DDR2 SDRAM Features Features Uses two 1Gb Micron die Two ranks (includes dual
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF12864HZ 1GB MT8HTF25664HZ 2GB. Features. 1GB, 2GB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM. Features
 DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF12864HZ 1GB MT8HTF25664HZ 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates:
DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM MT8HTF12864HZ 1GB MT8HTF25664HZ 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x64, SR) 200-Pin DDR2 SDRAM SODIMM Features Features 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates:
Standard: 64M x 8 (9 components)
 256MB - WD2RE256X09 512MB - WD2RE512X09 1GB - WD2RE01GX09 2GB - WD2RE02GH09 (Stacked, Preliminary*) DDR2-400, 533,667 One Rank, x Registered SDRAM DIMM Pb-free Features: 240-pin Registered ECC DDR2 SDRAM
256MB - WD2RE256X09 512MB - WD2RE512X09 1GB - WD2RE01GX09 2GB - WD2RE02GH09 (Stacked, Preliminary*) DDR2-400, 533,667 One Rank, x Registered SDRAM DIMM Pb-free Features: 240-pin Registered ECC DDR2 SDRAM
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services [email protected] 2 Storing data Possible
Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services [email protected] 2 Storing data Possible
Features. DDR3 Unbuffered DIMM Spec Sheet
 Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 240-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module (UDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC3-8500, PC3-10600, PC3-12800
Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 240-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module (UDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC3-8500, PC3-10600, PC3-12800
SDLC Controller. Documentation. Design File Formats. Verification
 January 15, 2004 Product Specification 11 Stonewall Court Woodcliff Lake, NJ 07677 USA Phone: +1-201-391-8300 Fax: +1-201-391-8694 E-mail: [email protected] URL: www.cast-inc.com Features AllianceCORE
January 15, 2004 Product Specification 11 Stonewall Court Woodcliff Lake, NJ 07677 USA Phone: +1-201-391-8300 Fax: +1-201-391-8694 E-mail: [email protected] URL: www.cast-inc.com Features AllianceCORE
DDR2 SDRAM UDIMM MT16HTF6464AY 512MB MT16HTF12864AY 1GB MT16HTF25664AY 2GB MT16HTF51264AY 4GB. Features
 DDR SDRAM UDMM MT6HTF6464AY 5MB MT6HTF864AY GB MT6HTF5664AY GB MT6HTF564AY 4GB 5MB, GB, GB, 4GB (x64, DR) 40-Pin DDR UDMM Features Features 40-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module Fast data transfer
DDR SDRAM UDMM MT6HTF6464AY 5MB MT6HTF864AY GB MT6HTF5664AY GB MT6HTF564AY 4GB 5MB, GB, GB, 4GB (x64, DR) 40-Pin DDR UDMM Features Features 40-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module Fast data transfer
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter
 NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
DDR3(L) 4GB / 8GB UDIMM
 DRAM (512Mb x 8) DDR3(L) 4GB/8GB UDIMM DDR3(L) 4GB / 8GB UDIMM Features Nanya Technology Corp. DDR3(L) 4Gb B-Die JEDEC DDR3(L) Compliant 1-8n Prefetch Architecture - Differential Clock(CK/ ) and Data Strobe(/
DRAM (512Mb x 8) DDR3(L) 4GB/8GB UDIMM DDR3(L) 4GB / 8GB UDIMM Features Nanya Technology Corp. DDR3(L) 4Gb B-Die JEDEC DDR3(L) Compliant 1-8n Prefetch Architecture - Differential Clock(CK/ ) and Data Strobe(/
White Paper Utilizing Leveling Techniques in DDR3 SDRAM Memory Interfaces
 White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops
 CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
Features. DDR3 SODIMM Product Specification. Rev. 1.7 Feb. 2016
 Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 204pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: DDR3-1066(PC3-8500) DDR3-1333(PC3-10600)
Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 204pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module (SODIMM) Fast data transfer rates: DDR3-1066(PC3-8500) DDR3-1333(PC3-10600)
Dual DIMM DDR2 and DDR3 SDRAM Interface Design Guidelines
 Dual DIMM DDR2 and DDR3 SDRAM Interface Design Guidelines May 2009 AN-444-1.1 This application note describes guidelines for implementing dual unbuffered DIMM DDR2 and DDR3 SDRAM interfaces. This application
Dual DIMM DDR2 and DDR3 SDRAM Interface Design Guidelines May 2009 AN-444-1.1 This application note describes guidelines for implementing dual unbuffered DIMM DDR2 and DDR3 SDRAM interfaces. This application
Experiment # 9. Clock generator circuits & Counters. Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa
 Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Mobile SDRAM. MT48H16M16LF 4 Meg x 16 x 4 banks MT48H8M32LF 2 Meg x 32 x 4 banks
 Features Mobile SDRAM MT48H6M6LF 4 Meg x 6 x 4 banks MT48H8M32LF 2 Meg x 32 x 4 banks Features Fully synchronous; all signals registered on positive edge of system clock V DD /V D =.7.95V Internal, pipelined
Features Mobile SDRAM MT48H6M6LF 4 Meg x 6 x 4 banks MT48H8M32LF 2 Meg x 32 x 4 banks Features Fully synchronous; all signals registered on positive edge of system clock V DD /V D =.7.95V Internal, pipelined
Achieving High Performance DDR3 Data Rates
 WP383 (v1.2) August 29, 2013 Achieving High Performance DDR3 Data Rates By: Adrian Cosoroaba Programmable devices frequently require an external memory interface to buffer data that exceeds the capacity
WP383 (v1.2) August 29, 2013 Achieving High Performance DDR3 Data Rates By: Adrian Cosoroaba Programmable devices frequently require an external memory interface to buffer data that exceeds the capacity
Modeling Registers and Counters
 Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
TIP-VBY1HS Data Sheet
 Preliminary DATA SHEET Preliminary TIP-VBY1HS Data Sheet V-by-One HS Standard IP for Xilinx FPGA Rev.1.00 Tokyo Electron Device Ltd. Rev1.00 1 Revision History The following table shows the revision history
Preliminary DATA SHEET Preliminary TIP-VBY1HS Data Sheet V-by-One HS Standard IP for Xilinx FPGA Rev.1.00 Tokyo Electron Device Ltd. Rev1.00 1 Revision History The following table shows the revision history
DDR SDRAM Small-Outline DIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB
 Features DDR SDRAM Small-Outline DIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB For the latest component data sheet, refer to the Micron's Web site: www.micron.com/products/modules Features 200-pin, small-outline,
Features DDR SDRAM Small-Outline DIMM MT16VDDF6464H 512MB MT16VDDF12864H 1GB For the latest component data sheet, refer to the Micron's Web site: www.micron.com/products/modules Features 200-pin, small-outline,
Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance. Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy
 Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy Agenda Introduction DDR4 Technology Expanded role of MRS Power Features Examined Reliability Features Examined Performance
Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy Agenda Introduction DDR4 Technology Expanded role of MRS Power Features Examined Reliability Features Examined Performance
Source-Synchronous Serialization and Deserialization (up to 1050 Mb/s) Author: NIck Sawyer
 Application Note: Spartan-6 FPGAs XAPP1064 (v1.2) November 19, 2013 Source-Synchronous Serialization and Deserialization (up to 1050 Mb/s) Author: NIck Sawyer Summary Spartan -6 devices contain input SerDes
Application Note: Spartan-6 FPGAs XAPP1064 (v1.2) November 19, 2013 Source-Synchronous Serialization and Deserialization (up to 1050 Mb/s) Author: NIck Sawyer Summary Spartan -6 devices contain input SerDes
Memory Module Specifications KVR667D2D4F5/4G. 4GB 512M x 72-Bit PC2-5300 CL5 ECC 240-Pin FBDIMM DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATIONS
 Memory Module Specifications KVR667DD4F5/4G 4GB 5M x 7-Bit PC-5300 CL5 ECC 40- FBDIMM DESCRIPTION This document describes s 4GB (5M x 7-bit) PC-5300 CL5 SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM) fully buffered ECC dual
Memory Module Specifications KVR667DD4F5/4G 4GB 5M x 7-Bit PC-5300 CL5 ECC 40- FBDIMM DESCRIPTION This document describes s 4GB (5M x 7-bit) PC-5300 CL5 SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM) fully buffered ECC dual
Sequential Logic. (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements )
 Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
8254 PROGRAMMABLE INTERVAL TIMER
 PROGRAMMABLE INTERVAL TIMER Y Y Y Compatible with All Intel and Most Other Microprocessors Handles Inputs from DC to 10 MHz 8 MHz 8254 10 MHz 8254-2 Status Read-Back Command Y Y Y Y Y Six Programmable
PROGRAMMABLE INTERVAL TIMER Y Y Y Compatible with All Intel and Most Other Microprocessors Handles Inputs from DC to 10 MHz 8 MHz 8254 10 MHz 8254-2 Status Read-Back Command Y Y Y Y Y Six Programmable
SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS
 SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS A Lattice Semiconductor White Paper May 2005 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503)
SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS A Lattice Semiconductor White Paper May 2005 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503)
Memory Module Specifications KVR667D2D8F5/2GI. 2GB 256M x 72-Bit PC2-5300 CL5 ECC 240-Pin FBDIMM DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATIONS
 Memory Module Specifications KVR667DD8F5/GI GB 56M x 7-Bit PC-5300 CL5 ECC 40- FBDIMM DESCRIPTION This document describes s GB (56M x 7-bit) PC-5300 CL5 (Synchronous DRAM) fully buffered ECC dual rank,
Memory Module Specifications KVR667DD8F5/GI GB 56M x 7-Bit PC-5300 CL5 ECC 40- FBDIMM DESCRIPTION This document describes s GB (56M x 7-bit) PC-5300 CL5 (Synchronous DRAM) fully buffered ECC dual rank,
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog
 A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
AXI Performance Monitor v5.0
 AXI Performance Monitor v5.0 LogiCORE IP Product Guide Vivado Design Suite Table of Contents IP Facts Chapter 1: Overview Advanced Mode...................................................................
AXI Performance Monitor v5.0 LogiCORE IP Product Guide Vivado Design Suite Table of Contents IP Facts Chapter 1: Overview Advanced Mode...................................................................
Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers
 ETEC 23 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 27 by Janna B. Gallaher Latches A temporary
ETEC 23 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 27 by Janna B. Gallaher Latches A temporary
Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance. Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy
 Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy Agenda Introduction DDR4 Technology Expanded role of MRS Power Features Examined Reliability Features Examined Performance
Tuning DDR4 for Power and Performance Mike Micheletti Product Manager Teledyne LeCroy Agenda Introduction DDR4 Technology Expanded role of MRS Power Features Examined Reliability Features Examined Performance
A N. O N Output/Input-output connection
 Memory Types Two basic types: ROM: Read-only memory RAM: Read-Write memory Four commonly used memories: ROM Flash, EEPROM Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM), SDRAM, RAMBUS, DDR RAM Generic pin configuration:
Memory Types Two basic types: ROM: Read-only memory RAM: Read-Write memory Four commonly used memories: ROM Flash, EEPROM Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM), SDRAM, RAMBUS, DDR RAM Generic pin configuration:
DDR2 SDRAM Unbuffered DIMM MT9HTF3272A 256MB MT9HTF6472A 512MB MT9HTF12872A 1GB
 256MB, 52MB, GB (x72, SR, ECC) 24-Pin DDR2 SDRAM UDIMM Features DDR2 SDRAM Unbuffered DIMM MT9HTF3272A 256MB MT9HTF6472A 52MB MT9HTF2872A GB For the latest data sheet, please refer to the Micron Web site:
256MB, 52MB, GB (x72, SR, ECC) 24-Pin DDR2 SDRAM UDIMM Features DDR2 SDRAM Unbuffered DIMM MT9HTF3272A 256MB MT9HTF6472A 52MB MT9HTF2872A GB For the latest data sheet, please refer to the Micron Web site:
Jerry Chu 2010/07/07 Vincent Chang 2010/07/07
 Product Model Name: AD1S400A512M3 Product Specification: DDR-400(CL3) 200-Pin SO-DIMM 512MB (64M x 64-bits) Issuing Date: 2010/07/07 Version: 0 Item: 1. General Description 2. Features 3. Pin Assignment
Product Model Name: AD1S400A512M3 Product Specification: DDR-400(CL3) 200-Pin SO-DIMM 512MB (64M x 64-bits) Issuing Date: 2010/07/07 Version: 0 Item: 1. General Description 2. Features 3. Pin Assignment
DDR3 SDRAM UDIMM MT16JTF25664AZ 2GB MT16JTF51264AZ 4GB MT16JTF1G64AZ 8GB. Features. 2GB, 4GB, 8GB (x64, DR) 240-Pin DDR3 UDIMM.
 DDR3 SDRAM UDIMM MT6JTF5664AZ GB MT6JTF564AZ 4GB MT6JTFG64AZ 8GB GB, 4GB, 8GB (x64, DR) 40-Pin DDR3 UDIMM Features Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as per component data sheet 40-pin,
DDR3 SDRAM UDIMM MT6JTF5664AZ GB MT6JTF564AZ 4GB MT6JTFG64AZ 8GB GB, 4GB, 8GB (x64, DR) 40-Pin DDR3 UDIMM Features Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as per component data sheet 40-pin,
DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM MT36HTF25672F 2GB MT36HTF51272F 4GB. Features. 2GB, 4GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM. Features
 SDRAM FBDIMM MT36HTF25672F 2GB MT36HTF51272F 4GB 2GB, 4GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered DIMM (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200, PC2-5300, or PC2-6400
SDRAM FBDIMM MT36HTF25672F 2GB MT36HTF51272F 4GB 2GB, 4GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered DIMM (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200, PC2-5300, or PC2-6400
Design and Implementation of Vending Machine using Verilog HDL
 2011 2nd International Conference on Networking and Information Technology IPCSIT vol.17 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Design and Implementation of Vending Machine using Verilog HDL Muhammad Ali
2011 2nd International Conference on Networking and Information Technology IPCSIT vol.17 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Design and Implementation of Vending Machine using Verilog HDL Muhammad Ali
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
DDR SDRAM RDIMM MT36VDDF12872 1GB MT36VDDF25672 2GB
 DDR SDRAM RDIMM MT36VDDF12872 1GB MT36VDDF25672 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 1GB, 2GB (x72, ECC, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM RDIMM Features Features 184-pin, registered
DDR SDRAM RDIMM MT36VDDF12872 1GB MT36VDDF25672 2GB For component data sheets, refer to Micron s Web site: www.micron.com 1GB, 2GB (x72, ECC, DR) 184-Pin DDR SDRAM RDIMM Features Features 184-pin, registered
ADATA Technology Corp. DDR3-1600(CL11) 240-Pin VLP ECC U-DIMM 4GB (512M x 72-bit)
 ADATA Technology Corp. Memory Module Data Sheet DDR3-1600(CL11) 240-Pin VLP ECC U-DIMM 4GB (512M x 72-bit) Version 0.1 Document Number : R11-0861 APPROVAL ISSUE Evan Sheu 2012/04/20 Masako Yang 2012/04/20
ADATA Technology Corp. Memory Module Data Sheet DDR3-1600(CL11) 240-Pin VLP ECC U-DIMM 4GB (512M x 72-bit) Version 0.1 Document Number : R11-0861 APPROVAL ISSUE Evan Sheu 2012/04/20 Masako Yang 2012/04/20
DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM MT18HTF12872FD 1GB MT18HTF25672FD 2GB. Features. 1GB, 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM. Features
 SDRAM FBDIMM MT18HTF12872FD 1GB MT18HTF25672FD 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered dual in-line memory module (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200,
SDRAM FBDIMM MT18HTF12872FD 1GB MT18HTF25672FD 2GB 1GB, 2GB (x72, DR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered dual in-line memory module (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200,
Fairchild Solutions for 133MHz Buffered Memory Modules
 AN-5009 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note April 1999 Revised December 2000 Fairchild Solutions for 133MHz Buffered Memory Modules Fairchild Semiconductor provides several products that are compatible
AN-5009 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note April 1999 Revised December 2000 Fairchild Solutions for 133MHz Buffered Memory Modules Fairchild Semiconductor provides several products that are compatible
To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC.
 8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
LLRF. Digital RF Stabilization System
 LLRF Digital RF Stabilization System Many instruments. Many people. Working together. Stability means knowing your machine has innovative solutions. For users, stability means a machine achieving its full
LLRF Digital RF Stabilization System Many instruments. Many people. Working together. Stability means knowing your machine has innovative solutions. For users, stability means a machine achieving its full
Manchester Encoder-Decoder for Xilinx CPLDs
 Application Note: CoolRunner CPLDs R XAPP339 (v.3) October, 22 Manchester Encoder-Decoder for Xilinx CPLDs Summary This application note provides a functional description of VHDL and Verilog source code
Application Note: CoolRunner CPLDs R XAPP339 (v.3) October, 22 Manchester Encoder-Decoder for Xilinx CPLDs Summary This application note provides a functional description of VHDL and Verilog source code
ThinkServer PC2-5300 DDR2 FBDIMM and PC2-6400 DDR2 SDRAM Memory options boost overall performance of ThinkServer solutions
 , dated September 30, 2008 ThinkServer PC2-5300 DDR2 FBDIMM and PC2-6400 DDR2 SDRAM Memory options boost overall performance of ThinkServer solutions Table of contents 2 Key prerequisites 2 Product number
, dated September 30, 2008 ThinkServer PC2-5300 DDR2 FBDIMM and PC2-6400 DDR2 SDRAM Memory options boost overall performance of ThinkServer solutions Table of contents 2 Key prerequisites 2 Product number
JEDEC STANDARD. Double Data Rate (DDR) SDRAM Specification JESD79C. (Revision of JESD79B) JEDEC SOLID STATE TECHNOLOGY ASSOCIATION MARCH 2003
 JEDEC STANDARD Double Data Rate (DDR) SDRAM Specification JESD79C (Revision of JESD79B) MARCH 2003 JEDEC SOLID STATE TECHNOLOGY ASSOCIATION NOTICE JEDEC standards and publications contain material that
JEDEC STANDARD Double Data Rate (DDR) SDRAM Specification JESD79C (Revision of JESD79B) MARCH 2003 JEDEC SOLID STATE TECHNOLOGY ASSOCIATION NOTICE JEDEC standards and publications contain material that
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
PLL Dynamic Reconfiguration Author: Karl Kurbjun and Carl Ribbing
 Application Note: Spartan-6 Family XAPP7 (v1.1) October 6, 011 PLL Dynamic Reconfiguration Author: Karl Kurbjun and Carl Ribbing Summary This application note provides a method to dynamically change the
Application Note: Spartan-6 Family XAPP7 (v1.1) October 6, 011 PLL Dynamic Reconfiguration Author: Karl Kurbjun and Carl Ribbing Summary This application note provides a method to dynamically change the
DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM MT9HTF6472F 512MB MT9HTF12872F 1GB. Features. 512MB, 1GB (x72, SR) 240-Pin DDR2 SDRAM FBDIMM. Features
 SDRAM FBDIMM MT9HTF6472F 512MB MT9HTF12872F 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x72, SR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered DIMM (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200, PC2-5300, or PC2-6400
SDRAM FBDIMM MT9HTF6472F 512MB MT9HTF12872F 1GB 512MB, 1GB (x72, SR) 240-Pin SDRAM FBDIMM Features Features 240-pin, fully buffered DIMM (FBDIMM) Fast data transfer rates: PC2-4200, PC2-5300, or PC2-6400
DDR3 SDRAM SODIMM MT16JSF25664HZ 2GB MT16JSF51264HZ 4GB. Features. 2GB, 4GB (x64, DR) 204-Pin Halogen-Free DDR3 SODIMM. Features
 DDR3 SDRAM SODIMM MT6JSF5664HZ GB MT6JSF564HZ 4GB GB, 4GB (x64, DR) 04-Pin Halogen-Free DDR3 SODIMM Features Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet
DDR3 SDRAM SODIMM MT6JSF5664HZ GB MT6JSF564HZ 4GB GB, 4GB (x64, DR) 04-Pin Halogen-Free DDR3 SODIMM Features Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet
Below is a diagram explaining the data packet and the timing related to the mouse clock while receiving a byte from the PS-2 mouse:
 PS-2 Mouse: The Protocol: For out mini project we designed a serial port transmitter receiver, which uses the Baud rate protocol. The PS-2 port is similar to the serial port (performs the function of transmitting
PS-2 Mouse: The Protocol: For out mini project we designed a serial port transmitter receiver, which uses the Baud rate protocol. The PS-2 port is similar to the serial port (performs the function of transmitting
IS42/45R86400D/16320D/32160D IS42/45S86400D/16320D/32160D
 IS42/45R86400D/16320D/32160D IS42/45S86400D/16320D/32160D 16Mx32, 32Mx16, 64Mx8 512Mb SDRAM FEATURES Clock frequency: 200, 166, 143 MHz Fully synchronous; all signals referenced to a positive clock edge
IS42/45R86400D/16320D/32160D IS42/45S86400D/16320D/32160D 16Mx32, 32Mx16, 64Mx8 512Mb SDRAM FEATURES Clock frequency: 200, 166, 143 MHz Fully synchronous; all signals referenced to a positive clock edge
DDR3 DIMM Slot Interposer
 DDR3 DIMM Slot Interposer DDR3-1867 Digital Validation High Speed DDR3 Digital Validation Passive 240-pin DIMM Slot Interposer Custom Designed for Agilent Logic Analyzers Compatible with Agilent Software
DDR3 DIMM Slot Interposer DDR3-1867 Digital Validation High Speed DDR3 Digital Validation Passive 240-pin DIMM Slot Interposer Custom Designed for Agilent Logic Analyzers Compatible with Agilent Software
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield
 DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
M25P05-A. 512-Kbit, serial flash memory, 50 MHz SPI bus interface. Features
 512-Kbit, serial flash memory, 50 MHz SPI bus interface Features 512 Kbits of flash memory Page program (up to 256 bytes) in 1.4 ms (typical) Sector erase (256 Kbits) in 0.65 s (typical) Bulk erase (512
512-Kbit, serial flash memory, 50 MHz SPI bus interface Features 512 Kbits of flash memory Page program (up to 256 bytes) in 1.4 ms (typical) Sector erase (256 Kbits) in 0.65 s (typical) Bulk erase (512
PT973216BG. 32M x 4BANKS x 16BITS DDRII. Table of Content-
 PT973216BG 32M x 4BANKS x 16BITS DDRII Table of Content- 1. FEATURES......... 3 2. Description...4 3. Pi n Confi gur ation............. 5 4. TFBGA Ball Out Diagrams......9 5. Block Diagrams...12 6. FUNCTIONAL
PT973216BG 32M x 4BANKS x 16BITS DDRII Table of Content- 1. FEATURES......... 3 2. Description...4 3. Pi n Confi gur ation............. 5 4. TFBGA Ball Out Diagrams......9 5. Block Diagrams...12 6. FUNCTIONAL
Wiki Lab Book. This week is practice for wiki usage during the project.
 Wiki Lab Book Use a wiki as a lab book. Wikis are excellent tools for collaborative work (i.e. where you need to efficiently share lots of information and files with multiple people). This week is practice
Wiki Lab Book Use a wiki as a lab book. Wikis are excellent tools for collaborative work (i.e. where you need to efficiently share lots of information and files with multiple people). This week is practice
DDR3 SDRAM SODIMM MT8JSF25664HDZ 2GB. Features. 2GB (x64, DR) 204-Pin DDR3 SODIMM. Features. Figure 1: 204-Pin SODIMM (MO-268 R/C A)
 DDR3 SDRAM SODIMM MT8JSF5664HDZ GB GB (x64, DR) 04-Pin DDR3 SODIMM Features Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 04-pin, small-outline dual in-line
DDR3 SDRAM SODIMM MT8JSF5664HDZ GB GB (x64, DR) 04-Pin DDR3 SODIMM Features Features DDR3 functionality and operations supported as defined in the component data sheet 04-pin, small-outline dual in-line
LatticeECP3 High-Speed I/O Interface
 April 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1180 LatticeECP3 devices support high-speed I/O interfaces, including Double Data Rate (DDR) and Single Data Rate (SDR) interfaces, using the logic built into the
April 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1180 LatticeECP3 devices support high-speed I/O interfaces, including Double Data Rate (DDR) and Single Data Rate (SDR) interfaces, using the logic built into the
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill
 Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Memory unit. 2 k words. n bits per word
 9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
Embedded Multi-Media Card Specification (e MMC 4.5)
 Product Features: Packaged NAND flash memory with e MMC 4.5 interface Compliant with e MMC Specification Ver 4.41 & 4.5. Bus mode - High-speed e MMC protocol - Provide variable clock frequencies
Product Features: Packaged NAND flash memory with e MMC 4.5 interface Compliant with e MMC Specification Ver 4.41 & 4.5. Bus mode - High-speed e MMC protocol - Provide variable clock frequencies
Creating a Controllable Oscillator Using the Virtex-5 FPGA IODELAY Primitive Author: Martin Kellermann
 Application Note: Virtex-5 FPGAs XAPP872 (v1.0) April 28, 2009 Creating a Controllable Oscillator Using the Virtex-5 FPGA IODELAY Primitive Author: Martin Kellermann Introduction. This application note
Application Note: Virtex-5 FPGAs XAPP872 (v1.0) April 28, 2009 Creating a Controllable Oscillator Using the Virtex-5 FPGA IODELAY Primitive Author: Martin Kellermann Introduction. This application note
DDS. 16-bit Direct Digital Synthesizer / Periodic waveform generator Rev. 1.4. Key Design Features. Block Diagram. Generic Parameters.
 Key Design Features Block Diagram Synthesizable, technology independent VHDL IP Core 16-bit signed output samples 32-bit phase accumulator (tuning word) 32-bit phase shift feature Phase resolution of 2π/2
Key Design Features Block Diagram Synthesizable, technology independent VHDL IP Core 16-bit signed output samples 32-bit phase accumulator (tuning word) 32-bit phase shift feature Phase resolution of 2π/2
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected]. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
TS555. Low-power single CMOS timer. Description. Features. The TS555 is a single CMOS timer with very low consumption:
 Low-power single CMOS timer Description Datasheet - production data The TS555 is a single CMOS timer with very low consumption: Features SO8 (plastic micropackage) Pin connections (top view) (I cc(typ)
Low-power single CMOS timer Description Datasheet - production data The TS555 is a single CMOS timer with very low consumption: Features SO8 (plastic micropackage) Pin connections (top view) (I cc(typ)
