Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms - Flowering Plants. Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Fungi?
|
|
|
- Charla Hunter
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta The Importance of Plant Collections Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants involves series of dramatic adaptations to the problem of life on land and being non- motile exhibits successive rounds of speciation and subsequent extinction sets the stage for the development of a land-based ecosystem with fungi and animals Angiosperms - Flowering Plants Angiosperms focus of the course comprise the phylum Magnoliophyta vast majority of plant diversity Fungi? Fungi collectively are not a natural group More closely related to animals than to plants What are the non-angiosperm land plants? DNA evidence has clarified much but not all of the relatioships of other phyla (= divisions) See first pages of Chpts 1 & 3 for more detail (Plant( Systematics)
2 Fungi? Traditional view of eukaryotic relationships root is in microbes with fungi/animals/plants forming a crown radiation Fungi? Turning the Crown Upside Down: Gene Tree Parsimony Roots the Eukaryotic Tree of Life New root is between fungi/animals AND plants/rest of microbes Fungi are here Green Plants are here Katz et al Systematic Biology Charales - stoneworts Green algal lineage Closest relatives to land plants Extinct Land Plants - the first plants Ordovician Period ( mya) First evidence of land life at 460 mya Microfossils of spores with sporopollenin (degradation resistant material like lignin) and similar to modern day bryophytes such as liverworts Found worldwide in shales that were deposited at the marine-terrestrial interface
3 bryophytes earliest land plants - non vascular gametophyte dominant, species 3 lineages they are not a natural group bryophytes hornworts mosses mosses Liverworts - Marchantiophyta Mosses - Bryophyta liverworts liverworts Hornworts - Anthoceratophyta Extinct Land Plants - first vascular plants Early Devonian Period ( mya) Rhynia seen in the early Devonian (Rhynie( Chert fossil) is one of first vascular plants 20 cm tall, no roots, no leaves, primitive vascular tissue Lycopodiophyta - club mosses 3 families, 1150 species sporophyte dominant, vascular, free sporing they are sister to all other vascular plants Lycopodium - club mosses Isoetes - quillworts Selaginella - spike mosses
4 Extinct Land Plants - the first ferns Late Devonian Period ( mya) First true ferns [Protopteridium]] - free sporing with complex sporangia & megaphylls Polypodiophyta - ferns species immense variation in habit and habitat spores produced in specialized sporangia need a lot of systematic work - tropics! Polypodiophyta - ferns includes the horsetails as unusual ferns! 15 species in Equisetum vascular plants, reduced leaves, terminal sporangia Polypodiophyta - ferns includes the strange whisk ferns! 6 species in 2 genera vascular plants, leafless green stemmed, lateral sporangia Psilotum habit Psilotum branch Psilotum sporangia
5 Extinct Land Plants - the seed plants Late Devonian Period ( mya) Extinct Land Plants first gymnosperms Permian Period ( mya) First seeds - seed ferns [Archaeosperma] Plants fern-like with dissected compound leaves, but produce naked seeds (embryo within protective coverings) Big trees with net-veined leaves Seed bearing (derived from female gametophyte) and pollen forming (from male gametophyte) Pinophyta - gymnosperms 870 species seed plants but seeds naked often divided into 4 phyla is one closer to angiosperms? conifers Pinophyta - gymnosperms 870 species seed plants but seeds naked often divided into 4 phyla is one closer to angiosperms? cycads pine spruce juniper male strobilus female strobili
6 Pinophyta - gymnosperms 870 species seed plants but seeds naked often divided into 4 phyla is one closer to angiosperms? Pinophyta - gymnosperms 870 species seed plants but seeds naked often divided into 4 phyla is one closer to angiosperms? gnetophytes mature seeds ginkgo Gnetum male strobili Welwitschia mirabilis Ephedra Extinct Land Plants first flowering plants Cretaceous Period ( mya) Magnoliophyta - angiosperms Near the Jurassic/Cretaceous border, the first Angiosperms are seen Triassic 275,000 + species seed plants with seeds encased in ovary flowers a key innovation Archaefructus
7 Angiosperms - Flowering Plants tremendous adaptive radiation on land (and back into water) Angiosperms - Flowering Plants tremendous adaptive radiation on land (and back into water) Eucalyptus regnans (Myrtaceae) over 100m tall and 19m dbh Eucalyptus regnans (Myrtaceae) -Tasmania Angiosperms - Flowering Plants tremendous adaptive radiation on land (and back into water) Wolffia microscopica (Araceae) less than 1mm long Angiosperms - Flowering Plants tremendous adaptive radiation on land (and back into water) Rafflesia arnoldii (Rafflesiaceae) from New Guinea, up to 1m across and 20lbs 0.1 mm
8 Angiosperms - Flowering Plants tremendous adaptive radiation on land (and back into water) largest inflorescence Amorphophallus titanum (Araceae) Angiosperms - Flowering Plants tremendous adaptive radiation on land (and back into water) largest numbers of flowers Corypha palm Angiosperms - Flowering Plants Magnoliophyta classification previously divided into two classes dicots and monocots artificial! we will use Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG III) classification system of 2009 Why Important? : most significant feature of angiosperms 1. unlike anything else in other plants & extremely variable & co-evolved with animals 2. floral features used in describing and id ing ing 3. plant specimens (herbarium) must include flowers or derived features 4. classification of angiosperms relies on flowers Calochortus - fairy lanterns & mariposas (images: T. Givnish)
9 What is it? specialized shoot = stem + leaves (folia) shoot is highly modified and determinate (ceased to grow) What is it? foliar theory of flower - J.W. von Goethe in Attempt to Interpret the Metamorphosis of Plants (1790) from Schleiden 1855 What is it? developmental/evolutionary origin of the flower still debated 1. Euanthial theory - (foliar theory) - single shoot anthers ovules 2. Pseudanthial theory - compound shoot or cone What is it? thus, a flower is a specialized shoot that: 1. is determinate (vs. indeterminate) 2. has a modified stem with compressed internodes 3. possesses modified leaves with various functions, these determined by gene arrays (e.g., ABC model)
10 What is it? What is it? The ABC model of floral part identity The Plant Cell,, 2010 The ABC model of floral part identity A B C sepals petals als stamens carpels What is it? thus, a flower is a specialized shoot that: 1. is determinate (vs. indeterminate) 2. has a modified stem with compressed internodes 3. possesses modified leaves with various functions, these determined by gene arrays (e.g., ABC model) read chpt 9 in Plant Systematics! 1st half deals with vegetative features - we will cover in lab 2 next week 2nd half deals with flowers/fruits - lab 3 following week 4. often clustered in an inflorescence (larger branch)
11 1. Peduncle: : floral stalk, the stem supporting the flower; sometimes referred to as the pedicel 2. Receptacle: : modified floral stem or axis from which arise the floral appendages or modified leaves 3. Sepal: : the outer whorl of leaves, green and protective; collectively called the calyx 4. Petal: : the second whorl of leaves, typically brightly colored, attracting pollinators; collectively called the corolla
12 5. Perianth: : collective term for sepals and petals Tepals if both similar or if only one reduced set (sepals) 8. Stamen: : the male structure of flower comprising filament and anther collectively, stamens are the androecium (= house of males ) 6. Filament: : slender stalk of the stamen supporting the anther; permits exsertion of anther with pollen out of flower 7. Anther: : fertile portion of stamen that dehisces to release pollen grains; ; composed of anther sacs
13 Nuphar stamens can be leaf-like in primitive angiosperms! Nectaries often near base of stamens - produce nectar reward for visitors who will move pollen ( pollinators( pollinators ) 13. Pistil: : flask-shaped, female structure comprising three main parts often referred to as carpel(s) all pistils (1 or more) are referred to as the gynoecium (= house of females ) 13. Pistil: : flask-shaped, female structure comprising three main parts often referred to as carpel(s) 12. Stigma: : receptive portion at top of style that receives and recognizes pollen
14 13. Pistil: : flask-shaped, female structure comprising three main parts often referred to as carpel(s) 11. Style: : slender stalk of pistil above ovary that the pollen tubes must pass through to reach eggs in ovules 13. Pistil: : flask-shaped, female structure comprising three main parts often referred to as carpel(s) 9. Ovary: : basal portion of pistil that contains ovules; at maturity becomes fruit with seeds Pollination biology Study of the pollen, its transfer, and movement down the style 13. Pistil: : flask-shaped, female structure comprising three main parts often referred to as carpel(s) 10. Ovules: : fertile portions of pistil that contain a female gametophyte (embryo sac); develop into seeds after fertilization
15 Monocarpic Pistil vs. carpel How do you know? 3 examples Carpels not fused 1. Monocarpic 2. Apocarpic Carpels fused 3. Syncarpic 1 floral leaf in gynoecium Folded leaf 1 carpel = 1 pistil This gynoecium is monocarpic (one carpel) Apocarpic If 6 leaves separately form carpels, then the flower has 6 carpels and 6 pistils, gynoecium is apocarpic (separate carpels) legumes 1 carpel = 1 pistil This gynoecium is monocarpic (one carpel) Caltha palustris - Marsh marigold 6 fruits (pistils) from 1 flower Gynoecium is apocarpic with 6 carpels or 6 pistils
16 Syncarpic Syncarpic 3 floral leaves in gynoecium fuse 3 carpels = 1 pistil 3 styles 3 carpels = 1 pistil 1 style tomato 2 carpels passion fruit 3 carpels starfruit 5 carpels This gynoecium is syncarpic This gynoecium is syncarpic number of fused carpels is often clear in a cross section of the fruit Placentation types - arrangement of ovules, provides hints to the number of carpels Placentation types - arrangement of ovules, provides hints to the number of carpels Marginal - found in almost all monocarpic or apocarpic pistils tomato 2 carpels passion fruit 3 carpels starfruit 5 carpels number of fused carpels is often clear in a cross section of the fruit = placenta tissue Axile - found in some syncarpic pistils
17 Placentation types - arrangement of ovules, provides hints to the number of carpels Placentation types - arrangement of ovules, provides hints to the number of carpels Parietal - found in some syncarpic pistils Free-central - found in a few syncarpic pistils Placentation types - arrangement of ovules, provides hints to the number of carpels Numerical plan - merosity, arrangement of perianth not necessarily stamens or carpels Basal - found in some monocarpic, apocarpic, or syncarpic pistils perianth spiralled Common in primitive angiosperms perianth 5-merous Common in eudicots
18 Numerical plan - merosity, arrangement of perianth not necessarily stamens or carpels Symmetry plan - perianth arrangement important in pollination biology perianth 4-merous Occasional in eudicots perianth 3-merous Common in monocots & some primitive angiosperms Flowers radially symmetrical Flowers actinomorphic Flowers bilaterally symmetrical Flowers zygomorphic Fusion of carpels Syncarpic pistil Connation: : fusion of floral parts from the same whorl Adnation: : fusion of floral parts from different whorls Simple adnation Stamens fused onto inner surface of fused (connation) petals Complex adnation Sepals, petals, and stamens fuse to form a hypanthium Fusion of stamens Staminal tube Fusion of petals Corolla tube
19 e.g., Drimys & sandwort No adnation! Adnation: : fusion of floral parts from different whorls Connation (fusion of similar parts) may or may not occur e.g., cherry & rose Adnation: : fusion of floral parts from different whorls Adnation of calyx, corolla, & stamens = hypanthium e.g., horse gentian & fuchsia Adnation: : fusion of floral parts from different whorls e.g., horse gentian & fuchsia Adnation: : fusion of floral parts from different whorls
20 e.g., horse gentian & fuchsia Adnation: : fusion of floral parts from different whorls Floral formula - shorthand notation ovary calyx, corolla, stamens hypanthium 4 sepals (CA( CAlyx) 4 petals (CO( COrolla) 8 stamens (Androecium)( 4 carpels (Gynoecium)( pedicel Oenothera biennis Evening primrose Onagraceae Floral formula - shorthand notation Floral formula - shorthand notation 4 sepals (CA( CAlyx) 4 petals (CO( COrolla) 8 stamens (Androecium)( 4 carpels (Gynoecium)( Carpels fused = 1 pistil 4 sepals (CA( CAlyx) 4 petals (CO( COrolla) 8 stamens (Androecium)( 4 carpels (Gynoecium)( Carpels fused = 1 pistil Ovary inferior Oenothera biennis Evening primrose Onagraceae Oenothera biennis Evening primrose Onagraceae
21 Floral formula - shorthand notation The flower what is it? a flower is a specialized shoot that: 4 sepals (CA( CAlyx) 4 petals (CO( COrolla) 8 stamens (Androecium)( 4 carpels (Gynoecium)( Carpels fused = 1 pistil Ovary inferior Hypanthium (+ hypanthium tube) Oenothera biennis Evening primrose Onagraceae 1. is determinate (vs. indeterminate) 2. has a modified stem with compressed internodes 3. possesses modified leaves with various functions, these determined by gene arrays (e.g., ABC model) 4. often clustered in an inflorescence (larger branch)
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Biology 213 Angiosperms. Introduction
 Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to
 Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Plant Reproduction. 2. Evolutionarily, floral parts are modified A. stems B. leaves C. roots D. stolons E. suberins
 Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II
 Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
PLANT DIVERSITY. EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae
 PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview Objectives bold Part I Floral Anatomy . calyx sepals corolla, petals, stamens, filament
 Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds
 Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Vascular Plants Bryophytes. Seedless Plants
 plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions Sepals Anther Stamens (male) Filament Stigma Pistil Style (female) Ovary Petals sepals petals stamens pistil
 Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit
 Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout
 PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth?
 1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice
 10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
BIOL 1030 TOPIC 5 LECTURE NOTES TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29)
 TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29) I. Vascular Plants (overview) plants with xylem and phloem 7 or 9 living phyla, depending on who you talk to able to dominate most terrestrial habitats because
TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29) I. Vascular Plants (overview) plants with xylem and phloem 7 or 9 living phyla, depending on who you talk to able to dominate most terrestrial habitats because
Dissect a Flower. Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
What's in a Flower. Ages: 8 to 12. Contributor: Susan Jaquette, Cornell Plantations volunteer
 Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS
 PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
8. Study the cladogram underline the derived characteristics and circle the organisms that developed from them.
 Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Chapter 3. Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction. Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos
 BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
most modern cladograms have Amborella and water lilies as a sister group (or groups) to the rest of the angiosperms
 Topic 7: Angiosperms, Flowers and Pollination Syndromes Phylum Anthophyta (Chs. 30, 38) Ι. Phylum Anthophyta flowering plants (antho flower) A. also known as angiosperms (angeion vessel or enclosure; sperma
Topic 7: Angiosperms, Flowers and Pollination Syndromes Phylum Anthophyta (Chs. 30, 38) Ι. Phylum Anthophyta flowering plants (antho flower) A. also known as angiosperms (angeion vessel or enclosure; sperma
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All. Evolution of Plants
 And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
Topic 26. The Angiosperms
 1 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant
1 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant
Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land,
 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
Fungi and plants practice
 Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Parts of a Flower and Pollination
 Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms
 Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms Survey of Angiosperms using APG system Amborella trichopoda Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms Survey of Angiosperms using APG system What is the APG classification? Basal angiosperms
Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms Survey of Angiosperms using APG system Amborella trichopoda Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms Survey of Angiosperms using APG system What is the APG classification? Basal angiosperms
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions. Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9. Chapter 6 Plant structure and function
 1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
The Nonvascular Plants & Seedless Vascular Plants
 The Nonvascular Plants & Seedless Vascular Plants Laboratory 4 Introduction Members of kingdom Plantae are all multicellular organisms exhibiting cellulose cell walls, an alternation of generations life
The Nonvascular Plants & Seedless Vascular Plants Laboratory 4 Introduction Members of kingdom Plantae are all multicellular organisms exhibiting cellulose cell walls, an alternation of generations life
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator
 Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR GENERAL BIOLOGY II BIO4135 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR GENERAL BIOLOGY II BIO4135 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman
Unit 1: What is Biology? Unit 2: Ecology Unit 3: The Life of a Cell Unit 4: Genetics Unit 5: Change Through Time Unit 6: Viruses, Bacteria, Protists,
 Unit 1: What is Biology? Unit 2: Ecology Unit 3: The Life of a Cell Unit 4: Genetics Unit 5: Change Through Time Unit 6: Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Unit 7: Plants Unit 8: Invertebrates Unit
Unit 1: What is Biology? Unit 2: Ecology Unit 3: The Life of a Cell Unit 4: Genetics Unit 5: Change Through Time Unit 6: Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Unit 7: Plants Unit 8: Invertebrates Unit
Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY
 Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring
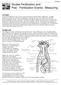 WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns
 Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
2. Fill in the blank. The of a cell is like a leader, directing and telling the different parts of the cell what to do.
 1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
version if desired, and Teacher Preparation Notes are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/.
 Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Introducing the parts of a flower
 Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Plant Growth & Development. Growth Stages. Differences in the Developmental Mechanisms of Plants and Animals. Development
 Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
nucleus cytoplasm membrane wall A cell is the smallest unit that makes up living and nonliving things.
 1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
How To Understand Plant Biology
 SECOND GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Distinguishing characteristics of vertebrates. LAB: Discovering characteristics of
SECOND GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Distinguishing characteristics of vertebrates. LAB: Discovering characteristics of
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers
 Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Plant Form and Function
 Part X Plant Form and Function Part Opener Title Text to come. Part opener figure 1 title. Figure legend. 733 Part opener figure 2 title. Figure legend. 734 Part X Plant Form and Function 37 Evolutionary
Part X Plant Form and Function Part Opener Title Text to come. Part opener figure 1 title. Figure legend. 733 Part opener figure 2 title. Figure legend. 734 Part X Plant Form and Function 37 Evolutionary
The Seed Plants. We have now reached the bottom of our key to the plant kingdom:
 The Seed Plants Final Review of the Kingdom Plantae. We have now reached the bottom of our key to the plant kingdom: A Plant is nonvascular Mosses, liverworts, hornworts A' Plant has vascular tissue B
The Seed Plants Final Review of the Kingdom Plantae. We have now reached the bottom of our key to the plant kingdom: A Plant is nonvascular Mosses, liverworts, hornworts A' Plant has vascular tissue B
The remarkable evolutionary success of flowering plants
 42 Plant Reproduction Concept Outline 42.1 Angiosperms have been incredibly successful, in part, because of their reproductive strategies. Rise of the Flowering Plants. Animal and wind dispersal of pollen
42 Plant Reproduction Concept Outline 42.1 Angiosperms have been incredibly successful, in part, because of their reproductive strategies. Rise of the Flowering Plants. Animal and wind dispersal of pollen
Bees and Flowers Partners in Pollination
 Bees and Flowers Partners in Pollination - Local Plant Community Investigation - Flower Dissection - Flower Collections - Build a Flower Build a Bee - Bee Collections - Making Pollen Slides Rural Science
Bees and Flowers Partners in Pollination - Local Plant Community Investigation - Flower Dissection - Flower Collections - Build a Flower Build a Bee - Bee Collections - Making Pollen Slides Rural Science
Plant Parts. Background Information
 Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Can you see the difference between wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers?
 Can you see the difference between wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers? Age of Students 10 14 years Duration 1 hour Summary Pollination is a very effective factor in the evolution of plants and
Can you see the difference between wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers? Age of Students 10 14 years Duration 1 hour Summary Pollination is a very effective factor in the evolution of plants and
How Plants Are Identified
 3 How Plants Are Identified T he easiest method, and the one probably used the most often for learning the names of the plants of a particular location or region, or just the name of a particular plant,
3 How Plants Are Identified T he easiest method, and the one probably used the most often for learning the names of the plants of a particular location or region, or just the name of a particular plant,
Classification of Angiosperms. Classification of Angiosperms
 Classification of Angiosperms Classification of Angiosperms classification is the 3rd goal of systematics ancient search for natural system of classification important non-western systems Parashara (India)
Classification of Angiosperms Classification of Angiosperms classification is the 3rd goal of systematics ancient search for natural system of classification important non-western systems Parashara (India)
Geraniaceae geranium family
 Geraniaceae geranium family Long-known for the prized ornamentals and house plants obtained from South African species. Nova Scotia hosts two genera and a half-dozen species. Most are herbs with lobed
Geraniaceae geranium family Long-known for the prized ornamentals and house plants obtained from South African species. Nova Scotia hosts two genera and a half-dozen species. Most are herbs with lobed
Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification
 Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification 1. Who proposed Five Kingdom Classification? Give the bases of classification. Ans. Whittaker in 1969 proposed five kingdom classification based on :- (i) Cell
Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification 1. Who proposed Five Kingdom Classification? Give the bases of classification. Ans. Whittaker in 1969 proposed five kingdom classification based on :- (i) Cell
Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones
 Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
The Parts of a Flower
 The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
Plants for primary pupils
 Plants for primary pupils Part 1: Parts of a flower Science and Plants for Schools (SAPS), an initiative launched in 1990, works with teachers to: develop new resources that support the teaching of plant
Plants for primary pupils Part 1: Parts of a flower Science and Plants for Schools (SAPS), an initiative launched in 1990, works with teachers to: develop new resources that support the teaching of plant
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development. Chapter 35
 Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
First Flower. Program Overview
 Program Overview NOVA presents the search for the first flowering plant. The program: recounts how one scientist discovered what might be the first flowering plant fossil, Archaefructus liaoningensis.
Program Overview NOVA presents the search for the first flowering plant. The program: recounts how one scientist discovered what might be the first flowering plant fossil, Archaefructus liaoningensis.
Biology Module 1 Diversity of Algae and Plants
 Biology Module 1 Biology Module 1 Diversity of Algae and Plants Prepared by Dr. Memory Tekere African Virtual university Université Virtuelle Africaine Universidade Virtual Africana African Virtual University
Biology Module 1 Biology Module 1 Diversity of Algae and Plants Prepared by Dr. Memory Tekere African Virtual university Université Virtuelle Africaine Universidade Virtual Africana African Virtual University
Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY. Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller. Other Commonly Used Names: none. Previously Used Scientific Names: none
 Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Berberidaceae (barberry) Rarity Ranks: G3/S1 State
Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Berberidaceae (barberry) Rarity Ranks: G3/S1 State
Chapter 32: An Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Name Period Concept 32.1 Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers 1. Like the fungi, animals are multicellular heterotrophs. How do they feed?
Name Period Concept 32.1 Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers 1. Like the fungi, animals are multicellular heterotrophs. How do they feed?
Protists and Fungi. What color are the cells in the living culture?
 Protists and Fungi Objectives 1. Recognize and identify (to genus) the organisms covered in lab. 2. Describe the characteristics of each organism. 3. Correctly classify the organisms. I. Protists The protists
Protists and Fungi Objectives 1. Recognize and identify (to genus) the organisms covered in lab. 2. Describe the characteristics of each organism. 3. Correctly classify the organisms. I. Protists The protists
Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types
 Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents?
 2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education. April, 2006
 Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Gymnosperms. Abstract
 Gymnosperms Susanne Renner Department of Biology, Menzingerstr. 67, University of Munich, Munich, Germany (renner@lrz.uni-muenchen.de) Abstract Gymnosperms (~1010 sp.) are grouped into four taxa: Coniferophyta,
Gymnosperms Susanne Renner Department of Biology, Menzingerstr. 67, University of Munich, Munich, Germany (renner@lrz.uni-muenchen.de) Abstract Gymnosperms (~1010 sp.) are grouped into four taxa: Coniferophyta,
BIO 182 General Biology (Majors) II with Lab. Course Package
 BIO 182 General Biology (Majors) II with Lab (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Course Package Modification Approved February 23, 2005 Modified April 3, 2009 COURSE INFORMATION New Course Course Modification
BIO 182 General Biology (Majors) II with Lab (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Course Package Modification Approved February 23, 2005 Modified April 3, 2009 COURSE INFORMATION New Course Course Modification
Plant Leaves: Holly Spines vs. Height
 Plant Leaves: Holly Spines vs. Height SC Academic Standards: 4.L.5A; 5.L.4A- B; 6.L.4A; 6.L.5B; 7.L.3B; 7.EC.5B; H.B.2B; H.B.6A NGSS DCI: 4- LS1.A; 5- LS2.A- B; MS- LS1- A- C; MS- LS2.A- C; MS- PS3.D;
Plant Leaves: Holly Spines vs. Height SC Academic Standards: 4.L.5A; 5.L.4A- B; 6.L.4A; 6.L.5B; 7.L.3B; 7.EC.5B; H.B.2B; H.B.6A NGSS DCI: 4- LS1.A; 5- LS2.A- B; MS- LS1- A- C; MS- LS2.A- C; MS- PS3.D;
Diversity and Evolution of Rosids!
 Diversity and Evolution of Rosids! *Malvales strongly supported order of 11 families Malvaceae... cacao, mustard, and capers...! Cistaceae Dipterocarpaceae *Malvales strongly supported order of 11 families
Diversity and Evolution of Rosids! *Malvales strongly supported order of 11 families Malvaceae... cacao, mustard, and capers...! Cistaceae Dipterocarpaceae *Malvales strongly supported order of 11 families
Problem Set 5 BILD10 / Winter 2014 Chapters 8, 10-12
 Chapter 8: Evolution and Natural Selection 1) A population is: a) a group of species that shares the same habitat. b) a group of individuals of the same species that lives in the same general location
Chapter 8: Evolution and Natural Selection 1) A population is: a) a group of species that shares the same habitat. b) a group of individuals of the same species that lives in the same general location
Alaska Forest Pest Control Supplemental Information. Category Twelve
 Alaska Forest Pest Control Supplemental Information Category Twelve In general, applicators who apply pesticides to property other than their own, or act as a pesticide consultant must obtain certification
Alaska Forest Pest Control Supplemental Information Category Twelve In general, applicators who apply pesticides to property other than their own, or act as a pesticide consultant must obtain certification
Systematics of hardy Theaceae and genus Stewartia. Koen Camelbeke Arboretum Wespelaar
 Systematics of hardy Theaceae and genus Stewartia Koen Camelbeke Arboretum Wespelaar Angiosperm Phylogeny Website Angiosperm Phylogeny Website Ericales Systematics Theaceae Family name Theaceae s.s. (versus
Systematics of hardy Theaceae and genus Stewartia Koen Camelbeke Arboretum Wespelaar Angiosperm Phylogeny Website Angiosperm Phylogeny Website Ericales Systematics Theaceae Family name Theaceae s.s. (versus
Chapter 14: Page 181
 Chapter 14: Page 181 Chapter 14: Page 182 The plant kingdom contains organisms that can be divided into two separate groups: nonvascular plants (like mosses) that absorb water through their entire body
Chapter 14: Page 181 Chapter 14: Page 182 The plant kingdom contains organisms that can be divided into two separate groups: nonvascular plants (like mosses) that absorb water through their entire body
Club Mosses, Ferns & Horsetails: the Seed-free Vascular Plants
 Club Mosses, Ferns & Horsetails: the Seed-free Vascular Plants Vascular Plants - a quick review Two unrelated groups within cryptogams seed free vascular plants are recognized as phyla: 1. Lycopodiophyta
Club Mosses, Ferns & Horsetails: the Seed-free Vascular Plants Vascular Plants - a quick review Two unrelated groups within cryptogams seed free vascular plants are recognized as phyla: 1. Lycopodiophyta
II. Vegetative Propagation. Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting
 II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
Pollination and fertilisation
 Pollination and fertilisation Teacher Guidance Introducing pollination and fertilisation Pollination is the transfer of pollen, from the stamens to the stigma. The pollen is often carried by insects and
Pollination and fertilisation Teacher Guidance Introducing pollination and fertilisation Pollination is the transfer of pollen, from the stamens to the stigma. The pollen is often carried by insects and
Plant Parts and Their Function
 Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
6 Kingdoms of Life. Prokaryotes. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes. DO HAVE: DNA Ribosomes Cytoplasm Cell membrane
 6 Kingdoms of Life The grouping of organisms into kingdoms is based on 3 factors: 1. Cell Type 2. Cell Number 3. Feeding Type Prokaryotes 1. Cell Type- The presence or absence of cellular structures such
6 Kingdoms of Life The grouping of organisms into kingdoms is based on 3 factors: 1. Cell Type 2. Cell Number 3. Feeding Type Prokaryotes 1. Cell Type- The presence or absence of cellular structures such
Practice Questions 1: Evolution
 Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
Life Science. A curriculum and activity guide for Carlsbad Caverns National Park. Middle School Biology
 Life Science A curriculum and activity guide for Carlsbad Caverns National Park Middle School Biology Life Science Biology Curriculum I. Introduction... 1 II. Curriculum unit overview and activities A.
Life Science A curriculum and activity guide for Carlsbad Caverns National Park Middle School Biology Life Science Biology Curriculum I. Introduction... 1 II. Curriculum unit overview and activities A.
The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Scale
 Two Conceptions of Earth History: Catastrophism Assumption: Great Effects Require Great Causes Earth History Dominated by Violent Events Uniformitarianism Assumption: We Can Use Cause And Effect to Determine
Two Conceptions of Earth History: Catastrophism Assumption: Great Effects Require Great Causes Earth History Dominated by Violent Events Uniformitarianism Assumption: We Can Use Cause And Effect to Determine
Functional Biology of Plants
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2252012/ Functional Biology of Plants Description: Functional Biology of Plants provides students and researchers with a clearly
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2252012/ Functional Biology of Plants Description: Functional Biology of Plants provides students and researchers with a clearly
Class Time: 30 minutes. Other activities in the Stem Cells in the Spotlight module can be found at: http://gslc.genetics.utah.edu/teachers/tindex/
 Teacher Guide: Color-Label-Learn: Creating Stem Cells for Research ACTIVITY OVERVIEW Abstract: Students color and label images on a worksheet and answer questions about the on-line content featured in
Teacher Guide: Color-Label-Learn: Creating Stem Cells for Research ACTIVITY OVERVIEW Abstract: Students color and label images on a worksheet and answer questions about the on-line content featured in
Strawberry Leaf Spot
 Strawberry Leaf Spot Cathy Heidenreich and Bill Turechek Introduction - Leaf spot is one of the most common and widespread diseases of strawberry. Mycosphaerella fragariae is also the cause of black seed
Strawberry Leaf Spot Cathy Heidenreich and Bill Turechek Introduction - Leaf spot is one of the most common and widespread diseases of strawberry. Mycosphaerella fragariae is also the cause of black seed
Adapted from activities and information found at University of Surrey Website http://www.mcs.surrey.ac.uk/personal/r.knott/fibonacci/fibnat.
 12: Finding Fibonacci patterns in nature Adapted from activities and information found at University of Surrey Website http://www.mcs.surrey.ac.uk/personal/r.knott/fibonacci/fibnat.html Curriculum connections
12: Finding Fibonacci patterns in nature Adapted from activities and information found at University of Surrey Website http://www.mcs.surrey.ac.uk/personal/r.knott/fibonacci/fibnat.html Curriculum connections
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function. I. Background
 Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Table 1: Kingdom Worksheet
 KINGDOM WORKSHEET Table 1: Kingdom Worksheet Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Cell Type prokaryotic prokaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic Cell Wall often present,
KINGDOM WORKSHEET Table 1: Kingdom Worksheet Kingdom Bacteria Archaea Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Cell Type prokaryotic prokaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic Cell Wall often present,
SIXTH GRADE PLANT LIFE
 SIXTH GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Defining classification. LAB: Exploring characteristics of the lower kingdoms POST:
SIXTH GRADE PLANT LIFE 2 weeks LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Defining classification. LAB: Exploring characteristics of the lower kingdoms POST:
A Morphological Study On Endemic Malabaila lasiocarpa Boiss. (Apiaceae) From Bingol (Turkey)
 Araştırma Makalesi/Research Article A Morphological Study On Endemic Malabaila lasiocarpa Boiss. (Apiaceae) From Bingol (Turkey) Ömer KILIÇ 1 Abstract- In this study morphological characters of Malabaila
Araştırma Makalesi/Research Article A Morphological Study On Endemic Malabaila lasiocarpa Boiss. (Apiaceae) From Bingol (Turkey) Ömer KILIÇ 1 Abstract- In this study morphological characters of Malabaila
Tech Prep Articulation
 Tech Prep Articulation Agriculture & Natural Resources Tech Prep Education: Tech Prep education in Missouri is an articulated two-year secondary and two or more year post-secondary education program which:
Tech Prep Articulation Agriculture & Natural Resources Tech Prep Education: Tech Prep education in Missouri is an articulated two-year secondary and two or more year post-secondary education program which:
Digitization of the Albion College Herbarium. Matthew Kleinow
 Digitization of the Albion College Herbarium Matthew Kleinow What is a Herbarium? Reference collection of dried or liquidpreserved plant specimens World s largest herbarium is at National Museum of Natural
Digitization of the Albion College Herbarium Matthew Kleinow What is a Herbarium? Reference collection of dried or liquidpreserved plant specimens World s largest herbarium is at National Museum of Natural
(1) Hybrid Cucumber Seed Production. Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago, Chile
 (1) Hybrid Cucumber Seed Production Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago, Chile (2) Introduction Cucurbitaceae family The Cucurbitaceae
(1) Hybrid Cucumber Seed Production Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago, Chile (2) Introduction Cucurbitaceae family The Cucurbitaceae
Plants Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Name: Plants Activity Materials: Question worksheet (pages 2-3) 16 Fact Cards (pages 4-8) Tape, Scissors, Classroom Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and cut them
Name: Plants Activity Materials: Question worksheet (pages 2-3) 16 Fact Cards (pages 4-8) Tape, Scissors, Classroom Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and cut them
Complete tests for CO 2 and H 2 Link observations of acid reactions to species
 Acids and Bases 1. Name common acids and bases found at home and at school 2. Use formulae for common acids and bases 3. Give examples of the uses of acids and bases 4. State that all solutions are acidic,
Acids and Bases 1. Name common acids and bases found at home and at school 2. Use formulae for common acids and bases 3. Give examples of the uses of acids and bases 4. State that all solutions are acidic,
Germination is the process in which a
 The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
IDENTIFICATION OF ORGANISMS
 reflect Take a look at the pictures on the right. Think about what the two organisms have in common. They both need food and water to survive. They both grow and reproduce. They both have similar body
reflect Take a look at the pictures on the right. Think about what the two organisms have in common. They both need food and water to survive. They both grow and reproduce. They both have similar body
