most modern cladograms have Amborella and water lilies as a sister group (or groups) to the rest of the angiosperms
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Newton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topic 7: Angiosperms, Flowers and Pollination Syndromes Phylum Anthophyta (Chs. 30, 38) Ι. Phylum Anthophyta flowering plants (antho flower) A. also known as angiosperms (angeion vessel or enclosure; sperma seed) B. ovules enclosed within carpel (parent diploid sporophytic tissue) at pollination 1. the vessel is the carpel, which is a modified leaf 2. carpels, especially their enlarged basal portion (the ovary), usually develop into fruit, which is unique to angiosperms C. about 250,000 known living species (dominant photosynthetic organisms on land) D. predominant source of human food E. most widespread and diverse plant phylum 1. range from microscopic to plants with leaves over 6 m long 2. flowers show incredible variety from species to species 3. variety of lifestyles includes parasites (ex.: mistletoe, dodder, beechdrops); mycotrophs (derive nutrients from fungi; ex.: Indian Pipe, others); epiphytes (ex.: some orchids); carnivorous (ex. pitcher plants, sundews, Venus flytrap) F. monophyletic group with seeds, refined xylem, double fertilization, and these synapomorphic characteristics: 1. seed contains endosperm 2. presence of flowers (modified stems and leaves) 3. true fruits G. evolutionary history 1. monophyletic group 2. origin about 140 MYA H. phylogeny 1. historically divided into two classes, dicots and monocots recent genetic analysis has shown that the traditional dicots are a paraphyletic group thus, the old classification scheme is being replaced 2. no conclusive cladogram has been produced for angiosperms studies are ongoing most modern cladograms have Amborella and water lilies as a sister group (or groups) to the rest of the angiosperms cladogram below from 1 of 9
2 various class-level groupings have been proposed, the overall naming and formal classification within Phylum Anthophyta is still in a state of flux nevertheless, by far most of the living angiosperm species are found within two monophyletic groups, eudicots and 3. eudicots monocots most have embryos have two cotyledons (seed leaves) leaves have netlike veins flower part typically in multiples of 4 or 5 groups of vascular tissues in a ring pollen grains mostly with 3 or more apertures endosperm mostly used up in mature eudicot seeds about 175,000 living species; includes nearly all flowering trees and shrubs about a sixth are annuals (entire growth cycle in one year or less) 4. monocots embryos have one cotyledon leaves have essentially parallel veins flower part typically in multiples of 3 groups of vascular tissues scattered pollen grains mostly with one aperture endosperm typically present in mature monocot seeds about 65,000 living species; no true wood, few annuals ΙΙ. Why were (and are) angiosperms successful? A. 130 MYA two major continental masses 1. Laurasia = North America, Europe, Asia 2. Gondwanaland = South America, Africa, Australia, Antarctica, India, New Zealand) B. angiosperms first appeared in Gondwanaland, in what was likely a drier interior region C. advantages of flowering plants 1. transfer of pollen over great distances promotes outcrossing 2. efficient seed dispersal via fruit 3. endosperm gives seedlings a fast start 4. leaves appropriate for fast growth in hot, dry environment D. coevolution with insects 1. dominant by ~80 MYA, second half of Cretaceous Period 2. all present angiosperm families represented by that time 3. many insect orders appeared or became more abundant at that time ΙΙΙ. Flowers 2 of 9
3 A. modified stems with modified leaves B. develop as primordium bud at end of stalk called pedicel C. pedicel widens at tip to form receptacle D. other flower parts attached to receptacle in four whorls; from outside in: 1. calyx sepals; usually green, leaf-like, and protect immature flower 2. corolla petals; usually colorful, attract pollinators; together with calyx called perianth 3. androecium stamens; male reproductive structures filament + anther microspores produced within anther, shed as pollen 4. gynoecium female reproductive structure center location is most protected formed from leaf-like structure with ovules along margin edges fold inwards around ovules, forming carpels primitive: many separate carpels advanced: carpels fused (called pistil) carpel/pistil segments ovary swollen base with 1 to hundreds of ovules; develops into fruit stigma tip; sticky and/or feathery to catch pollen style usually present; separates stigma from ovary nectaries may be present at base of pistil; secrete sugar, amino acids, and other compounds to attract pollinators E. know the structures of a flower [Figure 38.2] and their functions 3 of 9
4 Ις. typical Angiosperm life cycle A. female gametophyte BIOL 1030 TOPIC 7 LECTURE NOTES 1. single diploid megaspore mother cell in ovule undergoes meiosis while flower develops 2. of 4 haploid megaspores produced, usually 3 break down 3. remaining megaspore expands and replicates and divides until there are 8 haploid nuclei in two groups of 4 4. one nuclei from each group migrates toward center; these are polar nuclei 5. polar nuclei usually fuse to make a diploid nucleus, but may remain separate in either case, they wind up in a single cell 6. cell walls form around other nuclei, creating the 7-celled, 8-nucleate embryo sac or megagametophyte (female gametophyte) 7. meanwhile, two layers (integuments) of ovule develop into seed coat with micropyle (small opening) 8. in the megagametophyte, one of the cells closest to the micropyle becomes the egg; the other two there are synergids 9. the three cells on the other end (the antipodals) eventually break down B. male gametophyte 1. anthers with patches of tissue that become chambers lined with nutritive cells 2. each patch has many diploid microspore mother cells 3. microspore mother cell undergoes meiosis, making 4 haploid microspores that typically remain grouped in a tetrad 4. each microspore nucleus replicates and divides once (via mitosis) without cytokinesis (meaning they remain as one cell with two nuclei, a binucleate microspore) 5. usually, tetrad then breaks up 6. two-layered wall develops around each binucleate microspore, now called a pollen grain outer wall sculptured, appearance usually species-specific, often has chemicals that can react with an appropriate stigma to stimulate pollen tube formation apertures in outer wall where pollen tube may grow out; eudicots usually 3; monocots usually 1 C. pollination transfer of pollen to a stigma 1. usually between flowers of separate plants 2. agents include wind, water, gravity, mammals, birds, insects 3. various reward systems for animal agents (pollen, nectar, etc.) 4. evolution of floral characteristics associated with pollination 5. some plants self-pollinate (inbreeding) pollen to same plant 6. pollination followed by fertilization only if chemical signals are right D. fertilization 1. pollen grain cytoplasm absorbs substances from stigma 2. bulge forms through an aperture in pollen grain; becomes pollen tube 3. pollen tube follows chemical gradient through style to micropyle chemicals diffuse from embryo sac micropyle usually reached within a few days (up to a year in some species) 4 of 9
5 4. pollen grain has two nuclei; one, the generative nucleus, lags behind 5. generative nucleus undergoes mitosis to make two non-flagellated sperm; this may occur in pollen grain or in pollen tube (male gametophyte now mature) 6. pollen tube enters embryo sac, destroying a synergid 7. double fertilization essentially unique to angiosperms one sperm unites with egg, forming zygote other sperm unites with polar nuclei, forming 3N primary endosperm primary endosperm rapidly undergoes many cycles of mitosis, forming endosperm endosperm provides nutrients for embryo; in many seeds, it is gone by the time the seed is mature seed coat hardens remaining haploid cells degenerate now have seed with 2N embryo, 3N endosperm, and 2N seed coat (seed coat from parent female tissue) 5 of 9
6 ς. Seeds A. embryo quickly forms all systems, then growth arrested (dormancy) mature seed about 10% water, very low metabolic activity B. typically, dormancy occurs just after first leaves (cotyledons, or seed leaves) form C. stored food (in angiosperms, 3N endosperm and/or cotyledons) D. seed coat tough, relatively impermeable 1. protection from predators, pathogens 2. protection from desiccation, harsh conditions (crucial on land) 3. may allow seed to last hundreds of years E. dormancy broken only when conditions are right (seed bank in soil) F. germination = breaking dormancy = resuming metabolic activity, growing out of seed coat; occurs after water penetrates seed coat to embryo, bringing oxygen ςι. Fruits mature ovaries A. fleshy pomes (apples), drupes (peaches), true berries (blueberries, peppers), hesperidiums (oranges), pepos (melons, gourds), aggregate fruits (strawberries, raspberries), multiple fruits (pineapple, fig) B. dry follicles (milkweed, magnolia), legumes (peas, beans), siliques and silicles (mustards), capsules (irises, lilies, orchids), caryopses (grasses), nuts (chestnuts, hazelnuts, acorns), achenes (sunflowers), samaras (maples, elms, ashes), schizocarps (parsleys) C. dispersal 6 of 9
7 1. by wind wings maples parachutes dandelions, milkweeds dust-like seeds orchids 2. by water coconuts 3. by vertebrates fleshy, edible fruits (blue, black, red) seeds often deposited in feces dry, edible nuts, others squirrels bury and forget about them dry, inedible hooks to grasp hair, feathers (cockleburs, etc.) 4. by explosive dehiscence (jewelweed, others) ςιι. many angiosperms also have asexual (or vegetative) reproduction A. stolons runners long slender stems that grow along soil (ex.: strawberry) B. rhizomes underground stems common in grasses; bulbs and tubers are rhizomes specialized for storage (ex.: potato) C. suckers roots produce sprouts that grow into new plants (ex.: apple, raspberry, banana) D. adventitious leaves numerous plantlets develop from tissue in notches along leaves E. apomixes embryos in seeds may be produced asexually F. artificial: cuttings (for some species, can get roots to grow with appropriate environment) ςιιι.floral Evolution A. first flowers 1. numerous spirally arranged sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels 2. petals and sepals similar in color and form 3. all parts free (not fused) B. parts 1. complete calyx + corolla + androecium + gynoecium 2. incomplete one or more whorls absent 3. perfect has both androecium and gynoecium 4. imperfect missing either androecium or gynoecium 5. complete flowers are always perfect; incomplete flowers can be either perfect or imperfect C. trends 1. separate floral parts grouped together or fused connation fusing within a whorl adnation fusing between whorls (for example, sepals and petals fused together) 2. reduction or loss of floral parts 3. bilateral symmetry instead of radial symmetry ancestral type: radial symmetry; example: buttercups 7 of 9
8 derived type: bilateral symmetry; examples: snapdragons, orchids bilateral symmetry in some cases has arisen independently in different groups ΙΞ. Pollination mechanisms (pollination syndromes) A. wind passive, primitive (oaks, cottonwoods, birches, grasses) 1. copious amounts of pollen 2. most pollen travels no more than 100 m 3. flowers small, greenish, odorless 4. corollas reduced or absent 5. often grouped in large numbers, may hang down with tassels that wave in wind and shed pollen freely 6. male and female parts often well-separated on plant to reduce chance of self-pollination 7. often flower before leaves grow keeps leaves out of the way B. animals some cycads and gnetophytes also have this, so symplesiomorphic trait 1. bees most numerous of insect-pollinated plants use bees find via odor orient via shape, color, and texture usually blue or yellow flowers, bee sees in ultraviolet many have stripes or lines of dots to indicate nectaries (nectar guides) nectar offered as food for bees (pollen also) often close association between a bee species and a plant species flower only open when bees are active pollen collecting apparatus specific for particular plant 2. other insects butterflies flower usually has flat landing platform and long, slender floral tubes for long proboscis moths flower usually white, yellow, or other pale color, heavily scented, typically need to be found at night flies flower usually smells and somewhat appears like feces or rotting meat beetle large flowers, copious pollen; beetle may eat other flower parts 3. birds large amounts of nectar red bees can t see red, less likely to feed on the copious nectar usually odorless birds have a poor sense of smell often in long, thick tube 4. mammals (bats especially) uncommon, but for some species is the only means of pollination; variety of appearances C. self-pollination 1. small, inconspicuous flowers 2. shed pollen directly onto stigma (or falls there by gravity); often before bud opens 3. advantageous occasionally because no other plant is needed and no vector is needed good when pollinators aren t around (Artic, mountains) 8 of 9
9 4. if you are well-adapted, might as well produce clones 5. disadvantage of genetic load of bad mutations Ξ. Promoting outcrossing A. staminate and pistillate flowers B. dioecious separate sexes C. monoecious 1. dichogamous stamens and pistils reach maturity at different times 2. stigma and stamens don t touch (includes heterostyle) 3. genetic self-incompatibility pollen tube arrested or never germinates 9 of 9
Biology 213 Angiosperms. Introduction
 Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Plant Reproduction. 2. Evolutionarily, floral parts are modified A. stems B. leaves C. roots D. stolons E. suberins
 Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Chapter 3. Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction. Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos
 BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview Objectives bold Part I Floral Anatomy . calyx sepals corolla, petals, stamens, filament
 Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Topic 26. The Angiosperms
 1 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant
1 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds
 Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth?
 1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
Vascular Plants Bryophytes. Seedless Plants
 plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout
 PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
Dissect a Flower. Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II
 Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions Sepals Anther Stamens (male) Filament Stigma Pistil Style (female) Ovary Petals sepals petals stamens pistil
 Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice
 10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
8. Study the cladogram underline the derived characteristics and circle the organisms that developed from them.
 Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions. Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9. Chapter 6 Plant structure and function
 1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All. Evolution of Plants
 And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
The remarkable evolutionary success of flowering plants
 42 Plant Reproduction Concept Outline 42.1 Angiosperms have been incredibly successful, in part, because of their reproductive strategies. Rise of the Flowering Plants. Animal and wind dispersal of pollen
42 Plant Reproduction Concept Outline 42.1 Angiosperms have been incredibly successful, in part, because of their reproductive strategies. Rise of the Flowering Plants. Animal and wind dispersal of pollen
Parts of a Flower and Pollination
 Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS
 PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
Plant Parts. Background Information
 Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land,
 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to
 Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans.
Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit
 Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development. Chapter 35
 Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
PLANT DIVERSITY. EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae
 PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator
 Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Fungi and plants practice
 Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY
 Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
nucleus cytoplasm membrane wall A cell is the smallest unit that makes up living and nonliving things.
 1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
What's in a Flower. Ages: 8 to 12. Contributor: Susan Jaquette, Cornell Plantations volunteer
 Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring
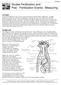 WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
BIOL 1030 TOPIC 5 LECTURE NOTES TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29)
 TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29) I. Vascular Plants (overview) plants with xylem and phloem 7 or 9 living phyla, depending on who you talk to able to dominate most terrestrial habitats because
TOPIC 5: SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS (CH. 29) I. Vascular Plants (overview) plants with xylem and phloem 7 or 9 living phyla, depending on who you talk to able to dominate most terrestrial habitats because
Germination is the process in which a
 The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
The Germination Of a Bean Photographs and article By Lily C. Gerhardt LCG1603@rit.edu Germination is the process in which a seed, spore, or fungi sprouts, or begins growth. Seed germination can occur after
2. Fill in the blank. The of a cell is like a leader, directing and telling the different parts of the cell what to do.
 1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function. I. Background
 Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Lecture 7: Plant Structure and Function I. Background A. Challenges for terrestrial plants 1. Habitat is divided a. Air is the source of CO2 for photosynthesis i. Sunlight cannot penetrate soil b. Soil
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns
 Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
II. Vegetative Propagation. Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting
 II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types
 Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Ch. 35 Plants have organs composed of different tissues, which in turn are composed of different cell types A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms - Flowering Plants. Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Fungi?
 Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta The Importance of Plant Collections Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta The Importance of Plant Collections Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants
The Simple Truth: We Can t Live Without Them
 The Great Pollinator Partnership poster has been reproduced as part of a cooperative effort of the North American Pollinator Protection Campaign to raise awareness of the importance of pollinators to our
The Great Pollinator Partnership poster has been reproduced as part of a cooperative effort of the North American Pollinator Protection Campaign to raise awareness of the importance of pollinators to our
Unit 3 Lesson 5: People Need Plants
 Focus Areas: Characteristics of Plants; Science Focus Skills: observing, identifying, drawing conclusions Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objectives To identify parts of a plant To recognize the importance
Focus Areas: Characteristics of Plants; Science Focus Skills: observing, identifying, drawing conclusions Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Objectives To identify parts of a plant To recognize the importance
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents?
 2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
Can you see the difference between wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers?
 Can you see the difference between wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers? Age of Students 10 14 years Duration 1 hour Summary Pollination is a very effective factor in the evolution of plants and
Can you see the difference between wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers? Age of Students 10 14 years Duration 1 hour Summary Pollination is a very effective factor in the evolution of plants and
PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY
 PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY David W. Lockwood Department of Plant Sciences & Landscape Systems University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996 D. C. Coston Agricultural Experiment Station Oklahoma State University
PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY David W. Lockwood Department of Plant Sciences & Landscape Systems University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996 D. C. Coston Agricultural Experiment Station Oklahoma State University
Plant Growth & Development. Growth Stages. Differences in the Developmental Mechanisms of Plants and Animals. Development
 Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones
 Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction
 Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes?
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
Plant Structure and Function Notes
 For plants, when they made the transition from water to land, they had to make adaptations for obtaining water and prevent loss by desiccation (drying out) -water also needed for fertilization of eggs
For plants, when they made the transition from water to land, they had to make adaptations for obtaining water and prevent loss by desiccation (drying out) -water also needed for fertilization of eggs
Sexual Reproduction. The specialized cells that are required for sexual reproduction are known as. And come from the process of: GAMETES
 Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination
 Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
Question Bank Seed : Structure, Types and Germination 1. Describe the structure of a seed. Ans. A mature seed consists of two essential parts : (i) the seed coat, and (ii) the embryo The Seed coat : A
Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Meiosis is a special form of cell division.
 Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
version if desired, and Teacher Preparation Notes are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/.
 Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education. April, 2006
 Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
Practice Questions 1: Evolution
 Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST
 4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK SPRING 2008 GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
4THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK SPRING 2008 GRADE 4 ELEMENTARY-LEVEL SCIENCE TEST WRITTEN TEST Student Name School Name Print your name and the name of your school on the lines above. The test
Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones
 Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Phototropism - plant growth response to light shoots bend toward light - positive
Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Tropisms, Photoperiodism, and Plant Hormones Plant Responses to Environmental Cues Phototropism - plant growth response to light shoots bend toward light - positive
Plants Scavenger Hunt Activity
 Name: Plants Activity Materials: Question worksheet (pages 2-3) 16 Fact Cards (pages 4-8) Tape, Scissors, Classroom Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and cut them
Name: Plants Activity Materials: Question worksheet (pages 2-3) 16 Fact Cards (pages 4-8) Tape, Scissors, Classroom Preparation: Print the fact cards on card stock or brightly-colored paper and cut them
Plant Parts and Their Function
 Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
Science Unit: Lesson 6: Plants Plant Parts and Their Function School year: 2004/2005 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Queen Alexandra Elementary School, Vancouver School District
The Seed Plants. We have now reached the bottom of our key to the plant kingdom:
 The Seed Plants Final Review of the Kingdom Plantae. We have now reached the bottom of our key to the plant kingdom: A Plant is nonvascular Mosses, liverworts, hornworts A' Plant has vascular tissue B
The Seed Plants Final Review of the Kingdom Plantae. We have now reached the bottom of our key to the plant kingdom: A Plant is nonvascular Mosses, liverworts, hornworts A' Plant has vascular tissue B
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Class Insecta - The insects
 A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers
 Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS
 CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
Introducing the parts of a flower
 Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
What Do Plants Need to Grow?
 Lesson #401 What Do Plants Need to Grow? Grades 2-4 Editors Mandi Bottoms Shaney Emerson Robin Satnick 2300 River Plaza Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 (916) 561-5625 (800) 700-2482 www.learnaboutag.org California
Lesson #401 What Do Plants Need to Grow? Grades 2-4 Editors Mandi Bottoms Shaney Emerson Robin Satnick 2300 River Plaza Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 (916) 561-5625 (800) 700-2482 www.learnaboutag.org California
Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort
 The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Things Plants Need There are certain things that every living thing needs in order to live and grow. Just like you, plants need
The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Things Plants Need There are certain things that every living thing needs in order to live and grow. Just like you, plants need
Pollination and fertilisation
 Pollination and fertilisation Teacher Guidance Introducing pollination and fertilisation Pollination is the transfer of pollen, from the stamens to the stigma. The pollen is often carried by insects and
Pollination and fertilisation Teacher Guidance Introducing pollination and fertilisation Pollination is the transfer of pollen, from the stamens to the stigma. The pollen is often carried by insects and
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *9282687787* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core October/November 2012 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
*9282687787* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core October/November 2012 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Plants for primary pupils
 Plants for primary pupils Part 1: Parts of a flower Science and Plants for Schools (SAPS), an initiative launched in 1990, works with teachers to: develop new resources that support the teaching of plant
Plants for primary pupils Part 1: Parts of a flower Science and Plants for Schools (SAPS), an initiative launched in 1990, works with teachers to: develop new resources that support the teaching of plant
Life Cycle of a Butterfly
 Name: Date: Life Cycle of a Butterfly Life cycle refers to the stages of development, growth and reproduction that a living thing goes through. The butterfly's life cycle is made up of four stages: egg,
Name: Date: Life Cycle of a Butterfly Life cycle refers to the stages of development, growth and reproduction that a living thing goes through. The butterfly's life cycle is made up of four stages: egg,
(1) Hybrid Cucumber Seed Production. Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago, Chile
 (1) Hybrid Cucumber Seed Production Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago, Chile (2) Introduction Cucurbitaceae family The Cucurbitaceae
(1) Hybrid Cucumber Seed Production Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago, Chile (2) Introduction Cucurbitaceae family The Cucurbitaceae
The Tiny Seed Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9
 Teacher s Guide to Third and Fourth Grade Reading and Writing Exercises for Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9 Developed by Jennifer A. Seitz For Florida
Teacher s Guide to Third and Fourth Grade Reading and Writing Exercises for Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9 Developed by Jennifer A. Seitz For Florida
Plant Structure and Function
 NQF Level: 2 US No: 116057 Learner Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Structure and Function My name:. Company:. Commodity:.................... Date:............... The availability of this product is due
NQF Level: 2 US No: 116057 Learner Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Structure and Function My name:. Company:. Commodity:.................... Date:............... The availability of this product is due
Bees and Flowers Partners in Pollination
 Bees and Flowers Partners in Pollination - Local Plant Community Investigation - Flower Dissection - Flower Collections - Build a Flower Build a Bee - Bee Collections - Making Pollen Slides Rural Science
Bees and Flowers Partners in Pollination - Local Plant Community Investigation - Flower Dissection - Flower Collections - Build a Flower Build a Bee - Bee Collections - Making Pollen Slides Rural Science
Introduction to Plant Propagation. Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM
 Introduction to Plant Propagation Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM Purposes for Plant Propagation Multiply the number of a species Perpetuate a species Maintain the youthfulness
Introduction to Plant Propagation Glenn T. Sako Assistant County Extension Agent CTAHR, UHM Purposes for Plant Propagation Multiply the number of a species Perpetuate a species Maintain the youthfulness
CHAPTER 20 COMMUNITY ECOLOGY
 CHAPTER 20 COMMUNITY ECOLOGY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The relationship between a predator and its prey is best illustrated by a. a snake eating a bird. c. a lion eating a zebra. b. a fox eating a mouse. d. a
CHAPTER 20 COMMUNITY ECOLOGY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The relationship between a predator and its prey is best illustrated by a. a snake eating a bird. c. a lion eating a zebra. b. a fox eating a mouse. d. a
XII. Biology, Grade 10
 XII. Biology, Grade 10 Grade 10 Biology Pilot Test The spring 2004 Grade 10 MCAS Biology Test was based on learning standards in the Biology content strand of the Massachusetts Science and Technology/Engineering
XII. Biology, Grade 10 Grade 10 Biology Pilot Test The spring 2004 Grade 10 MCAS Biology Test was based on learning standards in the Biology content strand of the Massachusetts Science and Technology/Engineering
The Nonvascular Plants & Seedless Vascular Plants
 The Nonvascular Plants & Seedless Vascular Plants Laboratory 4 Introduction Members of kingdom Plantae are all multicellular organisms exhibiting cellulose cell walls, an alternation of generations life
The Nonvascular Plants & Seedless Vascular Plants Laboratory 4 Introduction Members of kingdom Plantae are all multicellular organisms exhibiting cellulose cell walls, an alternation of generations life
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
The Parts of a Flower
 The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity
 12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
Exploring Seed Germination by Brad Williamson
 Exploring Seed Germination by Brad Williamson Background: Seeds are very remarkable. Laying dormant inside the seed is an embryo plant. Packed with the embryo is enough stored chemical energy to power
Exploring Seed Germination by Brad Williamson Background: Seeds are very remarkable. Laying dormant inside the seed is an embryo plant. Packed with the embryo is enough stored chemical energy to power
Promoting Pollination Farming for Native Bees
 Promoting Pollination Farming for Native Bees Overview Pollination, the transfer of pollen grains to fertilize the ovules of flowers to produce seeds and fruits, is essential to agriculture and natural
Promoting Pollination Farming for Native Bees Overview Pollination, the transfer of pollen grains to fertilize the ovules of flowers to produce seeds and fruits, is essential to agriculture and natural
Sexual Reproduction. and Meiosis. Sexual Reproduction
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
The Seed Challenge How Many Seeds Can You Get from a Single Seed?
 The Seed Challenge How Many Seeds Can You Get from a Single Seed? Grade Level: K-4 Catalog Number: 15-8973 Time to pollinate the flowers Time to harvest the seeds True leaves grow Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 Day
The Seed Challenge How Many Seeds Can You Get from a Single Seed? Grade Level: K-4 Catalog Number: 15-8973 Time to pollinate the flowers Time to harvest the seeds True leaves grow Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 Day
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions. Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions!
 AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
FOOD CHAINS, FOOD WEBS AND ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS
 FOOD CHAINS, FOOD WEBS AND ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS SECTION 1 In an ecosystem, plants capture the sun's energy and use it to convert inorganic compounds into energy-rich organic compounds. This process of using
FOOD CHAINS, FOOD WEBS AND ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS SECTION 1 In an ecosystem, plants capture the sun's energy and use it to convert inorganic compounds into energy-rich organic compounds. This process of using
WEED MANAGEMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 C 6 H A P TE R WEED MANAGEMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES After completely studying this chapter, you should: Be able to define a weed and its four stages of development. Understand the differences between annual,
C 6 H A P TE R WEED MANAGEMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES After completely studying this chapter, you should: Be able to define a weed and its four stages of development. Understand the differences between annual,
