PathoBasic - Vulva, Vagina, Cervix. E.Obermann
|
|
|
- Amy Singleton
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PathoBasic - Vulva, Vagina, Cervix E.Obermann
2 Vulva Inflammatory Changes Non-neoplastic lesions «Skin type lesions» Lichen sclerosus Infection: HSV, Candida Fibroepithelial stroma polyp Cutaneous Neoplasia Soft Tissue Neoplasia HPV related lesions Non HPV related lesions Angio..lesions
3 Vulva Inflammatory Changes Desquamat. inflamm. Vaginitis Non-neoplastic lesions Fallopian tube prolaps Adenosis Neoplasms Clear cell carcinoma
4 Vulva Non-neoplastic lesions Neoplasms Microgland. Hyperplasia Mesonephric Duct Remnant CIN Squamous cell carcinoma Ais Adenocarcinoma
5 Vulva Lichen sclerosus Clinical Issues Typically 5th decade "porcelain white" plaques Premalignant disease Early: Lichenoid lymphocytic infiltrate and vacuolization of basal epidermal layer Well developed: Hyalinization and edema in superficial dermis DD VIN, differentiated type Lichen planus Morphea Late-stage radiation dermatitis
6 Vulva Infection: HSV + Candida Herpes simplex infection Microscopic Pathology Ulcerated epidermis or intraepidermal blister Intracellular ballooning multinucleation, nuclear molding, and ground glass Differential Diagnoses Squamous cell carcinoma Reparative changes adjacent to ulcer Candida infection Microscopic Pathology Ortho- and parakeratosis with acanthosis and variable spongiosis Epidermal neutrophil migration ± subcorneal vesicles Hyphae, pseudohyphae, and budding yeast
7 Clinical Issues More common during pregnancy Vulva, vagina, and rarely cervix Local excision Macroscopic Features Usually < 5 cm Typically polypoid or pedunculated Vulva/Vagina/(Cervix) Fibroepithelial Polyp Microscopic Pathology Central fibrovascular core Variably cellular stroma Stellate and multinucleate stromal cells Cytologic features range from small, bland nuclei with dispersed chromatin to enlarged and hyperchromatic with irregular contours (pseudosarcomatous)
8 Vulva Usual VIN Clinical Issues Pruritus 4th-5th decade Full- or near full-thickness epithelial involvement Atypical parakeratosis ± koilocytotic atypia Nuclear enlargement with hyperchromasia Brisk mitotic activity often with abnormal forms and apoptosis Etc Grading 1-3 resp. LSIL/HSIL G2p16 HPV-related
9 Vulva Differentiated VIN Clinical Issues Typically 7th-8th decade Pruritus Epithelial thickening with prominent parakeratosis, elongation, and anastomosis of rete ridges Premature keratinization with squamous eddies and keratin pearls Enlarged, hypereosinophilic keratinocytes with prominent intracellular bridges Prominent cytologic atypia of basal layers Etc No grading No HPV association
10 Clinical issues Vulvovaginal region, also extragenital sites Subcutaneous mass, usually < 3 cm Local excision adequate treatment Benign, nonrecurring Vulva Cellular Angiofibrom Typically well-demarcated border Short intersecting fascicles of spindle-shaped cells Numerous small to medium-sized vessels Interspersed delicate collagen bundles Occasionally exhibits cytologic atypia
11 Clinical Issues Most common in 4th decade 30-40% risk of local, nondestructive recurrence Usually < 5 cm Multinodular growth with well-defined lobules Abundant myxoid stroma Thin-walled, curvilinear vessels Stromal inflammatory cells, particularly polymorphonuclear leukocytes Vulva Superficial Angiomyxoma
12 Vulva Deep aggressiv Angiomyxom Clinical Issues Reproductive-aged women 30-40% risk of local, destructive recurrence if incompletely excised Macroscopic Features Poorly demarcated with soft, gelatinous consistency Microscopic Pathology Infiltrative, uniformly hypocellular tumor Copious myxoid matrix containing bland spindleshaped stromal cells Medium to large-sized vessels, often with hyalinized walls Collections of smooth muscle ("myoid bundles")
13 Vagina Desquamative Inflammatory Vaginitis Etiology/Pathogenesis autoimmune or erosive lichen planus? Clinical Issues > 50 years bleeding, and purulent vaginal discharge erythema Majority require treatment > 1 year Dense acute and chronic inflammatory infiltrate Thinning &/or desquamation of squamous epithelium
14 Clinical Issues Chronic pain, dyspareunia, vaginal bleeding, discharge 1 months -30 years after hysterectomy Vagina Fallopian tube prolaps Tubal epithelium with secretory, ciliated, and intercalated cells Organized smooth muscle bundles Differential Diagnoses Polypoid granulation tissue Endometriosis Endometrioid adenocarcinoma Mesenchymal lesions of vagina
15 Vagina Adenosis Clinical Issues DES-related (90%) Müllerian-type epithelium replacing squamous mucosa or forming glands in lamina propria Simple or cystic glands ± papillary infoldings Squamous, microglandular, and intestinal metaplasia can occur Differential Diagnoses Endometriosis Clear cell carcinoma
16 Clinical Issues Exposure to DES Anterior wall, upper 1/3 of vagina Vaginal bleeding or discharge Tubulocystic (most common), papillary, solid Marked nuclear atypia Mitotic activity usually < 10/10 HPF Ancillary Tests CK7 and EMA positive Vagina Clear Cell Carcinoma Differential Diagnoses Atypical adenosis Arias-Stella reaction in adenosis or endometriosis Metastatic renal/ endometrial clear cell carcinoma
17 Cervix Microglandular Hyperplasie Clinical Issues Reproductive age Tightly packed tubular or cystically dilated glands Intraluminal mucin with sprinkling of acute inflammatory cells Scant intervening stroma with variable amounts of acute and chronic inflammation Differential Diagnoses Endometrial adenocarcinoma Endocervical adenocarcinoma Clear cell adenocarcinoma
18 Clinical issues Typically incidental finding Vagina Mesonephric Duct Remnants Located deep to normal endocervical glands Individual small clusters or linear arrays of small to medium-sized round tubules Intraluminal, densely eosinophilic material Ancillary Tests EMA, calretinin, pax-2, Bcl-2, androgen receptor, and CD10 (luminal) positive Differential Diagnoses Mesonephric carcinoma Cervical involvement by endometrial adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma in situ
19 Cervix Intraepithelial Neoplasia Acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, papillomatosis Koilocytotic atypia Mitoses typically in lower 1/3 (LSIL) or all layers (HSIL) Koilocytotic atypia Increased nuclear size and hyperchromasia Crowded, often uniformly enlarged nuclei with irregular nuclear contours Differential Diagnoses Squamous metaplasia Atrophy CIN2 p16
20 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Clinical Issues Abnormal Papanicolaou smear High-risk HPV (types 16, 18) most common Often squamous differentiation Variants: spindle, lymphoepithelial-like, "warty," verrucous, papillary, squamous/squamotransitional, basaloid Differential Diagnoses HSIL with endocervical gland involvement Adenoid basal carcinoma Glassy cell carcinoma Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (vs. basaloid SCC) Retraction artifact (vs. lymphovascular invasion) Displacement artifact (vs. lymphovascular invasion)
21 Clinical Issues Age: 38 years (mean) High-risk HPV infection (esp. HPV-18) Often coexistent squamous intraepithelial lesion Preservation of normal glandular architecture Abrupt transition from normal to neoplastic Enlarged, hyperchromatic, pseudostratified nuclei with apical eosinophilic to mucinous cytoplasm Apical mitoses and apoptotic bodies Cervix Adenocarcinoma in situ Differential Diagnoses Invasive endocervical adenocarcinoma Reactive endocervix
22 Clinical Issues Abnormal vaginal bleeding "Barrel-shaped" cervix No gross abnormality (~ 20%) Cervix Adenocarcinoma, usual type Closely packed or irregularly spaced glands Cribriform, microglandular, papillary, cystic, or solid growth Apical mitoses and apoptotic bodies frequent Ancillary Tests p16 + (strong diffuse), CEA +, Vimentin/ER/PR - Differential Diagnoses Microglandular hyperplasia Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ Endometrial adenocarcinoma
Guidelines for reporting histopathology of cervical carcinoma
 Guidelines for reporting histopathology of cervical carcinoma Naveena Singh, Consultant Pathologist Introduction Cancer management is multidisciplinary Histopathology report has a MAJOR impact on management
Guidelines for reporting histopathology of cervical carcinoma Naveena Singh, Consultant Pathologist Introduction Cancer management is multidisciplinary Histopathology report has a MAJOR impact on management
R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit
 R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit Ectoservikal squamous epithelium Endoservical columnar epithelium Dilated cystic endoservical glands lymphoplasmocytes R18:Squamous cell carcinoma insitu Neoplastic epithelium
R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit Ectoservikal squamous epithelium Endoservical columnar epithelium Dilated cystic endoservical glands lymphoplasmocytes R18:Squamous cell carcinoma insitu Neoplastic epithelium
Explanation of your PAP smear
 Explanation of your PAP smear Approximately 5-10% of PAP smears in the United States are judged to be abnormal. Too often, the woman who receives this news worries that she already has, or will develop,
Explanation of your PAP smear Approximately 5-10% of PAP smears in the United States are judged to be abnormal. Too often, the woman who receives this news worries that she already has, or will develop,
ATLAS OF HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY THYROID PAPILLARY CARCINOMA
 Papillary carcinoma is the most common of thyroid malignancies and occurs in all age groups but particularly in women under 45 years of age. There is a high rate of cervical metastatic disease and yet
Papillary carcinoma is the most common of thyroid malignancies and occurs in all age groups but particularly in women under 45 years of age. There is a high rate of cervical metastatic disease and yet
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist
 Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
TUMORS OF THE TESTICULAR ADNEXA and SPERMATIC CORD
 TUMORS OF THE TESTICULAR ADNEXA and SPERMATIC CORD Victor E. Reuter, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center [email protected] 66 th Annual Pathology Seminar California Society of Pathologists Short
TUMORS OF THE TESTICULAR ADNEXA and SPERMATIC CORD Victor E. Reuter, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center [email protected] 66 th Annual Pathology Seminar California Society of Pathologists Short
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL ABNORMAL PAP SMEAR (ABNORMAL CERVICAL CYTOLOGIC FINDINGS) Kathleen Dor
 1 ABNORMAL PAP SMEAR (ABNORMAL CERVICAL CYTOLOGIC FINDINGS) Kathleen Dor Cervical cytology screening has significantly decreased rates of mortality from cervical cancer; however, 400 women die each year
1 ABNORMAL PAP SMEAR (ABNORMAL CERVICAL CYTOLOGIC FINDINGS) Kathleen Dor Cervical cytology screening has significantly decreased rates of mortality from cervical cancer; however, 400 women die each year
Histopathology of Major Salivary Gland Neoplasms
 Histopathology of Major Salivary Gland Neoplasms Sam J. Cunningham, MD, PhD Faculty Advisor: Shawn D. Newlands, MD, PhD Faculty Advisor: David C. Teller, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch, Department
Histopathology of Major Salivary Gland Neoplasms Sam J. Cunningham, MD, PhD Faculty Advisor: Shawn D. Newlands, MD, PhD Faculty Advisor: David C. Teller, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch, Department
Polyps. Hyperplasias. CAP 2011: Course AP104. The High Risk Benign Endometrium. Mutter and Nucci 1
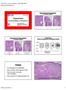 Course AP104 Endometrial Hyperplasia A morphologic Definition Hyperplasias Hormonal Effect or Precancer? George L. Mutter, MD Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA Endometrial
Course AP104 Endometrial Hyperplasia A morphologic Definition Hyperplasias Hormonal Effect or Precancer? George L. Mutter, MD Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA Endometrial
Diagnostic Challenge. Department of Pathology,
 Cytology of Pleural Fluid as a Diagnostic Challenge Paavo Pääkkö,, MD, PhD Chief Physician and Head of the Department Department of Pathology, Oulu University Hospital,, Finland Oulu University Hospital
Cytology of Pleural Fluid as a Diagnostic Challenge Paavo Pääkkö,, MD, PhD Chief Physician and Head of the Department Department of Pathology, Oulu University Hospital,, Finland Oulu University Hospital
INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES IN CERVICAL EPITHELIUM
 INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES IN CERVICAL EPITHELIUM Inflammation is a response of a tissue to injury, often caused by invading microorganisms. The suffix which indicates inflammation is "-itis" (the
INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES IN CERVICAL EPITHELIUM Inflammation is a response of a tissue to injury, often caused by invading microorganisms. The suffix which indicates inflammation is "-itis" (the
The menstrual cycle Hypophysis
 Normal endometrium Tumors of the uterine corpus by MB The endometrium comprises the zona functionalis zf (superficial two thirds) ) and the zona basalis zb (deep one third) The zf responds to hormonal
Normal endometrium Tumors of the uterine corpus by MB The endometrium comprises the zona functionalis zf (superficial two thirds) ) and the zona basalis zb (deep one third) The zf responds to hormonal
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Management of Abnormal Pap Smear Clinical Practice Guideline
 Management of Abnormal Pap Smear Clinical Guideline General Principles: The Papanicolaou (Pap) smear is widely credited with reducing mortality from cervical cancer, and remains the single best method
Management of Abnormal Pap Smear Clinical Guideline General Principles: The Papanicolaou (Pap) smear is widely credited with reducing mortality from cervical cancer, and remains the single best method
Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up
 Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up What is a Pap Smear? A Pap smear (also known as the Pap test) is a medical procedure in which a sample of cells from a woman's cervix (the end of the
Pap smears, cytology and CCHC lab work and follow up What is a Pap Smear? A Pap smear (also known as the Pap test) is a medical procedure in which a sample of cells from a woman's cervix (the end of the
Cytology : first alert of mesothelioma? Professor B. Weynand, UCL Yvoir, Belgium
 Cytology : first alert of mesothelioma? Professor B. Weynand, UCL Yvoir, Belgium Introduction 3 cavities with the same embryologic origin the mesoderme Pleura Exudates Pleura Peritoneum Pericardium 22%
Cytology : first alert of mesothelioma? Professor B. Weynand, UCL Yvoir, Belgium Introduction 3 cavities with the same embryologic origin the mesoderme Pleura Exudates Pleura Peritoneum Pericardium 22%
worry When to Cervical Abnormalities CME Workshop What s the situation? What are the trends? By Dianne Miller, MD, FRCSC In this article:
 CME Workshop When to worry Cervical Abnormalities By Dianne Miller, MD, FRCSC What s the situation? Over 600,000 Papanicolaou s (Pap) smears were performed in British Columbia in 2000. Approximately 13,400
CME Workshop When to worry Cervical Abnormalities By Dianne Miller, MD, FRCSC What s the situation? Over 600,000 Papanicolaou s (Pap) smears were performed in British Columbia in 2000. Approximately 13,400
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Spongiotic reaction pattern Spongiosis = Intercellular edema Elongation of bridges vesiculation, bullae?mechanism unclear Fluid comes from dermis Impo
 Spongiotic Reaction Pattern and review Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Spongiotic reaction pattern Spongiosis = Intercellular edema Elongation of bridges vesiculation, bullae?mechanism unclear Fluid comes from dermis
Spongiotic Reaction Pattern and review Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Spongiotic reaction pattern Spongiosis = Intercellular edema Elongation of bridges vesiculation, bullae?mechanism unclear Fluid comes from dermis
Something Old, Something New.
 Something Old, Something New. Michelle A. Fajardo, D.O. Loma Linda University Medical Center Clinical Presentation 6 year old boy, presented with hematuria Renal mass demonstrated by ultrasound & CT scan
Something Old, Something New. Michelle A. Fajardo, D.O. Loma Linda University Medical Center Clinical Presentation 6 year old boy, presented with hematuria Renal mass demonstrated by ultrasound & CT scan
The Benign Endometrial Hyperplasia Sequence
 Page 1 Slide 1 Introduction A mini lecture from www.endometrium endometrium.org The Benign Endometrial Hyperplasia Sequence This is Dr. George Mutter, I am a gynecologic pathologist at Harvard Medical
Page 1 Slide 1 Introduction A mini lecture from www.endometrium endometrium.org The Benign Endometrial Hyperplasia Sequence This is Dr. George Mutter, I am a gynecologic pathologist at Harvard Medical
Outline. Workup for metastatic breast cancer. Metastatic breast cancer
 Metastatic breast cancer Immunostain Update: Diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma, emphasizing distinction from GYN primary 1/3 of breast cancer patients will show metastasis 1 st presentation or 20-30
Metastatic breast cancer Immunostain Update: Diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma, emphasizing distinction from GYN primary 1/3 of breast cancer patients will show metastasis 1 st presentation or 20-30
Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass. Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic. Secondary / adaptation due to other cause.
 Disorders of Growth Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic Secondary / adaptation due to other cause. Neoplastic. Primary growth abnormality. Non-Neoplastic
Disorders of Growth Introduction: Tumor Swelling / new growth / mass Two types of growth disorders: Non-Neoplastic Secondary / adaptation due to other cause. Neoplastic. Primary growth abnormality. Non-Neoplastic
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
EIN. (Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia): Improved Criteria for diagnosing endometrial precancer. Stanley J. Robboy, MD, FCAP,
 EIN (Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia): Improved Criteria for diagnosing endometrial precancer Stanley J. Robboy, MD, FCAP, FFPath FRCPI (Hon), FRCPath (UK, Hon) Professor of Pathology, Duke University
EIN (Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia): Improved Criteria for diagnosing endometrial precancer Stanley J. Robboy, MD, FCAP, FFPath FRCPI (Hon), FRCPath (UK, Hon) Professor of Pathology, Duke University
PATHOLOGY OF THE PLEURA: Mesothelioma and mimickers Necessity of Immunohistochemistry. M. Praet
 PATHOLOGY OF THE PLEURA: Mesothelioma and mimickers Necessity of Immunohistochemistry M. Praet Pathology of the Pleura Normal serosa: visceral and parietal layers Inflammation Neoplasia: Primary: mesothelioma
PATHOLOGY OF THE PLEURA: Mesothelioma and mimickers Necessity of Immunohistochemistry M. Praet Pathology of the Pleura Normal serosa: visceral and parietal layers Inflammation Neoplasia: Primary: mesothelioma
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination
 Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Today s Topics. Tumors of the Peritoneum in Women
 Today s Topics Tumors of the Peritoneum in Women Charles Zaloudek, M.D. Department of Pathology 505 Parnassus Ave., M563 University of California, San Francisco San Francisco, CA USA [email protected]
Today s Topics Tumors of the Peritoneum in Women Charles Zaloudek, M.D. Department of Pathology 505 Parnassus Ave., M563 University of California, San Francisco San Francisco, CA USA [email protected]
Ovarian mucinous lesions. Ovarian mucinous lesions: Common diagnostic dilemmas. Ovarian mucinous lesions: problematic issues
 Ovarian mucinous lesions Ovarian mucinous lesions: Common diagnostic dilemmas Karuna Garg, MD University of California San Francisco Intestinal or usual type Seromucinous (Endocervical mucinous or Mullerian
Ovarian mucinous lesions Ovarian mucinous lesions: Common diagnostic dilemmas Karuna Garg, MD University of California San Francisco Intestinal or usual type Seromucinous (Endocervical mucinous or Mullerian
Effusions: Mesothelioma and Metastatic Cancers
 Effusions: Mesothelioma and Metastatic Cancers Malignant Mesothelioma Incidence: 2,500 cases/year ~60-80% pts with pleural MM relationship with asbestos exposure Other risk factors: radiation, other carcinogens,
Effusions: Mesothelioma and Metastatic Cancers Malignant Mesothelioma Incidence: 2,500 cases/year ~60-80% pts with pleural MM relationship with asbestos exposure Other risk factors: radiation, other carcinogens,
Gynecologic Pathology I Pathology of the Cervix, Vagina, and Vulva
 Carey Z. August, M.D. Gynecologic Pathology I UIC College of Medicine Attending Pathologist, Advocate Illinois Masonic Medical M2 Pathology Course Center Lecture #53 Clinical Assistant Professor of Pathology,
Carey Z. August, M.D. Gynecologic Pathology I UIC College of Medicine Attending Pathologist, Advocate Illinois Masonic Medical M2 Pathology Course Center Lecture #53 Clinical Assistant Professor of Pathology,
Cervical Cancer Screening and Management Guidelines: Changing Again, Huh?
 Cervical Cancer Screening and Management Guidelines: Changing Again, Huh? Summary of 2013 recommendations from ASC (American Cancer Society), ASCCP (American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology),
Cervical Cancer Screening and Management Guidelines: Changing Again, Huh? Summary of 2013 recommendations from ASC (American Cancer Society), ASCCP (American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology),
Cervical Cancer. Cervical smear test. The cervix. Dysplasia. Cervical cancer. The female reproductive system
 INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
INFORMATION SHEET Cervical Cancer This information sheet has been written to provide you with information about cervical cancer (cancer of the cervix). The sheet has information about the different types
Male. Female. Death rates from lung cancer in USA
 Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Common Breast Complaints:
 : Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
: Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
MALIGNANT MESOTHELIOMA UPDATE ON PATHOLOGY AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
 MALIGNANT MESOTHELIOMA UPDATE ON PATHOLOGY AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY Sisko Anttila, MD, PhD Jorvi Hospital Laboratory of Pathology Helsinki University Hospital Espoo, Finland 2nd Nordic Conference on Applied
MALIGNANT MESOTHELIOMA UPDATE ON PATHOLOGY AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY Sisko Anttila, MD, PhD Jorvi Hospital Laboratory of Pathology Helsinki University Hospital Espoo, Finland 2nd Nordic Conference on Applied
Tissue Types. 1. Epithelial Tissue (or epithelium) is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body
 Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR [email protected] Yale University School of Medicine
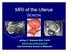 MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR [email protected] Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR [email protected] Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
CERVICAL AND VAGINAL CYTOLOGY Edmund S. Cibas
 S2638-01.qxd 12/11/02 11:42 Page 1 1 Edmund S. Cibas THE HISTORY OF THE PAP TEST SAMPLING AND PREPARATION METHODS Conventional Smears Liquid-based Preparations ThinPrep SurePath AUTOMATED SCREENING Historical
S2638-01.qxd 12/11/02 11:42 Page 1 1 Edmund S. Cibas THE HISTORY OF THE PAP TEST SAMPLING AND PREPARATION METHODS Conventional Smears Liquid-based Preparations ThinPrep SurePath AUTOMATED SCREENING Historical
Pathology of the Female Peritoneum, Common and Uncommon Problems
 Pathology of the Female Peritoneum, Common and Uncommon Problems An Update on Gynecologic Pathology Florence, Italy Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor of Pathology Pathology of the Female Peritoneum Keratin
Pathology of the Female Peritoneum, Common and Uncommon Problems An Update on Gynecologic Pathology Florence, Italy Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor of Pathology Pathology of the Female Peritoneum Keratin
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC
 Cervical Cancer WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September, 2015, Expires September, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Cervical Cancer WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September, 2015, Expires September, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
American Academy of Family Physicians
 American Academy of Family Physicians Barbara E. Stanford MD Grand Rapids Family Medicine Residency Wege Family Medicine HPV is transient in most women HPV-75% Normal ASCUS LSIL HSIL Cancer 80-90% 75%???
American Academy of Family Physicians Barbara E. Stanford MD Grand Rapids Family Medicine Residency Wege Family Medicine HPV is transient in most women HPV-75% Normal ASCUS LSIL HSIL Cancer 80-90% 75%???
Cytology of Lymph Nodes
 Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
MALIGNANT MESOTHELIOMA UPDATE ON PATHOLOGY AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
 MALIGNANT MESOTHELIOMA CLASSIFICATION MALIGNANT MESOTHELIOMA UPDATE ON PATHOLOGY AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY Sisko Anttila, MD, PhD Jorvi Hospital Laboratory of Pathology Helsinki University Hospital Espoo,
MALIGNANT MESOTHELIOMA CLASSIFICATION MALIGNANT MESOTHELIOMA UPDATE ON PATHOLOGY AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY Sisko Anttila, MD, PhD Jorvi Hospital Laboratory of Pathology Helsinki University Hospital Espoo,
Immunohistochemistry on cytology specimens from pleural and peritoneal fluid
 Immunohistochemistry on cytology specimens from pleural and peritoneal fluid Dr Naveena Singh Consultant Pathologist Bart health NHS Trust London United Kingdom Disclosures and Acknowledgements I have
Immunohistochemistry on cytology specimens from pleural and peritoneal fluid Dr Naveena Singh Consultant Pathologist Bart health NHS Trust London United Kingdom Disclosures and Acknowledgements I have
Effusion cytology. Dr Alpha Tsui Royal Melbourne Hospital 2008
 Effusion cytology Dr Alpha Tsui Royal Melbourne Hospital 2008 General points: -large unilateral effusion (>1 litre) in the elderly is highly suspicious for malignancy -effusions associated with malignancies
Effusion cytology Dr Alpha Tsui Royal Melbourne Hospital 2008 General points: -large unilateral effusion (>1 litre) in the elderly is highly suspicious for malignancy -effusions associated with malignancies
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
The society for lower genital tract disorders since 1964.
 The society for lower genital tract disorders since 1964. Updated Consensus Guidelines for Managing Abnormal Cervical Cancer Screening Tests and Cancer Precursors American Society for and Cervical Pathology
The society for lower genital tract disorders since 1964. Updated Consensus Guidelines for Managing Abnormal Cervical Cancer Screening Tests and Cancer Precursors American Society for and Cervical Pathology
CASE OF THE MONTH AUGUST-2015 DR. GURUDUTT GUPTA HEAD HISTOPATHOLOGY
 CASE OF THE MONTH AUGUST-2015 DR. GURUDUTT GUPTA HEAD HISTOPATHOLOGY CASE HISTORY 52Y MALE RIGHT RADICAL NEPHERECTOMY Case of right renal mass with IVC thrombus. History of surgery and RT for right occipital
CASE OF THE MONTH AUGUST-2015 DR. GURUDUTT GUPTA HEAD HISTOPATHOLOGY CASE HISTORY 52Y MALE RIGHT RADICAL NEPHERECTOMY Case of right renal mass with IVC thrombus. History of surgery and RT for right occipital
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Emerging Subtypes in Renal Cancer. Donna E. Hansel, MD PhD Professor of Pathology, UC San Diego Division Chief, Anatomic Pathology dhansel@ucsd.
 Emerging Subtypes in Renal Cancer Donna E. Hansel, MD PhD Professor of Pathology, UC San Diego Division Chief, Anatomic Pathology [email protected] Some General Comments Fuhrman nuclear grading clear cell
Emerging Subtypes in Renal Cancer Donna E. Hansel, MD PhD Professor of Pathology, UC San Diego Division Chief, Anatomic Pathology [email protected] Some General Comments Fuhrman nuclear grading clear cell
Cervical Cancer Prevention and Early Detection What is cervical cancer?
 Cervical Cancer Prevention and Early Detection What is cervical cancer? Cervical cancer starts in cells lining the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb). It is sometimes called the
Cervical Cancer Prevention and Early Detection What is cervical cancer? Cervical cancer starts in cells lining the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb). It is sometimes called the
A Contemporary Approach to Pathologic Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer
 A Contemporary Approach to Pathologic Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer Joseph T Rabban MD MPH Associate Professor, Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco [email protected] Overview
A Contemporary Approach to Pathologic Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer Joseph T Rabban MD MPH Associate Professor, Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco [email protected] Overview
Carcinoma of the vagina is a relatively uncommon disease, affecting only about 2,000 women in
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion. Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain
 Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
Index. F Factor VIII-related antigen, see VWF FactorXIIIa, for dermatofibroma, 272-275 5-HT, see Serotonin
 A Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma vs epithelioid angiosarcoma, 56-57 Acinic cell carcinoma of pancreas, 76-77 vs ductal adenocarcinoma, 74-75 vs islet cell tumor, 78-81 Adenomatoid tumor vs hemangioma,
A Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma vs epithelioid angiosarcoma, 56-57 Acinic cell carcinoma of pancreas, 76-77 vs ductal adenocarcinoma, 74-75 vs islet cell tumor, 78-81 Adenomatoid tumor vs hemangioma,
Disorders of the Vulva
 Disorders of the Vulva WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Certain health problems can affect the vulva (the outer part of the female genital area). Some problems are minor. Others
Disorders of the Vulva WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Certain health problems can affect the vulva (the outer part of the female genital area). Some problems are minor. Others
Understanding. Cervical Changes A Health Guide for Women. National Cancer Institute U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES
 National Cancer Institute Understanding Cervical Changes A Health Guide for Women U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health This guide helped me talk with my doctor after
National Cancer Institute Understanding Cervical Changes A Health Guide for Women U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health This guide helped me talk with my doctor after
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
Cervical Cancer Screening Guideline
 Cervical Cancer Screening Guideline Prevention 2 Abbreviations Used 2 Specimen Collection Techniques 3 Screening 4 Management Women 21 Years and Older Pap results 5 findings: ASC-US and LSIL 6 findings:
Cervical Cancer Screening Guideline Prevention 2 Abbreviations Used 2 Specimen Collection Techniques 3 Screening 4 Management Women 21 Years and Older Pap results 5 findings: ASC-US and LSIL 6 findings:
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Protocol for an integrated data request of test results from the laboratories of pathological anatomy. SNOMED 3.5VF - users version January 2016
 Protocol for an integrated data request of test results from the laboratories of pathological anatomy SNOMED 3.5VF - users version January 2016 Cancer diagnoses & early detection of cancer (breast, colorectal
Protocol for an integrated data request of test results from the laboratories of pathological anatomy SNOMED 3.5VF - users version January 2016 Cancer diagnoses & early detection of cancer (breast, colorectal
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Chapter 3. Testing and reporting the results of visual inspection with Lugol's iodine (VILI)
 Chapter 3 Testing and reporting the results of visual inspection with Lugol's iodine (VILI) Instruments and materials required: Examination table with knee crutches or leg rests or stirrups; Good light
Chapter 3 Testing and reporting the results of visual inspection with Lugol's iodine (VILI) Instruments and materials required: Examination table with knee crutches or leg rests or stirrups; Good light
How To Treat A Uterine Sarcoma
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition 2001 Uterus: Uterine Sarcomas Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Uterine sarcomas
Cervical Screening and HPV Vaccine Guidelines In Saudi Arabia. Prof. Mohammed Addar Chairmen Gyneoncology section KKUH, King Saud University
 Cervical Screening and HPV Vaccine Guidelines In Saudi Arabia Prof. Mohammed Addar Chairmen Gyneoncology section KKUH, King Saud University Burden of HPV related cancers l l Cervical Cancer of the cervix
Cervical Screening and HPV Vaccine Guidelines In Saudi Arabia Prof. Mohammed Addar Chairmen Gyneoncology section KKUH, King Saud University Burden of HPV related cancers l l Cervical Cancer of the cervix
SEMESTER VI 3 RD YEAR PATHOLOGY KIDNEY TUMORS
 SEMESTER VI 3 RD YEAR PATHOLOGY KIDNEY TUMORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the pathology of renal tumors. RENAL TUMORS RENAL PAPILLARY ADENOMA Common
SEMESTER VI 3 RD YEAR PATHOLOGY KIDNEY TUMORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the pathology of renal tumors. RENAL TUMORS RENAL PAPILLARY ADENOMA Common
Case of the. Month October, 2012
 Case of the Month October, 2012 Case The patient is a 47-year-old male with a 3-week history of abdominal pain. A CT scan of the abdomen revealed a suggestion of wall thickening at the tip of the appendix
Case of the Month October, 2012 Case The patient is a 47-year-old male with a 3-week history of abdominal pain. A CT scan of the abdomen revealed a suggestion of wall thickening at the tip of the appendix
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS (HPV) FACT SHEET
 HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS (HPV) FACT SHEET Background Information - Human Papillomavirus HPV is the name of a group of viruses that include more than 80 different types associated with a variety of epidermal
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS (HPV) FACT SHEET Background Information - Human Papillomavirus HPV is the name of a group of viruses that include more than 80 different types associated with a variety of epidermal
The develpemental origin of mesothelium
 Mesothelioma Tallinn 14.12.06 Henrik Wolff Finnish Institute of Occupational Health The develpemental origin of mesothelium Mesodermal cavities (pleura, peritoneum and pericardium ) are lined with mesenchymal
Mesothelioma Tallinn 14.12.06 Henrik Wolff Finnish Institute of Occupational Health The develpemental origin of mesothelium Mesodermal cavities (pleura, peritoneum and pericardium ) are lined with mesenchymal
Renal Pathology Update. Sundus Hussein MD, FRCPC
 Renal Pathology Update Sundus Hussein MD, FRCPC Case History A 45 year old male with incidentally discovered a 3.5 x 3.9 x 2.7 cm renal mass Handling partial nephrectomy Handling partial nephrectomy
Renal Pathology Update Sundus Hussein MD, FRCPC Case History A 45 year old male with incidentally discovered a 3.5 x 3.9 x 2.7 cm renal mass Handling partial nephrectomy Handling partial nephrectomy
Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma in Women A Study of 75 Cases With Emphasis on Their Morphologic Spectrum and Differential Diagnosis
 Anatomic Pathology / MALIGNANT PERITONEAL MESOTHELIOMA IN WOMEN Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma in Women A Study of 75 Cases With Emphasis on Their Morphologic Spectrum and Differential Diagnosis Patricia
Anatomic Pathology / MALIGNANT PERITONEAL MESOTHELIOMA IN WOMEN Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma in Women A Study of 75 Cases With Emphasis on Their Morphologic Spectrum and Differential Diagnosis Patricia
Cytopathology Case Presentation #8
 Cytopathology Case Presentation #8 Emily E. Volk, MD William Beaumont Hospital, Troy, MI Jonathan H. Hughes, MD Laboratory Medicine Consultants, Las Vegas, Nevada Clinical History 44 year old woman presents
Cytopathology Case Presentation #8 Emily E. Volk, MD William Beaumont Hospital, Troy, MI Jonathan H. Hughes, MD Laboratory Medicine Consultants, Las Vegas, Nevada Clinical History 44 year old woman presents
CHAPTER 5. Tumours of the Uterine Cervix
 CHAPTER 5 Tumours of the Uterine Cervix Cervical carcinoma is the second most common cancer in women worldwide. Chronic infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) is a necessary event in the evolution of
CHAPTER 5 Tumours of the Uterine Cervix Cervical carcinoma is the second most common cancer in women worldwide. Chronic infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) is a necessary event in the evolution of
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Carcinosarcoma of the Ovary
 Carcinosarcoma of the Ovary A Rare Finding Presented By: Kathryn Kiely Anisa I. Kanbour School of Cytotechnology of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Pittsburgh, PA Patient History 55 year old
Carcinosarcoma of the Ovary A Rare Finding Presented By: Kathryn Kiely Anisa I. Kanbour School of Cytotechnology of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Pittsburgh, PA Patient History 55 year old
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules KIDNEY. FLORIDA CANCER DATA SYSTEM MPH Kidney Site Specific Coding Rules
 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules KIDNEY 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways to view the Multiple l Primary/Histology
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules KIDNEY 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are many ways to view the Multiple l Primary/Histology
SCREENING FOR CANCER OF THE CERVIX
 SCREENING FOR CANCER OF THE CERVIX An Office Manual for Health Professionals This manual has been prepared by the Cervical Cancer Screening Program of the BC Cancer Agency to support effective use of the
SCREENING FOR CANCER OF THE CERVIX An Office Manual for Health Professionals This manual has been prepared by the Cervical Cancer Screening Program of the BC Cancer Agency to support effective use of the
Lung Carcinomas New 2015 WHO Classification. Spasenija Savic Pathology
 Lung Carcinomas New 2015 WHO Classification Spasenija Savic Pathology ***EXPECTED SPRING 2015*** This authoritative, concise reference book provides an international standard for oncologists and pathologists
Lung Carcinomas New 2015 WHO Classification Spasenija Savic Pathology ***EXPECTED SPRING 2015*** This authoritative, concise reference book provides an international standard for oncologists and pathologists
Introduction to Gynecologic Oncology
 Objectives Cervical Dysplasia and Cancer Introduction to Gynecologic Oncology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Western Ontario Discuss the incidence and risk factors for cervical dysplasia
Objectives Cervical Dysplasia and Cancer Introduction to Gynecologic Oncology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Western Ontario Discuss the incidence and risk factors for cervical dysplasia
How To Diagnose And Treat A Tumour In An Effusion
 Effusions of the Serous Cavities Annika Dejmek Professor/Consultant in Cytopathology Clinical Pathology; Department of Laboratory Medicine, Malmö, Lund University 5th EFCS Tutorial Trondheim 2012 Pleura
Effusions of the Serous Cavities Annika Dejmek Professor/Consultant in Cytopathology Clinical Pathology; Department of Laboratory Medicine, Malmö, Lund University 5th EFCS Tutorial Trondheim 2012 Pleura
PRIMARY SEROUS CARCINOMA OF PERITONEUM: A CASE REPORT
 PRIMARY SEROUS CARCINOMA OF PERITONEUM: A CASE REPORT Dott. Francesco Pontieri (*) U.O. di Anatomia Patologica P.O. di Rossano (CS) Dott. Gian Franco Zannoni Anatomia Patologica Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia
PRIMARY SEROUS CARCINOMA OF PERITONEUM: A CASE REPORT Dott. Francesco Pontieri (*) U.O. di Anatomia Patologica P.O. di Rossano (CS) Dott. Gian Franco Zannoni Anatomia Patologica Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia
Patologia neoplastica borderline della mammella"
 Patologia neoplastica borderline della mammella" Anna Sapino Department of Medical Sciences University of Torino (Italy) B3 Lesion of uncertain malignant potential This category mainly consists of lesions
Patologia neoplastica borderline della mammella" Anna Sapino Department of Medical Sciences University of Torino (Italy) B3 Lesion of uncertain malignant potential This category mainly consists of lesions
Histologic Subtypes of Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Histologic Subtypes of Renal Cell Carcinoma M. Scott Lucia, MD Associate Professor Chief of Genitourinary and Renal Pathology Director, Prostate Diagnostic Laboratory Dept. of Pathology University of Colorado
Histologic Subtypes of Renal Cell Carcinoma M. Scott Lucia, MD Associate Professor Chief of Genitourinary and Renal Pathology Director, Prostate Diagnostic Laboratory Dept. of Pathology University of Colorado
MODERN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
 MODERN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY Cambridge Illustrated Surgical Pathology Peiguo G. Chu City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, California Lawrence M. Weiss City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte,
MODERN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY Cambridge Illustrated Surgical Pathology Peiguo G. Chu City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, California Lawrence M. Weiss City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte,
Nicole Kounalakis, MD
 Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Management Nicole Kounalakis, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Goal of Breast Evaluation The goal of breast evaluation is to classify findings as: normal physiologic variations
Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Management Nicole Kounalakis, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Goal of Breast Evaluation The goal of breast evaluation is to classify findings as: normal physiologic variations
How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens
 Section of Pathology and Tumour Biology How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens Dr.H.Grabsch Warning. Most of the criteria, methodologies, evidence presented in this talk are based on studies in early
Section of Pathology and Tumour Biology How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens Dr.H.Grabsch Warning. Most of the criteria, methodologies, evidence presented in this talk are based on studies in early
The Cervical Screening Manual
 The Cervical Screening Manual A Guide for Health Departments and Providers Collaboration Partners: Chronic Disease and Injury Section Breast and Cervical Cancer Control Program Women s and Children s Health
The Cervical Screening Manual A Guide for Health Departments and Providers Collaboration Partners: Chronic Disease and Injury Section Breast and Cervical Cancer Control Program Women s and Children s Health
Case presentation. Awatif Al-Nafussi
 Case presentation Awatif Al-Nafussi Case History 49 year old DVT & small PE June 08, Pelvic mass Ca125 33 Laparotomy-TAHBSO, drainage of ascites Ovarian carcinoma Clinical diagnosis Multiple specimens
Case presentation Awatif Al-Nafussi Case History 49 year old DVT & small PE June 08, Pelvic mass Ca125 33 Laparotomy-TAHBSO, drainage of ascites Ovarian carcinoma Clinical diagnosis Multiple specimens
INFLAMMATORY PLEURAL EFFUSION
 PLEURA- LESIONS LESIONS OF PLEURA Primary Intra pleural bacterial infections Neoplasm (mesothelioma) Secondary A complication of some underlying disease PLEURAL EFFUSION Common manifestation of both primary
PLEURA- LESIONS LESIONS OF PLEURA Primary Intra pleural bacterial infections Neoplasm (mesothelioma) Secondary A complication of some underlying disease PLEURAL EFFUSION Common manifestation of both primary
Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas: A multidisciplinary approach to the prevention and early detection of invasive pancreatic cancer.
 This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
This lecture is drawn from the continuing medical education program Finding Hope: Prevention, Early Detection and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer, Nov, 2011. Robert P. Jury, MD Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas:
HKCPath Anatomical Pathology Peer Review and Scores : PDF version for download
 AP2003R1 http://hkcpath.org. Correspondence: [email protected] 1of 10 07/08/2003 HKCPath Anatomical Pathology Peer Review and Scores : PDF version for download AP141 Bone Marrow: Metastatic Carcinoma from
AP2003R1 http://hkcpath.org. Correspondence: [email protected] 1of 10 07/08/2003 HKCPath Anatomical Pathology Peer Review and Scores : PDF version for download AP141 Bone Marrow: Metastatic Carcinoma from
