Price Sales Ratio: Definition
|
|
|
- Millicent Morton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Price Sales Ratio: Definition The price/sales ratio is the ratio of the market value of equity to the sales. Price/ Sales= Market Value of Equity Consistency Tests Total Revenues The price/sales ratio is internally inconsistent, since the market value of equity is divided by the total revenues of the firm.
2 PS Ratios: The Inconsistency Test Assume that you are comparing price/sales ratios across firms in a sector, and that there are differences in financial leverage across firms. What type of firms will emerge with the lowest price/sales ratios? Low Leverage Firms Average Leverage Firms High Leverage Firms
3 Price/Sales Ratio: Cross Sectional Distribution 1000 PS Ratios: September Std. Dev = Mean = 3.7 N = Price/Sales Ratio
4 Price/Sales Ratio: A Test on Brazilian Consumer Products Company Market Value Sales P/S DHB Industria Teka-Tecelagem Viacao Lojas Arapua Cia TExtil Lohas Brasileiras Multibras Iochpe Sao Paulo Alpargatas Electrolux Do Brasil Sharp S.A Makro Brasmotor Gradiente Eletronica Cofap-CIA Fabric Lohas Americanas Globex Utilitdades Marcopolo Pirelli Fiacao Tecidos Arno Lohas Renner Confeccoes Cia Tecidos Average 0.53
5 Price/Sales Ratio: Is DHB cheap? Based upon the price/sales ratios, the cheap firms are DHB, Viacao and Lojas Arapua. The expensive firms are firms like Confeccoes, Cia Tecidos and Lohas Renner. Do you agree? Yes No If not, what might explain why there are such big differences across these firms?
6 Price/Sales Ratio: Determinants The price/sales ratio of a stable growth firm can be estimated beginning with a 2-stage equity valuation model: P 0 = DPS 1 r g n Dividing both sides by the sales per share: P 0 Sales 0 = PS = Net Profit Margin* Payout Ratio *(1+ g n ) r-g n
7 Price/Sales Ratio for High Growth Firm P 0 = When the growth rate is assumed to be high for a future period, the dividend discount model can be written as follows: EPS 0 *Payout Ratio *(1 +g) * 1 r - g (1+ g)n (1 + r) n + EPS 0 * Payout Ratio n *(1+g)n *(1+g n ) (r - g n )(1+ r) n Dividing both sides by the sales per share: Net Margin *Payout Ratio*(1+ g) * 1 P 0 = Sales 0 r - g (1+ g)n (1+ r) n + Net Margin n * Payout Ratio n *(1+g) n *(1 +g n ) (r - g n )(1 + r) n where Net Margin n = Net Margin in stable growth phase
8 Price Sales Ratios and Profit Margins The key determinant of price-sales ratios is the profit margin. A decline in profit margins has a two-fold effect. First, the reduction in profit margins reduces the price-sales ratio directly. Second, the lower profit margin can lead to lower growth and hence lower price-sales ratios. Expected growth rate = Retention ratio * Return on Equity = Retention Ratio *(Net Profit / Sales) * ( Sales / BV of Equity) = Retention Ratio * Profit Margin * Sales/BV of Equity
9 Price/Sales Ratio: An Example High Growth Phase Stable Growth Length of Period 5 years Forever after year 5 Net Margin 10% 6% Sales/BV of Equity Beta Payout Ratio 20% 60% Expected Growth (.1)(2.5)(.8)=20% (.06)(2.5)(.4)=.06 Riskless Rate =6% 0.10 * 0.2 * (1.20) * 1 (1.20)5 ( ) 5 PS = ( ) * 0.60 * (1.20)5 * (1.06) ( ) ( ) 5 = 1.06
10 Effect of Margin Changes Price/Sales Ratios and Net Margins PS Ratio % 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16% Net Margin
11 PS/Margins: Brazilian Consumer Products Company Market Value Sales P/S Net Margin DHB Industria Teka-Tecelagem Viacao Lojas Arapua Cia TExtil Lohas Brasileiras Multibras Iochpe Sao Paulo Alpargatas Electrolux Do Brasil Sharp S.A Makro Brasmotor Gradiente Eletronica Cofap-CIA Fabric Lohas Americanas Globex Utilitdades Marcopolo Pirelli Fiacao Tecidos Arno Lohas Renner Confeccoes Cia Tecidos Average
12 Regression Results: PS Ratios and Margins Regressing PS ratios against net margins, PS = (Net Margin) R 2 = 65.09% Thus, a 1% increase in the margin results in an increase of 0.08 in the price sales ratios. The regression also allows us to get predicted PS ratios for these firms
13 PS Ratios: Actual versus Predicted Values Company P/S Predicted PS PS / Predicted DHB Industria NMF Teka-Tecelagem NMF Viacao % Lojas Arapua % Cia TExtil % Lohas Brasileiras % Multibras % Iochpe NMF Sao Paulo Alpargatas % Electrolux Do Brasil % Sharp S.A % Makro % Brasmotor % Gradiente Eletronica % Cofap-CIA Fabric % Lohas Americanas % Globex Utilitdades % Marcopolo % Pirelli % Fiacao Tecidos % Arno % Lohas Renner % Confeccoes % Cia Tecidos %
14 Price-Sales Ratios and Cross-sectional Data Year Regression R squared 1987 PS = π β EGR MARGIN PS = π β EGR MARGIN PS = π β EGR MARGIN PS = π β EGR MARGIN PS = π β EGR MARGIN PS = Price /Sales Ratio at the end of the year MARGIN = Profit Margin for the year = Net Income / Sales for the year (in %) π = Payout Ratio = Dividends / Earnings... at the end of the year β = Beta of the stock
15 Price/Sales Ratio Regression: September 1997 Multiple R R Square Adjusted R Square Standard Error Analysis of Variance DF Sum of Squares Mean Square Regression Residual F = Signif F = Variables in the Equation Variable B SE B Beta T Sig T PROJGR PAYOUT BETA NETMGN (Constant)
16 Cross Sectional Regression for Brazil in 1997 Using data on 148 Brazilian companies from 1997, we regressed PS ratios against profit margins: PS = Margin R 2 = 15.17% (8.91) (2.82)
17 Cross Sectional Regression for India: November1997 With the sample of the 50 Indian firms which have GDRs listed on them, and regressing PS against Pre-tax Margin for these firms yields: PS = Margin ( R squared=54.22%) Hindalco is an Indian firm with one of the highest profit margins in the sample (30.08%). This is often used as a rationale for its current high price/sales ratio of Plugging in Hindalco s Margin into this equation would yield: Predicted PS for Hindalco= (.3008) = 3.31 On a relative basis, Hindalco is over valued.
18 Value/Sales Ratio: Definition The value/sales ratio is the ratio of the market value of the firm to the sales. Price/ Sales= Market Value of Equity + Market Value of Debt Total Revenues
19 Value/Sales Ratio: Cross Sectional Distribution 400 Value/Sales Ratios: September Std. Dev = Mean = 6.0 N = VS
20 Value/Sales Ratios: Analysis of Determinants If pre-tax operating margins are used, the appropriate value estimate is that of the firm. In particular, if one makes the assumption that Free Cash Flow to the Firm = EBIT (1 - tax rate): Net Capital expenditures and working capital requirements are zero. Then the Value of the Firm can be written as a function of the after-tax operating margin= (EBIT (1-t)/Sales (1+ g) n (1+ g) * 1 Value of Firm 0 (1 + WACC) n = After -tax Operating Margin * Sales 0 WACC - g + (1+ g) n *(1+ g n ) (WACC -g n )(1+ WACC) n g = Growth rate in after-tax operating income for the first n years g n = Growth rate in after-tax operating income after n years forever (Stable growth rate) WACC = Weighted average cost of capital
21 Value/Sales Ratio: An Example Consider, for example, the Value/Sales ratio of Coca Cola. The company had the following characteristics: After-tax Operating Margin =18.56% Sales/BV of Capital = 1.67 Return on Capital = 1.67* 18.56% = 31.02% Reinvestment Rate= 65.00% Expected Growth = 31.02% * 0.65 =20.16% (Stable Growth Rate=6%) Length of High Growth Period = 10 years Cost of Equity =12.33% E/(D+E) = 97.65% After-tax Cost of Debt = 4.16% D/(D+E) 2.35% Cost of Capital= 12.33% (.9765)+4.16% (.0235) = 12.13% Value of Firm 0 =.1856 * Sales 0 (1.2016) * 1 (1.2016)10 (1.1213) (1.2016) 10 * (1.06) ( )(1.1213) 10 = 9.17
22 Value Sales Ratios and Operating Margins Coca Cola: The Operating Margin Effect Value/Sales Ratio $ Value Value/Sales $ Value % 8% 10% 12% 14% 16% 18% 20% Operating Margin 0
23 Brand Name Premiums in Valuation You have been hired to value Coca Cola for an analyst reports and you have valued the firm at 9.17 times revenues, using the model described in the last few pages. Another analyst is arguing that there should be a premium added on to reflect the value of the brand name. Do you agree? Yes No Explain.
24 The value of a brand name One of the critiques of traditional valuation is that is fails to consider the value of brand names and other intangibles. The approaches used by analysts to value brand names are often adhoc and may significantly overstate or understate their value. One of the benefits of having a well-known and respected brand name is that firms can charge higher prices for the same products, leading to higher profit margins and hence to higher price-sales ratios and firm value. The larger the price premium that a firm can charge, the greater is the value of the brand name. In general, the value of a brand name can be written as: Value of brand name ={(V/S) b -(V/S) g }* Sales (V/S) b = Value of Firm/Sales ratio with the benefit of the brand name (V/S)g = Value of Firm/Sales ratio of the firm with the generic product
25 Illustration: Valuing a brand name: Coca Cola Coca Cola Generic Cola Company AT Operating Margin 18.56% 7.50% Sales/BV of Capital ROC 31.02% 12.53% Reinvestment Rate 65.00% 65.00% Expected Growth 20.16% 8.15% Length 10 years 10 yea Cost of Equity 12.33% 12.33% E/(D+E) 97.65% 97.65% AT Cost of Debt 4.16% 4.16% D/(D+E) 2.35% 2.35% Cost of Capital 12.13% 12.13% Value/Sales Ratio
26 Value of Coca Cola s Brand Name Value of Coke s Brand Name = ( ) ($18,546 million) = $ billion Value of Coke as a company = 9.17 ($18,546 million) = Billion Approximately 83.42% of the value of the company can be traced to brand name value
27 Value/Sales Ratio: Regression in September 1997 Multiple R R Square Adjusted R Square Standard Error Analysis of Variance DF Sum of Squares Mean Square Regression Residual F = Signif F = Variables in the Equation Variable B SE B Beta T Sig T REINV OPERMGN STDDEV (Constant)
28 Reviewing: The Four Steps to Understanding Multiples Define the multiple Describe the multiple Analyze the multiple Apply the multiple
Price-Book Value Ratio: Definition
 Price-Book Value Ratio: Definition The price/book value ratio is the ratio of the market value of equity to the book value of equity, i.e., the measure of shareholders equity in the balance sheet. Price/Book
Price-Book Value Ratio: Definition The price/book value ratio is the ratio of the market value of equity to the book value of equity, i.e., the measure of shareholders equity in the balance sheet. Price/Book
Modified dividend payout ratio =
 15 Modifying the model to include stock buybacks In recent years, firms in the United States have increasingly turned to stock buybacks as a way of returning cash to stockholders. Figure 13.3 presents
15 Modifying the model to include stock buybacks In recent years, firms in the United States have increasingly turned to stock buybacks as a way of returning cash to stockholders. Figure 13.3 presents
Value/EBITDA Multiple
 Value/EBITDA Multiple The Classic Definition Value EBITDA = Market Value of Equity + Market Value of Debt Earnings before Interest, Taxes and Depreciation The No-Cash Version Value EBITDA = Market Value
Value/EBITDA Multiple The Classic Definition Value EBITDA = Market Value of Equity + Market Value of Debt Earnings before Interest, Taxes and Depreciation The No-Cash Version Value EBITDA = Market Value
Relative PE Ratios. Aswath Damodaran
 Relative PE Ratios Aswath Damodaran Relative PE: Definition The relative PE ratio of a firm is the ratio of the PE of the firm to the PE of the market. Relative PE = PE of Firm / PE of Market While the
Relative PE Ratios Aswath Damodaran Relative PE: Definition The relative PE ratio of a firm is the ratio of the PE of the firm to the PE of the market. Relative PE = PE of Firm / PE of Market While the
Equity Valuation Project
 Equity Valuation Project Group: Mike Altman Alison Birch Erin Burns Joe Faber Santosh Lakhan Josh Sullivan Companies: Affiliated Computer Services Apple Computer Biosite Gundle Environmental Systems Infosys
Equity Valuation Project Group: Mike Altman Alison Birch Erin Burns Joe Faber Santosh Lakhan Josh Sullivan Companies: Affiliated Computer Services Apple Computer Biosite Gundle Environmental Systems Infosys
Price Earnings Ratio: Definition
 Price Earnings Ratio: Definition PE = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share There are a number of variants on the basic PE ratio in use. They are based upon how the price and the earnings are defined.
Price Earnings Ratio: Definition PE = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share There are a number of variants on the basic PE ratio in use. They are based upon how the price and the earnings are defined.
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: Basics
 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: Basics Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Discounted Cashflow Valuation: Basis for Approach Value = t=n CF t t =1(1+r) t where CF t is the cash flow in period t, r is the
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: Basics Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Discounted Cashflow Valuation: Basis for Approach Value = t=n CF t t =1(1+r) t where CF t is the cash flow in period t, r is the
Relative valuation and Technical Analysis
 Relative valuation and Technical Analysis Relative vs. fundamental valuation The DCF model is a method of fundamental valuation. Value of equity is the present value of future cash flows. Ignores the current
Relative valuation and Technical Analysis Relative vs. fundamental valuation The DCF model is a method of fundamental valuation. Value of equity is the present value of future cash flows. Ignores the current
Practice Exam (Solutions)
 Practice Exam (Solutions) June 6, 2008 Course: Finance for AEO Length: 2 hours Lecturer: Paul Sengmüller Students are expected to conduct themselves properly during examinations and to obey any instructions
Practice Exam (Solutions) June 6, 2008 Course: Finance for AEO Length: 2 hours Lecturer: Paul Sengmüller Students are expected to conduct themselves properly during examinations and to obey any instructions
CHAPTER 15 FIRM VALUATION: COST OF CAPITAL AND APV APPROACHES
 0 CHAPTER 15 FIRM VALUATION: COST OF CAPITAL AND APV APPROACHES In the last two chapters, we examined two approaches to valuing the equity in the firm -- the dividend discount model and the FCFE valuation
0 CHAPTER 15 FIRM VALUATION: COST OF CAPITAL AND APV APPROACHES In the last two chapters, we examined two approaches to valuing the equity in the firm -- the dividend discount model and the FCFE valuation
Fair Value: Fact or Opinion
 Fair Value: Fact or Opinion Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Fair value is in the eyes of the beholder Don t measure fair value by precision: As uncertainty about an asset s cash flows increase, the
Fair Value: Fact or Opinion Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Fair value is in the eyes of the beholder Don t measure fair value by precision: As uncertainty about an asset s cash flows increase, the
Value Multiples. Aswath Damodaran. Aswath Damodaran 1
 Value Multiples Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Value/Earnings and Value/Cashflow Ratios While Price earnings ratios look at the market value of equity relative to earnings to equity investors, Value
Value Multiples Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Value/Earnings and Value/Cashflow Ratios While Price earnings ratios look at the market value of equity relative to earnings to equity investors, Value
NIKE Case Study Solutions
 NIKE Case Study Solutions Professor Corwin This case study includes several problems related to the valuation of Nike. We will work through these problems throughout the course to demonstrate some of the
NIKE Case Study Solutions Professor Corwin This case study includes several problems related to the valuation of Nike. We will work through these problems throughout the course to demonstrate some of the
Chapter 13, ROIC and WACC
 Chapter 13, ROIC and WACC Lakehead University Winter 2005 Role of the CFO The Chief Financial Officer (CFO) is involved in the following decisions: Management Decisions Financing Decisions Investment Decisions
Chapter 13, ROIC and WACC Lakehead University Winter 2005 Role of the CFO The Chief Financial Officer (CFO) is involved in the following decisions: Management Decisions Financing Decisions Investment Decisions
Homework Solutions - Lecture 2
 Homework Solutions - Lecture 2 1. The value of the S&P 500 index is 1286.12 and the treasury rate is 3.43%. In a typical year, stock repurchases increase the average payout ratio on S&P 500 stocks to over
Homework Solutions - Lecture 2 1. The value of the S&P 500 index is 1286.12 and the treasury rate is 3.43%. In a typical year, stock repurchases increase the average payout ratio on S&P 500 stocks to over
CHAPTER 14 COST OF CAPITAL
 CHAPTER 14 COST OF CAPITAL Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. It is the minimum rate of return the firm must earn overall on its existing assets. If it earns more than this,
CHAPTER 14 COST OF CAPITAL Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. It is the minimum rate of return the firm must earn overall on its existing assets. If it earns more than this,
Stock Valuation: Gordon Growth Model. Week 2
 Stock Valuation: Gordon Growth Model Week 2 Approaches to Valuation 1. Discounted Cash Flow Valuation The value of an asset is the sum of the discounted cash flows. 2. Contingent Claim Valuation A contingent
Stock Valuation: Gordon Growth Model Week 2 Approaches to Valuation 1. Discounted Cash Flow Valuation The value of an asset is the sum of the discounted cash flows. 2. Contingent Claim Valuation A contingent
Corporate Finance: Final Exam
 Corporate Finance: Final Exam Answer all questions and show necessary work. Please be brief. This is an open books, open notes exam. For partial credit, when discounting, please show the discount rate
Corporate Finance: Final Exam Answer all questions and show necessary work. Please be brief. This is an open books, open notes exam. For partial credit, when discounting, please show the discount rate
Valuation. Aswath Damodaran Home Page: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar Email: adamodar@stern.nyu.edu This presentation is under seminars.
 Valuation Aswath Damodaran Home Page: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar Email: adamodar@stern.nyu.edu This presentation is under seminars. Aswath Damodaran 1 Some Initial Thoughts " One hundred thousand
Valuation Aswath Damodaran Home Page: http://www.stern.nyu.edu/~adamodar Email: adamodar@stern.nyu.edu This presentation is under seminars. Aswath Damodaran 1 Some Initial Thoughts " One hundred thousand
CLOSURE IN VALUATION: ESTIMATING TERMINAL VALUE
 1 CLOSURE IN VALUATION: ESTIMATING TERMINAL VALUE In the last chapter, we examined the determinants of expected growth. Firms that reinvest substantial portions of their earnings and earn high returns
1 CLOSURE IN VALUATION: ESTIMATING TERMINAL VALUE In the last chapter, we examined the determinants of expected growth. Firms that reinvest substantial portions of their earnings and earn high returns
The Value of Synergy. Aswath Damodaran 1
 The Value of Synergy 1 Valuing Synergy The key to the existence of synergy is that the target firm controls a specialized resource that becomes more valuable if combined with the bidding firm's resources.
The Value of Synergy 1 Valuing Synergy The key to the existence of synergy is that the target firm controls a specialized resource that becomes more valuable if combined with the bidding firm's resources.
multiples are easy to use and intuitive, they are also easy to misuse. Consequently, a
 1 RELATIVE VALUATION CHAPTER 8 In discounted cash flow valuation, the objective is to find the value of assets, given their cash flow, growth and risk characteristics. In relative valuation, the objective
1 RELATIVE VALUATION CHAPTER 8 In discounted cash flow valuation, the objective is to find the value of assets, given their cash flow, growth and risk characteristics. In relative valuation, the objective
The Marginal Cost of Capital and the Optimal Capital Budget
 WEB EXTENSION12B The Marginal Cost of Capital and the Optimal Capital Budget If the capital budget is so large that a company must issue new equity, then the cost of capital for the company increases.
WEB EXTENSION12B The Marginal Cost of Capital and the Optimal Capital Budget If the capital budget is so large that a company must issue new equity, then the cost of capital for the company increases.
BA 351 CORPORATE FINANCE. John R. Graham Adapted from S. Viswanathan LECTURE 10 THE ADJUSTED NET PRESENT VALUE METHOD
 BA 351 CORPORATE FINANCE John R. Graham Adapted from S. Viswanathan LECTURE 10 THE ADJUSTED NET PRESENT VALUE METHOD FUQUA SCHOOL OF BUSINESS DUKE UNIVERSITY 1 THE ADJUSTED NET PRESENT VALUE METHOD COPING
BA 351 CORPORATE FINANCE John R. Graham Adapted from S. Viswanathan LECTURE 10 THE ADJUSTED NET PRESENT VALUE METHOD FUQUA SCHOOL OF BUSINESS DUKE UNIVERSITY 1 THE ADJUSTED NET PRESENT VALUE METHOD COPING
Equity Valuation. Lecture Notes # 8. 3 Choice of the Appropriate Discount Rate 2. 4 Future Cash Flows: the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) 3
 Equity Valuation Lecture Notes # 8 Contents About Valuation 2 2 Present-Values 2 3 Choice of the Appropriate Discount Rate 2 4 Future Cash Flows: the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) 3 5 The Two-Stage Dividend-Growth
Equity Valuation Lecture Notes # 8 Contents About Valuation 2 2 Present-Values 2 3 Choice of the Appropriate Discount Rate 2 4 Future Cash Flows: the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) 3 5 The Two-Stage Dividend-Growth
Basics of Discounted Cash Flow Valuation. Aswath Damodaran
 Basics of Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Aswath Damodaran 1 Discounted Cashflow Valuation: Basis for Approach t = n CF Value = t t =1(1+ r) t where, n = Life of the asset CF t = Cashflow in period t r
Basics of Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Aswath Damodaran 1 Discounted Cashflow Valuation: Basis for Approach t = n CF Value = t t =1(1+ r) t where, n = Life of the asset CF t = Cashflow in period t r
VALUING FINANCIAL SERVICE FIRMS
 1 VALUING FINANCIAL SERVICE FIRMS Banks, insurance companies and other financial service firms pose a particular challenge for an analyst attempting to value them for two reasons. The first is the nature
1 VALUING FINANCIAL SERVICE FIRMS Banks, insurance companies and other financial service firms pose a particular challenge for an analyst attempting to value them for two reasons. The first is the nature
Private Company Valuation
 Private Company Valuation Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 179 Process of Valuing Private Companies Choosing the right model Valuing the Firm versus Valuing Equity Steady State, Two-Stage or Three-Stage
Private Company Valuation Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 179 Process of Valuing Private Companies Choosing the right model Valuing the Firm versus Valuing Equity Steady State, Two-Stage or Three-Stage
Finding the Right Financing Mix: The Capital Structure Decision
 Finding the Right Financing Mix: The Capital Structure Decision Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business Aswath Damodaran 1 First Principles Invest in projects that yield a return greater than the minimum
Finding the Right Financing Mix: The Capital Structure Decision Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business Aswath Damodaran 1 First Principles Invest in projects that yield a return greater than the minimum
LECTURE- 4. Valuing stocks Berk, De Marzo Chapter 9
 1 LECTURE- 4 Valuing stocks Berk, De Marzo Chapter 9 2 The Dividend Discount Model A One-Year Investor Potential Cash Flows Dividend Sale of Stock Timeline for One-Year Investor Since the cash flows are
1 LECTURE- 4 Valuing stocks Berk, De Marzo Chapter 9 2 The Dividend Discount Model A One-Year Investor Potential Cash Flows Dividend Sale of Stock Timeline for One-Year Investor Since the cash flows are
CHAPTER 8 STOCK VALUATION
 CHAPTER 8 STOCK VALUATION Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 5. The common stock probably has a higher price because the dividend can grow, whereas it is fixed on the preferred.
CHAPTER 8 STOCK VALUATION Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 5. The common stock probably has a higher price because the dividend can grow, whereas it is fixed on the preferred.
Estimating Growth. Aswath Damodaran. Aswath Damodaran 1
 Estimating Growth Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Ways of Estimating Growth in Earnings Look at the past The historical growth in earnings per share is usually a good starting point for growth estimation
Estimating Growth Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Ways of Estimating Growth in Earnings Look at the past The historical growth in earnings per share is usually a good starting point for growth estimation
Key Concepts and Skills Chapter 8 Stock Valuation
 Key Concepts and Skills Chapter 8 Stock Valuation Konan Chan Financial Management, Spring 2016 Understand how stock prices depend on future dividends and dividend growth Be able to compute stock prices
Key Concepts and Skills Chapter 8 Stock Valuation Konan Chan Financial Management, Spring 2016 Understand how stock prices depend on future dividends and dividend growth Be able to compute stock prices
I. Estimating Discount Rates
 I. Estimating Discount Rates DCF Valuation Aswath Damodaran 1 Estimating Inputs: Discount Rates Critical ingredient in discounted cashflow valuation. Errors in estimating the discount rate or mismatching
I. Estimating Discount Rates DCF Valuation Aswath Damodaran 1 Estimating Inputs: Discount Rates Critical ingredient in discounted cashflow valuation. Errors in estimating the discount rate or mismatching
II. Estimating Cash Flows
 II. Estimating Cash Flows DCF Valuation Aswath Damodaran 61 Steps in Cash Flow Estimation Estimate the current earnings of the firm If looking at cash flows to equity, look at earnings after interest expenses
II. Estimating Cash Flows DCF Valuation Aswath Damodaran 61 Steps in Cash Flow Estimation Estimate the current earnings of the firm If looking at cash flows to equity, look at earnings after interest expenses
How To Value A Stock
 Chapter 9 Valuing Stocks 9-1. Assume Evco, Inc., has a current price of $50 and will pay a $2 dividend in one year, and its equity cost of capital is 15%. What price must you expect it to sell for right
Chapter 9 Valuing Stocks 9-1. Assume Evco, Inc., has a current price of $50 and will pay a $2 dividend in one year, and its equity cost of capital is 15%. What price must you expect it to sell for right
Relative Valuation. Aswath Damodaran
 Relative Valuation 134 The Essence of relative valuation? In relative valuation, the value of an asset is compared to the values assessed by the market for similar or comparable assets. To do relative
Relative Valuation 134 The Essence of relative valuation? In relative valuation, the value of an asset is compared to the values assessed by the market for similar or comparable assets. To do relative
CHAPTER 8. Problems and Questions
 CHAPTER 8 Problems and Questions 1. Plastico, a manufacturer of consumer plastic products, is evaluating its capital structure. The balance sheet of the company is as follows (in millions): Assets Liabilities
CHAPTER 8 Problems and Questions 1. Plastico, a manufacturer of consumer plastic products, is evaluating its capital structure. The balance sheet of the company is as follows (in millions): Assets Liabilities
Chapter 9 The Cost of Capital ANSWERS TO SELEECTED END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS
 Chapter 9 The Cost of Capital ANSWERS TO SELEECTED END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 9-1 a. The weighted average cost of capital, WACC, is the weighted average of the after-tax component costs of capital -debt,
Chapter 9 The Cost of Capital ANSWERS TO SELEECTED END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 9-1 a. The weighted average cost of capital, WACC, is the weighted average of the after-tax component costs of capital -debt,
FSA Note: Summary of Financial Ratio Calculations
 FSA Note: Summary of Financial Ratio Calculations This note contains a summary of the more common financial statement ratios. A few points should be noted: Calculations vary in practice; consistency and
FSA Note: Summary of Financial Ratio Calculations This note contains a summary of the more common financial statement ratios. A few points should be noted: Calculations vary in practice; consistency and
] (3.3) ] (1 + r)t (3.4)
![] (3.3) ] (1 + r)t (3.4) ] (3.3) ] (1 + r)t (3.4)](/thumbs/39/18539117.jpg) Present value = future value after t periods (3.1) (1 + r) t PV of perpetuity = C = cash payment (3.2) r interest rate Present value of t-year annuity = C [ 1 1 ] (3.3) r r(1 + r) t Future value of annuity
Present value = future value after t periods (3.1) (1 + r) t PV of perpetuity = C = cash payment (3.2) r interest rate Present value of t-year annuity = C [ 1 1 ] (3.3) r r(1 + r) t Future value of annuity
GESTÃO FINANCEIRA II PROBLEM SET 2 - SOLUTIONS
 GESTÃO FINANCEIRA II PROBLEM SET - SOLUTIONS (FROM BERK AND DEMARZO S CORPORATE FINANCE ) LICENCIATURA UNDERGRADUATE COURSE 1 ST SEMESTER 010-011 Yield to Maturity Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds 8-3. The following
GESTÃO FINANCEIRA II PROBLEM SET - SOLUTIONS (FROM BERK AND DEMARZO S CORPORATE FINANCE ) LICENCIATURA UNDERGRADUATE COURSE 1 ST SEMESTER 010-011 Yield to Maturity Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds 8-3. The following
Bank Valuation: Comparable Public Companies & Precedent Transactions
 Bank Valuation: Comparable Public Companies & Precedent Transactions Picking a set of comparable companies or precedent transactions for a bank is very similar to what you d do for any other company here
Bank Valuation: Comparable Public Companies & Precedent Transactions Picking a set of comparable companies or precedent transactions for a bank is very similar to what you d do for any other company here
Chapter 11 The Cost of Capital ANSWERS TO SELECTED END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS
 Chapter 11 The Cost of Capital ANSWERS TO SELECTED END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 11-1 a. The weighted average cost of capital, WACC, is the weighted average of the after-tax component costs of capital -debt,
Chapter 11 The Cost of Capital ANSWERS TO SELECTED END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 11-1 a. The weighted average cost of capital, WACC, is the weighted average of the after-tax component costs of capital -debt,
Estimating Cost of Capital. 2. The cost of capital is an opportunity cost it depends on where the money goes, not where it comes from
 Estimating Cost of Capal 1. Vocabulary the following all mean the same thing: a. Required return b. Appropriate discount rate c. Cost of capal (or cost of money) 2. The cost of capal is an opportuny cost
Estimating Cost of Capal 1. Vocabulary the following all mean the same thing: a. Required return b. Appropriate discount rate c. Cost of capal (or cost of money) 2. The cost of capal is an opportuny cost
Bond Valuation. What is a bond?
 Lecture: III 1 What is a bond? Bond Valuation When a corporation wishes to borrow money from the public on a long-term basis, it usually does so by issuing or selling debt securities called bonds. A bond
Lecture: III 1 What is a bond? Bond Valuation When a corporation wishes to borrow money from the public on a long-term basis, it usually does so by issuing or selling debt securities called bonds. A bond
Chapter 8. Stock Valuation Process. Stock Valuation
 Stock Valuation Process Chapter 8 Stock Valuation: Investors use risk and return concept to determine the worth of a security. In the valuation process: The intrinsic value of any investment equals the
Stock Valuation Process Chapter 8 Stock Valuation: Investors use risk and return concept to determine the worth of a security. In the valuation process: The intrinsic value of any investment equals the
CHAPTER 12 RISK, COST OF CAPITAL, AND CAPITAL BUDGETING
 CHAPTER 12 RISK, COST OF CAPITAL, AND CAPITAL BUDGETING Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. No. The cost of capital depends on the risk of the project, not the source of the money.
CHAPTER 12 RISK, COST OF CAPITAL, AND CAPITAL BUDGETING Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. No. The cost of capital depends on the risk of the project, not the source of the money.
Dr. Pushpa Bhatt, Sumangala JK Department of Commerce, Bangalore University, India pushpa_bhatt12@rediffmail.com; sumangalajkashok@gmail.
 Journal of Finance, Accounting and Management, 3(2), 1-14, July 2012 1 Impact of Earnings per share on Market Value of an equity share: An Empirical study in Indian Capital Market Dr. Pushpa Bhatt, Sumangala
Journal of Finance, Accounting and Management, 3(2), 1-14, July 2012 1 Impact of Earnings per share on Market Value of an equity share: An Empirical study in Indian Capital Market Dr. Pushpa Bhatt, Sumangala
Value of Equity and Per Share Value when there are options and warrants outstanding. Aswath Damodaran
 Value of Equity and Per Share Value when there are options and warrants outstanding Aswath Damodaran 1 Equity Value and Per Share Value: A Test Assume that you have done an equity valuation of Microsoft.
Value of Equity and Per Share Value when there are options and warrants outstanding Aswath Damodaran 1 Equity Value and Per Share Value: A Test Assume that you have done an equity valuation of Microsoft.
FINC 3630: Advanced Business Finance Additional Practice Problems
 FINC 3630: Advanced Business Finance Additional Practice Problems Accounting For Financial Management 1. Calculate free cash flow for Home Depot for the fiscal year-ended February 1, 2015 (the 2014 fiscal
FINC 3630: Advanced Business Finance Additional Practice Problems Accounting For Financial Management 1. Calculate free cash flow for Home Depot for the fiscal year-ended February 1, 2015 (the 2014 fiscal
Acquisition Valuation
 Acquisition Valuation Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Issues in Acquisition Valuation Acquisition valuations are complex, because the valuation often involved issues like synergy and control, which
Acquisition Valuation Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 Issues in Acquisition Valuation Acquisition valuations are complex, because the valuation often involved issues like synergy and control, which
CHAPTER 3 LONG-TERM FINANCIAL PLANNING AND GROWTH
 CHAPTER 3 LONG-TERM FINANCIAL PLANNING AND GROWTH Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 5. The sustainable growth rate is greater than 20 percent, because at a 20 percent growth rate
CHAPTER 3 LONG-TERM FINANCIAL PLANNING AND GROWTH Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 5. The sustainable growth rate is greater than 20 percent, because at a 20 percent growth rate
Chapter 15: Debt Policy
 FIN 302 Class Notes Chapter 15: Debt Policy Two Cases: Case one: NO TAX All Equity Half Debt Number of shares 100,000 50,000 Price per share $10 $10 Equity Value $1,000,000 $500,000 Debt Value $0 $500,000
FIN 302 Class Notes Chapter 15: Debt Policy Two Cases: Case one: NO TAX All Equity Half Debt Number of shares 100,000 50,000 Price per share $10 $10 Equity Value $1,000,000 $500,000 Debt Value $0 $500,000
Templates available in Excel 97 (Excel 8) and higher versions:
 Excel Templates Templates available in Excel 97 (Excel 8) and higher versions: All of the Excel templates in Research Insight can be customized to fit your own particular needs. Company Fundamental Analysis
Excel Templates Templates available in Excel 97 (Excel 8) and higher versions: All of the Excel templates in Research Insight can be customized to fit your own particular needs. Company Fundamental Analysis
Goals. Stock Valuation. Dividend Discount Model Constant Dividends. Dividend Discount Model Constant Dividends
 Stock Valuation Economics 71a: Spring 2007 Mayo 11 Malkiel, 5, 6 (136-144), 8 Lecture notes 4.2 Goals Dividend valuation model dividend discount model Forecasting earnings, dividends, and prices Ratio
Stock Valuation Economics 71a: Spring 2007 Mayo 11 Malkiel, 5, 6 (136-144), 8 Lecture notes 4.2 Goals Dividend valuation model dividend discount model Forecasting earnings, dividends, and prices Ratio
FNCE 301, Financial Management H Guy Williams, 2006
 Stock Valuation Stock characteristics Stocks are the other major traded security (stocks & bonds). Options are another traded security but not as big as these two. - Ownership Stockholders are the owner
Stock Valuation Stock characteristics Stocks are the other major traded security (stocks & bonds). Options are another traded security but not as big as these two. - Ownership Stockholders are the owner
IESE UNIVERSITY OF NAVARRA OPTIMAL CAPITAL STRUCTURE: PROBLEMS WITH THE HARVARD AND DAMODARAN APPROACHES. Pablo Fernández*
 IESE UNIVERSITY OF NAVARRA OPTIMAL CAPITAL STRUCTURE: PROBLEMS WITH THE HARVARD AND DAMODARAN APPROACHES Pablo Fernández* RESEARCH PAPER No 454 January, 2002 * Professor of Financial Management, IESE Research
IESE UNIVERSITY OF NAVARRA OPTIMAL CAPITAL STRUCTURE: PROBLEMS WITH THE HARVARD AND DAMODARAN APPROACHES Pablo Fernández* RESEARCH PAPER No 454 January, 2002 * Professor of Financial Management, IESE Research
Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3
 Problem 1 (1) Book Value Debt/Equity Ratio = 2500/2500 = 100% Market Value of Equity = 50 million * $ 80 = $4,000 Market Value of Debt =.80 * 2500 = $2,000 Debt/Equity Ratio in market value terms = 2000/4000
Problem 1 (1) Book Value Debt/Equity Ratio = 2500/2500 = 100% Market Value of Equity = 50 million * $ 80 = $4,000 Market Value of Debt =.80 * 2500 = $2,000 Debt/Equity Ratio in market value terms = 2000/4000
From Reported to Actual Earnings
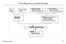 From Reported to Actual Earnings Firmʼs history Comparable Firms Operating leases - Convert into debt - Adjust operating income R&D Expenses - Convert into asset - Adjust operating income Normalize Earnings
From Reported to Actual Earnings Firmʼs history Comparable Firms Operating leases - Convert into debt - Adjust operating income R&D Expenses - Convert into asset - Adjust operating income Normalize Earnings
Leverage and Capital Structure
 Leverage and Capital Structure Ross Chapter 16 Spring 2005 10.1 Leverage Financial Leverage Financial leverage is the use of fixed financial costs to magnify the effect of changes in EBIT on EPS. Fixed
Leverage and Capital Structure Ross Chapter 16 Spring 2005 10.1 Leverage Financial Leverage Financial leverage is the use of fixed financial costs to magnify the effect of changes in EBIT on EPS. Fixed
Estimating Beta. Aswath Damodaran
 Estimating Beta The standard procedure for estimating betas is to regress stock returns (R j ) against market returns (R m ) - R j = a + b R m where a is the intercept and b is the slope of the regression.
Estimating Beta The standard procedure for estimating betas is to regress stock returns (R j ) against market returns (R m ) - R j = a + b R m where a is the intercept and b is the slope of the regression.
Corporate Finance & Options: MGT 891 Homework #6 Answers
 Corporate Finance & Options: MGT 891 Homework #6 Answers Question 1 A. The APV rule states that the present value of the firm equals it all equity value plus the present value of the tax shield. In this
Corporate Finance & Options: MGT 891 Homework #6 Answers Question 1 A. The APV rule states that the present value of the firm equals it all equity value plus the present value of the tax shield. In this
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: The Inputs. Aswath Damodaran
 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: The Inputs Aswath Damodaran 1 The Key Inputs in DCF Valuation Discount Rate Cost of Equity, in valuing equity Cost of Capital, in valuing the firm Cash Flows Cash Flows
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation: The Inputs Aswath Damodaran 1 The Key Inputs in DCF Valuation Discount Rate Cost of Equity, in valuing equity Cost of Capital, in valuing the firm Cash Flows Cash Flows
Measuring Investment Returns
 Measuring Investment Returns Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business Aswath Damodaran 156 First Principles Invest in projects that yield a return greater than the minimum acceptable hurdle rate. The
Measuring Investment Returns Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business Aswath Damodaran 156 First Principles Invest in projects that yield a return greater than the minimum acceptable hurdle rate. The
CHAPTER 14 FREE CASH FLOW TO EQUITY DISCOUNT MODELS
 1 CHAPTER 14 FREE CASH FLOW TO EQUITY DISCOUNT MODELS The dividend discount model is based upon the premise that the only cashflows received by stockholders is dividends. Even if we use the modified version
1 CHAPTER 14 FREE CASH FLOW TO EQUITY DISCOUNT MODELS The dividend discount model is based upon the premise that the only cashflows received by stockholders is dividends. Even if we use the modified version
1. This exam contains 12 pages. Please make sure your copy is not missing any pages.
 Name Solution Key Section ACCOUNTING 15.501 SPRING 2003 FINAL EXAM EXAM GUIDELINES 1. This exam contains 12 pages. Please make sure your copy is not missing any pages. 2. The exam must be completed within
Name Solution Key Section ACCOUNTING 15.501 SPRING 2003 FINAL EXAM EXAM GUIDELINES 1. This exam contains 12 pages. Please make sure your copy is not missing any pages. 2. The exam must be completed within
Option Pricing Applications in Valuation!
 Option Pricing Applications in Valuation! Equity Value in Deeply Troubled Firms Value of Undeveloped Reserves for Natural Resource Firm Value of Patent/License 73 Option Pricing Applications in Equity
Option Pricing Applications in Valuation! Equity Value in Deeply Troubled Firms Value of Undeveloped Reserves for Natural Resource Firm Value of Patent/License 73 Option Pricing Applications in Equity
USING THE EQUITY RESIDUAL APPROACH TO VALUATION: AN EXAMPLE
 Graduate School of Business Administration - University of Virginia USING THE EQUITY RESIDUAL APPROACH TO VALUATION: AN EXAMPLE Planned changes in capital structure over time increase the complexity of
Graduate School of Business Administration - University of Virginia USING THE EQUITY RESIDUAL APPROACH TO VALUATION: AN EXAMPLE Planned changes in capital structure over time increase the complexity of
Certified Financial Management Professional VS-1201
 Certified Financial Management Professional VS-1201 Certified Financial Management Professional Certified Financial Management Professional Certification Code VS-1201 Vskills certification for Financial
Certified Financial Management Professional VS-1201 Certified Financial Management Professional Certified Financial Management Professional Certification Code VS-1201 Vskills certification for Financial
Homework Solutions - Lecture 4
 Homework Solutions - Lecture 4 1. Estimate fundamental growth in EBIT for Nike based on the firm s reinvestment rate and ROC in the most recent year. Be sure to incorporate any necessary adjustments made
Homework Solutions - Lecture 4 1. Estimate fundamental growth in EBIT for Nike based on the firm s reinvestment rate and ROC in the most recent year. Be sure to incorporate any necessary adjustments made
Equity Analysis and Capital Structure. A New Venture s Perspective
 Equity Analysis and Capital Structure A New Venture s Perspective 1 Venture s Capital Structure ASSETS Short- term Assets Cash A/R Inventories Long- term Assets Plant and Equipment Intellectual Property
Equity Analysis and Capital Structure A New Venture s Perspective 1 Venture s Capital Structure ASSETS Short- term Assets Cash A/R Inventories Long- term Assets Plant and Equipment Intellectual Property
Features of Common Stock. The Stock Markets. Features of Preferred Stock. Valuation of Securities: Stocks
 Valuation of Securities: Stocks Econ 422: Investment, Capital & Finance University of Washington Eric Zivot Fall 27 January 31, 27 Features of Common Stock Voting rights (Cumulative vs. Straight) Proxy
Valuation of Securities: Stocks Econ 422: Investment, Capital & Finance University of Washington Eric Zivot Fall 27 January 31, 27 Features of Common Stock Voting rights (Cumulative vs. Straight) Proxy
CHAPTER 13 DIVIDEND DISCOUNT MODELS
 DIVIDEND DISCOUNT MODELS CHAPTER 13 In the strictest sense, the only cash flow you receive from a firm when you buy publicly traded stock is the dividend. The simplest model for valuing equity is the dividend
DIVIDEND DISCOUNT MODELS CHAPTER 13 In the strictest sense, the only cash flow you receive from a firm when you buy publicly traded stock is the dividend. The simplest model for valuing equity is the dividend
Valuing Financial Service Firms
 1 Valuing Financial Service Firms Aswath Damodaran April 2009 Valuing banks, insurance companies and investment banks has always been difficult, but the market crisis of 2008 has elevated the concern to
1 Valuing Financial Service Firms Aswath Damodaran April 2009 Valuing banks, insurance companies and investment banks has always been difficult, but the market crisis of 2008 has elevated the concern to
Understanding Financial Management: A Practical Guide Guideline Answers to the Concept Check Questions
 Understanding Financial Management: A Practical Guide Guideline Answers to the Concept Check Questions Chapter 3 Interpreting Financial Ratios Concept Check 3.1 1. What are the different motivations that
Understanding Financial Management: A Practical Guide Guideline Answers to the Concept Check Questions Chapter 3 Interpreting Financial Ratios Concept Check 3.1 1. What are the different motivations that
GESTÃO FINANCEIRA II PROBLEM SET 5 SOLUTIONS (FROM BERK AND DEMARZO S CORPORATE FINANCE ) LICENCIATURA UNDERGRADUATE COURSE
 GESTÃO FINANCEIRA II PROBLEM SET 5 SOLUTIONS (FROM BERK AND DEMARZO S CORPORATE FINANCE ) LICENCIATURA UNDERGRADUATE COURSE 1 ST SEMESTER 2010-2011 Chapter 18 Capital Budgeting and Valuation with Leverage
GESTÃO FINANCEIRA II PROBLEM SET 5 SOLUTIONS (FROM BERK AND DEMARZO S CORPORATE FINANCE ) LICENCIATURA UNDERGRADUATE COURSE 1 ST SEMESTER 2010-2011 Chapter 18 Capital Budgeting and Valuation with Leverage
STUDENT CAN HAVE ONE LETTER SIZE FORMULA SHEET PREPARED BY STUDENT HIM/HERSELF. FINANCIAL CALCULATOR/TI-83 OR THEIR EQUIVALENCES ARE ALLOWED.
 Test III-FINN3120-090 Fall 2009 (2.5 PTS PER QUESTION. MAX 100 PTS) Type A Name ID PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID ON THE TEST, ANSWER SHEET AND FORMULA SHEET. TURN IN THE TEST, OPSCAN ANSWER SHEET AND FORMULA
Test III-FINN3120-090 Fall 2009 (2.5 PTS PER QUESTION. MAX 100 PTS) Type A Name ID PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID ON THE TEST, ANSWER SHEET AND FORMULA SHEET. TURN IN THE TEST, OPSCAN ANSWER SHEET AND FORMULA
CHAPTER FOURTEEN. Simple Forecasting and Simple Valuation
 CHAPTER FOURTEEN Simple Forecasting and Simple Valuation Concept Questions C14.1 Book values give a good forecast when they are reviewed at their fair value: applying the required return to book value
CHAPTER FOURTEEN Simple Forecasting and Simple Valuation Concept Questions C14.1 Book values give a good forecast when they are reviewed at their fair value: applying the required return to book value
Financial Statement Analysis!
 Financial Statement Analysis! The raw data for investing Aswath Damodaran! 1! Questions we would like answered! Assets Liabilities What are the assets in place? How valuable are these assets? How risky
Financial Statement Analysis! The raw data for investing Aswath Damodaran! 1! Questions we would like answered! Assets Liabilities What are the assets in place? How valuable are these assets? How risky
Chapter 17 Does Debt Policy Matter?
 Chapter 17 Does Debt Policy Matter? Multiple Choice Questions 1. When a firm has no debt, then such a firm is known as: (I) an unlevered firm (II) a levered firm (III) an all-equity firm D) I and III only
Chapter 17 Does Debt Policy Matter? Multiple Choice Questions 1. When a firm has no debt, then such a firm is known as: (I) an unlevered firm (II) a levered firm (III) an all-equity firm D) I and III only
Value Enhancement: EVA and CFROI. Aswath Damodaran 1
 Value Enhancement: EVA and CFROI Aswath Damodaran 1 Alternative Approaches to Value Enhancement Maximize a variable that is correlated with the value of the firm. There are several choices for such a variable.
Value Enhancement: EVA and CFROI Aswath Damodaran 1 Alternative Approaches to Value Enhancement Maximize a variable that is correlated with the value of the firm. There are several choices for such a variable.
Valuation Overview. Valuation. General Thoughts on. Valuation. Valuation Models
 Valuation Overview Valuation Valuation Discounted cash flow models DDM FCFE Relative valuation over time across assets at a given time relative to comparables relative to the market 1 2 General Thoughts
Valuation Overview Valuation Valuation Discounted cash flow models DDM FCFE Relative valuation over time across assets at a given time relative to comparables relative to the market 1 2 General Thoughts
Chapter 7. . 1. component of the convertible can be estimated as 1100-796.15 = 303.85.
 Chapter 7 7-1 Income bonds do share some characteristics with preferred stock. The primary difference is that interest paid on income bonds is tax deductible while preferred dividends are not. Income bondholders
Chapter 7 7-1 Income bonds do share some characteristics with preferred stock. The primary difference is that interest paid on income bonds is tax deductible while preferred dividends are not. Income bondholders
CHAPTER 14 MARK TO MARKET: FINANCIAL SERVICE COMPANIES
 1 CHAPTER 14 MARK TO MARKET: FINANCIAL SERVICE COMPANIES Banks, insurance companies and other financial service firms pose special challenges for an analyst attempting to value them, for three reasons.
1 CHAPTER 14 MARK TO MARKET: FINANCIAL SERVICE COMPANIES Banks, insurance companies and other financial service firms pose special challenges for an analyst attempting to value them, for three reasons.
Company Share Price Valuation using Free Cash Flow To Equity
 Financial Modeling Templates Company Share Price Valuation using Free Cash Flow To Equity http://spreadsheetml.com/finance/valuation_freecashflowtoequity.shtml Copyright (c) 2009-2014, ConnectCode All
Financial Modeling Templates Company Share Price Valuation using Free Cash Flow To Equity http://spreadsheetml.com/finance/valuation_freecashflowtoequity.shtml Copyright (c) 2009-2014, ConnectCode All
Models of Risk and Return
 Models of Risk and Return Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 First Principles Invest in projects that yield a return greater than the minimum acceptable hurdle rate. The hurdle rate should be higher for
Models of Risk and Return Aswath Damodaran Aswath Damodaran 1 First Principles Invest in projects that yield a return greater than the minimum acceptable hurdle rate. The hurdle rate should be higher for
Dealing with Operating Leases in Valuation. Aswath Damodaran. Stern School of Business. 44 West Fourth Street. New York, NY 10012
 Dealing with Operating Leases in Valuation Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business 44 West Fourth Street New York, NY 10012 adamodar@stern.nyu.edu Abstract Most firm valuation models start with the after-tax
Dealing with Operating Leases in Valuation Aswath Damodaran Stern School of Business 44 West Fourth Street New York, NY 10012 adamodar@stern.nyu.edu Abstract Most firm valuation models start with the after-tax
ENTREPRENEURIAL FINANCE: Strategy Valuation and Deal Structure
 ENTREPRENEURIAL FINANCE: Strategy Valuation and Deal Structure Chapter 9 Valuation Questions and Problems 1. You are considering purchasing shares of DeltaCad Inc. for $40/share. Your analysis of the company
ENTREPRENEURIAL FINANCE: Strategy Valuation and Deal Structure Chapter 9 Valuation Questions and Problems 1. You are considering purchasing shares of DeltaCad Inc. for $40/share. Your analysis of the company
Estimating Cash Flows
 Estimating Cash Flows DCF Valuation 1 Steps in Cash Flow Estimation Estimate the current earnings of the firm If looking at cash flows to equity, look at earnings after interest expenses - i.e. net income
Estimating Cash Flows DCF Valuation 1 Steps in Cash Flow Estimation Estimate the current earnings of the firm If looking at cash flows to equity, look at earnings after interest expenses - i.e. net income
Total shares at the end of ten years is 100*(1+5%) 10 =162.9.
 FCS5510 Sample Homework Problems Unit04 CHAPTER 8 STOCK PROBLEMS 1. An investor buys 100 shares if a $40 stock that pays a annual cash dividend of $2 a share (a 5% dividend yield) and signs up for the
FCS5510 Sample Homework Problems Unit04 CHAPTER 8 STOCK PROBLEMS 1. An investor buys 100 shares if a $40 stock that pays a annual cash dividend of $2 a share (a 5% dividend yield) and signs up for the
You just paid $350,000 for a policy that will pay you and your heirs $12,000 a year forever. What rate of return are you earning on this policy?
 1 You estimate that you will have $24,500 in student loans by the time you graduate. The interest rate is 6.5%. If you want to have this debt paid in full within five years, how much must you pay each
1 You estimate that you will have $24,500 in student loans by the time you graduate. The interest rate is 6.5%. If you want to have this debt paid in full within five years, how much must you pay each
Unit 01. 1. Return computation with cash purchase vs. margin purchase
 FCS 5510 Formula Sheet *Note: The formulas I expect you to know are colored in Red. They are either more conceptually based, or are more commonly used than the others. You need to have a passing familiarity
FCS 5510 Formula Sheet *Note: The formulas I expect you to know are colored in Red. They are either more conceptually based, or are more commonly used than the others. You need to have a passing familiarity
TIP If you do not understand something,
 Valuing common stocks Application of the DCF approach TIP If you do not understand something, ask me! The plan of the lecture Review what we have accomplished in the last lecture Some terms about stocks
Valuing common stocks Application of the DCF approach TIP If you do not understand something, ask me! The plan of the lecture Review what we have accomplished in the last lecture Some terms about stocks
COST OF CAPITAL Compute the cost of debt. Compute the cost of preferred stock.
 OBJECTIVE 1 Compute the cost of debt. The method of computing the yield to maturity for bonds will be used how to compute the cost of debt. Because interest payments are tax deductible, only after-tax
OBJECTIVE 1 Compute the cost of debt. The method of computing the yield to maturity for bonds will be used how to compute the cost of debt. Because interest payments are tax deductible, only after-tax
The Adjusted-Present-Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1)
 IE Aufgabe 4 The Adjusted-Present-Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1) Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition by a small group of equity investors of a public or private company
IE Aufgabe 4 The Adjusted-Present-Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1) Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition by a small group of equity investors of a public or private company
Finance 3130 Corporate Finiance Sample Final Exam Spring 2012
 Finance 3130 Corporate Finiance Sample Final Exam Spring 2012 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or falsewith A for true and B for false. 1. Interest paid by a corporation is a tax deduction
Finance 3130 Corporate Finiance Sample Final Exam Spring 2012 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or falsewith A for true and B for false. 1. Interest paid by a corporation is a tax deduction
Equity Market Risk Premium Research Summary. 12 April 2016
 Equity Market Risk Premium Research Summary 12 April 2016 Introduction welcome If you are reading this, it is likely that you are in regular contact with KPMG on the topic of valuations. The goal of this
Equity Market Risk Premium Research Summary 12 April 2016 Introduction welcome If you are reading this, it is likely that you are in regular contact with KPMG on the topic of valuations. The goal of this
Using the Bloomberg terminal for data
 Using the Bloomberg terminal for data Contents of Package 1.Getting information on your company Pages 2-31 2.Getting information on comparable companies Pages 32-39 3.Getting macro economic information
Using the Bloomberg terminal for data Contents of Package 1.Getting information on your company Pages 2-31 2.Getting information on comparable companies Pages 32-39 3.Getting macro economic information
The Adjusted Present Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1
 Chapter 17 Valuation and Capital Budgeting for the Levered Firm 17A-1 Appendix 17A The Adjusted Present Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1 Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition
Chapter 17 Valuation and Capital Budgeting for the Levered Firm 17A-1 Appendix 17A The Adjusted Present Value Approach to Valuing Leveraged Buyouts 1 Introduction A leveraged buyout (LBO) is the acquisition
