Sample to Insight. IPA Training: Maximizing the Biological Interpretation of Gene, Transcript & Protein Expression Data with IPA
|
|
|
- Erick Elliott
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IPA Training: Maximizing the Biological Interpretation of Gene, Transcript & Protein Expression Data with IPA
2 Log into IPA: 2
3 How can IPA help you? IPA Deep pathway understanding of a single gene/protein Drug/therapeutic target discovery Biological understanding of large data sets, including Differential gene expression, array and RNAseq (transcriptomics) Isoform annotation (New) Differential protein expression (proteomics) Genes with loss/gain-of-function variants (New) Metabolomics mirna expression Gene List Chip-seq sirna screening Sequence Variants (see also Ingenuity Variant Analysis) Methylation Protein phosphorylation 5
4 Ingenuity Content Ingenuity Knowledge Base The Ingenuity Knowledge Base The Ingenuity Ontology Ingenuity Findings Ingenuity Expert Findings Manually curated Findings that are reviewed, from the full-text, rich with contextual details, and are derived from top journals. Ingenuity ExpertAssist Findings Automated text Findings that are reviewed, from abstracts, timely, and cover a broad range of publications. Ingenuity Modeled Knowledge Ingenuity Expert Knowledge Content we model such as pathways, toxicity lists, etc. Ingenuity Supported Third Party Information Content areas include Protein-Protein, mirna, biomarker, clinical trial information, and others
5 Core Analysis Steps File > New > Core Analysis Or File > Data Set Upload Upload Data (gene expression, protein expression, metabolomics, etc. Set Core Analysis Settings Run Analysis Interpret Results 7
6 Data Upload 8
7 Data Upload Format Examples Typical value-types that are uploaded to IPA Identifier List +differential expression +significance stat +RPKM (maximum RPKM between experimental condition and control recommended for RNAseq) 10
8 Uploading Multiple Observations Format for multi-observation upload Multiple experimental differential expressions can be grouped into a single spreadsheet and upload Nice-to-have if you are comparing a series of expression values such as a timecourse Be sure and name your observations at the time of upload in IPA Observation 1 Observation 2 11
9 Expression Value Calculation Verify the differential expression calculation Recommend Log 2 (ratio) differential expression Log 2 Experimental Condition Exp. Control Exp Ratio differential expression Experimental Condition Exp. Control Exp Fold Change If increased differential expression Experimental Condition Exp. Control Exp If decreased differential expression -1 Control Exp. Experimental Condition Exp. Fold change will never have values between 1 and -1 13
10 Typical Distribution of RPKM Values in RNAseq Data Filtering on absolute expression RNAseq measurements often result in many significant differential fold changes at low absolute transcript expression levels Including the maximum RPKM value of your experimental condition and control allows for later filtering on absolute expression value in addition to fold change and p-value Count of Genes Count of Max RPKM Values RPKM 14
11 Data Upload Best practices Calculate metrics outside of IPA (e.g. fold-change, p-value) Create an Excel spreadsheet or tab delimited file Only 1 header row allowed One column must have identifiers, preferably the left-most column Can have up to 20 observations IPA will only look at the top worksheet in an Excel workbook Group related observations into a single spreadsheet if possible Time course, drug concentration, cell lines, etc. Specify array platform (chip) if possible It is OK to use Not specified/applicable Pre-filter data at the lowest threshold that you have confidence in For example, probe measurement p-value of.05 or other criteria Use the Recalculate button to refresh the screen 15
12 Core Analysis Data Types Examples of data set types Differential gene expression, array and RNAseq (transcriptomics) Isoform annotation (New) Differential protein expression (proteomics) Genes with loss/gain-of-function variants (New) Metabolomics mirna expression Gene List Chip-seq sirna screening Sequence Variants (see also Ingenuity Variant Analysis) Methylation Protein phosphorylation 16
13 Why don t all of the molecules map? The gene ID might not correspond to a known gene product. For example, most ESTs are not found in the knowledge base (exception: ESTs that have a corresponding Entrez Gene identifier are found in the knowledge base). A gene/protein ID might correspond to several loci or more than one gene. Such identifiers are left unmapped in the application due to the ambiguity of the identity. Identifiers for species other than human, mouse or rat must map to human, mouse or rat orthologues in order to map in IPA. SNPs must map to a single gene. SNPs that fall greater than 2 KB upstream or 0.5 KB downstream of a gene coding region will not be mapped in IPA during data upload, since they cannot be unambiguously mapped to a single gene. There may be insufficient findings in the literature regarding some molecules. 22
14 How Do I Choose The Reference Set? If you are using a standard vendor platform supported by IPA, then that platform should be selected as your reference set. If you do not know the platform or the data were taken from different platforms, select a reference set that best estimates the entire population you evaluated. For gene expression data, select the Ingenuity Knowledge Base (genes only) For metabolomics, select the Ingenuity Knowledge Base (endogenous chemicals only) You have the option to having your uploaded data set used as the reference set (User Data Set) 23
15 Core Analysis Set-up 24
16 Fold-Change Cutoff Use cutoffs to refine set size per observation Ideal set size for IPA core analysis from gene expression data is typically Small sets will not have many directional effect z-scores (downstream functions, upstream regulators) Very large data sets will tend to have more noise p-value Cutoff Adapted from Conti et al (2007), BMC Genomics, 8, p268 26
17 Creating an IPA Core Analysis Make sure reference set matches source of molecules Assembles networks and identifies transcriptional regulators with only direct relationships. Results in networks in which members are nearer neighbors of one another and biases for binding relationships. Set data cutoff filters Click here to apply filter cutoffs and see number that are network and function eligible View other observations if a multiobservation data set Network and function eligible molecules should be for best results, but other values can work 28
18 Creating an IPA Core Analysis- Network Generation Option to exclude endogenous chemicals from networks Option to turn off molecular networks for a faster analysis Fine-tune format of networks Turn On Causal Network (Advanced Analytics) 29
19 Creating an IPA Core Analysis: Using Filters Several filters available. Set criteria to filter out findings of less interest. 30
20 Creating an IPA Core Analysis- Advanced Settings Make sure molecule coloring is set for a metric such as fold change, log ratio, etc. Confirm how you would like to resolve duplicates Deselect any observations that you would like to exclude from the analysis 31
21 Using Core Analysis Pre-filters Set criteria to filter out findings of less interest. Species Tissue Filter stringency A Stringent setting requires that each of a pair of molecules and the relationship that connects them meet the filter criteria A Relaxed filter requires that the gene or protein expression of the molecules connected by a relationship meet the filter criteria
22 Using Core Analysis Pre-filters, Cont. Unspecified refers to findings or molecules where cell/tissue/organ is not specified or classified Pre-filter Advantages Focuses IPA analysis on networks, biological functions, and canonical pathways on molecules and relationships closely related to the experiment. Pre filter Disadvantages Loss of information Loss of relationships that may be applicable to your species or tissue but were described in a different speices or tissue.
23
24 Large Scale Data Analysis 35
25 Gene/Protein Expression Analysis, Overview IPA Core Analysis Pathway Analysis Predicts pathways that are changing based on gene expression New tools to predict directional effects on the pathway (MAP overlay tool) Upstream Regulator Analysis Predicts what regulators caused changes in gene expression Predicts directional state of regulator Creates de novo pathways based on upstream regulators (Mechanistic Networks) Diseases and Functions Analysis Predicts effected biology (cellular processes, biological functions) based on gene expression and predicts directional change on that effect Increase in cell cycle Decrease in apoptosis Regulator Effects Models pathway interactions from predicted upstream regulators, through differentially expressed genes, to biological processes Networks Predicts non-directional gene interaction map 36
26 Molecule Activity Predictor (MAP)
27 Identify likely upstream regulators and their activity state IPA Upstream Regulator Analysis Use published experimental molecular interactions to identify upstream regulators MCF7 Cells Treated with Beta-Estradiol. Genes in uploaded data set are colored red and green. Identify upstream regulators by determining gene enrichment in downstream genes Predict the activity state of regulators by correlating literature reported effects with observed gene expression
28 Create de novo pathways of regulators and genes IPA Mechanistic Networks Identify potential upstream regulator signal transduction Using shared downstream gene effects and gene-gene interactions, pathways (mechanistic networks) are created. IPA Winter Release 2012
29 A novel approach to visualize and predict biological impact of gene expression changes Downstream Effects Analysis Identify key biological processes influenced by differentially expressed genes Understand whether cellular processes are being driven up or down by correlating observed expression with reported experimental gene effects Each box represents a biological process or disease The size of the box represents gene enrichment The color of the box indicates the predicted increase or decrease
30 New in IPA Spring 2014 Release (End of March) Regulator Effects Hypothesis for how a phenotype, function or disease is regulated in the dataset by activated or inhibited upstream regulators Explain impact of upstream molecules on downstream biology Explain potential mechanism for a phenotype or drug Define drug targets Discover novel (or confirm known) regulator disease/phenotype/function relationships
31 Network Analysis 42
32 Analyzing and Interpreting Results 44
33 Approaches to Viewing Results IPA will subdivide your data into slices based on molecule connectivity (networks), cellular functions, and involvement in canonical pathways Spend time surveying the information. Not everything is of scientific interest, look for slices of your data that address your scientific question, are consistent with known biological processes, are consistent with pathology, etc. Typically the goal will be to find a set of genes/molecules that can be looked at in greater detail by building a custom pathway If you are comparing observations, run comparison analysis.
34 IPA calculates two distinct statistics as part of a core analysis P-value: Calculated using a Right-Tailed Fisher s Exact Test Reflects the likelihood that the association or overlap between a set of significant molecules from your experiment and a given process/pathway/transcription neighborhood is due to random chance. The smaller the p-value the less likely that the association is random. The p-value does not consider the directional effect of one molecule on another, or the direction of change of molecules in the dataset. Z-score: Applied in some analysis types and provides predictions about upstream or downstream processes. Takes into account the directional effect of one molecule on another molecule or on a process, and the direction of change of molecules in the dataset.
35 Analyzing Results Canonical Pathway Analysis 50
36 Pathway Analysis What known biological pathways appear most significantly affected by the genes in my data set? What genes within a pathway are changing in expression and what effect might that change have on the pathway?
37 Pathway Analysis Interpretation Bar-chart represents significance of gene enrichment for any given pathway Significance is most important metric Ignore bumpy yellow line: ratio/percent coverage of a pathway subject to pathway size bias Bar-chart color indicates predicted directionality When considering pathway directionality, focus on 2 < z-score < -2 Just because a pathway does not have a good z-score does not make it uninteresting To open pathway, look for open pathway button on far right after bar-chart selection 52
38 Go to Help > Legend Print it out 53
39 Canonical Pathway (CP) Workflow Interpretation Tips Look for pathway biological themes Use Overlapping Pathway tab to filter and view pathways with shared genes Often lesser scoring pathways of a theme are simply subsets of genes found in a better scoring pathway Scan CP names for pathways of particular interest Statistical significance does not equal biological significance and visa-versa Pathways may have many second messengers which can be regulated posttranscriptionally View pathways by clicking the bar-chart and the OPEN PATHWAY button on right Use MAP tool (OVERLAY tool) to help interpretation Overlay other analyses as applicable Toggle overlay options
40 Pathway Navigation Scroll-wheel on mouse controls zoom, or use toolbar zoom buttons. Left-click selects (turns blue) Left-click-drag on nodes moves the node Right-click hold-and-drag moves your view Right-click brings up menu for controlling tool tip (mouse-over node pop-up) copy/paste Highlighting (colored outline) selection Navigation Control Node shapes indicate a protein s primary function, see Help>Legend Relationship lines indicate the type of relationship and the mouse-over letter the type of relationship, see Help>Legend
41 Pathway Navigation, continued Double-clicking a node brings up the node summary You can navigate to the Gene/Chem View page by clicking the protein name at the top of the summary window pane. Double-clicking a relationship line brings up the relationship summary Groups You can to the literature evidence findings by clicking the View relationships between: link at the top of the summary window pane. Groups are represented by a double outline applicable to any molecule shape. These represent cases where findings use a general gene name to describe a gene class or group of isoforms Complexes of different proteins are also given a double outline View members by left-click selecting, then right-click>show Membership
42 Molecule Activity Predictor (MAP) OVERLAY button -> MAP (Molecule Activity Predictor) Use observed expression changes to suggest functional effects on neighboring molecules Manually set activation states to observe predicted effects on canonical pathways 57
43 Overlay other uploaded data sets, analyses OVERLAY button -> Analyses, Data sets, and Lists Select other analyses from projects Useful for comparisons 58
44 Analyzing Results Upstream Regulators 59
45 Upstream Regulators and Networks What transcription factors likely led to observed gene expression changes? What de novo pathways can be created based on predicted upstream regulator interactions?
46 IPA Upstream Regulator Analysis Identify important signaling molecules for a more complete regulatory picture Quickly filter by molecule type Filter by biological context Generate regulators-targets Network to identify key relationships
47 IPA Upstream Regulator Analysis Use experimentally observed relationships (not predicted binding) between regulators and dataset genes to predict upstream transcriptional regulators. Calculate z-score to predict activation or inhibition of regulators based on relationships with dataset genes and direction of change of dataset genes. MCF7 Cells Treated with Beta-Estradiol. Genes in uploaded data set are colored red and green
48 IPA Upstream Regulator Analysis Directional Effects: Molecule Activity Predictor Examine Expression Relationship Consistency IPA Winter Release 2012
49 IPA Upstream Regulator Analysis Quickly filter by molecule type Filter by biological context Generate regulators-targets Network to identify key relationships
50 Considerations Entities with positive z-scores are known to elicit the same gene expression changes as seen in your data Entities you might want to knock-down to inhibit effects of experiment Entities with negative z-scores are known to elicit the opposite gene expression when active Entities you could add to an experiment to counter effects of experiment Contradictions between z-score direction prediction and measured gene expression could be the result of A discrepancy between protein activity and expression level Lag time between change in gene expression and effect of that expression A regulator with significant z-score but poor p-value could represent a situation where only a few downstream genes in your experimental condition correlate in expression, but many other genes may be expressed in other conditions (or is junk). A regulator with insignificant z-score and significant p-value could represent a situation where the genes in your data are downstream of the regulator, but their expression pattern is unique to your experimental condition (or is junk). 66
51 IPA Upstream Regulator Analysis How might these upstream regulators interact? Quickly filter by molecule type Filter by biological context Generate regulators-targets Network to identify key relationships
52 Mechanistic Networks IPA Mechanistic Networks Goal: To discover plausible sets of connected upstream regulators that can work together to elicit the gene expression changes observed in a dataset How: Take IPA Upstream Regulator results and computationally seek pairs of regulators predicted to affect the expression of a similar set of genes. Repeat to build a network: Upstream Regulator Upstream Transcription Factors IPA Winter Release 2012 Dataset Molecules
53 Mechanistic Networks How might the upstream molecule drive the observed expression changes? Hypothesis generation and visualization Each hypothesis generated indicates the molecules predicted to be in the signaling cascade IPA Winter Release 2012
54 Mechanistic Networks Recommend increasing stringency of criteria in most cases
55 Advanced Analytics Causal Networks Advanced Analytics requires an additional subscription fee
56 Causal Network Analysis Advanced Analytics Alternate method of predicting upstream regulators based on causal relationships and allowing multiple interaction steps to gene expression changes Identify potential novel master-regulators of your gene expression by creating pathways of literature-based relationships Expands predictions to include indirect upstream regulators not in mechanistic networks Causal Networks Master Regulator Genes with differential expression
57 Single- vs. Mechanistic- vs. Causal Networks Leveraging the network to create more upstream regulators Advanced Analytics: Causal Network Analysis Upstream Regulators Causal Network Regulator Dataset Upstream Regulator Upstream Regulators: TFs Mechanistic Network of Upstream Regulators Dataset Molecules
58 Turning on Causal Networks (with Advanced Analytics) 74
59 Advanced Analytics: Causal Network Analysis Beta-estradiol of MCF7 cells at 12 hr. SULT1E1 is top master regulator, but does not appear in upstream regulator table
60 SULT1E1 Causal Network SULT1E1 is an enzyme that converts estrone and estradiol to an inactive form Advanced Analytics: Causal Network Analysis Causal network predicts the absence, inhibition, or saturation of this enzyme in this experiment where estradiol was added exogenously SULT1E1 does not have downstream gene expression relationships and, thus, does not appear in the Upstream Regulator table or Mechanistic Networks Hypothesis: increasing SULT1E1 activity can have an anti-estrogen effect
61 Parameters Advanced Analytics: Causal Network Analysis Only considers edges of unambiguous direction of regulation to downstream genes Edges that cannot be assigned a direction of regulation, including all types of binding edges are excluded Included relationship types activation (A) inhibition (I) expression (E) transcription (T) group/complex membership edges (MB, considered activating) phosphorylation (P) Up to 3 interactions edges from root are considered Expression/Transcription must be last edge type
62 Causal Networks Advanced Analytics: Causal Network Analysis A I A I A A A 2 inhibitory edges 5 activating edges
63 Evaluation Advanced Analytics: Causal Network Analysis Two p-values are calculated Fishers Exact Test of whether there is a greater than expected proportion of downstream data set genes than expected by chance Network bias corrected p-value is a measure of how often a more significant result was seen in 10K iterations of selecting random data sets of genes with similar relationship number. z-score Activation z-score is calculated and represents the bias in gene regulation that predicts whether the upstream regulator exists in an activated or inactivated state z-score represents the number of standard deviations from the mean of a normal distribution of activity edges.
64 Analyzing Results Diseases & Functions (Downstream Effects) 80
65 Downstream Function/Process Analysis How are cellular processes are predicted to be changing based on my gene expression data? What genes are driving these directional changes?
66 A novel approach to visualize and predict biological impact of gene expression changes Downstream Effects Analysis Identify key biological processes influenced by differentially expressed genes Understand whether cellular processes are being driven up or down by correlating observed expression with reported experimental gene effects Each box represents a biological process or disease The size of the box represents gene enrichment The color of the box indicates the predicted increase or decrease
67 Downstream Effect on Bio Function Size of the Square Color by and Scale Toggle to the Bar Chart Click on a Square to Drill Down within that function
68 Ontology Levels Click to See the Specific Genes and Findings
69 Functional Category and Statistical Result Access Findings Prediction Logic Expression Value in Your Dataset
70
71 Functional Analysis (FA) Workflow Goal is understand biology and identify smaller subsets of genes that are of interest Genes related to a particular function can be : sent to a pathway for building and/or overlay analysis saved as a new Data Set and sent to Core Analysis for additional categorization and segmentation
72 Analyzing Results Regulator Effects 89
73 Regulator Effects Hypothesis for how a phenotype, function or disease is regulated in the dataset by activated or inhibited upstream regulators Explain impact of upstream molecules on downstream biology Explain potential mechanism for a phenotype or drug Define drug targets Discover novel (or confirm known) regulator disease/phenotype/function relationships
74 Concept of Functional Network Analysis Upstream Regulator Analysis B A C Functional Network Analysis A B C Targets in the dataset Algorithm Multiple iterations Disease or Function Disease or Function Disease or Function Disease or Function Downstream Effects Analysis 91
75 Customize Regulator Effects to answer your question Default: Genes, RNAs, proteins as regulators vs. Any type of disease or function Recommend decreasing p-value cutoffs to 1.0E-3 or lower in most cases. Recommend setting network size to 1 regulator and 1 function in addition to viewing with no value 93
76 Alternate presets to answer different questions Transcription factors and functions Compound as regulator of functions Minimal regulator to function networks QIAGEN Silicon Valley 94
77 Analyzing Results Networks 95
78 Networks in IPA To show as many interactions between user-specified molecules in a given dataset and how they might work together at the molecular level Highly-interconnected networks are likely to represent significant biological function 96
79 Networks Networks are assembled based on gene/molecule connectivity with other gene/molecules. Assumption: the more connected a gene/molecule, the more influence it has and the more important it is. Networks are assembled using decreasingly connected molecules from your data set. Genes/molecules from the Knowledge Base may be added to the network to fill or join areas lacking connectivity. A maximum of 35, 70, or 140 genes/molecules can comprise a network based on parameter settings. Networks are annotated with high-level functional categories. 97
80 How Networks Are Generated Focus molecules are seeds Focus molecules with the most interactions to other focus molecules are then connected together to form a network Non-focus molecules from the dataset are then added Molecules from the Ingenuity s KB are added Resulting Networks are scored and then sorted based on the score 98
81 Using the information in Networks Keep in mind.. Networks may contain smaller networks of connectivity related to specific functions. It might make sense to subset a network. (What does this mean? Just focus on subportions of the network?) Larger cellular networks may span IPA assembled networks. Merging networks may allow you to visualize these larger networks. Networks should be treated as starter pathways that you then modify based on your biological understanding of the system and the questions that you want to answer. Use the pathway building ( Build button) and Overlay tools to expand on your initial results. 99
82 Getting Help 100
83 Contact Us am-5pm Pacific Time (M-F) QIAGEN Redwood City/Silicon Valley 1700 Seaport Blvd., 3rd Floor Redwood City CA 94063, USA 101
84 Help for IPA For Help and Technical Support contact our Customer Support team by to or by phone to For getting started tutorials and training videos see the Tutorials link on the help menu within IPA To see case studies, application notes, and white papers visit To view our future scientific seminars, and to watch the series archive visit To see how IPA has been used and cited in over 9000 publications visit 102
85 IPA training videos: Search & explore IPA search and explore series videos: The Ingenuity Knowledge Base for IPA Searching and accessing the Knowledge Base Building a pathway: Filtering and growing Building a pathway: Exploring the path of interaction TRmuMVP9E Overlay contextual information Editing a pathway for publication 103
86 IPA training videos: Data analysis IPA data analysis series videos: Data analysis : Part 1 (Data upload) Data analysis : Part 2 (Results interpretation) Comparison analyses Analysis results Statistical calculation Canonical pathways Network Analysis Downstream effects analysis Upstream regulator analysis Human isoforms Molecular toxicology Biomarker filter and comparison analysis MicroRNA target filter 104
87 IPA tutorials Search for genes tutorial Analysis results tutorial Upload and analyze example eata tutorial Upload and analyze your own expression data tutorial Visualize connections among genes tutorial Learn about specialized features Human isoforms view tutorial Transcription factor analysis tutorial Downstream effects analysis tutorial 105
88 Comparing Core Analyses 106
89 Comparison Analysis Multiple Comparison Time course Does response Multiple Platforms and Data Integration Systems biology Combining SNP, CNA, mrna, microrna, proteomics, etc. Analysis Comparisons work best with Canonical Pathways, Upstream Regulators, and Disease and Functions Regulator Effects and Mechanistic Networks are similarly difficult to compare because these networks are created in the context of the single analysis. To compare these networks across analyses, open, view the network, and then use the OVERLAY -> Data Sets, Analyses, and Lists to overlay colored representation of gene changes. 107
90 Comparing Analyses Introduction to QIAGEN Ingenuity & IPA
91 Selecting Analyses to Compare 109
92 Analyzing Comparison Results Tabs at top navigate to the analysis-type of interest Heatmap can be generated using different calculation methods Heatmap can be based on different metrics depending on analysistype. 110
93 Analyzing Comparison Results Selecting heatmap element displays pathway or network with data-values overlay and MAP coloring (if applicable) 111
94 Analyzing Comparison Results Clicking GENE HEATMAP button displays gene expression values across observations 112
95 Micro-RNA Target Filter 113
96 Workflow for mirna Target Filter Filter mirna differential expression data set (if corresponding mrna differential expression data, filter as well) File -> New -> Filtered Data Set Start microrna Target Filter File -> New -> mirna Target Filter Open mirna filtered data set Using funnel in column headers, filter mapping based on information type/confidence Add annotation columns, if desired, by clicking the plus sign in column header and filter as desired
97 Workflow for mirna Target Filter If corresponding mrna, click ADD/REPLACE MRNA DATA SET to filter mrna mappings to genes in the mrna expression data set Click EXPRESSION PAIRING to pair the expression between the mirna and mrna Click the funnel in the column header of the expression pairing column to filter for the mirna-mrna pairing desired Click to summary tab to view a summary of mirna-mrna mappings For further analysis, select one or more mirnas from the summary tab and add the mirna and targets to a new pathway and perform overlays for interpretation of functions, pathways, drug targets, etc.
98 mirna data mirna Target Filter Molecule Type Pathways (Cancer/ Growth) mrna? 88 data points 13,690 targets 1,090 targets 333 targets 39 targets 32 targets Use Pathway tools to build hypothesis for microrna target association to melanoma metastasis.
99 microrna Content Details: Ingenuity Knowledge Base IPA has high-quality microrna-related findings (including both experimentally validated and predicted interactions) TarBase: experimentally validated microrna-mrna interactions Target Scan: predicted microrna-mrna interactions (low-confidence interactions were excluded) mirecords: experimentally validated human, rat, and mouse microrna-mrna interactions Literature Findings: microrna-related findings manually curated from published literature by scientific experts and structured into the Ingenuity Knowledge Base Single source for microrna content plus related biology enables biologically relevant target prioritization in minutes vs. weeks Extensive human, mouse, and rat coverage
100 mirna Naming and Mapping For Searching, IPA Supports: mirbase Identifiers Entrez Gene Symbols and Entrez Gene IDs Other synonyms used in the literature For Data Upload, IPA Supports: mirbase Identifiers for mature mirnas mirbase Accession Numbers (format MIMAT######) are preferred. These are stable identifiers. mirbase Name Identifiers (format: mmu-mir-###) are allowed. Since some mirna arrays provide annotations only with the name, we have provided mappings for them. These change over time so use MIMAT instead if available. Precursor identifiers are NOT supported Entrez Gene IDs (not Entrez Gene Symbols) HUGO gene symbols (human only)
101 mirna Naming and Mapping Mapping microrna IDs in IPA during Data Upload A given ID can only map to a single node in IPA mirna identifiers each map to either a group node or a locus-specific node: mirna identifiers that correspond to mature mirnas that do NOT appear in a group (ie, they arise from only one known precursor, and that precursor has no more than one known Entrez Gene ID/locus) are mapped to a locusspecific node. mirna identifiers corresponding to mature mirnas that ARE in a group map to that group. No mirna maps to more than one group node in IPA.
102 Working with mirna Groups Mature mirnas may arise from multiple precursors: A given mature form may arise from multiple distinct mirna precursors. A given precursor may arise from multiple distinct loci. Groups are created in the knowledge base to represent mature mirna s that may arise from multiple precursors or multiple loci. When authors refer to a particular mature mirna form that may arise from multiple distinct precursors and/or multiple genetic loci, the finding is mapped to a group concept that contains all potential parent precursors. Groups might have different network connections compared to the individual members of the group. Findings might be mapped to the individual members or to the group, depending on information provided by the author. Grow functionality does not look inside the groups. Additional steps will ensure that all members of group will be considered when applying Grow
103 Expanding groups prior to Growing will provide information on known molecular interactions for all members of the group.
104 Biomarker Filter 126
105 Introduction to Biomarker Analysis IPA-Biomarker analysis filters/refines candidate lists based on biological criteria such as association to a disease, normal presence in a fluid, or normal expression in a tissue/cell type/cell line and/or clinical usage. Species Tissues and Cell Lines Biofluids Diseases Clinical Biomarkers The output is a refined list of candidates It does not calculate functions, Canonical Pathways, or networks Different observations or datasets can be compared using the Comparison Biomarker Analysis Calculates unique and common molecules 127
106 Biomarker Filters The Biomarker Filter capability rapidly priorities biomarker candidates based on biological characteristics and clinical usage. Clinical Usage (Biomarkers): Identify biomarkers by their specific application, including markers for Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis, Disease Progression, markers of Drug Efficacy and Safety, and Patient Response to Therapy 128
107 Statistics in IPA
108 How the Fisher s Exact Test is Calculated Is the proportion of genes in my sample mapping to a gene set (those that are significant) similar to the proportion of all measureable genes (reference set) that map in the gene set? If the proportions are similar, there is no biological effect
109 Mapping Colorectal Cancer Expression Data to the Function Neoplasia 13,101 genes on chip 260 Filter for genes that change expression Sample 747 expressionsignificant genes IPA Map to neoplasia 260/747= genes map to neoplasia 3005/13,101= Are the proportions that map to neoplasia significantly different between the chip (reference set) and the sample? Do not map to neoplasia 487/747= 0.652
110 Calculating the Fisher s Exact Test A 2x2 contingency table is created based on the total population, the sample, and how many genes map to the function/pathway. This table is used to calculate the Fisher s Exact Test Neoplasia Not Neoplasia In Sample k n - k n Not in Sample m - k N + k - n - m N - n m N - m N m= Total that map to function/pathway N= Total k= Number that map to function/pathway in sample n= Total sample
111 Calculating the Fisher s Exact Test Numbers based on the colorectal cancer data mapping to neoplasia Neoplasia Not Neoplasia In Sample Not in Sample = Total that map to neoplasia on chip = Total on chip 260 = Number that map to neoplasia in sample 747 = Total sample Fisher s Exact Test p-value = 2.13 E-14
112 What Can We Say About Our Colorectal Cancer Data Set And Neoplasia? We can conclude that the proportion, or over representation, of genes mapping to neoplasia is not likely the result of sampling (and is likely an effect of the disease)
113 How Do I Choose The Reference Set? If you are using a standard vendor platform supported by IPA, then that platform should be selected as your reference set. If you do not know the platform or the data were taken from different platforms, select a reference set that best estimates the entire population you evaluated. For gene expression data, select the Ingenuity Knowledge Base (genes only) This setting uses all function- and pathway-eligible genes in the knowledge base. For metabolomics, select the Ingenuity Knowledge Base (endogenous chemicals only) You have the option to having your uploaded data set used as the reference set (User Data Set)
114 What About TaqMan or Similar Focus Array? Low density arrays are problematic because the genes that are being measured are usually not randomly chosen to start with, but are typically selected based on a priori function or pathway knowledge Let s assume a inflammatory cytokine array If you select the Ingenuity Knowledge Base as your reference, your p-values for inflammation functions and pathways will be artificially low (significant) because the array was heavily biased for these genes. If you upload every gene on the array, and select the User Data Set reference option, your p-values are statistically accurate, but inflammatory functions and pathways may not appear significant because the likelihood of having a random sample with similar proportions to inflammation processes is extremely high.
115 Multiple Testing Correction Benjamini-Hochberg method of multiple testing correction Based on the Fisher s exact test p-value Calculates false discovery Rate Threshold indicates the fraction of false positives among significant functions % (1/20) may be a false positive
116 Which p-value Calculation Should I Use? What is the significance of function X in relation to my dataset? Use Fisher s Exact test result What are all significant functions within this dataset? Use Benjamini-Hochberg multiple testing correction
117 z-scores and Normal Distribution A set of genes chosen at random should be about equally likely to have an increasing or decreasing effect, thus, about 50% each direction, or a z=0. A z-score represents the nonrandomness of directionality within a gene set
118 Activation z-score TR Every TR is analyzed Literature-based effect TR has on downstream genes Differential Gene Expression (Uploaded Data) Predicted activation state of TR: 1: activated (correlated), -1: inhibited (anti-correlated) = 4 6 = 2.04 z-score is statistical measure of correlation between relationship direction and gene expression. z-score > 2 or < -2 is considered significant Actual z-score can weighted by relationship, relationship bias, data bias
119 Downstream Effect z-score Differential Gene Expression (Uploaded Data) Literature-based effect genes have on process or function Bio Process/Function Predicted Effect- 1: Increasing (correlated), -1: inhibited (anti-correlated) = 1 5 =.447 z-score is statistical measure of correlation between relationship direction and gene expression. z-score > 2 or < -2 is considered significant Actual z-score is weighted by relationship, relationship bias, data bias
Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA )
 ProductProfile Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA ) For the analysis and interpretation of omics data IPA is a web-based software application for the analysis, integration, and interpretation of data derived
ProductProfile Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA ) For the analysis and interpretation of omics data IPA is a web-based software application for the analysis, integration, and interpretation of data derived
Analyzing microrna Data and Integrating mirna with Gene Expression Data in Partek Genomics Suite 6.6
 Analyzing microrna Data and Integrating mirna with Gene Expression Data in Partek Genomics Suite 6.6 Overview This tutorial outlines how microrna data can be analyzed within Partek Genomics Suite. Additionally,
Analyzing microrna Data and Integrating mirna with Gene Expression Data in Partek Genomics Suite 6.6 Overview This tutorial outlines how microrna data can be analyzed within Partek Genomics Suite. Additionally,
Tutorial for proteome data analysis using the Perseus software platform
 Tutorial for proteome data analysis using the Perseus software platform Laboratory of Mass Spectrometry, LNBio, CNPEM Tutorial version 1.0, January 2014. Note: This tutorial was written based on the information
Tutorial for proteome data analysis using the Perseus software platform Laboratory of Mass Spectrometry, LNBio, CNPEM Tutorial version 1.0, January 2014. Note: This tutorial was written based on the information
Frequently Asked Questions Next Generation Sequencing
 Frequently Asked Questions Next Generation Sequencing Import These Frequently Asked Questions for Next Generation Sequencing are some of the more common questions our customers ask. Questions are divided
Frequently Asked Questions Next Generation Sequencing Import These Frequently Asked Questions for Next Generation Sequencing are some of the more common questions our customers ask. Questions are divided
Guide for Data Visualization and Analysis using ACSN
 Guide for Data Visualization and Analysis using ACSN ACSN contains the NaviCell tool box, the intuitive and user- friendly environment for data visualization and analysis. The tool is accessible from the
Guide for Data Visualization and Analysis using ACSN ACSN contains the NaviCell tool box, the intuitive and user- friendly environment for data visualization and analysis. The tool is accessible from the
Understanding West Nile Virus Infection
 Understanding West Nile Virus Infection The QIAGEN Bioinformatics Solution: Biomedical Genomics Workbench (BXWB) + Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) Functional Genomics & Predictive Medicine, May 21-22,
Understanding West Nile Virus Infection The QIAGEN Bioinformatics Solution: Biomedical Genomics Workbench (BXWB) + Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) Functional Genomics & Predictive Medicine, May 21-22,
How to create and interpret the predictive analysis of a compound
 How to create and interpret the predictive analysis of a compound Platform with suite of tools Predict & understand biological effects of small molecules & compounds Predict targets and metabolites, potential
How to create and interpret the predictive analysis of a compound Platform with suite of tools Predict & understand biological effects of small molecules & compounds Predict targets and metabolites, potential
ProteinQuest user guide
 ProteinQuest user guide 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 With ProteinQuest you can... 3 1.2 ProteinQuest basic version 4 1.3 ProteinQuest extended version... 5 2. ProteinQuest dictionaries... 6 3. Directions for
ProteinQuest user guide 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 With ProteinQuest you can... 3 1.2 ProteinQuest basic version 4 1.3 ProteinQuest extended version... 5 2. ProteinQuest dictionaries... 6 3. Directions for
Analyzing the Effect of Treatment and Time on Gene Expression in Partek Genomics Suite (PGS) 6.6: A Breast Cancer Study
 Analyzing the Effect of Treatment and Time on Gene Expression in Partek Genomics Suite (PGS) 6.6: A Breast Cancer Study The data for this study is taken from experiment GSE848 from the Gene Expression
Analyzing the Effect of Treatment and Time on Gene Expression in Partek Genomics Suite (PGS) 6.6: A Breast Cancer Study The data for this study is taken from experiment GSE848 from the Gene Expression
What s New in Pathway Studio Web 11.1
 1 1 What s New in Pathway Studio Web 11.1 Elseiver is pleased to announce the release of Pathway Studio Web 11.1 for all database subscriptions (Mammal, Mammal+ChemEffect+DiseaseFx, Plant). This release
1 1 What s New in Pathway Studio Web 11.1 Elseiver is pleased to announce the release of Pathway Studio Web 11.1 for all database subscriptions (Mammal, Mammal+ChemEffect+DiseaseFx, Plant). This release
Using Illumina BaseSpace Apps to Analyze RNA Sequencing Data
 Using Illumina BaseSpace Apps to Analyze RNA Sequencing Data The Illumina TopHat Alignment and Cufflinks Assembly and Differential Expression apps make RNA data analysis accessible to any user, regardless
Using Illumina BaseSpace Apps to Analyze RNA Sequencing Data The Illumina TopHat Alignment and Cufflinks Assembly and Differential Expression apps make RNA data analysis accessible to any user, regardless
Microarray Data Analysis. A step by step analysis using BRB-Array Tools
 Microarray Data Analysis A step by step analysis using BRB-Array Tools 1 EXAMINATION OF DIFFERENTIAL GENE EXPRESSION (1) Objective: to find genes whose expression is changed before and after chemotherapy.
Microarray Data Analysis A step by step analysis using BRB-Array Tools 1 EXAMINATION OF DIFFERENTIAL GENE EXPRESSION (1) Objective: to find genes whose expression is changed before and after chemotherapy.
BBSRC TECHNOLOGY STRATEGY: TECHNOLOGIES NEEDED BY RESEARCH KNOWLEDGE PROVIDERS
 BBSRC TECHNOLOGY STRATEGY: TECHNOLOGIES NEEDED BY RESEARCH KNOWLEDGE PROVIDERS 1. The Technology Strategy sets out six areas where technological developments are required to push the frontiers of knowledge
BBSRC TECHNOLOGY STRATEGY: TECHNOLOGIES NEEDED BY RESEARCH KNOWLEDGE PROVIDERS 1. The Technology Strategy sets out six areas where technological developments are required to push the frontiers of knowledge
Microsoft Excel 2010 Part 3: Advanced Excel
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Excel 2010 Part 3: Advanced Excel Winter 2015, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Sorting Data...2 Sorting
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Excel 2010 Part 3: Advanced Excel Winter 2015, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Sorting Data...2 Sorting
Hierarchical Clustering Analysis
 Hierarchical Clustering Analysis What is Hierarchical Clustering? Hierarchical clustering is used to group similar objects into clusters. In the beginning, each row and/or column is considered a cluster.
Hierarchical Clustering Analysis What is Hierarchical Clustering? Hierarchical clustering is used to group similar objects into clusters. In the beginning, each row and/or column is considered a cluster.
AGILENT S BIOINFORMATICS ANALYSIS SOFTWARE
 ACCELERATING PROGRESS IS IN OUR GENES AGILENT S BIOINFORMATICS ANALYSIS SOFTWARE GENESPRING GENE EXPRESSION (GX) MASS PROFILER PROFESSIONAL (MPP) PATHWAY ARCHITECT (PA) See Deeper. Reach Further. BIOINFORMATICS
ACCELERATING PROGRESS IS IN OUR GENES AGILENT S BIOINFORMATICS ANALYSIS SOFTWARE GENESPRING GENE EXPRESSION (GX) MASS PROFILER PROFESSIONAL (MPP) PATHWAY ARCHITECT (PA) See Deeper. Reach Further. BIOINFORMATICS
CNV Univariate Analysis Tutorial
 CNV Univariate Analysis Tutorial Release 8.1 Golden Helix, Inc. March 18, 2014 Contents 1. Overview 2 2. CNAM Optimal Segmenting 4 A. Performing CNAM Optimal Segmenting..................................
CNV Univariate Analysis Tutorial Release 8.1 Golden Helix, Inc. March 18, 2014 Contents 1. Overview 2 2. CNAM Optimal Segmenting 4 A. Performing CNAM Optimal Segmenting..................................
Step by Step Guide to Importing Genetic Data into JMP Genomics
 Step by Step Guide to Importing Genetic Data into JMP Genomics Page 1 Introduction Data for genetic analyses can exist in a variety of formats. Before this data can be analyzed it must imported into one
Step by Step Guide to Importing Genetic Data into JMP Genomics Page 1 Introduction Data for genetic analyses can exist in a variety of formats. Before this data can be analyzed it must imported into one
Guide to Building Pathways in Mammal using Pathway Studio Web
 Guide to Building Pathways in Mammal using Pathway Studio Web Pathway Studio Web Document Version 1.2 1 The ResNet Mammal database contains a vast amount of information derived from Elsevier s large collection
Guide to Building Pathways in Mammal using Pathway Studio Web Pathway Studio Web Document Version 1.2 1 The ResNet Mammal database contains a vast amount of information derived from Elsevier s large collection
Analysis of ChIP-seq data in Galaxy
 Analysis of ChIP-seq data in Galaxy November, 2012 Local copy: https://galaxy.wi.mit.edu/ Joint project between BaRC and IT Main site: http://main.g2.bx.psu.edu/ 1 Font Conventions Bold and blue refers
Analysis of ChIP-seq data in Galaxy November, 2012 Local copy: https://galaxy.wi.mit.edu/ Joint project between BaRC and IT Main site: http://main.g2.bx.psu.edu/ 1 Font Conventions Bold and blue refers
> Semantic Web Use Cases and Case Studies
 > Semantic Web Use Cases and Case Studies Case Study: Applied Semantic Knowledgebase for Detection of Patients at Risk of Organ Failure through Immune Rejection Robert Stanley 1, Bruce McManus 2, Raymond
> Semantic Web Use Cases and Case Studies Case Study: Applied Semantic Knowledgebase for Detection of Patients at Risk of Organ Failure through Immune Rejection Robert Stanley 1, Bruce McManus 2, Raymond
Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation
 Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osterthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation Bering Limited Report generated on September 19, 2014 Contents 1 Dataset summary 2 1.1 Project
Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osterthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation Bering Limited Report generated on September 19, 2014 Contents 1 Dataset summary 2 1.1 Project
DeCyder Extended Data Analysis module Version 1.0
 GE Healthcare DeCyder Extended Data Analysis module Version 1.0 Module for DeCyder 2D version 6.5 User Manual Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction... 7 1.2 The DeCyder EDA User Manual... 9 1.3 Getting
GE Healthcare DeCyder Extended Data Analysis module Version 1.0 Module for DeCyder 2D version 6.5 User Manual Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction... 7 1.2 The DeCyder EDA User Manual... 9 1.3 Getting
Protein Protein Interaction Networks
 Functional Pattern Mining from Genome Scale Protein Protein Interaction Networks Young-Rae Cho, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University it My Definition of Bioinformatics
Functional Pattern Mining from Genome Scale Protein Protein Interaction Networks Young-Rae Cho, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University it My Definition of Bioinformatics
Step-by-Step Guide to Basic Expression Analysis and Normalization
 Step-by-Step Guide to Basic Expression Analysis and Normalization Page 1 Introduction This document shows you how to perform a basic analysis and normalization of your data. A full review of this document
Step-by-Step Guide to Basic Expression Analysis and Normalization Page 1 Introduction This document shows you how to perform a basic analysis and normalization of your data. A full review of this document
Exiqon Array Software Manual. Quick guide to data extraction from mircury LNA microrna Arrays
 Exiqon Array Software Manual Quick guide to data extraction from mircury LNA microrna Arrays March 2010 Table of contents Introduction Overview...................................................... 3 ImaGene
Exiqon Array Software Manual Quick guide to data extraction from mircury LNA microrna Arrays March 2010 Table of contents Introduction Overview...................................................... 3 ImaGene
Choices, choices, choices... Which sequence database? Which modifications? What mass tolerance?
 Optimization 1 Choices, choices, choices... Which sequence database? Which modifications? What mass tolerance? Where to begin? 2 Sequence Databases Swiss-prot MSDB, NCBI nr dbest Species specific ORFS
Optimization 1 Choices, choices, choices... Which sequence database? Which modifications? What mass tolerance? Where to begin? 2 Sequence Databases Swiss-prot MSDB, NCBI nr dbest Species specific ORFS
MicroStrategy Tips and Tricks
 MicroStrategy Tips and Tricks 1. If a prompt is required, it will have a red (Required) note. 2. If a prompt has been answered, it will have a green flag on the left-hand side of the screen. 3. You can
MicroStrategy Tips and Tricks 1. If a prompt is required, it will have a red (Required) note. 2. If a prompt has been answered, it will have a green flag on the left-hand side of the screen. 3. You can
School of Nursing. Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD
 Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD What we will cover during this webcast: Briefly discuss the approaches introduced in the paper: Genome Sequencing Genome Wide Association Studies Epigenomics Gene Expression
Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD What we will cover during this webcast: Briefly discuss the approaches introduced in the paper: Genome Sequencing Genome Wide Association Studies Epigenomics Gene Expression
InSyBio BioNets: Utmost efficiency in gene expression data and biological networks analysis
 InSyBio BioNets: Utmost efficiency in gene expression data and biological networks analysis WHITE PAPER By InSyBio Ltd Konstantinos Theofilatos Bioinformatician, PhD InSyBio Technical Sales Manager August
InSyBio BioNets: Utmost efficiency in gene expression data and biological networks analysis WHITE PAPER By InSyBio Ltd Konstantinos Theofilatos Bioinformatician, PhD InSyBio Technical Sales Manager August
Data Visualization. Brief Overview of ArcMap
 Data Visualization Prepared by Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., P.E., Srikanth Koka and Lauren Walker Department of Civil Engineering September 13, 2006 Contents: Brief Overview of ArcMap Goals of the Exercise
Data Visualization Prepared by Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., P.E., Srikanth Koka and Lauren Walker Department of Civil Engineering September 13, 2006 Contents: Brief Overview of ArcMap Goals of the Exercise
Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping WHITE PAPER
 Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping WHITE PAPER JMP Genomics Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping Introduction JMP Genomics offers several tools for the creation of linkage maps
Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping WHITE PAPER JMP Genomics Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping Introduction JMP Genomics offers several tools for the creation of linkage maps
Affiliated Provider Billing/Coding
 Affiliated Provider Billing/Coding RADIOLOGY BILLING Table of Contents Accessing icentra...2 Opening PowerChart...2 Finding and Selecting a Patient...2 Selecting a patient on the Patient List:...2 Searching
Affiliated Provider Billing/Coding RADIOLOGY BILLING Table of Contents Accessing icentra...2 Opening PowerChart...2 Finding and Selecting a Patient...2 Selecting a patient on the Patient List:...2 Searching
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2010
 Scientific Graphing in Excel 2010 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2010 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
Core Facility Genomics
 Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Outline. MicroRNA Bioinformatics. microrna biogenesis. short non-coding RNAs not considered in this lecture. ! Introduction
 Outline MicroRNA Bioinformatics Rickard Sandberg Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology (CMB) Karolinska Institutet! Introduction! microrna target site prediction! Useful resources 2 short non-coding RNAs
Outline MicroRNA Bioinformatics Rickard Sandberg Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology (CMB) Karolinska Institutet! Introduction! microrna target site prediction! Useful resources 2 short non-coding RNAs
SAP Business Intelligence ( BI ) Financial and Budget Reporting. 7.0 Edition. (Best Seller At Least 43 copies Sold)
 SAP Business Intelligence ( BI ) Financial and Budget Reporting 7.0 Edition (Best Seller At Least 43 copies Sold) November 2011 Table of Contents Log In... 3 Initial Variable Screen... 5 Multiple / Single
SAP Business Intelligence ( BI ) Financial and Budget Reporting 7.0 Edition (Best Seller At Least 43 copies Sold) November 2011 Table of Contents Log In... 3 Initial Variable Screen... 5 Multiple / Single
MultiExperiment Viewer Quickstart Guide
 MultiExperiment Viewer Quickstart Guide Table of Contents: I. Preface - 2 II. Installing MeV - 2 III. Opening a Data Set - 2 IV. Filtering - 6 V. Clustering a. HCL - 8 b. K-means - 11 VI. Modules a. T-test
MultiExperiment Viewer Quickstart Guide Table of Contents: I. Preface - 2 II. Installing MeV - 2 III. Opening a Data Set - 2 IV. Filtering - 6 V. Clustering a. HCL - 8 b. K-means - 11 VI. Modules a. T-test
MicroStrategy Desktop
 MicroStrategy Desktop Quick Start Guide MicroStrategy Desktop is designed to enable business professionals like you to explore data, simply and without needing direct support from IT. 1 Import data from
MicroStrategy Desktop Quick Start Guide MicroStrategy Desktop is designed to enable business professionals like you to explore data, simply and without needing direct support from IT. 1 Import data from
Lesson 3 - Processing a Multi-Layer Yield History. Exercise 3-4
 Lesson 3 - Processing a Multi-Layer Yield History Exercise 3-4 Objective: Develop yield-based management zones. 1. File-Open Project_3-3.map. 2. Double click the Average Yield surface component in the
Lesson 3 - Processing a Multi-Layer Yield History Exercise 3-4 Objective: Develop yield-based management zones. 1. File-Open Project_3-3.map. 2. Double click the Average Yield surface component in the
University of Arkansas Libraries ArcGIS Desktop Tutorial. Section 2: Manipulating Display Parameters in ArcMap. Symbolizing Features and Rasters:
 : Manipulating Display Parameters in ArcMap Symbolizing Features and Rasters: Data sets that are added to ArcMap a default symbology. The user can change the default symbology for their features (point,
: Manipulating Display Parameters in ArcMap Symbolizing Features and Rasters: Data sets that are added to ArcMap a default symbology. The user can change the default symbology for their features (point,
Gephi Tutorial Quick Start
 Gephi Tutorial Welcome to this introduction tutorial. It will guide you to the basic steps of network visualization and manipulation in Gephi. Gephi version 0.7alpha2 was used to do this tutorial. Get
Gephi Tutorial Welcome to this introduction tutorial. It will guide you to the basic steps of network visualization and manipulation in Gephi. Gephi version 0.7alpha2 was used to do this tutorial. Get
User Manual. Transcriptome Analysis Console (TAC) Software. For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. P/N 703150 Rev.
 User Manual Transcriptome Analysis Console (TAC) Software For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. P/N 703150 Rev. 1 Trademarks Affymetrix, Axiom, Command Console, DMET, GeneAtlas,
User Manual Transcriptome Analysis Console (TAC) Software For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. P/N 703150 Rev. 1 Trademarks Affymetrix, Axiom, Command Console, DMET, GeneAtlas,
MultiQuant Software 2.0 for Targeted Protein / Peptide Quantification
 MultiQuant Software 2.0 for Targeted Protein / Peptide Quantification Gold Standard for Quantitative Data Processing Because of the sensitivity, selectivity, speed and throughput at which MRM assays can
MultiQuant Software 2.0 for Targeted Protein / Peptide Quantification Gold Standard for Quantitative Data Processing Because of the sensitivity, selectivity, speed and throughput at which MRM assays can
I. Create the base view with the data you want to measure
 Developing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in Tableau The following tutorial will show you how to create KPIs in Tableau 9. To get started, you will need the following: Tableau version 9 Data: Sample
Developing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in Tableau The following tutorial will show you how to create KPIs in Tableau 9. To get started, you will need the following: Tableau version 9 Data: Sample
QuantStudio 3D AnalysisSuite Software: Relative Quantification
 HELP QuantStudio 3D AnalysisSuite Software: Relative Quantification for use with QuantStudio 3D Digital PCR System and QuantStudio 3D AnalysisSuite Server System Publication Number MAN0009636 Revision
HELP QuantStudio 3D AnalysisSuite Software: Relative Quantification for use with QuantStudio 3D Digital PCR System and QuantStudio 3D AnalysisSuite Server System Publication Number MAN0009636 Revision
Can SAS Enterprise Guide do all of that, with no programming required? Yes, it can.
 SAS Enterprise Guide for Educational Researchers: Data Import to Publication without Programming AnnMaria De Mars, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA ABSTRACT In this workshop, participants
SAS Enterprise Guide for Educational Researchers: Data Import to Publication without Programming AnnMaria De Mars, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA ABSTRACT In this workshop, participants
Two-Way ANOVA tests. I. Definition and Applications...2. II. Two-Way ANOVA prerequisites...2. III. How to use the Two-Way ANOVA tool?...
 Two-Way ANOVA tests Contents at a glance I. Definition and Applications...2 II. Two-Way ANOVA prerequisites...2 III. How to use the Two-Way ANOVA tool?...3 A. Parametric test, assume variances equal....4
Two-Way ANOVA tests Contents at a glance I. Definition and Applications...2 II. Two-Way ANOVA prerequisites...2 III. How to use the Two-Way ANOVA tool?...3 A. Parametric test, assume variances equal....4
Excel 2003: Ringtones Task
 Excel 2003: Ringtones Task 1. Open up a blank spreadsheet 2. Save the spreadsheet to your area and call it Ringtones.xls 3. Add the data as shown here, making sure you keep to the cells as shown Make sure
Excel 2003: Ringtones Task 1. Open up a blank spreadsheet 2. Save the spreadsheet to your area and call it Ringtones.xls 3. Add the data as shown here, making sure you keep to the cells as shown Make sure
Leukemia Drug Pathway Analyzer
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2673689/ Leukemia Drug Pathway Analyzer Description: Extra value: One year of free online updates included with this product There
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2673689/ Leukemia Drug Pathway Analyzer Description: Extra value: One year of free online updates included with this product There
Business Objects 4.1 Quick User Guide
 Business Objects 4.1 Quick User Guide Log into SCEIS Business Objects (BOBJ) 1. https://sceisreporting.sc.gov 2. Choose Windows AD for Authentication. 3. Enter your SCEIS User Name and Password: Home Screen
Business Objects 4.1 Quick User Guide Log into SCEIS Business Objects (BOBJ) 1. https://sceisreporting.sc.gov 2. Choose Windows AD for Authentication. 3. Enter your SCEIS User Name and Password: Home Screen
Modifying Colors and Symbols in ArcMap
 Modifying Colors and Symbols in ArcMap Contents Introduction... 1 Displaying Categorical Data... 3 Creating New Categories... 5 Displaying Numeric Data... 6 Graduated Colors... 6 Graduated Symbols... 9
Modifying Colors and Symbols in ArcMap Contents Introduction... 1 Displaying Categorical Data... 3 Creating New Categories... 5 Displaying Numeric Data... 6 Graduated Colors... 6 Graduated Symbols... 9
Pathway Analysis : An Introduction
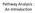 Pathway Analysis : An Introduction Experiments Literature and other KB Data Knowledge Structure in Data through statistics Structure in Knowledge through GO and other Ontologies Gain insight into Data
Pathway Analysis : An Introduction Experiments Literature and other KB Data Knowledge Structure in Data through statistics Structure in Knowledge through GO and other Ontologies Gain insight into Data
Course on Functional Analysis. ::: Gene Set Enrichment Analysis - GSEA -
 Course on Functional Analysis ::: Madrid, June 31st, 2007. Gonzalo Gómez, PhD. [email protected] Bioinformatics Unit CNIO ::: Contents. 1. Introduction. 2. GSEA Software 3. Data Formats 4. Using GSEA 5. GSEA
Course on Functional Analysis ::: Madrid, June 31st, 2007. Gonzalo Gómez, PhD. [email protected] Bioinformatics Unit CNIO ::: Contents. 1. Introduction. 2. GSEA Software 3. Data Formats 4. Using GSEA 5. GSEA
Basic Analysis of Microarray Data
 Basic Analysis of Microarray Data A User Guide and Tutorial Scott A. Ness, Ph.D. Co-Director, Keck-UNM Genomics Resource and Dept. of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology University of New Mexico HSC Tel.
Basic Analysis of Microarray Data A User Guide and Tutorial Scott A. Ness, Ph.D. Co-Director, Keck-UNM Genomics Resource and Dept. of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology University of New Mexico HSC Tel.
EARTHSOFT DNREC. EQuIS Data Processor Tutorial
 EARTHSOFT DNREC EQuIS Data Processor Tutorial Contents 1. THE STANDALONE EQUIS DATA PROCESSOR... 3 1.1 GETTING STARTED... 3 1.2 FORMAT FILE... 4 1.3 UNDERSTANDING THE DNREC IMPORT FORMAT... 5 1.4 REFERENCE
EARTHSOFT DNREC EQuIS Data Processor Tutorial Contents 1. THE STANDALONE EQUIS DATA PROCESSOR... 3 1.1 GETTING STARTED... 3 1.2 FORMAT FILE... 4 1.3 UNDERSTANDING THE DNREC IMPORT FORMAT... 5 1.4 REFERENCE
Lab 11: Budgeting with Excel
 Lab 11: Budgeting with Excel This lab exercise will have you track credit card bills over a period of three months. You will determine those months in which a budget was met for various categories. You
Lab 11: Budgeting with Excel This lab exercise will have you track credit card bills over a period of three months. You will determine those months in which a budget was met for various categories. You
Consistent Assay Performance Across Universal Arrays and Scanners
 Technical Note: Illumina Systems and Software Consistent Assay Performance Across Universal Arrays and Scanners There are multiple Universal Array and scanner options for running Illumina DASL and GoldenGate
Technical Note: Illumina Systems and Software Consistent Assay Performance Across Universal Arrays and Scanners There are multiple Universal Array and scanner options for running Illumina DASL and GoldenGate
Minería de Datos ANALISIS DE UN SET DE DATOS.! Visualization Techniques! Combined Graph! Charts and Pies! Search for specific functions
 Minería de Datos ANALISIS DE UN SET DE DATOS! Visualization Techniques! Combined Graph! Charts and Pies! Search for specific functions Data Mining on the DAG ü When working with large datasets, annotation
Minería de Datos ANALISIS DE UN SET DE DATOS! Visualization Techniques! Combined Graph! Charts and Pies! Search for specific functions Data Mining on the DAG ü When working with large datasets, annotation
G E N OM I C S S E RV I C ES
 GENOMICS SERVICES THE NEW YORK GENOME CENTER NYGC is an independent non-profit implementing advanced genomic research to improve diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases. capabilities. N E X T- G E
GENOMICS SERVICES THE NEW YORK GENOME CENTER NYGC is an independent non-profit implementing advanced genomic research to improve diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases. capabilities. N E X T- G E
ProteinPilot Report for ProteinPilot Software
 ProteinPilot Report for ProteinPilot Software Detailed Analysis of Protein Identification / Quantitation Results Automatically Sean L Seymour, Christie Hunter SCIEX, USA Pow erful mass spectrometers like
ProteinPilot Report for ProteinPilot Software Detailed Analysis of Protein Identification / Quantitation Results Automatically Sean L Seymour, Christie Hunter SCIEX, USA Pow erful mass spectrometers like
Basic Microsoft Excel 2007
 Basic Microsoft Excel 2007 The biggest difference between Excel 2007 and its predecessors is the new layout. All of the old functions are still there (with some new additions), but they are now located
Basic Microsoft Excel 2007 The biggest difference between Excel 2007 and its predecessors is the new layout. All of the old functions are still there (with some new additions), but they are now located
Just the Facts: A Basic Introduction to the Science Underlying NCBI Resources
 1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
Intellect Platform - The Workflow Engine Basic HelpDesk Troubleticket System - A102
 Intellect Platform - The Workflow Engine Basic HelpDesk Troubleticket System - A102 Interneer, Inc. Updated on 2/22/2012 Created by Erika Keresztyen Fahey 2 Workflow - A102 - Basic HelpDesk Ticketing System
Intellect Platform - The Workflow Engine Basic HelpDesk Troubleticket System - A102 Interneer, Inc. Updated on 2/22/2012 Created by Erika Keresztyen Fahey 2 Workflow - A102 - Basic HelpDesk Ticketing System
Data Visualization. Prepared by Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., Srikanth Koka Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University February 2004
 Data Visualization Prepared by Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., Srikanth Koka Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University February 2004 Contents Brief Overview of ArcMap Goals of the Exercise Computer
Data Visualization Prepared by Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., Srikanth Koka Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University February 2004 Contents Brief Overview of ArcMap Goals of the Exercise Computer
Excel 2003 Tutorials - Video File Attributes
 Using Excel Files 18.00 2.73 The Excel Environment 3.20 0.14 Opening Microsoft Excel 2.00 0.12 Opening a new workbook 1.40 0.26 Opening an existing workbook 1.50 0.37 Save a workbook 1.40 0.28 Copy a workbook
Using Excel Files 18.00 2.73 The Excel Environment 3.20 0.14 Opening Microsoft Excel 2.00 0.12 Opening a new workbook 1.40 0.26 Opening an existing workbook 1.50 0.37 Save a workbook 1.40 0.28 Copy a workbook
STATISTICA Formula Guide: Logistic Regression. Table of Contents
 : Table of Contents... 1 Overview of Model... 1 Dispersion... 2 Parameterization... 3 Sigma-Restricted Model... 3 Overparameterized Model... 4 Reference Coding... 4 Model Summary (Summary Tab)... 5 Summary
: Table of Contents... 1 Overview of Model... 1 Dispersion... 2 Parameterization... 3 Sigma-Restricted Model... 3 Overparameterized Model... 4 Reference Coding... 4 Model Summary (Summary Tab)... 5 Summary
A leader in the development and application of information technology to prevent and treat disease.
 A leader in the development and application of information technology to prevent and treat disease. About MOLECULAR HEALTH Molecular Health was founded in 2004 with the vision of changing healthcare. Today
A leader in the development and application of information technology to prevent and treat disease. About MOLECULAR HEALTH Molecular Health was founded in 2004 with the vision of changing healthcare. Today
Online Sharing User Manual
 Online Sharing User Manual June 13, 2007 If discrepancies between this document and Online Sharing are discovered, please contact [email protected]. Copyrights and Proprietary Notices The information
Online Sharing User Manual June 13, 2007 If discrepancies between this document and Online Sharing are discovered, please contact [email protected]. Copyrights and Proprietary Notices The information
Pulling a Random Sample from a MAXQDA Dataset
 In this guide you will learn how to pull a random sample from a MAXQDA dataset, using the random cell function in Excel. In this process you will learn how to export and re-import variables from MAXQDA.
In this guide you will learn how to pull a random sample from a MAXQDA dataset, using the random cell function in Excel. In this process you will learn how to export and re-import variables from MAXQDA.
Discovery and Quantification of RNA with RNASeq Roderic Guigó Serra Centre de Regulació Genòmica (CRG) [email protected]
 Bioinformatique et Séquençage Haut Débit, Discovery and Quantification of RNA with RNASeq Roderic Guigó Serra Centre de Regulació Genòmica (CRG) [email protected] 1 RNA Transcription to RNA and subsequent
Bioinformatique et Séquençage Haut Débit, Discovery and Quantification of RNA with RNASeq Roderic Guigó Serra Centre de Regulació Genòmica (CRG) [email protected] 1 RNA Transcription to RNA and subsequent
Dr Alexander Henzing
 Horizon 2020 Health, Demographic Change & Wellbeing EU funding, research and collaboration opportunities for 2016/17 Innovate UK funding opportunities in omics, bridging health and life sciences Dr Alexander
Horizon 2020 Health, Demographic Change & Wellbeing EU funding, research and collaboration opportunities for 2016/17 Innovate UK funding opportunities in omics, bridging health and life sciences Dr Alexander
Cluster software and Java TreeView
 Cluster software and Java TreeView To download the software: http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster/software.htm http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster/manual/treeview.html Cluster 3.0
Cluster software and Java TreeView To download the software: http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster/software.htm http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster/manual/treeview.html Cluster 3.0
Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction to Access
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction to Access Fall 2014, Version 1.2 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Starting Access...3
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction to Access Fall 2014, Version 1.2 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Starting Access...3
From Data to Foresight:
 Laura Haas, IBM Fellow IBM Research - Almaden From Data to Foresight: Leveraging Data and Analytics for Materials Research 1 2011 IBM Corporation The road from data to foresight is long? Consumer Reports
Laura Haas, IBM Fellow IBM Research - Almaden From Data to Foresight: Leveraging Data and Analytics for Materials Research 1 2011 IBM Corporation The road from data to foresight is long? Consumer Reports
岑 祥 股 份 有 限 公 司 技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803
 技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803 Overview of presentation Basic Biology of RNA interference Application of sirna for gene function? How to study mirna? How to deliver sirna and mirna? New prospects on RNAi research
技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803 Overview of presentation Basic Biology of RNA interference Application of sirna for gene function? How to study mirna? How to deliver sirna and mirna? New prospects on RNAi research
Heat Map Explorer Getting Started Guide
 You have made a smart decision in choosing Lab Escape s Heat Map Explorer. Over the next 30 minutes this guide will show you how to analyze your data visually. Your investment in learning to leverage heat
You have made a smart decision in choosing Lab Escape s Heat Map Explorer. Over the next 30 minutes this guide will show you how to analyze your data visually. Your investment in learning to leverage heat
Comparative genomic hybridization Because arrays are more than just a tool for expression analysis
 Microarray Data Analysis Workshop MedVetNet Workshop, DTU 2008 Comparative genomic hybridization Because arrays are more than just a tool for expression analysis Carsten Friis ( with several slides from
Microarray Data Analysis Workshop MedVetNet Workshop, DTU 2008 Comparative genomic hybridization Because arrays are more than just a tool for expression analysis Carsten Friis ( with several slides from
Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 30 UTRs by comparison of several mammals
 Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 30 UTRs by comparison of several mammals Xiaohui Xie 1, Jun Lu 1, E. J. Kulbokas 1, Todd R. Golub 1, Vamsi Mootha 1, Kerstin Lindblad-Toh
Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 30 UTRs by comparison of several mammals Xiaohui Xie 1, Jun Lu 1, E. J. Kulbokas 1, Todd R. Golub 1, Vamsi Mootha 1, Kerstin Lindblad-Toh
Discover more, discover faster. High performance, flexible NLP-based text mining for life sciences
 Discover more, discover faster. High performance, flexible NLP-based text mining for life sciences It s not information overload, it s filter failure. Clay Shirky Life Sciences organizations face the challenge
Discover more, discover faster. High performance, flexible NLP-based text mining for life sciences It s not information overload, it s filter failure. Clay Shirky Life Sciences organizations face the challenge
Visualization with Excel Tools and Microsoft Azure
 Visualization with Excel Tools and Microsoft Azure Introduction Power Query and Power Map are add-ins that are available as free downloads from Microsoft to enhance the data access and data visualization
Visualization with Excel Tools and Microsoft Azure Introduction Power Query and Power Map are add-ins that are available as free downloads from Microsoft to enhance the data access and data visualization
Sage Accpac ERP 5.6A. CRM Analytics for SageCRM I User Guide
 Sage Accpac ERP 5.6A CRM Analytics for SageCRM I User Guide 2009 Sage Software, Inc. All rights reserved. Sage, the Sage logos, and all SageCRM product and service names mentioned herein are registered
Sage Accpac ERP 5.6A CRM Analytics for SageCRM I User Guide 2009 Sage Software, Inc. All rights reserved. Sage, the Sage logos, and all SageCRM product and service names mentioned herein are registered
Excel 2007 - Using Pivot Tables
 Overview A PivotTable report is an interactive table that allows you to quickly group and summarise information from a data source. You can rearrange (or pivot) the table to display different perspectives
Overview A PivotTable report is an interactive table that allows you to quickly group and summarise information from a data source. You can rearrange (or pivot) the table to display different perspectives
ReceivablesVision SM Getting Started Guide
 ReceivablesVision SM Getting Started Guide March 2013 Transaction Services ReceivablesVision Quick Start Guide Table of Contents Table of Contents Accessing ReceivablesVision SM...2 The Login Screen...
ReceivablesVision SM Getting Started Guide March 2013 Transaction Services ReceivablesVision Quick Start Guide Table of Contents Table of Contents Accessing ReceivablesVision SM...2 The Login Screen...
Excel 2007 Basic knowledge
 Ribbon menu The Ribbon menu system with tabs for various Excel commands. This Ribbon system replaces the traditional menus used with Excel 2003. Above the Ribbon in the upper-left corner is the Microsoft
Ribbon menu The Ribbon menu system with tabs for various Excel commands. This Ribbon system replaces the traditional menus used with Excel 2003. Above the Ribbon in the upper-left corner is the Microsoft
Gene Expression Macro Version 1.1
 Gene Expression Macro Version 1.1 Instructions Rev B 1 Bio-Rad Gene Expression Macro Users Guide 2004 Bio-Rad Laboratories Table of Contents: Introduction..................................... 3 Opening
Gene Expression Macro Version 1.1 Instructions Rev B 1 Bio-Rad Gene Expression Macro Users Guide 2004 Bio-Rad Laboratories Table of Contents: Introduction..................................... 3 Opening
Analysis of Illumina Gene Expression Microarray Data
 Analysis of Illumina Gene Expression Microarray Data Asta Laiho, Msc. Tech. Bioinformatics research engineer The Finnish DNA Microarray Centre Turku Centre for Biotechnology, Finland The Finnish DNA Microarray
Analysis of Illumina Gene Expression Microarray Data Asta Laiho, Msc. Tech. Bioinformatics research engineer The Finnish DNA Microarray Centre Turku Centre for Biotechnology, Finland The Finnish DNA Microarray
MyOra 3.0. User Guide. SQL Tool for Oracle. Jayam Systems, LLC
 MyOra 3.0 SQL Tool for Oracle User Guide Jayam Systems, LLC Contents Features... 4 Connecting to the Database... 5 Login... 5 Login History... 6 Connection Indicator... 6 Closing the Connection... 7 SQL
MyOra 3.0 SQL Tool for Oracle User Guide Jayam Systems, LLC Contents Features... 4 Connecting to the Database... 5 Login... 5 Login History... 6 Connection Indicator... 6 Closing the Connection... 7 SQL
Microsoft Office System Tip Sheet
 Experience the 2007 Microsoft Office System The 2007 Microsoft Office system includes programs, servers, services, and solutions designed to work together to help you succeed. New features in the 2007
Experience the 2007 Microsoft Office System The 2007 Microsoft Office system includes programs, servers, services, and solutions designed to work together to help you succeed. New features in the 2007
Excel Tutorial. Bio 150B Excel Tutorial 1
 Bio 15B Excel Tutorial 1 Excel Tutorial As part of your laboratory write-ups and reports during this semester you will be required to collect and present data in an appropriate format. To organize and
Bio 15B Excel Tutorial 1 Excel Tutorial As part of your laboratory write-ups and reports during this semester you will be required to collect and present data in an appropriate format. To organize and
Thomson Reuters Biomarker Solutions: Hepatitis C Treatment Biomarkers and special considerations in patients with Asthma
 : Hepatitis C Treatment Biomarkers and special considerations in patients with Asthma Abstract This case study aims to demonstrate the process of biomarker identification and validation utilizing Thomson
: Hepatitis C Treatment Biomarkers and special considerations in patients with Asthma Abstract This case study aims to demonstrate the process of biomarker identification and validation utilizing Thomson
About PivotTable reports
 Page 1 of 8 Excel Home > PivotTable reports and PivotChart reports > Basics Overview of PivotTable and PivotChart reports Show All Use a PivotTable report to summarize, analyze, explore, and present summary
Page 1 of 8 Excel Home > PivotTable reports and PivotChart reports > Basics Overview of PivotTable and PivotChart reports Show All Use a PivotTable report to summarize, analyze, explore, and present summary
UCINET Visualization and Quantitative Analysis Tutorial
 UCINET Visualization and Quantitative Analysis Tutorial Session 1 Network Visualization Session 2 Quantitative Techniques Page 2 An Overview of UCINET (6.437) Page 3 Transferring Data from Excel (From
UCINET Visualization and Quantitative Analysis Tutorial Session 1 Network Visualization Session 2 Quantitative Techniques Page 2 An Overview of UCINET (6.437) Page 3 Transferring Data from Excel (From
Getting Started With Mortgage MarketSmart
 Getting Started With Mortgage MarketSmart We are excited that you are using Mortgage MarketSmart and hope that you will enjoy being one of its first users. This Getting Started guide is a work in progress,
Getting Started With Mortgage MarketSmart We are excited that you are using Mortgage MarketSmart and hope that you will enjoy being one of its first users. This Getting Started guide is a work in progress,
Introduction to transcriptome analysis using High Throughput Sequencing technologies (HTS)
 Introduction to transcriptome analysis using High Throughput Sequencing technologies (HTS) A typical RNA Seq experiment Library construction Protocol variations Fragmentation methods RNA: nebulization,
Introduction to transcriptome analysis using High Throughput Sequencing technologies (HTS) A typical RNA Seq experiment Library construction Protocol variations Fragmentation methods RNA: nebulization,
MS Excel Template Building and Mapping for Neat 5
 MS Excel Template Building and Mapping for Neat 5 Neat 5 provides the opportunity to export data directly from the Neat 5 program to an Excel template, entering in column information using receipts saved
MS Excel Template Building and Mapping for Neat 5 Neat 5 provides the opportunity to export data directly from the Neat 5 program to an Excel template, entering in column information using receipts saved
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
