A Taxonomy for Describing BI Cloud Services
|
|
|
- Dale Caldwell
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Taxonomy for Describing BI Cloud Services Oliver Norkus Jürgen Sauer University of Oldenburg, Department for Computing Science Escherweg 2, Oldenuburg, Germany ABSTRACT Cloud computing is still a driver of many innovations. The cloud comes with features nowadays required in the area of Business Intelligence (BI). BI Cloud offerings are proactive, integrated tools for reporting that are mobile accessible, flexible and scalable. BI in the Cloud is becoming increasingly popular, but a comprehensive reference architecture for describtion, comparison and evaluation of BI Cloud services does not exist yet. A universal model to describe Cloud services in general exists. This, however, is too generic to be applicable to BI Cloud services. Even several conceptual frameworks to describe and characterize explicit BI Cloud services exist. But, as they are developed by different groups and organizations, they differ in their intention, level of description, type of formulation, and in terms of which key issues of BI Cloud service evaluation are addressed. To help overcome the prevalent skepticism of enterprises regarding BI Cloud services, we surveyed different frameworks and approaches for describe and compare BI Cloud services. Based on this survey and the universal model for Cloud service offerings we propose a consolidated taxonomy as an extension of the existing general taxonomy with the aim to uniformly describe, compare and evaluate BI Cloud services. KEYWORDS Cloud service, Business Intelligence in the Cloud, BI as a Service, taxonomy, standardization. 1 INTRODUCTION The term Business Intelligence means the integrated IT-based management support. BI aims to improve the process of decision making. The focus is to provide relevant information to the business users (i.e., decision makers) at the right time at any place [1]. In particular, strategic, intercompany and explorative missions of BI have become the focus of discussion. These involve greater attention to poly-structured data sources, a stronger integration of more sophisticated methods of analysis (advanced, visual and predictive analytics), as well as a stronger orientation towards agility (e.g., via self-service BI). Together with the parallel conducted process integration as well as an addition of new internal and external user groups there is a need to revise established architecture. Especially by regarding that previously used BI systems are mostly rigid, complex and costly [2], cloud computing (CC) is more often used in the field of BI to improve flexibility, scalability and agility [3, 4]. CC is defined as a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e. g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction [5]. The combination of BI and CC is used more intensively. BI in the Cloud yet offers new technology combinations to provide individual and differentiated configurable, scalable and flexible analytical services. BI Cloud services have five main properties [4, 6]: The infrastructure is installed and maintained by the service provider. A BI Cloud service therefore makes available the necessary infrastructure for BI capabilities. So the business users do not have to manage it on their own. The infrastructure is scalable, so it can be expanded dynamically when required. In this way, it can be ensured that the de- ISBN: SDIWC 1
2 sired analysis can be performed more performant, even with multiple, simultaneous access. The access to the BI Cloud service is done via a browser, and is generally supported by all common mobile and stationary terminals by using standards (e.g., protocols, interfaces). By this, the business users can always access to the BI Cloud service. The use is flexible and dynamic, and can be performed at any time without the service customer to interact with the service provider to agree a time of use. The users pay for their measured consumption on the base of the utilization (pay-per-use). This can be based on the number of visits or based on the usage time. So, cost transparency and predictability is enabled. On the base of the novelty of BI Cloud services, there are not much field reports yet. The absence of standards and transparency especially for description and comparison of BI Cloud services promotes skepticism and incomprehension. There are several approaches to describe, characterize and compare BI Cloud service offerings. To help overcome the prevalent skepticism of enterprises regarding BI Cloud offerings, we surveyed different frameworks for BI Cloud service offerings. However, as they are defined and elaborated by different groups and organizations, they differ in their intention and scope, in their level of abstraction and the type of formalization. In addition, a model for universally describing Cloud services exists [7, 8]. But, this is so generic and universal, that it is not adequate applicable in the field of BI. Based on the survey and also taking into account the existing model for describing Cloud services, we conceptualize a consolidated taxonomy to uniformly describe, characterize and compare BI Cloud service offerings, regardless whether an organizations own offerings or the offerings of external providers are evaluated. In addition, we present the Business Intelligence Cloud Service Navigator (BI-CSN) as a suitable visualization technique to describe visually and compare BI Cloud service offerings. The contribution of this paper is a survey of different frameworks to describe BI Cloud service offerings. With the aim to abolish the skepticism of enterprises regarding BI Cloud services we identified their key factors and designing a defined and elaborated a taxonomy to describe and compare BI Cloud services. The rest of this paper is structured as follows: We present an overview on the surveyed BI Cloud service frameworks and models in section 2, within a description of the survey method. Based on the survey we proposed the consolidated feature models to provide a common foundation for BI Cloud service description and comparison for all roles, even for customers with a lack of basic understanding of the combination of BI and CC. We discuss the feature model and the individual factors of BI Cloud service offerings in section 3. We also present the BI-CSN as an appropriate visualization technique for the visual description and comparison of BI Cloud service offerings and requests in section 4. Within the application, we also have an effect on the evaluation. Finally, in section 5, we conclude with a short summary and remarks on future work. 2 SUBJECT OF RESEARCH This section contains an overview on the surveyed BI Cloud service frameworks, and a description of the surveyed method. We then summarized the differences between the individual frameworks and reference models, which represents the motivation for the consolidated taxonomy for BI Cloud services we propose in section 3. As of this writing, several models and conceptual frameworks to describe and characterize BI Cloud service offerings exist. To help clear away the skepticism of enterprises regarding BI as a service (BIaaS), we conducted a survey of these different frameworks. The surveyed approaches are: ISBN: SDIWC 2
3 Government and associations: BITKOM [9, 10, 11], Gartner [12], BARC [13, 14]. Industry: SAP [15, 16, 17], Microsoft [18, 19], QlikTech [20], Oracle [21, 22], IBM [23, 24], MicroStrategy [25], TATA [26]. Academia: Adabi [27], Ouf and Nasr [28], Chadha and Iyer [29], Tamer et al. [30], Grivas et al. [31], Demirkan and Delen [32], Baars and Kemper [2], Gurhar and Rathore [33], Gash et al. [34], Thompson and van der Walt [35], Haselmann and Vossen [36], Seufert and Bernhardt [37], Bernhardt and Balluch [38], Weinhardt et al. [39], Torkashvan and Haghighi [40, 41], Leinmeister et al. [42], Schirm et al. [43], Chang [44] and Ereth and Dahl [45]. 2.1 Survey Completeness As shown, the surveyed models represent approaches from different types of organizations; models that were developed by academia, by industry and by governmental structures or other associations. Regarding the industry models, we considered the models provided by SAP, Microsoft, Qlik- Tech, IBM and Oracle. These are representative IT companies and show significant activities in the area of BI in the Cloud [3, 38]. Regarding academia, we surveyed frameworks that represent individual models for BI Cloud and approaches that discuss individual topics such as technical or organizational capabilities. Finally, regarding models by governmental structures of other associations, we considered studies from Gartner, BITKOM, the German Federal Association for Information Technology, Telecommunication and New Media and BARC the German Business Application Research Center. 2.2 Survey Method The survey method is based on the methodology used by defining and elaborating the approach for description and comparison general Cloud services. Thus, the survey was conducted in several steps. We began by conducting a breathfirst search in order to identify relevant works; with the results described above in subsection 2.1. Next we described the surveyed works using feature models [46, 47, 48]. Feature models provide three benefits for the survey [8]: Accessibility: Like mind maps, feature models are simple and can be clearly arranged, represented, and compared to each other. Formality: Feature models are formal models that can be validated. Furhtermore, they allow modeling exclusions, multiple selections, and cardinality. Structure recognition: Feature models do not impose an organizational structure beforehand and even allow to model incomplete concepts. This is in contrast to tables, for example, wherein columns and rows typically have to be named. Figure 1 shows an example of a feature model. The root element is called Feature Model. The element has two sub features, one is mandatory and the other is optional. Again, both features have subfeatures that illustrate inclusion (and) and exclusion (or). Feature models allow an arbitrary model depth, but for the sake of understandability and readability, the modeling depths of different branches should be as uniform as possible [46, 8]. Legend: Mandatory Optional Or Alternative Abstract Concrete FeatureModel MandatoryFeature OptionalFeature Xor1SubFeature Xor2SubFeature Alt1SubFeature Alt2SubFeature Figure 1. An example of a feature model based on [8]. We then compared the surveyed BI Cloud service frameworks by analyzing the feature models, see subsection 2.3. Finally we synthesized ISBN: SDIWC 3
4 a consolidated feature model based on the analysis, to uniformly describe and evaluate Cloud service offerings, see section Survey Results We compared the surveyed BI Cloud service models by analyzing their feature models. For the sake of brevity, this section represents a short summary of the main results. We first summarize the models and then present an analysis. The analysis represents the motivation for the consolidated BI Cloud service feature model that we propose in section Models from Government and Associations The models created by governmental structures or other associations are intended to be vendorneutral models. These models describe the degree and intensity of utilisation and capabilities of BIaaS. Thereby a distinction is made between the focus on the deployment model (private, public, and hybrid) and for the architectural level (infrastructure, platform and software) Industry models The models created by the industry represents their specific BI Cloud service offering. There are descriptions in the fields of architecture, examples of use cases, visualization and configuration functions, service level agreements, data security, deployment model and accounting. For example, SAP [15, 16, 17] settle account on the base of usage hours and Microsoft [18, 19] according the resource using Models from academia Adabi [27] and Hasselmann and Vossen [36] deals with data management in the cloud. Ouf and Nars [28] as well as Baars and Kemper [2] present a layer architecture for BI Cloud services. Thompson and van der Walt [35] report from a survey primary in the sector of application of BI Cloud services and offer first statements to consolidation. Demirkan and Delen [32] provide a service-oriented architecture for putting BI in the cloud. Chadha and Iyer [29] show an overview of an architecture for easy implementation first steps to gain quick wins. Tamer et al. [30], Gurhar and Rathore [33] and Gash et al. [34] also show first architectural models, but consider merely aspects. Chadha and Iyer [29] go further and offer a meta model. Seufert and Bernhardt [37] offer a submodel for the aspect of service type. Bernhardt and Balluch [38] use this submodel and so classify some BI Cloud service offerings. Weinhardt et al. [39] present a framework for business models in Clouds. Torkashvan and Haghighi [40] present a framework for cloud service level agreement management and a general service oriented framework for cloud computing [41]. Leinmeister et al. [42] intestigate the stakeholder in the business perspective of CC. Schirm et al. [43] are dealing with sucess factors of BI Cloud solutions. Chang [44] analyse BI in the cloud in the application in the finance industry. Ereth and Dahl [45] present a first approach for a service-based evaluation concept Analysis There are several models, offerings and approaches of BIaaS. Differences in the offerings exists in the field of architecture model, visualization functions and userfriendliness as well as the billing model. From an architectural point of view, these offerings must be viewed as a black box, because the available information does not go far enough beyond marketingdriven product descriptions. The models from governmental structures and other associations provide primary market observations regarding the use of various offerings. In the academia area, there are already first conceptual considerations and approaches, which mainly focus on aspects and partly only include general statements. Table 1 gives an overview of our findings. As this table show, the surveyed references differ in their level of abstraction, the type of formalization (based on [8]): Level of abstraction: Does the respective reference describe one or more concrete ISBN: SDIWC 4
5 BI service offerings (instance), does it provide a generic description of BI Cloud (meta model), or does it discuss certain aspects (aspects)? Type of formalization: How is the respective framework described? Typically examples are taxonomies, block diagrams, ontologies, lists and plain text. Table I illustrates that the surveyed references are mostly informal, which hinders comparison and leaves space for unwanted interpretation. The lack of a formal yet comprehensible BI Cloud reference model that represents the curated aggregation of the works of many represents the motivation for the BI Cloud service feature model we propose in the next section. 3 FACTORS OF BI CLOUD SERVICE OFFERINGS As a recent work in the research project Future Business Clouds (FBC) [7], different frameworks and approaches for Cloud service offerings description in general were surveyed and based on this a consolidated reference architecture was proposed [8]. Thus, there is a comprehensive and complete [7, 8], accepted and used [49, 50, 51] approach for universal description of Cloud service offerings. As noted even by publishing this, the approach needs further extension and specification [8]. The existing framework with factors of Cloud service offerings in general represent the base enhanced here. In the following, the identified BI specific factors are presented as an extension of the existing generic framework. For the sake of brevity, in this paper, only the added features are displayed. For a first overview here is referred to Fig. 7, wherein the added features are marked by coloring them green. Based on the analysis in subsubsection 2.3 and as an extension of the existing approach, we designed a consolidated feature model to uniformly describe and evaluate BI Cloud service offerings. In this section we describe the factors of BI Cloud service offerings and in following section 4 we present the BI-CSN as a suitable visualization technique to visually describe and compare BI Cloud services. With this we will have an effect on the application and evaluation. The feature model, as shown in Fig. 2, consists of nine main features for service description: the description of the service type, deployment, pricing, roles, service integration aspects, sourcing options, service level agreements (SLAs), organization specific aspects, and Cloud service characteristics. Additions have resulted in the following sub-models: service type, service level agreement, organizational specific aspects and pricing model. Legend: Mandatory Abstract Concrete BIaaS_Feature_Model ServiceType Deployment Pricing Role Integration Sourcing SLA Characteristics Organization Figure 2. Main features of the taxonomy based on [8] 3.1 Service Type The generic framework considers the service types Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Mashup as a Service with the subfeature Business Process as a Service (BPaaS). To describe BI Cloud service offerings this feature model was extended by the subtypes Visualization as a Service (VaaS), Model as a Service (MaaS), Datawarehouse System (DWS) and Data as a Service (DaaS), see Fig. 3. Firstly, the service types VaaS and MaaS are ordered beneath SaaS because they both describe Software that follows the SaaS approach. VaaS represents all display and presentation aspects whereover analytical functions ISBN: SDIWC 5
6 can be used. This includes for example Dashboards, Scorecards and Reports. MaaS covers the aspects of flexibility in the form of selfservice BI (e.g. modifying reports, redefining scores) and offers several analytical functions by providing On-Line Analytical Process (OLAP) and Data Mining functionalities. Secondly, the PaaS feature was extended by the subfeature Datawarehouse System as a platform service. DWS covers the management of the Cloud BI system. This includes e. g. development of analytical functions, the configuration of the extract, transform and load (ETL) process, the control of data flows, the user management and the creation of multidimensional data models for the use in reports. Thirdly, the service type DaaS is ordered beneath IaaS, cause the focus is on storage. IaaS is devided in the infrastructure features storage (DaaS) and computing. DaaS includes the provision of infrastructure in the form of storage explicitly for Data Warehouses, data marts, BI repositories and staging areas for the ETL process. indicators (KPIs), as well as agreed change processes. Both, the functional and nonfunctional got extended by service qualities that are important to describe BI Cloud service offerings. The functional qualities for example now contain the feature Availability, Backups and Data Recovery. The non-functional on the other hand got extended by the qualities Data Protection, Access Authorization and Laws. Legend: SLA Mandatory Optional Abstract Concrete Qualities Processes Functional NonFunctional DataIO Usability ResponseTime ErrorBehavior Availability Backups DataRecovery Locality Performance UsagePrice Integrability Safety DataProtection AccessAuthorization Laws Legend: Mandatory Optional Abstract Concrete SaaS VaaS MaaS Dashboard Scorecard Report OLAP DataMining SelfServiceBI Measures Modalities Termination Incentives Penalties KPIs PaaS DWS Development Configuration Figure 4. Service Level Agreements ServiceType StagingArea IaaS MashupAsAService DaaS Computing BPaaS Figure 3. Service Type 3.2 Service Level Agreement Repository DataMarts DataWareHouse Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are of central importance for the successful cooperation between the participants in a BI Cloud environment. Figure 4 shows the extended SLA feature model. The model considers functional and non-functional service qualities, agreed governance aspects such as key performance 3.3 Organizational specific aspects To establish trust among the participants in a BI Cloud environment, organizations must be able to state their reputation and to assess their capabilities. The model considers the organizations reputation as well as the organizations capabilities, see Fig. 5. Regarding the reputation the model consider certificates, reference projects, KPIs, benchmarks and reports, and further information such as websites. On the other hand, an organizations capabilities depend on the given resources, employee knowledge, technical skills and business skill. Further the capabilities or trust were extended by the feature Support. This feature describes if ISBN: SDIWC 6
7 the cloud service provider offers support services inclusive or if the customer has to pay for it separately. Company Trust BusinessSkills TechnicalSkills KnowledgeBase Resources Support Information ExpertAssesments Legend: Mandatory Optional Abstract Concrete 4 BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE CLOUD SERVICE NAVIGATOR Regarding the description of a concrete BI Cloud service, a feature of the BI Cloud feature model presented in section III can either be said to be present or not. This presence or absence can be represented visually by coloring these two states of each BI Cloud service description feature in a given graphical representation of the feature hierarchy. Reputation Benchmarks KPIs References Certificates Figure 5. Organizational specific aspects 3.4 Pricing model As Fig. 6 shows, the pricing model is distinguished between Free, Pay per Usage and Abonnement. Free means free use, for example, to attract new customers. Pay per Usage covers payment based on measured usage. Abonnement stands for periodic payments for a recurring use. Filed under Pay per Usage are pay-per-time-ofuse, pay-per-usage and pay-per-unit. Within pay-per-time-of-use is mentioned a payment for certain period of use. Pay-per-usage covers the payment for the number of consideration respective views of a reports (e. g. pay-perreport). A resource-based billing, e.g. payment for calculation power units or storage requirements, so used hardware resources, is summarized with pay-per-unit. Pricing Free PayperUse Abonnement PayperUsage PayperUnit PayperTimeofUse Figure 6. Pricing model Legend: Alternative Abstract Concrete Figure 7. BI-CSN: CSN extended by BI specific featured (colored: green). Several visual representations to describe and characterize BI Cloud services exist. For example, Grivas et al. [31] and Seufert and Bernhardt [37] uses informal boxes and lines diagrams, Chadha and Iyer [29] uses tables and other like Thompson and van der Walt [35] just use text. We developed BI Cloud Service Navigators (BI-CSN) as enlargement of the existing Cloud Service Navigator [8] for describing generic Cloud services. Thereby, BI-CSNs are based on Sunburst diagrams. The goal of this visualization is to support the fast perception of service description. In this section, we first present our BI-CSN in subsection 4.1. Next to that, we discuss the ISBN: SDIWC 7
8 application in section 4.2 and the evaluation in subsection BI-CSN The CSN was extended by the mentioned BI specifics to be able to describe BI Cloud service offerings. The new BI specifics were arranged in the BI-CSN shown in Fig. 7. The root of the feature hierarchy is placed at the center of the BI-CSN. The child features are then concentric placed in surrounding rings. Features on the same level of hierarchy are placed on the same ring as siblings, while sub features are placed in the outer sections that their ancestors cut from the pie. Present service descriptions are colored and absent features would be transparent. The green colored features in Fig. 7 are the new BI specifics, which are added based on factors of BI Cloud service offerings as result of the survey and the consolidation. By using the BI-CSN to describe existing BI Cloud service the coloring represents the service properties. Present features will be colored and absent feature will be transparent. The application of the taxonomy by using the BI-CSN is following in the next section. analyzed data can be visualized through different types of diagrams. Thereby, Power BI follows the MaaS and VaaS approach. Power BI is based on the Microsoft Platform Windows Azure which is hosted in a Virtual-Private Cloud in Microsofts own data centers. The scale of the demand can be performed in self management and the accounting is based on the resources used. Microsoft offers detailed SLA with assurances e.g. in security, maintenance, response times. Support has to be aditionally orded and payed. 4.2 Application In total, the BI-CSN was applied to eight BI Cloud service offerings. Here, to not over extend this paper, are shown two cases the BI Cloud service Power BI from Microsoft and the BI Cloud service SAP HANA Cloud from SAP. In the BI-CSN (Power BI in Fig. 8 and SAP HANA Cloud in Fig. 9) the blue colored features means that these features are present and the transparent (white) features are absent. Figure 8 shows the specified BI-CSN for the BI Cloud offer Microsoft Power BI. Microsoft Office 365 with Microsoft Excel and supplemented with Microsoft Sharepoint Online represents the main components of Power BI. Power BI follows the SaaS approach and offers the possibilities to visualize, to model and to analyze data for example by using OLAP functions and Data Mining. Furthermore, the Figure 8. BI-CSN for Microsoft Power BI An other BI Cloud service offering that was used for the evaluation was the SAP HANA Cloud Platform, see Fig. 9. SAP HANA Cloud is offered as a Platform as a Service in the sense of a Data Warehouse System as platform service (DWSaaS). On this plattform the VaaS and MaaS offerings SAP BI OnDemand and Lumira Cloud are deployed. Further considered here, is the platform offering. The SAP HANA Cloud is hosted by Amazon, so that a third party is involved. Just as Microsoft, SAP offers detailed SLA aspects. ISBN: SDIWC 8
9 Within expert dialogues on this subject, we presented the taxonomy and the application to several offerings and discussed it. The completeness and feasibility has been confirmed there. By visualizing the consideration deals with the BI-CSN, the comparability showed the visually simple as possible. A comparison of existing factors of a BI Cloud services is easily possible by visually obervation of the specific BI-CSN. Also, with the BI-CSN the requirements of customers can be described and these can simply be compared with existing BI Cloud services to find the most appropriate service. 5 CONCLUSION Figure 9. BI-CSN for SAP HANA Cloud 4.3 Evaluation As part of a comprehensive literature review (see section 2), many approaches in the area of BI Cloud have been discovered. We identified and removed dublicates, unrelevant references and reviews and editorials. We identifies approaches of different groups - that s why our approach is based on a certain wide opinion. On the base of the survey and their analysis, the conceptualization of the taxonomy was performed as part of an interative design science process with repetetive incremental steps. The individual factors of the references were successively compared, considered and consolidated. This ensures that our architecture is on the current state of the status of scientific, industry and governmental and other associations. The application is importance to demonstrate the feseability. So we took eight BI Cloud offerings and used our taxonomy to describe them (due to the brevity, the application is displayed on two BI Cloud services, see section 4.2). In the application it was found out, that our architecture is completely inasmuch as all features of the observed offerings were covered. In this article, a taxonomy for the description and comparison of BI Cloud services was introduced. This is a tool for orientation and understanding of the subject area BI in the cloud. The taxonomy can also be used to identify and evaluate business needs and to support the selection of suitable offerings. To help overcome the prevalent skepticism of enterprises regarding BI Cloud services, we surveyed different frameworks for BI Cloud service description. Based on this survey, we proposed a consolidated taxonomy in the form of a feature model to uniformly describe, compare and evaluate BI Cloud services, regardless of whether an organizations own offers or the offers of external providers are evaluated. In addition, we present the BI-CSN as a suitable visualization technique to describe visually and compare BI Cloud service offerings and requests. Based on the application of the BI-CSN on existing services we evaluated and demonstrated the feasibility and completeness. However, there are several open issues that we consider as future work: The proposed framework should be continuously adapted to the developments in order not to lose validity and soundness by the appearance of new BI cloud service facets. An automatic selection of BI Cloud offerings can be realized by using the taxonomy for describing business requirements and to compare these with service descriptions to find a suitable service for the ISBN: SDIWC 9
10 considered scenario. Here in particular, existing approaches from the service-oriented field (e. g. service oriented architecture (SOA), unified service description language (USDL) etc.) could be used. For the future development of BI Cloud systems and services this new domain should be standardized. A standardized architecture could provide transparency, reduce uncertainty and help to raise the potentials. Some questions of enterprise, system and software architecture are not still clear and transparent clarified. Therefore many offerings are in an early maturity and heterogeneous. With this contribution is a first step in the direction of standardization is done. Regarding the overall goal of the contribution, we consider our work as an important step towards reducing the skepticism in BI Cloud services, since it provides a consolidated view on their features. We delivered a taxonomy that can be used for the description, comparison, selection of BI Cloud services. REFERENCES [1] H. Chen, R. Chiang and V. C. Storey, Business Intelligence and Analytics: From Big Data to Big Impact, MIS quarterly, vol. 36(4), pp , [2] H. Baars and H. G. Kemper, Business intelligence in the cloud?, PACIS 2010 Proceedings, Paper 145, [3] O. Norkus and H.-J. Appelrath, Towards a Business Intelligence Cloud, Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Informatics Engineering and Information Science (ICIEIS2014) Lodz University of Technology, Lodz, Poland, pp 5566, September [4] O. Norkus et al., An Approach for a Cloud-based Contribution Margin Dashboard in the Field of Electricity Trading, In: Douglas Cunningham, Petra Hofstedt, Klaus Meer, Ingo Schmitt (Hrsg.): INFORMATIK 2015, Lecture Notes in Informatics (LNI), Gesellschaft fr Informatik, Bonn 2015, Bonner Kllen Verlag, 9/2015. [5] P. Mell and T. Grance, The NIST Denition of Cloud Computing, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Information Technology Laboratory, Gaithersburg, NIST, Special Publication , September [6] O. Norkus, B. Friedrich, F. Merkel, I. Schweer, Margin Control as a Cloud Service (Deckungsbeitragsrechnung als Cloud-Dienst), In: Norbert Gronau (Ed.): ERP Management, 15(2), GITO Verlag, pp , vol 5, [7] H.-J. Appelrath, H. Kagermann and H. Krcmar, Future Business Clouds: A contribution to the project of the future Internet-based services for the economy (Future Business Clouds: Ein Beitrag zum Zukunftsprojekt Internetbasierte Dienste fr die Wirtschaft), Herbert Utz Verlag, 2014 [8] S. Gudenkauf, M. Josefiok, A. Göring and O. Norkus, A Reference Architecture for Cloud Service Offers, Software Engineering for Business Information Systems, [9] M. Weber et al. Cloud Computing Monitor 2015, BITKOM KPMG, [10] M. Weber et al. Cloud Computing Monitor 2013, BITKOMKPMG, [11] M. Weber et al., Cloud Computing - Evoluton in der Technik, Revolution im Business, BITKOM- Leitfaden, BITKOM, [12] R. Sallam et al., Magic Quadrant for Business Intelligence and Analytics Platforms, Gartner, [13] C. Bange, T. Grosser, N. Janoschek, Big Data Use Cases - Getting real on data monetization, BARC, [14] C. Bange, S. Roggers, Cloud Business Intelligence and Data Management as a Service - A Global Survey on Adoption, Challenes and Outlook, BARC, [15] SAP analytics/business-intelligence/ software/data-visualization/ cloud.html, last visit: [16] SAP, analytics/lumira/cloud.html,last visit: [17] SAP, sap-ag.de/ sapidp/ E.pdf, last visit: ISBN: SDIWC 10
11 [18] Microsoft, com/de-de/server-cloud/cloud-os/ data-insights.aspx, last visit: [19] Microsoft, de-de/cloud/glossar/bi.aspx, last visit: [20] Qlik, products/, last visit: [21] Oracle, solutions/business-intelligence/ cloud-ready-oracle-bi pdf, last visit: [22] S. Datta and D. Gupta, Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control 12c: Complete, Integrated and Business-Driven Cloud Management, Oracle Corporation, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065, U.S.A., Oracle White Paper, October [23] M. Behrendt et al., Introduction and Architecture Overview IBM Cloud Computing Reference Architecture 2.0, IBM, Tech. Rep., [24] IBM, software/analytics/cloud/, last visit: [25] MicroStrategy, Architecture for enterprise business intelligence, MicroStrategy, WhitePaper. [26] L. Menon, B. Rehani Business Intelligence on the Cloud: Overview and Use Cases, WhitePaper, TATA Consultancy Services, [27] D. J. Abadi, Data Management in the Cloud: Limitations and Opportunities, IEEE Data Engineering Bull, 2009, 32 ed, pp [28] S. Ouf and M. Nasr, The cloud computing: the future of BI in the cloud, International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering, 2011, 3rd ed, pp [29] B. Chadha and M. Iyer, BI in a Cloud: Defining the Architecture for Quick Wins, SETLabs Briefing, 2010, 8 ed, pp [30] C. Tamer, M. Kiley, N. Ashrafi, J. Kuilbar, Risk and benefits of business intelligence in the cloud, In Northeast Decision Sciences Institute Annual Meeting Proceedings (pp ). [31] S. G. Grivas, T. U. Kumar, and H. Wache, Cloud broker: Bringing intelligence into the cloud, IEEE 3rd International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD), pp , [32] H. Demirkan and D. Delen, Leveraging the capabilities of service-orientied decision support systems: Putting analytics and big data in cloud, Decision Support Systems 55, Journal, Elsevier B.B., pp , [33] Y. S. Gurjar and V. S. Rathore. Cloud business intelligenceis what business need today, International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, vol. 1.6, pp 81-86, [34] D. Gash, T. Ariyachandra and M. Frolick, Looking to the clouds for business intelligence, Journal of Internet Commerce vol. 10.4, pp , [35] W. J. Thompson und J. S. van der Walt, Business intelligence in the cloud, SA Journal of Information Management, vol. 12(1), pp. 1-5, [36] T. Haselmann and G. Vossen, Database-asa-Service for small and mediem enterprises (Database-as-a-Service fr kleine und mittlere Unternehmen), Working Paper, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik, Westfälische Wilhelms- Universität Münster, Münster, vol. 3, [37] A. Seufert and N. Bernhardt, Business Intelligence and Cloud Computing (Business Intelligence und Cloud Computing), HMD Praxis der Wirtschaftsinformatik, vol. 47(5), pp. 3441, [38] N. Bernhardt and K. Balluch, Self-service Business Intelligence in the Cloud - requirements, security aspects, concepts (Self-Service Business Intelligence in der Cloud - Anforderungen, Sicherheitsaspekte, Konzepte), BI Spektrum, vol. 1, pp , [39] C. Weinhardt et al., Cloud Computing - A Classification, Business Models and Reserach Directions, Business & Information System Engineering, pp , vol 5, [40] M. Torkashvan, H. Haghighi, CSLAM: A framework for cloud service level agreement management based on WSLA, Sixth International Symposium on Telecommunications (IST), IEEE, pp , [41] M. Torkashvan, H. Haghighi, A service oriented framework for cloud computing, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Systems, ACM, paper no. 25, ISBN: SDIWC 11
12 [42] S. Leinmeister, M. Böhm, C. Riedl, Christoph, H. Krcmar, The business perspective of cloud computing: actors, roles and value networks, ECIS 2010 Proceedings, Paper 56, [43] N. Schirm, T. Frank, M. Henkel, F. Bensberg, Success factors for cloud-based cusiness intelligence solutions (Erfolgsfaktoren cloudbasierter Business Intelligence Lösungen), Proceedings der 12. Internationalen Tagung Wirtschaftsinformatik (WI2015), [44] V. Chang, The business intelligence as a service in the cloud, Future Generation Computer Systems, Volume 37, pp , [45] J. Ereth, D. Dahl, Business intelligence in the cloud: fundamentals for a service-based evaluation concept, Tagungsband des 5. Workshops Business Intelligence der GI-Fachgruppe Business Intelligence, Paper No. 1, [46] D. Batory, Feature Models, Grammars and Propositional Formulas, Proceedings of the 9th international conference on Software Product Lines, ser. SPLC05. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2005, pp [47] K. Czarnecki and U. W. Eisenecker, Generative Programming: Methods, Tool, and Applications, 6th ed, Addison Wesley, April [48] K. Czarnecki and S. Helsen, Feature-based survey of model transformation approaches, IBM Systems Journal, vol. 45, no. 3, pp , [49] S. Kolb and G. Wirtz, Towards application portability in platform as a service, Service Oriented System Engineering (SOSE), 2014 IEEE 8th International Symposium on. IEEE, [50] A. Göring, S. Gudenkauf, M. Josefiok and O. Norkus, A taxonomy for describing cloud service offers (Eine Taxonomie zur Beschreibung von Cloud-Dienstangeboten), VDE-Kongress 2014, VDE VERLAG, [51] V. Andrikopoulos, A. Darsow, D. Karastoyanova, F. Leymann, CloudDSFThe Cloud Decision Support Framework for Application Migration, Service-Oriented and Cloud Computing, pp. 1-16, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg Table 1. Results of Literature Analysis Reference Level of Formality Abstraction meta model aspect instance informal in part formal formal BITKOM [9, 10, 11] X X Gartner [12] X X BARC [13, 14] X X SAP [15, 16, 17] X X Microsoft [18, 19] X X QlikTech [20] X X Oracle [21] X X IBM [23, 24] X X MicroStrategy [25] X X TATA [26] X X Adabi [27] X X Ouf and Nasr [28] X X Chadha and Iyer [29] X X Tamer et al. [30] X X Grivas et al. [31] X X Demirkan and Delen [32] X X Baars and Kemper [2] X X Gurhar and Rathore [33] X X Gash et al. [34] X X Thompson and van der Walt [35] X X Haselmann and Vossen [36] X X Seufert and Bernhardt [37] X X Bernhardt and Balluch [38] X X Weinhardt et al. [39] X X Torkashvan and X X Haghighi [40, 41] Leinmeister X X et al. [42] Schirm et al. [43] X X Chang [44] X X Ereth and Dahl [45] X X ISBN: SDIWC 12
Towards a Business Intelligence Cloud
 Towards a Business Intelligence Cloud Oliver Norkus and H.-Jürgen Appelrath University of Oldenburg Escherweg 2, 26121 Oldenburg, Germany [norkus, appelrath]@offis.de ABSTRACT The requirements for Business
Towards a Business Intelligence Cloud Oliver Norkus and H.-Jürgen Appelrath University of Oldenburg Escherweg 2, 26121 Oldenburg, Germany [norkus, appelrath]@offis.de ABSTRACT The requirements for Business
Leveraging Standard Software from the Cloud with Service-Oriented EAM
 Leveraging Standard Software from the Cloud with Service-Oriented EAM Helge Buckow, Hans-Jürgen Groß, Gunther Piller, Norbert Stumpf, Oliver F. Nandico, Johannes Willkomm, Alfred Zimmermann SOA Innovation
Leveraging Standard Software from the Cloud with Service-Oriented EAM Helge Buckow, Hans-Jürgen Groß, Gunther Piller, Norbert Stumpf, Oliver F. Nandico, Johannes Willkomm, Alfred Zimmermann SOA Innovation
Comparative Analysis of the Main Business Intelligence Solutions
 148 Informatica Economică vol. 17, no. 2/2013 Comparative Analysis of the Main Business Intelligence Solutions Alexandra RUSANEANU Faculty of Cybernetics, Statistics and Economic Informatics Bucharest
148 Informatica Economică vol. 17, no. 2/2013 Comparative Analysis of the Main Business Intelligence Solutions Alexandra RUSANEANU Faculty of Cybernetics, Statistics and Economic Informatics Bucharest
Improving IT Service Management Architecture in Cloud Environment on Top of Current Frameworks
 Improving IT Service Management Architecture in Cloud Environment on Top of Current Frameworks Fatemeh Arabalidousti 1 and Ramin Nasiri 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University,
Improving IT Service Management Architecture in Cloud Environment on Top of Current Frameworks Fatemeh Arabalidousti 1 and Ramin Nasiri 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University,
Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative Analysis of the Main Providers
 60 Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative Analysis of the Main Providers Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative
60 Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative Analysis of the Main Providers Business Intelligence. A Presentation of the Current Lead Solutions and a Comparative
Integrating SAP and non-sap data for comprehensive Business Intelligence
 WHITE PAPER Integrating SAP and non-sap data for comprehensive Business Intelligence www.barc.de/en Business Application Research Center 2 Integrating SAP and non-sap data Authors Timm Grosser Senior Analyst
WHITE PAPER Integrating SAP and non-sap data for comprehensive Business Intelligence www.barc.de/en Business Application Research Center 2 Integrating SAP and non-sap data Authors Timm Grosser Senior Analyst
Cloud Computing For Distributed University Campus: A Prototype Suggestion
 Cloud Computing For Distributed University Campus: A Prototype Suggestion Mehmet Fatih Erkoç, Serhat Bahadir Kert [email protected], [email protected] Yildiz Technical University (Turkey) Abstract
Cloud Computing For Distributed University Campus: A Prototype Suggestion Mehmet Fatih Erkoç, Serhat Bahadir Kert [email protected], [email protected] Yildiz Technical University (Turkey) Abstract
CLOUD COMPUTING: A NEW VISION OF THE DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM
 CLOUD COMPUTING: A NEW VISION OF THE DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM Taha Chaabouni 1 and Maher Khemakhem 2 1 MIRACL Lab, FSEG, University of Sfax, Sfax, Tunisia [email protected] 2 MIRACL Lab, FSEG, University
CLOUD COMPUTING: A NEW VISION OF THE DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM Taha Chaabouni 1 and Maher Khemakhem 2 1 MIRACL Lab, FSEG, University of Sfax, Sfax, Tunisia [email protected] 2 MIRACL Lab, FSEG, University
BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE. Keywords: business intelligence, architecture, concepts, dashboards, ETL, data mining
 BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE Bogdan Mohor Dumitrita 1 Abstract A Business Intelligence (BI)-driven approach can be very effective in implementing business transformation programs within an enterprise framework.
BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE Bogdan Mohor Dumitrita 1 Abstract A Business Intelligence (BI)-driven approach can be very effective in implementing business transformation programs within an enterprise framework.
MOC 20467B: Designing Business Intelligence Solutions with Microsoft SQL Server 2012
 MOC 20467B: Designing Business Intelligence Solutions with Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to design business intelligence solutions
MOC 20467B: Designing Business Intelligence Solutions with Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to design business intelligence solutions
A New Cloud Computing Architecture by Integrating Recent Best Reference Frameworks
 A New Cloud Computing Architecture by Integrating Recent Best Reference Frameworks Niloofar Khanghahi 1 and Ramin Nasiri 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Central Tehran
A New Cloud Computing Architecture by Integrating Recent Best Reference Frameworks Niloofar Khanghahi 1 and Ramin Nasiri 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Central Tehran
STRATEGIC AND FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE USING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE SOLUTIONS
 STRATEGIC AND FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE USING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE SOLUTIONS Boldeanu Dana Maria Academia de Studii Economice Bucure ti, Facultatea Contabilitate i Informatic de Gestiune, Pia a Roman nr.
STRATEGIC AND FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE USING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE SOLUTIONS Boldeanu Dana Maria Academia de Studii Economice Bucure ti, Facultatea Contabilitate i Informatic de Gestiune, Pia a Roman nr.
TRENDS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE SYSTEMS
 9 8 TRENDS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE SYSTEMS Assist. Prof. Latinka Todoranova Econ Lit C 810 Information technology is a highly dynamic field of research. As part of it, business intelligence
9 8 TRENDS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE SYSTEMS Assist. Prof. Latinka Todoranova Econ Lit C 810 Information technology is a highly dynamic field of research. As part of it, business intelligence
See Appendix A for the complete definition which includes the five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.
 Cloud Strategy Information Systems and Technology Bruce Campbell What is the Cloud? From http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-145/sp800-145.pdf Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous,
Cloud Strategy Information Systems and Technology Bruce Campbell What is the Cloud? From http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-145/sp800-145.pdf Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous,
The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing
 Special Publication 800-145 The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing Recommendations of the National Institute of Standards and Technology Peter Mell Timothy Grance NIST Special Publication 800-145 The NIST
Special Publication 800-145 The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing Recommendations of the National Institute of Standards and Technology Peter Mell Timothy Grance NIST Special Publication 800-145 The NIST
Cloud Computing Services and its Application
 Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 4, Number 1 (2014), pp. 107-112 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Cloud Computing Services and its
Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 4, Number 1 (2014), pp. 107-112 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Cloud Computing Services and its
Cloud Computing: The Next Computing Paradigm
 Cloud Computing: The Next Computing Paradigm Ronnie D. Caytiles 1, Sunguk Lee and Byungjoo Park 1 * 1 Department of Multimedia Engineering, Hannam University 133 Ojeongdong, Daeduk-gu, Daejeon, Korea [email protected],
Cloud Computing: The Next Computing Paradigm Ronnie D. Caytiles 1, Sunguk Lee and Byungjoo Park 1 * 1 Department of Multimedia Engineering, Hannam University 133 Ojeongdong, Daeduk-gu, Daejeon, Korea [email protected],
A Study on Analysis and Implementation of a Cloud Computing Framework for Multimedia Convergence Services
 A Study on Analysis and Implementation of a Cloud Computing Framework for Multimedia Convergence Services Ronnie D. Caytiles and Byungjoo Park * Department of Multimedia Engineering, Hannam University
A Study on Analysis and Implementation of a Cloud Computing Framework for Multimedia Convergence Services Ronnie D. Caytiles and Byungjoo Park * Department of Multimedia Engineering, Hannam University
OIT Cloud Strategy 2011 Enabling Technology Solutions Efficiently, Effectively, and Elegantly
 OIT Cloud Strategy 2011 Enabling Technology Solutions Efficiently, Effectively, and Elegantly 10/24/2011 Office of Information Technology Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 The Colorado Cloud...
OIT Cloud Strategy 2011 Enabling Technology Solutions Efficiently, Effectively, and Elegantly 10/24/2011 Office of Information Technology Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 The Colorado Cloud...
OVERVIEW Cloud Deployment Services
 OVERVIEW Cloud Deployment Services Audience This document is intended for those involved in planning, defining, designing, and providing cloud services to consumers. The intended audience includes the
OVERVIEW Cloud Deployment Services Audience This document is intended for those involved in planning, defining, designing, and providing cloud services to consumers. The intended audience includes the
Data Doesn t Communicate Itself Using Visualization to Tell Better Stories
 SAP Brief Analytics SAP Lumira Objectives Data Doesn t Communicate Itself Using Visualization to Tell Better Stories Tap into your data big and small Tap into your data big and small In today s fast-paced
SAP Brief Analytics SAP Lumira Objectives Data Doesn t Communicate Itself Using Visualization to Tell Better Stories Tap into your data big and small Tap into your data big and small In today s fast-paced
Migration to Cloud Computing: a Sample Survey Based on a Research in Progress on the Investigation of Standard Based Interoperability Protocols
 Migration to Cloud Computing: a Sample Survey Based on a Research in Progress on the Investigation of Standard Based Interoperability Protocols for the Convergence of Cloud Computing, Servcie Oriented
Migration to Cloud Computing: a Sample Survey Based on a Research in Progress on the Investigation of Standard Based Interoperability Protocols for the Convergence of Cloud Computing, Servcie Oriented
Perspectives on Moving to the Cloud Paradigm and the Need for Standards. Peter Mell, Tim Grance NIST, Information Technology Laboratory 7-11-2009
 Perspectives on Moving to the Cloud Paradigm and the Need for Standards Peter Mell, Tim Grance NIST, Information Technology Laboratory 7-11-2009 2 NIST Cloud Computing Resources NIST Draft Definition of
Perspectives on Moving to the Cloud Paradigm and the Need for Standards Peter Mell, Tim Grance NIST, Information Technology Laboratory 7-11-2009 2 NIST Cloud Computing Resources NIST Draft Definition of
CLOUD ARCHITECTURE DIAGRAMS AND DEFINITIONS
 CLOUD ARCHITECTURE DIAGRAMS AND DEFINITIONS April 2014 Cloud Conceptual Reference Model The ease of use a Cloud Consumer experiences results from a complex, behind-the-scenes, orchestration of interchangeable,
CLOUD ARCHITECTURE DIAGRAMS AND DEFINITIONS April 2014 Cloud Conceptual Reference Model The ease of use a Cloud Consumer experiences results from a complex, behind-the-scenes, orchestration of interchangeable,
Cloud Computing. Chapter 1 Introducing Cloud Computing
 Cloud Computing Chapter 1 Introducing Cloud Computing Learning Objectives Understand the abstract nature of cloud computing. Describe evolutionary factors of computing that led to the cloud. Describe virtualization
Cloud Computing Chapter 1 Introducing Cloud Computing Learning Objectives Understand the abstract nature of cloud computing. Describe evolutionary factors of computing that led to the cloud. Describe virtualization
Security Considerations for Public Mobile Cloud Computing
 Security Considerations for Public Mobile Cloud Computing Ronnie D. Caytiles 1 and Sunguk Lee 2* 1 Society of Science and Engineering Research Support, Korea [email protected] 2 Research Institute of
Security Considerations for Public Mobile Cloud Computing Ronnie D. Caytiles 1 and Sunguk Lee 2* 1 Society of Science and Engineering Research Support, Korea [email protected] 2 Research Institute of
CHAPTER 8 CLOUD COMPUTING
 CHAPTER 8 CLOUD COMPUTING SE 458 SERVICE ORIENTED ARCHITECTURE Assist. Prof. Dr. Volkan TUNALI Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences / Maltepe University Topics 2 Cloud Computing Essential Characteristics
CHAPTER 8 CLOUD COMPUTING SE 458 SERVICE ORIENTED ARCHITECTURE Assist. Prof. Dr. Volkan TUNALI Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences / Maltepe University Topics 2 Cloud Computing Essential Characteristics
Permanent Link: http://espace.library.curtin.edu.au/r?func=dbin-jump-full&local_base=gen01-era02&object_id=154091
 Citation: Alhamad, Mohammed and Dillon, Tharam S. and Wu, Chen and Chang, Elizabeth. 2010. Response time for cloud computing providers, in Kotsis, G. and Taniar, D. and Pardede, E. and Saleh, I. and Khalil,
Citation: Alhamad, Mohammed and Dillon, Tharam S. and Wu, Chen and Chang, Elizabeth. 2010. Response time for cloud computing providers, in Kotsis, G. and Taniar, D. and Pardede, E. and Saleh, I. and Khalil,
A Study on Service Oriented Network Virtualization convergence of Cloud Computing
 A Study on Service Oriented Network Virtualization convergence of Cloud Computing 1 Kajjam Vinay Kumar, 2 SANTHOSH BODDUPALLI 1 Scholar(M.Tech),Department of Computer Science Engineering, Brilliant Institute
A Study on Service Oriented Network Virtualization convergence of Cloud Computing 1 Kajjam Vinay Kumar, 2 SANTHOSH BODDUPALLI 1 Scholar(M.Tech),Department of Computer Science Engineering, Brilliant Institute
A Model-based Software Architecture for XML Data and Metadata Integration in Data Warehouse Systems
 Proceedings of the Postgraduate Annual Research Seminar 2005 68 A Model-based Software Architecture for XML and Metadata Integration in Warehouse Systems Abstract Wan Mohd Haffiz Mohd Nasir, Shamsul Sahibuddin
Proceedings of the Postgraduate Annual Research Seminar 2005 68 A Model-based Software Architecture for XML and Metadata Integration in Warehouse Systems Abstract Wan Mohd Haffiz Mohd Nasir, Shamsul Sahibuddin
ITIL AS A FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGEMENT OF CLOUD SERVICES
 ITIL AS A FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGEMENT OF CLOUD SERVICES Soňa Karkošková 1, George Feuerlicht 2 1 Faculty of Information Technology, University of Economics, Prague, W. Churchill Sqr. 4, 130 67 Prague 3, Czech
ITIL AS A FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGEMENT OF CLOUD SERVICES Soňa Karkošková 1, George Feuerlicht 2 1 Faculty of Information Technology, University of Economics, Prague, W. Churchill Sqr. 4, 130 67 Prague 3, Czech
WHITE PAPER: STRATEGIC IMPACT PILLARS FOR EFFICIENT MIGRATION TO CLOUD COMPUTING IN GOVERNMENT
 WHITE PAPER: STRATEGIC IMPACT PILLARS FOR EFFICIENT MIGRATION TO CLOUD COMPUTING IN GOVERNMENT IntelliDyne, LLC MARCH 2012 STRATEGIC IMPACT PILLARS FOR EFFICIENT MIGRATION TO CLOUD COMPUTING IN GOVERNMENT
WHITE PAPER: STRATEGIC IMPACT PILLARS FOR EFFICIENT MIGRATION TO CLOUD COMPUTING IN GOVERNMENT IntelliDyne, LLC MARCH 2012 STRATEGIC IMPACT PILLARS FOR EFFICIENT MIGRATION TO CLOUD COMPUTING IN GOVERNMENT
Cloud Computing Architecture: A Survey
 Cloud Computing Architecture: A Survey Abstract Now a day s Cloud computing is a complex and very rapidly evolving and emerging area that affects IT infrastructure, network services, data management and
Cloud Computing Architecture: A Survey Abstract Now a day s Cloud computing is a complex and very rapidly evolving and emerging area that affects IT infrastructure, network services, data management and
How To Understand Cloud Usability
 Published in proceedings of HCI International 2015 Framework for Cloud Usability Brian Stanton 1, Mary Theofanos 1, Karuna P Joshi 2 1 National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD,
Published in proceedings of HCI International 2015 Framework for Cloud Usability Brian Stanton 1, Mary Theofanos 1, Karuna P Joshi 2 1 National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD,
Armanino McKenna LLP Welcomes You To Today s Webinar:
 Armanino McKenna LLP Welcomes You To Today s Webinar: Business Intelligence Are You Data Rich & Information Poor? The presentation will begin in a few moments About the Presenter(s) John Horner, Director
Armanino McKenna LLP Welcomes You To Today s Webinar: Business Intelligence Are You Data Rich & Information Poor? The presentation will begin in a few moments About the Presenter(s) John Horner, Director
Cloud Computing for Architects
 Cloud Computing for Architects This four day, hands-on boot camp begins with an examination of the Cloud Computing concept, the structure and key characteristics of Clouds, and takes a look under the hood
Cloud Computing for Architects This four day, hands-on boot camp begins with an examination of the Cloud Computing concept, the structure and key characteristics of Clouds, and takes a look under the hood
Usage of Cloud Computing: where do we stand and where are we going in Switzerland?
 Usage of Cloud Computing: where do we stand and where are we going in Switzerland? A survey conducted by Stefanie Huthmacher under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Stella Grivas Gatziu Olten, 31 July 2010
Usage of Cloud Computing: where do we stand and where are we going in Switzerland? A survey conducted by Stefanie Huthmacher under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Stella Grivas Gatziu Olten, 31 July 2010
PLATFORM-AS-A-SERVICE (PAAS): THE ADOXX METAMODELLING PLATFORM
 PLATFORM-AS-A-SERVICE (PAAS): THE ADOXX METAMODELLING PLATFORM Dimitris Karagiannis and Niksa Visic University of Vienna, Knowledge Engineering Research Group, Brünnerstr. 72, A-1210 Vienna, Austria {dk,
PLATFORM-AS-A-SERVICE (PAAS): THE ADOXX METAMODELLING PLATFORM Dimitris Karagiannis and Niksa Visic University of Vienna, Knowledge Engineering Research Group, Brünnerstr. 72, A-1210 Vienna, Austria {dk,
CLOUD SECURITY SECURITY ASPECTS IN GEOSPATIAL CLOUD. Guided by Prof. S. K. Ghosh Presented by - Soumadip Biswas
 CLOUD SECURITY SECURITY ASPECTS IN GEOSPATIAL CLOUD Guided by Prof. S. K. Ghosh Presented by - Soumadip Biswas PART 1 A brief Concept of cloud Issues in cloud Security Issues A BRIEF The Evolution Super
CLOUD SECURITY SECURITY ASPECTS IN GEOSPATIAL CLOUD Guided by Prof. S. K. Ghosh Presented by - Soumadip Biswas PART 1 A brief Concept of cloud Issues in cloud Security Issues A BRIEF The Evolution Super
Towards Management of SLA-Aware Business Processes Based on Key Performance Indicators
 Towards Management of SLA-Aware Business Processes Based on Key Performance Indicators Branimir Wetzstein, Dimka Karastoyanova, Frank Leymann Institute of Architecture of Application Systems, University
Towards Management of SLA-Aware Business Processes Based on Key Performance Indicators Branimir Wetzstein, Dimka Karastoyanova, Frank Leymann Institute of Architecture of Application Systems, University
Logical Data Models for Cloud Computing Architectures
 Logical Data Models for Cloud Computing Architectures Augustine (Gus) Samba, Kent State University Describing generic logical data models for two existing cloud computing architectures, the author helps
Logical Data Models for Cloud Computing Architectures Augustine (Gus) Samba, Kent State University Describing generic logical data models for two existing cloud computing architectures, the author helps
ORACLE OLAP. Oracle OLAP is embedded in the Oracle Database kernel and runs in the same database process
 ORACLE OLAP KEY FEATURES AND BENEFITS FAST ANSWERS TO TOUGH QUESTIONS EASILY KEY FEATURES & BENEFITS World class analytic engine Superior query performance Simple SQL access to advanced analytics Enhanced
ORACLE OLAP KEY FEATURES AND BENEFITS FAST ANSWERS TO TOUGH QUESTIONS EASILY KEY FEATURES & BENEFITS World class analytic engine Superior query performance Simple SQL access to advanced analytics Enhanced
<Insert Picture Here> Oracle BI Standard Edition One The Right BI Foundation for the Emerging Enterprise
 Oracle BI Standard Edition One The Right BI Foundation for the Emerging Enterprise Business Intelligence is the #1 Priority the most important technology in 2007 is business intelligence
Oracle BI Standard Edition One The Right BI Foundation for the Emerging Enterprise Business Intelligence is the #1 Priority the most important technology in 2007 is business intelligence
Worldwide Advanced and Predictive Analytics Software Market Shares, 2014: The Rise of the Long Tail
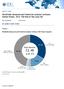 MARKET SHARE Worldwide Advanced and Predictive Analytics Software Market Shares, 2014: The Rise of the Long Tail Alys Woodward Dan Vesset IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide Advanced and Predictive
MARKET SHARE Worldwide Advanced and Predictive Analytics Software Market Shares, 2014: The Rise of the Long Tail Alys Woodward Dan Vesset IDC MARKET SHARE FIGURE FIGURE 1 Worldwide Advanced and Predictive
Implementing XML-based Role and Schema Migration Scheme for Clouds
 Implementing XML-based Role and Schema Migration Scheme for Clouds Gurleen Kaur 1, Sarbjeet Singh 2 Computer Science and Engineering, UIET Panjab University, Chandigarh, India 1 [email protected]
Implementing XML-based Role and Schema Migration Scheme for Clouds Gurleen Kaur 1, Sarbjeet Singh 2 Computer Science and Engineering, UIET Panjab University, Chandigarh, India 1 [email protected]
A Secure System Development Framework for SaaS Applications in Cloud Computing
 A Secure System Development Framework for SaaS Applications in Cloud Computing Eren TATAR, Emrah TOMUR AbstractThe adoption of cloud computing is ever increasing through its economical and operational
A Secure System Development Framework for SaaS Applications in Cloud Computing Eren TATAR, Emrah TOMUR AbstractThe adoption of cloud computing is ever increasing through its economical and operational
BI SURVEY 14. The world s largest survey of business intelligence software users
 THE BI SURVEY 14 The world s largest survey of business intelligence software users This document is a specially produced summary by BARC of the headline results for EVIDANZA This document is not to be
THE BI SURVEY 14 The world s largest survey of business intelligence software users This document is a specially produced summary by BARC of the headline results for EVIDANZA This document is not to be
California Enterprise Architecture Framework. Cloud Computing (CC) Reference Architecture (RA)
 California Enterprise Architecture Framework Cloud Computing (CC) Reference Architecture (RA) Version 1.0 Final January 2, 2014 This Page is Intentionally Left Blank Version 1.0 Final ii January 2, 2014
California Enterprise Architecture Framework Cloud Computing (CC) Reference Architecture (RA) Version 1.0 Final January 2, 2014 This Page is Intentionally Left Blank Version 1.0 Final ii January 2, 2014
ABSTRACT: [Type text] Page 2109
![ABSTRACT: [Type text] Page 2109 ABSTRACT: [Type text] Page 2109](/thumbs/39/19436718.jpg) International Journal Of Scientific Research And Education Volume 2 Issue 10 Pages-2109-2115 October-2014 ISSN (e): 2321-7545 Website: http://ijsae.in ABSTRACT: Database Management System as a Cloud Computing
International Journal Of Scientific Research And Education Volume 2 Issue 10 Pages-2109-2115 October-2014 ISSN (e): 2321-7545 Website: http://ijsae.in ABSTRACT: Database Management System as a Cloud Computing
Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects
 Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects Abstract: Build a model to investigate system and discovering relations that connect variables in a database
Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects Abstract: Build a model to investigate system and discovering relations that connect variables in a database
Cloud Computing. Course: Designing and Implementing Service Oriented Business Processes
 Cloud Computing Supplementary slides Course: Designing and Implementing Service Oriented Business Processes 1 Introduction Cloud computing represents a new way, in some cases a more cost effective way,
Cloud Computing Supplementary slides Course: Designing and Implementing Service Oriented Business Processes 1 Introduction Cloud computing represents a new way, in some cases a more cost effective way,
Cloud Computing and Government Services August 2013 Serdar Yümlü SAMPAŞ Information & Communication Systems
 eenviper White Paper #4 Cloud Computing and Government Services August 2013 Serdar Yümlü SAMPAŞ Information & Communication Systems 1 Executive Summary Cloud computing could revolutionise public services
eenviper White Paper #4 Cloud Computing and Government Services August 2013 Serdar Yümlü SAMPAŞ Information & Communication Systems 1 Executive Summary Cloud computing could revolutionise public services
Introduction to Oracle Business Intelligence Standard Edition One. Mike Donohue Senior Manager, Product Management Oracle Business Intelligence
 Introduction to Oracle Business Intelligence Standard Edition One Mike Donohue Senior Manager, Product Management Oracle Business Intelligence The following is intended to outline our general product direction.
Introduction to Oracle Business Intelligence Standard Edition One Mike Donohue Senior Manager, Product Management Oracle Business Intelligence The following is intended to outline our general product direction.
Analytical Survey Model on Consumption of Cloud Service Models
 Analytical Survey Model on Consumption of Cloud Service Models Om Prakash Karada, Abhishek Pipliya, Parul Thakur & Neha Kamdar Malwa Institute of Technology, Indore E-mail : [email protected], [email protected],
Analytical Survey Model on Consumption of Cloud Service Models Om Prakash Karada, Abhishek Pipliya, Parul Thakur & Neha Kamdar Malwa Institute of Technology, Indore E-mail : [email protected], [email protected],
Keywords Distributed Computing, On Demand Resources, Cloud Computing, Virtualization, Server Consolidation, Load Balancing
 Volume 5, Issue 1, January 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Survey on Load
Volume 5, Issue 1, January 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Survey on Load
BI Platforms User Survey, 2011: Customers Rate Their BI Platform Vendors
 BI Platforms User Survey, 2011: Customers Rate Their BI Platform Vendors Gartner RAS Core Research Note G00211769, Rita L. Sallam, 4 April 2011, RA1 07132011 Gartner recently surveyed business intelligence
BI Platforms User Survey, 2011: Customers Rate Their BI Platform Vendors Gartner RAS Core Research Note G00211769, Rita L. Sallam, 4 April 2011, RA1 07132011 Gartner recently surveyed business intelligence
The Next Generation of IT Management. Jason Andrew Vice President, Marketing & Communications
 The Next Generation of IT Management Jason Andrew Vice President, Marketing & Communications BMC Has Outperformed the Market Growing Stock Price Over 130 Percent in 5 Years BMC +134% IBM +76% HP +50% NASDAQ
The Next Generation of IT Management Jason Andrew Vice President, Marketing & Communications BMC Has Outperformed the Market Growing Stock Price Over 130 Percent in 5 Years BMC +134% IBM +76% HP +50% NASDAQ
Business Intelligence Systems Optimization to Enable Better Self-Service Business Users
 Business Intelligence Systems Optimization to Enable Better Self-Service Business Users Safwan Sulaiman 1, Jorge Marx Gómez 1, Joachim Kurzhöfer 2 1 Very Large Business Applications / University of Oldenburg
Business Intelligence Systems Optimization to Enable Better Self-Service Business Users Safwan Sulaiman 1, Jorge Marx Gómez 1, Joachim Kurzhöfer 2 1 Very Large Business Applications / University of Oldenburg
Perspectives on Cloud Computing and Standards. Peter Mell, Tim Grance NIST, Information Technology Laboratory
 Perspectives on Cloud Computing and Standards Peter Mell, Tim Grance NIST, Information Technology Laboratory Caveats and Disclaimers This presentation provides education on cloud technology and its benefits
Perspectives on Cloud Computing and Standards Peter Mell, Tim Grance NIST, Information Technology Laboratory Caveats and Disclaimers This presentation provides education on cloud technology and its benefits
HiTech. White Paper. A Next Generation Search System for Today's Digital Enterprises
 HiTech White Paper A Next Generation Search System for Today's Digital Enterprises About the Author Ajay Parashar Ajay Parashar is a Solution Architect with the HiTech business unit at Tata Consultancy
HiTech White Paper A Next Generation Search System for Today's Digital Enterprises About the Author Ajay Parashar Ajay Parashar is a Solution Architect with the HiTech business unit at Tata Consultancy
[Analysts: Dr. Carsten Bange, Larissa Seidler, September 2013]
![[Analysts: Dr. Carsten Bange, Larissa Seidler, September 2013] [Analysts: Dr. Carsten Bange, Larissa Seidler, September 2013]](/thumbs/25/5058208.jpg) BARC RESEARCH NOTE SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence with SAP HANA [Analysts: Dr. Carsten Bange, Larissa Seidler, September 2013] This document is not to be shared, distributed or reproduced in
BARC RESEARCH NOTE SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence with SAP HANA [Analysts: Dr. Carsten Bange, Larissa Seidler, September 2013] This document is not to be shared, distributed or reproduced in
Food & Beverage Industry Brief
 KudzuCreative Content Creation Food & Beverage Industry Brief KudzuCreative kudzucreative.com Content Created for, Microsoft Dynamics AX Gold Partner [email protected] NOT YOUR FATHER S FUNCTIONALITY
KudzuCreative Content Creation Food & Beverage Industry Brief KudzuCreative kudzucreative.com Content Created for, Microsoft Dynamics AX Gold Partner [email protected] NOT YOUR FATHER S FUNCTIONALITY
A Knowledge Management Framework Using Business Intelligence Solutions
 www.ijcsi.org 102 A Knowledge Management Framework Using Business Intelligence Solutions Marwa Gadu 1 and Prof. Dr. Nashaat El-Khameesy 2 1 Computer and Information Systems Department, Sadat Academy For
www.ijcsi.org 102 A Knowledge Management Framework Using Business Intelligence Solutions Marwa Gadu 1 and Prof. Dr. Nashaat El-Khameesy 2 1 Computer and Information Systems Department, Sadat Academy For
journey to a hybrid cloud
 journey to a hybrid cloud Virtualization and Automation VI015SN journey to a hybrid cloud Jim Sweeney, CTO GTSI about the speaker Jim Sweeney GTSI, Chief Technology Officer 35 years of engineering experience
journey to a hybrid cloud Virtualization and Automation VI015SN journey to a hybrid cloud Jim Sweeney, CTO GTSI about the speaker Jim Sweeney GTSI, Chief Technology Officer 35 years of engineering experience
Whitepaper Data Governance Roadmap for IT Executives Valeh Nazemoff
 Whitepaper Data Governance Roadmap for IT Executives Valeh Nazemoff The Challenge IT Executives are challenged with issues around data, compliancy, regulation and making confident decisions on their business
Whitepaper Data Governance Roadmap for IT Executives Valeh Nazemoff The Challenge IT Executives are challenged with issues around data, compliancy, regulation and making confident decisions on their business
The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing (Draft)
 Special Publication 800-145 (Draft) The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing (Draft) Recommendations of the National Institute of Standards and Technology Peter Mell Timothy Grance NIST Special Publication
Special Publication 800-145 (Draft) The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing (Draft) Recommendations of the National Institute of Standards and Technology Peter Mell Timothy Grance NIST Special Publication
Private Cloud for the Enterprise: Platform ISF
 Private Cloud for the Enterprise: Platform ISF A Neovise Vendor Perspective Report 2009 Neovise, LLC. All Rights Reserved. Background Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network
Private Cloud for the Enterprise: Platform ISF A Neovise Vendor Perspective Report 2009 Neovise, LLC. All Rights Reserved. Background Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network
Organization of Business Intelligence
 Organization of Business Intelligence The advantage gained by companies using competency centers to coordinate their business intelligence initiatives BARC Institute, Wurzburg, August 2008 Business Business
Organization of Business Intelligence The advantage gained by companies using competency centers to coordinate their business intelligence initiatives BARC Institute, Wurzburg, August 2008 Business Business
Rapid Development of Smart and Self-Adaptive Cloud, Mobile & IoT Applications - Accelerating the Last Mile of Cloud Computing
 Rapid Development of Smart and Self-Adaptive Cloud, Mobile & IoT Applications - Accelerating the Last Mile of Cloud Computing Jesse Shiah CEO and Co-founder [email protected] 2013 AgilePoint,
Rapid Development of Smart and Self-Adaptive Cloud, Mobile & IoT Applications - Accelerating the Last Mile of Cloud Computing Jesse Shiah CEO and Co-founder [email protected] 2013 AgilePoint,
Applying Business Architecture to the Cloud
 Applying Business Architecture to the Cloud Mike Rosen, Chief Scientist Mike.Rosen@ WiltonConsultingGroup.com Michael Rosen Agenda n What do we mean by the cloud? n Sample architecture and cloud support
Applying Business Architecture to the Cloud Mike Rosen, Chief Scientist Mike.Rosen@ WiltonConsultingGroup.com Michael Rosen Agenda n What do we mean by the cloud? n Sample architecture and cloud support
A New Approach Towards Integrated Cloud Computing Architecture
 A New Approach Towards Integrated Cloud Computing Architecture Niloofar Khanghahi 1 and Ramin Nasiri 2 and Mahsa Razavi 3 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Central Tehran Branch,
A New Approach Towards Integrated Cloud Computing Architecture Niloofar Khanghahi 1 and Ramin Nasiri 2 and Mahsa Razavi 3 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Central Tehran Branch,
CHOOSING THE RIGHT CLOUD COMPUTING SOLUTION FOR YOU
 CHOOSING THE RIGHT CLOUD COMPUTING SOLUTION FOR YOU ABSTRACT Dan Smedescu This article provides an introduction to cloud computing and choosing a vendor. The first part includes definitions and service
CHOOSING THE RIGHT CLOUD COMPUTING SOLUTION FOR YOU ABSTRACT Dan Smedescu This article provides an introduction to cloud computing and choosing a vendor. The first part includes definitions and service
Kent State University s Cloud Strategy
 Kent State University s Cloud Strategy Table of Contents Item Page 1. From the CIO 3 2. Strategic Direction for Cloud Computing at Kent State 4 3. Cloud Computing at Kent State University 5 4. Methodology
Kent State University s Cloud Strategy Table of Contents Item Page 1. From the CIO 3 2. Strategic Direction for Cloud Computing at Kent State 4 3. Cloud Computing at Kent State University 5 4. Methodology
SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence 4.1 One Strategy for Enterprise BI. May 2013
 SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence 4.1 One Strategy for Enterprise BI May 2013 SAP s Strategic Focus on Business Intelligence Core Self-service Mobile Extreme Social Core for innovation Complete
SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence 4.1 One Strategy for Enterprise BI May 2013 SAP s Strategic Focus on Business Intelligence Core Self-service Mobile Extreme Social Core for innovation Complete
Multi-Tenant Engineering Architecture in SaaS
 Multi-Tenant Engineering Architecture in SaaS Sunil Kumar Khatri Himanshu Singhal Khushboo Bahri ABSTRACT Multi-Tenancy in SaaS (Software as a Service) architecture is the concept leveraging cloud computing
Multi-Tenant Engineering Architecture in SaaS Sunil Kumar Khatri Himanshu Singhal Khushboo Bahri ABSTRACT Multi-Tenancy in SaaS (Software as a Service) architecture is the concept leveraging cloud computing
Figure 1 Cloud Computing. 1.What is Cloud: Clouds are of specific commercial interest not just on the acquiring tendency to outsource IT
 An Overview Of Future Impact Of Cloud Computing Shiva Chaudhry COMPUTER SCIENCE DEPARTMENT IFTM UNIVERSITY MORADABAD Abstraction: The concept of cloud computing has broadcast quickly by the information
An Overview Of Future Impact Of Cloud Computing Shiva Chaudhry COMPUTER SCIENCE DEPARTMENT IFTM UNIVERSITY MORADABAD Abstraction: The concept of cloud computing has broadcast quickly by the information
The Key Technology Research of Virtual Laboratory based On Cloud Computing Ling Zhang
 International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 2015) The Key Technology Research of Virtual Laboratory based On Cloud Computing Ling Zhang Nanjing Communications
International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 2015) The Key Technology Research of Virtual Laboratory based On Cloud Computing Ling Zhang Nanjing Communications
Microsoft Business Intelligence solution. What makes Microsoft BI difference
 Business Intelligence today Microsoft Business Intelligence solution What makes Microsoft BI difference Case study and Demo Gartner BI Platform Software Revenue (in $Billions) CIO Priorities: Data Analysis
Business Intelligence today Microsoft Business Intelligence solution What makes Microsoft BI difference Case study and Demo Gartner BI Platform Software Revenue (in $Billions) CIO Priorities: Data Analysis
Tableau Metadata Model
 Tableau Metadata Model Author: Marc Reuter Senior Director, Strategic Solutions, Tableau Software March 2012 p2 Most Business Intelligence platforms fall into one of two metadata camps: either model the
Tableau Metadata Model Author: Marc Reuter Senior Director, Strategic Solutions, Tableau Software March 2012 p2 Most Business Intelligence platforms fall into one of two metadata camps: either model the
Huawei OceanStor Backup Software Technical White Paper for NetBackup
 Huawei OceanStor Backup Software Technical White Paper for NetBackup Huawei Page 1 of 14 Copyright Huawei. 2014. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
Huawei OceanStor Backup Software Technical White Paper for NetBackup Huawei Page 1 of 14 Copyright Huawei. 2014. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
The Service, The Cloud & The Method: The Connection Points
 The Service, The Cloud & The Method: The Connection Points Thomas Erl SOA Systems Inc. Prentice Hall Service-Oriented Computing Series Started in 2003 Text Books are an Official Part of the SOACP Curriculum
The Service, The Cloud & The Method: The Connection Points Thomas Erl SOA Systems Inc. Prentice Hall Service-Oriented Computing Series Started in 2003 Text Books are an Official Part of the SOACP Curriculum
8. Business Intelligence Reference Architectures and Patterns
 8. Business Intelligence Reference Architectures and Patterns Winter Semester 2008 / 2009 Prof. Dr. Bernhard Humm Darmstadt University of Applied Sciences Department of Computer Science 1 Prof. Dr. Bernhard
8. Business Intelligence Reference Architectures and Patterns Winter Semester 2008 / 2009 Prof. Dr. Bernhard Humm Darmstadt University of Applied Sciences Department of Computer Science 1 Prof. Dr. Bernhard
A Cloud Computing Handbook for Business
 White Paper A Cloud Computing Handbook for Business By Dr. Wolfgang Rohde, Douglas Clark and Jimmy Hum A Cloud Computing Handbook for Business Abstract Business demands for more flexible and cost effective
White Paper A Cloud Computing Handbook for Business By Dr. Wolfgang Rohde, Douglas Clark and Jimmy Hum A Cloud Computing Handbook for Business Abstract Business demands for more flexible and cost effective
Business Intelligence In SAP Environments
 Business Intelligence In SAP Environments BARC Business Application Research Center 1 OUTLINE 1 Executive Summary... 3 2 Current developments with SAP customers... 3 2.1 SAP BI program evolution... 3 2.2
Business Intelligence In SAP Environments BARC Business Application Research Center 1 OUTLINE 1 Executive Summary... 3 2 Current developments with SAP customers... 3 2.1 SAP BI program evolution... 3 2.2
Sebis Study: Cloud Adoption and Strategy 2013
 This publication can be cited as: Monahov, Ivan; Shumaiev, Klym; Matthes, Florian: Sebis Study: Cloud Adoption and Strategy 2013, version 0.9, December, 2013. Ivan Monahov, Klym Shumaiev, Florian Matthes
This publication can be cited as: Monahov, Ivan; Shumaiev, Klym; Matthes, Florian: Sebis Study: Cloud Adoption and Strategy 2013, version 0.9, December, 2013. Ivan Monahov, Klym Shumaiev, Florian Matthes
E-learning Using Cloud Computing
 International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 1 (2014), pp. 41-46 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm E-learning
International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 1 (2014), pp. 41-46 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm E-learning
Strategic approach to cloud computing deployment
 Strategic approach to cloud computing deployment Slavko Gajin, (GN3plus, SA7T1) Datacenter IaaS workshop 2014 11-12. September, 2014 Cloud and NRENs Cloud is the latest big thing affecting NREN users Do
Strategic approach to cloud computing deployment Slavko Gajin, (GN3plus, SA7T1) Datacenter IaaS workshop 2014 11-12. September, 2014 Cloud and NRENs Cloud is the latest big thing affecting NREN users Do
Necto on Azure The Ultimate Cloud Solution for BI
 Necto on Azure The Ultimate Cloud Solution for BI TECHNICAL WHITEPAPER Introduction Organizations of all sizes and sectors need Business Intelligence (BI) to scale operations, improve performance and remain
Necto on Azure The Ultimate Cloud Solution for BI TECHNICAL WHITEPAPER Introduction Organizations of all sizes and sectors need Business Intelligence (BI) to scale operations, improve performance and remain
CLOUD SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENTS Meeting Customer and Provider needs
 CLOUD SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENTS Meeting Customer and Provider needs Eric Simmon January 28 th, 2014 BACKGROUND Federal Cloud Computing Strategy Efficiency improvements will shift resources towards higher-value
CLOUD SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENTS Meeting Customer and Provider needs Eric Simmon January 28 th, 2014 BACKGROUND Federal Cloud Computing Strategy Efficiency improvements will shift resources towards higher-value
Revitalising your Data Centre by Injecting Cloud Computing Attributes. Ricardo Lamas, Cloud Computing Consulting Architect IBM Australia
 Revitalising your Data Centre by Injecting Attributes Ricardo Lamas, Consulting Architect IBM Australia Today s datacenters face enormous challenges: I need to consolidate to reduce sprawl and OPEX. I
Revitalising your Data Centre by Injecting Attributes Ricardo Lamas, Consulting Architect IBM Australia Today s datacenters face enormous challenges: I need to consolidate to reduce sprawl and OPEX. I
