Hair Restoration Update
|
|
|
- Annis Horn
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ١ Hair Restoration Update By Dr.Tarek Ahmed Said Lecturer of Plastic Surgery, Cairo University Hair on a man's head is an important emblem of health, youth and vitality (Vogel, 2000). For a long time physicians and surgeons searched for a cause and cure for alopecia. Ancient Egyptians recorded their efforts in this regards thousands of years ago (Swinehart, 1996). With the advances made in the field of aesthetic surgery, many aesthetic options became available for addressing the problem of hair loss. However, the increase in number and sophistication of surgical modalities has still not produced one ideal solution that is applicable to all cases of alopecia. In fact, what appears to be a straightforward problem is usually as complex as any in the field of plastic surgery. Multiple variables like hair color, texture or others have an enormous influence on the final outcome of alopecia management. Excellent results of hair restoration can be obtained with good knowledge of the different options of treatment and with proper long-term planning of management (Hubbard, 1997). This article reviews from the surgical aspect, the management of the most troublesome hair disorder, hair loss. Hair anatomy and physiology Hair grows from follicles, which are stocking-like infoldings of the superficial epithelium, each of which encloses at its base a small stud of dermis known as the dermal papilla. The cylinder of hair may be regarded as a holocrine secretion arising by division of cells in the region known as the bulb. The follicles are sloped in the dermis and longer ones extend into the subcutaneous layer. An oblique muscle, the errector pilorum, runs from a point in the mid-region of the follicle wall to the dermo-epidermal junction. Above the muscle, one or more sebaceous glands and in some regions of the body, an apocrine gland open into the follicle. The bulk of any hair is composed of a thick cortex made up of keratinized cells, which in pigmented hairs contain melanin granules. The cortex is surround by a cuticle and may have a continuous or discontinuous core or medulla (Dawber et al, 1998). The average scalp contains terminal coarse, medullated & pigmented hairs and many more vellus and indeterminate fine hypopigmented unmedullated hairs. At any time approximately 90% of terminal hairs are in the anagen (growing phase) lasting around 1000 days and the rest is in the catagen (regression) phase lasting typically 3-4 months. The shedding of around 100 hairs daily is normal (Swinehart, 1996).
2 ٢ Aetiopathology of Alopecia Alopecia can be caused by a wide variety of conditions, most important of which from the surgical point of view is androgenetic alopecia (common baldness) and cicatricial alopecia. Alopecia can be caused by a variety of skin disorders, most important of which is alopecia areata. Other causes include, hereditary defects, metabolic, endocrinal, nutritional defects, bad use of cosmetics, or exposure to chemicals, chemotherapeutic agents or irradiation (Sommer & Wilson, 1999). The course of alopecia in these conditions is cause dependent, some cases are reversible after removal of the aetiological factor and some are not (Dawber et al, 1998). They are beyond the scope of hair restoration and will not be discussed in this article. Androgenetic Alopecia (Common baldness, male pattern & female pattern baldness) Aetiology Androgenetic alopecia remains the main cause of male pattern baldness (MPB) & female pattern baldness (FPB) (Koo et al, 2000). Both types of alopecia are caused by the gradual deterioration of terminal hairs into vellus ones caused by the genetically determined increased level of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which is the metabolite of testosterone produced by 5-α reductase enzyme. DHT acts on androgen binding receptors on the hair follicles. It is not known why androgenetic alopecia starts nearly always on the crown and spreads inferiorly eventually sparing only the lower temples and the lower posterior scalp. At present although the genetic basis of androgenetic baldness in confirmed, the predisposing genes are not identified, however the relatively strong concordance of the degree of baldness in fathers and sons is not consistent with simple Mendelian trait and a polygenic basis is therefore most likely (Hoffmann & Happle, 2000) Male pattern baldness (MPB) Classification Male pattern baldness may be classified by one of several methods. The most widely classification was proposed by Norwood (1975). It should be emphasized however, that only few patients fit exactly into these classifications, more likely each patient is visualized as being in transition from one type into a more advanced one.
3 ٣ Type I: Minimal recession along hairline Type II: Early bilateral temporal recession stopping at least 2 cm anterior to a vertical coronal plane passing through external auditory canals Type III: More bitemporal recession approaching that vertical coronal line and more posterior recession of anterior hairline Type III Vertex: A zone of coronal baldness appears and the bitemporal recession may not be as deep as in type III Type IV: A larger zone of vertex alopecia and a deeper bitemporal recession and a deeper posterior recession of hairline. The three alopecia zones seem moving centrally to join each other. Type V: The three zones join each other Type VI: The patient posses a complete alopecic zone in the anterior, central or posterior crown. A horseshoe shaped zone of hair persists in the parietal and occipital regions. Type VII: An advanced form of alopecia where only a fringe of hair persists in the lower parietal and lower occipital areas. Type VIII: Occasionally a patient has almost no hair-bearing zone at all. Type A variants: In these variants of types II, III, IV & V the hairline recession proceeds directly posterior without simultaneous development of vertex alopecia. This pattern is often incomplete and the hairline frequently does not recede as far inferiorly in the parietal or occipital regions. Figure 1 : Norwood's MPB classification (Norwood, 1975)
4 ٤ Female pattern baldness (FPB) Ludwig (1977) has more recently proposed a classification for FPB into three types. Unless suffering from a verilizing disease, females generally never lose anterior hairline, rather female pattern baldness is characterized by incomplete coronal hair loss, with diffuse thinning across the anterior, central & posterior crown. FPB is classified into mild, moderate and severe types. In all types the hair in the usual parieto-occipital donor region is healthy, making females good candidates for extensive hair transplantation surgery. Figure 2 : Ludwig's FPB classification (Ludwig, Treatment of androgenetic alopecia Medical treatment Hormonal treatment Hormonal therapy of androgenetic baldness is based of inhibition of 5- α reductase (5AR), the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone to its metabolite DHT responsible for initiation and progression of androgenetic alopecia. Antiandrogen therapy Finasteride (Propecia) A pure 5AR inhibitor, which has been used for the management of benign prostatic hypertrophy. It blocks the peripheral conversion of testosterone to DHT resulting in a significant decrease in its level in the scalp. It has been recently introduced for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. It is mainly effective in the crown area with no or little effect on receding anterior hairline & temples. Any results achieved by treatment will be lost on cessation of treatment. Anti-Androgenic effects of finasteride have been found to be temporary (Hogan & Chamberlain, 2000). Trials are conducted on the use of finasteride as a topical formulation and encouraging results have been obtained (Sintov et al, 2000). Other Anti-Androgens Drugs like spironolactone or the combination of CPA (cyproterone) & ethinyl-estradiol have been shown in high doses to produce a significant
5 ٥ increase in cosmetically useful hair. However this line of therapy has a lot of major disadvantages inhibiting its wide use including: 1-Anti-androgenic effect in males 2-The treatment should be continued for at least 1 year before a subjective improvement is reached 3-Complete reversal of hair loss cannot be achieved if treatment is not started within 2 years form the start of alopecia (Dawber et al, 1998). Non Hormonal treatment Topical Minoxidil (Rogaine) It is by far the most widely used medical treatment available for androgenetic alopecia. The oral form of the drug used in the 1970s for the treatment of hypertension was observed to have the side effect of stimulating hair growth. Subsequent studies on the local form of Minoxidil 2% ointment in an alcohol and water base containing 10% propylene glycol (Rogaine) have yielded encouraging results and it is now the drug of choice for medical control of androgenetic alopecia. Recently a 5% solution of Minoxidil became available as Rogaine Extra Strength for Men (Farrell & Epstein, 1999). Minoxidil is a powerful vasodilator, which increases blood flow to the scalp, but it is not clear whether this action or direct action on hair follicles is responsible for hair growth as many other vasodilators have been tested and none of them showed the ability to grow hair. It causes conversion of vellus into terminal hairs in up to 30% of individuals (Reitschel & Duncan 1987). Terminal hairs appear to regrow at the margins but complete coverage of bald areas in seen in less than 10% of cases. The clinical results show that it works best in early stages of baldness with bald area of maximum diameter less than 10 cm. An additional benefit is that topical Minoxidil seems to prevent further alopecia with continuous use. Topical Minoxidil appears to be a safe therapy with side effects only of local irritation and a low incidence of contact dermatitis. Minoxidil has the disadvantage of loss of the gained results and failure of protection from further alopecia once the drug is stopped (De Villez, 1985). Surgical treatment An individual is born with a fixed number of hairs. The surgeon can stretch the scalp, lift it, rotate it to another more desired location or move hair from one location to another, but unless experimental hair follicle cloning is refined, surgeons cannot create more hairs. So, the goal of hair restoration surgery remains the maximum, most efficient use of present and future donor areas to cover patient's present and future predicted hair loss pattern.
6 ٦ The state of the art surgical treatment for hair restoration is hair transplantation. Yet, the armamentarium of the surgeon includes also alopecia reduction, with or without the use of scalp extension by expansion, scalp lifting or the use of scalp flaps again with or without scalp expansion. Principle Hair Transplantation Hair transplantation is the backbone of hair restoration surgery. It is the primary or secondary mode in almost all cases. Often it is used alone employing grafts of different sizes in a carefully planned approach, at other times grafts accompany scalp reductions or scalp flaps. Hair transplantation is based on the concept of "donor dominance" in MPB (Orentreich, 1959). If a graft is taken from an area destined to be permanently hair bearing and is transplanted into an area of MPB or future MPB, it will after an initial short period of effluvium, continue to grow hair in its new site. Thus all planning of redistribution of permanent hair is predicated on an accurate assessment of the ultimate extent of alopecia and its counterpart, the permanent donor rim (Unger, 1997). Hair transplantation has evolved through successive waves of innovation. The use of large punch grafts was the initial means of transplantation from the 1950s till the early 1980s (Orentreich, 1959).It was met with considerable excitement, which was replaced over the years with some disappointment and a tainted reputation. This was mainly due to the unnatural pluggy appearance that large punch grafts produced. In the 1980s the concept of minigrafts evolved through the work of Marritt (1984). In the 1990s the concept of follicular unit has revolutionized hair transplantation (Swerdloff & Kabaker, 1999). Human hair emerges from the scalp in groupings known as follicular units. In follicular unit transplantation (Jimenez & Ruifernandez, 1999). Follicular unit transplantation is a method of hair restoration surgery where hair is transplanted in its naturally occurring individual follicular unit. This led to the use of smaller micrografts and finally single hair transplants (Bernstein & Rassman, 1999). Using different-sized smaller grafts helps avoiding the corn rowing "the doll's head appearance" and dramatically improves results (Marritt, 1993). Types of hair grafts There are various types of hair grafts are defined by Knudsed (1994):
7 ٧ 1.Standard grafts: Round grafts mm or sometimes larger containing 8-10 hairs and placed into holes punched out with slightly smaller round trephines. 2.Minigrafts: Grafts containing 3-4 hairs (small minigrafts) or less commonly 5-6 hairs (large minigrafts). They are obtained by sectioning strips of donor tissue or less commonly larger round grafts. If placed in scalpel slits in the donor area they are called slit grafts, and if placed into holes made with a round trephine they are called round minigrafts. 3-Micrografts: 1-2 hair grafts obtained by sectioning strips of donor tissue. They are placed into holes prepared by a 16-gauge needle. Figure 3 : types of hair grafts (Hubbard, 1997) The majority of surgeons now employ a variety of grafts according to zones. Standard grafts should be used in areas where maximum density is desired. Micrografts and minigrafts are utilized whenever the ultimate hair density objective is less than maximum density. Micrografts are virtually always used in the hairline zone followed posteriorly by an area of minigrafts that are all one size or increasing in size in different zones (Buchwack, 1994). Zones of varying-sized grafts should be considered at other border areas as well. In more severe baldness, it may become difficult or impossible for grafts to span the distance between the temporal fringes because donor hair in these patients is limited. For these patients, either no surgery or creation of an isolated frontal forelock is planned. In general, small slit grafts are superior to small round minigrafts in producing light coverage with minimal clumpiness. This is because of their linear shape. Slit grafts will also produce a greater increase of hair density than small rounded minigrafts when working on an area that still contains hair
8 ٨ because making round holes will always remove some of the existing hairs. Scalpel incisions for slit micrografts can be made between original hair follicles without damaging them, thus the net increase in hair will be equal to the amount of transplanted hairs. On the other hand, greater hair density can be produced with round grafts as a part of bald skin is actually removed at the same time round grafts are added. Megasessions of thousands of micro and minigrafts in a single sitting and dense packing of the bald area is the best solution to accomplish the maximum result in the least number of sessions (Swinehart, 1996). Planning Planning is essential in hair transplantation, poor planning can easily lead to unsatisfactory results which may be impossible to correct. This may be because of unanticipated progression of hair loss, exhaustion of grafts or missized, misplaced or misdirected grafts or scars. Norwood (1992) described 6 major factors in patient selection and planning 1- Classification: Using Norwood's Classification, good candidates for hair transplantation are types III, IV & V. Candidacy of types VI, VII depend greatly on other major factors. 2- Scalp & hair color: Best result of hair transplantation is achieved when there is little contrast between scalp and hair colors as an optical illusion gives a more dense and natural appearance. Dark hair transplantation on light colored scalps is problematic, more and smaller grafts should be used to soften the contrasting effect. Scalp coloring agents may help minimize this contrast (Unger, 1995) 3- Curliness: Curliness is favorable as it inherently covers and camouflages any tufted arrangement (Randall & Schauder, 1993). 4- Texture (Caliber): Surgeon must choose less coarse hair to cover the hairline by harvesting from lower occipital area or just above the ears. The thin hairs can be easily combed backwards and has a more natural look. 5- Density: Greater density is an advantage in the donor area, in fact low density of the donor area may rule out hair transplantation. However, this may yield dense grafts producing a pluggy appearance. For those patients, smaller minigrafts and micrografts should be used 6- Amount of donor hair: Again very small donor area as in types VII & VIII rule out this procedure. Donor site anesthesia With the patient in the prone position, hair in the previously marked donor area is trimmed to a length of 2-3 mm.
9 ٩ The donor area is anesthetized with a 50/50 mixture of 1% xylocaine and 1: epinephrine and 0.5% plain bupivacaine, approximately 15 cm of each is injected into a 1 X 15-cm donor area. After waiting for minutes to allow for maximum vasoconstriction, the surgeons infiltrates the donor area with approximately 30 cc of tumescent solution (0.1 % xylocaine with epinephrine 1: ) to add more local anesthesia and tumesces the donor region, lifting the scalp away from, the occipitalis muscle fascia and occipital vessels and causing hair follicles to stand erect at less acute angle from the scalp (Swinehart, 1996). Donor hair harvesting Two donor zones are used: one inferiorly in the occipital area and another one more superiorly extending from the midline into the parietal area and as far anteriorly as a line drawn perpendicularly from the tragus. There are basically two methods for donor harvesting; first, the multibladed knife that can be loaded with 3-8 blades to produce 3-8 thin strips with a single pass of the knife and secondly, the creation of an elliptical incision using a single blade to harvest one strip of scalp tissue for further dissection into micrografts. Many surgeons prefer the second method as it avoids inadvertent damage to the hair follicles in the harvested strip that may be produced by a faulty angle of the multibladed knife (Limmer, 1996). The depth of strips should include approximately 2 cm of subfollicular fat to avoid follicle damage and to prevent unnecessary bleeding from deeper dissection (Marritt & Konior, 1994). A no 15 scalpel is used to produce a triangular tapering of both ends. One end of the donor tissue is held with a small-toothed forceps and small curved scissors are used to separate tissues from its underlying bed. Wound is closed in a running continuous fashion. Figure 4: Donor sites (Swinehart, 1996)
10 ١٠ Graft dissection Micrograft dissection is a demanding, tedious, yet critical process in extensive micrograft hair transplantation. Dissection is done under either microscope or at least 2.5 X loop magnification under two different light sources at different angles (Cooley & Vogel, 1999). The hair bearing skin strip is placed over a sterile tongue depressor and stabilized by another tongue depressor held by the surgeon's nondominant hand. A single-edged razor blade is used to cut the skin strip into fine slices approximately mm thick. Slices are cut exactly parallel to the direction of hair follicles to avoid damaging them. The blade should be changed every 10 cuts or whenever the slightest dullness or drag is felt. The fat is then carefully trimmed from the bottom of each slice. These slices are placed into chilled saline prior to dissection. Each slice is dissected by a razor blade or fine scissors into micrografts bearing I-2 hairs. Micrografts are then deepithelialized by slicing off the top of the graft at approximately a 45-degree angle to skin surface. This will allow the hair to align itself in a single file and will minimize the possibility of compression of hair into unsightly dense dark area of coarse hair. Grafts are then sorted according to their hair content into petri dishes containing chilled saline (Marked by colored tape to identify different sizes) and held on ice packs until needed for implantation. With the growing use of lengthy megasessions of 1000 hair transplantation or more, the issue of graft survival outside the body for some hours is important. According to Limmer (1994), 90% of 1-mm grafts survive an 8-hour interval outside the body provided they are kept in 4ºC chilled saline (Raposio et al, 1999). Figure 5 : Graft dissection (Swinehart, 1996)
11 ١١ Anesthesia of recipient site With the patient is in the supine position the anterior recipient zone is anesthetized using the same technique used in the donor area. Bilateral blocks of lateral zygomaticotemporal, supraorbital & supratrochlear nerves are done using a 50/50 mixture of 1% xylocaine and 1: epinephrine and 0.5% bupivacaine. After minutes ring block of the whole recipient area is done using the same mixture. During graft insertion, sponges soaked with 1% xylocaine with 1: epinephrine is directly applied to the recipient site, may grant additional hemostasis as the anesthetic diffuses into the recipient sites (Swinehart, 1996). Recipient site preparation The skill of hair replacement surgeon is maximally reflected in his grafting of the recipient site. Creation of slits Instruments used to create slits, holes as well as microdilators should be carefully matched to the anticipated sizes of the grafts. Many instruments can be used including: needles, small blades, or small punches. Microslits are placed between existing hair follicles in patients with earlier thinning or with previous micrografting sessions. These microslits can be created with a no gauge needle or with the use of high-energy pulsed CO 2 laser (Fitzpatrick & Marchell, 2000) and can be very closely spaced in bald scalps in micrografts sessions. Placement of microdilators Dilators are small devices temporarily placed into recipient slits. They are favored by some surgeons as they keep slit or hole open, facilitate graft insertion, act as markers for accurate spacing, maximize recipient site visibility in areas with existing hair, aid in hemostasis and prevent piggybacking or missing recipient slits (Marritt, 1988). Other hair restoring surgeons find dilators time-consuming and cumbersome and therefore rarely use them (Tessler, 1996). Insertion plan In the recipient site, the surgeon always establishes the fine zones destined to receive micrografts. The hairline is best created with 100 or more closely spaced single hair micrografts. Posterior crown baldness can be filled with larger minigrafts. The hair zones are carefully planned, delineated and marked to receive one-, two-, three- or four-hair grafts. The angle of each slit is carefully created to match the angle and direction of the patient's original
12 ١٢ remaining hair; these angles are often oriented radially. When grafting a posterior whorl attention should be directed to the center, location of remaining hair and orientation (clock or anti-clock wise) (Pomerantez, 1999). Graft insertion It is important to avoid graft trauma. A head light magnification system dramatically decreases the amount of existing hair trauma (Brandy, 2000). Curved fine jeweler's forceps with diamond tipped jaws are used. The surgeon may line up the grafts on the scalp or on his non-dominant hand. Procedure is best performed with one assistant removing the dilator immediately prior to insertion of the graft by the surgeon. Grafts are not grasped from their follicular end to avoid damaging the hair matrices. Steady pressure is applied to control any bleeding in the area and to ensure that the grafts are flush with the surrounding skin. Care is taken to avoid burying the grafts beneath the level of the skin. It is better to leave a graft protruding slightly above the surrounding skin than below it, as inclusion cyst may result from the latter (Whitworth et al, 1999). Figure 6 : Graft insertion (Swinehart, 1996) Bandaging A small overnight dressing that does not cover the ears is applied and the patient should return the next day for confirmation that the grafts are still in position properly and for careful cleaning away of any blood clots that may have developed overnight (Slough & Miner, 1997).
13 ١٣ Postoperative Course Small crusts will form over the grafts and usually fall over the first 2 weeks. The grafts will shed their hairs in 2-6 weeks. New hair growth usually begins weeks after surgery and patient should be informed that it would take at least 6 month postoperatively for hair to grow and to give a good idea about the final appearance. The use of 2-3 % Minoxidil solution twice daily for 5-6 weeks postoperatively will often accelerate hair growth. Scalp (alopecia) reduction and scalp lifting Scalp or alopecia reduction is defined as the removal of bald skin on any part of the scalp with extension of the remaining hear-bearing scalp to cover the resulting defect. It can be used alone as an exclusive method of hair restoration in older men with stable area of crown baldness (Unger & Unger, 1978) but more commonly it is used as an adjunct to hair transplantation to reduce the size of the bald area to be transplanted (Tessler, 1996). Increasing the surface area of hear bearing scalp depend on two phenomena, mechanical & biological creep Mechanical creep (alopecia reduction) Unwaving and alignment of collagen bundles give rise to a limited amount of scalp expansion over a short time as in intraoperative scalp expansion or during scalp reduction or scalp lifting (Blanchard & Blanchard, 1977). Scalp reduction is most suitable for crown and midscalp (Unger, 1988). The surgeon can use a variety of incision patterns to customize direction and advancement and better hiding of scars (Unger, 1992) (Schauder et al, 1992). Figure 7 : Alopecia reduction incisions (Hubbard,
14 ١٤ More extensive alopecia reduction (Bilateral scalp & bilateral temporal lifts) The bilateral scalp lift Bilateral scalp lift is a form of alopecia reduction with extensive dissection and undermining of hair bearing scalp allows for excision of a larger amount of the bald area of the scalp. Doppler identification of both superficial temporal arteries should be done prior to surgery. Then an incision is made approximately one cm posterior of the temporal hairline but well in front of the marked superficial temporal artery. The bilateral occipitoparietal incision is extended superiorly following the outline of the crown. The initial undermining is carried out in the avascular plane beneath the galea but above the temporalis muscle fascia. The dissection continues lateral to the inferior extension of the ear lobe in the hairless postauricular area. Then the undermining is directed posteriorly to the central portion of the scalp. The undermining is initially subgaleal till the nuchal ridge. When the occipitalis muscle is encountered, it is divided bilaterally and the dissection is continued by splitting the trapizius and sternocleidomastoid muscle fasciae and undermining superficial to their muscle bulks till the nape of the neck is reached. The surgeon literally has the entire scalp in his hands and he can perform a clean sweep from one ear to the other. Final hemostasis is performed and a drain is inserted through a stab wound. The bilateral scalp flap is then lifted and the amount of posterior overlap over the bald area is determined. Approximately the posterior third of the bald scalp is excised and the posterior aspect of the scalp flap is secured by a stable suture. Then the temporal flaps are advanced medially, the amount of overlap again evaluated and excised and the wound is closed by deep subcutaneous sutures and then a running buried 4-0 prolene suture (Brandy, 1993). The bilateral temporal lift The 2nd of the 2 commonly used scalp lifting patterns, generally following bilateral scalp lift by 3 or more months and may be aided by the insertion of a Frechet extender at the time of the previous scalp lift. Scar from previous bilateral scalp lift is excised, dissection is done in the same plane of previous operation but then the advancement of flaps is done from the temporal areas towards the center excising the remainder of the bald area and closing the wound with drainage in the mid-scalp (Swinehart, 1996). Figure 8 : Bilateral scalp lift (Lt) & bilateral temporal lift (Rt). (Swinehart, 1996)
15 ١٥ Biologic creep (alopecia reduction with scalp expansion) This is the predominant phenomenon in both chronic scalp expansion or scalp extension and involves actual synthesis of new collagen bundles that greatly improve the results obtained by alopecia reduction maneuvers overcoming scalp tightness and the resistance of the galea that inhibit closure of defect resulting form bald area removal. Scalp expansion This depends on actual volumetric expansion of the hair-bearing scalp. One or more silastic saline filled expanders are placed under the hear bearing scalp through incisions at the junction of bald and hairy scalp. Expanders are filled with saline 2-3 times weekly for a period of 6-8 weeks. After completion of expansion, flaps of the expanded scalp can be used to cover the defect resulting from removal of the bald area (Guzel et al, 2000). Most popular flaps include: 1-The expanded BAT flap (Bilateral advancement transposition flap), which uses bilateral vertical temporal posteriorly based transposition flaps. It provides excellent frontal coverage with a more natural hairline and a desirable temporal recession. It also has the advantages of ideal hair direction, ease of design and the absence of dog-ear deformity. 2-The expanded TAT Flap (Triple advancement transposition flap), which is similar to BAT flap with the addition of a third, expanded occipital flap to cover the bald crown and vertex areas. The transposed occipital flap combination avoids midline vertex scar and is an advantage to the patient for postoperative styling of hair in that region (Anderson, 1994). Figure 9 : BAT & TAT flaps (Hubbard, 1997)
16 ١٦ Scalp extension This is a form of non-volumetric scalp expansion where there is only a linear increase in the scalp area by the use of Frechet extenders implanted under the bald scalp. The extender is formed of two parallel silicone elastomer strips (elastic and possessing a memory), oriented perpendicularly to, and stitched to two titanium strips. These strips each contain hooks, which are engaged to the undersurface of the galea of the hair-bearing scalp on either sides of the bald area. The entire expander rests when implanted, on a thin pliable silicone elastomer sheet, which serves as a bed over which the contracting parallel strips can recoil without damaging the periostium. The extender is generally placed through a midline excision, the bald and hair-bearing scalp is undermined as far as possible, the amount of overlap of bald skin along skin incision is evaluated and this amount is excised completing the first alopecia reduction surgery. The extender is then implanted. The first row of hooks is engaged to the galea under one side of hair bearing scalp, the extender is elongated to at least double its original size, then the next row of hooks is engaged to galea under the hair bearing scalp on the other side. The scalp wound is then closed in the usual surgical fashion. Continuous traction by the hooks of the contracting extender produce gradual narrowing of the bald area bringing hear bearing scalp from both sides closer to each other. The desired stretch is obtained generally over only 4 weeks, then the device is removed and a second more extensive scalp reduction is performed. Complications of extender are few in the form of pain from the hooks, which can be alleviated by a pain killer, and infection, which is usually easy to control by antibiotics (Frechet, 1993). Figure 10: Frechet extender (Frechet, 1993)
17 ١٧ Scalp flaps Dramatic results in the treatment of alopecia have been obtained by various flaps, most popular of which is the parietooccipital flap (Juri's Flap) for reconstruction of the anterior hairline. However, because of a number of disadvantages the use of flaps has fallen out of favor. The hair orientation is in the wrong direction and without prior expansion the closure of the donor site is difficult and limits flap width. Also tension on closure tends to create a noticeable scarring. The area harvested is under risk of further alopecia and a scar at the frontal hairline cannot be avoided (Juri, 1975). Figure 11: Juri's Parietooccipital flap (Vallis, 1987) Planning hair restoration surgery for common baldness It is of paramount importance that hair restoration surgeon formulate a master plan for each patient. The master plan is based not only on the present patient's appearance but on the anticipated appearance in the years to come. For patients with hairline alopecia only (Norwood types I,II), the best solution is to use hair micrografting to recreate a new hairline using graft bearing I-3 hairs, and placing single haired grafts as the frontal transional zone between the bald forehead and the actual hairline. For patients with more extensive alopecia, a combination of scalp reduction or scalp lifting with micrografting may offer the best solution. Posterior crown baldness is treated first by scalp reduction or lifting followed by micrografting for alopecic hairline and anterior crown. Megasession micrografting, offers the potential for treatment of larger bald area with extensive micrografting alone (Swinehart, 1996).
18 ١٨ The future of hair restoration in common baldness The future carries much hope for great achievements in the hair restoration field. The search continues to identify the hair loss gene(s), the exact pattern of its inheritance, and its location on a specific chromosome. Trials to characterize the cellular location and molecular structure of dihydrotestosterone will enable scientists to develop drugs that can stimulate or block hair growth. Further research on 5-α reductase inhibitors including the development of topical creams is certainly warranted. In vivo hair follicle cloning is still in its infancy but the ability to effect in vivo follicle cloning will be a giant leap in the scope of hair restoration surgery. Although new developments surface daily in the field of instrumentation, yet the dream of every hair transplant surgeon is a device that can slice the donor scalp graft, dissect it into hair grafts and then implant it into the recipient site in a totally automated process that determine the exact number and size of the grafts and avoids injury of existing hair. A new device has been developed which can be considered a first step in that direction and still needs much evaluation is the System Calvitron micrograft sectioning device which takes the flat donor strip and dices it into multiple slices by pressing a hinged top containing multiple sharp knives onto the strip. The dissected grafts are then suctioned one by one into a saline filled tube and are then surgically implanted in previously prepared slits by a foot switch-controlled, hydraulically powered handpiece (Swinehart, 1996). Cicatricial alopecia Cicatricial alopecia results from accidental trauma including burns & scalds, bacterial infections & fungal infection, following tumor excision and radiodermatitis. Whatever the type of scarring alopecia, once the process has been shown to be static, surgical correction of cicatricial alopecia is started (Roenigk & Wheeland, 1987). The backbone of the treatment of cicatricial alopecia is the use of scalp flaps to transfer hair-bearing skin from inconspicuous areas to more obvious ones. One of the prime objectives in treating those patients is to re-establish a frontal hairline. Knowledge of the arterial supply and the direction it takes through the scalp is essential in designing the proper flap. Rotation flaps Small areas of cicatricial alopecia can often be excised and replaced with hair bearing rotation flaps that are usually larger than the original area of alopecia. The flap margin which will be the axis of rotation over which the flap will travel should be at least 5 times the length of the defect to be covered (Dingman & Argenta, 1982)
19 ١٩ Transposition flaps The knowledge of pattern of arterial supply of the scalp has allowed the use of narrow based long pedicle flaps which have the great advantage of easy rotation and less wasting of hair bearing skin in the dog ear that usually form at the base of wide based flaps. The most popular of these flaps is the Juri flap mentioned earlier in the creation of frontal hairline in male pattern baldness Bipedicled flaps They are used only in selected cases of cicatricial alopecia to transfer hearing bearing skin from the occipital region to the critical frontal area. Tissue expansion The introduction of tissue expanders has revolutionized the surgical treatment of cicatricial alopecia. The use of one or two expanders under hair bearing scalp can produce a considerable expansion of hair bearing skin, which can be used, in a variety of flaps to cover the alopecic part of the scalp (Silfen et al, 2000). Hair transplantation Hair micro grafting appears to be a promising restorative technique for the inelastic plaques of postburn alopecia provided that there is good elasticity and hair density over the occipital donor site (Moreno & Fresneda, 1999). Artificial Hair Implantation Recently, a new concept of artificial hair implantation has been introduced and started to gain popularity in certain parts of the world. Artificial hairs "Biofibre " are made of a synthetic co-polyamide which has characteristics similar to prolene but with the advantage of resistance to environmental factors. Fibres come with a knot at their inferior end and when inserted by a special apparatus, the knot is secured under the galea. It is claimed to have the advantages of simplicity, safety, ease of application, and immediate aesthetic result.it may be a possible solution of problems connected with lack of a donor area, with an atrophic or cicatricial scalp, with patient's refusal of invasive technique. Yet, it has the disadvantages of the need of periodical medical check-ups and periodical maintenance treatment. It has been licensed for use in Egypt in 1999, yet its use needs a lot of evaluation and experience before it can be a widely used option for the treatment of alopecia (D'Ugo, 1997). Alopecia Areata Alopecia areata cases constitute about 2% of new dermatological outpatient attendances in the UK and USA. At present cases of AA cannot be
20 ٢٠ attributable to a single cause (Messenger & Simpson, 1997). Two major factors have been incriminated in the aetiology of AA, namely, Genetic factors and Autoimmunity (Friedmann, 1981). The characteristic initial lesion is commonly a circumscribed totally bald smooth patch with a very varied subsequent progress. The initial patch may regrow within a few months or further patches may appear after a 3-6 weeks interval and then in a cyclical fashion. A succession of discrete patches may rapidly become confluent by the diffuse loss of the remaining hair (Messenger & Simpson, 1997). The variable and uncertain natural history of AA accounts for the multiplicity of uncritical claims of a large variety of therapeutic procedures: 1-Non specific counter irritants (Dithranol, Phenol) Feidler-Weiss & Buys (1987) reported a good cosmetic response in 25% of cases but with the side effects of pruritis & local erythema 2-Systemic corticosteroids Systemic corticosteroids will restore normal hair growth in many cases but the risks of using systemic high doses of steroids and the re-occurrence of hair loss on cessation of treatment rarely justifies this line of therapy (Unger & Schemmer, 1978). 3-Topical and intralesional steroids Can be used to accelerate regrowth if a disfiguring alopecic patch (Abell & Munro, 1973). 4-Topical immunotherapy The use of potent sensitizing diphencyprone DCP to induce contact dermatitis of the scalp has produced regrowth of hair in some sufferers. (Madani & Shapiro, 2000). It is felt to be the treatment of choice by many dermatologists (Bolduc & Shapiro, 2000). 5-Photochemotherapy (PUVA) Usage of combination of 8-methoxypsolaren & UVA (Lassus et al, 1984) & total body PUVA (Monfrecola et al, 1987) have been found to induce hair regrowth in a number of cases but the needed high dose of irradiation make this line of therapy rarely justified 6-Topical Minoxidil The mechanism of action of Minoxidil in cases of alopecia areata is still unknown but promising initial trials necessitate further evaluation (Fiedler- Weiss, 1984). 7-Immune modulation (Cyclosporin) Oral cyclosporin produces hair regrowth in alopecia totalis but the drug is both nephrotoxic and hepatotoxic. Topical cyclosporin has reported success in producing patchy hair regrowth, which need further evaluation (Dawber et al, 1998).
21 ٢١ Abell E., Munro D.D. References Intralesional treatment of alopecia areata with triamcinolone acetonide by jet injection Br J Dermatol, 1973; 88: Anderson R.D. Scalp expansion for the treatment of male pattern baldness. Perspectives in Plast Surg, 1994; 8: 1 B.Sough D.B & Miner J.E. Male pattern alopecia. Surgical Options Dermatologic clinics. 1997; 15 (4) October: Bernstein R.M. & Rassman W.R. The logic of follicular transplantation. Dermatol Clin, 1999; 17 (2): Blanchard G., & Blanchard B. Obliteration of alopecia by hair-lifting: a new concept and technique. J Natl Med Assoc, 1977; 69: 639 Bolduc C. & Shapiro J. DPCP for the treatment of alopecia areata Skin Therapy Lett, 2000; 5 (5): 3-4 Brandy D.A. Scalp lifting J Dermatol Surg Oncol, 1993; 19: Brandy D.A. A technique of hair-grafting in between existing follicles in patients with early pattern baldness Dermatol Surg, 2000; 26 (8): Buchwack K. Standard grafts, minigrafts and micrografts. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, 1994; 2: 149 Cooley J.E. & Vogel J.E. Follicular trauma and the role of dissecting microscope in hair transplantation. A multicenter study. Dermatol Clin, 1999; 17 (2): Dawber R.P.R., de Berker D. & Wojnarowska F. Disorders of hair In text book of dermatology
22 ٢٢ 6th edition, 1998: Edited by Champon R.H., Burton J.L., Burnsr D.A. & Breathnach S.M. Blackwell Science Limited De Villez R.L. Topical minoxidil therapy in hereditary androgenetic alopecia. Arch Dermatol, 1985; 121: Dingman R.O. & Argenta L.C. The surgical repair of traumatic defects of the scalp. Clin Plast Surg, 1982; 12: 131 D'Ugo A. Follow-up study of 503 patients three years after surgical implantation of artificial fibres on the scalp. 2 nd World post graduate course of plastic aesthetic and restorative surgery and aesthetic medicine, St.Petersberg May 20-23, 1997 Biofibre Internet Website : Farrell S.E. & Epstein S.K. Overdose of Rogaine Extra Strength for Men topical minoxidil preparation. J Toxico Clin Toxicol, 1999; 37 (6): Fiedler-Weiss V.C. Potential mechanisms of minoxidil-induced hair growth in alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol, 1987; 16: Fiedler-Weiss V.C., & Buys C.M. Evaluation of anthralin in the treatment of alopecia areata. Arch Dermatol, 1987; 123: Fitzpatrick R.E & Marchell N.L. Laser hair transplantation II. Dermatol Surg, 2000; 26 (5): Frechet P. Scalp extension J Dermatol Surg Oncol, 1993; 19: Friedmann P.S Alopecia areata and autoimmunity Br J Dermatol, 1981; 105: Guzel M.Z., Aydin Y., Hariri S. & Altintas M. Aesthetic results f treatment of large alopecia with total scalp expansion Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2000; 24 (2):
23 ٢٣ Hoffmann R. & Happle R. Current understanding of androgenetic alopecia. Part I: etiopathogenesis. Eur J Dermatol, 2000 ; 10 (4) : Hogan D.J & Chamberlain M. Male pattern baldness South Med J, 2000; 93 (7): Hubbard T.J. Hair restoration Surgery In Georgiade's Plastic, maxillofacial and reconstructive surgery 3 rd Edition, 1997: Edited by Georgiade G.S, Riefkohl R., & Levin L.S. Williams & Wilkins Jimenez F. & Ruifernandez J.M. Distribution of human hair in follicular units. A mathematical model for estimating donor size in follicular transplantation. Dermatol Surg, 1999; 25 (4): Juri J. Use of parietooccipital flaps in the surgical treatment of baldness. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1975; 55: 456. Knudsed R. Presentation at the 2 nd annual meeting of the international society of hair restoration surgery, Toronto, 1994 Cited in Georgiade's Plastic, maxillofacial and reconstructive surgery 3 rd Edition, 1997: 665 Edited by Georgiade G.S, Riefkohl R., & Levin L.S. Williams & Wilkins Koo S.H., Chung H.S, Yoon E.S. & Park S.H A new classification of male pattern baldness and a clinical study of the anterior hairline. Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2000; 24 (1): Lassus A., Eskwlinen A., & Johansson E. Treatment of alopecia areata with three different PUVA modalities Photodermatology, 1984; 1: Limmer B. International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery Meeting, Toronto, September 9 th, 1994 Cited in Swinehart's Color atlas of hair restoration First edition, 1996: 281 Appleton & Lange
24 ٢٤ Limmer B. Elliptical donor harvesting In Hair replacement: surgical and medical 3 rd edition, 1996: Edited by Stough D. Mosby Ludwig E. Classification of the types of androgenetic alopecia (Common baldness) occurring in the female sex Br J Dermatol, 1977; 97: Madani S. & Shapiro J. Alopecia areata update. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2000; 42 (4): Marritt E. Single-hair transplantation for hairline refinement: a practical solution. J Dermatol Surg Oncol, 1984; 10: 962 Marritt E. Micro-graft dilators: in pursuit of the undetectable hairline. J Dermatol Surg Oncol, 1988; 14: Marritt E. Transplantation of single hairs from the scalp as eye lashes. J Dermatol Surg Oncol, 1993; 6: Marritt E., & Konior R.J Patient selection candidacy and treatment plan for hair replacement surgery Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, 1994; 2: 111 Messenger A. & Simpson N.B. Alopecia Areata In diseases of the hair and scalp 3 rd edition, 1997: Edited by Dawber R.P.R. Blackwell Science Limited Monfrecola G., D'Anna F., & Delfino M. Topical hematoporphyrin plus PUVA for the treatment of alopecia areata. Photodermatology, 1987; 4: Moreno A.G & Fresneda C.A. Hair grafting in postburn alopecia Dermatol Surg, 1999; 25 (5):
25 ٢٥ Norwood O.T Male pattern baldness: Classification and incidence' South Med J, 1975; 68: Norwood O.T. Patient selection, hair transplant design and hair style J Dermatol Surg Oncol, 1992; 18: 386 Orentreich N. Autografts in alopecias and other selected dermatological conditions Ann NY Acad Sci, 1959; 83: 463 Pomerantez M.A. Creating a hairline Dermatol Clin, 1999; 17 (2): Randall J., & Schauder C. Current concepts in alopecia correction in the black patient. Am J Cosm Surg, 1993; 10:3 Rapioso E., Cella A., Panarese P., Mantero S., Nordstm R.E. & Santi P. Effects of cooling micrografts in hair transplantation surgery. Dermatol Surg, 1999; 25 (9): Reitschel R.L., & Duncan S.H. Safety and efficacy of topical minoxidil in the management of androgenetic alopecia J Am Acad Dermatol, 1987; 16: Roenigk R.K. & Wheeland R.G. Tissue expansion in cicatricial alopecia. Arch Dermatol, 1987; 123: Schauder C.S., Stough D.B & Chu T.P Modified S pattern for scalp reduction. Am J Cosm Surg, 1992; 9: Silfen R., Hudson D.A., Soldin M.G. & Skoll P.J. Tissue expansion for frontal hairline in severe alopecia in a child. Burns, 2000; 26 (3): Sintov A. Serafimovich S. & Gihar A. New topical antiandrogenic formulation can stimulate hair growth in human bald scalp grafted into mice. Int J Pharm, 2000; 194 (1):
26 ٢٦ Sommer M. & Wilson C. Therapeutic approaches to the management of common baldness Int J Clin Pract, 1999; 53 (5): Swerdloff J. & Kabaker S. The state of the art. Donor site harvest, graft yield estimation and recipient site preparation for follicular unit hair transplantation. Arch Facial Plast Surg, 1999; 1 (1): Swinehart J.M. Color atlas of hair restoration First edition, 1996 Appleton & Lange Tessler M.E Hair transplant surgery Recent Advances in Plastic Surgery, 1996; 5: Unger M.G. The modified major scalp reduction J Dermatol Surg Oncol, 1988; 14: Unger M.G. Scalp reduction. Clin Dermatol, 1992; 10: Unger M.G. & Unger W.P. Management of alopecia of the scalp by a combination of excisions and transplantations. J Dermatol Surg Oncol, 1978; 4: 670 Unger W.P. Hair transplantation 3 rd edition 1995: 183 Marcel Dekker Unger W.P. Treatment of Baldness In Grabb and Smith's Plastic Surgery 5 th Edition 1997: Edited by Aston S.J, Beasley R.W & Thorne C.H.M. Lippincott-Raven Unger W.P., & Schemmer R.J. Corticosteroids in the treatment of alopecia totalis Arch Dermatol 1978; 114:
27 ٢٧ Vallis C.P. Hair transplantation In Essentials of plastic, maxillofacial and reconstructive surgery. 1 st edition, 1987: Edited by Georgiade N.G., Georgiade G.S, Riefkohl R & Barwick W.J Williams & Wilkins Vogel J.E. Correction of the cornrow hair transplantation and other common problems in surgical hair restoration. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2000; 105 (4): Whitworth J.M, Stough D.B, Limmer B., Seager D, Boudjema P. Barrera A. Choi Y.C & Mangubat A. A comparison of graft implantation techniques for hair transplantation. Semin Cutan Med Surg, 1999; 18 (2):
STATE OF THE ART SURGICAL TECHNIQUE: FOLLICULAR UNIT HAIR GRAFTING
 STATE OF THE ART SURGICAL TECHNIQUE: FOLLICULAR UNIT HAIR GRAFTING Author: Jeffrey S. Epstein, M.D., F.A.C.S. Clinical Professor, University of Miami Private Practice, Miami, FL 305.666.1774 305.666.6708
STATE OF THE ART SURGICAL TECHNIQUE: FOLLICULAR UNIT HAIR GRAFTING Author: Jeffrey S. Epstein, M.D., F.A.C.S. Clinical Professor, University of Miami Private Practice, Miami, FL 305.666.1774 305.666.6708
www.healthoracle.org 1
 How does hair grow and should it recycle? A single hair follicle grows its hair strand over a period of four to six years (the anagen phase). It then rests for two to four months (the telogen phase), after
How does hair grow and should it recycle? A single hair follicle grows its hair strand over a period of four to six years (the anagen phase). It then rests for two to four months (the telogen phase), after
Clin Plastic Surg 32 (2005) 163 170. Hair Restoration. Alfonso Barrera, MD, FACS
 Clin Plastic Surg 32 (2005) 163 170 Hair Restoration Alfonso Barrera, MD, FACS Baylor College of Medicine, 902 Frostwood, Suite #163, Houston, TX 77024, USA The use of micrografts (one or two hair follicular
Clin Plastic Surg 32 (2005) 163 170 Hair Restoration Alfonso Barrera, MD, FACS Baylor College of Medicine, 902 Frostwood, Suite #163, Houston, TX 77024, USA The use of micrografts (one or two hair follicular
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN Skin is the largest organ of the body. The average adult has 18 square feet of skin which account for 16% of the total body weight. Skin acts as a physical barrier for you to the
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN Skin is the largest organ of the body. The average adult has 18 square feet of skin which account for 16% of the total body weight. Skin acts as a physical barrier for you to the
X-Plain Alopecia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Alopecia Reference Summary Introduction Hair loss is very common in both men and women. You or someone you love may be experiencing hair loss. Hair follicle Learning about normal hair growth is
X-Plain Alopecia Reference Summary Introduction Hair loss is very common in both men and women. You or someone you love may be experiencing hair loss. Hair follicle Learning about normal hair growth is
Integumentary System Individual Exercises
 Integumentary System Individual Exercises 1. A physician performs an incision and drainage of a subcutaneous abscess in his office for a particularly uncooperative established patient. How should this
Integumentary System Individual Exercises 1. A physician performs an incision and drainage of a subcutaneous abscess in his office for a particularly uncooperative established patient. How should this
Understanding Hair Loss and the ARTAS Robotic Hair Transplant
 Understanding Hair Loss and the ARTAS Robotic Hair Transplant The ARTAS Robotic System Table of Contents PART 1: Understanding Hair Loss 5 6 7 Why am I losing my hair? Why is my hair thinning? How far
Understanding Hair Loss and the ARTAS Robotic Hair Transplant The ARTAS Robotic System Table of Contents PART 1: Understanding Hair Loss 5 6 7 Why am I losing my hair? Why is my hair thinning? How far
What is androgenetic alopecia?
 What is androgenetic alopecia? Androgenetic alopecia is also called male pattern alopecia. It refers to a symptom that develops after puberty, influenced by the androgen, where thinning and/or loss of
What is androgenetic alopecia? Androgenetic alopecia is also called male pattern alopecia. It refers to a symptom that develops after puberty, influenced by the androgen, where thinning and/or loss of
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY
 MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY UMass Memorial Medical Center 55 Lake Avenue North Worcester, MA 01655 (508) 856-1666 Dr. Mary Maloney This booklet is intended to explain Mohs surgery to you. It is not, however,
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY UMass Memorial Medical Center 55 Lake Avenue North Worcester, MA 01655 (508) 856-1666 Dr. Mary Maloney This booklet is intended to explain Mohs surgery to you. It is not, however,
Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift. Plastic Surgery. For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures. Revolutionizing. Soft-Tissue Fixation
 Plastic Surgery Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures Revolutionizing Soft-Tissue Fixation DESIGNED FOR SIMPLICITY AND PREDICTABILITY The versatile design can be applied
Plastic Surgery Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures Revolutionizing Soft-Tissue Fixation DESIGNED FOR SIMPLICITY AND PREDICTABILITY The versatile design can be applied
PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System
 U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS PHaSES Range PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System Limbs & Things is pleased to introduce the PHaSES Range. The range is based upon our well known basic & general
U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS PHaSES Range PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System Limbs & Things is pleased to introduce the PHaSES Range. The range is based upon our well known basic & general
Oxford University Hospitals. NHS Trust. Dermatology Department Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia. Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Dermatology Department Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Information for patients What is Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA)? FFA is a condition which causes hair loss, mainly
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Dermatology Department Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Information for patients What is Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA)? FFA is a condition which causes hair loss, mainly
Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!!
 Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!! Presented by: Susan Ward, CPC, CPC-H, CPC-I, CPCD, CEMC, CPRC 1 1 CPT GUIDELINES Agenda CPT DEFINITIONS OP REPORT CASES 2 Definitions Cyst - a closed sac having
Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!! Presented by: Susan Ward, CPC, CPC-H, CPC-I, CPCD, CEMC, CPRC 1 1 CPT GUIDELINES Agenda CPT DEFINITIONS OP REPORT CASES 2 Definitions Cyst - a closed sac having
Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot
 Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
5 Upper eyelid blepharoplasty
 5 Upper eyelid blepharoplasty INSTRUMENTS Marking pen No. 15 scalpel blade Blade handle Castroviejo needle holder Castroviejo calipers 0.5 fixation forceps Westcott scissors 6-0 prolene suture Bovie cautery
5 Upper eyelid blepharoplasty INSTRUMENTS Marking pen No. 15 scalpel blade Blade handle Castroviejo needle holder Castroviejo calipers 0.5 fixation forceps Westcott scissors 6-0 prolene suture Bovie cautery
Chapter 11. Everting skin edges
 Chapter 11 PRIMARY WOUND CLOSURE KEY FIGURE: Everting skin edges In primary wound closure, the skin edges of the wound are sutured together to close the defect. Whenever possible and practical, primary
Chapter 11 PRIMARY WOUND CLOSURE KEY FIGURE: Everting skin edges In primary wound closure, the skin edges of the wound are sutured together to close the defect. Whenever possible and practical, primary
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT POLICY
 TITLE: Scar Revision/Keloid PAGE: 1of 9 This Medical policy is not a guarantee of benefits or coverage, nor should it be deemed as medical advice. In the event of any conflict concerning benefit coverage,
TITLE: Scar Revision/Keloid PAGE: 1of 9 This Medical policy is not a guarantee of benefits or coverage, nor should it be deemed as medical advice. In the event of any conflict concerning benefit coverage,
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift. Plastic Surgery. For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures. Revolutionizing. Soft-Tissue Fixation
 Plastic Surgery Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures Revolutionizing Soft-Tissue Fixation DESIGNED FOR SIMPLICITY AND PREDICTABILITY The versatile design can be applied
Plastic Surgery Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures Revolutionizing Soft-Tissue Fixation DESIGNED FOR SIMPLICITY AND PREDICTABILITY The versatile design can be applied
UROLOGY GROUP of PRINCETON
 UROLOGY GROUP of PRINCETON 134 STANHOPE STREET, PRINCETON, NJ 08540 PHONE 609-924-6487 FAX 609-921-7020 BARRY ROSSMAN, M.D. ALEX VUKASIN, M.D. KAREN LATZKO, D.O. ALEXEI WEDMID, M.D. VASECTOMY, THE NO SCALPEL
UROLOGY GROUP of PRINCETON 134 STANHOPE STREET, PRINCETON, NJ 08540 PHONE 609-924-6487 FAX 609-921-7020 BARRY ROSSMAN, M.D. ALEX VUKASIN, M.D. KAREN LATZKO, D.O. ALEXEI WEDMID, M.D. VASECTOMY, THE NO SCALPEL
STOP HAIR LOSS DR JOYCE LIM DERMATOLOGIST PARAGON MEDICAL CENTRE #11-16/20
 STOP HAIR LOSS DR JOYCE LIM DERMATOLOGIST PARAGON MEDICAL CENTRE #11-16/20 HAIR LOSS Types of Hair loss What causes them What are the solutions HAIR LOSS PATCHY HAIR LOSS PATCHY HAIR LOSS Single/ Multiple
STOP HAIR LOSS DR JOYCE LIM DERMATOLOGIST PARAGON MEDICAL CENTRE #11-16/20 HAIR LOSS Types of Hair loss What causes them What are the solutions HAIR LOSS PATCHY HAIR LOSS PATCHY HAIR LOSS Single/ Multiple
Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach
 Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
HIRSUTISM. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 HIRSUTISM What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about hirsutism. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and provides
HIRSUTISM What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about hirsutism. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and provides
Aestheticare Cosmetic Surgery Institute Dr. Ronald E. Moser 30260 Rancho Viejo Rd. San Juan Capistrano, CA 92675 (800) 662-1055
 Breast augmentation, or augmentation mammoplasty, is one of the most common plastic surgery procedures performed today. Over time, factors such as age, genetics, pregnancy, weight changes, sun exposure,
Breast augmentation, or augmentation mammoplasty, is one of the most common plastic surgery procedures performed today. Over time, factors such as age, genetics, pregnancy, weight changes, sun exposure,
Arizona State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee STANDARD INSTITUTIONAL GUIDELINE RODENT SURGERY
 Arizona State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee STANDARD INSTITUTIONAL GUIDELINE RODENT SURGERY It is the policy of the IACUC that all survival surgeries involving rodents be conducted
Arizona State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee STANDARD INSTITUTIONAL GUIDELINE RODENT SURGERY It is the policy of the IACUC that all survival surgeries involving rodents be conducted
Blepharoplasty - Eyelid Surgery
 Blepharoplasty - Eyelid Surgery Introduction Eyelid surgery repairs sagging or drooping eyelids. The surgery is also known as blepharoplasty, or an eyelid lift. Sagging or drooping eyelids happen naturally
Blepharoplasty - Eyelid Surgery Introduction Eyelid surgery repairs sagging or drooping eyelids. The surgery is also known as blepharoplasty, or an eyelid lift. Sagging or drooping eyelids happen naturally
Descemet s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK)
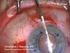 Descemet s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK) Your doctor has decided that you will benefit from a corneal transplant operation. This handout will explain your options to you. It explains the differences
Descemet s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK) Your doctor has decided that you will benefit from a corneal transplant operation. This handout will explain your options to you. It explains the differences
VARICOSE VEINS. Information Leaflet. Your Health. Our Priority. VTE Ambulatory Clinic Stepping Hill Hospital
 VARICOSE VEINS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Varicose Veins There are no accurate figures for the number of people with varicose veins. Some studies suggest that 3 in 100 people
VARICOSE VEINS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Varicose Veins There are no accurate figures for the number of people with varicose veins. Some studies suggest that 3 in 100 people
where hair grows Hair Restoration NO SCARS NO PAIN NO STRIPS It s your Hair - 100% Natural Results
 where hair grows Hair Restoration NO SCARS NO PAIN NO STRIPS It s your Hair - 100% Natural Results GOING BALD? HAIR LOSS? THINNING? NO MORE! - HAIR RESTORATION FROM FUECLINICS Hair transplantation involves
where hair grows Hair Restoration NO SCARS NO PAIN NO STRIPS It s your Hair - 100% Natural Results GOING BALD? HAIR LOSS? THINNING? NO MORE! - HAIR RESTORATION FROM FUECLINICS Hair transplantation involves
Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris. Emerging Applications
 Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Emerging Applications About Acne Vulgaris Very common - Affects 80% of population Almost every person experiences acne Most common reason to visit dermatologist
Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Emerging Applications About Acne Vulgaris Very common - Affects 80% of population Almost every person experiences acne Most common reason to visit dermatologist
PROPERTIES OF THE HAIR AND SCALP
 PROPERTIES OF THE HAIR AND SCALP 1. The scientific study of hair, its diseases and care is called: a. dermatology c. biology b. trichology d. cosmetology 2. The two parts of a mature hair strand are the
PROPERTIES OF THE HAIR AND SCALP 1. The scientific study of hair, its diseases and care is called: a. dermatology c. biology b. trichology d. cosmetology 2. The two parts of a mature hair strand are the
Give us a table of facelift complications. How would you treat each? Answers from Cummings:
 Give us a table of facelift complications. How would you treat each? Answers from Cummings: Hematoma The most common perioperative complication of rhytidectomy is hematoma, which occurs in 1% to 10% of
Give us a table of facelift complications. How would you treat each? Answers from Cummings: Hematoma The most common perioperative complication of rhytidectomy is hematoma, which occurs in 1% to 10% of
Blepharoplasty & Cosmetic eyelid surgery
 Our cosmetic surgery team at The USF Eye Institute offers a wide variety of cosmetic procedures of the eyelids and face with the goal of obtaining a natural and rejuvenated appearance. Dr.Leyngold has
Our cosmetic surgery team at The USF Eye Institute offers a wide variety of cosmetic procedures of the eyelids and face with the goal of obtaining a natural and rejuvenated appearance. Dr.Leyngold has
ABDOMINOPLASTY - FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)
 Executive Level E1, Excen Centre, 119 Willoughby Road, Crows Nest 2065 Tel: 02 9817 7585 www.mycosmeticclinic.net AFFORDABILITY WITH EXCELLENCE Liposuction Breast Augmentation Abdominoplasty Eyelids Surgery
Executive Level E1, Excen Centre, 119 Willoughby Road, Crows Nest 2065 Tel: 02 9817 7585 www.mycosmeticclinic.net AFFORDABILITY WITH EXCELLENCE Liposuction Breast Augmentation Abdominoplasty Eyelids Surgery
Kensington Eye Center 4701 Randolph Road, #G-2 Rockville, MD 20852 (301) 881-5701 www.keceyes.com
 Kensington Eye Center 4701 Randolph Road, #G-2 Rockville, MD 20852 (301) 881-5701 www.keceyes.com Natasha L. Herz, MD INFORMED CONSENT FOR DESCEMET S STRIPPING and AUTOMATED ENDOTHELIAL KERATOPLASTY (DSAEK)
Kensington Eye Center 4701 Randolph Road, #G-2 Rockville, MD 20852 (301) 881-5701 www.keceyes.com Natasha L. Herz, MD INFORMED CONSENT FOR DESCEMET S STRIPPING and AUTOMATED ENDOTHELIAL KERATOPLASTY (DSAEK)
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
CHAPTER 17 SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DEEP VALVE INCOMPETENCE Original author: Seshadri Raju Abstracted by Gary W. Lemmon Introduction Deep vein valvular incompetence happens when the valves in the veins (tubes
Wound Management and Basic Suturing Techniques. Disclosures
 Wound Management and Basic Suturing Techniques 10 July 2016 Douglas Winstanley, DO FAAD FACMS West Michigan Dermatology Grand Rapids MI Hugh Greenway s 33 nd Annual Cutaneous Anatomy and Surgery Course
Wound Management and Basic Suturing Techniques 10 July 2016 Douglas Winstanley, DO FAAD FACMS West Michigan Dermatology Grand Rapids MI Hugh Greenway s 33 nd Annual Cutaneous Anatomy and Surgery Course
Chapter 33. Nerve Physiology
 Chapter 33 NERVE AND VASCULAR INJURIES OF THE HAND KEY FIGURES: Digital nerve location on finger Epineurial repair Nerves and blood vessels of the hand and fingers usually are quite delicate, and some
Chapter 33 NERVE AND VASCULAR INJURIES OF THE HAND KEY FIGURES: Digital nerve location on finger Epineurial repair Nerves and blood vessels of the hand and fingers usually are quite delicate, and some
 no!no! Thermicon: A Novel, Home-based Hair Removal Device Dr. Mira Barki Yavne, Israel Introduction Lasers and intense pulsed light sources have become a popular method for long-term removal of unwanted
no!no! Thermicon: A Novel, Home-based Hair Removal Device Dr. Mira Barki Yavne, Israel Introduction Lasers and intense pulsed light sources have become a popular method for long-term removal of unwanted
Breast Augmentation Amsterdam Plastic Surgery Breast Augmentation Overview
 Breast Augmentation Amsterdam Plastic Surgery Breast Augmentation Overview The long-lasting results of breast augmentation are not limited to just physical changes as data documents that many patients
Breast Augmentation Amsterdam Plastic Surgery Breast Augmentation Overview The long-lasting results of breast augmentation are not limited to just physical changes as data documents that many patients
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Hair Loss: An Insider Guide to Hair Restoration and Replacement
 Hair Loss: An Insider Guide to Hair Restoration and Replacement November 2013 Why you may want more hair. Typically, people don t realize their hair is thinning until they ve lost 50% of it. By age 35,
Hair Loss: An Insider Guide to Hair Restoration and Replacement November 2013 Why you may want more hair. Typically, people don t realize their hair is thinning until they ve lost 50% of it. By age 35,
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE
 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Basic modules: List of individual modules Basic Module 1 Basic principles of general and dental medicine
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Basic modules: List of individual modules Basic Module 1 Basic principles of general and dental medicine
Basal Cell Carcinoma Affecting the Eye Your Treatment Explained
 Basal Cell Carcinoma Affecting the Eye Your Treatment Explained Patient Information Introduction This booklet is designed to give you information about having a Basal Cell Carcinoma near your eye and the
Basal Cell Carcinoma Affecting the Eye Your Treatment Explained Patient Information Introduction This booklet is designed to give you information about having a Basal Cell Carcinoma near your eye and the
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
What are spider veins? What is the best treatment for spider veins?
 Laser Spider/Leg Vein Q & A What are spider veins? Millions of women and men are bothered by unsightly spider veins on their faces and legs. Spider veins or telangiectasias are those small red, blue and
Laser Spider/Leg Vein Q & A What are spider veins? Millions of women and men are bothered by unsightly spider veins on their faces and legs. Spider veins or telangiectasias are those small red, blue and
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
How To Know If You Can See Without Glasses Or Contact Lense After Lasik
 The LASIK experience I WHO CAN HAVE LASIK? To be eligible for LASIK you should be at least 21 years of age, have healthy eyes and be in good general health. Your vision should not have deteriorated significantly
The LASIK experience I WHO CAN HAVE LASIK? To be eligible for LASIK you should be at least 21 years of age, have healthy eyes and be in good general health. Your vision should not have deteriorated significantly
THYMECTOMY. Thymectomy. Common questions patients ask about thymectomies. www.myasthenia.org
 THYMECTOMY Thymectomy Common questions patients ask about thymectomies. www.myasthenia.org The following are some of the most common questions asked when a thymectomy is being considered for adult and
THYMECTOMY Thymectomy Common questions patients ask about thymectomies. www.myasthenia.org The following are some of the most common questions asked when a thymectomy is being considered for adult and
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY
 Mary E. Maloney, MD Director Professor of Medicine David E. Geist, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Dori Goldberg, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Mark J. Scharf, MD Professor of Medicine Jason D.
Mary E. Maloney, MD Director Professor of Medicine David E. Geist, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Dori Goldberg, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Mark J. Scharf, MD Professor of Medicine Jason D.
Surgical scissors and forceps Product List
 Surgical scissors and forceps Product List Sr. No Items Picture of Product Product specification 1 Grasping forceps-- 5 MM Grasping forceps are used to remove stones and retrieve foreign objects under
Surgical scissors and forceps Product List Sr. No Items Picture of Product Product specification 1 Grasping forceps-- 5 MM Grasping forceps are used to remove stones and retrieve foreign objects under
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Package Leaflet: Information for the user Propecia 1 mg film-coated Tablets Finasteride
 Package Leaflet: Information for the user Propecia 1 mg film-coated Tablets Finasteride This medicine is for use in men only Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
Package Leaflet: Information for the user Propecia 1 mg film-coated Tablets Finasteride This medicine is for use in men only Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because
How To Harvest Fat From The Infratemporal Fossila
 Techniques in Cosmetic Surgery Harvesting Fat from the Infratemporal Fossa Bahman Guyuron, M.D., and Kevin Rose, M.D. Cleveland, Ohio As part of forehead rejuvenation and surgical treatment of migraine
Techniques in Cosmetic Surgery Harvesting Fat from the Infratemporal Fossa Bahman Guyuron, M.D., and Kevin Rose, M.D. Cleveland, Ohio As part of forehead rejuvenation and surgical treatment of migraine
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias. A simple guide to help answer your questions
 Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER PROPECIA 1 mg film-coated Tablets (finasteride)
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER PROPECIA 1 mg film-coated Tablets (finasteride) This medicine is for use in men only Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start to take this medicine.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER PROPECIA 1 mg film-coated Tablets (finasteride) This medicine is for use in men only Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start to take this medicine.
41 Assisting with Minor Surgery
 Learning Outcomes 41.1 Define the medical assistant s role in minor surgical procedures. 41-2 CHAPTER 41 Assisting with Minor Surgery 41.2 Describe types of wounds and explain how they heal. 41.3 Describe
Learning Outcomes 41.1 Define the medical assistant s role in minor surgical procedures. 41-2 CHAPTER 41 Assisting with Minor Surgery 41.2 Describe types of wounds and explain how they heal. 41.3 Describe
Tissue Reinforcement with Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix following Correction of Severe Breast Deformity
 Tissue Reinforcement with Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix following Correction of Severe Breast Deformity Robert Cohen, MD, FACS* Paradise Valley, AZ Case summary A 41-year old woman with a history
Tissue Reinforcement with Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix following Correction of Severe Breast Deformity Robert Cohen, MD, FACS* Paradise Valley, AZ Case summary A 41-year old woman with a history
COPYRIGHT ASPS. Breast Augmentation. The Symbol of Excellence in Plastic Surgery
 Breast Augmentation The Symbol of Excellence in Plastic Surgery A public education service of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons and the American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. This brochure
Breast Augmentation The Symbol of Excellence in Plastic Surgery A public education service of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons and the American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. This brochure
Duckworth & Kent Ophthalmic Titanium Surgical Instruments
 Duckworth & Kent Ophthalmic Titanium Surgical Instruments at the Leading Edge LASIK Instruments Duckworth and Kent is the first and original manufacturer and supplier of titanium surgical instruments.
Duckworth & Kent Ophthalmic Titanium Surgical Instruments at the Leading Edge LASIK Instruments Duckworth and Kent is the first and original manufacturer and supplier of titanium surgical instruments.
Breast Augmentation. If you are dissatisfied with your breast size, augmentation surgery is a choice to consider. Breast augmentation can:
 Breast Augmentation What is Breast Augmentation? Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume
Breast Augmentation What is Breast Augmentation? Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
What is a dental implant?
 What is a dental implant? Today, the preferred method of tooth replacement is a dental implant. They replace missing tooth roots and form a stable foundation for replacement teeth that look, feel and function
What is a dental implant? Today, the preferred method of tooth replacement is a dental implant. They replace missing tooth roots and form a stable foundation for replacement teeth that look, feel and function
Breast Reconstruction Options. Department of Plastic Surgery #290 Santa Clara Homestead Campus
 Breast Reconstruction Options Department of Plastic Surgery #290 Santa Clara Homestead Campus Importance of Breast Reconstruction As successes in treating breast cancer have grown, more women have been
Breast Reconstruction Options Department of Plastic Surgery #290 Santa Clara Homestead Campus Importance of Breast Reconstruction As successes in treating breast cancer have grown, more women have been
Selection & Use of Surgical Needles
 Selection & Use of Surgical Needles EThALLOy * INTELLIGENT GEOMETRy ADVANCED NEEDLE COATING The Selection & Use of Surgical Needles EThICON Products needles are manufactured in a wide range of types, shapes,
Selection & Use of Surgical Needles EThALLOy * INTELLIGENT GEOMETRy ADVANCED NEEDLE COATING The Selection & Use of Surgical Needles EThICON Products needles are manufactured in a wide range of types, shapes,
There are a wide range of factors that can impact on the health of the hair and hair growth.
 Welcome to Viviscal Viviscal, one of the best selling hair growth supplement in the US, is now available with TVSN. The Viviscal brand of hair care products is enjoying rapid and substantial growth in
Welcome to Viviscal Viviscal, one of the best selling hair growth supplement in the US, is now available with TVSN. The Viviscal brand of hair care products is enjoying rapid and substantial growth in
Please visit your examination provider s website for the most current bulletin prior to testing. IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS
 NATIONAL BARBER THEORY EXAMINATION CANDIDATE INFORMATION BULLETIN Please visit your examination provider s website for the most current bulletin prior to testing. The National Barber Theory Examination
NATIONAL BARBER THEORY EXAMINATION CANDIDATE INFORMATION BULLETIN Please visit your examination provider s website for the most current bulletin prior to testing. The National Barber Theory Examination
Breast Reconstruction Frequently Asked Questions
 Breast Reconstruction Frequently Asked Questions GENERAL Do I need to have breast reconstruction? It is never medically necessary to have breast reconstruction. This is considered an elective procedure,
Breast Reconstruction Frequently Asked Questions GENERAL Do I need to have breast reconstruction? It is never medically necessary to have breast reconstruction. This is considered an elective procedure,
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
 Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Chapter 12. Anatomy of Skin. Epidermis. Dermis
 Chapter 12 SKIN GRAFTS KEY FIGURES: Skin anatomy with graft thickness Humby knife Using the dermatome Using the Humby knife Mesher Skin graft Tying the dressing in place Defatting the FTSG A skin graft
Chapter 12 SKIN GRAFTS KEY FIGURES: Skin anatomy with graft thickness Humby knife Using the dermatome Using the Humby knife Mesher Skin graft Tying the dressing in place Defatting the FTSG A skin graft
Corporate Medical Policy Reconstructive Eyelid Surgery and Brow Lift
 Corporate Medical Policy Reconstructive Eyelid Surgery and Brow Lift File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: reconstructive_eyelid_surgery_and_brow_lift 1/2000 9/2015 9/2016
Corporate Medical Policy Reconstructive Eyelid Surgery and Brow Lift File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: reconstructive_eyelid_surgery_and_brow_lift 1/2000 9/2015 9/2016
Preparing to Suture. 6 th Annual Pediatric Advanced Practice Conference Tuesday, February 9, 2016 1:30 pm. Workshop B: Suturing for Beginners
 Preparing to Suture Kristen Devick, MPAS, PA-C University of Colorado Department of Emergency Medicine NONE! Skin Anatomy Trott, 2012, p.11 Preparing to suture Initial evaluation Hemostasis Anesthesia
Preparing to Suture Kristen Devick, MPAS, PA-C University of Colorado Department of Emergency Medicine NONE! Skin Anatomy Trott, 2012, p.11 Preparing to suture Initial evaluation Hemostasis Anesthesia
Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Hair Chemistry. Chapter 1. Hair Relaxers Science, Design, and Application www.alluredbooks.com
 Hair Relaxers Science, Design, and Application www.alluredbooks.com Chapter 1 Hair Chemistry We all know that the hair on our head is dead, but underneath the scalp, within the hair follicle, is a surprisingly
Hair Relaxers Science, Design, and Application www.alluredbooks.com Chapter 1 Hair Chemistry We all know that the hair on our head is dead, but underneath the scalp, within the hair follicle, is a surprisingly
Hair loss? I ve got a grip on it! Brochure for women on hair loss and its treatment. Dependably effective against hair loss
 Hair loss? I ve got a grip on it! Brochure for women on hair loss and its treatment Dependably effective against hair loss Hair is part of a woman s natural beauty. Hair loss is more than a medical problem
Hair loss? I ve got a grip on it! Brochure for women on hair loss and its treatment Dependably effective against hair loss Hair is part of a woman s natural beauty. Hair loss is more than a medical problem
FREEDOM INGUINAL Hernia Repair System TECHNIQUE GUIDE
 FREEDOM INGUINAL Hernia Repair System TECHNIQUE GUIDE The following describes the open surgical preparation and implantation technique for the Freedom Inguinal Hernia Repair System. 1) Anesthesia can be
FREEDOM INGUINAL Hernia Repair System TECHNIQUE GUIDE The following describes the open surgical preparation and implantation technique for the Freedom Inguinal Hernia Repair System. 1) Anesthesia can be
Hair Loss. The medical term for hair loss is alopecia and there are many types. What is the normal cycle of hair growth and loss?
 Hair Loss By Eamonn Brady (MPSI) The medical term for hair loss is alopecia and there are many types. What is the normal cycle of hair growth and loss? Hair is composed of protein called keratin. Keratin
Hair Loss By Eamonn Brady (MPSI) The medical term for hair loss is alopecia and there are many types. What is the normal cycle of hair growth and loss? Hair is composed of protein called keratin. Keratin
Tucson Eye Care, PC. Informed Consent for Cataract Surgery And/Or Implantation of an Intraocular Lens
 Tucson Eye Care, PC Informed Consent for Cataract Surgery And/Or Implantation of an Intraocular Lens INTRODUCTION This information is provided so that you may make an informed decision about having eye
Tucson Eye Care, PC Informed Consent for Cataract Surgery And/Or Implantation of an Intraocular Lens INTRODUCTION This information is provided so that you may make an informed decision about having eye
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
Hair & Fiber. (Unit 5)
 37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
The «three-in-one» Microkeratome for traditional LASIK, EPI-LASIK, and anterior and posterior Lamellar Keratoplasty
 The «three-in-one» Microkeratome for traditional LASIK, EPI-LASIK, and anterior and posterior Lamellar Keratoplasty Ziemer Group We develop and produce diagnostic and surgical products for the ophthalmic
The «three-in-one» Microkeratome for traditional LASIK, EPI-LASIK, and anterior and posterior Lamellar Keratoplasty Ziemer Group We develop and produce diagnostic and surgical products for the ophthalmic
INFORMED CONSENT DERMABRASION
 INFORMED CONSENT DERMABRASION INSTRUCTION This is an informed-consent document which has been prepared to help your plastic surgeon inform you about dermabrasion, its risks, and alternative treatments.
INFORMED CONSENT DERMABRASION INSTRUCTION This is an informed-consent document which has been prepared to help your plastic surgeon inform you about dermabrasion, its risks, and alternative treatments.
LASIK EPILASIK FEMTOSECOND LASER. Advantages
 LASIK EPILASIK FEMTOSECOND LASER Advantages There are many advantages to having laser vision correction. Laser vision correction gives most patients the freedom to enjoy their normal daily activities without
LASIK EPILASIK FEMTOSECOND LASER Advantages There are many advantages to having laser vision correction. Laser vision correction gives most patients the freedom to enjoy their normal daily activities without
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
A Patient s Guide to Guyon s Canal Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
Skin cancer Patient information
 Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
Skin cancer Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This
The Use of MEDIHONEY for Wound Management in Oncology
 The Use of MEDIHONEY for Wound Management in Oncology Presenter: Patrice M. Dillow, MSN, APRN, CWOCN Cancer Treatment Centers of America Midwestern Regional Medical Center A Magnet Hospital This presentation
The Use of MEDIHONEY for Wound Management in Oncology Presenter: Patrice M. Dillow, MSN, APRN, CWOCN Cancer Treatment Centers of America Midwestern Regional Medical Center A Magnet Hospital This presentation
CONSENT FORM. Procedure: Descemet s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK)
 CONSENT FORM Procedure: Descemet s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK) Surgeon: Jeffrey W. Liu, M.D. Peninsula Laser Eye Medical Group 1174 Castro Street, Ste. 100 Mountain View, CA 94040
CONSENT FORM Procedure: Descemet s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK) Surgeon: Jeffrey W. Liu, M.D. Peninsula Laser Eye Medical Group 1174 Castro Street, Ste. 100 Mountain View, CA 94040
Scout Vessel Guard. A cover for vessels during anterior lumbar spine surgery.
 Scout Vessel Guard. A cover for vessels during anterior lumbar spine surgery. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Scout Vessel Guard 2
Scout Vessel Guard. A cover for vessels during anterior lumbar spine surgery. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Scout Vessel Guard 2
Integra. Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
INFORMED CONSENT FOR LASIK SURGERY
 IMPORTANT: READ EVERY WORD! This information is to help you make an informed decision about having laser assisted in-situ keratomileusis (LASIK) surgery to treat your nearsightedness, farsightedness and/or
IMPORTANT: READ EVERY WORD! This information is to help you make an informed decision about having laser assisted in-situ keratomileusis (LASIK) surgery to treat your nearsightedness, farsightedness and/or
ADVANCED SUTURING WORKSHOP ANN BECKER, APRN-CNP; TONI PRATT-REID, APRN-CNP
 ADVANCED SUTURING WORKSHOP ANN BECKER, APRN-CNP; TONI PRATT-REID, APRN-CNP SUTURING WORKSHOP! The technique of suturing, as a method for closing cutaneous wounds has been a part of medicine for hundreds
ADVANCED SUTURING WORKSHOP ANN BECKER, APRN-CNP; TONI PRATT-REID, APRN-CNP SUTURING WORKSHOP! The technique of suturing, as a method for closing cutaneous wounds has been a part of medicine for hundreds
Informed Consent For Laser Hair Removal
 Informed Consent For Laser Hair Removal INSTRUCTIONS This informed-consent document has been prepared to help inform you about laser procedures, its risks, as well as alternative treatment(s). It is important
Informed Consent For Laser Hair Removal INSTRUCTIONS This informed-consent document has been prepared to help inform you about laser procedures, its risks, as well as alternative treatment(s). It is important
ANTERIOR CERVICAL DISCECTOMY AND FUSION. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Cervical Spine
 Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
Anterior In the human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or position of one structure relative to another Cervical Relating to the neck, in the spine relating to the first seven vertebrae
