ICSU mobilizes the knowledge and resources of the international science community for the benefit of society, to:
|
|
|
- Elijah Adams
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 About ICSU ROAP ICSU Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific was inaugurated on the 19 September by the Deputy Prime Minister of Malaysia, Y.A.B. Dato Seri Najib Tun Abdul Razak. The new office will promote the development of science throughout Asia and the Pacific and help strengthen the voice of developing countries in this region. It will also ensure that its scientists become involved in those aspects of the ICSU Strategic Plan that are especially relevant for this area. Mission Statement ICSU mobilizes the knowledge and resources of the international science community for the benefit of society, to: identify and address major issues of importance to science and society Facilitate interaction amongst scientists across all disciplines and from all countries Promote the participation of all scientists in the international scientific endeavour, regardless of face, citizenship, language, political stance or gender Provide independent, authoritative advice to stimulate constructive dialogue between the scientific community and governments, civil society, and the private sector Suggested citation : International Council for Science Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific (2008) Science Plan on Hazards and Disasters : Earthquakes, Floods and Landslides II ICSU ROAP 2008
3 SCIENCE PLAN ON HAZARDS AND DISASTERS Earthquakes, Floods And Landslides Report of ICSU ROAP Planning Group on Natural and Human Induced Enviromental Hazards and Disasters June 2008 III
4 IV contents
5 PREFACE ACKNOWLEDGEMNTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY BACKGROUND 1 Importance of the Asia and Pacific Region 2 ICSU International Programme on Hazards and Disasters 4 Rationale of ROAP Interest in Hazards and Disasters 4 VISION, AIM AND OBJECTIVES OF THE SCIENCE PLAN 6 HAZARDS AND DISASTERS IN ASIA AND THE PACIFIC 7 Earthquakes 8 Introduction 8 Global Distribution 8 Monitoring and Observation System 9 Hazard Mapping 9 Hazard Mapping 9 Earthquake Scenarios 10 Prevention and Mitigation 10 Building Codes 10 Micro-zonation 10 Education and Awareness 11 Non-engineered Structures 11 Warning Systems 11 Earthquakes 11 Tsunamis 11 Triggered Earthquakes 12 Case Studies 12 Linkages 12 Suggested Areas of Project Development 13 Floods 13 Introduction 13 Flood Prevention and Mitigation 13 Demonstration Studies, Projects and Interdisciplinary Linkages 14 Improving Monitoring Systems 14 Predictability, Hazard Assessment and Regional Flood 14 Warning Systems Major Research Activities 15 Geographical Flood Hazard Mapping 15 Investigations of Flood Mechanisms 15 Effects of Climate Change 15 Suggested Areas of Project Development 15 Landslides 15 Introduction 15 Landslide Causes 16 Increase of Shear Stress 16 Decrease of Shear Resistance 16 Climate Change in Landslide Initiation 16 Monitoring and Observation Systems 17 Predictability and Hazard Assessment 17 Prevention and Mitigation 17 Linkages 17 Human Activity 17 Climate Change 18 Cooperation with Other International Initiatives 18 Suggested Areas of Project Development 18 Disaster Management and Capacity Building 18 Introduction 18 Role of Social Sciences 19 Improving the Quality of Decision-making 19 Economic Valuation of Losses and Damage 19 Macroeconomic Costs and Disasters 20 Microeconomic Losses 21 V
6 Role of the Private Sector and Civil Societies 21 Capacity Building 21 Policy Relevance 22 Information Gathering and Sharing 22 Community Interest, Education and Awareness 22 Suggested Areas of Project Development 22 Building and Enhancing Regional Capacity Building 22 for Disaster Risk Reduction Building Self-sustaining Capacity at Various Levels 23 for Different Hazards Establishing Continuity in Capacity Building 23 THE PLAN FOR ASIA AND THE PACIFIC 25 Earthquakes 26 Floods 27 Landslides 28 Disaster Management and Capacity Building 29 CONCLUSIONS 30 BIBLIOGRAPHY 31 ANNEXURE S 32 Annex I Terms of References 32 Annex II Planning Group on Hazards and Disasters 33 Annex III International Collaboration on Natural Hazards 35 Annex IV Acronyms 37 VI
7 Preface The impact of natural and human-induced environmental hazards and disasters on humans and the environment continues to rise. ICSU is in the process of establishing a major new international initiative on natural and human-induced environmental hazards and disasters. Keeping the above in mind and considering that the geographical area covered by ICSU Regional Office for Asia and Pacific (ROAP) accounts for more than one-half of the world population, and about 80% of all losses due to natural hazards globally, ROAP has identified work in natural and humaninduced hazards and disasters as a priority. A Science Plan on Hazards and Disasters was needed to address research needs in three categories of hazards and disasters, namely earthquakes, floods and landslides. The niche of the proposed Science Plan is to utilize the latest knowledge and best practices to address problems related to earthquakes, floods and landslides in the Asia Pacific region so as to prevent hazards becoming disasters. We hope to make an impact on mitigating natural and humaninduced hazards and disasters in the Asia Pacific region. Harsh Gupta Chair ICSU ROAP Science Planning Group on Hazards and Disasters A Planning Group consisting of experts in natural and human-induced hazards and disasters, especially of earthquakes, floods and landslides, was established. The group met twice and was engaged in much electronic exchanges to produce a draft science plan. All relevant local, regional and international programmes on these hazards were reviewed. It was noted that despite advances in the natural and social sciences of hazards and disasters, losses of lives and properties have continued to increase. It was recognized that the available scientific knowledge is not optimally utilized in forecasting hazards and estimating risks, and that greater outreach would benefit the public, particularly in a large part of the geographical area covered by ROAP. This document is an outcome of extensive discussions among the members of the Planning Group and consultations with several other experts. We are aware that the task at hand is very complex. VII
8 Acknowledgements Many individuals and organizations contributed to the preparation of this plan. A full list of the members of the ICSU ROAP Science Planning Group is given in Annex II. Special thanks are due to the presenters at the Regional Conference on Natural and Human-induced Hazards and Disasters organized by ICSU ROAP in September 2006 that laid the foundation for this Plan. They included Gordon McBean, Tom Beer, Chen Dehui, Cecep Subaraya, Yap Kok Seng, Daniel Murdiyarso, Joe Chung and Kenji Satake. Three other presenters, Harsh Gupta, Chamhuri Siwar and Kyoji Sassa, became members of the Science Planning group with Harsh Gupta as the Chair of the Planning Group. Additionally, Trieu Dinh Cao, James Terry, Christel Rose and Seree Supharatid also provided valuable input to the work of the group. Thanks are also due to the members of the ICSU Regional Committee for Asia and the Pacific under the chairmanship of Anupam Varma for their ideas, reviews and comments. Interactions with Thomas Rosswall, Howard Moore and Patricia Ocampo-Thomason of the ICSU Secretariat were useful. Vineet Gahalaut, Uma Anuradha, Nor Zaneedarwaty Norman and Hizam Jaafar contributed at various stages of the production of this document. VIII
9 Executive Summary With the passage of time, the impacts of natural and human-induced environmental hazards and disasters continue to increase. The important question is: Why, despite advances in the natural and social sciences of hazards and disasters, do losses continue to increase? Keeping this in mind ICSU created a Planning Group to make suitable recommendations for implementation. The geographical area covered by ICSU ROAP accounts for more than one half of the world s population and for almost 80% of all losses due to natural hazards globally. The classical examples in the recent past are: the Sumatra earthquake of 2004 and the resultant tsunami that claimed some 250,000 human lives and inflicted unprecedented economic losses; two tropical storms that caused 130,000 deaths in Bangladesh in 1991; and the 2002 landslide in Nepal which affected 265,000 people. China had a massive earthquake on May 12, 2008 claiming about 70,000 lives. ICSU had already taken a major initiative to address the issue of Natural Hazards, ROAP chose Natural and Human-Induced Environmental Hazards and Disasters in Asia and the Pacific as a priority area in September At the Board Meeting of ROAP in Tehran, Iran, in March 2007, it was decided that ROAP shall focus on three natural hazards, namely floods, earthquakes and landslides. There are several bodies, and national and international programmes operating in hazard-related studies; ICSU ROAP s effort is to collaborate in a few niche areas. The group noted the special situation for the ROAP geographical area due to the presence of a large number of islands vulnerable to hazards in the region. Involvement of social scientists is necessary to ensure that benefits of current-day knowledge are appropriately implemented to reduce hazards. We recognize that the results of basic research form the foundation of all scientific and technical interventions. We shall emphasize on the use of the available results and interweave them with social sciences to make them effective. The major recommendations are highlighted below. Earthquakes Several countries in the Asia Pacific region do not have adequate earthquake recording facilities, which need to be identified and improved. The development of scenarios of present-day losses (social and economic), if earlier earthquakes recur, and building codes for earthquake-prone countries is also necessary. A major effort is required to estimate the accelerations at the surface taking into consideration the local ground conditions and use them for micro-zonation of major cities. Self-designed non-engineered homes can be improved enormously by simple inexpensive retrofitting. It is also important to learn to live with earthquakes in earthquake-prone areas. This is where promotion of public awareness plays a vital role. Artificial water reservoirs have triggered damaging earthquakes. There are ways and means now available to find safer sites. A few (four to five) case studies of earthquakes would be very helpful. Floods An effort is required to set up sophisticated flood prediction and warning systems as has been already done in many developed countries. It would be important to identify vulnerability of countries to flooding and develop suitable building codes and construction regulations and a IX
10 robust methodology to implement them. It is also crucial to communicate information related to flood prevention and mitigation to communities for their use. The proposed flood related work would be coordinated with other existing national and international programmes. The science plan suggests to develop projects relevant to the problems identified. We hope to improve the situation in the Asia Pacific region with support and collaboration of all concerned so that fewer hazard events develop into disasters. Landslides Rapid population growth has intensified urban, mountain and coastal development in the Asia and the Pacific region, which are increasing human-induced landslide hazard and landslide vulnerability in urbanized areas. Application of landslide prevention technology is required in areas such as cultural heritage sites and other locations of high-societal values, where relocation and early warning are not possible or very difficult. The most cost-effective measure to mitigate landslide disasters is early warning and evacuation. Timely prediction and early warning technology, suitable for the Asia and the Pacific region should be developed. A few case studies of landslides would be very helpful. Disaster Management and Capacity Building It has been recognized that the available scientific knowledge is not being fully utilized in forecasting the hazards, estimating the risks, and the necessary outreach for the benefit of the public, particularly in a large part of the area covered by ROAP. It is important to stress the role of social sciences in understanding hazards and their mitigation; and the role of the private sector and civil societies in building and enhancing regional capacity for disaster reduction, building self-sustaining capacity at various levels for different hazards and establishing continuity in capacity building. X
11 01 Background Background
12 Importance of the Asia and the Pacific (AP) Region Earthquake, Floods and Landslides The geographical area covered by ICSU Regional Office for Asia and Pacific accounts for more than one-half of the world s population and for almost 80% of all losses due to natural hazards globally (Figure 1.1). The classical examples in recent years are the Tangshan earthquake of China in 1976 accounting for 242,000 human lives lost; the Kobe earthquake of Japan in 1995 claiming some 6,000 human lives and the economic losses in excess of US$150 billion; the Sumatra earthquake of 2004, the resultant tsunami claiming some 250,000 human lives and unprecedented economic losses; and the Muzaffarabad earthquake of 2005 claiming some 88,000 human lives. Japanese seismologists have estimated that a possible future earthquake of M7.5 in the vicinity of Tokyo would cost about US$1.2 trillion. in Bangladesh on 29 April 1991; in China material damage during the summer 1998 floods rose up to US$30 billion; in India, the Mumbai flooding with the unprecedented rainfall of 994 mm on July, 2005 caused 1000 deaths and US$750 million worth economical losses. Asia-Pacific region also has significant landslide problems. The landslides in Nepal during 2002 displaced 265,865 people. Another unique feature of the Asia-Pacific region is the large number of island countries and islands in the region, which are inherently more vulnerable to earthquakes, floods and landslides. At least 40 people died in the Solomon Islands after a tsunami swept ashore following the M8.1 earthquake on 2 April Tropical cyclone Ami created havoc in the island country, Fiji, and the resulting torrential rains caused the worst-ever flooding in many rivers on Vanua Leve Island of Fiji claiming 17 human lives. 2 Figure 1.1 Natural disaster occurrences by disaster type and percentages of people killed by natural disasters by continent (Source: UN/ISDR CRED and EMDAT www. em-dat.net ) In addition to earthquakes, floods have been a major natural hazard in the Asia and the Pacific region. Several serious and dramatic flood events, which were mostly induced by tropical cyclones or torrential rain, have occurred. For example floods and strong winds induced by two tropical storms caused 130,000 deaths High population densities, poor constructions, inadequate preparations and lack of general awareness among the inhabitants in disaster-prone areas are the major factors contributing to hazards becoming disasters. For example an M6.2 earthquake in Latur, western India, on 29 September 1993 claimed an estimated 10,000 human lives. The reasons for such a large number of lives lost were a very high population density, people living in non-engineered houses, which had little resistance against horizontal accelerations of earthquake, and the fact that the earthquake occurred at about 4 am local time when everyone was asleep inside homes. Most of the self-made homes in Latur and the nearby regions collapsed causing such a large number of deaths.
13 The Asian region also has to its discredit a large number of cases of triggered earthquake sequences as a result of impoundment of artificial water reservoirs. Earthquake exceeding M6 occurred at Hsingfengkiang Reservoir in China and Koyna Reservoir in India. As far as floods are concerned, very high population densities and inappropriate uses of natural water outlets increase the flood disaster in the AP region. For example, in Bangladesh as many as 80 million people are vulnerable to flooding each year. In India a total area of 40 million hectares is at risk from flooding each year. The unprecedented flooding in Mumbai on July 2005 was due to the 944 mm rainfall in 24 hours and the fact that the natural outlet, River Mithi, was silted and as a consequence had lost most of its carrying capacity. Another factor for the occurrence of floods is the misuse of polythene bags, covers, etc. which are disposed of indiscriminately, chocking the water outlets. Background
14 Earthquake, Floods and Landslides ICSU International Programme on Hazards and Disasters With the passage of time the impacts of natural hazards continue to increase around the world. The globalization and growth of human societies and their escalating complexity and the changing climate will further increase the risks of natural hazards. The objective of the proposed research programme Integrated Research on Disaster Risk the Challenge of Natural and Human-induced Environmental Hazards (acronym: IRDR) would be to undertake coordinated international multidisciplinary research leading to more effective global societal responses to the risks associated with natural and human-induced environmental hazards. This would lead to enhanced capacity around the world to address hazards and make informed decisions on actions to reduce their impacts, such that in ten years, when comparable events occur, there would be a reduction in relative loss of life, fewer adversely impacted and wiser investments and choices made by civil society. The proposed Science Plan would focus on natural and human-induced environmental hazards, including hazards related to hydro meteorological and geophysical trigger events, i.e. earthquakes, volcanoes, flooding, storms, heat waves, droughts and fires, tsunamis, coastal erosion, landslides, aspects of climate change, space weather and impact by near-earth objects, and related events. This programme is being developed around three broad research objectives. These are: 1. Characterizing hazards, vulnerability and risk; 2. Understanding decision making in complex and changing risk contexts; 3. Reducing risk and curbing losses through knowledge-based actions. A preliminary report prepared by the Planning Group was discussed at the ICSU -Unions joint meeting held in Rome, Italy on 23 and 24 April There were very positive comments and interactions. It was felt that there is a need for more detailed consultations with all the stakeholders. It was therefore decided to approach the CSPR to extend the tenure of the ICSU Planning Group on Natural and Human -induced Hazards till the General Assembly of ICSU in A discussion meeting with all the stakeholders and a planning group was held from 29 to 31 October 2007 in Paris. The report of the Planning Group will be put for discussion at the ICSU General Assembly scheduled for October Rationale of ROAP Interest in Hazards and Disasters Realizing that the geographical region covered by ROAP accounts for more than 80% of natural and human-induced hazards globally, Natural and Humaninduced Environmental Hazards and Disasters emerged as a priority area of work for ROAP at its inauguration meeting in November Later, detailed discussions were held and it was decided that ROAP should concentrate on Hydro-Meteorological and Geophysical Hazards. The overall global benefits of the programme would be dependent on global capacity building and recognition of the value of risk reduction activities, which are likely to come through successful case studies and demonstration projects. In addition, there would be three crosscutting themes: 1. Capacity building; 2. Case studies and demonstration projects.; 3. Assessment, data management and monitoring.
15 At the 3rd ROAP Regional Committee meeting held in Tehran, Iran on 6 and 7 March 2007, there were further discussions, and after taking into consideration several issues pertaining to natural hazards in the ROAP region, it was decided that ROAP shall concentrate on Earthquakes, Landslides and Floods. The Asia-Pacific region has the highest vulnerability, globally, to these three hazards (Tables 1, 2 and 3). It was also realized that the available scientific knowledge is not being fully utilized in forecasting the hazards, estimating the risks, and undertaking the necessary outreach for the benefit of the public, particularly in the Asia Pacific region. Table 1 Top seven countries affected by earthquakes (From: Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters, CRED, EM-DAT) Country Date Killed China P Rep 27 July ,000 China P Rep 22 May ,000 China P Rep 16 Dec ,000 Japan 1 Sep ,000 Soviet Union 5 Oct ,000 Italy 28 Dec ,000 Pakistan 8 Oct ,338 China P Rep 26 Dec ,000 Peru 31 May ,794 Pakistan 31 May ,000 China P Rep 12 May ,000 India 26 Jan ,000 Table 2 Top five countries affected by floods Country Date Killed China P Rep July ,700,000 China P Rep July ,000,000 China P Rep July ,000 China P Rep ,000 China P Rep ,000 China P Rep July ,000 Guatemala Oct ,000 China P Rep Aug ,000 Venezuela 15 Dec ,000 Bangladesh July ,700 Myanmar May ,000 Table 3 Top seven countries affected by landslides. Country Date Killed Brazil 11 Jan ,000,000 India Jul ,500,000 India 12 Sep ,100,000 Afghanistan 13 Jan ,000 Nepal 15 Jul ,865 Indonesia 31 March ,548 Philippines 19 Dec ,988 India 17 Aug ,000 Bolivia Feb ,000 Brazil 30 Jul ,000 Background
16 Vision The plan envisages an integrated approach to the management of natural and human-induced environmental hazards and disasters to reduce the risk of resultant losses of life and property. Aim 02 Vision, Aim and Objectives Of The Science Plan The science plan aims to enhance the science of management of hazards and disasters management in Asia and the Pacific and contribute to reducing the likelihood of hazards becoming disasters. Objectives The Natural and Human-induced Environmental Hazards and Disasters Research Programme would undertake coordinated multidisciplinary research leading to more effective societal responses to the risks associated with natural and human-induced environmental hazards in the Asia Pacific region. The legacy of the programme would be an enhanced capacity to address hazards and make informed decisions on actions to reduce their impacts related to loss of lives and properties. There are several ongoing efforts in the region related to natural hazards and disasters, particularly dealing with earthquakes, floods and landslides. A list of such organizations is provided in Annex III. The ICSU ROAP science plan aims to identify niches and gaps in the current efforts and discover a way to improve the situation, in collaboration with all concerned.
17 03 Hazards And Disasters In Asia And The Pacific
18 Earthquake, Floods and Landslides EARTHQUAKES Introduction Earthquakes are one of the worst natural calamities. According to conservative estimates, in recorded history, tens of millions of people have lost their lives in earthquakes and damage has run into hundreds of billions of dollars. In the recent past, the 1976 Tangshan earthquake in the People s Republic of China claimed 242,000 human lives and is qualified to be the deadliest twentieth century earthquake. The 1995 Kobe earthquake in Japan is the most expensive natural disaster and is estimated to have caused economic losses of 150 to 200 billion US dollars. The percentage of human lives lost due to earthquakes in developing countries has increased as shown in Figure 3.1. Figure 3.1 Earthquakecaused fatalities. Note the increase in the percentage of human lives lost in the developing countries. (USAID S office of US Foreign Disaster Assistance) Global Distribution During the 1960s, with the deployment of World-Wide Standard Seismograph Network (WWSSN) where about 120 seismic stations with similar equipment were deployed globally, earthquake location capabilities improved by several folds and the plate boundaries in the form of narrow belts of earthquakes were recognized (Figure 3.2). Basically, there are three major belts, which account for almost 95% of earthquake activity. Figure 3.2 The distribution of earthquakes during the period and major plate boundaries. It may be noted that globally, more than 75% of earthquake energy is released in the circum-pacific belt, about 20% in the Alpine-Himalayan belt, and the remaining 5% through the mid-oceanic ridges and other Stable Continental Region. For a tsunami to hit Indian Ocean rim-countries it is necessary that a tsunamigenic earthquake occurs and its magnitude is larger than M 7, and the possible locations of such events are indicated in blue circle and ellipse. 8
19 The belt along which most of the earthquakes occur is called the Circum-Pacific belt which goes around the rim of the Pacific Ocean right from the southern tip of South America through Central America, California, Aleutian Islands, Japan down to New Zealand. The second most active belt is the Alpine- Himalaya seismic belt which starts from southeast Asia near Java-Sumatra, continues through Andaman Nicobar Islands, India-Burma border region, swings through north India in the foothills of Himalaya and then moves west through Iran into Greece and Italy. The third major seismic belt consists of midoceanic ridges, which account for small magnitude earthquakes. These can be seen in Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Oceans. Globally, hundreds thousands of earthquakes occur annually. Approximate annual frequencies of earthquake occurrence in the world are given in Table 4. Table 4 Approximate annual frequencies of earthquake occurrence in the world (USGS) Descriptor Magnitude Annual frequency in the world Great 8 and higher 1 Major Strong Moderate Light ,000 Minor ,000 Very minor(micro) ,300, About 8,000 per day Monitoring and Observations Systems At present, there are extremes in earthquake instrumentation in the Asia Pacific region. Some of the countries are among the best equipped anywhere in the world, while there are other counties which do not have even the bare minimum. In addition to seismographs, during the last decades of the 20th century, there has been a revolutionary development in assessing the strain accumulation, which leads to the occurrence of earthquakes. The most practical and popular device is the global positioning system (GPS). Again, there are countries in the Asia Pacific region which are flooded by GPS stations, and others, which do not have an adequate coverage. There is a need to identify gaps. One of the aims of the ROAP initiative could be to assess the need in various countries and find ways to fill the gaps. Hazard Mapping Hazard Mapping Recognizing natural disasters as a major threat to human lives and development, the United Nations declared as the International Decade of Natural Disaster Reduction (IDNDR). The flagship programme of IDNDR was the Global Seismic Hazard Assessment Programme (GSHAP). Under this programme some 500 scientists from all over the world worked to prepare the Global Seismic Hazard Map, which depicts peak ground acceleration (PGA) at the bedrock given in units of meters per second square. Figures 3.3 and 3.4 are the maps of anticipated peak ground accelerations in the ROAP region. A major effort could be to estimate the accelerations at the surface and use them for micro-zonation of major cities. Figure 3.5 shows the plate motions as computed using GPS and other devices for the Asia Pacific region. Figure.3.3 Seismic hazard map of Asia depicting peak ground acceleration (PGA), given in m/s2, with a 10% chance of exceedance in 50 years ( Figure 3.4 Seismic hazard map of the Australia-South Pacific- Southeast Asia region depicting peak ground accelerations (PGA), given in m/s2, with a 10% chance of exceedance in 50 years. Hazards And Disasters In Asia And The Pacific
20 Time of occurrence Deaths in Deaths in part- Total collapsed house collapsed house potential (%) (%) deaths Midnight (sleeping) ,000 Morning (awake and sleeping) ,000 Noon Time (out working) ,000 Table 5 Estimates of human lives likely to be lost if the Kangra Earthquake of 1995, which claimed 20,000 lives, was to occur today (Arya, 1992) Earthquake, Floods and Landslides Figure 3.5 Plate motion (in ITRF 2000) in Asia and Pacific region (Kreemer et al. 2003) (Geophys.J. Int., 154,8-34) Earthquake Scenarios A very important issue is to develop earthquake scenarios. In an interesting study, it was investigated that if the Kangra earthquake of 1905 in the foothills of Himalaya in India repeats, how many lives would be lost. The 1905 earthquake had claimed around 20,000 lives. It is noted that with the passage of time the population density in the Kangra region has increased several folds over the last 100 years; at the same time, the style of making homes/dwellings has totally changed. Earlier most homes were singlestoried wooden houses, whereas now there are twoor three-stories non-engineered houses, which have little strength to withstand horizontal accelerations. Wood is simply not available for construction. The result is that the estimated loss of lives has increased, as shown in Table 5. The Muzaffarabad earthquake of 2005 occurred in similar environment at about 9 am local time and claimed 73,338 human lives. This justifies the estimates of the lives likely to be lost in a future Kangra equivalent earthquake. Similar estimates are available for certain parts of the Asia Pacific region. It is necessary to develop earthquake scenarios for many countries such as Myanmar, Thailand, and others. Prevention and Mitigation Building Codes Building codes exist for several parts of the Asia Pacific region. However, the most important issue is their appropriate implementation. In the Asian Seismological Commissions deliberations held in Yerevan, Armenia, in 2004, this issue was discussed at length and the conclusion was that while in the developed world the loss of human lives by earthquakes has decreased, there is an increase in the economic losses. But in the developing world, there is an increase in both, the human lives lost and the economic losses. A major cause of this is inappropriate implementation of the building codes. So a major effort is required in assessing the current status of building codes, their appropriate development where required and implementation. Micro-zonation For major cities located in earthquake-prone areas, it is important to develop micro-zonation maps, which are useful in constructing earthquake resistant structures. These maps basically depict anticipated accelerations at ground surface in different spectral frequencies. Appropriate micro-zonation has been carried out for several cities in Japan, China, India and elsewhere. Figure 3.6 gives a micro-zonation map of Jabalpur in India. A major effort is required to make use of the GSHAP calculations which provide anticipated accelerations at the bed rock and by appropriately calculating the effect of media between the bed rock and ground surface, computing the accelerations on the ground and then estimating the risk taking into consideration several other factors such as the liquefaction potential, quality of construction, and population density. It is important to carry out this effort for major cities in the earthquake-prone areas of the Asia Pacific region. 10
How can we defend ourselves from the hazard of Nature in the modern society?
 How can we defend ourselves from the hazard of Nature in the modern society?, University of Bologna President of the EGU Division of Natural Hazards Email: stefano.tinti@unibo.it nh@egu.eu GIFT 2013 Natural
How can we defend ourselves from the hazard of Nature in the modern society?, University of Bologna President of the EGU Division of Natural Hazards Email: stefano.tinti@unibo.it nh@egu.eu GIFT 2013 Natural
Flash Flood Science. Chapter 2. What Is in This Chapter? Flash Flood Processes
 Chapter 2 Flash Flood Science A flash flood is generally defined as a rapid onset flood of short duration with a relatively high peak discharge (World Meteorological Organization). The American Meteorological
Chapter 2 Flash Flood Science A flash flood is generally defined as a rapid onset flood of short duration with a relatively high peak discharge (World Meteorological Organization). The American Meteorological
International Flood Network
 International Flood Network Flood Devastation Increasing Floods are natural phenomena caused by rain, but flood damage is influenced by various social as well as natural factors. The scale and form of
International Flood Network Flood Devastation Increasing Floods are natural phenomena caused by rain, but flood damage is influenced by various social as well as natural factors. The scale and form of
Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives
 Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives Abdul Muhusin, Deputy Director Department of Meteorology, Maldives Fourth Technical
Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives Abdul Muhusin, Deputy Director Department of Meteorology, Maldives Fourth Technical
PACIFIC CATASTROPHE RISK ASSESSMENT AND FINANCING INITIATIVE
 PACIFIC CATASTROPHE RISK ASSESSMENT AND FINANCING INITIATIVE NIUE SEPTEMBER 11 COUNTRY RISK PROFILE: NIUE Niue is expected to incur, on average,.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
PACIFIC CATASTROPHE RISK ASSESSMENT AND FINANCING INITIATIVE NIUE SEPTEMBER 11 COUNTRY RISK PROFILE: NIUE Niue is expected to incur, on average,.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation
 The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 How do changes
The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 How do changes
Climate Change Impacts in the Asia/Pacific Region
 Climate Change Impacts in the Asia/Pacific Region Global CC threat CC in the A/P region The Stern Review and IPCC 4 th Assessment Report both state that climate change will have adverse impact on people
Climate Change Impacts in the Asia/Pacific Region Global CC threat CC in the A/P region The Stern Review and IPCC 4 th Assessment Report both state that climate change will have adverse impact on people
CONFEDERATION OF ASIA-PACIFIC CHAMBERS OF COMMERCE AND INDUSTRY (CACCI)
 CONFEDERATION OF ASIA-PACIFIC CHAMBERS OF COMMERCE AND INDUSTRY (CACCI) Policy Paper on Flexible Responses to Environmental Uncertainty and Infrastructure Resolved as of 3 rd October,. A. BACKGROUND 1.
CONFEDERATION OF ASIA-PACIFIC CHAMBERS OF COMMERCE AND INDUSTRY (CACCI) Policy Paper on Flexible Responses to Environmental Uncertainty and Infrastructure Resolved as of 3 rd October,. A. BACKGROUND 1.
Natural Disasters & Assessing Hazards and Risk. Natural Hazards and Natural Disasters
 Page 1 of 9 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Natural Disasters & Assessing Hazards and Risk This page last updated on 19-Aug-2014 Natural Hazards and Natural Disasters
Page 1 of 9 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Natural Disasters & Assessing Hazards and Risk This page last updated on 19-Aug-2014 Natural Hazards and Natural Disasters
Flood After Fire Fact Sheet
 FACT SHEET Flood After Fire Fact Sheet Risks and Protection Floods are the most common and costly natural hazard in the nation. Whether caused by heavy rain, thunderstorms, or the tropical storms, the
FACT SHEET Flood After Fire Fact Sheet Risks and Protection Floods are the most common and costly natural hazard in the nation. Whether caused by heavy rain, thunderstorms, or the tropical storms, the
A disaster occurs at the point of contact between social activities and a natural phenomenon of unusual scale.
 Hazard Mapping and Vulnerability Assessment Mr. Toshiaki Udono Senior Project Manager, Kansai Division, PASCO Corporation, Japan Mr. Awadh Kishor Sah Project Manager, Project Implementation Department,
Hazard Mapping and Vulnerability Assessment Mr. Toshiaki Udono Senior Project Manager, Kansai Division, PASCO Corporation, Japan Mr. Awadh Kishor Sah Project Manager, Project Implementation Department,
 Disaster Prevention Measures in Global-Local Context 4 th World Water Forum Dr. Yoshihiko Yamashita CTI Engineering Co., Ltd Association of Japanese Consulting Engineers Outline of Presentation Up-to to-date
Disaster Prevention Measures in Global-Local Context 4 th World Water Forum Dr. Yoshihiko Yamashita CTI Engineering Co., Ltd Association of Japanese Consulting Engineers Outline of Presentation Up-to to-date
New Brunswick s Flood Risk Reduction Strategy. Province of New Brunswick PO 6000, Fredericton NB E3B 5H1. www.gnb.ca
 New Brunswick s Flood Risk Reduction Strategy i New Brunswick s Flood Risk Reduction Strategy Province of New Brunswick PO 6000, Fredericton NB E3B 5H1 2014 www.gnb.ca ISBN 978-1-4605-0533-5 (print edition)
New Brunswick s Flood Risk Reduction Strategy i New Brunswick s Flood Risk Reduction Strategy Province of New Brunswick PO 6000, Fredericton NB E3B 5H1 2014 www.gnb.ca ISBN 978-1-4605-0533-5 (print edition)
Hitting the Poor Impact of Natural Catastrophes in Economies at Various Stages of Development
 Hitting the Poor Impact of Natural Catastrophes in Economies at Various Stages of Development Angelika Wirtz, Head of NatCatSERVICE Geo Risks Research, Munich Reinsurance IDRC 2008 Davos Contents Munich
Hitting the Poor Impact of Natural Catastrophes in Economies at Various Stages of Development Angelika Wirtz, Head of NatCatSERVICE Geo Risks Research, Munich Reinsurance IDRC 2008 Davos Contents Munich
Resolution XII.13. Wetlands and disaster risk reduction
 12 th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Wetlands (Ramsar, Iran, 1971) Punta del Este, Uruguay, 1-9 June 2015 Resolution XII.13 Wetlands and disaster risk reduction 1. RECALLING
12 th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Wetlands (Ramsar, Iran, 1971) Punta del Este, Uruguay, 1-9 June 2015 Resolution XII.13 Wetlands and disaster risk reduction 1. RECALLING
GEOTECHNICAL ISSUES OF LANDSLIDES CHARACTERISTICS MECHANISMS PREPARDNESS: BEFORE, DURING AND AFTER A LANDSLIDE QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSIONS
 GEOTECHNICAL ISSUES OF LANDSLIDES CHARACTERISTICS MECHANISMS PREPARDNESS: BEFORE, DURING AND AFTER A LANDSLIDE QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSIONS Huge landslide Leyte, Phillipines, 1998 2000 casulties Small debris
GEOTECHNICAL ISSUES OF LANDSLIDES CHARACTERISTICS MECHANISMS PREPARDNESS: BEFORE, DURING AND AFTER A LANDSLIDE QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSIONS Huge landslide Leyte, Phillipines, 1998 2000 casulties Small debris
Application of Space Technology for Disaster monitoring and assessment current state in Vietnam
 Application of Space Technology for Disaster monitoring and assessment current state in Vietnam Lai Anh Khoi SPACE TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE 8th GEOSS Asian Pacific Symposium Beijing, Sep. 09-11, 2015 Types
Application of Space Technology for Disaster monitoring and assessment current state in Vietnam Lai Anh Khoi SPACE TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE 8th GEOSS Asian Pacific Symposium Beijing, Sep. 09-11, 2015 Types
The correct answers are given below. Some talking points have been added for the teachers use.
 Natural Resources Canada 2011: Lesson Plan Grades 11 and 12 Landslide activity 5b: Landslides in Canada quiz Description: This is an independent study activity for grades 11 and 12. Students will read
Natural Resources Canada 2011: Lesson Plan Grades 11 and 12 Landslide activity 5b: Landslides in Canada quiz Description: This is an independent study activity for grades 11 and 12. Students will read
District Disaster Risk Management Planning
 District Disaster Risk Management Planning GUIDELINES JULY 2007 National Disaster Management Authority 1. Introduction Notifications for establishment of the District Disaster Management Authorities (DDMAs)
District Disaster Risk Management Planning GUIDELINES JULY 2007 National Disaster Management Authority 1. Introduction Notifications for establishment of the District Disaster Management Authorities (DDMAs)
Disaster Risk Management: prevention and urgent repair procedures for infrastructure and facilities
 Disaster Risk Management: prevention and urgent repair procedures for infrastructure and facilities Jacob Greenstein Ph.D, PE, EGAT/ I&E EGAT workshop-december 2009 1 Natural disasters-new trends Natural
Disaster Risk Management: prevention and urgent repair procedures for infrastructure and facilities Jacob Greenstein Ph.D, PE, EGAT/ I&E EGAT workshop-december 2009 1 Natural disasters-new trends Natural
Improved Warnings for Natural Hazards: A Prototype System for Southern California
 Improved Warnings for Natural Hazards: A Prototype System for Southern California Yehuda Bock Research Geodesist Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California San Diego, La Jolla, Calif.
Improved Warnings for Natural Hazards: A Prototype System for Southern California Yehuda Bock Research Geodesist Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California San Diego, La Jolla, Calif.
Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Domestic Policy Framework on Adaptation to Climate Change in Water Resources: Case Study for India. Working Together to Respond to Climate Change
 Domestic Policy Framework on Adaptation to Climate Change in Water Resources: Case Study for India Working Together to Respond to Climate Change WATER ACCOUNTING OF INDIA S TOTAL WATER RESOURCES Unutilizable
Domestic Policy Framework on Adaptation to Climate Change in Water Resources: Case Study for India Working Together to Respond to Climate Change WATER ACCOUNTING OF INDIA S TOTAL WATER RESOURCES Unutilizable
THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF THE HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL PREDICTION CENTER
 THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF THE HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL PREDICTION CENTER FISCAL YEARS 2012 2016 INTRODUCTION Over the next ten years, the National Weather Service (NWS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF THE HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL PREDICTION CENTER FISCAL YEARS 2012 2016 INTRODUCTION Over the next ten years, the National Weather Service (NWS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
How To Develop An Early Warning System
 149 SECTION AREA Saving lives through early warning systems and emergency preparedness Maryam Golnaraghi Ph.D, chief; James Douris, technical officer and Jean-Baptiste Migraine, junior professional officer,
149 SECTION AREA Saving lives through early warning systems and emergency preparedness Maryam Golnaraghi Ph.D, chief; James Douris, technical officer and Jean-Baptiste Migraine, junior professional officer,
Chincha and Cañete, Peru, Based
 Reconstruction of Ica, Pisco, Chincha and Cañete, Peru, Based on Updated Hazard Maps Julio Kuroiwa Professor emeritus National University of Engineering and UNDP Reconstruction Program/Sustainable Cities.
Reconstruction of Ica, Pisco, Chincha and Cañete, Peru, Based on Updated Hazard Maps Julio Kuroiwa Professor emeritus National University of Engineering and UNDP Reconstruction Program/Sustainable Cities.
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Climate Change Long Term Trends and their Implications for Emergency Management August 2011
 Climate Change Long Term Trends and their Implications for Emergency Management August 2011 Overview A significant amount of existing research indicates that the world s climate is changing. Emergency
Climate Change Long Term Trends and their Implications for Emergency Management August 2011 Overview A significant amount of existing research indicates that the world s climate is changing. Emergency
sample The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation
 sample The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 Impacts
sample The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 Impacts
NATIONAL REPORT AUSTRIA
 26th Session of the EFC Working Party on the Impact of Climate Change on Natural Hazards in Austria NATIONAL REPORT AUSTRIA Seite 1 16.04.2009 Global increase of temperatures: between 1.8 C and 4.0 C (IPCC
26th Session of the EFC Working Party on the Impact of Climate Change on Natural Hazards in Austria NATIONAL REPORT AUSTRIA Seite 1 16.04.2009 Global increase of temperatures: between 1.8 C and 4.0 C (IPCC
Country and Regional Reports on GEOSS-related Activities. Ms. Taniya Koswatta Coordinator, APN Secretariat
 Country and Regional Reports on GEOSS-related Activities Ms. Taniya Koswatta Coordinator, APN Secretariat What is APN An inter-governmental network of 22 countries in the Asia- Pacific to foster global
Country and Regional Reports on GEOSS-related Activities Ms. Taniya Koswatta Coordinator, APN Secretariat What is APN An inter-governmental network of 22 countries in the Asia- Pacific to foster global
Flooding Fast Facts. flooding), seismic events (tsunami) or large landslides (sometime also called tsunami).
 Flooding Fast Facts What is a flood? Flooding is the unusual presence of water on land to a depth which affects normal activities. Flooding can arise from: Overflowing rivers (river flooding), Heavy rainfall
Flooding Fast Facts What is a flood? Flooding is the unusual presence of water on land to a depth which affects normal activities. Flooding can arise from: Overflowing rivers (river flooding), Heavy rainfall
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Natural Disasters 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Global Flood Alert System (GFAS)
 An Introduction of Global Flood Alert System (GFAS) Kazuo UMEDA Director of 2 nd Research Department, Infrastructure Development Institute-JAPAN Target: Reduction of Human Loss World s s natural disaster
An Introduction of Global Flood Alert System (GFAS) Kazuo UMEDA Director of 2 nd Research Department, Infrastructure Development Institute-JAPAN Target: Reduction of Human Loss World s s natural disaster
Burnt River Black River and Gull River Flood Contingency Plan
 Burnt River Black River and Gull River Flood Contingency Plan Objective: The objective of this plan is to preplan and prepare for flooding events in the Burnt River, Black River and Gull River area of
Burnt River Black River and Gull River Flood Contingency Plan Objective: The objective of this plan is to preplan and prepare for flooding events in the Burnt River, Black River and Gull River area of
Earthquakes. Earthquakes: Big Ideas. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Geohazards: Minimizing Risk, Maximizing Awareness The Role of the Insurance Industry
 Geohazards: Minimizing Risk, Maximizing Awareness The Role of the Insurance Industry Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe Head of Geo Risks Research Munich Re International Year of Planet Earth, Paris, 13 February 2008
Geohazards: Minimizing Risk, Maximizing Awareness The Role of the Insurance Industry Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe Head of Geo Risks Research Munich Re International Year of Planet Earth, Paris, 13 February 2008
Types of flood risk. What is flash flooding? 3/16/2010. GG22A: GEOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE Hydrology. Main types of climatically influenced flooding:
 GG22A: GEOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE Hydrology Types of flood risk Main types of climatically influenced flooding: 1. Flash (rapid-onset) 2. Lowland (slow-rise) 3. Coastal (not covered here) But! Causal factors
GG22A: GEOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE Hydrology Types of flood risk Main types of climatically influenced flooding: 1. Flash (rapid-onset) 2. Lowland (slow-rise) 3. Coastal (not covered here) But! Causal factors
HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK
 SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface
 TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
The Caribbean Disaster Mitigation Project: Supporting Sustainable Responses to Natural Hazards
 The Caribbean Disaster Mitigation Project: Supporting Sustainable Responses to Natural Hazards Steven Stichter Caribbean Disaster Mitigation Project (CDMP) Unit of Sustainable Development and Environment
The Caribbean Disaster Mitigation Project: Supporting Sustainable Responses to Natural Hazards Steven Stichter Caribbean Disaster Mitigation Project (CDMP) Unit of Sustainable Development and Environment
Landslides. Landslides-1. March 2007
 Landslides Learn if landslides, including debris flows, could occur in your area by contacting local officials, your state geological survey or department of natural resources, or the geology department
Landslides Learn if landslides, including debris flows, could occur in your area by contacting local officials, your state geological survey or department of natural resources, or the geology department
ICOLD POSITION PAPER ON DAM SAFETY AND EARTHQUAKES
 ICOLD POSITION PAPER ON DAM SAFETY AND EARTHQUAKES August 2012 Dam Safety and Earthquakes Position Paper of International Commission on Large Dams (ICOLD) Prepared by ICOLD Committee on Seismic Aspects
ICOLD POSITION PAPER ON DAM SAFETY AND EARTHQUAKES August 2012 Dam Safety and Earthquakes Position Paper of International Commission on Large Dams (ICOLD) Prepared by ICOLD Committee on Seismic Aspects
CSCAP MEMORANDUM No. 15 The Security Implications of Climate Change
 CSCAP MEMORANDUM No. 15 The Security Implications of Climate Change A Memorandum from the Council for Security Cooperation in the Asia Pacific (CSCAP) June 2010 CSCAP Memorandum No. 15 The Security Implications
CSCAP MEMORANDUM No. 15 The Security Implications of Climate Change A Memorandum from the Council for Security Cooperation in the Asia Pacific (CSCAP) June 2010 CSCAP Memorandum No. 15 The Security Implications
Earthquake Hazards and Risks
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Flood Emergency Response Planning: How to Protect Your Business from a Natural Disaster RIC005
 Flood Emergency Response Planning: How to Protect Your Business from a Natural Disaster RIC005 Speakers: Tom Chan, CEO, Global Risk Miyamoto Greg Bates, Principal, Global Risk Consultants Learning Objectives
Flood Emergency Response Planning: How to Protect Your Business from a Natural Disaster RIC005 Speakers: Tom Chan, CEO, Global Risk Miyamoto Greg Bates, Principal, Global Risk Consultants Learning Objectives
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): CLIMATE CHANGE. 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
 Climate Resilience Sector Project (RRP TON 46351) Sector Road Map SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): CLIMATE CHANGE 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Tonga is being affected by climate change,
Climate Resilience Sector Project (RRP TON 46351) Sector Road Map SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): CLIMATE CHANGE 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities 1. Tonga is being affected by climate change,
FLOOD RISK RECENT TRENDS AND POLICY RESPONSES
 FLOOD RISK RECENT TRENDS AND POLICY RESPONSES DEVELOPING WESTMINSTER S LOCAL PLAN Booklet No. 2 LDF Consultation - CMP Revision November 2013 INTRODUCTION CLLR ROBERT DAVIS Westminster is at risk of flooding
FLOOD RISK RECENT TRENDS AND POLICY RESPONSES DEVELOPING WESTMINSTER S LOCAL PLAN Booklet No. 2 LDF Consultation - CMP Revision November 2013 INTRODUCTION CLLR ROBERT DAVIS Westminster is at risk of flooding
Landslides & Mudflows
 1 2 - What is a Landslide? - Geologic hazard Common to almost all 50 states Annual global Billions in losses Thousands of deaths and injuries 3 1 - What is a Landslide? - Gravity is driving force Some
1 2 - What is a Landslide? - Geologic hazard Common to almost all 50 states Annual global Billions in losses Thousands of deaths and injuries 3 1 - What is a Landslide? - Gravity is driving force Some
Graduate School of Disaster Prevention Kangwon National University. http://college.kangwon.ac.kr/prevention/main.jsp
 Graduate School of Disaster Prevention Kangwon National University 1joongang-Ro Samcheok-city, Gangwon-Do, Republic of Korea http://college.kangwon.ac.kr/prevention/main.jsp Outline Natural disasters such
Graduate School of Disaster Prevention Kangwon National University 1joongang-Ro Samcheok-city, Gangwon-Do, Republic of Korea http://college.kangwon.ac.kr/prevention/main.jsp Outline Natural disasters such
Disaster Risk Reduction UNESCO s contribution to a global challenge
 United Nations International Geoscience Programme Disaster Risk Reduction UNESCO s contribution to a global challenge UNESCO and Disaster Risk Reduction UNESCO operates at the interface between natural
United Nations International Geoscience Programme Disaster Risk Reduction UNESCO s contribution to a global challenge UNESCO and Disaster Risk Reduction UNESCO operates at the interface between natural
DISASTER RISK DETECTION AND MANAGEMENT COURSES SETUP SCENARIO AT MAKERERE UNIVERSITY. Makerere University
 DISASTER RISK DETECTION AND MANAGEMENT COURSES SETUP SCENARIO AT MAKERERE UNIVERSITY CASE OF THE DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY Derek Muhwezi 2 MISSION OF THE DEPARTMENT To provide and promote quality education,
DISASTER RISK DETECTION AND MANAGEMENT COURSES SETUP SCENARIO AT MAKERERE UNIVERSITY CASE OF THE DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY Derek Muhwezi 2 MISSION OF THE DEPARTMENT To provide and promote quality education,
Multi-Jurisdictional Hazard Mitigation Plan
 Flooding General Flooding is the leading cause of death among all types of natural disasters throughout the United States, with its ability to roll boulders the size of cars, tear out trees, and destroy
Flooding General Flooding is the leading cause of death among all types of natural disasters throughout the United States, with its ability to roll boulders the size of cars, tear out trees, and destroy
5-2. Dissemination of Earthquake Risk Reduction and Recovery Preparedness Model Programme
 5-2. Dissemination of Earthquake Risk Reduction and Recovery Preparedness Model Programme 5-2-1. Background Asian Region is the most disaster prone regions in the world. Many countries in the region are
5-2. Dissemination of Earthquake Risk Reduction and Recovery Preparedness Model Programme 5-2-1. Background Asian Region is the most disaster prone regions in the world. Many countries in the region are
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
CRS 610 Ventura County Flood Warning System Website
 CRS 610 Ventura County Flood Warning System Website Purpose This document gives instructions and a description of the information available via the Ventura County Watershed Protection District s (VCWPD)
CRS 610 Ventura County Flood Warning System Website Purpose This document gives instructions and a description of the information available via the Ventura County Watershed Protection District s (VCWPD)
HAZARD VULNERABILITY & RISK ASSESSMENT
 Hazard Vulnerability Analysis Purpose and Scope A Hazard Vulnerability Analysis (HVA) evaluates risk associated with a specific hazard. During this analysis, the hazard is evaluated for its probability
Hazard Vulnerability Analysis Purpose and Scope A Hazard Vulnerability Analysis (HVA) evaluates risk associated with a specific hazard. During this analysis, the hazard is evaluated for its probability
FLOOD FORECASTING PRACTICE IN NORTHERN CALIFORNIA
 FLOOD FORECASTING PRACTICE IN NORTHERN CALIFORNIA California Department of Water Resources Post Office Box 219000, Sacramento, California 95821 9000 USA By Maurice Roos, Chief Hydrologist ABSTRACT Although
FLOOD FORECASTING PRACTICE IN NORTHERN CALIFORNIA California Department of Water Resources Post Office Box 219000, Sacramento, California 95821 9000 USA By Maurice Roos, Chief Hydrologist ABSTRACT Although
Belmont Forum Collaborative Research Action on Mountains as Sentinels of Change
 Belmont Forum Collaborative Research Action on Mountains as Sentinels of Change 1. Background and rationale Mountains exist in many regions of the world and are home to a significant fraction of the world
Belmont Forum Collaborative Research Action on Mountains as Sentinels of Change 1. Background and rationale Mountains exist in many regions of the world and are home to a significant fraction of the world
ARkStorm: California s Other Big One!
 ARkStorm: California s Other Big One! Understanding the Impacts of Massive Winter Storms Mark Jackson Meteorologist in Charge NOAA/National Weather Service Los Angeles/Oxnard What is ARkStorm? Emergency-preparedness
ARkStorm: California s Other Big One! Understanding the Impacts of Massive Winter Storms Mark Jackson Meteorologist in Charge NOAA/National Weather Service Los Angeles/Oxnard What is ARkStorm? Emergency-preparedness
Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological Disasters in Southeast Asia with a Focus on Thailand
 Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological Disasters in Southeast Asia with a Focus on Thailand Manfred Koch Department of Geohydraulics and Engineering Hydrology University of Kassel Germany
Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological Disasters in Southeast Asia with a Focus on Thailand Manfred Koch Department of Geohydraulics and Engineering Hydrology University of Kassel Germany
Geospatial Software Solutions for the Environment and Natural Resources
 Geospatial Software Solutions for the Environment and Natural Resources Manage and Preserve the Environment and its Natural Resources Our environment and the natural resources it provides play a growing
Geospatial Software Solutions for the Environment and Natural Resources Manage and Preserve the Environment and its Natural Resources Our environment and the natural resources it provides play a growing
EL Civics Objective 16 (Emergencies) Level: Beginning Low & Beginning High Task #1: Identify Emergencies & Disasters
 EL Civics Objective 16 (Emergencies) Level: Beginning Low & Beginning High Task #1: Identify Emergencies & Disasters Language & Literacy Objectives: 1. Identify what constitutes an emergency or disaster,
EL Civics Objective 16 (Emergencies) Level: Beginning Low & Beginning High Task #1: Identify Emergencies & Disasters Language & Literacy Objectives: 1. Identify what constitutes an emergency or disaster,
Safety of Small/Rural Dams and Barrier Lake Management
 Safety of Small/Rural Dams and Barrier Lake Management A. Introduction 1. Lessons learnt and recommendations are provided for artificial dams and barrier lakes. In the case of artificial dams, emphasis
Safety of Small/Rural Dams and Barrier Lake Management A. Introduction 1. Lessons learnt and recommendations are provided for artificial dams and barrier lakes. In the case of artificial dams, emphasis
Bolton s Flood Risk Management Strategy
 Bolton s Flood Risk Management Strategy www.bolton.gov.uk Public Summary Bolton s Flood Risk Management Strategy Public Summary Introduction Over 5.5 million properties in England and Wales are at risk
Bolton s Flood Risk Management Strategy www.bolton.gov.uk Public Summary Bolton s Flood Risk Management Strategy Public Summary Introduction Over 5.5 million properties in England and Wales are at risk
1. Incredible India. Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India
 1. Incredible India Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India The DCSF supported Action plan for Geography is delivered
1. Incredible India Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India The DCSF supported Action plan for Geography is delivered
How To Predict Climate Change
 A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events the focus of Chapter 3 Presented by: David R. Easterling Chapter 3:Changes in Climate Extremes & their Impacts on the Natural Physical
A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events the focus of Chapter 3 Presented by: David R. Easterling Chapter 3:Changes in Climate Extremes & their Impacts on the Natural Physical
California Standards Grades 9 12 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping
 California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
Continents join together and split apart.
 KEY CONCEPT Continents change position over time. BEFORE, you learned Earth s main layers are the core, the mantle, and the crust The lithosphere and asthenosphere are the topmost layers of Earth The lithosphere
KEY CONCEPT Continents change position over time. BEFORE, you learned Earth s main layers are the core, the mantle, and the crust The lithosphere and asthenosphere are the topmost layers of Earth The lithosphere
SECTION 3.2 CLIMATE AND PRECIPITATION
 SECTION 3.2 CLIMATE AND PRECIPITATION Ulster County Climate Data A preliminary analysis of the Preserve s weather data shows that the average temperature has risen about two degrees over the past 114 years.
SECTION 3.2 CLIMATE AND PRECIPITATION Ulster County Climate Data A preliminary analysis of the Preserve s weather data shows that the average temperature has risen about two degrees over the past 114 years.
Standard Operating Procedures for Flood Preparation and Response
 Standard Operating Procedures for Flood Preparation and Response General Discussion Hurricanes, tropical storms and intense thunderstorms support a conclusion that more severe flooding conditions than
Standard Operating Procedures for Flood Preparation and Response General Discussion Hurricanes, tropical storms and intense thunderstorms support a conclusion that more severe flooding conditions than
City of Cambridge Climate Protection Action Committee. Recommendations for Adaptation to Climate Change. Purpose
 City of Cambridge Climate Protection Action Committee Recommendations for Adaptation to Climate Change Purpose The Climate Protection Action Committee (CPAC) is an advisory body to the City Manager on
City of Cambridge Climate Protection Action Committee Recommendations for Adaptation to Climate Change Purpose The Climate Protection Action Committee (CPAC) is an advisory body to the City Manager on
London Borough of Waltham Forest LOCAL FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGY. Summary Document
 LOCAL FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGY Summary Document October 2013 Local Flood Risk Management Strategy Summary 1 Introduction 2 Partner responsibilities 3 What do we know about flooding in the borough?
LOCAL FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGY Summary Document October 2013 Local Flood Risk Management Strategy Summary 1 Introduction 2 Partner responsibilities 3 What do we know about flooding in the borough?
Anchorage All-Hazard Mitigation Plan October 2004
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Municipality of Anchorage (MOA) is vulnerable to a wide range of natural, technological, and human/societal hazards including earthquakes, avalanches, and hazardous material accidents.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Municipality of Anchorage (MOA) is vulnerable to a wide range of natural, technological, and human/societal hazards including earthquakes, avalanches, and hazardous material accidents.
NATHAN world map of natural hazards. 2011 version
 world map of natural hazards 2011 version World Map of Natural Hazards Geointelligence for your business A new name but the recipe for success is the same: In the 2011 version, we are offering both proven
world map of natural hazards 2011 version World Map of Natural Hazards Geointelligence for your business A new name but the recipe for success is the same: In the 2011 version, we are offering both proven
Climate Change. Lauma M. Jurkevics - DWR, Southern Region Senior Environmental Scientist
 Climate Change A n o t h e r F a c t o r i n M a n a g i n g S o u t h e r n C a l i f o r n i a s W a t e r R e s o u r c e s Lauma M. Jurkevics - DWR, Southern Region Senior Environmental Scientist USEPA-Region
Climate Change A n o t h e r F a c t o r i n M a n a g i n g S o u t h e r n C a l i f o r n i a s W a t e r R e s o u r c e s Lauma M. Jurkevics - DWR, Southern Region Senior Environmental Scientist USEPA-Region
Flood Risk Management
 Flood Risk Management Value of Flood Risk Management Every year floods sweep through communities across the United States taking lives, destroying property, shutting down businesses, harming the environment
Flood Risk Management Value of Flood Risk Management Every year floods sweep through communities across the United States taking lives, destroying property, shutting down businesses, harming the environment
Flood Risk Management
 Flood Risk Management Value of Flood Risk Management Value to Individuals and Communities Every year floods sweep through communities across the United States taking lives, destroying property, shutting
Flood Risk Management Value of Flood Risk Management Value to Individuals and Communities Every year floods sweep through communities across the United States taking lives, destroying property, shutting
Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space Fifty-eighth session
 10 June 2015 English only Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space Fifty-eighth session Vienna, 10-19 June 2015 The United Nations/Germany International Conference on Earth Observation Global Solutions
10 June 2015 English only Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space Fifty-eighth session Vienna, 10-19 June 2015 The United Nations/Germany International Conference on Earth Observation Global Solutions
Guideline for Stress Testing the Climate Resilience of Urban Areas
 Netherlands Ministry of Infrastructure and Environment Delta Programme Urban Development and Reconstruction Guideline for Stress Testing the Climate Resilience of Urban Areas Extended summary Version 1.0
Netherlands Ministry of Infrastructure and Environment Delta Programme Urban Development and Reconstruction Guideline for Stress Testing the Climate Resilience of Urban Areas Extended summary Version 1.0
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
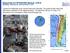 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
Extreme Events in the Atmosphere
 Cover Extreme Events in the Atmosphere Basic concepts Academic year 2013-2014 ICTP Trieste - Italy Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio Stel 1 Outline of the lecture Definition of extreme weather event. It is
Cover Extreme Events in the Atmosphere Basic concepts Academic year 2013-2014 ICTP Trieste - Italy Dario B. Giaiotti and Fulvio Stel 1 Outline of the lecture Definition of extreme weather event. It is
CHAPTER 8 Natural Disasters
 CHAPTER 8 Natural Disasters Chapter 8 Natural Disasters 55 Toll of Natural Disasters South Asia is extremely vulnerable to natural disasters, with more than 900 events reported since 1970 alone. Between
CHAPTER 8 Natural Disasters Chapter 8 Natural Disasters 55 Toll of Natural Disasters South Asia is extremely vulnerable to natural disasters, with more than 900 events reported since 1970 alone. Between
32 Contingencies MAR/APR.06
 32 Contingencies MAR/APR.06 New Catastrophe Models for Hard Times B Y P A T R I C I A G R O S S I A N D H O W A R D K U N R E U T H E R Driven by the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters
32 Contingencies MAR/APR.06 New Catastrophe Models for Hard Times B Y P A T R I C I A G R O S S I A N D H O W A R D K U N R E U T H E R Driven by the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters
Natural Disaster Impact on Business and Communities in Taiwan. Dr. Chung-Sheng Lee. NCDR Chinese Taipei
 Natural Disaster Impact on Business and Communities in Taiwan Dr. Chung-Sheng Lee NCDR Chinese Taipei 1 Brief Introduction of NCDR 2 Organizational Chart of NCDR NDPPC: National Disaster Preparation and
Natural Disaster Impact on Business and Communities in Taiwan Dr. Chung-Sheng Lee NCDR Chinese Taipei 1 Brief Introduction of NCDR 2 Organizational Chart of NCDR NDPPC: National Disaster Preparation and
 1 2 A very short description of the functional center network: regarding the Hydraulic and Hydrogeological risk, the national alert system is ensured by the National Civil Protection Department (DPCN),
1 2 A very short description of the functional center network: regarding the Hydraulic and Hydrogeological risk, the national alert system is ensured by the National Civil Protection Department (DPCN),
CONFERENCE ON CATASTROPHIC RISKS AND INSURANCE 22-23 November 2004 INSURANCE OF ATMOSPHERIC PERILS CHALLENGES AHEAD.
 DIRECTORATE FOR FINANCIAL AND ENTERPRISE AFFAIRS CONFERENCE ON CATASTROPHIC RISKS AND INSURANCE 22-23 November 2004 INSURANCE OF ATMOSPHERIC PERILS CHALLENGES AHEAD Peter Zimmerli (Swiss Re) Background
DIRECTORATE FOR FINANCIAL AND ENTERPRISE AFFAIRS CONFERENCE ON CATASTROPHIC RISKS AND INSURANCE 22-23 November 2004 INSURANCE OF ATMOSPHERIC PERILS CHALLENGES AHEAD Peter Zimmerli (Swiss Re) Background
[ Climate Data Collection and Forecasting Element ] An Advanced Monitoring Network In Support of the FloodER Program
![[ Climate Data Collection and Forecasting Element ] An Advanced Monitoring Network In Support of the FloodER Program [ Climate Data Collection and Forecasting Element ] An Advanced Monitoring Network In Support of the FloodER Program](/thumbs/33/16326315.jpg) [ Climate Data Collection and Forecasting Element ] An Advanced Monitoring Network In Support of the FloodER Program December 2010 1 Introduction Extreme precipitation and the resulting flooding events
[ Climate Data Collection and Forecasting Element ] An Advanced Monitoring Network In Support of the FloodER Program December 2010 1 Introduction Extreme precipitation and the resulting flooding events
FLOOD RISKS IN LONDON
 Environment Committee FLOOD RISKS IN LONDON Summary of findings April 2014 About this summary 2 This is a summary of the findings of the Environment Committee s investigation into flood risk. In January
Environment Committee FLOOD RISKS IN LONDON Summary of findings April 2014 About this summary 2 This is a summary of the findings of the Environment Committee s investigation into flood risk. In January
FLOOD CONTROL FOR SPECIFIC TYPES OF FLOODS. A.F. Mandych Department of Physical Geography and Land Use, Institute of Geography, Moscow, Russia
 FLOOD CONTROL FOR SPECIFIC TYPES OF FLOODS A.F. Mandych Department of Physical Geography and Land Use, Institute of Geography, Moscow, Russia Keywords: control, dam, dike (dyke), embankment, flood, flood
FLOOD CONTROL FOR SPECIFIC TYPES OF FLOODS A.F. Mandych Department of Physical Geography and Land Use, Institute of Geography, Moscow, Russia Keywords: control, dam, dike (dyke), embankment, flood, flood
Risk and vulnerability assessment of the build environment in a dynamic changing society
 Risk and vulnerability assessment of the build environment in a dynamic changing society Limnei Nie SINTEF Building and infrastructure, P.O.Box 124 Blindern, NO-0314 Oslo, Norway. linmei.nie@sintef.no
Risk and vulnerability assessment of the build environment in a dynamic changing society Limnei Nie SINTEF Building and infrastructure, P.O.Box 124 Blindern, NO-0314 Oslo, Norway. linmei.nie@sintef.no
Town of Warwick, Village of Florida, Village of Greenwood Lake and Village of Warwick MULTI JURISIDICTIONAL, MULTI HAZARD MITIGATION PLAN DRAFT
 Town of Warwick, Village of Florida, Village of Greenwood Lake and Village of Warwick MULTI JURISIDICTIONAL, MULTI HAZARD MITIGATION PLAN DRAFT Appendix B Historical Hazard Documentation Rev #0 May 2013
Town of Warwick, Village of Florida, Village of Greenwood Lake and Village of Warwick MULTI JURISIDICTIONAL, MULTI HAZARD MITIGATION PLAN DRAFT Appendix B Historical Hazard Documentation Rev #0 May 2013
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
FLOOD PROTECTION AND ECOSYSTEM SERVICES IN THE CHEHALIS RIVER BASIN. May 2010. Prepared by. for the. 2010 by Earth Economics
 FLOOD PROTECTION AND ECOSYSTEM SERVICES IN THE CHEHALIS RIVER BASIN May 2010 Prepared by for the Execubve Summary The Chehalis Basin experienced catastrophic flooding in 2007 and 2009. In response, the
FLOOD PROTECTION AND ECOSYSTEM SERVICES IN THE CHEHALIS RIVER BASIN May 2010 Prepared by for the Execubve Summary The Chehalis Basin experienced catastrophic flooding in 2007 and 2009. In response, the
ENGINEERING-BASED EARTHQUAKE RISK MANAGEMENT
 ENGINEERING-BASED EARTHQUAKE RISK MANAGEMENT MRP Engineering Newsletter February 2012 The world recently experienced several major earthquakes, which caused severe local impacts and major worldwide repercussions.
ENGINEERING-BASED EARTHQUAKE RISK MANAGEMENT MRP Engineering Newsletter February 2012 The world recently experienced several major earthquakes, which caused severe local impacts and major worldwide repercussions.
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist. Introduction. Climatic controls
 Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
A. Flood Management in Nevada
 Nevada Division of Water Planning A. Flood Management in Nevada Introduction Flooding has been a concern for Nevada communities since the first settlers moved to the territory in the mid-1800 s. Fourteen
Nevada Division of Water Planning A. Flood Management in Nevada Introduction Flooding has been a concern for Nevada communities since the first settlers moved to the territory in the mid-1800 s. Fourteen
Long Term Recovery and Rehabilitation. Issues for discussion. Recovery
 Long Term Recovery and Rehabilitation Issues for discussion Recovery The restoration, and improvement where appropriate, of facilities, livelihoods and living conditions of disaster-affected communities,
Long Term Recovery and Rehabilitation Issues for discussion Recovery The restoration, and improvement where appropriate, of facilities, livelihoods and living conditions of disaster-affected communities,
Towards a Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction
 Towards a Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Introduction 1. The Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 Building the Resilience of Nations and Communities to Disasters (HFA) is the inspiration
Towards a Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Introduction 1. The Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 Building the Resilience of Nations and Communities to Disasters (HFA) is the inspiration
NATURAL AND HUMAN INDUCED HAZARDS Vol. I - Case Studies of Natural Disasters - Chen Yong and Li Juan
 CASE STUDIES OF NATURAL DISASTERS Chen Yong and Li Juan China Seismological Bureau, Beijing, China Keywords: Flood, Earthquake, Hurricane, Volcanic eruption, Tsunamis, Landslides Contents 1. 1998 Yangtze
CASE STUDIES OF NATURAL DISASTERS Chen Yong and Li Juan China Seismological Bureau, Beijing, China Keywords: Flood, Earthquake, Hurricane, Volcanic eruption, Tsunamis, Landslides Contents 1. 1998 Yangtze
