Scintigraphic evaluation of myocardial perfusion for the
|
|
|
- Shana Small
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Protocols: Is There an Ideal Protocol?* Syed Sajid Husain Department of Nuclear Medicine/PET, VA Western New York Healthcare System, Buffalo, New York Is there an ideal myocardial perfusion imaging protocol? In order to answer this question and choose a protocol for clinical use, one must understand the characteristics of the available radiopharmaceuticals, the protocol variables, and the advantages and disadvantages of each. After reading this article, the technologist should be able to list the ideal characteristics of a myocardial perfusion imaging agent, describe and compare the characteristics of myocardial perfusion imaging agents, discuss the relationship between coronary blood flow and myocardial uptake of various tracers, describe imaging protocols, and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each protocol. Key Words: myocardial perfusion imaging; tracer kinetics; coronary blood flow; myocardial uptake; Tl; Tc J Nucl Med Technol 2007; 35:3 9 Received Nov. 7, 2006; revision accepted Jan. 29, For correspondence or reprints contact: Syed Sajid Husain, 3495 Bailey Ave., Buffalo, NY syed.husain@med.va.gov *NOTE: FOR CE CREDIT, YOU CAN ACCESS THIS ACTIVITY THROUGH THE SNM WEB SITE ( THROUGH MARCH COPYRIGHT ª 2007 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine, Inc. Scintigraphic evaluation of myocardial perfusion for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease is a valuable noninvasive diagnostic imaging modality. Tl was introduced as a myocardial perfusion imaging agent in the early 1970s and remained in common use until the mid-1980s, when Tc-labeled radiopharmaceuticals were developed and, for the most part, replaced thallium for evaluating myocardial perfusion abnormalities. The numbers of procedures performed have grown exponentially since the advent of Tc-labeled radiopharmaceuticals for myocardial perfusion imaging. The development of new radiopharmaceuticals, a newer generation of advanced g-cameras with SPECT capabilities, and PET has dramatically revolutionized myocardial perfusion imaging. It is only natural to expect that this evolutionary process would lead to the development of various imaging protocols dealing with many variables, such as those pertaining to g-cameras, radiopharmaceuticals, reimbursement issues, hospital discharge policies, scheduling logistics for outpatient clinics, and patients demographics and convenience. The purpose of this review was to compare the salient features of the available protocols, the advantages and disadvantages of each protocol, and the kinetics of various radiotracers to gain a better understanding of the many and often competing imaging protocols. There is a plethora of literature dealing with numerous issues pertaining to every available protocol. Novices are often confused when deciding which protocol to use. Following is a basic review of the physical properties, biodistribution, and kinetics of each radiotracer. RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS Ideally, a radiopharmaceutical for myocardial perfusion imaging should have the following characteristics: myocardial uptake directly proportional to blood flow, high extraction fraction, high target-to-background ratio, and good myocardial retention and photon flux for optimal imaging. Tl Tl is a cyclotron-produced potassium analog radioisotope with a half-life of 73 h. It produces g-energy rays of 170 kev (;10%) and 135 kev (;3%). The photons resulting from electron capture have energies of kev (abundance) and are the photons used for imaging. The firstpass myocardial extraction of Tl is ;85%; however, only about 3% 5% of the total injected dose localizes in the myocardium when injected at peak exercise. The initial Tl uptake within the myocardium occurs through the active Na-K adenosine triphosphatase transport system. After the initial extraction, Tl redistributes within the myocardium. Tl has a relatively short myocardial retention. The injected dose is low ( MBq [3 4 mci]). The counting statistics are fair. The radiation dosimetry is not favorable because of the high total body absorbed dose, 0.68 rad (1). Tc-Sestamibi Sestamibi is an isonitrile compound that, when labeled with Tc, has a half-life of 6 h. It produces g-energy rays of 140 kev (abundance), which are ideal for imaging. Tc-Sestamibi is extracted from the coronary circulation in proportion to the coronary blood flow. The first-pass myocardial extraction fraction of Tc-sestamibi is 55% 68%. IDEAL MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING Husain 3
2 The myocardial extraction is lower than that of Tl but adequate. Tc-Sestamibi myocardial cellular retention occurs specifically within the mitochondria as a result of an electrostatic interaction. Myocardial retention is prolonged. The myocardial uptake of Tc-sestamibi is ;1.2% 1.5% of the injected dose. Unlike Tl, Tcsestamibi shows minimal redistribution. The injected dose of Tc-sestamibi is higher than that of Tl, resulting in better counting statistics for imaging. The radiation dosimetry is favorable, with a total body absorbed dose of 0.50 rad (1). Tc-Tetrofosmin Tetrofosmin is a diphospine compound that, when labeled with Tc, has a half-life of 6 h and produces g-energy rays of 140 kev. Tc-Tetrofosmin is taken up by the myocardium in proportion to the coronary blood flow. The first-pass myocardial extraction fraction is ;54%. Approximately 1.2% of the injected dose localizes in the myocardium. The myocardial uptake, retention, and blood clearance of Tc-tetrofosmin are similar to those of Tcsestamibi. There is little redistribution. The hepatic clearance of Tc-tetrofosmin is faster than that of Tc-sestamibi (1). As with Tc-sestamibi, the injected dose is higher than that of Tl, resulting in better counting statistics. Tc-Teboroxime Teboroxime is a boronic acid derived, neutral lipophilic compound that, when labeled with Tc, has a half-life of 6 h and produces g-energy rays of 140 kev. Myocardial cell uptake is proportional to coronary blood flow. Being a neutral lipophilic compound, it passively diffuses across the myocardial cell membrane. The first-pass myocardial extraction fraction is high (.90%), and the washout is rapid. There is no redistribution. The injected dose is higher than that of other agents, resulting in good counting statistics for imaging. The radiation dosimetry is not favorable, with a total body absorbed dose of 0.83 rad (1). This imaging agent is not commercially available in the United States at this time. It is, however, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a myocardial perfusion imaging agent. Tc-N-NOET Tc-N-NOET is a new myocardial perfusion imaging agent that is comparable to Tl. It is a neutral lipophilic agent. Biodistribution studies have demonstrated selective myocardial localization. Myocardial uptake is directly proportional to coronary blood flow. The first-pass myocardial extraction fraction is high. Tc-N-NOET redistributes like Tl, thus allowing initial stress and delayed rest imaging. Clearance of pulmonary activity is rapid. The image quality is good because of low background interference. The stress and rest images provide comparable information for the diagnosis of ischemia (2,3). This agent is not yet approved for routine use in the United States. COMPARISON OF TL AND 99M TC-LABELED MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING TRACER KINETICS Following is a brief discussion of various tracer kinetic parameters for Tl and Tc-sestamibi showing how the 2 radiotracers differ. A detailed discussion of these parameters is beyond the scope of this article. The myocellular uptake of Tl is dependent on Na-K adenosine triphosphatase. The myocardial uptake of Tl declines with Na-K pump inhibition from adenosine triphosphate depletion. The myocellular uptake of Tcsestamibi reflects the mean plasma membrane potential. Tc-Sestamibi is retained within the mitochondria as a result of an electrostatic interaction. It declines to low levels with severe cell injury (4). Myocardial transmicrovascular transport of Tl and Tc-sestamibi is variable at different blood flow levels. The capillary permeability for Tl is greater than that for Tc-sestamibi. The parenchymal cell permeability surface area for Tc-sestamibi is much higher than that for Tl (5). The tracer kinetics of Tl and Tc-sestamibi across myocytes are affected by low-flow ischemia. During lowflow ischemia, the information provided by Tl or Tcsestamibi SPECT imaging is dependent on myocardial perfusion and not on a cellular metabolic disorder (6). RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CORONARY BLOOD FLOW AND MYOCARDIAL UPTAKE OF VARIOUS RADIOTRACERS The various kinetics and biodistributions of different radiotracers determine myocardial uptake, retention, redistribution, and washout. The relationship between coronary blood flow and the myocardial uptake of radiotracers is not linear. All commonly used radiopharmaceuticals show a plateau roll-off at higher blood flow levels. The radiotracers show a significant roll-off at coronary blood flow levels exceeding 2.5 ml/min/g. The roll-off is the smallest for Tl and is larger for Tc-sestamibi and Tctetrofosmin (7). A comparison of the first-pass myocardial extraction fractions of various technetium-labeled agents and thallium is shown in Table 1. PHYSICAL AND BIOLOGIC COMPARISONS OF MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING AGENTS There are significant differences in the physical and biologic properties of Tl and Tc-labeled radiopharmaceuticals. TABLE 1 Comparison of First-Pass Myocardial Extraction Fractions of Various Tc-Labeled Agents and Tl Agent % Extraction fraction Tl Tc-Sestamibi Tc-Tetrofosmin 54 Tc-Teboroxime.90 Tc-NOET JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE TECHNOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 1 March 2007
3 Table 2 shows a comparison of various factors affecting the myocardial uptake of the radiotracers. VARIOUS IMAGING PROTOCOLS Tl Imaging Myocardial perfusion imaging with Tl was commonly used until Tc-labeled radiotracers became available. The most commonly used procedure involves administering ;148 MBq (;4 mci) of Tl at peak exercise. Stress imaging is performed immediately after the Tl injection (beginning within 5 7 min of the injection). Delayed rest (redistribution) images are obtained at 3 4 h after injection. There are several variations of delayed imaging, which can be done at up to 24 h to assess viability. In addition, a Tl reinjection technique with an additional booster dose of MBq ( mci) is used to assess myocardial viability. Myocardial Perfusion Imaging with Tc-Labeled Radiopharmaceuticals (Sestamibi or Tetrofosmin) Two-Day Protocol. Two-day protocols are best in terms of taking advantage of the physical properties, pharmacokinetics, and acquisition, processing, and display parameters of Tc-labeled agents. Typical doses for 1- and 2-d protocols are shown in Table 3. The advantages of 2-d protocols are as follows: flexibility of scheduling stress rest imaging; better patient flow; ability to image obese patients; higher dose; better gated rest stress imaging; no cross talk or cross contamination; optimal defect contrast with minimal background activity; elimination of day 2 study if stress study is normal; and high accuracy for detecting coronary artery disease in patients with a low likelihood of coronary artery disease. The disadvantages of 2-d protocols are as follows: the need for 2 d; inconvenience for patients; delay in diagnosis; and camera time relative to that used for dual-isotope simultaneous acquisition, which is not recommended because of energy window cross talk. Imaging Protocol for Tc-Labeled Agents. For stress imaging, 555 MBq 1.11 GBq (15 30 mci) is injected at peak exercise. Gated SPECT is performed from 15 min to TABLE 3 Doses of Tc-Labeled Agents for Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy* Protocol Sestamibi Tetrofosmin One-day protocol First dose 8 10 mci 5 8 mci Second dose mci mci Two-day protocol First dose mci mci Second dose mci mci *Reprinted from Crawford ES, Husain SS. Nuclear Cardiac Imaging: Terminology and Technical Aspects. Reston, VA: Society of Nuclear Medicine; 2003:29. 2 h after injection, preferably within min, to maximize stress myocardial defect contrast and minimize hepatobiliary and gastrointestinal interference. For rest imaging, 555 MBq 1.11 GBq (15 30 mci) is injected at rest. Gated SPECT is performed within min after injection. A 60-min delay is optimal for adequate hepatobiliary clearance of the radiotracer. Imaging too soon after injection will result in increased residual liver activity and increased counts in the adjacent inferior wall because of scatter and scaling. Waiting too long will decrease total myocardial count density and increase gastrointestinal interference. The optimal imaging window is when radiotracer activity has cleared from the liver and not concentrated in the gastrointestinal tract, that is, loops of bowel and the stomach (retrograde flow). In the event that there is a significant splanchnic or bowel overlap with the inferior wall, various maneuvers, such as drinking water or milk or eating fatty food, can be tried to alleviate the problem before repeating delayed imaging. One-Day Rest Stress or Stress Rest Protocol Performed with Sestamibi or Tetrofosmin. The rest stress sequence is significantly better than the stress rest sequence in terms of detecting the reversibility of stress-induced perfusion deficits. With the stress rest sequence, the rest activity obscures some of the stress defect, resulting in the degradation TABLE 2 Physical and Biologic Comparisons of Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Agents Factor Tc-Sestamibi or Tc-tetrofosmin Tl Extraction fraction Lower Higher Myocardial retention Prolonged Comparatively shorter Myocardial washout Slower Rapid Redistribution Minimal Significant Myocardial perfusion at high blood flow Same Same Injected dose Higher Lower Counting statistics Better Fair Physical half-life 6 h 73.1 h Photon energy 140 kev kev (abundance), 170 kev (;10%), and 135 kev (;3%) Radiation dosimetry More favorable Less favorable IDEAL MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING Husain 5
4 of image contrast and a reduction in the detection of true reversibility. With the rest stress sequence, there is a greater difference in counts between normal and abnormal areas of the myocardium on stress images. This difference results in better normalization of the abnormality on rest images. A 3- to 4-h delay between rest imaging and stress imaging allows radioactivity to decay by 29% 37%, thereby providing better image contrast (8,9). However, the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology guidelines (10) offer the option to proceed immediately from rest imaging to stress imaging during a 1-d protocol as long as the higher dose is times the lower dose. Images from a 2-d protocol and images from a 1-d (rest stress) protocol are shown in Figure 1. Both studies are normal. The studies were obtained with the same camera. The images from the studies are very comparable in features and quality. One-Day Dual-Isotope Acquisition Protocol A 1-d dual-isotope protocol with Tl and Tcsestamibi can be performed with separate acquisition or FIGURE 1. (a) Images obtained with 2-d Tc-sestamibi protocol. Findings are normal. (b) Images obtained with 1-d Tc-sestamibi protocol. Findings are normal. 6 JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE TECHNOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 1 March 2007
5 simultaneous acquisition. In a separate acquisition of Tl rest images, the contribution of Tl to the Tc energy window is negligible (;2.9%). Correction for cross contamination between the 2 energy windows is not required. The overall sensitivity and specificity for the detection of coronary artery disease are ;90% (11,12). Dual-Isotope Separate-Acquisition Protocol. For the rest Tl stress Tc protocol, MBq (3 4 mci) of Tl is injected in the upright position to decrease lung uptake. Rest Tl SPECT is performed after min. When rest imaging is complete, the patient is sent for treadmill or pharmacologic stress testing. Next, 555 MBq 1.11 GBq (15 30 mci) of the Tc-labeled agent is injected, and SPECT acquisition is begun at 15 min after injection. For viability assessment, the patient can be given a second injection of thallium and reimaged on the following morning; alternatively, thallium can be given the night before imaging begins. Figure 2 is a diagram of dual-isotope imaging protocol options. The images from a normal dualisotope study are shown in Figure 3. The advantages of the dual-isotope separate-acquisition protocol are as follows: a short duration of the entire study (,2 h); no need for cross talk correction; insignificant contribution of counts from Tl to the Tc window; minimization of the problem of cross contamination; optimal defect contrast; comparable rest and stress images; true rest study, which allows a better evaluation of reversible defects; viability assessment; favorable dosimetry; patient convenience; and sensitivity and specificity of ;90%. The disadvantages of the dual-isotope separate-acquisition protocol are as follows: comparison of stress rest images obtained with 2 isotopes with different characteristics; variability in attenuation factors; differences in image resolution; greater Compton scatter of Tl than of Tc; greater myocardial wall thickness with Tl than with Tc because of increased scatter; less-than-optimal transient ischemic dilatation evaluation because of left ventricular cavity being larger with Tc; difficulty in evaluating minimal reversible defects; and low photon energy of Tl, a feature that is not ideal for obese patients. Figure 4 shows the normal cavity size difference between a Tl scan and a Tc-labeled agent scan. Myocardial wall thickness is greater with Tl than with Tc-labeled agents. This normal difference in cavity size is attributable to Tl scatter. Dual-Isotope Simultaneous-Acquisition Protocol. The dual-isotope simultaneous-acquisition protocol is based on the unproven assumption that the effect of cross talk between the energy windows of Tl and Tc is insignificant. Downscatter of high-energy Tc-sestamibi into the lower-energy Tl window results in an ;20% reduction in defect contrast with Tl and in the overestimation of defect reversibility (12). Downscatter correction methods are not conclusive and have not been clinically validated. For the simultaneous rest Tl stress Tc-sestamibi SPECT protocol, 111 MBq (3.0 mci) of Tl is injected at rest. The stress study is performed within 30 min. After the stress acquisition, 925 MBq (25 mci) of Tc-sestamibi is injected at peak exercise, and dual SPECT studies are acquired within 30 min. The advantages of the dual-isotope simultaneousacquisition protocol are as follows: no need for 2 separate imaging sessions; reduced camera acquisition time; shorter study duration; fewer motion artifacts than with separate rest and stress acquisitions; and exact registration between images obtained with Tl and images obtained with Tc. The disadvantages of the dual-isotope simultaneousacquisition protocol involve cross talk and downscatter; the contribution of scattered and primary photons from the FIGURE 2. Dual-isotope imaging. Reprinted from Crawford ES, Husain SS. Nuclear Cardiac Imaging: Terminology and Technical Aspects. Reston, VA: Society of Nuclear Medicine; 2003;33. IDEAL MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING Husain 7
6 best. The 1-d rest stress Tc-labeled agent myocardial perfusion imaging protocol may be a better choice for some clinics. The 1-d dual-isotope separate-acquisition protocol is a good alternative. The dual-isotope simultaneousacquisition protocol is a suboptimal choice until an approach for downscatter correction is conclusive and validated clinically. Again, there is no single best protocol. Each protocol has advantages and disadvantages, which must be understood and taken into consideration when one is choosing a protocol. The staff members in each clinic need to determine which protocol will work best for them and consistently maintain it for better comparison when repeat studies are performed on the same patient. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The author acknowledges the contributions of Elpida S. Crawford, Nuclear Medicine Technology Program, School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, State University of New York at Buffalo, who kindly provided comments on this article and developed the continuing education questions. REFERENCES 1. Crawford ES, Husain SS. Nuclear Cardiac Imaging: Terminology and Technical Aspects. Reston, VA: Society of Nuclear Medicine; Fagret D, Marie PY, Brunotte F, et al. Myocardial perfusion imaging with technetium--tc NOET: comparison with thallium- and coronary angiography. J Nucl Med. 1995;36: Sinusas AJ. Technetium -N-NOET: although not equivalent to thallium-, it still offers new opportunities [comment]. J Nucl Cardiol. 2000;7: Piwnica-Worms D, Chiu ML, Kronauge JF. Divergent kinetics of Tl and Tc-sestamibi in cultured chick ventricular myocytes during ATP depletion. Circulation. 1992;85: Leppo JA, Meerdink DJ. Comparison of the myocardial uptake of a technetiumlabeled isonitrile analog and thallium. Circ Res. 1989;65: Ayalew A, Marie PY, Menu P, et al. Tl and Tc-MIBI retention in an isolated heart model of low-flow ischemia and stunning: evidence of negligible impact of myocyte metabolism on tracer kinetics. J Nucl Med. 2002;43: Zaret B, Beller G. Clinical Nuclear Cardiology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby; 2005: Van Train KF, Garcia EV, Maddahi J, et al. Multicenter trial validation for quantitative analysis of same-day rest-stress technetium--sestamibi myocardial tomograms. J Nucl Med. 1994;35: Taillefer R, Gagnon A, Laflamme L, et al. Same day injections of tc methoxy isobutyl isonitrile (hexamibi) for myocardial tomographic imaging: comparison between rest-stress and stress-rest injection sequences. Eur J Nucl Med. 1989;15: Henzlova MJ, Cerqueira MD, Mahmarian JJ, Yao SS; Quality Assurance Committee of the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology. Stress protocols and tracers. J Nucl Cardiol. 2006;13:e80 e Berman DS, Kait H, Friedman JD, et al. Separate acquisition rest thallium-/ stress technetium- sestamibi dual-isotope myocardial perfusion singlephoton emission computed tomography: a clinical validation study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;22: Kiat H, Germano G, Friedman J, et al. Comparative feasibility of separate or simultaneous rest thallium-/stress technetium--sestamibi dual-isotope myocardial perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med. 1994;35: IDEAL MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING Husain 9
Rb 82 Cardiac PET Scanning Protocols and Dosimetry. Deborah Tout Nuclear Medicine Department Central Manchester University Hospitals
 Rb 82 Cardiac PET Scanning Protocols and Dosimetry Deborah Tout Nuclear Medicine Department Central Manchester University Hospitals Overview Rb 82 myocardial perfusion imaging protocols Acquisition Reconstruction
Rb 82 Cardiac PET Scanning Protocols and Dosimetry Deborah Tout Nuclear Medicine Department Central Manchester University Hospitals Overview Rb 82 myocardial perfusion imaging protocols Acquisition Reconstruction
123 Main St NY, New York 12345 ph: (202) 555 5555 fax: (202) 555 5555
 Patient Name: DOE, JOHN D. Gender: M Date of Study: 4/2/2013 Date of birth: 6/28/1962 Age: 50 Medical Record #: 45869725 Ordering Physician: JANE INTERNIST, MD History: Atypical Angina, Abn ECG, High Cholesterol,
Patient Name: DOE, JOHN D. Gender: M Date of Study: 4/2/2013 Date of birth: 6/28/1962 Age: 50 Medical Record #: 45869725 Ordering Physician: JANE INTERNIST, MD History: Atypical Angina, Abn ECG, High Cholesterol,
Part A: Structure and Organization
 Part A: Structure and Organization Radioactive Materials License NRC (or State) radioactive materials license present Personnel Medical Director Meets Medical Director responsibility requirements Meets
Part A: Structure and Organization Radioactive Materials License NRC (or State) radioactive materials license present Personnel Medical Director Meets Medical Director responsibility requirements Meets
Objectives. Cardiac Substrate Metabolism. 2004 SNM Mid-Winter Educational Symposium
 Myocardial Viability Imaging With PET Marcelo F. Di Carli,, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Conflict of Interest: : No Relations to disclose To review: Basic principles
Myocardial Viability Imaging With PET Marcelo F. Di Carli,, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Conflict of Interest: : No Relations to disclose To review: Basic principles
Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method
 Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method Christopher Martel, M.Sc., CHP Lisa Thornhill,, NRRPT, RT(NM) Boston University Medical Center Thyroid Carcinoma New cases and deaths in
Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method Christopher Martel, M.Sc., CHP Lisa Thornhill,, NRRPT, RT(NM) Boston University Medical Center Thyroid Carcinoma New cases and deaths in
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging. Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet
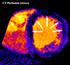 MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
AI CPT Codes. x x. 70336 MRI Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s)
 Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Code Category Description Auth Required Medicaid Medicare 0126T IMT Testing Common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) study for evaluation of atherosclerotic burden or coronary heart disease risk factor
Accurate Coding of Nuclear Medicine Procedures. Unravel Coding Basics
 Accurate Coding of Nuclear Medicine Procedures Presented by: Denise A. Merlino, MBA, CNMT, CPC Merlino Healthcare Consulting Corp. 1 Unravel Coding Basics October 27, 2009 2 1 Coding Basic Steps diagnosis
Accurate Coding of Nuclear Medicine Procedures Presented by: Denise A. Merlino, MBA, CNMT, CPC Merlino Healthcare Consulting Corp. 1 Unravel Coding Basics October 27, 2009 2 1 Coding Basic Steps diagnosis
doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.11.013 This information is current as of October 16, 2008
 Task Force 5: Training in Nuclear Cardiology: Endorsed by the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology Manuel D. Cerqueira, Daniel S. Berman, Marcelo F. Di Carli, Heinrich R. Schelbert, Frans J. Th. Wackers,
Task Force 5: Training in Nuclear Cardiology: Endorsed by the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology Manuel D. Cerqueira, Daniel S. Berman, Marcelo F. Di Carli, Heinrich R. Schelbert, Frans J. Th. Wackers,
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology)
 STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
STUDY PLAN FOR THE CERTIFICATE OF THE HIGHER SPECIALIZATION IN ( Diagnostic Radiology) plan number :15/11/97/NT I-GENERAL RULES AND CONDITIONS: 1- This plan conforms to the regulations of granting the
PET and PET/CT in Clinical Trials
 PET and PET/CT in Clinical Trials Nathan C. Hall, M.D., Ph.D. The Ohio State University Medical Center CALGB Imaging Core Lab CALGB Imaging Committee Outline Introduction to PET Positron Emitter Physics
PET and PET/CT in Clinical Trials Nathan C. Hall, M.D., Ph.D. The Ohio State University Medical Center CALGB Imaging Core Lab CALGB Imaging Committee Outline Introduction to PET Positron Emitter Physics
Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without Contrast Material, Followed By Contrast Material(S) And Further Sections
 1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
1199SEIU BENEFIT AND PENSION FUNDS High Tech Diagnostic Radiology and s # 1 70336 Magnetic Resonance (Eg, Proton) Imaging, Temporomandibular Joint(S) 2 70450 Computed Tomography, Head Or Brain; Without
CARDIOLOGY PROCEDURES REQUIRING PRECERTIFICATION
 CLINICAL POLICY CARDIOLOGY PROCEDURES REQUIRING PRECERTIFICATION Policy Number: CARDIOLOGY 026.6 T2 Effective Date: May 1, 2015 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE... BENEFIT
CLINICAL POLICY CARDIOLOGY PROCEDURES REQUIRING PRECERTIFICATION Policy Number: CARDIOLOGY 026.6 T2 Effective Date: May 1, 2015 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE... BENEFIT
CPT CODE PROCEDURE DESCRIPTION. CT Scans 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ CONTRAST 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ CONTRAST
 CPT CODE PROCEDURE DESCRIPTION CT Scans 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ CONTRAST 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ CONTRAST 70480 CT ORBIT W/O CONTRAST 70481 CT ORBIT W/ CONTRAST 70482
CPT CODE PROCEDURE DESCRIPTION CT Scans 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ CONTRAST 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ CONTRAST 70480 CT ORBIT W/O CONTRAST 70481 CT ORBIT W/ CONTRAST 70482
Nuclear medicine. Answering your questions
 Nuclear medicine Answering your questions ANSTO s OPAL research reactor in Sydney What is nuclear medicine? This is a branch of medicine that uses radiation from radioactive tracers to provide information
Nuclear medicine Answering your questions ANSTO s OPAL research reactor in Sydney What is nuclear medicine? This is a branch of medicine that uses radiation from radioactive tracers to provide information
Nuclear Medicine Coding 101 June 16, 2008 Contac me: DENISE@MERLINOHCCC.COM 1-888-60M-HCCC, 1-888-606-4222
 Nuclear Medicine Coding 101 June 16, 2008 Contac me: DENISE@MERLINOHCCC.COM 1-888-60M-HCCC, 1-888-606-4222 Presented by: Denise A. Merlino, MBA, CNMT, CPC, FSNMTS Disclosures SNM ASNC Bracco Diagnostics
Nuclear Medicine Coding 101 June 16, 2008 Contac me: DENISE@MERLINOHCCC.COM 1-888-60M-HCCC, 1-888-606-4222 Presented by: Denise A. Merlino, MBA, CNMT, CPC, FSNMTS Disclosures SNM ASNC Bracco Diagnostics
Nuclear PACS: Problems, Solutions
 Nuclear PACS: Problems, Solutions by Jerold W. Wallis, MD Introduction Reprinted with permission: Wallis JW. Nuclear PACS: Problems, Solutions. Decisions in Imaging Economics. 2004;6;21-25. There is increasing
Nuclear PACS: Problems, Solutions by Jerold W. Wallis, MD Introduction Reprinted with permission: Wallis JW. Nuclear PACS: Problems, Solutions. Decisions in Imaging Economics. 2004;6;21-25. There is increasing
Quality Assurance in Blood Cell Labelling
 Quality Assurance in Blood Cell Labelling Sietske Rubow Radiopharmacist Nuclear Medicine Tygerberg Hospital and Stellenbosch University smr@sun.ac.za Overview What is QA QA in Blood Cell Labelling Staff
Quality Assurance in Blood Cell Labelling Sietske Rubow Radiopharmacist Nuclear Medicine Tygerberg Hospital and Stellenbosch University smr@sun.ac.za Overview What is QA QA in Blood Cell Labelling Staff
What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac Nuclear Medicine Cardiac nuclear medicine imaging evaluates the heart for coronary artery disease and cardiomyopathy. It also may be used to help determine whether the heart
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac Nuclear Medicine Cardiac nuclear medicine imaging evaluates the heart for coronary artery disease and cardiomyopathy. It also may be used to help determine whether the heart
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Section 8: Clinical Exercise Testing. a maximal GXT?
 Section 8: Clinical Exercise Testing Maximal GXT ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 5 ACSM Manual: Chapter 8 HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Outline What is the purpose of a maximal GXT? Who should have a maximal GXT (and
Section 8: Clinical Exercise Testing Maximal GXT ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 5 ACSM Manual: Chapter 8 HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Outline What is the purpose of a maximal GXT? Who should have a maximal GXT (and
Absorption of Drugs. Transport of a drug from the GI tract
 Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
Nuclear Medicine Accreditation Program Requirements
 Nuclear Medicine Accreditation Program Requirements OVERVIEW... 2 MEDICARE IMPROVEMENT F PATIENTS AND PROVIDERS ACT OF 2008 (MIPPA)... 2 MANDATY ACCREDITATION TIME REQUIREMENTS... 3 WITHDRAWN, ADDED, REPLACEMENT
Nuclear Medicine Accreditation Program Requirements OVERVIEW... 2 MEDICARE IMPROVEMENT F PATIENTS AND PROVIDERS ACT OF 2008 (MIPPA)... 2 MANDATY ACCREDITATION TIME REQUIREMENTS... 3 WITHDRAWN, ADDED, REPLACEMENT
CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers
 CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast
CPT * Codes Included in AIM Preauthorization Program for 2013 With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast
Non-invasive functional testing in 2014
 Non-invasive functional testing in 2014 Bjarne Nørgaard Department Cardiology B Aarhus University Hospital Skejby, Disclosures: Research grants: Edwards and Siemens Non-invasive functional testing in 2014
Non-invasive functional testing in 2014 Bjarne Nørgaard Department Cardiology B Aarhus University Hospital Skejby, Disclosures: Research grants: Edwards and Siemens Non-invasive functional testing in 2014
Dedicated computer software to radiation dose optimization for the staff performing nuclear medicine procedures
 NUKLEONIKA 2012;57(4):497 502 ORIGINAL PAPER Dedicated computer software to radiation dose optimization for the staff performing nuclear medicine procedures Katarzyna Matusiak, Jakub Kosek Abstract. Nuclear
NUKLEONIKA 2012;57(4):497 502 ORIGINAL PAPER Dedicated computer software to radiation dose optimization for the staff performing nuclear medicine procedures Katarzyna Matusiak, Jakub Kosek Abstract. Nuclear
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain
 Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET
 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
Radiation and Pregnancy
 Radiation and Pregnancy General Special attention must be paid to the pregnant, potentially pregnant, or breast feeding patient. The developing embryo or fetus is particularly sensitive to radiation. If
Radiation and Pregnancy General Special attention must be paid to the pregnant, potentially pregnant, or breast feeding patient. The developing embryo or fetus is particularly sensitive to radiation. If
University of Texas Medical School at Houston. April 14, 2015
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control Center WO66-G609 Silver Spring, MD 20993-0002 University of Texas Medical
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control Center WO66-G609 Silver Spring, MD 20993-0002 University of Texas Medical
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology
 Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
 Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging version 3.0, approved June 15, 2002 Authors: H. William Strauss, MD (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY);
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging version 3.0, approved June 15, 2002 Authors: H. William Strauss, MD (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY);
Crosswalk for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Imaging Codes G0230 G0030, G0032, G0034, G0036, G0038, G0040, G0042, G0044, G0046
 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) CPT to HCPCS Level Crosswalk Changes below from CMS Change Request 3741 Transmittals 518 & 31 published on April 1, 2005; mplementation of CPT codes are effective January
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) CPT to HCPCS Level Crosswalk Changes below from CMS Change Request 3741 Transmittals 518 & 31 published on April 1, 2005; mplementation of CPT codes are effective January
Diagnostic Imaging Prior Review Code List 3 rd Quarter 2016
 Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6 Abdomen/Pelvis Combination 101 Service 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by 74176 Computed tomography, abdomen and pelvis;
Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6 Abdomen/Pelvis Combination 101 Service 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by 74176 Computed tomography, abdomen and pelvis;
Medical Physics and Radioactivity
 Medical Physics and Radioactivity Radioactivity Unstable nucleus Electromagnetic wave particle Atoms which emit electromagnetic radiation or a particle by the spontaneous transformation of their nucleus
Medical Physics and Radioactivity Radioactivity Unstable nucleus Electromagnetic wave particle Atoms which emit electromagnetic radiation or a particle by the spontaneous transformation of their nucleus
Society of Nuclear Medicine 1850 Samuel Morse Drive Reston, VA 20190-5316 www.snm.org
 What is nuclear medicine? Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that is used to diagnose and treat diseases in a safe and painless way. Nuclear medicine procedures permit the determination of medical
What is nuclear medicine? Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that is used to diagnose and treat diseases in a safe and painless way. Nuclear medicine procedures permit the determination of medical
Sodium Fluoride PET/CT Bone Imaging: Theory and Practice
 Sodium Fluoride PET/CT Bone Imaging: Theory and Practice George Segall, M.D. Stanford University Why F-18 Fluoride? Faster Higher Resolution Anatomic Correlation Chemiadsorption Hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2
Sodium Fluoride PET/CT Bone Imaging: Theory and Practice George Segall, M.D. Stanford University Why F-18 Fluoride? Faster Higher Resolution Anatomic Correlation Chemiadsorption Hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2
Nursing 113. Pharmacology Principles
 Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
The Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline For Parathyroid Scintigraphy
 The Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline For Parathyroid Scintigraphy Version 3.0, approved June 2004 Authors: Bennett S. Greenspan, MD (University of Missouri Medical Center, Columbia, MO);
The Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline For Parathyroid Scintigraphy Version 3.0, approved June 2004 Authors: Bennett S. Greenspan, MD (University of Missouri Medical Center, Columbia, MO);
PET Accreditation Program Requirements
 PET Accreditation Program Requirements OVERVIEW... 2 MEDICARE IMPROVEMENT F PATIENTS AND PROVIDERS ACT OF 2008 (MIPPA)... 2 MANDATY ACCREDITATION TIME REQUIREMENTS... 3 WITHDRAWN, ADDED, REPLACEMENT UNITS...
PET Accreditation Program Requirements OVERVIEW... 2 MEDICARE IMPROVEMENT F PATIENTS AND PROVIDERS ACT OF 2008 (MIPPA)... 2 MANDATY ACCREDITATION TIME REQUIREMENTS... 3 WITHDRAWN, ADDED, REPLACEMENT UNITS...
Mississippi Medicaid. Provider Reference Guide. For Part 220. Radiology Services
 Mississippi Medicaid Provider Reference Guide For Part 220 Radiology Services This is a companion document to the Mississippi Administrative Code Title 23 and must be utilized as a reference only. Table
Mississippi Medicaid Provider Reference Guide For Part 220 Radiology Services This is a companion document to the Mississippi Administrative Code Title 23 and must be utilized as a reference only. Table
CARDIOLOGY Delineation of Privileges
 CARDIOLOGY Delineation of Privileges APPLICANT: INITIAL APPOINTMENT REQUIREMENTS: BASIC EDUCATION: M.D. or D.O. from an accredited school of medicine or osteopathy. Successful completion of an ACGME or
CARDIOLOGY Delineation of Privileges APPLICANT: INITIAL APPOINTMENT REQUIREMENTS: BASIC EDUCATION: M.D. or D.O. from an accredited school of medicine or osteopathy. Successful completion of an ACGME or
Effect of Spinal Cord Stimulation on Myocardial Flow Reserve in Patients with Refractory Angina Pectoris
 Effect of Spinal Cord Stimulation on Myocardial Flow Reserve in Patients with Refractory Angina Pectoris Antti Varis, Heikki Ukkonen, Antti Saraste, Tuija Vasankari, Satu Tunturi, Markku Taittonen, Pirkka
Effect of Spinal Cord Stimulation on Myocardial Flow Reserve in Patients with Refractory Angina Pectoris Antti Varis, Heikki Ukkonen, Antti Saraste, Tuija Vasankari, Satu Tunturi, Markku Taittonen, Pirkka
Drug Excretion. Renal Drug Clearance. Drug Clearance and Half-Life. Glomerular Filtration II. Glomerular Filtration I. Drug Excretion and Clearance
 t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
MYOCARDIAL PET/CT SCAN (FDG tracer)
 MYOCARDIAL PET/CT SCAN (FDG tracer) Contact information and registration: Meilahti Hospital, Department of Nuclear Medicine Tower Hospital, Haartmaninkatu 4, 00290 Helsinki tel. 09-471 72554 Appointment
MYOCARDIAL PET/CT SCAN (FDG tracer) Contact information and registration: Meilahti Hospital, Department of Nuclear Medicine Tower Hospital, Haartmaninkatu 4, 00290 Helsinki tel. 09-471 72554 Appointment
For many years, physicians have been faced with the. SPECT/CT Physical Principles and Attenuation Correction*
 SPECT/CT Physical Principles and Attenuation Correction* James A. Patton 1 and Timothy G. Turkington 2 1 Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee; and 2 Duke University Medical Center,
SPECT/CT Physical Principles and Attenuation Correction* James A. Patton 1 and Timothy G. Turkington 2 1 Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee; and 2 Duke University Medical Center,
Radiopharmaceuticals that can be used for alleviating pain caused by bone metastases:
 Methodological letter of Nuclear Medicine Professional College and Radiotherapy and Oncology Professional College on the treatment of bone metastases with open radioactive isotopes Bone metastases of tumours
Methodological letter of Nuclear Medicine Professional College and Radiotherapy and Oncology Professional College on the treatment of bone metastases with open radioactive isotopes Bone metastases of tumours
Noninvasive testing can provide useful information for
 CONTINUING EDUCATION Roles of Nuclear Cardiology, Cardiac Computed Tomography, and Cardiac Magnetic Resonance: Noninvasive Risk Stratification and a Conceptual Framework for the Selection of Noninvasive
CONTINUING EDUCATION Roles of Nuclear Cardiology, Cardiac Computed Tomography, and Cardiac Magnetic Resonance: Noninvasive Risk Stratification and a Conceptual Framework for the Selection of Noninvasive
Medical Applications of radiation physics. Riccardo Faccini Universita di Roma La Sapienza
 Medical Applications of radiation physics Riccardo Faccini Universita di Roma La Sapienza Outlook Introduction to radiation which one? how does it interact with matter? how is it generated? Diagnostics
Medical Applications of radiation physics Riccardo Faccini Universita di Roma La Sapienza Outlook Introduction to radiation which one? how does it interact with matter? how is it generated? Diagnostics
Seminar 7. Medical application of radioisotopes - radiotherapy
 Seminar 7 Medical application of radioisotopes - radiotherapy Radioisotopes in medical diagnosis. Gamma camera. Radionuclide imaging (PET, SPECT). Radiotherapy. Sources of radiation. Treatment planning.
Seminar 7 Medical application of radioisotopes - radiotherapy Radioisotopes in medical diagnosis. Gamma camera. Radionuclide imaging (PET, SPECT). Radiotherapy. Sources of radiation. Treatment planning.
BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY
 BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Internists Specific Requirements For Osteopathic Subspecialty Training In Cardiology
BASIC STANDARDS FOR RESIDENCY TRAINING IN CARDIOLOGY American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Internists Specific Requirements For Osteopathic Subspecialty Training In Cardiology
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016
 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review by AIM Effective 01/01/2016 When a service is authorized only one test per group is payable. *Secondary codes or add-on codes do not require preauthorization or separate
http://www.bls.gov/oco/ocos104.htm
 http://www.bls.gov/oco/ocos104.htm Nuclear Medicine Technologists Nature of the Work Training, Other Qualifications, and Advancement Employment Job Outlook Projections Data Earnings OES Data Related Occupations
http://www.bls.gov/oco/ocos104.htm Nuclear Medicine Technologists Nature of the Work Training, Other Qualifications, and Advancement Employment Job Outlook Projections Data Earnings OES Data Related Occupations
Quantitative Imaging In Clinical Trials Using PET/CT: Update
 Quantitative Imaging In Clinical Trials Using PET/CT: Update Paul Kinahan, Robert Doot Imaging Research Laboratory Department of Radiology University of Washington, Seattle, WA Supported by RSNA Quantitative
Quantitative Imaging In Clinical Trials Using PET/CT: Update Paul Kinahan, Robert Doot Imaging Research Laboratory Department of Radiology University of Washington, Seattle, WA Supported by RSNA Quantitative
Carol M. Anderson, MD 2614 E Ramblewood San Antonio,TX 78070 830-549-1111 (Office) 210-399-3143 (Fax) dranderson@wonderfullywellmedical.
 Carol M. Anderson, MD 2614 E Ramblewood San Antonio,TX 78070 830-549-1111 (Office) 210-399-3143 (Fax) dranderson@wonderfullywellmedical.com APPOINTMENTS Founder and President Wonderfully Well Center for
Carol M. Anderson, MD 2614 E Ramblewood San Antonio,TX 78070 830-549-1111 (Office) 210-399-3143 (Fax) dranderson@wonderfullywellmedical.com APPOINTMENTS Founder and President Wonderfully Well Center for
Magnetic Resonance Quantitative Analysis. MRV MR Flow. Reliable analysis of heart and peripheral arteries in the clinical workflow
 Magnetic Resonance Quantitative Analysis MRV MR Flow Reliable analysis of heart and peripheral arteries in the clinical workflow CAAS MRV Functional Workflow Designed for imaging specialists, CAAS MRV
Magnetic Resonance Quantitative Analysis MRV MR Flow Reliable analysis of heart and peripheral arteries in the clinical workflow CAAS MRV Functional Workflow Designed for imaging specialists, CAAS MRV
Principles of Medical Ultrasound. Pai-Chi Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University
 Principles of Medical Ultrasound Pai-Chi Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University What is Medical Ultrasound? Prevention: actions taken to avoid diseases. Diagnosis: the process
Principles of Medical Ultrasound Pai-Chi Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University What is Medical Ultrasound? Prevention: actions taken to avoid diseases. Diagnosis: the process
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Adenosine stress DECT equivalent to SPECT, MRI for myocardium evaluation By Eric Barnes AuntMinnie.com staff writer November 21, 2008
 Adenosine stress DECT equivalent to SPECT, MRI for myocardium evaluation By Eric Barnes AuntMinnie.com staff writer November 21, 2008 A new power combo consisting of adenosine stress and dual-energy CT
Adenosine stress DECT equivalent to SPECT, MRI for myocardium evaluation By Eric Barnes AuntMinnie.com staff writer November 21, 2008 A new power combo consisting of adenosine stress and dual-energy CT
CORE SmPC FOR RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS
 CORE SmPC FOR RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS The QRD Product Information template with explanatory notes and the convention to be followed for QRD templates provide general guidance on format and text and should
CORE SmPC FOR RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS The QRD Product Information template with explanatory notes and the convention to be followed for QRD templates provide general guidance on format and text and should
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 40, No. 6, 2002 2002 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/02/$22.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 40, No. 6, 2002 2002 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/02/$22.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(02)02118-6
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 40, No. 6, 2002 2002 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/02/$22.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(02)02118-6
SMF Awareness Seminar 2014
 SMF Awareness Seminar 2014 Clinical Evaluation for In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices Dr Jiang Naxin Health Sciences Authority Medical Device Branch 1 In vitro diagnostic product means Definition of IVD
SMF Awareness Seminar 2014 Clinical Evaluation for In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices Dr Jiang Naxin Health Sciences Authority Medical Device Branch 1 In vitro diagnostic product means Definition of IVD
MARKET CONDUCT EXAMINATION REPORT. AETNA HEALTH INC. (a Delaware corporation) NAIC#95245
 MARKET CONDUCT EXAMINATION REPORT ON AETNA HEALTH INC. (a Delaware corporation) NAIC#95245 980 Jolly Road Blue Bell, PA 19422 As of April 6, 2010 Table of Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 2 INTRODUCTION...
MARKET CONDUCT EXAMINATION REPORT ON AETNA HEALTH INC. (a Delaware corporation) NAIC#95245 980 Jolly Road Blue Bell, PA 19422 As of April 6, 2010 Table of Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 2 INTRODUCTION...
A Proposal for an Advanced Cardiovascular Imaging Training Track
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 48, No. 7, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.04.096
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 48, No. 7, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.04.096
It is important to stratify cardiac risks in individual patients
 Preoperative Risk Stratification Using Stress Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy with Electrocardiographic Gating Jun Hashimoto, MD 1 ; Takayuki Suzuki, MD 1 ; Tadaki Nakahara, MD 1 ; Shigeru Kosuda, MD
Preoperative Risk Stratification Using Stress Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy with Electrocardiographic Gating Jun Hashimoto, MD 1 ; Takayuki Suzuki, MD 1 ; Tadaki Nakahara, MD 1 ; Shigeru Kosuda, MD
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7
 Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
NUCLEAR MEDICINE TECHNOLOGY CERTIFICATE APPLICATION INSTRUCTIONS
 State of California Health and Human Services Agency California Department of Public Health Radiologic Health Branch NUCLEAR MEDICINE TECHNOLOGY CERTIFICATE APPLICATION INSTRUCTIONS The State of California
State of California Health and Human Services Agency California Department of Public Health Radiologic Health Branch NUCLEAR MEDICINE TECHNOLOGY CERTIFICATE APPLICATION INSTRUCTIONS The State of California
6/5/2014. Objectives. Acute Coronary Syndromes. Epidemiology. Epidemiology. Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology
 Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
PET PROS PET Professional Resources and Outreach Source. A summary of the recommendations and practice guidelines of professional groups
 PET PROS PET Professional Resources and Outreach Source A summary of the recommendations and practice guidelines of professional groups Background: The SNMMI PET/CT Utilization Task Force (UTF) was formed
PET PROS PET Professional Resources and Outreach Source A summary of the recommendations and practice guidelines of professional groups Background: The SNMMI PET/CT Utilization Task Force (UTF) was formed
Procedure Codes. RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY
 Procedure Codes 2011 RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY 2D3D Therapeutic radiology treatment planning; simple 77261 Therapeutic
Procedure Codes 2011 RadConsult provides real-time decision support for physicians who order high-cost imaging procedures RADIATION THERAPY 2D3D Therapeutic radiology treatment planning; simple 77261 Therapeutic
Captus 3000 Thyroid Uptake And Well System
 (201) 825-9500 / (800) 631-3826 THRYOID UPTAKE SYSTEMS 51 Captus 3000 Thyroid Uptake And Well System The Ultimate... User Friendly... Intuitive Performing Thyroid Uptake measurements has never been easier.
(201) 825-9500 / (800) 631-3826 THRYOID UPTAKE SYSTEMS 51 Captus 3000 Thyroid Uptake And Well System The Ultimate... User Friendly... Intuitive Performing Thyroid Uptake measurements has never been easier.
ACR SNM SPR PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR THE PERFORMANCE OF CARDIAC SCINTIGRAPHY
 The American College of Radiology, with more than 30,000 members, is the principal organization of radiologists, radiation oncologists, and clinical medical physicists in the United States. The College
The American College of Radiology, with more than 30,000 members, is the principal organization of radiologists, radiation oncologists, and clinical medical physicists in the United States. The College
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
General Nuclear Medicine
 Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
2015 Reimbursement Guide
 Reimbursement Guide - Cardiology 2015 Reimbursement Guide for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging including radiopharmaceuticals and related product information 2015 Reimbursement Guide for Myocardial Perfusion
Reimbursement Guide - Cardiology 2015 Reimbursement Guide for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging including radiopharmaceuticals and related product information 2015 Reimbursement Guide for Myocardial Perfusion
The IAC Standards and Guidelines for Nuclear/PET Accreditation
 The IAC Standards and Guidelines for Nuclear/PET Accreditation Table of Contents All entries in Table of Contents are linked to the corresponding sections. Introduction...4 Part A: Organization...5 Section
The IAC Standards and Guidelines for Nuclear/PET Accreditation Table of Contents All entries in Table of Contents are linked to the corresponding sections. Introduction...4 Part A: Organization...5 Section
What Is A Nuclear Medicine And Medical Setting?
 With nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, physicians can obtain unique insights into a patient s body that allow for a more personalized approach to the evaluation and management of heart disease, cancer
With nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, physicians can obtain unique insights into a patient s body that allow for a more personalized approach to the evaluation and management of heart disease, cancer
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease.
 Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
We Need to Expand Medical Isotope Production!
 INTERVIEW: DR. GUY TURQUET DE BEAUREGARD We Need to Expand Medical Isotope Production! Dr. Turquet de Beauregard, a nuclear physicist with 15 years experience in nuclear medicine, is the vice president
INTERVIEW: DR. GUY TURQUET DE BEAUREGARD We Need to Expand Medical Isotope Production! Dr. Turquet de Beauregard, a nuclear physicist with 15 years experience in nuclear medicine, is the vice president
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Industrial tracers - Finding leaks and blockages
 Cancer Treatment Alpha radiation is used to treat various forms of cancer. This process, called unsealed source radiotherapy, involves inserting tiny amounts of radium-226 into cancerous organs. The alpha
Cancer Treatment Alpha radiation is used to treat various forms of cancer. This process, called unsealed source radiotherapy, involves inserting tiny amounts of radium-226 into cancerous organs. The alpha
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev (nintedanib)
 EMA/738120/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev (nintedanib) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure that
EMA/738120/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev (nintedanib) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure that
European Academy of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology
 European Academy of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology Framework for Specialist Training in Dental and Maxillofacial Radiology Background The scope of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology DMFR (Dental and Maxillofacial
European Academy of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology Framework for Specialist Training in Dental and Maxillofacial Radiology Background The scope of DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology DMFR (Dental and Maxillofacial
Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine
 Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine Douglas Van Nostrand, MD, FACP, FACNM Director, Nuclear Medicine
Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine Douglas Van Nostrand, MD, FACP, FACNM Director, Nuclear Medicine
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
Your Career Direction
 Radiologic Sciences Program at UNM/HSC School of Medicine Your Career Direction BSRS Degree Completion Medical Imaging (Management) Nuclear Medicine Computed Tomography (Certificate option) Magnetic Resonance
Radiologic Sciences Program at UNM/HSC School of Medicine Your Career Direction BSRS Degree Completion Medical Imaging (Management) Nuclear Medicine Computed Tomography (Certificate option) Magnetic Resonance
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Procedure Guidelines for Radionuclide Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
 Procedure Guidelines for Radionuclide Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Adopted by the British Cardiac Society, the British Nuclear Cardiology Society, and the British Nuclear Medicine Society Writing Group:
Procedure Guidelines for Radionuclide Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Adopted by the British Cardiac Society, the British Nuclear Cardiology Society, and the British Nuclear Medicine Society Writing Group:
Vascular Effects of Caffeine
 Vascular Effects of Caffeine John P. Higgins MD, MBA, MPHIL, FACC, FACP, FAHA, FACSM, FASNC, FSGC Director of Exercise Physiology Memorial Hermann Sports Medicine Institute Chief of Cardiology, Lyndon
Vascular Effects of Caffeine John P. Higgins MD, MBA, MPHIL, FACC, FACP, FAHA, FACSM, FASNC, FSGC Director of Exercise Physiology Memorial Hermann Sports Medicine Institute Chief of Cardiology, Lyndon
patient safety A commitment to GE Healthcare
 GE Healthcare A commitment to patient safety GE Healthcare is committed to providing radiopharmaceuticals that are compounded and dispensed accurately. Quality assurance and patient safety are the cornerstones
GE Healthcare A commitment to patient safety GE Healthcare is committed to providing radiopharmaceuticals that are compounded and dispensed accurately. Quality assurance and patient safety are the cornerstones
1. In the general symbol cleus, which of the three letters. 2. What is the mass number of an alpha particle?
 1. In the general symbol cleus, which of the three letters Z A X for a nu represents the atomic number? 2. What is the mass number of an alpha particle? 3. What is the mass number of a beta particle? 4.
1. In the general symbol cleus, which of the three letters Z A X for a nu represents the atomic number? 2. What is the mass number of an alpha particle? 3. What is the mass number of a beta particle? 4.
Bon Secours St. Mary s School of Medical Imaging Course Descriptions by Semester Class of 2009. CRS 101 Clinical Radiation Science 3
 Bon Secours St. Mary s School of Medical Imaging Course Descriptions by Semester Class of 2009 First Year Fall REV.5/07 Credits CRS 101 Clinical Radiation Science 3 A clinical education course designed
Bon Secours St. Mary s School of Medical Imaging Course Descriptions by Semester Class of 2009 First Year Fall REV.5/07 Credits CRS 101 Clinical Radiation Science 3 A clinical education course designed
There are 2 types of clinical trials that are of interest to the. The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine
 The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine Michael M. Graham, PhD, MD The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine was formed to provide quality assurance of both
The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine Michael M. Graham, PhD, MD The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine was formed to provide quality assurance of both
CHEST PAIN EVALUATION TOOL
 CHEST PAIN EVALUATION TOOL Chest pain or discomfort is one of the commonest causes for presentation to the Emergency Room (ER) or physicians office. There are many causes for chest discomfort. The serious
CHEST PAIN EVALUATION TOOL Chest pain or discomfort is one of the commonest causes for presentation to the Emergency Room (ER) or physicians office. There are many causes for chest discomfort. The serious
Quality Assurance Testing of AtomLab Dose Calibrators
 (Manufacturer s* Instructions) Introduction The following procedures are the manufacturer s instructions for qualifying AtomLab 100, 100+, 200, 300, 400, and 500 dose calibrators in accordance with NRC
(Manufacturer s* Instructions) Introduction The following procedures are the manufacturer s instructions for qualifying AtomLab 100, 100+, 200, 300, 400, and 500 dose calibrators in accordance with NRC
Imaging Technology. Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist
 Imaging Technology Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist Diagnostic Medical
Imaging Technology Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist, Nuclear Medicine Technologist, Radiation Therapist, Radiologic Technologist Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, Dosimetrist Diagnostic Medical
Ischemia and Infarction
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Ischemia and Infarction HST.035 Spring 2003 In the US: ~50% of deaths are due to
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Ischemia and Infarction HST.035 Spring 2003 In the US: ~50% of deaths are due to
Medical Radioisotopes Production Without A Nuclear Reactor
 Medical Radioisotopes Production Without A Nuclear Reactor Henk van der Keur Laka Foundation, 22 May 2010 www.laka.org Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 The Emergence and Development of Nuclear Medicine 4 2.1
Medical Radioisotopes Production Without A Nuclear Reactor Henk van der Keur Laka Foundation, 22 May 2010 www.laka.org Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 The Emergence and Development of Nuclear Medicine 4 2.1
REVIEW ARTICLE CME ARTICLE. Clinical decision support systems in myocardial perfusion imaging
 REVIEW ARTICLE CME ARTICLE Clinical decision support systems in myocardial perfusion imaging Ernest V. Garcia, PhD, a J. Larry Klein, MD, b and Andrew T. Taylor, MD a a Department of Radiology and Imaging
REVIEW ARTICLE CME ARTICLE Clinical decision support systems in myocardial perfusion imaging Ernest V. Garcia, PhD, a J. Larry Klein, MD, b and Andrew T. Taylor, MD a a Department of Radiology and Imaging
