Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform
|
|
|
- Delilah Flowers
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 9 *Flavio Celestino Ferrante **Gabriele Garnero Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform Keywords: Cadastral Reform, Cadastral Cartography, Real Estate Values. Abstract This article outlines the methods and activities, in the field of mapping, in support of the important process of renewal of the entire cadastral system. It describes the technology and spatial data currently available that can assist in setting up complex issues of reforming appraisal system and, more generally, in the processes against tax evasion in real estate. INTRODUCTION The recent introduction of the IMU (Municipal Property Tax) has again highlighted the vexed question of inequality existing in cadastral appraisal systems, recently pointed out by the Director of Agenzia del Territorio (hereinafter AdT) in hearing at the Chamber of Deputies, VI Finance Committee of 13 September 2012; the hypothesis of a radical reform of cadastral appraisal systems is becoming increasingly significant. In the context of the current debate, below are the principles and criteria on which it is assumed to base the revision of the cadastral appraisal system laying out: use of statistical functions expressing the relationship between the market value, location and positional and building features for each cadastral destination and for each geographical area; use of per square meter as a measurement of urban real estate. As can be seen from the principles and the above operational criteria, the data concerning the geolocalization of properties in relation to the urban context and to the characteristics of manufactured building play a fundamental role in the revision process, for the correct determination of cadastral appraisal systems and for the time and resources needed for their acquisition. To effectively address these challenges, we need a precise, complete and qualified knowledge of Italian real estate. It seems appropriate to point out, already in the introduction, that, regardless of the technology platform which will be illustrated below, the effectiveness of the results depend strongly on the data quality (completeness, consistency, accuracy, updating, positional accuracy, etc..) and especially by their degree of correlation in various archives. This paper aims to offer a contribution to the documentation and comprehension of geo-referenced data of the real estate in Italy and processing and analysis tools, both concerning the hypothesis of a reform of the cadastral appraisal system and more generally the fight against tax evasion in real *Revenue Agency - Central Directorate for Cadastre and Cartography Area Manager for Cartographic Services Section (flavio.ferrante@agenziaentrate.it) **University and Polytechnic of Turin - DIST Interuniversity Department of Regional and Urban Studies and Planning (gabriele.garnero@unito.it)
2 10 Flavio Celestino Ferrante and Gabriele Garnero estate, both in relation to the regular institutional Agency s activities recently incorporated in the Agenzia delle Entrate. In the first part of the article we will discuss AdT data and the technologies of the Agency and then the data and technologies outside the domain of the Agency, but closely related to and interoperable with the first one. DATA AND TECHNOLOGIES OF AGENZIA DEL TERRITORIO The Agenzia del Territorio is today a complex and dynamic body, characterized by the massive use of advanced technologies that allow communication with remote users through web platforms. The level of computerization achieved in data updating is high, especially in the selection and development of innovative technological solutions allowing real-time updating of the cartographical, cadastral and Real Estate Advertising archives in respect of the total transparency of administrative procedures. The AdT, strong in its roots and conscious of the need of constant updating, now puts at the service of the Country its information, skills, knowledge and know-how for the implementation of a modern land governance. In order to develop important and essential synergies with other public bodies and agencies, the Agency believes in its mission of assuming the role of inter-institutional mediator in order to facilitate the information flow, its sharing and the development of innovative technological solutions (Garnero, Cogoni, 2012; Ferrante, 2009). The real strength of the organization is the asset of knowledge and data concerning the Italian real estate, inherited from the previous government departments: Catasto, Servizi Tecnici Erariali e Conservatorie dei Registri Immobiliari, together with an extraordinary asset of expertise of its employees. The information asset managed by the Agency is divided into three systems: the cadastral information system, with more than 82 million parcels of the land cadastre and 63 million of real estate units, described in their technical and census characteristics and enriched by the plans of each unit, a prerogative unique in Europe; Sistema informativo della Pubblicità Immobiliare, with over 45 million mechanized notes and 40 million notes in digital format, for the owners identification of the actual property rights; Sistema Informativo dell Osservatorio del Mercato Immobiliare, with over 340,000 sheets of the characteristics of the buildings of 1,280 municipalities and more than 180,000 real estate values concerning 31,000 census areas for 17 building types, in almost all Italian municipalities. Thanks to the investment of significant resources, the Agency is currently engaged in the creation of advanced and innovative methods of consultation and use of their knowledge through an infrastructure called Anagrafe Immobiliare Integrata, addressed to all the administrations, institutions, professionals and citizens dealing with the government of the territory; according to Article 19 of Legislative Decree 31 May 2010, n. 78, it is the result of the integration of the three systems described above. The Anagrafe Immobiliare Integrata is a technological and organizational infrastructure, on a geographical basis, made by Web-GIS technology and able to correlate the cadastral mapping, the Cadastre (census archives of land, buildings and floor plans) and the archives of the Conservatoria dei Registri Immobiliari e dell Osservatorio del Mercato Immobiliare. Through an advanced and easy-to-use geographic interface, achieved by the integration of cadastral maps with high definition orthophotos and road graphs, will allow citizens, professionals, public administrations and institutions to navigate, via the internet, throughout the nation and perform with extreme simplicity, the visura ipo-catastale, integrating the map data, the Land and Building Cadaster (objects) with those of the Conservatoria dei registri immobiliari (subjects).
3 Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform 11 The cartographic heritage of the Cadaster After this general overview, now we focus the attention on the mapping system of the Cadaster which forms the basis of the real estate geo-localizing in Italy. The term geo-localizing means the capability of the cadastral information system to identify a property, throughout the country, in a simple and unambiguous way. The Agency manages, on behalf of the State, the real estate information system in Italy, in terms of identification, description of the technical characteristics and economic evaluation and registration of rights. The geo-localizing of real estates is based on the cadastral mapping system. Since 1960, the cadaster, as an official cartographic body of the State, is responsible for the management of cadastral maps and especially its continuous updating. The mapping system of the Cadaster is now completed, and relatively uniform, throughout the country; it is based on large-scale mapping and entirely managed in vector format, it is connected to the administrative and census archives through a unique identifier for the entire national territory, consisting of the number of parcel. The system is now integrated with high-resolution digital ortho imagery and road graphs, but the real strength is its updating system. The maps and census updating system The inextricable link between the technical component of the map and the legal and administrativecensus component, represented by the register identifier (parcel number), must be constantly updated and aligned in both archives throughout all stages of preservation, in order to make effective land registry information in all tax, civil and land governance proceedings. Data updating in separate files and the maintenance of their congruence over time, even in relation to the large amount of documents presented every year at the offices, has always represented to the Cadaster a challenge and a goal to be pursued at all costs. In the more general framework, for the exchange of information with other local authorities where the Cadastral database is characterized by a great potential, in order to meet the needs of territorial knowledge, punctual and prompt updating of archives by automated and standardized procedures is essential to ensure the constant updating and synchronization of information provided by the various cadastral archives. To cope with the amount of more than 600,000 updating acts presented every year at the provincial offices of the Cadaster handling an average of 1,500,000 parcels, in order to eliminate any possible subjectivity in technical examination of documents, the updating system of maps and census data of Catasto dei Terreni has been fully automated by a new computer procedure called Pregeo10: in the new system, the updating of land archives begins with the request, via the internet, of the map (estratto della mappa) and the corresponding census data by the professional; the provincial Office, after the appropriate checks in the database, transmits to the professional, usually within a day and no more than two, the requested map including all the necessary information for the preparation of the updating act; on the basis of the documentation received and the land survey carried out, the professional prepares the updating act, in Pregeo10 environment; after all the formal and substantial check, the procedure, determines directly at the professional if the updating acts will be automatically registered in the archives or not; the documentation prepared by a professional, is sent, via the internet, to the provincial Office in charge; a fully automatic management and control system, based on the Pregeo10 procedure, checks the correctness of the act and the congruence of the data with those previously found in the archives
4 12 Flavio Celestino Ferrante and Gabriele Garnero and, in case of positive exit, provides for the automatic cartographic and census updating, otherwise returns the act to the professional indicating the reasons that have prevented the registration of documents and corrective actions; the process ends with the automatic transmission to the professional of the updated map and census data. Figure 1 Diagram of the automatic update process with the Pregeo10 procedure The new updating system, developed by the Agency with the active participation of concerned National Boards of Professional Associations, is entered into force throughout the country on October 15, By achieving this important goal, the Cadaster has marked another important milestone of efficiency and administrative culture. The new updating system, based on the sharing of rules and data on the web, qualifies the Cadaster as Public Administration type 2.0. The coordinate system of cadastral maps and its interoperability with other data of land knowledge During the 70 years of its formation, from 1886 to 1956 (Kraus, 1994), the Italian Cadaster for the classification of its cartography had the need to create more than 800 different coordinate systems which have been, until recently, a major obstacle to real estate geo-referencing and interoperability and the automatic integration of cadastral system with other data bases of land knowledge such as ortho-images, technical maps, Territorial Data Bases, planning instruments, road graphs, etc..
5 Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform 13 Figure 2 Cadastral coordinate systems in Italy In order to unify the coordinate systems and to transform cadastral maps in the national Roma1940 system, a scientific, organizational and technological effort has been required, which involved the Cadaster in the last 10 years, and today we can say that it is in a conclusive phase (Godone, Garnero, 2013; Ferrante, 2009; Chiabrando, Garnero, Godone, 2008). The transformation of the cartography in the national system has already been implemented on more than 80% of the national territory, with rigorous methodology, ensuring a decimeter accuracy in the coordinates conversion. At the time of the publication of this paper, the activities are still ongoing, carried out in cooperation with the University of Rome La Sapienza, Department of Hydraulics, Transport and Roads, in order to validate solutions made by the Cadaster and to guarantee the correct transition from cadastral coordinates systems to Roma1940 system.
6 14 Flavio Celestino Ferrante and Gabriele Garnero The transformation of the remaining 20% of the territory has been achieved only with analog methods, however ensuring a metric accuracy; the activities are currently on progress for the transformation of this part of the residual maps, with rigorous methods, and are scheduled for completion by the end of Figure 3 Coverage of the areas where parameters are available for the rigorous transition from cadastral system to the national system As required by the INSPIRE Directive, all European countries should share their geographical data in a unified reference system; with the DPCM of November 10, 2011 the new National Geodetic System was officially adopted in Italy, carried out by the ETRF2000 (at the epoch ) of the European Reference System ETRS89. In order to achieve this extra step from the national to the European geodetic system, the Cadaster has partnered with the Istituto Geografico Militare, which has developed the transformation grids allowing the direct transformation from the national to the ETRF2000 system. By the end of this year (2012), the cadastral mapping system can be re-projected by the user into
7 Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform 15 the WGS84 system, within the ETRF2000 reference frame. It is hardly necessary to point out that the availability of cadastral maps in the new unified reference system represents an added value for the whole cadastral information system, as it ensures full interoperability and automatic integration with other data of land knowledge, also with those outside the domain of the Cadaster. The recovery of the accuracy of the maps and the creation of topological congruence through the enhancement of original maps The original map is an invaluable asset of technical, legal and historical information; this original and unique map is still used as supporting evidence in the regulation of boundaries and, if only for this reason, it should be preserved from the injuries of time. The plan already started in 2008, provides the acquisition and geo-referencing of the cartaforte where the original map is represented. In view of its high tech features, the integration of the original maps, in digital format, into the information system of the Cadaster will improve the quality of the vector maps acquired by the most updated media, but of lower quality, and retrieve the systematic errors inevitably introduced by the process of computerization and updating; the partly automatic and interactive process initially provides for the calibration of the vector map on the original one. As described in a previous study by the same authors, the automatic creation of topological congruence is automatically recreated first within each sheet of the map and then between adjacent maps, and finally, through an interactive intervention, all the problems the automatic procedure could not define are solved. It is hardly necessary to point out how this condition is essential for achieving the mosaic (territorial continuum) and then making applicable all the potentials based on the topology which GIS technology makes available today. Recovery of the coherence of the data in maps with the Catasto dei Terreni census data The maps and the corresponding census archives are, as already mentioned, closely related and must be constantly updated and congruent, in order to fulfill all the fiscal and civil functions of a modern cadaster, especially if some complex and difficult projects, such as the reform of the cadastral appraisal system, should be carried out. Throughout the first period of preservation of the Cadaster and until the end of the 80s of the last century, the map updating was obtained separately from the corresponding census records: it was performed by cadastral technicians, on paper supports, manually registering the changes in the technical documents. This method of updating has led, over time, to a gradual but inevitable misalignment between the two archives. Currently, since the late 80s, cartographic and census archives are updated simultaneously by the Pregeo procedure previously mentioned: it thus guarantees the complete congruence of archives in the data flows which have to be updated. Therefore it is necessary to provide for the recovery of past misalignments, before starting the automatic procedures. Many changes were made in this direction, both targeted (projects for internal use, collaborations with external institutions) and put into practice in case of use (resolution of any misalignment before releasing the extracts of the map), aimed to resolving mismatches between the map and census archives of the Catasto dei Terreni and the census data of the building cadaster. As shown in the following two images, the misalignments still found are focused only on a dozen of cadastral offices. Testing activities are currently underway for the adoption of a new organizational model that will allow their resolution, without any impact on the ordinary activities of the offices.
8 16 Flavio Celestino Ferrante and Gabriele Garnero Figure 4 Misalignment between cartographic and census archives: parcels present in maps and not registered in the census archives of the Land Cadaster (left) and parcels present in the census archives of the Land Cadaster and not represented in the map (right) Recovery of the coherence between the data in the maps and the census data of the Catasto dei Fabbricati The Catasto dei Fabbricati (building cadaster), as known, was established in the late 30s of the last century, and has been, for some regions, based on urban maps completely detached from the map of the Catasto dei Terreni (land cadaster): this condition has generated over time a number of mismatches between the map and census data of the Catasto dei Terreni and the census data of the building cadaster. Aware of the need of aligning the two registers, from more than a decade, the AdT is engaged, with extensive qualified internal resources, in achieving the correlation between the cartographic and census maps of the Catasto dei Terreni with those of the Catasto dei Fabbricati; currently the activities are still in progress. The consistency of the data in the archives, introduces the map geo-referencing of the housing units in the archive of Catasto dei Fabbricati. This creates the conditions that enable the full exploitation of the potentials of modern GIS systems. It is hardly necessary to point out how the effectiveness of the analysis and, consequently, of the solutions, depend strongly on the degree of correlation between the archives.
9 Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform 17 TECHNOLOGIES AND DATA OUTSIDE THE DOMAIN OF THE AGENZIA DEL TERRITORIO The ortho imagery produced by Agea and identification of unknown buildings in the Cadaster In the context of spatial information available throughout the Country, the ortho images produced by Agea (Agenzia per le Erogazioni in Agricoltura) certainly occupy an important position in the context of the checks provided by the Community regulations for the management of the contributions granted under the CAP (Common Agricultural Policy). Agea is responsible, according to Decree 99/2004, of the coordination and management of the SIAN - National Agricultural Information System where a full aero-photogrammetric coverage is provided every three years throughout the entire national territory and the production of the cultivation themes based on cadastral maps, in regard of agricultural land. The Decree 82/2005 (Digital Administration Code) establishes the principle of the reuse of the data generated by each Public Administration and their accessibility, through appropriate agreements, by other administrations concerned. From 2010, in order to optimize its aspects related to the reuse of ortho images, the planning of survey programs has changed, which now become on a regional basis rather than provincial, and opens the possibility for the concerned administrations, to acquire jointly to Agea ortho imagery with the ground pixel resolution 20 cm instead of 50 cm institutionally provided: this increase in resolution, in case it would be implemented, will start from the next three years and will lead to a real improvement in the possibilities of using the ortho maps produced within the SIAN for real estate updating. The ortho images with ground pixel resolution of 20 cm would allow to determine with greater accuracy the positional and close range parameters properties and, consequently, to refine the appraisal of urban housing units, considerably limiting the direct intervention on the ground. In the broader context of the fight against tax evasion, the AdT has undertaken a long series of actions aimed to identify potential evasion in real estate projects with high technological contents. In the recent past, according to the provisions of the Finance Act of 2007, as it is known, the AdT has undertaken a significant project to identify the buildings unknown by the Cadaster. The project, characterized by an advanced technology, was prepared in collaboration with AdT, Agea and Sogei (Società Generale di Informatica) and is one of the most significant examples of cooperation and integration between information systems of Public Administrations. Thanks to a special agreement signed in May 2007, the agencies have identified the common ground where their skills might find useful synergies for the government and citizens, in the general interest of the State. In order to achieve this goal, a general survey of the whole country has been carried out, with the exception of the Autonomous Provinces of Trento and Bolzano. The local survey was carried out through the integration of cadastral maps in vector format with digital high-definition color ortho images, the Digital Terrain Model (DTM), the Digital Surface Model (DSM) and near-infrared images. The first step, carried out on the basis of the DTM and DSM, has involved the automatic identification of existing land features; these were then classified, first in relation to the height and then with the aid of near infrared images: it was possible to discriminate the vegetation from other artifacts, thus identifying buildings in automatic mode. The spatial intersection between polygons related to objects on the ground identified and the polygons of the buildings present in the cadastral maps allowed to highlight the parcels on which buildings were found which are not present in the cadastral maps. The results obtained were then subjected to systematic quality control, performed through the conventional photo-interpretation on the same digital high resolution ortho photos (pixels 50 cm), in order to eliminate errors that an automated process at industrial level inevitably entails, especially in relation of the quality of the used data.
10 18 Flavio Celestino Ferrante and Gabriele Garnero The final product of the activity, carried out in synergy with Agea, consists of a list of the parcels on which buildings were found which are not present in the maps of the Cadaster; the list of the parcels was then intersected with the data of the various cadastral archives. This operation has eliminated, from the initial parcels, the ones known in the Catasto dei Terreni, as in other internal records. The project, which began in mid-2007, was concluded in the early 2010 and has identified over 2,000,000 parcels on which there are unknown buildings. Among the positive effects of this project, the full availability for the Cadaster, of the high-definition ortho images immediately integrated with the cadastral maps in their systems must be highlighted, for the development of important projects, not least for the reform of the Cadaster. According to the current provisions of law (Decree Law 78/2010, Art. 19, Paragraph 12), from 1th January 2011, the AdT, on the basis of new information related to technical and administrative checks, remote sensing and ground surveys must provide to start the constant monitoring of the territory by identifying, in collaboration with municipalities, other buildings not declared in the Catasto dei Terreni. In order to achieve these statutory provisions and to make a more effective investigation, the AdT is considering the possibility of making use of advanced technological solutions such as aerial images acquired by oblique sensors, as explained in the following paragraphs. Figure 5 Oblique sensors integrated into the process of photogrammetric surveys
11 Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform 19 Applications relating to the use of Google Earth and Microsoft Virtual Earth The diffusion of shared web tools providing completely free of charge repertoires of dynamic aerial and satellite imagery on a global scale is now well established: the basics of Google Earth and Microsoft Virtual Earth we all quickly learned to know and use for no professional applications are becoming real integrated tools proposed as a repository of spatial information not limited to data entered in network by the managers of the system, but as instruments in which it is possible to integrate and share information in different ways (Ferrante, 2010; Garnero, Ferrante, 2009). Recently, this potential has been extended to the world of geographic information systems, with the opportunity to integrate local databases with remote databases of images: the instrument is of great interest for the study of territorial and landscape issues, given the integration of GIS tools already widely used in the field, and good image quality and potentially continuously updated, allowing a careful reading of the territory and its modifications. Its implementation in the GIS also allows an active participation in the process of spatial analysis, with the option to extract data interpreted from the images in vector and/or alphanumeric geographic database. There have already been numerous studies on the possibilities of use of these innovative supports in the processes of territorial and landscape analysis, in order to identify the scale threshold beyond which the basics in subject no longer constitute a support geometrically reliable. Virtual Earth and Google Earth using a reference system that, at least in Italy, is not employed in other applications: the system Web Mercator WGS84, as codified in EPSG Geodetic Parameter Dataset. L EPSG ( European Petroleum Survey Group ), an agency currently included in OGP Surveying and Positioning Committee, body of the International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (OGP) which provides to maintain and to issue a worldwide database of cartographic and geodetic reference systems and their transformation parameters. For the purpose of this paper, the geo-referenced images of Google Street View implemented within Google Maps and Google Earth are particularly useful providing panoramic views of 360 horizontally and 290 vertically along the streets (at a minimum distance of meters apart) and allows users to view portions of cities around the world at ground level. Figure 6 Google Street View Car in acquisition (Source Wikipedia)
12 20 Flavio Celestino Ferrante and Gabriele Garnero Introduced in May 2007, the service Street View is active in Italy from October 2008; especially in 2009, there has been a rapid increase of the streets served: the cover is shown dragging an orange man (Pegman, present in task bar) and placing him in a point on the road, in order to activate the corresponding panoramic photography. To carry out the photos, Google Street View uses special cameras (the Dodeca 2360, equipped with 11 objectives and produced by the Canadian company Immersive Media ) located on the roof of cars. Pedestrian areas, parks and roads, bicycles are used instead of the specially equipped vehicle: the service is now extended to most of the main roads and urban streets of many large and small urban centers, with a coverage extended to all Italian regions, the coverage of the updated service is available online at It is clear that the ability to view, if nothing else, the street fronts of the areas already served by the service, can be of immediate and quick use in order to allow users a first visual access to the extrinsic characteristics of the buildings and surrounding areas. Oblique photogrammetry On the national market several companies are operating, able to realize, in addition to traditional nadir ones, photogrammetric surveys performed with sets of cameras arranged so as to capture the territory features with oblique angles, so as to give priority to the acquisition of the facades of buildings. The industrial solutions going under the name of Pictometry, Midas of Track air, ione of Visual lntelligence,...,involve the use of survey systems consisting of several cameras rigidly connected to each other, mounted on a single support on which the inertial sensor is applied (IMU) for the acquisition of the angular components of the image. In Pictometry and Midas systems there are 5 cameras, 4 of them are installed with an inclination of from the vertical, according to the four directions of view and perpendicular to each other (forward, backward, left and right); the fifth camera is installed as the traditional photogrammetric cameras in order to capture the territory flown over from the zenith. Frames are triggered simultaneously and are therefore five images that share the same instant. The tools available allow, as well as to manage the large mass of data in navigation environments from the base ortho image, to make queries and quantitative measurements on the plano-altimetric size of buildings, thus providing the operators with performing tools for the analysis and check of buildings. As known to the authors, aerial oblique images are currently available, throughout the national territory, of all the provincial capitals and major towns with a population of over 50,000 inhabitants, with photos from Furthermore, during 2010 and 2011, the Autonomous Region of Sardinia has arranged for services relating to the contract for the Attività di riprese fotografiche a bassa quota negli agglomerati urbani della Sardegna e relativi contesti architettonici, referred to centri di antica e prima formazione o centri matrice, as defined in the art. 51 of Norme di Attuazione del Piano Paesaggistico Regionale. All urban centers have been acquired, with technology Pictometry and with ground pixel resolution of the order of magnitude of 5 cm, so as to document the landscape context in which centri matrice are located and to highlight morphological and settlement differences between centers, with particular reference to the morphology of the plains, hills, mountains, coasts, slopes, etc... The set of nadir and oblique photos allow to better understand the way in which these centers have developed, and to pick up the different building types through the analysis of the fronts of buildings and the internal parts, as well as to highlight the issues concerning the restoration and renovation of fine buildings, with a purpose of monitoring the territory, from the urban point of view in relation to
13 Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform 21 the city center and the surrounding buildings. The high definition allows to document the current state of the buildings and road plots, so as to permit the establishment of a photographic support to institutional planning and regulation of the land (Cina, Ferrante, Piras, Porporato, 2012). Figure 7 Consultation of oblique images of a center of the Sardinia Region From the above, it therefore appears that the availability of already realized oblique images, relatively recent and, as previously described, directly relatable with cadastral maps with the technology to be described later, is not negligible, as it is likely to cover not less than 70% of built areas, so it is reasonable to hypothesize the development of this asset of information for the previously explained purposes, reasonably quickly, so as to avoid the natural obsolescence of the same. Among the technologies readily available, the system BLOM-urbex allows you to integrate the cadastral maps with orthophotos, displayed in the center of the screen, while the side shows the oblique images related to the same area. But it is still difficult, especially in city centers and in particular in those with complex morphology, to univocally identify the selected perspective views of the building on the cadastral map of which we want to know the characteristics. This ambiguity is resolved with the technology that will be discussed later, on the occasion of the description of 3D models of buildings. Many have also considered the possibility of integrating photogrammetric surveys performed by Agea, already mentioned above, with at least 2 oblique cameras, in order to obtain, at the same time the acquisition of frames for ortho images and oblique images to be used for applications in the built environment. Such surveys, if systematically realized, cannot of course be compared to the ones especially produced as oblique, because of the obvious shortcomings relative to the scale and therefore the size of the pixels, of insufficient capture directions and consequent deficiencies of information, with directions of building profiles completely excluded from the acquisition. Anyway it is correct to consider that such possibilities, which should be produced with very low costs because of the simultaneity with the primary observations, could be profitably used in contexts outside the city, where there are less issues of mutual coverage between buildings and where it is
14 22 Flavio Celestino Ferrante and Gabriele Garnero not and, it cannot be economically feasible an oblique survey in canonical way. In the economic context characterizing the present time, however is natural to consider the exploitation of what is available and usable with what can be achieved with sustainable costs, so as to ensure the economic feasibility to what is necessary to achieve the objectives. Surveys with UAV The only identification and documentation of the extrinsic characteristics of buildings could be obtained also with instruments of decidedly lower performance and less expensive than those described above as, for the applications in question, a metric quality is not required in order to perform measurements and quantitative estimates, but rather a good photographic quality that allows the operator to identify photographically all or most of the features to be detected in an inspection in the countryside, or at least to limit the visits to the controversial cases. There is thus an increasing interest in the possibility of using pseudo-amateur photographic equipment on board of unmanned aircraft, technically defined drones or UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle), this means aircraft with varying size from ones for military applications to small toy model aircraft. The availability of GNSS positioning systems sufficiently precise can be obtained with very small size and weight (generally U-Blox), together with the existence of microscopic accelerometers and gyro sensors with MEMS technology, with software controlled now generally available in open source, opens new possibility of realization of systems for the acquisition of digital images on board of aircraft of various sizes. The recent regulations issued by ENAC ( National Agency for Civil Aviation ) NI , dated August 2, 2012 on the Rilascio di permesso di volo per Aeromobile a Pilotaggio Remoto per l effettuazione di attività sperimentale defines precisely the activities of so-called mini - and micro-uavs (respectively weighing less than 20 and 5 kg) and at up to a limit of 150 kg in respect of activities which, though still described as experimental, can obviously have interesting professional consequences. In the near future, it will also be possible to perform low altitude surveys, with tools like APR (Aircraft in Remote Steering), to recover photogrammetric information that would not be acquired through inspection, both for lack of access and for economic reasons. Technology for the virtual reconstruction of built areas The availability of information already acquired and also the possibility that other acquisition channels are activated, for large parts of the territory as for decidedly sub-regional context, allows to define a profitable use of these observation methods within the cadastral issues, even in relation to the availability of technologies that can be easily customized for these specific needs. An operator setting himself the aim of verifying the extrinsic characteristics of buildings using aerial oblique images, should be able to operate in a dedicated software, which allows him to see the cadastral map integrated with the ortho image, and should be able to see oblique images with the help of software minimizing the possibility of misidentification of the building while synchronizing the oblique view on the building pointed on the map. To this aim, in addition to the customization of the environments of consultation of the oblique images which we have been previously shown, the implementation is now feasible, albeit in a simplified mode, of a 3D City Model dedicated to cadastral applications. This term is technically defined as a consultation environment in which the buildings are reconstructed geometrically as solid and whose faces are draped from the information available on the radiometric frames: in this way the user forgets the frames and finds a virtual model reconstructed on which he can perform the observations or possibly measurements.
15 Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform 23 The construction of the 3D City Model has long been present within the geomatic products available on the market, but only the recent improvements in the techniques of autocorrelation allow to plan of generation processes achievable in entirely automatic mode, with consequent reduction of costs of production and therefore openings to more generalized use. Figura 8 Prototypal realization of a 3D City Model using an oblique Midas (property Blom CGR) survey with Menci Software, technology on the city of Milan Of course, once available, the performed basic may be exploited and also used for different purposes, for example for the integrated protection and control, in municipal databases. INTEGRATION OF GIS TECHNOLOGY AND DATA INSIDE AND OUTSIDE THE DOMAIN OF ADT As shown in the Introduction, it appears how for the implementation of plans of cadastral surveys reforming, geographic data (cadastral maps, orthoimagery, LiDAR data, oblique images captured by sensors, road graphs, Osservatorio del Mercato Immobiliare zoning,...) and alphanumeric (DB censuario, terreni ed urbano, DB of OMI, of Conservatorie dei Registri Immobiliari, ) knowledge of the real estate Italian are strategic. The effective exploitation of all these information components in a suitable environment that can integrate and correlate data from different sources, is essential for the success of the project of reforming the estimate of the Catasto dei Fabbricati. The environment able to integrate geographical and alphanumeric data along with the technologies, as known, is the GIS (Geographic Information System). For issues related to the reform of the cadaster, GIS platforms allow for example to correlate data of the Urban Building Units (UIU) directly to the cadastral map: the operator can perform precise analyzes or statistics of any attribute of UIU (value/rent, classification, consistency ) and represent reports on cadastral maps which, when suitably integrated with the high resolution orthophotos, allows to correlate the data position and/or overlooking with classification or consistency of the data of UIU.
16 24 Flavio Celestino Ferrante and Gabriele Garnero The figure below shows, for example, on the cadastral map integrated with the orthophotos, reports of a statistical analysis conducted on the data of classification of the Urban Building Units of a central area of Rome, a comparison between the statistical data of classification of building units both those within the same building and those in the same area of study, highlighting some of the inequalities in classification that the cadastral survey review should cancel or at least reduce. Figura 9 Cadastral maps integrated with orthophoto maps and graphs. Results of the analysis on spatial data "classification" of Unità Immobiliari Urbane (pie charts and their legend) It is thus possible to integrate and analyze, on the same GIS platform, data relating to the characteristics of the extrinsic buildings: such information can be effectively drawn from close-up images of the sensors acquired simultaneously with the nadir images and allows, as indicated, to relate the buildings fronts with "buildings polygons" represented on the cadastral map, without any ambiguity. CONCLUSIONS The position/overlooking data and those relating to the extrinsic characteristics of the building thus allow to effectively implement the estimation algorithm for the value of the building and severely limiting the direct intervention on the ground, with an obvious containment of time and costs. The assumed GIS platform is crucial in analysis and management of data, in preparation for the estimation of property values, but it becomes particularly strategic in the final phase of the process,
17 Technologies and spatial data for modern land governance. Tools to support the cadastral reform 25 that is, when it comes to review and harmonize values and UIU rents of neighboring buildings belonging to different areas characterized by different values of the real estate market or to different municipalities or even to different provinces or regions. References Chiabrando, R., Garnero, G., Godone, D. (2008), Basi dati condivise per l analisi e la progettazione territoriale: Google Earth e Virtual Earth cambiano le prospettive sulla gestione dei dati territoriali, Congresso AIIA 2008: Segni dell uomo e trasformazioni del paesaggio: analisi storica e prospettive di valorizzazione, Marina di Pisticci (MT), settembre Cina, A., Ferrante, F., Piras, M., Porporato., C. (2012), La trasformazione dal Datum Catastale al Datum Roma 1940 e ETRF2000, Territorio Italia, n. 1/2012. Di Filippo, S., Ferrante, F., Garnero, G., Gnesivo, P. R., Rao, S. (2005), Unificazione dei sistemi d asse catastali di piccola estensione, Atti del Convegno Nazionale SIFET 2005, Palermo-Mondello, giugno-luglio Ferrante, F. (2010), Il sistema di aggiornamento della cartografia catastale, Un tesoro Ritrovato, Cangemi Editore Ferrante, F. (2009), Il nuovo sistema di aggiornamento del Catasto dei Terreni, Rivista dell Agenzia del Territorio, n. 2/2009. Ferrante, F. (2009), L integrazione del catasto con Google Earth, Google Maps e Street-View, Territorio Informa, gennaio/marzo Garnero, G., Cogoni, A. (2012), Activity at low altitude photography in urban agglomerations of Sardinia and its architectural context, in Planning Support Tools: Policy Analysis, Implementation and Evaluation. Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Informatics and Urban and Regional Planning INPUT 2012, E-book ISBN code: , Franco Angeli, Milano, Garnero, G., Ferrante, F. (2009), La valorizzazione delle mappe originali di impianto del catasto per la ricostruzione delle congruenze topologiche tra fogli adiacenti, Atti della XIII Conferenza Nazionale ASITA, Bari, dicembre Godone, D., Garnero G. (2013), The role of morphom etric parameters in Digital Terrain Models interpolation accuracy: a case study, European Journal of Remote Sensing, n. 46/2013 (doi: /EuJRS ). Kraus, K. (1994), Fotogrammetria (trad. italiana di S. Dequal), Ed. Levrotto e Bella, Torino, Paroli, A. (1958), Metodi e strumenti di Rilevamento nei 70 anni di formazione del Catasto Terreni, Rivista del Catasto e dei Servizi Tecnici Erariali, Nuova serie anno XIII n. 4/1958
Agenzia del Territorio - Largo Leopardi, 5-00185 Roma - THE ITALIAN CADASTRAL SYSTEM MANAGING BODY AGENZIA DEL TERRITORIO
 PLENARY SESSION 1 Knowledge to manage The Italian Cadastre and the Real Estate Taxation Franco Maggio Central Director for Cadastre and Cartography Agenzia del Territorio - Largo Leopardi, 5-00185 Roma
PLENARY SESSION 1 Knowledge to manage The Italian Cadastre and the Real Estate Taxation Franco Maggio Central Director for Cadastre and Cartography Agenzia del Territorio - Largo Leopardi, 5-00185 Roma
HIDDEN BUILDINGS PROJECT
 UNECE Working Party on Land Administration HIDDEN BUILDINGS PROJECT an Italian best practice for a more effective land administration Eng. Marco SELLERI WPLA SIXTH SESSION Geneva, 19 th of June, 2009 Agenzia
UNECE Working Party on Land Administration HIDDEN BUILDINGS PROJECT an Italian best practice for a more effective land administration Eng. Marco SELLERI WPLA SIXTH SESSION Geneva, 19 th of June, 2009 Agenzia
MULTIPURPOSE USE OF ORTHOPHOTO MAPS FORMING BASIS TO DIGITAL CADASTRE DATA AND THE VISION OF THE GENERAL DIRECTORATE OF LAND REGISTRY AND CADASTRE
 MULTIPURPOSE USE OF ORTHOPHOTO MAPS FORMING BASIS TO DIGITAL CADASTRE DATA AND THE VISION OF THE GENERAL DIRECTORATE OF LAND REGISTRY AND CADASTRE E.ÖZER, H.TUNA, F.Ç.ACAR, B.ERKEK, S.BAKICI General Directorate
MULTIPURPOSE USE OF ORTHOPHOTO MAPS FORMING BASIS TO DIGITAL CADASTRE DATA AND THE VISION OF THE GENERAL DIRECTORATE OF LAND REGISTRY AND CADASTRE E.ÖZER, H.TUNA, F.Ç.ACAR, B.ERKEK, S.BAKICI General Directorate
Tourist mature destinations as complex spaces. Notes about the elaboration process of an atlas of Costa del Sol
 Tourist mature destinations as complex spaces. Notes about the elaboration process of an atlas of Costa del Sol Sergio J. Reyes Corredera Universidad de Málaga, ETS Arquitectura, Málaga, España. e-mail:
Tourist mature destinations as complex spaces. Notes about the elaboration process of an atlas of Costa del Sol Sergio J. Reyes Corredera Universidad de Málaga, ETS Arquitectura, Málaga, España. e-mail:
ITALIAN SPATIAL DATA INFRASTRUCTURE
 Il Sistema Informativo Catastale: una risorsa per le politiche di governo del territorio Roma, 10-11 dicembre 2008 ITALIAN SPATIAL DATA INFRASTRUCTURE Elettra Cappadozzi National Centre for ICT in the
Il Sistema Informativo Catastale: una risorsa per le politiche di governo del territorio Roma, 10-11 dicembre 2008 ITALIAN SPATIAL DATA INFRASTRUCTURE Elettra Cappadozzi National Centre for ICT in the
The Status of Geospatial Information Management in China
 The Status of Geospatial Information Management in China Submitted by the National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation of China 1. Administration System The National Administration
The Status of Geospatial Information Management in China Submitted by the National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation of China 1. Administration System The National Administration
3D GIS: It s a Brave New World
 3D GIS: It s a Brave New World Reida ELWANNAS, United Arab Emirates Key words: 3D Models, CityGML, GIS SUMMARY For the past several decades we have been enjoying the power of GIS. The introduction of 2.5D
3D GIS: It s a Brave New World Reida ELWANNAS, United Arab Emirates Key words: 3D Models, CityGML, GIS SUMMARY For the past several decades we have been enjoying the power of GIS. The introduction of 2.5D
STATE OF NEVADA Department of Administration Division of Human Resource Management CLASS SPECIFICATION
 STATE OF NEVADA Department of Administration Division of Human Resource Management CLASS SPECIFICATION TITLE PHOTOGRAMMETRIST/CARTOGRAPHER V 39 6.102 PHOTOGRAMMETRIST/CARTOGRAPHER II 33 6.110 PHOTOGRAMMETRIST/CARTOGRAPHER
STATE OF NEVADA Department of Administration Division of Human Resource Management CLASS SPECIFICATION TITLE PHOTOGRAMMETRIST/CARTOGRAPHER V 39 6.102 PHOTOGRAMMETRIST/CARTOGRAPHER II 33 6.110 PHOTOGRAMMETRIST/CARTOGRAPHER
Digital Cadastral Maps in Land Information Systems
 LIBER QUARTERLY, ISSN 1435-5205 LIBER 1999. All rights reserved K.G. Saur, Munich. Printed in Germany Digital Cadastral Maps in Land Information Systems by PIOTR CICHOCINSKI ABSTRACT This paper presents
LIBER QUARTERLY, ISSN 1435-5205 LIBER 1999. All rights reserved K.G. Saur, Munich. Printed in Germany Digital Cadastral Maps in Land Information Systems by PIOTR CICHOCINSKI ABSTRACT This paper presents
OBLIQUE AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHY TOOL FOR BUILDING INSPECTION AND DAMAGE ASSESSMENT
 OBLIQUE AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHY TOOL FOR BUILDING INSPECTION AND DAMAGE ASSESSMENT A. Murtiyoso 1, F. Remondino 2, E. Rupnik 2, F. Nex 2, P. Grussenmeyer 1 1 INSA Strasbourg / ICube Laboratory, France Email:
OBLIQUE AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHY TOOL FOR BUILDING INSPECTION AND DAMAGE ASSESSMENT A. Murtiyoso 1, F. Remondino 2, E. Rupnik 2, F. Nex 2, P. Grussenmeyer 1 1 INSA Strasbourg / ICube Laboratory, France Email:
High Resolution Digital Surface Models and Orthoimages for Telecom Network Planning
 Renouard, Lehmann 241 High Resolution Digital Surface Models and Orthoimages for Telecom Network Planning LAURENT RENOUARD, S ophia Antipolis FRANK LEHMANN, Berlin ABSTRACT DLR of Germany and ISTAR of
Renouard, Lehmann 241 High Resolution Digital Surface Models and Orthoimages for Telecom Network Planning LAURENT RENOUARD, S ophia Antipolis FRANK LEHMANN, Berlin ABSTRACT DLR of Germany and ISTAR of
The Chillon Project: Aerial / Terrestrial and Indoor Integration
 The Chillon Project: Aerial / Terrestrial and Indoor Integration How can one map a whole castle efficiently in full 3D? Is it possible to have a 3D model containing both the inside and outside? The Chillon
The Chillon Project: Aerial / Terrestrial and Indoor Integration How can one map a whole castle efficiently in full 3D? Is it possible to have a 3D model containing both the inside and outside? The Chillon
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction
 Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
Innovation, Quality and Improvement of Registry Services
 versione 11 dicembre 2013 Innovation, Quality and Improvement of Registry Services Cristiano Cannarsa Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Sogei S.p.A. Presidenza Italiana del Comitato Permanente del Catasto
versione 11 dicembre 2013 Innovation, Quality and Improvement of Registry Services Cristiano Cannarsa Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Sogei S.p.A. Presidenza Italiana del Comitato Permanente del Catasto
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION GIS Syllabus - Version 1.2 January 2007 Copyright AICA-CEPIS 2009 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION GIS Syllabus - Version 1.2 January 2007 Copyright AICA-CEPIS 2009 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed
High Resolution RF Analysis: The Benefits of Lidar Terrain & Clutter Datasets
 0 High Resolution RF Analysis: The Benefits of Lidar Terrain & Clutter Datasets January 15, 2014 Martin Rais 1 High Resolution Terrain & Clutter Datasets: Why Lidar? There are myriad methods, techniques
0 High Resolution RF Analysis: The Benefits of Lidar Terrain & Clutter Datasets January 15, 2014 Martin Rais 1 High Resolution Terrain & Clutter Datasets: Why Lidar? There are myriad methods, techniques
3-D Object recognition from point clouds
 3-D Object recognition from point clouds Dr. Bingcai Zhang, Engineering Fellow William Smith, Principal Engineer Dr. Stewart Walker, Director BAE Systems Geospatial exploitation Products 10920 Technology
3-D Object recognition from point clouds Dr. Bingcai Zhang, Engineering Fellow William Smith, Principal Engineer Dr. Stewart Walker, Director BAE Systems Geospatial exploitation Products 10920 Technology
Cartographic Projections
 Cartographic Projections Cartographic Projections Paolo Zatelli Alfonso Vitti Dept. Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Trento Paolo Zatelli University of Trento 1 / 18 Cartographic Projections
Cartographic Projections Cartographic Projections Paolo Zatelli Alfonso Vitti Dept. Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Trento Paolo Zatelli University of Trento 1 / 18 Cartographic Projections
Implementation of Recent Metadata Directives and Guidelines in Public Administration: the Experience of Sardinia Region
 Implementation of Recent Metadata Directives and Guidelines in Public Administration: the Experience of Sardinia Region Luisa Manigas, Michele Beneventi, Luca Corvetto, Rita Vinelli and Marco Melis Region
Implementation of Recent Metadata Directives and Guidelines in Public Administration: the Experience of Sardinia Region Luisa Manigas, Michele Beneventi, Luca Corvetto, Rita Vinelli and Marco Melis Region
Andrea Bondì, Irene D Urso, Matteo Ombrelli e Paolo Telaroli (Thetis S.p.A.) Luisa Sterponi e Cesar Urrutia (Spacedat S.r.l.) Water Calesso (Marco
 Generation of a digital elevation model of the Wadi Lebda basin, Leptis Magna - Lybia Andrea Bondì, Irene D Urso, Matteo Ombrelli e Paolo Telaroli (Thetis S.p.A.) Luisa Sterponi e Cesar Urrutia (Spacedat
Generation of a digital elevation model of the Wadi Lebda basin, Leptis Magna - Lybia Andrea Bondì, Irene D Urso, Matteo Ombrelli e Paolo Telaroli (Thetis S.p.A.) Luisa Sterponi e Cesar Urrutia (Spacedat
Assessment Tasks Pass theory exams at > 70%. Meet, or exceed, outcome criteria for projects and assignments.
 CENTRAL OREGON COMMUNITY COLLEGE: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM PROGRAM 1 CENTRAL OREGON COMMUNITY COLLEGE Associate Degree Geographic Information Systems Program Outcome Guide (POG) Program Outcome Guide
CENTRAL OREGON COMMUNITY COLLEGE: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM PROGRAM 1 CENTRAL OREGON COMMUNITY COLLEGE Associate Degree Geographic Information Systems Program Outcome Guide (POG) Program Outcome Guide
How To Make An Orthophoto
 ISSUE 2 SEPTEMBER 2014 TSA Endorsed by: CLIENT GUIDE TO DIGITAL ORTHO- PHOTOGRAPHY The Survey Association s Client Guides are primarily aimed at other professionals such as engineers, architects, planners
ISSUE 2 SEPTEMBER 2014 TSA Endorsed by: CLIENT GUIDE TO DIGITAL ORTHO- PHOTOGRAPHY The Survey Association s Client Guides are primarily aimed at other professionals such as engineers, architects, planners
LIDAR and Digital Elevation Data
 LIDAR and Digital Elevation Data Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) is being used by the North Carolina Floodplain Mapping Program to generate digital elevation data. These highly accurate topographic
LIDAR and Digital Elevation Data Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) is being used by the North Carolina Floodplain Mapping Program to generate digital elevation data. These highly accurate topographic
Total Program's Units
 Associate Degree Program Department of Civil and Architectural Technology Major : Survey Technology First Semester NO 5 6 Code SRV 0 SRV 0 SRV 0 ENG 0 MTH 7 CMT 0 Course Title Land survey Survey drawing
Associate Degree Program Department of Civil and Architectural Technology Major : Survey Technology First Semester NO 5 6 Code SRV 0 SRV 0 SRV 0 ENG 0 MTH 7 CMT 0 Course Title Land survey Survey drawing
3D MODELING OF LARGE AND COMPLEX SITE USING MULTI-SENSOR INTEGRATION AND MULTI-RESOLUTION DATA
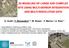 3D MODELING OF LARGE AND COMPLEX SITE USING MULTI-SENSOR INTEGRATION AND MULTI-RESOLUTION DATA G. Guidi 1, F. Remondino 2, 3, M. Russo 1, F. Menna 4, A. Rizzi 3 1 Dept.INDACO, Politecnico of Milano, Italy
3D MODELING OF LARGE AND COMPLEX SITE USING MULTI-SENSOR INTEGRATION AND MULTI-RESOLUTION DATA G. Guidi 1, F. Remondino 2, 3, M. Russo 1, F. Menna 4, A. Rizzi 3 1 Dept.INDACO, Politecnico of Milano, Italy
The national archive of urban street numbers (ANNCSU)
 The national archive of urban street numbers (ANNCSU) Rome, 21/11/2014 Pag 1 Agenzia delle Entrate Largo Leopardi, 5 00185 Roma Agenda Relevant legislation Preliminary remarks Activities carried out so
The national archive of urban street numbers (ANNCSU) Rome, 21/11/2014 Pag 1 Agenzia delle Entrate Largo Leopardi, 5 00185 Roma Agenda Relevant legislation Preliminary remarks Activities carried out so
Qatar National Geospatial Infrastructure
 Qatar National Geospatial Infrastructure Since 1990 up to 2030 and beyond Mohammad Abd El-Wahab Hamouda GIS Consultant & Chairman of GIS Coordinators Group The Center for GIS Ministry of Municipality and
Qatar National Geospatial Infrastructure Since 1990 up to 2030 and beyond Mohammad Abd El-Wahab Hamouda GIS Consultant & Chairman of GIS Coordinators Group The Center for GIS Ministry of Municipality and
Technical and innovative tools and methods in support of CAP Geo referencing methods/lpis Polish experience Padova, May 27th 2015
 Technical and innovative tools and methods in support of CAP Geo referencing methods/lpis Polish experience This event is supported by the European Union Programme Hercule III (2014 2020). This programme
Technical and innovative tools and methods in support of CAP Geo referencing methods/lpis Polish experience This event is supported by the European Union Programme Hercule III (2014 2020). This programme
ISTANBUL DECLARATION ON CADASTRE IN THE WORLD CADASTRE SUMMIT 2015
 ISTANBUL DECLARATION ON CADASTRE IN THE WORLD CADASTRE SUMMIT 2015 Let us Cadastre the World... 1. INTRODUCTION Land had represented wealth and power from the first settlement to the end of 1700s. As a
ISTANBUL DECLARATION ON CADASTRE IN THE WORLD CADASTRE SUMMIT 2015 Let us Cadastre the World... 1. INTRODUCTION Land had represented wealth and power from the first settlement to the end of 1700s. As a
Survey and Mapping Activities in Vietnam *
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.100/CRP.1 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Eighteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 26-29 October 2009 Item 7(a) of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.100/CRP.1 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Eighteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 26-29 October 2009 Item 7(a) of the provisional
A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA
 A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA N. Zarrinpanjeh a, F. Dadrassjavan b, H. Fattahi c * a Islamic Azad University of Qazvin - nzarrin@qiau.ac.ir
A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA N. Zarrinpanjeh a, F. Dadrassjavan b, H. Fattahi c * a Islamic Azad University of Qazvin - nzarrin@qiau.ac.ir
Territori,theItalianWebPortalofCadastresandHistoricalCartographyCartography. Cartography. By Mauro Tosti Croce & Saverio Pialli
 Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: H Interdisciplinary Volume 14 Issue 2 Version1.0 Year2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: H Interdisciplinary Volume 14 Issue 2 Version1.0 Year2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Introduction to GIS (Basics, Data, Analysis) & Case Studies. 13 th May 2004. Content. What is GIS?
 Introduction to GIS (Basics, Data, Analysis) & Case Studies 13 th May 2004 Content Introduction to GIS Data concepts Data input Analysis Applications selected examples What is GIS? Geographic Information
Introduction to GIS (Basics, Data, Analysis) & Case Studies 13 th May 2004 Content Introduction to GIS Data concepts Data input Analysis Applications selected examples What is GIS? Geographic Information
Technology Trends In Geoinformation
 Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: drkadir@jupem.gov.my www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: drkadir@jupem.gov.my www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
APLS 2011. GIS Data: Classification, Potential Misuse, and Practical Limitations
 APLS 2011 GIS Data: Classification, Potential Misuse, and Practical Limitations GIS Data: Classification, Potential Misuse, and Practical Limitations Goals & Objectives Develop an easy to use geospatial
APLS 2011 GIS Data: Classification, Potential Misuse, and Practical Limitations GIS Data: Classification, Potential Misuse, and Practical Limitations Goals & Objectives Develop an easy to use geospatial
3D Model of the City Using LiDAR and Visualization of Flood in Three-Dimension
 3D Model of the City Using LiDAR and Visualization of Flood in Three-Dimension R.Queen Suraajini, Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering Guindy, Anna University, India, suraa12@gmail.com
3D Model of the City Using LiDAR and Visualization of Flood in Three-Dimension R.Queen Suraajini, Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering Guindy, Anna University, India, suraa12@gmail.com
SHOALS Toolbox: Software to Support Visualization and Analysis of Large, High-Density Data Sets
 SHOALS Toolbox: Software to Support Visualization and Analysis of Large, High-Density Data Sets by Jennifer M. Wozencraft, W. Jeff Lillycrop, and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering
SHOALS Toolbox: Software to Support Visualization and Analysis of Large, High-Density Data Sets by Jennifer M. Wozencraft, W. Jeff Lillycrop, and Nicholas C. Kraus PURPOSE: The Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering
Adaptation of High Resolution Ikonos Images to Googleearth for Zonguldak Test Field
 Adaptation of High Resolution Ikonos Images to Googleearth for Zonguldak Test Field Umut G. SEFERCIK, Murat ORUC and Mehmet ALKAN, Turkey Key words: Image Processing, Information Content, Image Understanding,
Adaptation of High Resolution Ikonos Images to Googleearth for Zonguldak Test Field Umut G. SEFERCIK, Murat ORUC and Mehmet ALKAN, Turkey Key words: Image Processing, Information Content, Image Understanding,
LASER SCANNER APPLICATION ON COMPLEX SHAPES OF ARCHITECTURE. PROFILES EXTRACTION PROCESSING AND 3D MODELLING.
 LASER SCANNER APPLICATION ON COMPLEX SHAPES OF ARCHITECTURE. PROFILES EXTRACTION PROCESSING AND 3D MODELLING. Carlo MONTI Full Professor E-mail: carlo.monti@polimi.it Luigi FREGONESE Research Assegnist
LASER SCANNER APPLICATION ON COMPLEX SHAPES OF ARCHITECTURE. PROFILES EXTRACTION PROCESSING AND 3D MODELLING. Carlo MONTI Full Professor E-mail: carlo.monti@polimi.it Luigi FREGONESE Research Assegnist
METHODOLOGY FOR LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY AND HAZARD MAPPING USING GIS AND SDI
 The 8th International Conference on Geo-information for Disaster Management Intelligent Systems for Crisis Management METHODOLOGY FOR LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY AND HAZARD MAPPING USING GIS AND SDI T. Fernández
The 8th International Conference on Geo-information for Disaster Management Intelligent Systems for Crisis Management METHODOLOGY FOR LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY AND HAZARD MAPPING USING GIS AND SDI T. Fernández
Supervised Classification workflow in ENVI 4.8 using WorldView-2 imagery
 Supervised Classification workflow in ENVI 4.8 using WorldView-2 imagery WorldView-2 is the first commercial high-resolution satellite to provide eight spectral sensors in the visible to near-infrared
Supervised Classification workflow in ENVI 4.8 using WorldView-2 imagery WorldView-2 is the first commercial high-resolution satellite to provide eight spectral sensors in the visible to near-infrared
GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEM FOR THE CULTURAL HERITAGE AND PROTECTED LANDSCAPE OF REGIONE TOSCANA
 77 GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEM FOR THE CULTURAL HERITAGE AND PROTECTED LANDSCAPE OF REGIONE TOSCANA R. Costantini a, *, L. Angeli a, R. Ferrari a, L. Innocenti a, M. Del Buono b a Consorzio LaMMA,
77 GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEM FOR THE CULTURAL HERITAGE AND PROTECTED LANDSCAPE OF REGIONE TOSCANA R. Costantini a, *, L. Angeli a, R. Ferrari a, L. Innocenti a, M. Del Buono b a Consorzio LaMMA,
Perspective of Permanent Reference Network KOPOS in Kosova
 143 Perspective of Permanent Reference Network KOPOS in Kosova Meha, M. and Çaka, M. Kosovo Cadastral Agency, Kosovo Archive Building II nd floor, P.O. 10000, Prishtina, Republic of Kosovo, E-mail: mmeha@yahoo.com,
143 Perspective of Permanent Reference Network KOPOS in Kosova Meha, M. and Çaka, M. Kosovo Cadastral Agency, Kosovo Archive Building II nd floor, P.O. 10000, Prishtina, Republic of Kosovo, E-mail: mmeha@yahoo.com,
L Aquila, 22 Ottobre The 2008 SDI: a knowledge based system Venice, 21-23 March 2011. Cartogra. SIT e la C
 1 afia Palazzo Franchetti Venice Italy International Conference Data Dt Flow From Space to Earth Applications and interoperability The SDI: a knowledge based system Maurizio De Gennaro, Silvano De Zorzi,
1 afia Palazzo Franchetti Venice Italy International Conference Data Dt Flow From Space to Earth Applications and interoperability The SDI: a knowledge based system Maurizio De Gennaro, Silvano De Zorzi,
GIS for Transportation Infrastructure Management
 GIS for Transportation Infrastructure GIS for Transportation Infrastructure Being able to visualize your assets and the surrounding environment when you build, upgrade, or repair transportation infrastructure
GIS for Transportation Infrastructure GIS for Transportation Infrastructure Being able to visualize your assets and the surrounding environment when you build, upgrade, or repair transportation infrastructure
Jean François Aumont (1), Bastien Mancini (2). (1) Image processing manager, Delair-Tech, (2) Managing director, Delair-Tech. Project : Authors:
 Jean François Aumont (1), Bastien Mancini (2). (1) Image processing manager, Delair-Tech, (2) Managing director, Delair-Tech. White paper DT26X DT-3BANDS XL APXL Project : Authors: Date:
Jean François Aumont (1), Bastien Mancini (2). (1) Image processing manager, Delair-Tech, (2) Managing director, Delair-Tech. White paper DT26X DT-3BANDS XL APXL Project : Authors: Date:
COMPARISON OF AERIAL IMAGES, SATELLITE IMAGES AND LASER SCANNING DSM IN A 3D CITY MODELS PRODUCTION FRAMEWORK
 COMPARISON OF AERIAL IMAGES, SATELLITE IMAGES AND LASER SCANNING DSM IN A 3D CITY MODELS PRODUCTION FRAMEWORK G. Maillet, D. Flamanc Institut Géographique National, Laboratoire MATIS, Saint-Mandé, France
COMPARISON OF AERIAL IMAGES, SATELLITE IMAGES AND LASER SCANNING DSM IN A 3D CITY MODELS PRODUCTION FRAMEWORK G. Maillet, D. Flamanc Institut Géographique National, Laboratoire MATIS, Saint-Mandé, France
Development of Automatic shooting and telemetry system for UAV photogrammetry INTRODUCTION
 Development of Automatic shooting and telemetry system for UAV photogrammetry Jinwoo PARK 1, Minseok KIM 1, Khin Mar Yee 1, Chuluong CHOI 1 1 Department of Spatial Information Engineering, Pukyong National
Development of Automatic shooting and telemetry system for UAV photogrammetry Jinwoo PARK 1, Minseok KIM 1, Khin Mar Yee 1, Chuluong CHOI 1 1 Department of Spatial Information Engineering, Pukyong National
.FOR. Forest inventory and monitoring quality
 .FOR Forest inventory and monitoring quality FOR : the asset to manage your forest patrimony 2 1..FOR Presentation.FOR is an association of Belgian companies, created in 2010 and supported by a university
.FOR Forest inventory and monitoring quality FOR : the asset to manage your forest patrimony 2 1..FOR Presentation.FOR is an association of Belgian companies, created in 2010 and supported by a university
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC TECHNIQUES FOR MEASUREMENTS IN WOODWORKING INDUSTRY
 PHOTOGRAMMETRIC TECHNIQUES FOR MEASUREMENTS IN WOODWORKING INDUSTRY V. Knyaz a, *, Yu. Visilter, S. Zheltov a State Research Institute for Aviation System (GosNIIAS), 7, Victorenko str., Moscow, Russia
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC TECHNIQUES FOR MEASUREMENTS IN WOODWORKING INDUSTRY V. Knyaz a, *, Yu. Visilter, S. Zheltov a State Research Institute for Aviation System (GosNIIAS), 7, Victorenko str., Moscow, Russia
Opportunities for the generation of high resolution digital elevation models based on small format aerial photography
 Opportunities for the generation of high resolution digital elevation models based on small format aerial photography Boudewijn van Leeuwen 1, József Szatmári 1, Zalán Tobak 1, Csaba Németh 1, Gábor Hauberger
Opportunities for the generation of high resolution digital elevation models based on small format aerial photography Boudewijn van Leeuwen 1, József Szatmári 1, Zalán Tobak 1, Csaba Németh 1, Gábor Hauberger
Mongolian National Spatial Data Infrastructure
 Mongolian National Spatial Data Infrastructure S.Enkhtuya Chief of Spatial Data Infrastructure Department of Administration of Land Affairs, Geodesy and Cartography Beijing. 2014 ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Mongolian National Spatial Data Infrastructure S.Enkhtuya Chief of Spatial Data Infrastructure Department of Administration of Land Affairs, Geodesy and Cartography Beijing. 2014 ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
VOL. 2, NO. 3, March 2012 ISSN 2222-9833 ARPN Journal of Systems and Software 2009-2011 AJSS Journal. All rights reserved
 Five Aspects of Application Integration Requirements Fazilat Hojaji MS of Information Technology Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & IT Department Hafez ST,Tehran, Iran
Five Aspects of Application Integration Requirements Fazilat Hojaji MS of Information Technology Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & IT Department Hafez ST,Tehran, Iran
REGIONAL CENTRE FOR TRAINING IN AEROSPACE SURVEYS (RECTAS) MASTER IN GEOINFORMATION PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT
 REGIONAL CENTRE FOR TRAINING IN AEROSPACE SURVEYS (RECTAS) MASTER IN GEOINFORMATION PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME DESCRIPTION October 2014 1. The programme The academic programme shall be referred
REGIONAL CENTRE FOR TRAINING IN AEROSPACE SURVEYS (RECTAS) MASTER IN GEOINFORMATION PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME DESCRIPTION October 2014 1. The programme The academic programme shall be referred
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS
 INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
INDIVIDUAL COURSE DETAILS A. Name of Institution NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH TARAMANI CHENNAI 600 113 [An Autonomous Institute under Ministry of Human Resource Development,
SKY LIGHT SYSTEMS. Success stories. Nabla Quadro srl
 SKY LIGHT SYSTEMS Success stories Nabla Quadro srl Via G. Peroni 442/444 00131 Roma, Italy Tel. 0680368963 Fax. 0680368901 www.nablaquadro.it infomail@nablaquadro.it September 2015 2 Contents 0. Preface
SKY LIGHT SYSTEMS Success stories Nabla Quadro srl Via G. Peroni 442/444 00131 Roma, Italy Tel. 0680368963 Fax. 0680368901 www.nablaquadro.it infomail@nablaquadro.it September 2015 2 Contents 0. Preface
4.03 Vertical Control Surveys: 4-1
 4. HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL CONTROL 4.01 General: Sufficient horizontal and, if applicable, vertical control surveys shall be established by the Contractor for all photogrammetric mapping purposes. Prior
4. HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL CONTROL 4.01 General: Sufficient horizontal and, if applicable, vertical control surveys shall be established by the Contractor for all photogrammetric mapping purposes. Prior
A GIS helps you answer questions and solve problems by looking at your data in a way that is quickly understood and easily shared.
 A Geographic Information System (GIS) integrates hardware, software, and data for capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information. GIS allows us to view,
A Geographic Information System (GIS) integrates hardware, software, and data for capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information. GIS allows us to view,
TRAFFIC NOISE MONITORING IN THE CITY OF MILAN: CONSTRUCTION OF A REPRESENTATIVE STATISTICAL COLLECTION OF ACOUSTIC TRENDS
 TRAFFIC NOISE MONITORING IN THE CITY OF MILAN: CONSTRUCTION OF A REPRESENTATIVE STATISTICAL COLLECTION OF ACOUSTIC TRENDS Zambon Giovanni, Angelini Fabio, Salvi Diego, Zanaboni Walter and Smiraglia Maura
TRAFFIC NOISE MONITORING IN THE CITY OF MILAN: CONSTRUCTION OF A REPRESENTATIVE STATISTICAL COLLECTION OF ACOUSTIC TRENDS Zambon Giovanni, Angelini Fabio, Salvi Diego, Zanaboni Walter and Smiraglia Maura
A Book and a WebSite on. Information Systems for Urban Planning A Hypermedia Co-operative Approach
 A Book and a WebSite on Information Systems for Urban Planning A Hypermedia Co-operative Approach Robert LAURINI http://lisi.insa-lyon.fr/~laurini/isup 1 Objectives of the book Not another GIS book!! Survey
A Book and a WebSite on Information Systems for Urban Planning A Hypermedia Co-operative Approach Robert LAURINI http://lisi.insa-lyon.fr/~laurini/isup 1 Objectives of the book Not another GIS book!! Survey
GEOENGINE MSc in Geomatics Engineering (Master Thesis) Anamelechi, Falasy Ebere
 Master s Thesis: ANAMELECHI, FALASY EBERE Analysis of a Raster DEM Creation for a Farm Management Information System based on GNSS and Total Station Coordinates Duration of the Thesis: 6 Months Completion
Master s Thesis: ANAMELECHI, FALASY EBERE Analysis of a Raster DEM Creation for a Farm Management Information System based on GNSS and Total Station Coordinates Duration of the Thesis: 6 Months Completion
Mapping Solar Energy Potential Through LiDAR Feature Extraction
 Mapping Solar Energy Potential Through LiDAR Feature Extraction WOOLPERT WHITE PAPER By Brad Adams brad.adams@woolpert.com DESIGN GEOSPATIAL INFRASTRUCTURE November 2012 Solar Energy Potential Is Largely
Mapping Solar Energy Potential Through LiDAR Feature Extraction WOOLPERT WHITE PAPER By Brad Adams brad.adams@woolpert.com DESIGN GEOSPATIAL INFRASTRUCTURE November 2012 Solar Energy Potential Is Largely
IP-S2 Compact+ 3D Mobile Mapping System
 IP-S2 Compact+ 3D Mobile Mapping System 3D scanning of road and roadside features Delivers high density point clouds and 360 spherical imagery High accuracy IMU options without export control Simple Map,
IP-S2 Compact+ 3D Mobile Mapping System 3D scanning of road and roadside features Delivers high density point clouds and 360 spherical imagery High accuracy IMU options without export control Simple Map,
3D Point Cloud Analytics for Updating 3D City Models
 3D Point Cloud Analytics for Updating 3D City Models Rico Richter 25 th May 2015 INSPIRE - Geospatial World Forum 2015 Background Hasso Plattner Institute (HPI): Computer Graphics Systems group of Prof.
3D Point Cloud Analytics for Updating 3D City Models Rico Richter 25 th May 2015 INSPIRE - Geospatial World Forum 2015 Background Hasso Plattner Institute (HPI): Computer Graphics Systems group of Prof.
CASE STUDY LANDSLIDE MONITORING
 Introduction Monitoring of terrain movements (unstable slopes, landslides, glaciers, ) is an increasingly important task for today s geotechnical people asked to prevent or forecast natural disaster that
Introduction Monitoring of terrain movements (unstable slopes, landslides, glaciers, ) is an increasingly important task for today s geotechnical people asked to prevent or forecast natural disaster that
CityGML goes to Broadway
 CityGML goes to Broadway Thomas H. Kolbe, Barbara Burger, Berit Cantzler Chair of Geoinformatics thomas.kolbe@tum.de September 11, 2015 Photogrammetric Week 2015, Stuttgart The New York City Open Data
CityGML goes to Broadway Thomas H. Kolbe, Barbara Burger, Berit Cantzler Chair of Geoinformatics thomas.kolbe@tum.de September 11, 2015 Photogrammetric Week 2015, Stuttgart The New York City Open Data
IP-S3 HD1. Compact, High-Density 3D Mobile Mapping System
 IP-S3 HD1 Compact, High-Density 3D Mobile Mapping System Integrated, turnkey solution Ultra-compact design Multiple lasers minimize scanning shades Unparalleled ease-of-use No user calibration required
IP-S3 HD1 Compact, High-Density 3D Mobile Mapping System Integrated, turnkey solution Ultra-compact design Multiple lasers minimize scanning shades Unparalleled ease-of-use No user calibration required
How To Fuse A Point Cloud With A Laser And Image Data From A Pointcloud
 REAL TIME 3D FUSION OF IMAGERY AND MOBILE LIDAR Paul Mrstik, Vice President Technology Kresimir Kusevic, R&D Engineer Terrapoint Inc. 140-1 Antares Dr. Ottawa, Ontario K2E 8C4 Canada paul.mrstik@terrapoint.com
REAL TIME 3D FUSION OF IMAGERY AND MOBILE LIDAR Paul Mrstik, Vice President Technology Kresimir Kusevic, R&D Engineer Terrapoint Inc. 140-1 Antares Dr. Ottawa, Ontario K2E 8C4 Canada paul.mrstik@terrapoint.com
Assessment of Workforce Demands to Shape GIS&T Education
 Assessment of Workforce Demands to Shape GIS&T Education Gudrun Wallentin, Barbara Hofer, Christoph Traun gudrun.wallentin@sbg.ac.at University of Salzburg, Dept. of Geoinformatics Z_GIS, Austria www.gi-n2k.eu
Assessment of Workforce Demands to Shape GIS&T Education Gudrun Wallentin, Barbara Hofer, Christoph Traun gudrun.wallentin@sbg.ac.at University of Salzburg, Dept. of Geoinformatics Z_GIS, Austria www.gi-n2k.eu
Solutions for Central and Federal Governments
 Solutions for Central and Federal Governments Intergraph s Advanced Geospatial Solutions for for Central and Federal Government Operations Central and federal governments are continually asked to do more
Solutions for Central and Federal Governments Intergraph s Advanced Geospatial Solutions for for Central and Federal Government Operations Central and federal governments are continually asked to do more
Understanding Raster Data
 Introduction The following document is intended to provide a basic understanding of raster data. Raster data layers (commonly referred to as grids) are the essential data layers used in all tools developed
Introduction The following document is intended to provide a basic understanding of raster data. Raster data layers (commonly referred to as grids) are the essential data layers used in all tools developed
Development of Large-Scale Land Information System (LIS) by Using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Field Surveying
 Engineering, 2012, 4, 107-118 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/eng.2012.42014 Published Online February 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Development of Large-Scale Land Information System (LIS) by Using
Engineering, 2012, 4, 107-118 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/eng.2012.42014 Published Online February 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Development of Large-Scale Land Information System (LIS) by Using
The RapidEye optical satellite family for high resolution imagery
 'Photogrammetric Week 01' D. Fritsch & R. Spiller, Eds. Wichmann Verlag, Heidelberg 2001. Scherer, Krischke 139 The RapidEye optical satellite family for high resolution imagery STEFAN SCHERER and MANFRED
'Photogrammetric Week 01' D. Fritsch & R. Spiller, Eds. Wichmann Verlag, Heidelberg 2001. Scherer, Krischke 139 The RapidEye optical satellite family for high resolution imagery STEFAN SCHERER and MANFRED
PI: Riccardo Lanari (IREA CNR) email:lanari.r@irea.cnr.it
 On the exploitation and validation of COSMO-SkyMed interferometric SAR data for digital terrain modelling and surface deformation analysis in extensive urban areas (ID: 1441) Project partners: Istituto
On the exploitation and validation of COSMO-SkyMed interferometric SAR data for digital terrain modelling and surface deformation analysis in extensive urban areas (ID: 1441) Project partners: Istituto
<Insert Picture Here> Data Management Innovations for Massive Point Cloud, DEM, and 3D Vector Databases
 Data Management Innovations for Massive Point Cloud, DEM, and 3D Vector Databases Xavier Lopez, Director, Product Management 3D Data Management Technology Drivers: Challenges & Benefits
Data Management Innovations for Massive Point Cloud, DEM, and 3D Vector Databases Xavier Lopez, Director, Product Management 3D Data Management Technology Drivers: Challenges & Benefits
Green Move Web Viewer: critical issues and implementation
 GIT Geology and Information Technology 8a Riunione del Gruppo di Geologia informatica Sezione della Società Geologica Italiana Chiavenna, 17-19 giugno 2013 Polo Territoriale di Como Laboratorio di Geomatica
GIT Geology and Information Technology 8a Riunione del Gruppo di Geologia informatica Sezione della Società Geologica Italiana Chiavenna, 17-19 giugno 2013 Polo Territoriale di Como Laboratorio di Geomatica
APPLICATION OF GOOGLE EARTH FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF BASE MAP IN THE CASE OF GISH ABBAY SEKELA, AMHARA STATE, ETHIOPIA
 APPLICATION OF GOOGLE EARTH FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF BASE MAP IN THE CASE OF GISH ABBAY SEKELA, AMHARA STATE, ETHIOPIA Abineh Tilahun Department of Geography and environmental studies, Adigrat University,
APPLICATION OF GOOGLE EARTH FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF BASE MAP IN THE CASE OF GISH ABBAY SEKELA, AMHARA STATE, ETHIOPIA Abineh Tilahun Department of Geography and environmental studies, Adigrat University,
How To Use Data From Copernicus And Big Data To Help The Environment
 Copernicus and Big Data: Challenges and Opportunities Alessandro Annoni European Commission Joint Research Centre www.jrc.ec.europa.eu Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation Big
Copernicus and Big Data: Challenges and Opportunities Alessandro Annoni European Commission Joint Research Centre www.jrc.ec.europa.eu Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation Big
The 2014 Italian Presidency of the Permanent Committee on Cadastre in the E.U.
 The 2014 Italian Presidency of the Permanent Committee on Cadastre in the E.U. Athens, 25 th June 2014 Eng. Franco MAGGIO Central Director for Cadastre and Cartography Page 1 Agenda Overview of the Italian
The 2014 Italian Presidency of the Permanent Committee on Cadastre in the E.U. Athens, 25 th June 2014 Eng. Franco MAGGIO Central Director for Cadastre and Cartography Page 1 Agenda Overview of the Italian
Resolution Enhancement of Photogrammetric Digital Images
 DICTA2002: Digital Image Computing Techniques and Applications, 21--22 January 2002, Melbourne, Australia 1 Resolution Enhancement of Photogrammetric Digital Images John G. FRYER and Gabriele SCARMANA
DICTA2002: Digital Image Computing Techniques and Applications, 21--22 January 2002, Melbourne, Australia 1 Resolution Enhancement of Photogrammetric Digital Images John G. FRYER and Gabriele SCARMANA
COUNTRY REPORT GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN NEPAL
 COUNTRY REPORT ON GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN NEPAL Government of Nepal Ministry of Land Reform and Management SURVEY DEPARTMENT PO Box 9435 Min Bhavan, Kathmandu Nepal Tel : + 977 1 4622713 +
COUNTRY REPORT ON GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT IN NEPAL Government of Nepal Ministry of Land Reform and Management SURVEY DEPARTMENT PO Box 9435 Min Bhavan, Kathmandu Nepal Tel : + 977 1 4622713 +
Photogrammetric Point Clouds
 Photogrammetric Point Clouds Origins of digital point clouds: Basics have been around since the 1980s. Images had to be referenced to one another. The user had to specify either where the camera was in
Photogrammetric Point Clouds Origins of digital point clouds: Basics have been around since the 1980s. Images had to be referenced to one another. The user had to specify either where the camera was in
Positioning Aware Solutions for Smart Grid. Enterprise Geospatial & Business Development Manager- GIS DC (Trimble, MEIA Region)
 Positioning Aware Solutions for Smart Grid Presented by: Pankaj Gupta Enterprise Geospatial & Business Development Manager- GIS DC (Trimble, MEIA Region) Overview: Position-aware solutions for Smart Grid
Positioning Aware Solutions for Smart Grid Presented by: Pankaj Gupta Enterprise Geospatial & Business Development Manager- GIS DC (Trimble, MEIA Region) Overview: Position-aware solutions for Smart Grid
Guidelines for the use of the OGP P6/11 bin grid GIS data model
 Guidelines for the use of the OGP P6/11 bin grid GIS data model Report No. 483-6g July 2013 This document is a companion document to the OGP P6/11 Seismic bin grid data exchange format description (2012)
Guidelines for the use of the OGP P6/11 bin grid GIS data model Report No. 483-6g July 2013 This document is a companion document to the OGP P6/11 Seismic bin grid data exchange format description (2012)
VENETOREGION ROAD NETWORK ROAD MAPPING LASER SCANNING FACILITY MANAGEMENT
 VENETOREGION ROAD NETWORK ROAD MAPPING LASER SCANNING FACILITY MANAGEMENT ing. Augusto Burchi burchi@sitecoinf.it Siteco profile Italian software house specialized in GIS and RDBMS dedicated to Road networks
VENETOREGION ROAD NETWORK ROAD MAPPING LASER SCANNING FACILITY MANAGEMENT ing. Augusto Burchi burchi@sitecoinf.it Siteco profile Italian software house specialized in GIS and RDBMS dedicated to Road networks
KEY WORDS: Geoinformatics, Geoinformation technique, Remote Sensing, Information technique, Curriculum, Surveyor.
 CURRICULUM OF GEOINFORMATICS INTEGRATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Kirsi VIRRANTAUS*, Henrik HAGGRÉN** Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Department of Surveying
CURRICULUM OF GEOINFORMATICS INTEGRATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Kirsi VIRRANTAUS*, Henrik HAGGRÉN** Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Department of Surveying
Aerial imagery and geographic information systems used in the asbestos removal process in Poland
 Towards Horizon 2020 Lasaponara R., Masini N., Biscione M., Editors EARSeL, 2013 Aerial imagery and geographic information systems used in the asbestos removal process in Małgorzata Krówczyńska 1, Ewa
Towards Horizon 2020 Lasaponara R., Masini N., Biscione M., Editors EARSeL, 2013 Aerial imagery and geographic information systems used in the asbestos removal process in Małgorzata Krówczyńska 1, Ewa
THE VIRTUAL OFFICE: A COLLABORATIVE APPROACH TO SURVEYS AND GIS FOR URBAN RENOVATION IN THE BETHLEHEM AREA CONSERVATION AND MANAGEMENT PLAN BY UNESCO
 THE VIRTUAL OFFICE: A COLLABORATIVE APPROACH TO SURVEYS AND GIS FOR URBAN RENOVATION IN THE BETHLEHEM AREA CONSERVATION AND MANAGEMENT PLAN BY UNESCO Elisa Palazzo a, Luca Gentili b a Visiting fellow at
THE VIRTUAL OFFICE: A COLLABORATIVE APPROACH TO SURVEYS AND GIS FOR URBAN RENOVATION IN THE BETHLEHEM AREA CONSERVATION AND MANAGEMENT PLAN BY UNESCO Elisa Palazzo a, Luca Gentili b a Visiting fellow at
Verification of data in GIS Management System for State Real Estate
 Dorota LATOS, Marcin LATOS, Marcin GAŁUSZKIEWICZ, Paweł KAMIŃSKI, Poland Key words: verification, data, management system, real estate At present, GIS is being used in all fields of economic activity and
Dorota LATOS, Marcin LATOS, Marcin GAŁUSZKIEWICZ, Paweł KAMIŃSKI, Poland Key words: verification, data, management system, real estate At present, GIS is being used in all fields of economic activity and
Spatial Data Warehouse (SDW) & AltaLIS. Presentation to NSGIC. National States Geographic Information Council. Annapolis, Maryland.
 Spatial Data Warehouse (SDW) & AltaLIS Presentation to NSGIC National States Geographic Information Council Annapolis, Maryland February 24, 2013 Spatial Data Warehouse (SDW) & AltaLIS A DATA related Public-Private
Spatial Data Warehouse (SDW) & AltaLIS Presentation to NSGIC National States Geographic Information Council Annapolis, Maryland February 24, 2013 Spatial Data Warehouse (SDW) & AltaLIS A DATA related Public-Private
REGIONAL SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT: A GIS APPROACH TO SPATIAL DATA ANALYSIS. Lynn Copeland Hardegree, Jennifer M. Wozencraft 1, Rose Dopsovic 2 INTRODUCTION
 REGIONAL SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT: A GIS APPROACH TO SPATIAL DATA ANALYSIS Lynn Copeland Hardegree, Jennifer M. Wozencraft 1, Rose Dopsovic 2 ABSTRACT: Regional sediment management (RSM) requires the capability
REGIONAL SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT: A GIS APPROACH TO SPATIAL DATA ANALYSIS Lynn Copeland Hardegree, Jennifer M. Wozencraft 1, Rose Dopsovic 2 ABSTRACT: Regional sediment management (RSM) requires the capability
VCS REDD Methodology Module. Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities
 1 VCS REDD Methodology Module Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities Version 1.0 May 2009 I. SCOPE, APPLICABILITY, DATA REQUIREMENT AND OUTPUT PARAMETERS Scope This module
1 VCS REDD Methodology Module Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities Version 1.0 May 2009 I. SCOPE, APPLICABILITY, DATA REQUIREMENT AND OUTPUT PARAMETERS Scope This module
Information technology infrastructures and services for creating a library's unified information system
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Proceedings of the IATUL Conferences 1999 IATUL Proceedings Information technology infrastructures and services for creating a library's unified information system Attilio
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Proceedings of the IATUL Conferences 1999 IATUL Proceedings Information technology infrastructures and services for creating a library's unified information system Attilio
Movicon in energy efficiency management: the ISO 50001 standard
 Movicon in energy efficiency management: the ISO 50001 standard The importance of energy consumption within the company reflects the importance of the world energy crisis due to a growing demand and the
Movicon in energy efficiency management: the ISO 50001 standard The importance of energy consumption within the company reflects the importance of the world energy crisis due to a growing demand and the
Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping
 Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping NRS 516, Spring 2016 Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural
Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping NRS 516, Spring 2016 Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural
IP-S2 HD. High Definition 3D Mobile Mapping System
 IP-S2 HD High Definition 3D Mobile Mapping System Integrated, turnkey solution High Density, Long Range LiDAR sensor for ultimate in visual detail High Accuracy IMU and DMI Odometry for positional accuracy
IP-S2 HD High Definition 3D Mobile Mapping System Integrated, turnkey solution High Density, Long Range LiDAR sensor for ultimate in visual detail High Accuracy IMU and DMI Odometry for positional accuracy
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF THE HOUGH TRANSFORMATION IN THE FRAME OF AUTOMATED BUILDING EXTRACTION
 ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF THE HOUGH TRANSFORMATION IN THE FRAME OF AUTOMATED BUILDING EXTRACTION G. Vozikis a,*, J.Jansa b a GEOMET Ltd., Faneromenis 4 & Agamemnonos 11, GR - 15561 Holargos, GREECE
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF THE HOUGH TRANSFORMATION IN THE FRAME OF AUTOMATED BUILDING EXTRACTION G. Vozikis a,*, J.Jansa b a GEOMET Ltd., Faneromenis 4 & Agamemnonos 11, GR - 15561 Holargos, GREECE
GPS Based Low Cost Intelligent Vehicle Tracking System (IVTS)
 2012 International Conference on Traffic and Transportation Engineering (ICTTE 2012) IPCSIT vol. 26 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore GPS Based Low Cost Intelligent Vehicle Tracking System (IVTS) Dr.
2012 International Conference on Traffic and Transportation Engineering (ICTTE 2012) IPCSIT vol. 26 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore GPS Based Low Cost Intelligent Vehicle Tracking System (IVTS) Dr.
The Scientific Data Mining Process
 Chapter 4 The Scientific Data Mining Process When I use a word, Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, it means just what I choose it to mean neither more nor less. Lewis Carroll [87, p. 214] In
Chapter 4 The Scientific Data Mining Process When I use a word, Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, it means just what I choose it to mean neither more nor less. Lewis Carroll [87, p. 214] In
Subdivision Mapping: Making the Pieces Fit David P. Thaler, GIS Analyst A geographit White Paper, June 2009
 Subdivision Mapping: Making the Pieces Fit P David P. Thaler, GIS Analyst A geographit White Paper, June 2009 1525 Oregon Pike, Suite 202 Lancaster, PA USA 17601-7300 Phone: 717-399-7007 Fax: 717-399-7015
Subdivision Mapping: Making the Pieces Fit P David P. Thaler, GIS Analyst A geographit White Paper, June 2009 1525 Oregon Pike, Suite 202 Lancaster, PA USA 17601-7300 Phone: 717-399-7007 Fax: 717-399-7015
