Risk Assessment for Medical Devices. Linda Braddon, Ph.D. Bring your medical device to market faster 1
|
|
|
- Nora Gilmore
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Risk Assessment for Medical Devices Linda Braddon, Ph.D. Bring your medical device to market faster 1
2 My Perspective Work with start up medical device companies Goal: Making great ideas into profitable products We see the same mistakes over and over again Bring your medical device to market faster 2
3 Why do a Risk Assessment? You have to do it. It is one of the first things FDA will ask for! Required by law (21 CFR Section 820) Appears on regulatory submission checklists Will help define testing that should be done to prove the safety of your device Helps to eliminate costs associated with recalls Offers a measure of protection from liability It is the right thing to do Bring your medical device to market faster 3
4 Risk Assessment is: Definition: An iterative process of assessing a product s benefit / risk balance Goal: Developing and implementing tools to minimize risk while preserving its benefit Timing: Should be done through product s lifecycle Bring your medical device to market faster 4
5 Useful Resources ISO Application of risk management to medical devices FDA Guidance Incorporating human factors into risk management FDA Guidance Premarketing Risk Assessment The focus of this talk is aimed at outlining the specifics for ISO compliance Bring your medical device to market faster 5
6 Management Responsibility Provide evidence of commitment to risk management Adequate resources Qualified personnel (need appropriate records for proof) Have a policy for determining risk Review effectiveness of risk management policy Determine how acceptable risk will be determined Periodic review Bring your medical device to market faster 6
7 Risk Management: The Steps Make a plan Implement plan Report results Bring your medical device to market faster 7
8 Implement plan Identify Evaluate Control Re-evaluate Communicate Bring your medical device to market faster 8
9 Make a plan Bring your medical device to market faster 9
10 Why have a plan? Organized approach is necessary for success Plan provides roadmap Plan encourages objectivity* Prevents important elements from being forgotten Ex: Lifecycle of device will alter risk and risk evaluations Verification of activities is required and does not often happen if not in a plan. Needs to have a formal way to integrate production and post-production information into risk management Bring your medical device to market faster 10
11 Risk Management Plan Activities must be planned Plan must be part of RM file Plan includes: Planned activities Assignment of responsibilities Requirements for review of RM activities Criteria for risk acceptability Verification activities Activities related to collection and review of production and post-production information Bring your medical device to market faster 11
12 Risk Management Plan Activities must be planned Plan must be part of RM file Plan includes: Planned activities Assignment of responsibilities Requirements for review of RM activities Criteria for risk acceptability Verification activities Activities related to collection and review of production and post-production information Bring your medical device to market faster 12
13 Risk Management Team - Qualified Personell Expertise in following areas: How is device constructed? How does device work? How is device produced? How is device used clinically? *Experts should be trained on how to apply the RM process. Records of qualification to provide objective evidence needs to be collected. Records of resumes, training, etc does not have to be kept in the RM file but should be pointed to Bring your medical device to market faster 13
14 Risk Management through Lifecycle RM does not stop when medical device goes into production. During prototyping, evaluating risk levels is often a rough estimation of risk. Use of real device by real users WILL HIGHLIGHT new and different levels of risk not considered in earlier phases. Bring your medical device to market faster 14
15 Start a Risk Management File Bring your medical device to market faster 15
16 Risk Management File Provides traceability for each identified hazard to: Risk analysis Risk Evaluation Implementation and verification of risk control measures Assessment of acceptability of residual risk Risk management file does not need to physically contain all the records and documents but should at least contain references to their location. File can be in any form (notebook, secure files on network, etc ) Bring your medical device to market faster 16
17 Risk Analysis Process Description of medical device that was analyzed ID of person(s) and organizations who performed analysis Scope Broad: for the development of a new medical device Narrow: evaluation of X change to an existing device Date(s) assessment was performed Bring your medical device to market faster 17
18 Analsyis Techniques Preliminary Hazards Analysis (PHA) Early in development Often little information or history Generic hazardous situations Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) Top down view What is the undesirable event? Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) How could each component fail? How does a combination of components fail? Hazard and Operability Study (HAZOP) Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) Bring your medical device to market faster 18
19 First questions to ask Bring your medical device to market faster 19
20 Key questions to ask about device: What is intended use? Manufacturer shall document the intended use and reasonably foreseeable misuse. Identify and document characteristics When possible, define limits What are the device characteristics? This is where design inputs do double duty for risk assessment and design control ID of hazards: How can it fail, break or hurt someone? Estimation of risk for hazards Bring your medical device to market faster 20
21 How to start the analysis: Questions to Ask (ISO Annex C) Intended use? Will the device be implanted? Will device be in contact with patient or other people? Is energy delivered or extracted from the patient? Is a substance delivered or extracted from the patient? Are biological materials processed by device for subsequent re-use? How is the device sterilized? Will device be routinely cleaned? Will medical device modify patient enviromentment? Bring your medical device to market faster 21
22 More questions Are measurements taken? Is device interpretative? Does device work with other devices? Are there unwanted outputs of energy or substances? Susceptible to environmental influence (ex: vibrations, spills) Does device influence environment? (radiation, etc ) Does device have consumables? Is maintanence or calibration necessary? Is there software? Bring your medical device to market faster 22
23 Still more questions. Is there a restricted shelf life? Are there delayed or long term use effects? Will it be subject to mechanical forces? What determines lifetime of device (batteries?) Is the device intended for single use? How should the device be decommissioned or disposed of? Does installation or use require special training? How will the info for safe use be provided? Will a new manufacturing process need to be established? Bring your medical device to market faster 23
24 Questions, questions, questions Is successful use dependent on human factors? Can the user interface contribute to user error? Can distractions cause use errors? Are there connecting parts or accessories? (External fixation) Is there a control interface? Does device display information? Is device controlled by a menu? Will device be used by a person with special needs? Can user interface be used to initiate user actions? Bring your medical device to market faster 24
25 Are we done with questions? Is there an alarm system? Can the device be deliberately misused? Does the device hold data critical to patient care? Is device mobile or portable? Bring your medical device to market faster 25
26 Scoring the risk Bring your medical device to market faster 26
27 Tools for Evaluating Risk Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) Failure Mode Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) Bring your medical device to market faster 27
28 Fault Tree Analysis First identify a failure or safety hazard Next identify all possible ways to create hazard For example: Hazard = Electrical Shock How could this happen Transformer failure Safety Ground Failure Bring your medical device to market faster 28
29 Fault Tree Analysis Bring your medical device to market faster 29
30 What is an FMEA? Failure Mode Effects Analysis Goal: Eliminate failures before they happen Does not require complicated statistical analysis Does require human resource and time Focused on: Preventing defects Enhancing Safety Increasing Customer Satisfaction Bring your medical device to market faster 30
31 FMEA / FMECA FMECA Same as FMEA with addition of criticality and often used interchangably Assumes defect at component level Assess the effect Identifies Potential Solutions Bring your medical device to market faster 31
32 FMEA When should this be performed? When to perform Beginning of design effort Part of EACH design review Through the life cycle of device Types Design FMEA: Focuses on what could go wrong with a product in both manufacturing operation and in service as a result of a weakness in the design Process FMEA: Concentrates on reasons for potential failure during manufacturing and in service System FMEA: Looks for potential problems and bottlenecks in larger processes, such as production lines Bring your medical device to market faster 32
33 FMEA Teams Team leader: Guides team through process, keeps notes, organizes Often 4 to 6 team members Design / Process engineer End users Sales / Marketing People familiar with product / process AND unfamiliar individuals with fresh perspectives Bring your medical device to market faster 33
34 Steps of FMEA Review design Brainstorm failure modes List effects of failure (device and patient) Assign a severity, occurrence and detection rating Calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN) Prioritize failure modes based on RPN Take action to eliminate or reduce high risk failures Calculate new RPN Repeat corrective actions if necessary Bring your medical device to market faster 34
35 Estimating Risk Severity of occurrence Probability or likelihood of occurrence Detection of occurrence Bring your medical device to market faster 35
36 Severity: Safety vs Functional RATING Patient Safety Severity Evaluation Criteria No Health Hazard: No physical effect of the physiological complaints anticipated Limited Health Hazard: Extended Procedure Time Physiological complaints Temporary minor physical effect Moderate Health Hazard: Additional procedure required Temporary but significant physical effects Permanent minor physical effects Severe Health Hazard: Permanent significant physical effects Catastrophic: Life Threatening RATING Device Functionality Severity Evaluation Criteria Insignificant: Cosmetic defect The failure will not have any perceptible effect on the performance of the product Low Significance: User nuisance Dissatisfaction on the part of the end user Product may be operable at reduced performance Moderate Significance: Compromised function / loss of minor function The user may notice a negative impact on the product or system performance High Significance: Compromised function / loss of major function Loss of system function - device completely unusable Extreme Significance: Regulatory issue Involves non-compliance with government regulations Bring your medical device to market faster 36
37 Design FMEA Rating: Occurence RATING Occurrence Evaluation Criteria for Design FMEA Qualitative Approach : Probability of Failure due to specific cause 1 Remote: Failure unlikely 2 Low: Relatively few 3 Moderate: Occasional 4 High: Repeated failures 5 Extreme: Almost inevitable Probability: Qualitative vs Quantitative Better to have a very accurate qualitative definition versus an inaccurate quantitative description. Bring your medical device to market faster 37
38 Design FMEA rating: Detection RATING Detection Evaluation Criteria for Design FMEA Failure Mode likely to be detected during: 1 Prototype / Sample Production Design house work Design Verification and Validation Benchtop testing or cadaver studies 2 3 Process Validation Manufacturing facility validation for consistent product. 4 Initial Clinical Use After implanted in humans 5 After Commercialization after mass production and use (this is FDA reportable event) Bring your medical device to market faster 38
39 Is risk acceptable? Bring your medical device to market faster 39
40 Acceptable risk continued Bring your medical device to market faster 40
41 Bring your medical device to market faster 41
42 Now, what do you do about the risk? Bring your medical device to market faster 42
43 Risk Control Control options Implementation of control measures Residual risk evaluation Risk / Benefit analysis Risk from control measures Completeness of risk control Bring your medical device to market faster 43
44 Risk Control Can the risk be reduced? How best can the risk be controlled? Design of device (best) Protective measures Information on safety Once risk control measures have been identified, they must be implemented and evaluated for effectiveness. Bring your medical device to market faster 44
45 Risk Control Redesign Add protective measure Provide safety information Bring your medical device to market faster 45
46 Has the risk control worked? Bring your medical device to market faster 46
47 Implementation of Risk Control Verification Verification is required to: Make sure risk control has been implemented in the final design. To ensure the measure, as implemented, actually reduces risk. Bring your medical device to market faster 47
48 Identification of Hazards Vary vague in ISO manufacturer shall compile documentation Common ways of identifying hazards: Fault tree Hazards Analysis Bring your medical device to market faster 48
49 Is the remaining risk acceptable? Bring your medical device to market faster 49
50 Remaining Risk Residual risk evaluation Is the risk acceptable? Can the risk be reduced (decrease severity, occurrence or detection)? Risk / Benefit Analysis Is the benefit worth the risk when further risk mitigation is not possible or practical? New Risks arising from risk management Completeness of Risk Control For example, maybe there are not electrical risks to your device but you may want to consider documenting that fact. Bring your medical device to market faster 50
51 Residual Risk: Moving from weeds to balcony Broad perspective What do you do about the remaining risk? Low as reasonably practicable approach Does benefit outweigh risk? Bring your medical device to market faster 51
52 Communication, communication, communication. Did I mention communication? Bring your medical device to market faster 52
53 Risk Management Report High level document that provides evidence that plan has been fulfilled and objective achieved Prior to release for commercial distribution Has RM been appropriately implemented? Is overall residual risk acceptable? Are appropriate methods in place to obtain relevant production and post-production information? Report needs to be reviewed by appropriate personelle. Bring your medical device to market faster 53
54 Production and Post Production Information Must collect and review information about the medical device during production and post production phases. Consider things like: Installation Use Maintenance Should collect and review publicly available information about similar medical devices Is there an new or not considered risk? Bring your medical device to market faster 54
55 Basic concepts of risk management Identification of hazards Risk estimation Risk acceptability Risk control Risk / Benefit Analysis Overall risk evaluation Bring your medical device to market faster 55
56 Hazards arising from faults A fault does not always result in a hazardous situation A hazardous situation does not always result in harm. Types of Faults: Random Faults (electronic component fails) Systemic faults (fuse to prevent harm is at the wrong rating or an assay does not detect a new strain of a disease) Bring your medical device to market faster 56
57 Getting help Bring your medical device to market faster 57
58 Guidance for Conducting Risk Assessments ANSI/AAMI/ISO Defines 3 regions of risk Broadly acceptable region ALARP Region Intolerable region FDA Guidance for Industry: Incorporating human factors engineering in risk management FDA Guidance for Industry: Premarketing Risk Assessment (specifically for drug products including biological drug products FDA Guidance for Industry: Design Control for Medical Device Manufacturers Speaks to design review and risk assessment is an important part of design review Bring your medical device to market faster 58
59 ISO The manufacturer shall establish, document, and maintain throughout the lifecycle an ongoing process for identifying hazards associated with a medical device, estimating and evaluating associated risks, controlling these risks and monitoring the effectiveness of controls and shall include: Risk analysis Risk evaluation Risk Control Production and post production information Bring your medical device to market faster 59
60 Insights for the trenches Bring your medical device to market faster 60
61 Biggest Mistakes We See Risk assessment as an afterthought Static document versus living document It shouldn t be just a checked off item for FDA Team assigned to perform FMEA Not diverse Too close to design Not using a yellow light as a warning Bring your medical device to market faster 61
62 Scoring Changes Depending on Phase of Lifecycle RATING Detection Evaluation Criteria for Design FMEA Failure Mode likely to be detected during: Prototype / Sample Production Design Verification and Validation Process Validation Initial Clinical Use After Commercialization RATING Detection Evaluation Criteria for Process FMEA Failure Mode likely to be detected during: Remote probability of leaving manufacturing area containing the defect. Obvious defect. Low probability of product leaving the manufacturing area containing the defect. Defect easily detectable. Moderate probability of product leaving the manufacturing area containing the defect. Defect is somewhat more difficult to detect. High probability of product leaving the manufacturing area containing the defect. Detection requires special inspection. Very high probability of product leaving manufacturing area with defect. Defect may not be found with sophisticated detection techniques. Bring your medical device to market faster 62
63 Risk Assessment of Human Factors Devices used in ways not anticipated Device used in anticipated way that was not properly controlled Device is inconsistent with user s intuition on how it should work Bring your medical device to market faster 63
64 Details of Analysis Component level Combination level Effect of sequence of events Bring your medical device to market faster 64
65 When is risk management finished? Never as long as your device is available There are mistakes you will not find until it has been used and abused. Part of a RM plan is to make sure management is evaluating risk on a reasonable schedule. Must have a plan to act swiftly if something unexpected happens Bring your medical device to market faster 65
66 Risk Assessment Good for device and company Making sure Design, Regulatory and Manufacturing are on the same page Bring your medical device to market faster 66
ISO 14971: Overview of the standard
 FDA Medical Device Industry Coalition ISO 14971: Overview of the standard Risk Management Through Product Life Cycle: An Educational Forum William A. Hyman Department of Biomedical Engineering Texas A&M
FDA Medical Device Industry Coalition ISO 14971: Overview of the standard Risk Management Through Product Life Cycle: An Educational Forum William A. Hyman Department of Biomedical Engineering Texas A&M
Medical Software Development. International standards requirements and practice
 Medical Software Development International standards requirements and practice Food and Drug Administration What? A public health agency Why? Protect American consumers How? By enforcing the Federal Food,
Medical Software Development International standards requirements and practice Food and Drug Administration What? A public health agency Why? Protect American consumers How? By enforcing the Federal Food,
Risk Assessment and Management. Allen L. Burgenson Manager, Regulatory Affairs Lonza Walkersville Inc.
 Risk Assessment and Management Allen L. Burgenson Manager, Regulatory Affairs Lonza Walkersville Inc. Standard Disclaimer Standard Disclaimer: This presentation is the opinion of the presenter, and does
Risk Assessment and Management Allen L. Burgenson Manager, Regulatory Affairs Lonza Walkersville Inc. Standard Disclaimer Standard Disclaimer: This presentation is the opinion of the presenter, and does
Risk Assessment Tools for Identifying Hazards and Evaluating Risks Associated with IVD Assays
 Risk Assessment Tools for Identifying Hazards and Evaluating Risks Associated with IVD Assays Robert C. Menson, PhD AACC Annual Meeting Philadelphia, PA 22 July 2003 What Risks Must Be Managed? Risk to
Risk Assessment Tools for Identifying Hazards and Evaluating Risks Associated with IVD Assays Robert C. Menson, PhD AACC Annual Meeting Philadelphia, PA 22 July 2003 What Risks Must Be Managed? Risk to
Software-based medical devices from defibrillators
 C O V E R F E A T U R E Coping with Defective Software in Medical Devices Steven R. Rakitin Software Quality Consulting Inc. Embedding defective software in medical devices increases safety risks. Given
C O V E R F E A T U R E Coping with Defective Software in Medical Devices Steven R. Rakitin Software Quality Consulting Inc. Embedding defective software in medical devices increases safety risks. Given
Title: Basic Principles of Risk Management for Medical Device Design
 Title: Basic Principles of Risk Management for Medical Device Design WHITE PAPER Author: Ganeshkumar Palanichamy Abstract Medical devices developed for human application are used for diagnostic or treatment
Title: Basic Principles of Risk Management for Medical Device Design WHITE PAPER Author: Ganeshkumar Palanichamy Abstract Medical devices developed for human application are used for diagnostic or treatment
QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT (QRM): A REVIEW
 Lotlikar et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 2013, 3(2), 149-154 149 Available online at http://jddtonline.info REVIEW ARTICLE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT (QRM): A REVIEW Lotlikar MV Head Corporate
Lotlikar et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 2013, 3(2), 149-154 149 Available online at http://jddtonline.info REVIEW ARTICLE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT (QRM): A REVIEW Lotlikar MV Head Corporate
Life Sciences Product Development Artifacts Survey Results
 Life Sciences Product Development Artifacts Survey Results White Paper About the Survey Seapine Software conducted this survey over a six-week period during the first quarter of 2011. A total of 150 respondents
Life Sciences Product Development Artifacts Survey Results White Paper About the Survey Seapine Software conducted this survey over a six-week period during the first quarter of 2011. A total of 150 respondents
Quality Risk Management Tools Quality Risk Management Tool Selection When to Select FMEA: QRM Tool Selection Matrix
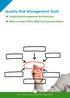 Quality Risk Management Tools Quality Risk Management Tool Selection When to Select FMEA: QRM Tool Selection Matrix 26 Quality Risk Management Tools The ICH Q9 guideline, Quality Risk Management, provides
Quality Risk Management Tools Quality Risk Management Tool Selection When to Select FMEA: QRM Tool Selection Matrix 26 Quality Risk Management Tools The ICH Q9 guideline, Quality Risk Management, provides
Best Practice In A Change Management System
 Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Best Practice In A Change Management System President Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Change Control and Its Role in a Continuous Improvement Environment 3 Benefits
Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Best Practice In A Change Management System President Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Change Control and Its Role in a Continuous Improvement Environment 3 Benefits
Quality Risk Management - The Medical Device Experience. Niamh Nolan Principal Design Assurance Engineer Boston Scientific
 Quality Risk Management - The Medical Device Experience Niamh Nolan Principal Design Assurance Engineer Boston Scientific Agenda Intent of Risk Management (RM) and Associated Regulations Overview of RM
Quality Risk Management - The Medical Device Experience Niamh Nolan Principal Design Assurance Engineer Boston Scientific Agenda Intent of Risk Management (RM) and Associated Regulations Overview of RM
Improved Utilization of Self-Inspection Programs within the GMP Environment A Quality Risk Management Approach
 Improved Utilization of Self-Inspection Programs within the GMP Environment A Quality Risk Management Approach Barbara Jeroncic Self-inspection is a well-established and vital part of the pharmaceutical
Improved Utilization of Self-Inspection Programs within the GMP Environment A Quality Risk Management Approach Barbara Jeroncic Self-inspection is a well-established and vital part of the pharmaceutical
FINAL DOCUMENT. Implementation of risk management principles and activities within a Quality Management System. The Global Harmonization Task Force
 GHTF/SG3/N15R8 FINAL DOCUMENT Title: Implementation of risk management principles and activities within a Quality Management System Authoring Group: GHTF Study Group 3 Endorsed by: The Global Harmonization
GHTF/SG3/N15R8 FINAL DOCUMENT Title: Implementation of risk management principles and activities within a Quality Management System Authoring Group: GHTF Study Group 3 Endorsed by: The Global Harmonization
FDA Perspectives on Human Factors in Device Development
 FDA Perspectives on in Device Development Molly Follette Story, PhD FDA /CDRH / ODE Understanding Regulatory Requirements for Usability Testing RAPS Webinar June 7, 2012 Overview What are human factors
FDA Perspectives on in Device Development Molly Follette Story, PhD FDA /CDRH / ODE Understanding Regulatory Requirements for Usability Testing RAPS Webinar June 7, 2012 Overview What are human factors
RISK MANAGEMENT FOR INFRASTRUCTURE
 RISK MANAGEMENT FOR INFRASTRUCTURE CONTENTS 1.0 PURPOSE & SCOPE 2.0 DEFINITIONS 3.0 FLOWCHART 4.0 PROCEDURAL TEXT 5.0 REFERENCES 6.0 ATTACHMENTS This document is the property of Thiess Infraco and all
RISK MANAGEMENT FOR INFRASTRUCTURE CONTENTS 1.0 PURPOSE & SCOPE 2.0 DEFINITIONS 3.0 FLOWCHART 4.0 PROCEDURAL TEXT 5.0 REFERENCES 6.0 ATTACHMENTS This document is the property of Thiess Infraco and all
Software Development for Medical Devices
 Software Development for Medical Devices Overcoming the Challenges of Compliance, Quality and Cost Software is fast becoming the differentiator for manufacturers of medical devices. The rewards of software
Software Development for Medical Devices Overcoming the Challenges of Compliance, Quality and Cost Software is fast becoming the differentiator for manufacturers of medical devices. The rewards of software
QA GLP audits. Alain Piton. Antipolis,, France. alain.piton@galderma.com
 Risk based assessment applied to QA GLP audits Alain Piton Galderma R&D, Sophia-Antipolis Antipolis,, France alain.piton@galderma.com RISK BASED ASSESSMENT FOR GLP AUDITS INTRODUCTION Since the origin
Risk based assessment applied to QA GLP audits Alain Piton Galderma R&D, Sophia-Antipolis Antipolis,, France alain.piton@galderma.com RISK BASED ASSESSMENT FOR GLP AUDITS INTRODUCTION Since the origin
How To Validate Software
 General Principles of Software Validation; Final Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff Document issued on: January 11, 2002 This document supersedes the draft document, "General Principles of Software Validation,
General Principles of Software Validation; Final Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff Document issued on: January 11, 2002 This document supersedes the draft document, "General Principles of Software Validation,
Media fills Periodic performance qualification (Re-Validation)
 Media fills Periodic performance qualification (Re-Validation) Minimum number of Simulations Number of units Contaminated Units Action a Two per Year (Retrospective & Prospective Validation) < 5000 5000
Media fills Periodic performance qualification (Re-Validation) Minimum number of Simulations Number of units Contaminated Units Action a Two per Year (Retrospective & Prospective Validation) < 5000 5000
How To Write Software
 1 Medical Device Software - Software Life Cycle Processes IEC 62304 2 Credits John F. Murray Software Compliance Expert U.S. Food and Drug Administration Marcie R. Williams Medical Device Fellow Ph.D.
1 Medical Device Software - Software Life Cycle Processes IEC 62304 2 Credits John F. Murray Software Compliance Expert U.S. Food and Drug Administration Marcie R. Williams Medical Device Fellow Ph.D.
Software Development for Medical Devices
 Overcoming the Challenges of Compliance, Quality and Cost An MKS White Paper Introduction Software is fast becoming the differentiator for manufacturers of medical devices. The rewards available from software
Overcoming the Challenges of Compliance, Quality and Cost An MKS White Paper Introduction Software is fast becoming the differentiator for manufacturers of medical devices. The rewards available from software
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry Q9 Quality Risk Management U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
Guidance for Industry Q9 Quality Risk Management U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
Risk Management and the Impact of EN ISO 14971:2012 Annex Z
 Risk Management and the Impact of EN ISO 14971:2012 Annex Z BSI 2014 Medical Device Mini-Roadshow Ibim Tariah Ph.D Technical Director, Healthcare Solutions Copyright 2014 BSI. All rights reserved. 1 Risk
Risk Management and the Impact of EN ISO 14971:2012 Annex Z BSI 2014 Medical Device Mini-Roadshow Ibim Tariah Ph.D Technical Director, Healthcare Solutions Copyright 2014 BSI. All rights reserved. 1 Risk
Quality Risk Management ICH Q9 & ISO 14971. Presented by Michael Kerr 11 th November 2011
 Quality Risk Management ICH Q9 & ISO 14971 Presented by Michael Kerr 11 th November 2011 Agenda Risk Concept QRM Fundamentals Regulatory Expectations Warning Letters / Observations Application of QRM Introduction:
Quality Risk Management ICH Q9 & ISO 14971 Presented by Michael Kerr 11 th November 2011 Agenda Risk Concept QRM Fundamentals Regulatory Expectations Warning Letters / Observations Application of QRM Introduction:
The FDA Perspective on Human Factors in Medical Device Software Development
 The FDA Perspective on in Medical Device Development Molly Follette Story, PhD FDA /CDRH / ODE 2012 IQPC Design for Medical Devices Europe Munich, Germany Februar y1, 2012 Overview Guidance for FDA premarket
The FDA Perspective on in Medical Device Development Molly Follette Story, PhD FDA /CDRH / ODE 2012 IQPC Design for Medical Devices Europe Munich, Germany Februar y1, 2012 Overview Guidance for FDA premarket
Quality Risk Management in Pharmaceutical Industry: A Review
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.6, No.3, pp 908-914, July-Aug 2014 Quality Risk Management in Pharmaceutical Industry: A Review V Vijayakumar Reddy*,
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.6, No.3, pp 908-914, July-Aug 2014 Quality Risk Management in Pharmaceutical Industry: A Review V Vijayakumar Reddy*,
Overview of Medical Device Design Controls in the US. By Nandini Murthy, MS, RAC
 Overview of Medical Device Controls in the US By Nandini Murthy, MS, RAC 18 controls are a regulatory requirement for medical devices. In the US, compliance with the design controls section of 21 Code
Overview of Medical Device Controls in the US By Nandini Murthy, MS, RAC 18 controls are a regulatory requirement for medical devices. In the US, compliance with the design controls section of 21 Code
Developing a Mobile Medical App? How to determine if it is a medical device and get it cleared by the US FDA
 Developing a Mobile Medical App? How to determine if it is a medical device and get it cleared by the US FDA In this presentation: App stats: Explosive growth Examples already cleared by the US FDA Is
Developing a Mobile Medical App? How to determine if it is a medical device and get it cleared by the US FDA In this presentation: App stats: Explosive growth Examples already cleared by the US FDA Is
Controlling Risks Risk Assessment
 Controlling Risks Risk Assessment Hazard/Risk Assessment Having identified the hazards, one must assess the risks by considering the severity and likelihood of bad outcomes. If the risks are not sufficiently
Controlling Risks Risk Assessment Hazard/Risk Assessment Having identified the hazards, one must assess the risks by considering the severity and likelihood of bad outcomes. If the risks are not sufficiently
Safety Risk Management in RT: A Software Manufacturer Perspective
 Safety Risk Management in RT: A Software Manufacturer Perspective Jim Schewe, Ph.D. Philips Radiation Oncology Systems AAPM Spring Clinical Meeting March 16, 2014 1 Learning Objectives For the session
Safety Risk Management in RT: A Software Manufacturer Perspective Jim Schewe, Ph.D. Philips Radiation Oncology Systems AAPM Spring Clinical Meeting March 16, 2014 1 Learning Objectives For the session
FMEA and FTA Analysis
 FMEA and FTA Analysis Why it is Coming to Your Hospital and Your Laboratory Tina A. Krenc Director, R&D Phase Systems Abbott Laboratories 1 Agenda Background on requirements for risk management Tools to
FMEA and FTA Analysis Why it is Coming to Your Hospital and Your Laboratory Tina A. Krenc Director, R&D Phase Systems Abbott Laboratories 1 Agenda Background on requirements for risk management Tools to
Controlling Risks Safety Lifecycle
 Controlling Risks Safety Lifecycle Objective Introduce the concept of a safety lifecycle and the applicability and context in safety systems. Lifecycle Management A risk based management plan for a system
Controlling Risks Safety Lifecycle Objective Introduce the concept of a safety lifecycle and the applicability and context in safety systems. Lifecycle Management A risk based management plan for a system
MEDICAL DEVICE GUIDANCE
 May 2014 MEDICAL DEVICE GUIDANCE GN-23: Guidance on Labelling for Medical Devices PREFACE This document is intended to provide general guidance. Although we have tried to ensure that the information contained
May 2014 MEDICAL DEVICE GUIDANCE GN-23: Guidance on Labelling for Medical Devices PREFACE This document is intended to provide general guidance. Although we have tried to ensure that the information contained
QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT Q9 Current Step 4 version
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT Q9 Current Step 4 version
Quality Risk Management
 PS/INF 1/2010 * * Quality Risk Management Quality Risk Management Implementation of ICH Q9 in the pharmaceutical field an example of methodology from PIC/S Document > Authors: L. Viornery (AFSSAPS) Ph.
PS/INF 1/2010 * * Quality Risk Management Quality Risk Management Implementation of ICH Q9 in the pharmaceutical field an example of methodology from PIC/S Document > Authors: L. Viornery (AFSSAPS) Ph.
Quality Risk Management Understanding and Control the Risk in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Industry
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 4 Issue 1 January 2015 PP.29-41 Quality Risk Management Understanding and Control the
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 4 Issue 1 January 2015 PP.29-41 Quality Risk Management Understanding and Control the
Implementation of ANSI/AAMI/IEC 62304 Medical Device Software Lifecycle Processes.
 Implementation of ANSI/AAMI/IEC 62304 Medical Device Software Lifecycle Processes.. www.pharmout.net Page 1 of 15 Version-02 1. Scope 1.1. Purpose This paper reviews the implementation of the ANSI/AAMI/IEC
Implementation of ANSI/AAMI/IEC 62304 Medical Device Software Lifecycle Processes.. www.pharmout.net Page 1 of 15 Version-02 1. Scope 1.1. Purpose This paper reviews the implementation of the ANSI/AAMI/IEC
3.0 Risk Assessment and Analysis Techniques and Tools
 3.0 Risk Assessment and Analysis Techniques and Tools Risks are determined in terms of the likelihood that an uncontrolled event will occur and the consequences of that event occurring. Risk = Likelihood
3.0 Risk Assessment and Analysis Techniques and Tools Risks are determined in terms of the likelihood that an uncontrolled event will occur and the consequences of that event occurring. Risk = Likelihood
State of Medical Device Development. 2014 State of Medical Device Development seapine.com 1
 State of Medical Device Development 2014 2014 State of Medical Device Development seapine.com 1 Executive Summary The demand for smarter, safer, more connected medical devices has introduced new complexities
State of Medical Device Development 2014 2014 State of Medical Device Development seapine.com 1 Executive Summary The demand for smarter, safer, more connected medical devices has introduced new complexities
IVD Regulation Overview. Requirements to Assure Quality & Effectiveness
 IVD Regulation Overview Requirements to Assure Quality & Effectiveness CLIAC Jan. 2002 Statutory and Regulatory Requirements Statute: Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act Food and Drugs Act of 1906 Food and Drug
IVD Regulation Overview Requirements to Assure Quality & Effectiveness CLIAC Jan. 2002 Statutory and Regulatory Requirements Statute: Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act Food and Drugs Act of 1906 Food and Drug
Design Verification The Case for Verification, Not Validation
 Overview: The FDA requires medical device companies to verify that all the design outputs meet the design inputs. The FDA also requires that the final medical device must be validated to the user needs.
Overview: The FDA requires medical device companies to verify that all the design outputs meet the design inputs. The FDA also requires that the final medical device must be validated to the user needs.
Risk Management in IEC 60601-1 3 rd Edition. Presented by Alberto Paduanelli Medical Devices Lead Auditor, MHS-UK, TÜV SÜD Product Service
 Risk Management in IEC 60601-1 3 rd Edition Presented by Alberto Paduanelli Medical Devices Lead Auditor, MHS-UK, TÜV SÜD Product Service General Information Time of presentation: 50-60 min. Questions
Risk Management in IEC 60601-1 3 rd Edition Presented by Alberto Paduanelli Medical Devices Lead Auditor, MHS-UK, TÜV SÜD Product Service General Information Time of presentation: 50-60 min. Questions
Effective Software Verification for Medical Devices
 STERLINGTECH AND KLOCWORK WHITE PAPER NOVEMBER 2009 Effective Software Verification for Medical Devices Achieving compliance and meeting productivity goals with static analysis In addition to producing
STERLINGTECH AND KLOCWORK WHITE PAPER NOVEMBER 2009 Effective Software Verification for Medical Devices Achieving compliance and meeting productivity goals with static analysis In addition to producing
University of Paderborn Software Engineering Group II-25. Dr. Holger Giese. University of Paderborn Software Engineering Group. External facilities
 II.2 Life Cycle and Safety Safety Life Cycle: The necessary activities involving safety-related systems, occurring during a period of time that starts at the concept phase of a project and finishes when
II.2 Life Cycle and Safety Safety Life Cycle: The necessary activities involving safety-related systems, occurring during a period of time that starts at the concept phase of a project and finishes when
Guidance for Industry: Quality Risk Management
 Guidance for Industry: Quality Risk Management Version 1.0 Drug Office Department of Health Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this document... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. What is risk?... 4 5. Integrating
Guidance for Industry: Quality Risk Management Version 1.0 Drug Office Department of Health Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this document... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. What is risk?... 4 5. Integrating
FMEA Failure Risk Scoring Schemes
 FMEA Failure Risk Scoring Schemes 1-10 Scoring for Severity, Occurrence and Detection CATEGORY Severity 10 9 8 7 6 5 3 2 1 Hazardous, without warning Hazardous, with warning Very High High Moderate Low
FMEA Failure Risk Scoring Schemes 1-10 Scoring for Severity, Occurrence and Detection CATEGORY Severity 10 9 8 7 6 5 3 2 1 Hazardous, without warning Hazardous, with warning Very High High Moderate Low
General Principles of Software Validation; Final Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff
 General Principles of Software Validation; Final Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff Document issued on: January 11, 2002 This document supersedes the draft document, "General Principles of Software Validation,
General Principles of Software Validation; Final Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff Document issued on: January 11, 2002 This document supersedes the draft document, "General Principles of Software Validation,
Failure Analysis Methods What, Why and How. MEEG 466 Special Topics in Design Jim Glancey Spring, 2006
 Failure Analysis Methods What, Why and How MEEG 466 Special Topics in Design Jim Glancey Spring, 2006 Failure Analysis Methods Every product or process has modes of failure. An analysis of potential failures
Failure Analysis Methods What, Why and How MEEG 466 Special Topics in Design Jim Glancey Spring, 2006 Failure Analysis Methods Every product or process has modes of failure. An analysis of potential failures
A Risk Management Capability Model for use in Medical Device Companies
 A Risk Management Capability Model for use in Medical Device Companies John Burton Vitalograph Ltd. Gort Rd. Business Park Ennis Ireland 353.65.686471 john.burton@vitalograph.ie Fergal Mc Caffery Lero
A Risk Management Capability Model for use in Medical Device Companies John Burton Vitalograph Ltd. Gort Rd. Business Park Ennis Ireland 353.65.686471 john.burton@vitalograph.ie Fergal Mc Caffery Lero
FINAL DOCUMENT. Global Harmonization Task Force
 FINAL DOCUMENT Global Harmonization Task Force Title: Quality management system Medical Devices Guidance on corrective action and preventive action and related QMS processes Authoring Group: Study Group
FINAL DOCUMENT Global Harmonization Task Force Title: Quality management system Medical Devices Guidance on corrective action and preventive action and related QMS processes Authoring Group: Study Group
Quality Assurance Manual
 Quality Assurance Manual Revised April 30, 2014 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. All product names are trademarks
Quality Assurance Manual Revised April 30, 2014 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. All product names are trademarks
US Perspective on the Regulatory Assessment of Benefit-Risk of Vaccines
 US Perspective on the Regulatory Assessment of Benefit-Risk of Vaccines Norman W. Baylor Biologics Consulting Group, Inc. 23-25 June 2014 Foundation Merieux Conference Center OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION Introduction
US Perspective on the Regulatory Assessment of Benefit-Risk of Vaccines Norman W. Baylor Biologics Consulting Group, Inc. 23-25 June 2014 Foundation Merieux Conference Center OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION Introduction
Reliability Analysis A Tool Set for. Aron Brall
 Reliability Analysis A Tool Set for Improving Business Processes Aron Brall ManTech International 1 Introduction Outline Defining Business Process Reliability Quantifying Business Process Reliability Business
Reliability Analysis A Tool Set for Improving Business Processes Aron Brall ManTech International 1 Introduction Outline Defining Business Process Reliability Quantifying Business Process Reliability Business
Annex 2. WHO guidelines on quality risk management. 1. Introduction 62. 2. Glossary 67 3. Quality risk management process 70
 Annex 2 WHO guidelines on quality risk management 1. Introduction 62 1.1 Background and scope 62 1.2 Principles of quality risk management 64 2. Glossary 67 3. Quality risk management process 70 3.1 Initiating
Annex 2 WHO guidelines on quality risk management 1. Introduction 62 1.1 Background and scope 62 1.2 Principles of quality risk management 64 2. Glossary 67 3. Quality risk management process 70 3.1 Initiating
Edwin Lindsay Principal Consultant. Compliance Solutions (Life Sciences) Ltd, Tel: + 44 (0) 7917134922 E-Mail: elindsay@blueyonder.co.
 Edwin Lindsay Principal Consultant, Tel: + 44 (0) 7917134922 E-Mail: elindsay@blueyonder.co.uk There were no guidelines/ regulations There was no training No Procedures No Inspectors Inform All staff of
Edwin Lindsay Principal Consultant, Tel: + 44 (0) 7917134922 E-Mail: elindsay@blueyonder.co.uk There were no guidelines/ regulations There was no training No Procedures No Inspectors Inform All staff of
CONCEPTS OF FOOD SAFETY QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. Mrs. Malini Rajendran
 CONCEPTS OF FOOD SAFETY AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Mrs. Malini Rajendran Brief background 1963 - The Codex Alimentarius Commission was created by FAO and WHO to develop food standards, guidelines and
CONCEPTS OF FOOD SAFETY AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Mrs. Malini Rajendran Brief background 1963 - The Codex Alimentarius Commission was created by FAO and WHO to develop food standards, guidelines and
Mobile Medical Application Development: FDA Regulation
 Mobile Medical Application Development: FDA Regulation Mobile Medical Applications: Current Environment Currently over 100,000 mobile health related applications are available for download; there is an
Mobile Medical Application Development: FDA Regulation Mobile Medical Applications: Current Environment Currently over 100,000 mobile health related applications are available for download; there is an
Dealing with risk. Why is risk management important?
 Why is risk management important? Things don t always go according to plan: a company s sales manager changes employment in the middle of an important project, a packaging machine breaks down, a lathe
Why is risk management important? Things don t always go according to plan: a company s sales manager changes employment in the middle of an important project, a packaging machine breaks down, a lathe
TÜV Rheinland Functional Safety Program Functional Safety Engineer Certification
 TÜV Rheinland Functional Safety Program Functional Safety Engineer Certification The TÜV Rheinland Functional Safety Program is a unique opportunity to provide certified evidence of competency in functional
TÜV Rheinland Functional Safety Program Functional Safety Engineer Certification The TÜV Rheinland Functional Safety Program is a unique opportunity to provide certified evidence of competency in functional
Motivations. spm - 2014 adolfo villafiorita - introduction to software project management
 Risk Management Motivations When we looked at project selection we just took into account financial data In the scope management document we emphasized the importance of making our goals achievable, i.e.
Risk Management Motivations When we looked at project selection we just took into account financial data In the scope management document we emphasized the importance of making our goals achievable, i.e.
How to Use the Design Process to Manage Risk: Elements of Design Controls and Why It Matters
 environmental failure analysis & prevention health technology development How to Use the Design Process to Manage Risk: Elements of Design Controls and Why It Matters Kevin L. Ong, Ph.D., P.E. Managing
environmental failure analysis & prevention health technology development How to Use the Design Process to Manage Risk: Elements of Design Controls and Why It Matters Kevin L. Ong, Ph.D., P.E. Managing
Application of Quality Risk Management to Pharmaceutical Operations. Eldon Henson, Vice President, Quality Operations
 Application of Quality Risk Management to Pharmaceutical Operations Eldon Henson, Vice President, Quality Operations Key Topics of Discussion Definition of Quality Risk Management (QRM) Overview of PDA
Application of Quality Risk Management to Pharmaceutical Operations Eldon Henson, Vice President, Quality Operations Key Topics of Discussion Definition of Quality Risk Management (QRM) Overview of PDA
Quality Management System Manual
 Quality Management System Manual Assurance ISO / AS Manual Quality Management System EXCEEDING ALL EXPECTATIONS Since our inception in 1965, Swiss-Tech has supplied the medical, aerospace, hydraulic, electronic
Quality Management System Manual Assurance ISO / AS Manual Quality Management System EXCEEDING ALL EXPECTATIONS Since our inception in 1965, Swiss-Tech has supplied the medical, aerospace, hydraulic, electronic
GOOD DESIGN PRACTICE FOR MEDICAL DEVICES AND EQUIPMENT A FRAMEWORK
 GOOD DESIGN PRACTICE FOR MEDICAL DEVICES AND EQUIPMENT A FRAMEWORK By: Karen Alexander John Clarkson Engineering Centre, University of Cambridge and Duncan Bishop Stewart Fox Cambridge Consultants Limited
GOOD DESIGN PRACTICE FOR MEDICAL DEVICES AND EQUIPMENT A FRAMEWORK By: Karen Alexander John Clarkson Engineering Centre, University of Cambridge and Duncan Bishop Stewart Fox Cambridge Consultants Limited
WHITEPAPER: SOFTWARE APPS AS MEDICAL DEVICES THE REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
 WHITEPAPER: SOFTWARE APPS AS MEDICAL DEVICES THE REGULATORY LANDSCAPE White paper produced by Maetrics For more information, please contact global sales +1 610 458 9312 +1 877 623 8742 globalsales@maetrics.com
WHITEPAPER: SOFTWARE APPS AS MEDICAL DEVICES THE REGULATORY LANDSCAPE White paper produced by Maetrics For more information, please contact global sales +1 610 458 9312 +1 877 623 8742 globalsales@maetrics.com
Risk Assessment Worksheet and Management Plan
 Customer/Project Name: The Basics There are four steps to assessing and managing risks, and effective risk management requires all four of them. 1. Identify the risks 2. Qualify the risks a. Assess each
Customer/Project Name: The Basics There are four steps to assessing and managing risks, and effective risk management requires all four of them. 1. Identify the risks 2. Qualify the risks a. Assess each
Medical Product Software Development and FDA Regulations Software Development Practices and FDA Compliance
 Medical Product Development and FDA Regulations IEEE Orange County Computer Society March 27, 2006 Carl R. Wyrwa Medical Product Development and FDA Regulations Introduction Regulated FDA Overview Medical
Medical Product Development and FDA Regulations IEEE Orange County Computer Society March 27, 2006 Carl R. Wyrwa Medical Product Development and FDA Regulations Introduction Regulated FDA Overview Medical
Designing an Effective Risk Matrix
 Designing an Effective Risk Matrix HENRY OZOG INTRODUCTION Risk assessment is an effective means of identifying process safety risks and determining the most cost-effective means to reduce risk. Many organizations
Designing an Effective Risk Matrix HENRY OZOG INTRODUCTION Risk assessment is an effective means of identifying process safety risks and determining the most cost-effective means to reduce risk. Many organizations
JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 21/2012, ISSN 1642-6037
 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 21/2012, ISSN 1642-6037 FDA, medical software, recall, safety of medical devices. Leszek DREWNIOK 1, Ewelina PIEKAR 1, Mirosław STASIAK 1, Remigiusz MANIURA
JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 21/2012, ISSN 1642-6037 FDA, medical software, recall, safety of medical devices. Leszek DREWNIOK 1, Ewelina PIEKAR 1, Mirosław STASIAK 1, Remigiusz MANIURA
Project Risk Management. Presented by Stephen Smith
 Project Risk Management Presented by Stephen Smith Introduction Risk Management Insurance Business Financial Project Risk Management Project A temporary endeavour undertaken to create a unique product
Project Risk Management Presented by Stephen Smith Introduction Risk Management Insurance Business Financial Project Risk Management Project A temporary endeavour undertaken to create a unique product
Quality Risk Management The Pharmaceutical Experience Ann O Mahony Quality Assurance Specialist Pfizer Biotech Grange Castle
 Quality Risk Management 11 November 2011 Galway, Ireland Quality Risk Management The Pharmaceutical Experience Ann O Mahony Quality Assurance Specialist Pfizer Biotech Grange Castle Overview Regulatory
Quality Risk Management 11 November 2011 Galway, Ireland Quality Risk Management The Pharmaceutical Experience Ann O Mahony Quality Assurance Specialist Pfizer Biotech Grange Castle Overview Regulatory
Standard Operating Procedure Title: Quality Risk Management Techniques
 Department Quality Management Document no QMS-135 Title Quality Risk Management Techniques Prepared by: Date: Supersedes: Checked by: Date: Date Issued: Approved by: Date: Review Date: 1.0 Purpose This
Department Quality Management Document no QMS-135 Title Quality Risk Management Techniques Prepared by: Date: Supersedes: Checked by: Date: Date Issued: Approved by: Date: Review Date: 1.0 Purpose This
3.4.4 Description of risk management plan Unofficial Translation Only the Thai version of the text is legally binding.
 - 1 - Regulation of Department of Industrial Works Re: Criteria for hazard identification, risk assessment, and establishment of risk management plan B.E. 2543 (2000) ---------------------------- Pursuant
- 1 - Regulation of Department of Industrial Works Re: Criteria for hazard identification, risk assessment, and establishment of risk management plan B.E. 2543 (2000) ---------------------------- Pursuant
Empowering the Quality and Regulatory Compliance Functions
 Empowering the Quality and Regulatory Compliance Functions Management must take steps to ensure that regulatory and quality compliance is everyone s responsibility. By: J. Glenn George, Kenneth Imler,
Empowering the Quality and Regulatory Compliance Functions Management must take steps to ensure that regulatory and quality compliance is everyone s responsibility. By: J. Glenn George, Kenneth Imler,
Quality Risk Management Principles and Industry Case Studies
 Final Draft Rev. December 28, 2008 Quality Risk Management Principles and Industry Case Studies T. Frank 1, S. Brooks 2, R. Creekmore 3, B. Hasselbalch 4, K. Murray 5, K. Obeng 6, S. Reich 5, E. Sanchez
Final Draft Rev. December 28, 2008 Quality Risk Management Principles and Industry Case Studies T. Frank 1, S. Brooks 2, R. Creekmore 3, B. Hasselbalch 4, K. Murray 5, K. Obeng 6, S. Reich 5, E. Sanchez
The use of risk assessment tools for microbiological assessment of cleanroom environments. by Tim Sandle
 The use of risk assessment tools for microbiological assessment of cleanroom environments by Tim Sandle Email: tim.sandle@bpl.co.uk / timsandle@btinternet.com Web: www.pharmig.blogspot.com Environmental
The use of risk assessment tools for microbiological assessment of cleanroom environments by Tim Sandle Email: tim.sandle@bpl.co.uk / timsandle@btinternet.com Web: www.pharmig.blogspot.com Environmental
Document issued on: May 11, 2005
 Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff Guidance for the Content of Premarket Submissions for Software Contained in Medical Devices Document issued on: May 11, 2005 This document supersedes Guidance for the
Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff Guidance for the Content of Premarket Submissions for Software Contained in Medical Devices Document issued on: May 11, 2005 This document supersedes Guidance for the
CAPA - the importance of data analysis
 CAPA - the importance of data analysis Presented by: Sue Jacobs QMS Consulting, Inc. 1 847 359 4456 sue@qmsconsultant.com QMS Consulting, Inc. 2007 1 Topics Regulatory Requirements Design Controls and
CAPA - the importance of data analysis Presented by: Sue Jacobs QMS Consulting, Inc. 1 847 359 4456 sue@qmsconsultant.com QMS Consulting, Inc. 2007 1 Topics Regulatory Requirements Design Controls and
With the introduction of GAMP 5, A
 Online Exclusive from PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING The Official Magazine of ISPE January/February 2012, Vol. 32 No. 1 www.pharmaceuticalengineering.org Copyright ISPE 2012 This article presents the case
Online Exclusive from PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING The Official Magazine of ISPE January/February 2012, Vol. 32 No. 1 www.pharmaceuticalengineering.org Copyright ISPE 2012 This article presents the case
On-Site Risk Management Audit Checklist for Program Level 3 Process
 On-Site Risk Management Audit Checklist for Program Level 3 Process Auditor name: Date: I. Facility Information: Facility name: Facility location: County: Contact name: RMP Facility I.D. Phone Number:
On-Site Risk Management Audit Checklist for Program Level 3 Process Auditor name: Date: I. Facility Information: Facility name: Facility location: County: Contact name: RMP Facility I.D. Phone Number:
LSST Hazard Analysis Plan
 LSST Hazard Analysis Plan Large Synoptic Survey Telescope 950 N. Cherry Avenue Tucson, AZ 85719 www.lsst.org 1. REVISION SUMMARY: Contents 1 Introduction... 5 2 Definition of Terms... 5 2.1 System... 5
LSST Hazard Analysis Plan Large Synoptic Survey Telescope 950 N. Cherry Avenue Tucson, AZ 85719 www.lsst.org 1. REVISION SUMMARY: Contents 1 Introduction... 5 2 Definition of Terms... 5 2.1 System... 5
ASSESSMENT OF THE ISO 26262 STANDARD, ROAD VEHICLES FUNCTIONAL SAFETY
 ASSESSMENT OF THE ISO 26262 STANDARD, ROAD VEHICLES FUNCTIONAL SAFETY Dr. Qi Van Eikema Hommes SAE 2012 Government/Industry Meeting January 25, 2012 1 Outline ISO 26262 Overview Scope of the Assessment
ASSESSMENT OF THE ISO 26262 STANDARD, ROAD VEHICLES FUNCTIONAL SAFETY Dr. Qi Van Eikema Hommes SAE 2012 Government/Industry Meeting January 25, 2012 1 Outline ISO 26262 Overview Scope of the Assessment
Occupational safety risk management in Australian mining
 IN-DEPTH REVIEW Occupational Medicine 2004;54:311 315 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqh074 Occupational safety risk management in Australian mining J. Joy Abstract Key words In the past 15 years, there has been a
IN-DEPTH REVIEW Occupational Medicine 2004;54:311 315 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqh074 Occupational safety risk management in Australian mining J. Joy Abstract Key words In the past 15 years, there has been a
FDA Title 21 CFR Part 11:Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures; Final Rule (1997)
 www.qadata.co.za Introduction FDA Title 21 CFR Part 11:Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures; Final Rule (1997) INITIAL REGULATION RELEASED High profile audit findings Industry complaints to wasting
www.qadata.co.za Introduction FDA Title 21 CFR Part 11:Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures; Final Rule (1997) INITIAL REGULATION RELEASED High profile audit findings Industry complaints to wasting
Revision Date Author Description of change. 10 07Jun13 Mark Benton Removed Admin. Manager from approval
 Page 2 of 15 Document Revision History Revision Date Author Description of change 10 07Jun13 Mark Benton Removed Admin. Manager from approval 12Feb13 Mark Benton 08 01Oct12 Mark Benton 07 8/30/2012 Refer
Page 2 of 15 Document Revision History Revision Date Author Description of change 10 07Jun13 Mark Benton Removed Admin. Manager from approval 12Feb13 Mark Benton 08 01Oct12 Mark Benton 07 8/30/2012 Refer
4. Critical success factors/objectives of the activity/proposal/project being risk assessed
 ARTC Risk Management Work Instruction 2: 1. Conduct Risk Assessment Workshop This Work Instruction provides general guidelines for conducting a generic Risk Assessment workshop. The instructions supplement
ARTC Risk Management Work Instruction 2: 1. Conduct Risk Assessment Workshop This Work Instruction provides general guidelines for conducting a generic Risk Assessment workshop. The instructions supplement
Guide to Distribution of Cosmetic Products in Ireland
 Guide to Distribution of Cosmetic Products in Ireland ADV-G0012-2 17 JUNE 2013 This guide does not purport to be an interpretation of law and/or regulations and is for guidance purposes only. CONTENTS
Guide to Distribution of Cosmetic Products in Ireland ADV-G0012-2 17 JUNE 2013 This guide does not purport to be an interpretation of law and/or regulations and is for guidance purposes only. CONTENTS
FMEA and HACCP: A comparison. Steve Murphy Marc Schaeffers
 FMEA and HACCP: A comparison Steve Murphy Marc Schaeffers FMEA and HACCP: A comparison Introduction FMEA and Control planning is being used more and more in industry. In the food industry companies use
FMEA and HACCP: A comparison Steve Murphy Marc Schaeffers FMEA and HACCP: A comparison Introduction FMEA and Control planning is being used more and more in industry. In the food industry companies use
The purpose of this Supplier Quality Standard is to communicate the expectations and requirements of Baxter Healthcare Corporation to its suppliers.
 Supplier Quality Standard 1.0 Purpose The purpose of this Supplier Quality Standard is to communicate the expectations and requirements of Baxter Healthcare Corporation to its suppliers. These expectations
Supplier Quality Standard 1.0 Purpose The purpose of this Supplier Quality Standard is to communicate the expectations and requirements of Baxter Healthcare Corporation to its suppliers. These expectations
IEC 61508 Overview Report
 IEC 61508 Overview Report A Summary of the IEC 61508 Standard for Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-Related Systems exida Sellersville, PA 18960, USA +1-215-453-1720
IEC 61508 Overview Report A Summary of the IEC 61508 Standard for Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-Related Systems exida Sellersville, PA 18960, USA +1-215-453-1720
Corrective and Preventive Action Background & Examples Presented by:
 Corrective and Preventive Action Background & Examples Presented by: Kimberly Lewandowski-Walker Food and Drug Administration Division of Domestic Field Investigations Office of Regulatory Affairs Overview
Corrective and Preventive Action Background & Examples Presented by: Kimberly Lewandowski-Walker Food and Drug Administration Division of Domestic Field Investigations Office of Regulatory Affairs Overview
Risk Management and Cybersecurity for Devices that Contain Software. Seth D. Carmody, Ph.D. 12 th Medical Device Quality Congress March 18, 2015
 Risk Management and Cybersecurity for Devices that Contain Software Seth D. Carmody, Ph.D. 12 th Medical Device Quality Congress March 18, 2015 Main Points Establish a Cybersecurity Risk Management Program
Risk Management and Cybersecurity for Devices that Contain Software Seth D. Carmody, Ph.D. 12 th Medical Device Quality Congress March 18, 2015 Main Points Establish a Cybersecurity Risk Management Program
Usability of Medical Applications Ved Line Kagenow Svenstrup, lks@delta.dk
 Usability of Medical Applications Ved Line Kagenow Svenstrup, lks@delta.dk What is usability? The user, rather than the system, at the center of the process. Risk of operating errors that can cause injury
Usability of Medical Applications Ved Line Kagenow Svenstrup, lks@delta.dk What is usability? The user, rather than the system, at the center of the process. Risk of operating errors that can cause injury
Risk Management Primer
 Risk Management Primer Purpose: To obtain strong project outcomes by implementing an appropriate risk management process Audience: Project managers, project sponsors, team members and other key stakeholders
Risk Management Primer Purpose: To obtain strong project outcomes by implementing an appropriate risk management process Audience: Project managers, project sponsors, team members and other key stakeholders
Meeting your Electrical Safety Testing & Quality Requirements
 Meeting your Electrical Safety Testing & Quality Requirements Vincent Crabtree PhD Project Manager/Regulatory Advisor StarFish Medical 1 of 23 Contents 1. What are Standards and 60601? 2. Gap Analysis
Meeting your Electrical Safety Testing & Quality Requirements Vincent Crabtree PhD Project Manager/Regulatory Advisor StarFish Medical 1 of 23 Contents 1. What are Standards and 60601? 2. Gap Analysis
PACKAGING QUALITY ASSURANCE IN SUPPLY CHAIN
 PACKAGING QUALITY ASSURANCE IN SUPPLY CHAIN Agnieszka Cholewa-Wójcik, PhD Cracow University of Economics Rakowicka Street 27, 31-510 Kraków, Poland Phone: +48 122 935 167 E-mail: cholewaa@uek.krakow.pl
PACKAGING QUALITY ASSURANCE IN SUPPLY CHAIN Agnieszka Cholewa-Wójcik, PhD Cracow University of Economics Rakowicka Street 27, 31-510 Kraków, Poland Phone: +48 122 935 167 E-mail: cholewaa@uek.krakow.pl
(Refer Slide Time: 01:52)
 Software Engineering Prof. N. L. Sarda Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 2 Introduction to Software Engineering Challenges, Process Models etc (Part 2) This
Software Engineering Prof. N. L. Sarda Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 2 Introduction to Software Engineering Challenges, Process Models etc (Part 2) This
ELECTRICAL SAFETY RISK ASSESSMENT
 ELECTRICAL SAFETY RISK ASSESSMENT The intent of this procedure is to perform a risk assessment, which includes a review of the electrical hazards, the associated foreseeable tasks, and the protective measures
ELECTRICAL SAFETY RISK ASSESSMENT The intent of this procedure is to perform a risk assessment, which includes a review of the electrical hazards, the associated foreseeable tasks, and the protective measures
Intland s Medical Template
 Intland s Medical Template Traceability Browser Risk Management & FMEA Medical Wiki Supports compliance with IEC 62304, FDA Title 21 CFR Part 11, ISO 14971, IEC 60601 and more INTLAND codebeamer ALM is
Intland s Medical Template Traceability Browser Risk Management & FMEA Medical Wiki Supports compliance with IEC 62304, FDA Title 21 CFR Part 11, ISO 14971, IEC 60601 and more INTLAND codebeamer ALM is
ORACLE CONSULTING GROUP
 ORACLE CONSULTING GROUP An Official United States Agent Firm for Foreign Establishments CONSULTING MEMORANDUM: DEALING WITH A MEDICAL DEVICE IN THE U.S. 5398 Golder Ranch Rd., Ste. 1 Tucson, Arizona 85739
ORACLE CONSULTING GROUP An Official United States Agent Firm for Foreign Establishments CONSULTING MEMORANDUM: DEALING WITH A MEDICAL DEVICE IN THE U.S. 5398 Golder Ranch Rd., Ste. 1 Tucson, Arizona 85739
