The use of risk assessment tools for microbiological assessment of cleanroom environments. by Tim Sandle
|
|
|
- Nora Poole
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The use of risk assessment tools for microbiological assessment of cleanroom environments by Tim Sandle / Web: Environmental monitoring describes the microbiological testing undertaken in order to detect changing trends of microbial count and microflora within cleanroom or controlled environments. The results obtained provide information about the physical construction of the room, the performance of the HVAC system, personnel cleanliness, gowning practices, the equipment and cleaning operations. Over the past decade environmental monitoring has become more sophisticated in moving from random sampling, using an imaginary grid over the room and testing in each grid, to the current focus on risk assessment and the use of risk assessment tools to determine the most appropriate methods for environmental monitoring. A risk assessment procedure is required to determine locations for environmental monitoring. Such risk based approaches are recommended in ISO and regulatory authorities are increasingly asking drug manufacturers about this subject. Risk based approaches include FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis); FTA (Fault Tree Analysis) and HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points), all of which employ a scoring approach 1. At present, no definitive method exists and the various approaches differ in their process and the degree of complexity involved. However, the two most commonly used appear to be HACCP (which originated in the food industry) and FMEA (which was developed for the engineering industry) (Whyte and Eaton, 2004a). These various analytical tools are similar, in that they involve: Constructing diagrams of work flows Pin-pointing areas of greatest risk Examining potential sources of contamination Deciding on the most appropriate sample methods Helping to establish alert and action levels Taking into account changes to the work process / seasonal activities These risk assessment approaches are not only concerned with selecting environmental monitoring locations. They integrate the environmental monitoring system with a complete review of operations within the clean room to ensure those facilities, operations and practices are also satisfactory. The approaches recognise a 1 Other approaches include FMECA (Failure Mode Effect and Criticality Analysis); HAZOP (Hazard and Operational Studies); QMRA (Quantitative Microbiological Risk Assessment); MPRM (Modular Process Risk Model); SRA (System Risk Analysis); Method for Limitation of Risks and Risk Profiling.
2 risk, rate the level of the risk and then set out a plan to minimise, control and monitor the risk. The monitoring of the risk will help to determine the frequency, locations for and level of environmental monitoring (for example, refer to an article by Sandle [2003a], for a more detailed example). This paper explores an example from three different techniques: A simple conceptualisation of a risk using a table HACCP FMEA Example 1: The Tabular Approach An example of analysing the risks which environmental monitoring are designed to detect, through a simple table, would be: Area or Equipment: Sterility Testing Isolator Risk: Contamination due to build up of microbial counts in the isolator environment Failure or Situation: Failure to adequately clean after a use EFFECT Minimising the risk (Mitigations to reduce risk) Monitoring If isolators are not cleaned regularly there is a possibility of micro-organisms remaining in the environment. Cleaning surfaces using water to remove dirt or spillages prior to the application of a suitable disinfectant. The disinfectant used must have a wide spectrum of efficacy but not be aggressive to the isolator material. The isolator should be designed so that it is easy to clean. An environmental monitoring programme (using settle plates, air samples, contact plates, swabs and finger plates) will show the areas of greatest risk. This data should be examined for trends. For out-of-limits environmental monitoring results appropriate corrective and preventative actions should be put in place.
3 Example 2: HACCP The principles behind constructing an HACCP analysis are: 1. Identify hazards (contamination risks) and assess their severity. 2. Determine critical control points (CCP s) 3. Establish critical limits 4. Establish system to monitor control of the CCP s 5. Establish the corrective action (when CCP is not under control) 6. Establish procedures for verification to confirm that the HACCP system is working effectively 7. Establish documentation and reporting systems for all procedures Each of these seven key points is a vital step in developing the risk assessment. The seven points include: 1. To identify sources of contamination, construct a risk diagram / diagrams. This will show sources and routes of contamination. Examples include: a) Areas adjacent to clean room / Isolator (e.g. airlocks, changing rooms) b) Air supply c) Room air d) Surfaces e) People f) Machine g) Equipment 2. Assess the importance of these sources and if they are / are not hazards that need to be controlled. Examples include: a) The amount of contamination on, or in, the source that is available for transfer. b) Ease by which the contamination is dispersed or transferred. c) The proximity of the source to the critical point where the product is exposed. d) How easily the contamination can pass through the control method. The use of a scoring method can be very helpful. 3. Identify the methods that can be used to control these hazards. For example: a) Air supply / HEPA filters b) Dirty areas adjacent to cleanroom / Isolator (including differential pressures; airflow movement) c) Room air (air change rates; use of barriers) d) Surfaces (sterilisation; effectiveness of cleaning / disinfection procedures)
4 e) People (cleanroom clothing and gloves; room ventilation; training) f) Machines and equipment (sterilisation, effectiveness of cleaning, exhaust systems) 4. Determine valid sampling methods to monitor either the hazards or their control methods or both. For example: a) HEPA filter integrity tests b) Air supply velocity, air change rates c) Room pressure differentials d) Particle counts e) Air samplers; settle plates, contact plates etc. 5. Establish a monitoring schedule with alert and action levels and corrective measures to be taken (for when these levels are exceeded). For example: a) The greater the hazard, the greater the amount of monitoring required. b) Trend analysis for alert and action levels: in or out of control. 6. Verify that the contamination control system is working effectively by reviewing key targets like product rejection rate, sampling results, control methods and so on. These may need to be modified over time. For example: a) System for data review b) Examine filling trials c) Audit d) Reassess hazards, effectiveness of control systems, frequency of monitoring, appropriateness of alert and action levels. 7. Establish and maintain documentation. For example: a) Describe the steps being taken b) Describe the monitoring p[procedures c) Describe the reporting and review procedures Before implementing HACCP it is important to train all staff involved in the process and to use a multi-disciplinary team. For example, this may be made up of personnel from production, engineering, QC/QA, validation and so on. Example 3: FMEA FMEA schemes vary in their approach, scoring and categorisation. All approaches share in common a numerical approach. The example here, based on a sterility testing isolator, was to assign a score (from 1 to 5) to each of the following categories: i) Severity
5 ii) iii) Occurrence Detection Where: i) Severity is the consequence of a failure ii) Occurrence is the likelihood of the failure happening (based on past experience) iii) Detect is based on the monitoring systems in place and on how likely a failure can be detected. By asking a series of questions each main part of the clean room or isolator system can be broken down into key parts. Such questions included: i) What is the function of the equipment? How are its performance requirements? ii) How can it fail to fulfil these functions? iii) What can cause each failure? iv) What happens when each failure occurs? v) How much does each failure matter? What are its consequences? vi) What can be done to predict or prevent each failure? vii) What should be done if a suitable proactive task cannot be found? The scoring is 1 (very good) to 5 (very bad). Therefore, a likelihood of high severity would be rated 5; high occurrence rated 5; but a good detection system would be rated 1. Using these criteria a final FMEA score is produced: x 125 From: severity score x occurrence score x detect score Depending upon the score produced it can be decided whether further action is needed. There is no published guidance on what the score that dictates some form of action should be. A suggested score is 27 for the cut-off value where action was required. This was based on 27 being the score derived when the mid-score is applied to all three categories (i.e. the numerical value '3' from severity (3) x occurrence (3) x detect (3)) and the supposition that if the mid-rating (or a higher number) was scored for all three categories then as a minimum the system should be examined in greater detail. An example of one area of an isolator operation (the risks associated with the room in which the isolator is housed) is examined below.
6 Description of critical area: The isolator is situated in an unclassified room. There is not requirement to place a sterility testing isolator in a classified room. FMEA schematic: Process step Failure Mode Significance of failure Severity of consequence (score) Loading isolators pre-sanitisation / performing sterility testing That contamination from the room could enter transfer or main isolators Reduced efficency of transfer isolator sanitisation / contamination inside main isolator 3 Measures to detect failure Occurrence (score) Detection systems Detection (score) Would be shown from reduced evaporation rate for isolator sanitisation / poor environmental monitoring results in main isolator / potential sterility test failures / sanitisation cycle has been validated using biological indictors of 10 6 spores 1 Isolator room is monitored monthly for viables and particles / staff wear overshoes on entry / Dycem mat in place / entry to room has controlled access / environmental monitoring performed inside main isolator / isolators are at positive pressure to the room and air is HEPA filtered 1 FMEA score: 3 x 1 x 1 = 3 Analysis: There is no problem considered from the room environment. Entry to the room is controlled; the sanitisation cycle has been challenged with a level of microorganisms far greater than would ever be found in the environment (spores of Geobacillus stearothermophilus); all items entering the isolator are sanitised (using a chlorine dioxide based sporicidal disinfectant) and the isolator itself is an effective positive pressure barrier to the outside (at >15 pascals). As detailed earlier, environmental monitoring is performed inside the isolator during testing. This monitoring, which has an action level of 1 cfu, is designed to detect any potential contamination inside the isolator environment. Numerical approaches A third component of the risk assessment approach is to evaluate the risk once an activity has taken place. By using a largely numerically driven set of tools then repeatability and reproducibility can be ensured. Examples of individual out of limits results and data sets relating to an operation are examined below, using examples from an aseptic filling process. Following this an example of an overall assessment of
7 different processes over time are explored. Numerical approaches are useful in applying a level of consistency between one decision and another. Conclusion The use of risk assessment approaches is an important current GMP topics in microbiological environmental monitoring. This paper has outlined some possible tools for such a risk assessment approach. However, each suite of clean rooms or isolator will be subtly different. The microbiologist needs to consider each aspect of the environment and decide what level of monitoring best suits their system, and then to justify the techniques used and the locations selected. The approach adopted should be detailed in a written rationale and approved by senior management. After this a rigorous and defensible system will be in place to satisfy regulatory expectations, and to aid the user in risk assessing problematic environmental monitoring situations and results. References and further reading BS EN ISO :2003: Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments Biocontamination control Part 1: General principles and methods ISO Cleanrooms and Associated Controlled Environments Classification of Air Cleanliness ISO Cleanrooms and Associated Controlled Environments Specifications for Testing and Monitoring to prove continued compliance with ISO PDA Technical Report No. 13 (revised): 'Fundamentals of an Environmental Monitoring Programme', September / October 2001 Reich, et al. (2003): Developing a Viable Microbiological Environmental Monitoring Program for Nonsterile Pharmaceutical Operations, Pharm. Technol., March, pp Sandle, T. (2003a): The use of a risk assessment in the pharmaceutical industry the application of FMEA to a sterility testing isolator: a case study, European Journal of Parenteral and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2003; 8(2): Sandle, T (2003b): Selection and use of cleaning and disinfection agents in pharmaceutical manufacturing in Hodges, N and Hanlon, G. (2003): Industrial Pharmaceutical Microbiology Standards and Controls, Euromed Communications, England Whyte, W. (2001): Cleanroom Technology: Fundamentals of Design, Testing and Operation
8 Whyte, W. and Eaton, T. (2004a): Microbiological contamination models for use in risk assessment during pharmaceutical production, European Journal of Parenteral and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 9, No.1, pp11-15 Whyte, W. and Eaton, T. (2004b): Microbiological risk assessment in pharmaceutical cleanrooms, European Journal of Parenteral and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 9, No.1, pp16-23 Whyte, W. and Eaton, T. (2004c): Assessing microbial risk to patients from aseptically manufactured pharmaceuticals, European Journal of Parenteral and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 9, No.3, pp71-79
Environmental Monitoring Risk Assessment
 Environmental Monitoring Risk Assessment By Tim Sandle INTRODUCTION Environmental Monitoring describes the microbiological testing undertaken in order to detect changing trends of microbial counts and
Environmental Monitoring Risk Assessment By Tim Sandle INTRODUCTION Environmental Monitoring describes the microbiological testing undertaken in order to detect changing trends of microbial counts and
Qualification of an Environmental Monitoring Program
 [ Scott Sutton Qualification of an Environmental Monitoring Program Scott Sutton Microbiology Topics discusses various topics in microbiology of practical use in validation and compliance. We intend this
[ Scott Sutton Qualification of an Environmental Monitoring Program Scott Sutton Microbiology Topics discusses various topics in microbiology of practical use in validation and compliance. We intend this
Particle Monitoring Requirements in Pharmaceutical Cleanrooms
 Particle Monitoring Requirements in Pharmaceutical Cleanrooms All drugs must be manufactured in accordance with the current Good Manufacturing Practice (cgmp) regulations. Pharmaceutical manufacturers
Particle Monitoring Requirements in Pharmaceutical Cleanrooms All drugs must be manufactured in accordance with the current Good Manufacturing Practice (cgmp) regulations. Pharmaceutical manufacturers
Environmental Monitoring of Clean Rooms
 Environmental Monitoring of Raul Duarte President DDK Scientific, Corp. Copyright DDK Scientific, Corp. 2008, 2009, DDK Scientific, Corp. Proprietary A manufacturing facility for pharmaceutical products
Environmental Monitoring of Raul Duarte President DDK Scientific, Corp. Copyright DDK Scientific, Corp. 2008, 2009, DDK Scientific, Corp. Proprietary A manufacturing facility for pharmaceutical products
Environmental Monitoring
 Environmental Monitoring Purpose of Environmental Monitoring Critical process within the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Determines the microbial and particulate content of cleanroom air and
Environmental Monitoring Purpose of Environmental Monitoring Critical process within the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Determines the microbial and particulate content of cleanroom air and
CLEAN ROOM MONITORING REGULATORY STANDARDS
 CLEAN ROOM MONITORING REGULATORY STANDARDS Air Classification as per Schedule M Maximum permitted number of particles / m3 equal or above at rest in operation 0.5µm 5.0µm 0.5µm 5.0µm A 3,520 29 3,500 29
CLEAN ROOM MONITORING REGULATORY STANDARDS Air Classification as per Schedule M Maximum permitted number of particles / m3 equal or above at rest in operation 0.5µm 5.0µm 0.5µm 5.0µm A 3,520 29 3,500 29
Risk-Based Environmental Monitoring. Marsha Stabler Hardiman Senior Consultant Concordia ValSource Wednesday September 17, 2014 FDA/PQRI
 Risk-Based Environmental Monitoring Marsha Stabler Hardiman Senior Consultant Concordia ValSource Wednesday September 17, 2014 FDA/PQRI Presenter Marsha Stabler Hardiman Over 20 years experience in the
Risk-Based Environmental Monitoring Marsha Stabler Hardiman Senior Consultant Concordia ValSource Wednesday September 17, 2014 FDA/PQRI Presenter Marsha Stabler Hardiman Over 20 years experience in the
ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING & MONITORING: Deciphering Compliance Requirements for Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Manufacturers A WHITE PAPER
 A WHITE PAPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING & MONITORING: Deciphering Compliance Requirements for Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Manufacturers By Scott Mackin A WHITE PAPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING & MONITORING:
A WHITE PAPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING & MONITORING: Deciphering Compliance Requirements for Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Manufacturers By Scott Mackin A WHITE PAPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING & MONITORING:
CLASSIFICATION OF CLEANROOMS
 CLASSIFICATION OF CLEANROOMS Cleanrooms are classified by the cleanliness of their air. The method most easily understood and most universally applied is the one suggested in the earlier versions (A to
CLASSIFICATION OF CLEANROOMS Cleanrooms are classified by the cleanliness of their air. The method most easily understood and most universally applied is the one suggested in the earlier versions (A to
ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING
 ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING Assessment and verification of the adequacy of the aseptic compounding environment is essential. Environmental monitoring programs are designed to promptly identify potential sources
ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING Assessment and verification of the adequacy of the aseptic compounding environment is essential. Environmental monitoring programs are designed to promptly identify potential sources
GMP ANNEX 1 REVISION 2008, INTERPRETATION OF MOST IMPORTANT CHANGES FOR THE MANUFACTURE OF STERILE MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CONVENTION PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CO-OPERATION SCHEME PI 032-2 8 January 2010 RECOMMENDATION GMP ANNEX 1 REVISION 2008, INTERPRETATION OF MOST IMPORTANT CHANGES FOR THE MANUFACTURE
PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CONVENTION PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CO-OPERATION SCHEME PI 032-2 8 January 2010 RECOMMENDATION GMP ANNEX 1 REVISION 2008, INTERPRETATION OF MOST IMPORTANT CHANGES FOR THE MANUFACTURE
Manufacturing. Environmental Monitoring Particle Counts Are Easy B IOP ROCESSTECHNICAL. Scott E. Mackler
 B IOP ROCESSTECHNICAL Environmental Monitoring Particle Counts Are Easy Scott E. Mackler Manufacturing pharmaceutical and biotechnology products requires that the appropriate level of quality be designed
B IOP ROCESSTECHNICAL Environmental Monitoring Particle Counts Are Easy Scott E. Mackler Manufacturing pharmaceutical and biotechnology products requires that the appropriate level of quality be designed
Cleanroom. For. Sterile Manufacturing Facilities
 Cleanroom For Sterile Manufacturing Facilities Praphon Angtrakool Food and Drug Administration 1 WHO TRS No. 823 Annex 1, 1992 (1) General 17.1 The production of sterile preparations should be carried
Cleanroom For Sterile Manufacturing Facilities Praphon Angtrakool Food and Drug Administration 1 WHO TRS No. 823 Annex 1, 1992 (1) General 17.1 The production of sterile preparations should be carried
Everything you want to know about USP 797
 Everything you want to know about USP 797 Dr. Linda D. Lee Director of Operations Waste Management Healthcare Solutions September. 22, 2009 Goals High level understanding of USP 797 Who does it apply too
Everything you want to know about USP 797 Dr. Linda D. Lee Director of Operations Waste Management Healthcare Solutions September. 22, 2009 Goals High level understanding of USP 797 Who does it apply too
Validating and Monitoring the Cleanroom
 6 Validating and Monitoring the Cleanroom Kevina O Donoghue Overview... 6-1 Cleanroom Design... 6-1 Principles of Cleanroom Validation and Testing... 6-2 Cleanroom Validation... 6-2 So How Does One Determine
6 Validating and Monitoring the Cleanroom Kevina O Donoghue Overview... 6-1 Cleanroom Design... 6-1 Principles of Cleanroom Validation and Testing... 6-2 Cleanroom Validation... 6-2 So How Does One Determine
International Standard ISO 14644
 International Standard ISO 14644 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments Praphon Angtrakool Food and Drug Administration 1 International Standard : ISO 14644 ISO 14644 consists of the following
International Standard ISO 14644 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments Praphon Angtrakool Food and Drug Administration 1 International Standard : ISO 14644 ISO 14644 consists of the following
Cleaning. By the end of this chapter, you will be able to: Introduction. Definitions. Chapter 9
 Chapter 9 By the end of this chapter, you will be able to: l Define the terms cleaning, decontamination, disinfection l List the factors that affect disinfection l Describe the aims of a cleaning schedule
Chapter 9 By the end of this chapter, you will be able to: l Define the terms cleaning, decontamination, disinfection l List the factors that affect disinfection l Describe the aims of a cleaning schedule
Basic Requirements For Aseptic Manufacturing Of Sterile Medicinal Products A Comparison Between Europe And USA
 Basic Requirements For Aseptic Manufacturing Of Sterile Medicinal Products A Comparison Between Europe And USA Wissenschaftliche Prüfungsarbeit zur Erlangung des Titels Master of Drug Regulatory Affairs
Basic Requirements For Aseptic Manufacturing Of Sterile Medicinal Products A Comparison Between Europe And USA Wissenschaftliche Prüfungsarbeit zur Erlangung des Titels Master of Drug Regulatory Affairs
Qualification of Cleanrooms and Environmental Monitoring - Practical Approaches in Europe
 Qualification of Cleanrooms and Environmental Monitoring - Practical Approaches in Europe 1 Dr. Doris Herrmann Zum Eselsbachtal 20 67657 Kaiserslautern Doris.Herrmann@GMP-unlimited.de www.gmp-unlimited.com
Qualification of Cleanrooms and Environmental Monitoring - Practical Approaches in Europe 1 Dr. Doris Herrmann Zum Eselsbachtal 20 67657 Kaiserslautern Doris.Herrmann@GMP-unlimited.de www.gmp-unlimited.com
TSI BIOTRAK REAL-TIME VIABLE PARTICLE COUNTER FACILITY MONITORING SYSTEMS
 TSI BIOTRAK REAL-TIME VIABLE PARTICLE COUNTER FACILITY MONITORING SYSTEMS APPLICATION NOTE CC-105 (US) Introduction This application note will demonstrate how real-time viable particle count data will
TSI BIOTRAK REAL-TIME VIABLE PARTICLE COUNTER FACILITY MONITORING SYSTEMS APPLICATION NOTE CC-105 (US) Introduction This application note will demonstrate how real-time viable particle count data will
Media fills Periodic performance qualification (Re-Validation)
 Media fills Periodic performance qualification (Re-Validation) Minimum number of Simulations Number of units Contaminated Units Action a Two per Year (Retrospective & Prospective Validation) < 5000 5000
Media fills Periodic performance qualification (Re-Validation) Minimum number of Simulations Number of units Contaminated Units Action a Two per Year (Retrospective & Prospective Validation) < 5000 5000
Environmental Monitoring
 Chapter 10 Environmental Monitoring By the end of this chapter, you will be able to: l List the types of environmental testing l Name three types of checks that are carried out to ensure the isolator is
Chapter 10 Environmental Monitoring By the end of this chapter, you will be able to: l List the types of environmental testing l Name three types of checks that are carried out to ensure the isolator is
EU GMP Annex 1 Update 2008: Airborne Particle Counting
 EU GMP Annex 1 Update 2008: Airborne Particle Counting Airborne Particle Counting for Pharmaceutical Facilities: Update 2008, EU GMP Annex 1 Morgan Polen - VP of Applications Technology, Lighthouse Worldwide
EU GMP Annex 1 Update 2008: Airborne Particle Counting Airborne Particle Counting for Pharmaceutical Facilities: Update 2008, EU GMP Annex 1 Morgan Polen - VP of Applications Technology, Lighthouse Worldwide
Risk Based Environmental Monitoring (EM) and EM Data Management and Trending
 Risk Based Environmental Monitoring (EM) and EM Data Management and Trending An Industry Roundtable Discussion Marsha Stabler Hardiman and Parsa Famili March 11, 2015 PDA NE Chapter Meeting Presenters
Risk Based Environmental Monitoring (EM) and EM Data Management and Trending An Industry Roundtable Discussion Marsha Stabler Hardiman and Parsa Famili March 11, 2015 PDA NE Chapter Meeting Presenters
Selection of Disinfectants for Use in the Pharmaceutical Industry. Tim Sandle Head of Microbiology Bio Products Laboratory
 Selection of Disinfectants for Use in the Pharmaceutical Industry Tim Sandle Head of Microbiology Bio Products Laboratory Introduction Cleaning and disinfection of surfaces are essential steps for maintaining
Selection of Disinfectants for Use in the Pharmaceutical Industry Tim Sandle Head of Microbiology Bio Products Laboratory Introduction Cleaning and disinfection of surfaces are essential steps for maintaining
Risk Assessment and Management. Allen L. Burgenson Manager, Regulatory Affairs Lonza Walkersville Inc.
 Risk Assessment and Management Allen L. Burgenson Manager, Regulatory Affairs Lonza Walkersville Inc. Standard Disclaimer Standard Disclaimer: This presentation is the opinion of the presenter, and does
Risk Assessment and Management Allen L. Burgenson Manager, Regulatory Affairs Lonza Walkersville Inc. Standard Disclaimer Standard Disclaimer: This presentation is the opinion of the presenter, and does
Best Practice In A Change Management System
 Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Best Practice In A Change Management System President Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Change Control and Its Role in a Continuous Improvement Environment 3 Benefits
Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Best Practice In A Change Management System President Quality & Compliance Associates, LLC Change Control and Its Role in a Continuous Improvement Environment 3 Benefits
DRAFT GUIDANCE. This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only.
 Guidance for Industry Current Good Manufacturing Practice Interim Guidance for Human Drug Compounding Outsourcing Facilities Under Section 503B of the FD&C Act DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is
Guidance for Industry Current Good Manufacturing Practice Interim Guidance for Human Drug Compounding Outsourcing Facilities Under Section 503B of the FD&C Act DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is
Particle Counting and Environmental Monitoring In Pharmaceutical / Life Sciences
 Particle Counting and Environmental Monitoring In Pharmaceutical / Life Sciences LIGHTHOUSE WORLDWIDE SOLUTIONS WWW.GOLIGHTHOUSE.COM Introduction The pharmaceutical and medical device industries are developing
Particle Counting and Environmental Monitoring In Pharmaceutical / Life Sciences LIGHTHOUSE WORLDWIDE SOLUTIONS WWW.GOLIGHTHOUSE.COM Introduction The pharmaceutical and medical device industries are developing
QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT (QRM): A REVIEW
 Lotlikar et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 2013, 3(2), 149-154 149 Available online at http://jddtonline.info REVIEW ARTICLE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT (QRM): A REVIEW Lotlikar MV Head Corporate
Lotlikar et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 2013, 3(2), 149-154 149 Available online at http://jddtonline.info REVIEW ARTICLE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT (QRM): A REVIEW Lotlikar MV Head Corporate
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry Q9 Quality Risk Management U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
Guidance for Industry Q9 Quality Risk Management U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
USP <797> Cleanroom Design and Environmental Monitoring. Andrew King, USP <797> Specialist CETA Member RCCP-SC
 USP Cleanroom Design and Environmental Monitoring Andrew King, USP Specialist CETA Member RCCP-SC Objectives The objectives of this presentation: To summarize basic cleanroom concepts and how
USP Cleanroom Design and Environmental Monitoring Andrew King, USP Specialist CETA Member RCCP-SC Objectives The objectives of this presentation: To summarize basic cleanroom concepts and how
Sterile Cleanroom Management
 Sterile Cleanroom Management Lynn Stanard, Sr. Quality Manager, Berkshire Corporation When manufacturing in an aseptic environment, it is critical to ensure that the various cleanroom consumables, such
Sterile Cleanroom Management Lynn Stanard, Sr. Quality Manager, Berkshire Corporation When manufacturing in an aseptic environment, it is critical to ensure that the various cleanroom consumables, such
Cleaning and Disinfection Agenda. 1. Cleanroom Classification. Cleanroom Classification. What does contamination mean? Types of contamination
 Cleaning and Disinfection Agenda CLEANING AND DISINFECTION TECHNIQUES Barbara Wessels Key Account Manager Ecolab Contamination Control October 2014 1. Cleanroom classification and definition 2. Sources
Cleaning and Disinfection Agenda CLEANING AND DISINFECTION TECHNIQUES Barbara Wessels Key Account Manager Ecolab Contamination Control October 2014 1. Cleanroom classification and definition 2. Sources
GUIDELINES ON TEST METHODS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING FOR ASEPTIC DISPENSING FACILITIES
 GUIDELINES ON TEST METHODS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING FOR ASEPTIC DISPENSING FACILITIES PRODUCED BY A WORKING GROUP OF THE SCOTTISH QUALITY ASSURANCE SPECIALIST INTEREST GROUP SECOND EDITION FEBRUARY
GUIDELINES ON TEST METHODS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING FOR ASEPTIC DISPENSING FACILITIES PRODUCED BY A WORKING GROUP OF THE SCOTTISH QUALITY ASSURANCE SPECIALIST INTEREST GROUP SECOND EDITION FEBRUARY
Leila Kakko Tampere University of Applied science TRADITIONAL FOOD IN COMBATING FOODBORNE PATHOGENS 2011
 Leila Kakko Tampere University of Applied science TRADITIONAL FOOD IN COMBATING FOODBORNE PATHOGENS 2011 World Food Programme Food quality control is necessary to ensure that food aid supplies are safe,
Leila Kakko Tampere University of Applied science TRADITIONAL FOOD IN COMBATING FOODBORNE PATHOGENS 2011 World Food Programme Food quality control is necessary to ensure that food aid supplies are safe,
Improved Utilization of Self-Inspection Programs within the GMP Environment A Quality Risk Management Approach
 Improved Utilization of Self-Inspection Programs within the GMP Environment A Quality Risk Management Approach Barbara Jeroncic Self-inspection is a well-established and vital part of the pharmaceutical
Improved Utilization of Self-Inspection Programs within the GMP Environment A Quality Risk Management Approach Barbara Jeroncic Self-inspection is a well-established and vital part of the pharmaceutical
Quality Risk Management
 PS/INF 1/2010 * * Quality Risk Management Quality Risk Management Implementation of ICH Q9 in the pharmaceutical field an example of methodology from PIC/S Document > Authors: L. Viornery (AFSSAPS) Ph.
PS/INF 1/2010 * * Quality Risk Management Quality Risk Management Implementation of ICH Q9 in the pharmaceutical field an example of methodology from PIC/S Document > Authors: L. Viornery (AFSSAPS) Ph.
Understanding USP 797
 DDK Scientific, Corp. Raul Duarte June 2008 Copyright DDK Scientific, Corp. 2008, 2009 DDK Scientific, Corp. Proprietary The purpose of USP 797 is to prevent harm and fatality to patients that could result
DDK Scientific, Corp. Raul Duarte June 2008 Copyright DDK Scientific, Corp. 2008, 2009 DDK Scientific, Corp. Proprietary The purpose of USP 797 is to prevent harm and fatality to patients that could result
CONCEPTS OF FOOD SAFETY QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. Mrs. Malini Rajendran
 CONCEPTS OF FOOD SAFETY AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Mrs. Malini Rajendran Brief background 1963 - The Codex Alimentarius Commission was created by FAO and WHO to develop food standards, guidelines and
CONCEPTS OF FOOD SAFETY AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Mrs. Malini Rajendran Brief background 1963 - The Codex Alimentarius Commission was created by FAO and WHO to develop food standards, guidelines and
New changes to cleanroom & clean air device classifications: ISO 14644 1 & 2
 New changes to cleanroom & clean air device classifications: ISO 14644 1 & 2 This white paper describes the changes outlined in the Draft International Standard (DIS) editions of ISO 14644-1 and ISO 14644-2.
New changes to cleanroom & clean air device classifications: ISO 14644 1 & 2 This white paper describes the changes outlined in the Draft International Standard (DIS) editions of ISO 14644-1 and ISO 14644-2.
The Environmental Monitoring Program In a GMP Environment
 I, MICROBIOLOGY T PICS The Environmental Monitoring Program In a GMP Environment Scott Sutton "Microbiology Topics" discusses various topics in microbiology of practical use in validation and compliance.
I, MICROBIOLOGY T PICS The Environmental Monitoring Program In a GMP Environment Scott Sutton "Microbiology Topics" discusses various topics in microbiology of practical use in validation and compliance.
QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT Q9 Current Step 4 version
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT Q9 Current Step 4 version
Quality Risk Management Tools Quality Risk Management Tool Selection When to Select FMEA: QRM Tool Selection Matrix
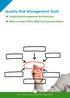 Quality Risk Management Tools Quality Risk Management Tool Selection When to Select FMEA: QRM Tool Selection Matrix 26 Quality Risk Management Tools The ICH Q9 guideline, Quality Risk Management, provides
Quality Risk Management Tools Quality Risk Management Tool Selection When to Select FMEA: QRM Tool Selection Matrix 26 Quality Risk Management Tools The ICH Q9 guideline, Quality Risk Management, provides
Principles. of Pharmaceutical Facility Design. Full Time Part Time Online. www.dpseng.com.sg
 Principles of Pharmaceutical Facility Design Full Time Part Time Online www.dpseng.com.sg Contents 1. Welcome 2. Programme Overview 3. Programme Content www.dpseng.com.sg 2 Welcome Transition into a new
Principles of Pharmaceutical Facility Design Full Time Part Time Online www.dpseng.com.sg Contents 1. Welcome 2. Programme Overview 3. Programme Content www.dpseng.com.sg 2 Welcome Transition into a new
Introduction. Contamination sources
 Introduction Tim Sandle www.pharmamicro.com Cleanrooms and environmental monitoring Contamination sources Contamination control The human microbiome and the microbial ecology of people Case study: Microorganisms
Introduction Tim Sandle www.pharmamicro.com Cleanrooms and environmental monitoring Contamination sources Contamination control The human microbiome and the microbial ecology of people Case study: Microorganisms
Regulations Concerning
 Regulations Concerning Airborne Particle Counting Two types of activities performed with an airborne particle counter: Classification focuses primarily on the environment Particle Counting Applications
Regulations Concerning Airborne Particle Counting Two types of activities performed with an airborne particle counter: Classification focuses primarily on the environment Particle Counting Applications
GUIDANCE ON THE SAFE HANDLING OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY (mab) PRODUCTS
 GUIDANCE ON THE SAFE HANDLING OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY (mab) PRODUCTS 5 th Edition November 2015 NHS Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Committee 2015 British Oncology Pharmacists Association Pharmaceutical
GUIDANCE ON THE SAFE HANDLING OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY (mab) PRODUCTS 5 th Edition November 2015 NHS Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Committee 2015 British Oncology Pharmacists Association Pharmaceutical
Impact Assessment in a Science & Risk Based Environment. R. Legland 11/04/11
 Impact Assessment in a Science & Risk Based Environment R. Legland 11/04/11 Background US GMP s EU GMP s Japan GMP s ICH Q8, Q9, Q10 Guidance ASTM Standard E2500-07 Science and Risk Based Approach to Determine
Impact Assessment in a Science & Risk Based Environment R. Legland 11/04/11 Background US GMP s EU GMP s Japan GMP s ICH Q8, Q9, Q10 Guidance ASTM Standard E2500-07 Science and Risk Based Approach to Determine
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) 1 Overview
 Manufacturing Technology Committee Risk Management Working Group Risk Management Training Guides Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) 1 Overview Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point
Manufacturing Technology Committee Risk Management Working Group Risk Management Training Guides Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) 1 Overview Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point
Design, Operation and Management of GTP/GMP Cell Engineering Facilities
 Design, Operation and Management of GTP/GMP Cell Engineering Facilities Scott R. Burger, MD Advanced Cell & Gene Therapy BFDA 2007 International Symposium on Regulation of Human Cell and Tissue- Based
Design, Operation and Management of GTP/GMP Cell Engineering Facilities Scott R. Burger, MD Advanced Cell & Gene Therapy BFDA 2007 International Symposium on Regulation of Human Cell and Tissue- Based
Quality Risk Management Principles and Industry Case Studies
 Final Draft Rev. December 28, 2008 Quality Risk Management Principles and Industry Case Studies T. Frank 1, S. Brooks 2, R. Creekmore 3, B. Hasselbalch 4, K. Murray 5, K. Obeng 6, S. Reich 5, E. Sanchez
Final Draft Rev. December 28, 2008 Quality Risk Management Principles and Industry Case Studies T. Frank 1, S. Brooks 2, R. Creekmore 3, B. Hasselbalch 4, K. Murray 5, K. Obeng 6, S. Reich 5, E. Sanchez
SUPPLEMENTARY GUIDELINES ON GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICES (GMP): VALIDATION
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION ORGANISATION MONDIALE DE LA SANTE Working document QAS/03.055/Rev.2 RESTRICTED SUPPLEMENTARY GUIDELINES ON GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICES (GMP): VALIDATION This document has followed
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION ORGANISATION MONDIALE DE LA SANTE Working document QAS/03.055/Rev.2 RESTRICTED SUPPLEMENTARY GUIDELINES ON GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICES (GMP): VALIDATION This document has followed
Risk Assessment for Medical Devices. Linda Braddon, Ph.D. Bring your medical device to market faster 1
 Risk Assessment for Medical Devices Linda Braddon, Ph.D. Bring your medical device to market faster 1 My Perspective Work with start up medical device companies Goal: Making great ideas into profitable
Risk Assessment for Medical Devices Linda Braddon, Ph.D. Bring your medical device to market faster 1 My Perspective Work with start up medical device companies Goal: Making great ideas into profitable
Guide to in situ leak testing of HEPA filter configurations that cannot be conventionally scan tested
 DOP Solutions Technical Document: Guide to in situ leak testing of HEPA filter configurations that cannot be conventionally scan tested Issue 1: Prepared by Neil Stephenson and Tim Triggs and edited by
DOP Solutions Technical Document: Guide to in situ leak testing of HEPA filter configurations that cannot be conventionally scan tested Issue 1: Prepared by Neil Stephenson and Tim Triggs and edited by
Raleigh, NC May 12 th & 13 th 2016. Meeting The New ISO Cleanroom Standards And Changing EU Guidance How Will You Comply?
 Raleigh, NC May 12 th & 13 th 2016 Meeting The New ISO Cleanroom Standards And Changing EU Guidance How Will You Comply? The International Cleanroom Standards (ISO 14644-1 & 2) have been updated, these
Raleigh, NC May 12 th & 13 th 2016 Meeting The New ISO Cleanroom Standards And Changing EU Guidance How Will You Comply? The International Cleanroom Standards (ISO 14644-1 & 2) have been updated, these
Hazardous Drug. Cleanroom. Standards
 Hazardous Drug Cleanroom Standards Module 3 Table of Contents Section A... 1 A.1 International Standards Organization (ISO) Classifications... 1 A.2 Hazardous Drug Cleanroom and Anteroom... 1 A.2.1 Location
Hazardous Drug Cleanroom Standards Module 3 Table of Contents Section A... 1 A.1 International Standards Organization (ISO) Classifications... 1 A.2 Hazardous Drug Cleanroom and Anteroom... 1 A.2.1 Location
Guidance for Industry: Starting Material Supplier Management
 Guidance for Industry: Starting Material Supplier Management Version 1.0 Drug Office Department of Health. Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this document... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Selecting and
Guidance for Industry: Starting Material Supplier Management Version 1.0 Drug Office Department of Health. Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this document... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Selecting and
Quality Risk Analysis: Value for Money in the Pharmaceutical Industry
 Chapter 17 Quality Risk Analysis: Value for Money in the Pharmaceutical Industry Jordi Botet Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/50450 1. Introduction
Chapter 17 Quality Risk Analysis: Value for Money in the Pharmaceutical Industry Jordi Botet Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/50450 1. Introduction
MOHD NASRUL MOHAMAD NOOR
 QUALITY ASSURANCE IN ASEPTIC WHO Collaborating Centre For Regulatory Control of Pharmaceuticals DISPENSING : MAINTENANCE OF CLEAN ROOM & EQUIPMENT Member of Pharmaceutical Inspection Cooperation Scheme
QUALITY ASSURANCE IN ASEPTIC WHO Collaborating Centre For Regulatory Control of Pharmaceuticals DISPENSING : MAINTENANCE OF CLEAN ROOM & EQUIPMENT Member of Pharmaceutical Inspection Cooperation Scheme
Monitoring. Compliant and Reasonable. 5-6 May 2015, Berlin, Germany
 Environmental Monitoring Workshops How to Establish an Environmental Monitoring Programme Interpretation of OOS Results Compliant and Reasonable 5-6 May 2015, Berlin, Germany SPEAKERS: Oxoid, UK Sauflon
Environmental Monitoring Workshops How to Establish an Environmental Monitoring Programme Interpretation of OOS Results Compliant and Reasonable 5-6 May 2015, Berlin, Germany SPEAKERS: Oxoid, UK Sauflon
GUIDE TO GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS ANNEX 15 *
 PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CONVENTION PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CO-OPERATION SCHEME PS/INF 11/2015 1 April 2015 GUIDE TO GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS ANNEX 15 * * Entry into force:
PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CONVENTION PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CO-OPERATION SCHEME PS/INF 11/2015 1 April 2015 GUIDE TO GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS ANNEX 15 * * Entry into force:
BEHAVIOUR EXPERIENCE MEDIA FILL QUALIFICATION TRAINING MONITORING GOWNING PERSONAL ATTRIBUTES QUALIFICATION
 QUALIFICATION OF ASEPTIC OPERATORS Jaap Koster EXPERIENCE BEHAVIOUR MEDIA FILL QUALIFICATION TRAINING MONITORING GOWNING QUALIFICATION PERSONAL ATTRIBUTES 2 TRAINING GENERAL PRINCIPLES Personnel should
QUALIFICATION OF ASEPTIC OPERATORS Jaap Koster EXPERIENCE BEHAVIOUR MEDIA FILL QUALIFICATION TRAINING MONITORING GOWNING QUALIFICATION PERSONAL ATTRIBUTES 2 TRAINING GENERAL PRINCIPLES Personnel should
How to Estimate the Cost of a. Laboratory Renovation. Candidate Number: 0714144
 How to Estimate the Cost of a Laboratory Renovation Candidate Number: 0714144 December 15, 2014 1 Table of Contents Cover Page Page 1 Table of Contents Page 2 Introduction Page 3 Types & Methods of Measurements
How to Estimate the Cost of a Laboratory Renovation Candidate Number: 0714144 December 15, 2014 1 Table of Contents Cover Page Page 1 Table of Contents Page 2 Introduction Page 3 Types & Methods of Measurements
Quality Risk Management The Pharmaceutical Experience Ann O Mahony Quality Assurance Specialist Pfizer Biotech Grange Castle
 Quality Risk Management 11 November 2011 Galway, Ireland Quality Risk Management The Pharmaceutical Experience Ann O Mahony Quality Assurance Specialist Pfizer Biotech Grange Castle Overview Regulatory
Quality Risk Management 11 November 2011 Galway, Ireland Quality Risk Management The Pharmaceutical Experience Ann O Mahony Quality Assurance Specialist Pfizer Biotech Grange Castle Overview Regulatory
Design, Construction, Commission, and Qualification of Critical Utility Systems: Part III
 Design, Construction, Commission, and Qualification of Critical Utility Systems: Part III BY DAVID W. VINCENT AND HERBERT MATHESON HEATING, VENTILATION, AND AIR CONDITIONING (HVAC) SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION
Design, Construction, Commission, and Qualification of Critical Utility Systems: Part III BY DAVID W. VINCENT AND HERBERT MATHESON HEATING, VENTILATION, AND AIR CONDITIONING (HVAC) SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION
Quality Risk Management ICH Q9 & ISO 14971. Presented by Michael Kerr 11 th November 2011
 Quality Risk Management ICH Q9 & ISO 14971 Presented by Michael Kerr 11 th November 2011 Agenda Risk Concept QRM Fundamentals Regulatory Expectations Warning Letters / Observations Application of QRM Introduction:
Quality Risk Management ICH Q9 & ISO 14971 Presented by Michael Kerr 11 th November 2011 Agenda Risk Concept QRM Fundamentals Regulatory Expectations Warning Letters / Observations Application of QRM Introduction:
Particle testing in cleanroom high-pressure gas lines to ISO 14644 made easy with the MET ONE 3400 gas calibrations
 Particle testing in cleanroom high-pressure gas lines to ISO 14644 made easy with the MET ONE 3400 gas calibrations B e c k m a n C o u l t e r L i f e S c i e n c e s 2 5 0 S. K r a e m e r B o u l e
Particle testing in cleanroom high-pressure gas lines to ISO 14644 made easy with the MET ONE 3400 gas calibrations B e c k m a n C o u l t e r L i f e S c i e n c e s 2 5 0 S. K r a e m e r B o u l e
Quality Risk Management in Pharmaceutical Industry: A Review
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.6, No.3, pp 908-914, July-Aug 2014 Quality Risk Management in Pharmaceutical Industry: A Review V Vijayakumar Reddy*,
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.6, No.3, pp 908-914, July-Aug 2014 Quality Risk Management in Pharmaceutical Industry: A Review V Vijayakumar Reddy*,
Annex 2. WHO guidelines on quality risk management. 1. Introduction 62. 2. Glossary 67 3. Quality risk management process 70
 Annex 2 WHO guidelines on quality risk management 1. Introduction 62 1.1 Background and scope 62 1.2 Principles of quality risk management 64 2. Glossary 67 3. Quality risk management process 70 3.1 Initiating
Annex 2 WHO guidelines on quality risk management 1. Introduction 62 1.1 Background and scope 62 1.2 Principles of quality risk management 64 2. Glossary 67 3. Quality risk management process 70 3.1 Initiating
EUROPEAN COMMISSION ENTERPRISE AND INDUSTRY DIRECTORATE-GENERAL. EudraLex The Rules Governing Medicinal Products in the European Union
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION ENTERPRISE AND INDUSTRY DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Consumer goods Pharmaceuticals Brussels, 25 November 2008 (rev.) EudraLex The Rules Governing Medicinal Products in the European Union Volume
EUROPEAN COMMISSION ENTERPRISE AND INDUSTRY DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Consumer goods Pharmaceuticals Brussels, 25 November 2008 (rev.) EudraLex The Rules Governing Medicinal Products in the European Union Volume
Annex 4 Supplementary guidelines on good manufacturing practices: validation
 World Health Organization WHO Technical Report Series, No. 937, 2006 Annex 4 Supplementary guidelines on good manufacturing practices: validation 1. Introduction 2. Scope 3. Glossary 4. Relationship between
World Health Organization WHO Technical Report Series, No. 937, 2006 Annex 4 Supplementary guidelines on good manufacturing practices: validation 1. Introduction 2. Scope 3. Glossary 4. Relationship between
On-Site GMP Training GMP COMPLIANCE TECHNICAL
 PharmaNet On-Site GMP Training GMP COMPLIANCE TECHNICAL 284 E Lake Mead Pkwy Suite C-278 Henderson, NV 89015 Phone: 702-558-0094 Fax: 702-558-0079 www.gmpseminars.com Key to Level of Program Level A: Program
PharmaNet On-Site GMP Training GMP COMPLIANCE TECHNICAL 284 E Lake Mead Pkwy Suite C-278 Henderson, NV 89015 Phone: 702-558-0094 Fax: 702-558-0079 www.gmpseminars.com Key to Level of Program Level A: Program
Annex 7 Application of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) methodology to pharmaceuticals
 World Health Organization WHO Technical Report Series, No. 908, 2003 Annex 7 Application of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) methodology to pharmaceuticals 1. Introduction Traditionally,
World Health Organization WHO Technical Report Series, No. 908, 2003 Annex 7 Application of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) methodology to pharmaceuticals 1. Introduction Traditionally,
White Paper. Life Sciences Industry Solution Blueprint for Environmental Monitoring Systems (EMS) ISPE Guidance and Best Practices.
 White Paper Life Sciences Industry Solution Blueprint for Environmental Monitoring Systems (EMS) Author: Roberto Zerbi, Global Industries Solutions Life Sciences, Invensys What s Inside: 1. Introduction
White Paper Life Sciences Industry Solution Blueprint for Environmental Monitoring Systems (EMS) Author: Roberto Zerbi, Global Industries Solutions Life Sciences, Invensys What s Inside: 1. Introduction
Annex 2. WHO good manufacturing practices for pharmaceutical products: main principles 1
 Annex 2 WHO good manufacturing practices for pharmaceutical products: main principles 1 Introduction 79 General considerations 80 Glossary 81 Quality management in the medicines industry: philosophy and
Annex 2 WHO good manufacturing practices for pharmaceutical products: main principles 1 Introduction 79 General considerations 80 Glossary 81 Quality management in the medicines industry: philosophy and
HVAC Design Requirements
 Maintenance of HVAC HVAC Design Requirements Air Flow Diagram แบบ Recirculation Air Flow Diagram แบบ Once Through Definition Of Conditions As built At rest In operation air air air Maintenance GMP Requirements
Maintenance of HVAC HVAC Design Requirements Air Flow Diagram แบบ Recirculation Air Flow Diagram แบบ Once Through Definition Of Conditions As built At rest In operation air air air Maintenance GMP Requirements
Air and Water Balancing - Sound and Vibration Testing - Cleanroom Services - Building Commissioning Building Envelope Testing Thermal Imaging
 NEUDORFER ENGINEERS, INC. provides our customer with unbiased, professional, performance testing of Cleanrooms. We are committed to providing you, our customer, with value-added expertise in an effort
NEUDORFER ENGINEERS, INC. provides our customer with unbiased, professional, performance testing of Cleanrooms. We are committed to providing you, our customer, with value-added expertise in an effort
Guidance on safe use of Autoclaves
 Safety Office Reviewed: Dec 2013 Reviewed: DD Month Year Guidance on safe use of Autoclaves 1. Hazards & Uses There are several different types of hazard associated with the use of autoclaves. The main
Safety Office Reviewed: Dec 2013 Reviewed: DD Month Year Guidance on safe use of Autoclaves 1. Hazards & Uses There are several different types of hazard associated with the use of autoclaves. The main
ISOLATOR TECHNOLOGY MANUFACTURING
 ISOLATOR TECHNOLOGY MANUFACTURING Design Qualification Experience Complimentary WEBINAR Wednesday, December 12, 2007 This webinar presents the methods used at Baxter s Halle, Germany facility for the design
ISOLATOR TECHNOLOGY MANUFACTURING Design Qualification Experience Complimentary WEBINAR Wednesday, December 12, 2007 This webinar presents the methods used at Baxter s Halle, Germany facility for the design
Annex 6 WHO good manufacturing practices for sterile pharmaceutical products
 World Health Organization WHO Technical Report Series, No. 961, 2011 Annex 6 WHO good manufacturing practices for sterile pharmaceutical products Introduction Following implementation of these WHO good
World Health Organization WHO Technical Report Series, No. 961, 2011 Annex 6 WHO good manufacturing practices for sterile pharmaceutical products Introduction Following implementation of these WHO good
Mould Mould A Basic Guide
 Mould A Basic Guide Summary Mould is a fact of life. Moulds will grow practically everywhere people live and work. Mould is recognized as an occupational hazard for indoor workers as well as outdoor workers
Mould A Basic Guide Summary Mould is a fact of life. Moulds will grow practically everywhere people live and work. Mould is recognized as an occupational hazard for indoor workers as well as outdoor workers
MHRA Questions and Answers for Specials manufacturer s
 1. Introduction & Purpose 2. Scope 3. Q & As 4. Glossary 5. Reference documents 6. Revision History 1 INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE The purpose of this document is to provide guidance for Manufacturing Specials
1. Introduction & Purpose 2. Scope 3. Q & As 4. Glossary 5. Reference documents 6. Revision History 1 INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE The purpose of this document is to provide guidance for Manufacturing Specials
ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING / TESTING TO CONFORM WITH ISO14644 & TGA GMP REQUIREMENTS
 ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING / TESTING TO CONFORM WITH ISO14644 & TGA GMP REQUIREMENTS PRESENTATION TO RACI 20 TH APRIL 2016 PAUL MORGAN DIRECTOR CRITICAL CERTIFICATION PTY LTD CHANGES TO ISO14644 PART 1 CHANGES
ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING / TESTING TO CONFORM WITH ISO14644 & TGA GMP REQUIREMENTS PRESENTATION TO RACI 20 TH APRIL 2016 PAUL MORGAN DIRECTOR CRITICAL CERTIFICATION PTY LTD CHANGES TO ISO14644 PART 1 CHANGES
Quality Assurance. Disclosure for Lilli Møller Andersen. No relevant financial relationships exist for any issue mentioned in this presentation
 Quality Assurance Disclosure for Lilli Møller Andersen No relevant financial relationships exist for any issue mentioned in this presentation Agenda Quality Assurance Quality Management System Quality
Quality Assurance Disclosure for Lilli Møller Andersen No relevant financial relationships exist for any issue mentioned in this presentation Agenda Quality Assurance Quality Management System Quality
Commercial Manufacturing - Qualification & Validation-related GMP Deficiencies and Other Lifecycle Considerations
 Commercial Manufacturing - Qualification & Validation-related GMP Deficiencies and Other Lifecycle Considerations Kevin O Donnell PhD Market Compliance Manager, IMB PDA / FDA Conference Pharmaceutical
Commercial Manufacturing - Qualification & Validation-related GMP Deficiencies and Other Lifecycle Considerations Kevin O Donnell PhD Market Compliance Manager, IMB PDA / FDA Conference Pharmaceutical
VALIDATION OF ASEPTIC PROCESSES
 PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CONVENTION PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CO-OPERATION SCHEME PI 007-6 1 January 2011 RECOMMENDATION ON THE VALIDATION OF ASEPTIC PROCESSES PIC/S January 2011 Reproduction prohibited
PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CONVENTION PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CO-OPERATION SCHEME PI 007-6 1 January 2011 RECOMMENDATION ON THE VALIDATION OF ASEPTIC PROCESSES PIC/S January 2011 Reproduction prohibited
DISCUSSION TOOL PRESENTED TO THE AABB CT REGULATORY AFFAIRS SUBSECTION
 1 US FDA Form 483: A Case Study DISCUSSION TOOL PRESENTED TO THE AABB CT REGULATORY AFFAIRS SUBSECTION DEVELOPED BY FRAN RABE 2 Introduction This case study is intended to extract portions of information
1 US FDA Form 483: A Case Study DISCUSSION TOOL PRESENTED TO THE AABB CT REGULATORY AFFAIRS SUBSECTION DEVELOPED BY FRAN RABE 2 Introduction This case study is intended to extract portions of information
HACCP System. Introduction
 Introduction The company is committed to supplying safe products for consumption. As part of this commitment, all products and processes used in the manufacture of food products are subject to hazard analysis
Introduction The company is committed to supplying safe products for consumption. As part of this commitment, all products and processes used in the manufacture of food products are subject to hazard analysis
Controlling Risks Risk Assessment
 Controlling Risks Risk Assessment Hazard/Risk Assessment Having identified the hazards, one must assess the risks by considering the severity and likelihood of bad outcomes. If the risks are not sufficiently
Controlling Risks Risk Assessment Hazard/Risk Assessment Having identified the hazards, one must assess the risks by considering the severity and likelihood of bad outcomes. If the risks are not sufficiently
GHPGMP HACP. Are You Confused? Aditya Birla Retail Limited
 GHPGMP HACP Are You Confused? Ms Shashi Sareen, Head, Quality Aditya Birla Retail Limited COVERAGE What do we understand by GHP/ GMP & HACCP Where do the confusions arise? Implementation of GMP & HACCP
GHPGMP HACP Are You Confused? Ms Shashi Sareen, Head, Quality Aditya Birla Retail Limited COVERAGE What do we understand by GHP/ GMP & HACCP Where do the confusions arise? Implementation of GMP & HACCP
STUDY GUIDE: ABATTOIR HYGIENE
 STUDY GUIDE: ABATTOIR HYGIENE In Collaboration with the Directorate Veterinary Services National Department of Agriculture January 2007 Study guide Abattoir Hygiene January 2007 1 CONTENTS MODULES ABATTOIR
STUDY GUIDE: ABATTOIR HYGIENE In Collaboration with the Directorate Veterinary Services National Department of Agriculture January 2007 Study guide Abattoir Hygiene January 2007 1 CONTENTS MODULES ABATTOIR
Occupational safety risk management in Australian mining
 IN-DEPTH REVIEW Occupational Medicine 2004;54:311 315 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqh074 Occupational safety risk management in Australian mining J. Joy Abstract Key words In the past 15 years, there has been a
IN-DEPTH REVIEW Occupational Medicine 2004;54:311 315 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqh074 Occupational safety risk management in Australian mining J. Joy Abstract Key words In the past 15 years, there has been a
Occupational/Industrial Hygiene Knowledge and Competency Requirements
 Occupational/Industrial Hygiene Knowledge and Competency Requirements I. PREFACE The International Occupational Hygiene Association's (IOHA's) National Accreditation Recognition (NAR) Committee holds a
Occupational/Industrial Hygiene Knowledge and Competency Requirements I. PREFACE The International Occupational Hygiene Association's (IOHA's) National Accreditation Recognition (NAR) Committee holds a
CLEANROOMS IN PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTION
 Mikhail Kitain CLEANROOMS IN PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTION Bachelor s thesis Building Services March 2010 DESCRIPTION Date of the bachelor's thesis 14.03.2010 Author(s) Mikhail Kitain Degree programme and
Mikhail Kitain CLEANROOMS IN PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTION Bachelor s thesis Building Services March 2010 DESCRIPTION Date of the bachelor's thesis 14.03.2010 Author(s) Mikhail Kitain Degree programme and
The Perfect Partnership for GMP Cleaning Services. Total Cleaning Solutions from Micronclean & Isocleanse
 The Perfect Partnership for GMP Cleaning Services Total Cleaning Solutions from Micronclean & Isocleanse 02 03 The Micronclean Offer Micronclean have offered a specialist ISO Class 4/GMP Grade B cleanroom
The Perfect Partnership for GMP Cleaning Services Total Cleaning Solutions from Micronclean & Isocleanse 02 03 The Micronclean Offer Micronclean have offered a specialist ISO Class 4/GMP Grade B cleanroom
Practical Series Seminars and Workshops INTENSIVE TRAINING IN ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING, DISINFECTANT QUALIFICATION AND CLEANROOM CONTAMINATION CONTROL
 QUALIFICATION AND CLEANROOM CONTAMINATION CONTROL Who should attend: Quality Assurance, Quality Control, Operations, Regulatory and Manufacturing Supervisors, Cleanroom Operators and Facilities Personnel
QUALIFICATION AND CLEANROOM CONTAMINATION CONTROL Who should attend: Quality Assurance, Quality Control, Operations, Regulatory and Manufacturing Supervisors, Cleanroom Operators and Facilities Personnel
AMENDED January 27, 2015
 Proposed Language To Amend 1735 in Article 4.5 of Division 17 of Title 16 of the California Code of Regulations to read as follows: 1735. Compounding in Licensed Pharmacies. (a) Compounding means any of
Proposed Language To Amend 1735 in Article 4.5 of Division 17 of Title 16 of the California Code of Regulations to read as follows: 1735. Compounding in Licensed Pharmacies. (a) Compounding means any of
