Fluorescence Competition Assay for the Assessment of ATP Binding to an Isolated Domain of Na +, K + -ATPase
|
|
|
- Erick Page
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physiol. Res. 53: 09-3, 004 Fluorescence Competition Assay for the Assessment of AP Binding to an Isolated Domain of Na +, + -APase M. UBALA,, J. PLÁŠE, E. AMLER Institute of Physics, Charles University Prague, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, Czech Republic Received October, 00 Accepted May 4, 003 Summary An equation allowing estimation of the dissociation constant for binding of a non-fluorescent ligand to the enzyme is presented that is based on the competitive replacement of the ligand by its fluorescent analog. We derived an explicit formula for the probe fluorescence intensity, which is suitable for nonlinear least-squares analysis. We used this formula to evaluate the binding of AP to the large cytoplasmic loop of Na +, + -APase. he estimated value of D (6. ± 0.7 mm) is comparable with the results from other laboratories for similar constructs obtained by a different method. ey words Competition Dissociation constant Fluorescence Enzyme-ligand interaction NP-AP Introduction Fluorescence analysis represents a powerful tool for investigating the interaction of biopolymers with various ligands. Unfortunately, the ligands of interest do not usually emit strong fluorescence, and/or the biopolymers themselves exhibit fluorescence that may exceed considerably the weak ligand emission (e.g. when proteins that contain multiple aromatic acids are studied). o overcome this problem, fluorescent analogs of many important ligands have been synthesized that are capable of emitting bright fluorescence in a spectral range that is far from that of the biopolymer autofluorescence. However, even a small fluorochrome attached to the ligand may obviously influence the dissociation constant that characterizes the binding of the ligand to its specific binding site. herefore, the results of such binding assays must be interpreted very carefully. In many studies, an accurate quantitative evaluation of dissociation constants for ligand binding is essential. o obtain the correct value of a dissociation constant that is free of fluorochrome-related artifacts, the binding assays must be performed in the presence of a pure ligand whose binding to the binding site competes with the fluorescent analog. he evaluation of experimental data from such competition assays still relies on a few approximate formulas, although this method was introduced many years ago (Moczydlowski and Fortes 98, Horovitz and Levitzki 987, Corin et al. 99, akkar et al. 999). In this paper, we present an explicit formula that is suitable for fitting experimental titration data from competition binding assays, and thus for determining a dissociation constant of the pure ligand. As an example of the use of this formula we studied the binding of AP to the H 4 -H 5 loop of Na + / + - APase, in order to understand how this process is PHYSIOLOGICAL RESEARCH ISSN Institute of Physiology, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Prague, Czech Republic Fax physres@biomed.cas.cz
2 0 ubala et al. Vol. 53 influenced by various loop mutations. Na + / + -APase, a membrane enzyme transporting sodium ions outside and potassium ions inside the cell at the expense of energy from AP hydrolysis, consists of two subunits. he α- subunit is a protein with 0 transmembrane helices that is responsible for AP binding and hydrolysis as well as transport of ions. he β-subunit is a glycoprotein that is important for proper maturation of the enzyme in a membrane (for review see otyk and Amler 995). Recent reports also suggest its role in + -transport (Abriel et al. 999) and possible oligomerization (Ivanov et al. 00). he AP-binding site is localized on the α-subunit within the H 4 -H 5 loop, which is a large cytoplasmic loop between transmembrane helices 4 and 5 (Lingrel and untzweiler 994). It has been shown that this loop retains its tertiary structure even when separated from the rest of the protein, and can thus still bind AP (ran and Farley 999). Recently, we have shown that the H 4 -H 5 loop is able to bind ',3'-O-(,4,6-trinitrophenyl) adenosine 5'- triphosphate (NP-AP). We found that this fluorescent probe is suitable for investigating the AP binding to this loop (ubala et al. 003). NP-AP is a well-known fluorescent analog of AP that is only moderately fluorescent in aqueous solutions, while its fluorescence quantum yield increases about seven-fold upon the probe binding to APase (Hiratsuka and Uchida 973, Hiratsuka 976). However, when interpreting the results of assays performed with NP-AP, we have to take into account the fact that its interaction with proteins may not mimic perfectly the behavior of pure AP, because i) it is more bulky, and ii) it can interact with APase through its trinitrophenyl moiety. Methods Protein preparation he GS-fusion protein of the H 4 -H 5 loop (sequence Leu354-Ile604) was expressed in E. coli and purified on Sephadex column as described earlier (ubala et al. 00). he stock solution of this protein was kept at 0 C in 50 mm ris-hcl (ph 7.5). Fluorescence measurements Fluorescence intensity of NP-AP stained protein solutions was measured using FluoroMax- (Jobin Yvon/Spex), in 0.4x cm quarz cuvettes at room temperature ( C). he excitation and emission wavelengths were chosen at 46 nm and 57 nm, respectively. o improve the signal-to-noise ratio, both the excitation and the emission band pass were set at 0 nm and the integration time to 5 s. Measured fluorescence intensities were corrected for both blank signal due to a protein emission and scattered excitation light. Protein staining and titration experiments NP-AP (Molecular Probes, Oregon, USA) was kept as 00 µm aqueous stock solution. Aliquots of this stock solution were added to protein samples, and the stained samples stirred gently before fluorescence measurements started about min after adding the dye to the protein. In titration experiments, sequential additions of NP-AP were made into the identical cuvettes in a total volume of ml. Protein, NP-AP and AP concentrations were corrected for the corresponding diluting. For simple titration experiments with NP-AP, GS-fusion protein was diluted to a concentration of.6 µm with 50 mm ris-hcl, ph 7.5. he competitive assays in the presence of AP were performed with.6 µm GS-fusion protein in 50 mm ris-hcl and with 0 mm AP. In these solutions, ph was adjusted to 7.5 after the addition of AP. Results Explicit formula describing probe fluorescence intensity in the presence of a competing non-fluorescent ligand For one binding site per enzyme, the equilibrium binding of fluorescence probe to an enzyme obeys the equation () [ P ][ E ] P = [ PE ] where P is the dissociation constant, [ is free probe concentration, [E] is free protein concentration, and [PE] is the concentration of protein-bound probe. he total probe concentration, [, and the total concentration of protein, [E], can be expressed as () [ = [ + [PE] (3) [E] = [E] + [PE] hus the total intensity of fluorescence from stained protein solutions, F, consists of two components, a signal due to the free probe, F f, and a signal due to the bound probe, F b, (4) F = F f + F b
3 004 Fluorescence Assessment of AP binding Under experimental conditions typical of usual binding experiment we can write for the emission from the free probe (5) F f = [ Q where Q is a multiplicative constant that reflects both the photophysical properties of free probe and the sensitivity of fluorimeter. For F b we can write (6) F b = γ [PE] Q where γ is the ratio of respective fluorescence intensities of bound and free probe (fluorescence enhancement). he value of Q can be readily assessed by measuring the fluorescence intensity from probe solutions in pure buffer. For practical reasons we will present the following formulas using a normalized fluorescence intensity F /Q, which we will denote F. In our preceding paper (ubala et al. 003) we derived an explicit formula describing the dependence of the normalized fluorescence intensity on the dissociation constant P and experimental parameters [, [E], and γ: (7) We have also shown that the use of this explicit formula for fitting experimental titration data is superior to the use of linearized plots, such as Scatchard plot, because any linearization inevitably affects also the noise distribution in experimental data. his noise transformation may result in erroneous estimations of dissociation constants. In case of the simultaneous binding of NP-AP and pure AP that compete for the same binding site (in general terms, of the simultaneous binding of any nonfluorescent ligand competing with its fluorescent analog), an additional equilibrium equation that describes the binding of pure AP to the enzyme must be combined with Eq.. For the AP binding to the enzyme we can write (8) γ F = [ + [ + [ E] + P ([ P ] [ E] + ) 4 [ [ E] + P [ E ][ A ] = A [ AE ] where [A] is the concentration of free AP and [AE] is the concentration of AP bound to the enzyme. hen the total AP concentration is obviously (9) [A] = [A] + [AE] and Eq. (3) must be replaced by (0) [E] = [E] + [PE] + [AE] With some algebra, one can combine Eq.8 with equations (), (), (4) - (6), (9) and (0) to obtain an explicit equation for A () where the denominator of the fraction shown in parentheses stands for [AE]. We also tried to derive an explicit formula from Eq. analogous to Eq.7. his has resulted in a cubic equation for F. A way to solve similar problems in radioactive labeling assays was presented by Wang (995), but we have not found their approach suitable for practical use in fluorescence competitive assays. Fortunately, the binding of pure AP to the H 4 -H 5 loop is much weaker than the binding of its fluorescent analog, i.e. it holds that A >> P. herefore, a reasonable extent of competition between these two ligands will only be observed if [A] >> [. Optimum titration experiments with NP-AP have been performed with the maximal value of [ close to [E]. Under these conditions [A] >> [E] > [AE], and finally [A] /[AE] >>. hen the number in Eq. () can be neglected and transform this equation into a relatively simple quadratic equation: () (F - [ ) - (F - [ ) (γ-) ([ + [E] + P + [A] P / A ) + (γ-) [ [E] = 0 that yields finally: (3) F = [ + γ [ + [ E] + P + [ A] A = P( F [ ) [ A] γ[ F P( F [ ) F [ [ E] γ[ F γ ( ) P [ P ] + [ E] + P + [ A] 4[ [ E] A Competitive binding of NP-AP and AP to H 4 -H 5 loop of the GS-fusion protein As shown in our previous study of NP-AP binding to the H 4 -H 5 loop of the GS fusion protein, the dissociation constant for NP-AP is P = 3.0 ± 0.3 µm, P A
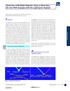
4 ubala et al. Vol. 53 and the fluorescence enhancement factor is γ = 7.0 ± 0.7 (ubala et al. 003). We found also that fusion with the GS protein has no influence on NP-AP or AP binding to the H 4 -H 5 loop. o assess the dissociation constant for pure AP, titration experiments with NP-AP were performed in the presence of AP. Since the binding of AP to the H 4 -H 5 loop appeared to be much weaker than the binding of NP-AP, we had to use very high concentrations of AP ( 5 mm) to see some significant competition between NP-AP and AP binding. At this concentration, AP added to GS-fusion protein stained with NP-AP will inevitably cause a substantial shift in the ph of the solution. herefore, we had to carry out the competition assays at a constant AP concentration. Fig.. Dependence of relative fluorescence intensity on NP-AP concentration. H 4-H 5 loop-gs-fusion protein (.6 µm) was incubated with increasing concentration of NP-AP in 50 mm ris-hcl, ph 7.5 (circles, data taken from ubala et al. 003) or in 50 mm ris-hcl + 0 mm AP, ph 7.5 (triangles). For comparison, titration in 50 mm ris-hcl in the absence of any protein is shown (squares). Binding of NP-AP to the protein results in an increase of fluorescence intensity. he presence of AP in the solution inhibited this binding. he GS fusion protein was dissolved in 50 mm ris buffer containing 0 mm AP (ph 7.5). After adding purified protein to this buffer, the concentration of AP decreased to 9.36 mm. his solution was titrated with aliquots of NP-AP and corrections for AP and protein dilution were calculated. Figure shows the titration plots. hese experimental curves were fitted to Eq. (3) using least-squares analysis, with A left as a fit parameter and γ and P fixed to values found in preceding pure NP-AP titration experiments. hree independent series of titration yielded a A value of 6. ± 0.7 mm. Discussion Fluorimetry can easily be used as a powerful tool in quantitative studies of enzyme-ligand interaction, provided that one of the interacting species exhibits an intrinsic fluorescence whose intensity varies upon ligand binding. Eq.7 describes this situation adequately, as shown in our preceding paper. In the present paper we analyze the case of competitive binding of a non-fluorescent ligand and its fluorescent analog to a non-fluorescent protein, and present an explicit formula (Eq.3) that makes it possible to assess fluorimetrically the dissociation constant for the binding of non-fluorescent ligand to a non-fluorescent protein. his formula is applicable to the ligands and their fluorescent analogs that satisfy the following requirements: (i) the non-fluorescent ligand and the fluorescent probe compete for the same binding site, (ii) the pure ligand is not fluorescent and neither is the macromolecule, (iii) the fluorescent analog of the ligand exhibits a considerable increase (or decrease, γ < ) of fluorescence intensity upon its binding to the protein, and (iv) the dissociation constant of the fluorescent analog is much lower than that of the pure ligand. If the above requirements are fulfilled, Eq.3 can be used for fitting experimental titration curves by the least-squares analysis. Even in a situation when condition (iv) is not fulfilled, the value of the dissociation constant can still be assessed using Eq. that is free of approximations. In this case we have to calculate the A value for each particular set of ligand, probe and protein concentrations and the corresponding intensity of probe fluorescence, and then to determine a mean value. We employed Eq.3 to evaluate experimental data from titration experiments that had been designed to determine the dissociation constant for AP binding to the H 4 -H 5 loop in GS fusion protein, with NP-AP used as the fluorescent analog of AP. As demonstrated in Figure, a reasonable difference between respective titration curves for NP-AP only and for NP-AP in the presence of AP was found for.6 µm GS-fusion protein when the concentration of NP-AP ranged from 0.4 to 4.0 µm and the AP concentration was 0 mm. his suggests that the actual values of [A], [E] and [AE] as used in our experiments justify the approximation described above in the Results, and thus the fitting of experimental data to Eq.3.
5 004 Fluorescence Assessment of AP binding 3 he observed value of the dissociation constant for AP binding to the H 4 -H 5 loop of Na +, + -APase was 6. ± 0.7 mm. his value is comparable with dissociation constants that ran and Farley (999) found for Na -AP binding to several different GS-fusion proteins containing the cytoplasmic domain of α -subunit of Na +, + -APase. he published data ranged from to mm (ran and Farley 999). hese authors interpreted this fact in terms of a possibility that the cytoplasmic domains of Na +, + -APase, when expressed as fusion proteins, are folded in an E -like conformation to which AP binds with relatively low affinity. he fact that the dissociation constant for pure AP binding is about three orders of magnitude higher than that for NP-AP suggests a certain stabilizing role of the trinitrophenyl moiety in the interaction of this AP analog with the H4-H5 loop of the fusion protein. Acknowledgements his work was supported by MSM30000 grant from he Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic and Research Projects AVOZ 509 and CZE00/033. References ABRIEL H, HASLER U, GEERING, HORISBERGER JD: Role of the intracellular domain of the β subunit in Na, pump function. Biochim Biophys Acta 48: 85-96, 999 CORIN AF, MCLEDRON G, ZHANG Q, HAE RA, FALVO J, LU S, CICCARELLI RB, HOLZSCHU D: Effects of surface amino acid replacements in cytochrome c peroxidase on complex formation with cytochrome c. Biochemistry 30: , 99 HIRASUA : Fluorescence properties of ' (or 3')-O-(,4,6-trinitrophenyl) adenosine 5'-triphosphate and its use in the study of binding to heavy meromyosin APase. Biochim Biophys Acta 453: 93-97, 976 HIRASUA, UCHIDA : Preparation and properties of ' (or 3')-O-(,4,6-trinitrophenyl) adenosine 5'- triphosphate, an analog of adenosine triphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta 30: , 973 HOROVIZ A, LEVIZI A: An accurate method for determination of receptor-ligand and enzyme inhibitor dissociation constants from displacement curves. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: , 987 IVANOV AV, MODYANOV NN, ASARI A: Role of the self-association of β subunits in the oligomeric structure of Na + / + -APase. Biochem J 364: 93-99, 00 AAR, BOXENBAUM H, MAYERSOHN M: Estimation of I in a competitive enzyme-inhibition model: comparisons among three methods of data analysis. Drug Metab Dispos 7: , 999 OY A, AMLER E: Na,-adenosinetriphosphatase: the paradigm of a membrane transport protein. Physiol Res 44: 6-74, 995 UBALA M, HOFBAUEROVÁ, ERICH R, OPECÝ V Jr, RUMSCHEID R, PLÁŠE J, EISINGER J, SCHONER W, AMLER E: Phe(475) and Glu(446) but not Ser(445) participate in AP-binding to the alphasubunit of Na + / + -APase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 97:54-59, 00 UBALA M, PLÁŠE J, AMLER E: Limitations in linearized analyses of binding equilibria: binding of NP-AP to the H 4 -H 5 loop of Na/-APase. Eur Biophys J 3: , 003. LINGREL JB, UNZWEILER : Na +, + -APase. J Biol Chem 69: , 994. MOCZYDLOWSI EG, FORES PAG: Characterization of ',3'-O-(,4,6-trinitrocyclohexadienylidine)adenosine 5'- triphosphate as a fluorescent probe of the AP site of sodium and potassium transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem 56: , 98 RAN CM, FARLEY RA: Catalytic activity of an isolated domain of Na,-APase expressed in Escherichia coli. Biophys J 77: 58-66, 999 WANG ZX: An exact mathematical expression for describing competitive binding of two different ligands to a protein molecule. FEBS Lett 360: -4, 995 Reprint requests Jaromír Plášek, Institute of Physics, Charles University, e arlovu 5, 6 Prague, Czech Republic, plasek@karlov.mff.cuni.cz
Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999. free [A] (µm)
![Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999. free [A] (µm) Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999. free [A] (µm)](/thumbs/40/21435474.jpg) Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999 Equilibrium experiments study how the concentration of reaction products change as a function of reactant concentrations and/or reaction conditions. For
Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999 Equilibrium experiments study how the concentration of reaction products change as a function of reactant concentrations and/or reaction conditions. For
JBS FUNDAMENT Thermofluor Screen
 Cat. No. CS-330 Amount 1 Kit For in vitro use only. Quality guaranteed for 3 months. Store at 4 C. Application Screen for thermal stability of proteins as a function of the FUNDAMENTAL variables ph and
Cat. No. CS-330 Amount 1 Kit For in vitro use only. Quality guaranteed for 3 months. Store at 4 C. Application Screen for thermal stability of proteins as a function of the FUNDAMENTAL variables ph and
Recognition Kinetics of Biomolecules at the Surface of Different-Sized Spheres
 Supporting Material Recognition Kinetics of Biomolecules at the Surface of Different-Sized Spheres Jun Hu, Cong-Ying Wen, Zhi-Ling Zhang, Min Xie, Hai-Yan Xie, and Dai-Wen Pang * Key Laboratory of Analytical
Supporting Material Recognition Kinetics of Biomolecules at the Surface of Different-Sized Spheres Jun Hu, Cong-Ying Wen, Zhi-Ling Zhang, Min Xie, Hai-Yan Xie, and Dai-Wen Pang * Key Laboratory of Analytical
Molecular Spectroscopy
 Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit. Product Number FITC1 Storage Temperature 2 8 C
 FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit Product Number FITC1 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit is suitable for the conjugation of polyclonal and
FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit Product Number FITC1 Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The FluoroTag FITC Conjugation Kit is suitable for the conjugation of polyclonal and
(From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Nebraska College of Medicine, Omaha)
 THE INHIBITION OF THE ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY OF ACTOMYOSIN BY MAGNESIUM IONS BY IRVIN BRAVERMAN A.~ SERGIUS MORGULIS (From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Nebraska College of Medicine,
THE INHIBITION OF THE ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY OF ACTOMYOSIN BY MAGNESIUM IONS BY IRVIN BRAVERMAN A.~ SERGIUS MORGULIS (From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Nebraska College of Medicine,
Human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles stabilized with. intermolecular disulfide bonds. Supporting Information
 Human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles stabilized with intermolecular disulfide bonds Wentan Wang, Yanbin Huang*, Shufang Zhao, Ting Shao and Yi Cheng* Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University,
Human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles stabilized with intermolecular disulfide bonds Wentan Wang, Yanbin Huang*, Shufang Zhao, Ting Shao and Yi Cheng* Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University,
Hydrogen Peroxide Cell-Based Assay Kit
 Hydrogen Peroxide Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600050 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Hydrogen Peroxide Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600050 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
(c) How would your answers to problem (a) change if the molecular weight of the protein was 100,000 Dalton?
 Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Induction of Enzyme Activity in Bacteria:The Lac Operon. Preparation for Laboratory: Web Tutorial - Lac Operon - submit questions
 Induction of Enzyme Activity in Bacteria:The Lac Operon Preparation for Laboratory: Web Tutorial - Lac Operon - submit questions I. Background: For the last week you explored the functioning of the enzyme
Induction of Enzyme Activity in Bacteria:The Lac Operon Preparation for Laboratory: Web Tutorial - Lac Operon - submit questions I. Background: For the last week you explored the functioning of the enzyme
Chapter 10 Acid-Base titrations Problems 1, 2, 5, 7, 13, 16, 18, 21, 25
 Chapter 10 AcidBase titrations Problems 1, 2, 5, 7, 13, 16, 18, 21, 25 Up to now we have focused on calculations of ph or concentration at a few distinct points. In this chapter we will talk about titration
Chapter 10 AcidBase titrations Problems 1, 2, 5, 7, 13, 16, 18, 21, 25 Up to now we have focused on calculations of ph or concentration at a few distinct points. In this chapter we will talk about titration
Real-time PCR: Understanding C t
 APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
Fluorescent dyes for use with the
 Detection of Multiple Reporter Dyes in Real-time, On-line PCR Analysis with the LightCycler System Gregor Sagner, Cornelia Goldstein, and Rob van Miltenburg Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Penzberg, Germany
Detection of Multiple Reporter Dyes in Real-time, On-line PCR Analysis with the LightCycler System Gregor Sagner, Cornelia Goldstein, and Rob van Miltenburg Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Penzberg, Germany
Austin Peay State University Department of Chemistry Chem 1111. The Use of the Spectrophotometer and Beer's Law
 Purpose To become familiar with using a spectrophotometer and gain an understanding of Beer s law and it s relationship to solution concentration. Introduction Scientists use many methods to determine
Purpose To become familiar with using a spectrophotometer and gain an understanding of Beer s law and it s relationship to solution concentration. Introduction Scientists use many methods to determine
ACID-BASE TITRATIONS: DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE BY TITRATION WITH HYDROCHLORIC ACID BACKGROUND
 #3. Acid - Base Titrations 27 EXPERIMENT 3. ACID-BASE TITRATIONS: DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE BY TITRATION WITH HYDROCHLORIC ACID BACKGROUND Carbonate Equilibria In this experiment a solution of hydrochloric
#3. Acid - Base Titrations 27 EXPERIMENT 3. ACID-BASE TITRATIONS: DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE BY TITRATION WITH HYDROCHLORIC ACID BACKGROUND Carbonate Equilibria In this experiment a solution of hydrochloric
Problem Set 6 UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy. 13-1. Express the following absorbances in terms of percent transmittance:
 Problem Set 6 UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy 13-1. Express the following absorbances in terms of percent transmittance: a 0.051 b 0.918 c 0.379 d 0.261 e 0.485 f 0.072 A = log P o /P = log1/t = - log T
Problem Set 6 UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy 13-1. Express the following absorbances in terms of percent transmittance: a 0.051 b 0.918 c 0.379 d 0.261 e 0.485 f 0.072 A = log P o /P = log1/t = - log T
Chem 405 Biochemistry Lab I Experiment 2 Quantitation of an unknown protein solution.
 Chem 405 Biochemistry Lab I Experiment 2 Quantitation of an unknown protein solution. Introduction: The determination of protein concentration is frequently required in biochemical work. Several methods
Chem 405 Biochemistry Lab I Experiment 2 Quantitation of an unknown protein solution. Introduction: The determination of protein concentration is frequently required in biochemical work. Several methods
Technical Note. Roche Applied Science. No. LC 18/2004. Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR
 Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 18/2004 Purpose of this Note Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR The LightCycler Instrument uses several detection channels to monitor the amplification of
Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 18/2004 Purpose of this Note Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR The LightCycler Instrument uses several detection channels to monitor the amplification of
Outline. 1. Experiment. 2. Sample analysis and storage. 3. Image analysis and presenting data. 4. Probemaker
 Tips and tricks Note: this is just an informative document with general recommendations. Please contact support@olink.com should you have any queries. Document last reviewed 2011-11-17 Outline 1. Experiment
Tips and tricks Note: this is just an informative document with general recommendations. Please contact support@olink.com should you have any queries. Document last reviewed 2011-11-17 Outline 1. Experiment
2.500 Threshold. 2.000 1000e - 001. Threshold. Exponential phase. Cycle Number
 application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
Enzyme Kinetics: Properties of â-galactosidase
 Enzyme Kinetics: Properties of â-galactosidase Preparation for Laboratory: Read the introduction to this laboratory before doing the Web Tutorial - Beta Galactosidase. Additional background: Freeman, skim
Enzyme Kinetics: Properties of â-galactosidase Preparation for Laboratory: Read the introduction to this laboratory before doing the Web Tutorial - Beta Galactosidase. Additional background: Freeman, skim
to 370C in a matter of seconds. Materials and Methods.-Yeast spheroplasts were prepared, resuspended to a concentration
 A MUTANT OF YEAST APPARENTLY DEFECTIVE IN THE INITIATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS* BT LELAND H. HARTWELLt AND CALVIN S. MCLAUGHLIN DEPARTMENT OF MOLECULAR AND CELL BIOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA (IRVINE)
A MUTANT OF YEAST APPARENTLY DEFECTIVE IN THE INITIATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS* BT LELAND H. HARTWELLt AND CALVIN S. MCLAUGHLIN DEPARTMENT OF MOLECULAR AND CELL BIOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA (IRVINE)
Nucleic Acid Purity Assessment using A 260 /A 280 Ratios
 Nucleic Acid Purity Assessment using A 260 /A 280 Ratios A common practice in molecular biology is to perform a quick assessment of the purity of nucleic acid samples by determining the ratio of spectrophotometric
Nucleic Acid Purity Assessment using A 260 /A 280 Ratios A common practice in molecular biology is to perform a quick assessment of the purity of nucleic acid samples by determining the ratio of spectrophotometric
Enzymes: Amylase Activity in Starch-degrading Soil Isolates
 Enzymes: Amylase Activity in Starch-degrading Soil Isolates Introduction This week you will continue our theme of industrial microbiologist by characterizing the enzyme activity we selected for (starch
Enzymes: Amylase Activity in Starch-degrading Soil Isolates Introduction This week you will continue our theme of industrial microbiologist by characterizing the enzyme activity we selected for (starch
NO CALCULATORS OR CELL PHONES ALLOWED
 Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit. HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit. 96 Tests. Table of Contents.
 For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit 96 Tests HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit Cat# 4690-096-K Cat# 4690-096-K Table of Contents
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit 96 Tests HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit Cat# 4690-096-K Cat# 4690-096-K Table of Contents
Technical Note. Roche Applied Science. No. LC 19/2004. Color Compensation
 Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 19/2004 Purpose of this Note Color The LightCycler System is able to simultaneously detect and analyze more than one color in each capillary. Due to overlap
Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 19/2004 Purpose of this Note Color The LightCycler System is able to simultaneously detect and analyze more than one color in each capillary. Due to overlap
P i Per Pyrophosphate Assay Kit
 P i Per Pyrophosphate Assay Kit Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Concentration Storage Stability Amplex Red reagent (Component A, MW = 257) 5 vials, 0.26 mg each DMSO, anhydrous
P i Per Pyrophosphate Assay Kit Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Concentration Storage Stability Amplex Red reagent (Component A, MW = 257) 5 vials, 0.26 mg each DMSO, anhydrous
Lecture 11 Enzymes: Kinetics
 Lecture 11 Enzymes: Kinetics Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, 6th ed., Chapter 8, pp. 216-225 Key Concepts Kinetics is the study of reaction rates (velocities). Study of enzyme kinetics is useful for
Lecture 11 Enzymes: Kinetics Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, 6th ed., Chapter 8, pp. 216-225 Key Concepts Kinetics is the study of reaction rates (velocities). Study of enzyme kinetics is useful for
9. Analysis of an Acid-Base Titration Curve: The Gran Plot
 9. Analysis of an Acid-Base Titration Curve: The Gran Plot In this experiment, you will titrate a sample of pure potassium hydrogen phthalate (Table 10-4) with standard NaOH. A Gran plot will be used to
9. Analysis of an Acid-Base Titration Curve: The Gran Plot In this experiment, you will titrate a sample of pure potassium hydrogen phthalate (Table 10-4) with standard NaOH. A Gran plot will be used to
Introduction, Noncovalent Bonds, and Properties of Water
 Lecture 1 Introduction, Noncovalent Bonds, and Properties of Water Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer: Chapter 1 problems in textbook: chapter 1, pp. 23-24, #1,2,3,6,7,8,9, 10,11; practice problems at end
Lecture 1 Introduction, Noncovalent Bonds, and Properties of Water Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer: Chapter 1 problems in textbook: chapter 1, pp. 23-24, #1,2,3,6,7,8,9, 10,11; practice problems at end
SOLUBILITY, IONIC STRENGTH AND ACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS
 SOLUBILITY, IONIC STRENGTH AND ACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS References: 1. See `References to Experiments' for text references.. W. C. Wise and C. W. Davies, J. Chem. Soc., 73 (1938), "The Conductivity of Calcium
SOLUBILITY, IONIC STRENGTH AND ACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS References: 1. See `References to Experiments' for text references.. W. C. Wise and C. W. Davies, J. Chem. Soc., 73 (1938), "The Conductivity of Calcium
High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B. PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014
 High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014 Introduction This report describes the epitope mapping of autoimmune sera
High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014 Introduction This report describes the epitope mapping of autoimmune sera
Calculating Nucleic Acid or Protein Concentration Using the GloMax Multi+ Microplate Instrument
 Calculating Nucleic Acid or Protein Concentration Using the GloMax Multi+ Microplate Instrument Technical Note INTRODUCTION Direct measurements of nucleic acid samples at OD 260 or protein samples at OD
Calculating Nucleic Acid or Protein Concentration Using the GloMax Multi+ Microplate Instrument Technical Note INTRODUCTION Direct measurements of nucleic acid samples at OD 260 or protein samples at OD
Chemistry 201. Practical aspects of buffers. NC State University. Lecture 15
 Chemistry 201 Lecture 15 Practical aspects of buffers NC State University The everyday ph scale To review what ph means in practice, we consider the ph of everyday substances that we know from experience.
Chemistry 201 Lecture 15 Practical aspects of buffers NC State University The everyday ph scale To review what ph means in practice, we consider the ph of everyday substances that we know from experience.
VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND
 Figure from: http://www.embl.de/nmr/sattler/teaching Why NMR (instead of X ray crystallography) a great number of macromolecules won't crystallize) natural environmant (water) ligand binding and inter
Figure from: http://www.embl.de/nmr/sattler/teaching Why NMR (instead of X ray crystallography) a great number of macromolecules won't crystallize) natural environmant (water) ligand binding and inter
Unfolding and Aggregation of mabs Application Note NT-PR-005
 Unfolding and Aggregation of mabs Application Note NT-PR-005 Analysis of formulation-dependent colloidal and conformational stability of monoclonal antibodies Franziska Söltl 1, Jonathan Derix 1, Michaela
Unfolding and Aggregation of mabs Application Note NT-PR-005 Analysis of formulation-dependent colloidal and conformational stability of monoclonal antibodies Franziska Söltl 1, Jonathan Derix 1, Michaela
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
Lab #11: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant
 Lab #11: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
Lab #11: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
EZ-Link NHS-Biotin Reagents
 ITRUCTI EZ-Link -Biotin Reagents 3747. Meridian Road P.. Box 117 Rockford, IL 61105 20217 21336 21343 0237.4 umber Description 20217 EZ-Link -Biotin, 100 mg, -hydroxysuccinimidobiotin Molecular Weight:
ITRUCTI EZ-Link -Biotin Reagents 3747. Meridian Road P.. Box 117 Rockford, IL 61105 20217 21336 21343 0237.4 umber Description 20217 EZ-Link -Biotin, 100 mg, -hydroxysuccinimidobiotin Molecular Weight:
Optimizing Performance of the Transcreener ADP Assay for the BioTek Synergy 2 and 4 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers
 Optimizing Performance of the Transcreener ADP Assay for the BioTek Synergy 2 and 4 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers Brad Larson 1, Karen Kleman-Leyer 1, Xavier Amouretti 2 1 BellBrook Labs, Madison, WI,
Optimizing Performance of the Transcreener ADP Assay for the BioTek Synergy 2 and 4 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers Brad Larson 1, Karen Kleman-Leyer 1, Xavier Amouretti 2 1 BellBrook Labs, Madison, WI,
PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR. Results Interpretation Guide
 PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR Results Interpretation Guide Pathogen Detection Systems by Real Time PCR Microbial offers real time PCR based systems for the detection of pathogenic bacteria
PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR Results Interpretation Guide Pathogen Detection Systems by Real Time PCR Microbial offers real time PCR based systems for the detection of pathogenic bacteria
ENZYME KINETICS ENZYME-SUBSTRATE PRODUCTS
 ENZYME KINETICS INTRODUCTION The study of reaction rates catalyzed by enzymes and the factors affecting them is generally referred to as enzyme kinetics. The basic components of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
ENZYME KINETICS INTRODUCTION The study of reaction rates catalyzed by enzymes and the factors affecting them is generally referred to as enzyme kinetics. The basic components of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
Application Note. Separation of three monoclonal antibody variants using MCSGP. Summary
 Application Note Separation of three monoclonal antibody variants using MCSGP Category Matrix Method Keywords Analytes ID Continuous chromatography, Biochromatography; FPLC Protein A-purified monoclonal
Application Note Separation of three monoclonal antibody variants using MCSGP Category Matrix Method Keywords Analytes ID Continuous chromatography, Biochromatography; FPLC Protein A-purified monoclonal
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small
 The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
INSTRUCTION Probemaker
 INSTRUCTION Probemaker Instructions for Duolink In Situ Probemaker PLUS (Art. no. 92009-0020) and Duolink In Situ Probemaker MINUS (Art. no. 92010-0020) Table of content 1. Introduction 4 2. Applications
INSTRUCTION Probemaker Instructions for Duolink In Situ Probemaker PLUS (Art. no. 92009-0020) and Duolink In Situ Probemaker MINUS (Art. no. 92010-0020) Table of content 1. Introduction 4 2. Applications
Experiment 5: Phase diagram for a three-component system (Dated: April 12, 2010)
 Experiment 5: Phase diagram for a three-component system (Dated: April 12, 2010) I. INTRODUCTION It is sometimes necessary to know the mutual solubilities of liquids in a two-phase system. For example,
Experiment 5: Phase diagram for a three-component system (Dated: April 12, 2010) I. INTRODUCTION It is sometimes necessary to know the mutual solubilities of liquids in a two-phase system. For example,
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display
 Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Anion chromatography using on-line recycled eluents
 Journal of Chromatography A, 1089 (2005) 82 86 Anion chromatography using on-line recycled eluents Takashi Yokoyama, Hitoe Maekubo, Asami Sakai, Michio Zenki Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,
Journal of Chromatography A, 1089 (2005) 82 86 Anion chromatography using on-line recycled eluents Takashi Yokoyama, Hitoe Maekubo, Asami Sakai, Michio Zenki Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science,
LAB TOPIC 4: ENZYMES. Enzyme catalyzed reactions can be expressed in the following way:
 LAB TOPIC 4: ENZYMES Objectives Define enzyme and describe the activity of enzymes in cells. Discuss the effects of varying enzyme concentrations on the rate of enzyme activity. Discuss the effects of
LAB TOPIC 4: ENZYMES Objectives Define enzyme and describe the activity of enzymes in cells. Discuss the effects of varying enzyme concentrations on the rate of enzyme activity. Discuss the effects of
An acid is a substance that produces H + (H 3 O + ) Ions in aqueous solution. A base is a substance that produces OH - ions in aqueous solution.
 Chapter 8 Acids and Bases Definitions Arrhenius definitions: An acid is a substance that produces H + (H 3 O + ) Ions in aqueous solution. A base is a substance that produces OH - ions in aqueous solution.
Chapter 8 Acids and Bases Definitions Arrhenius definitions: An acid is a substance that produces H + (H 3 O + ) Ions in aqueous solution. A base is a substance that produces OH - ions in aqueous solution.
Experiment 7 (Lab Period 8) Quantitative Determination of Phosphatase Activity
 Experiment 7 (Lab Period 8) Quantitative Determination of Phosphatase Activity Phosphatases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of organic-phosphate compounds, releasing inorganic phosphate from the
Experiment 7 (Lab Period 8) Quantitative Determination of Phosphatase Activity Phosphatases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of organic-phosphate compounds, releasing inorganic phosphate from the
Copyright 1999 2010 by Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 12
 Introduction to Absorbance Spectroscopy A single beam spectrophotometer is comprised of a light source, a monochromator, a sample holder, and a detector. An ideal instrument has a light source that emits
Introduction to Absorbance Spectroscopy A single beam spectrophotometer is comprised of a light source, a monochromator, a sample holder, and a detector. An ideal instrument has a light source that emits
ph: Measurement and Uses
 ph: Measurement and Uses One of the most important properties of aqueous solutions is the concentration of hydrogen ion. The concentration of H + (or H 3 O + ) affects the solubility of inorganic and organic
ph: Measurement and Uses One of the most important properties of aqueous solutions is the concentration of hydrogen ion. The concentration of H + (or H 3 O + ) affects the solubility of inorganic and organic
VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: TEXT AND METHODOLOGY Q2(R1)
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: TEXT AND METHODOLOGY
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: TEXT AND METHODOLOGY
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/339/ra80/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Manipulation of receptor oligomerization as a strategy to inhibit signaling by TNF superfamily members Julia T. Warren,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/339/ra80/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Manipulation of receptor oligomerization as a strategy to inhibit signaling by TNF superfamily members Julia T. Warren,
Biology 309 Lab Notebook
 Name: Biology 309 Lab Notebook This is a guided lab notebook for you to keep well-organized notes about procedures and record experimental data for experiments as they are performed. It is guided because,
Name: Biology 309 Lab Notebook This is a guided lab notebook for you to keep well-organized notes about procedures and record experimental data for experiments as they are performed. It is guided because,
Figure 5. Energy of activation with and without an enzyme.
 Biology 20 Laboratory ENZYMES & CELLULAR RESPIRATION OBJECTIVE To be able to list the general characteristics of enzymes. To study the effects of enzymes on the rate of chemical reactions. To demonstrate
Biology 20 Laboratory ENZYMES & CELLULAR RESPIRATION OBJECTIVE To be able to list the general characteristics of enzymes. To study the effects of enzymes on the rate of chemical reactions. To demonstrate
Spectroscopic Characterization of Cytochrome C Entrapped in AOT Reverse Micelles. Kristen Grinstead
 Spectroscopic Characterization of Cytochrome C Entrapped in AOT Reverse Micelles Kristen Grinstead Chemistry Department Marshall University One John Marshall Drive Huntington, WV 25755 grinstead1@marshall.edu
Spectroscopic Characterization of Cytochrome C Entrapped in AOT Reverse Micelles Kristen Grinstead Chemistry Department Marshall University One John Marshall Drive Huntington, WV 25755 grinstead1@marshall.edu
Introduction to flow cytometry
 Introduction to flow cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology. Discover more with our introduction to flow cytometry. Flow cytometry is now a widely used method for analyzing the expression
Introduction to flow cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology. Discover more with our introduction to flow cytometry. Flow cytometry is now a widely used method for analyzing the expression
Marmara Üniversitesi Fen-Edebiyat Fakültesi Kimya Bölümü / Biyokimya Anabilim Dalı PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PROTEINS
 EXPERIMENT VI PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PROTEINS I- Protein isolation and dialysis In order to investigate its structure and properties a protein must be obtained in pure form. Since proteins
EXPERIMENT VI PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PROTEINS I- Protein isolation and dialysis In order to investigate its structure and properties a protein must be obtained in pure form. Since proteins
Chemistry 111 Laboratory Experiment 7: Determination of Reaction Stoichiometry and Chemical Equilibrium
 Chemistry 111 Laboratory Experiment 7: Determination of Reaction Stoichiometry and Chemical Equilibrium Introduction The word equilibrium suggests balance or stability. The fact that a chemical reaction
Chemistry 111 Laboratory Experiment 7: Determination of Reaction Stoichiometry and Chemical Equilibrium Introduction The word equilibrium suggests balance or stability. The fact that a chemical reaction
The Rate Constant for Fluorescence Quenching 1
 The Rate Constant for Fluorescence Quenching 1 Purpose This experiment utilizes fluorescence intensity measurements to determine the rate constant for the fluorescence quenching of anthracene or perylene
The Rate Constant for Fluorescence Quenching 1 Purpose This experiment utilizes fluorescence intensity measurements to determine the rate constant for the fluorescence quenching of anthracene or perylene
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
IAM Chromatography. HPLC Separation Tools for Membrane Protein Purification and Drug Membrane Permeability Prediction
 IAM Chromatography Immobilized Artificial Membrane (IAM) technology is an innovative approach to chromatography in which the chromatographic surface emulates the lipid environment of the cell membrane.
IAM Chromatography Immobilized Artificial Membrane (IAM) technology is an innovative approach to chromatography in which the chromatographic surface emulates the lipid environment of the cell membrane.
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology November 1996 ICH Guidance for Industry Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology Additional copies are available from:
Guidance for Industry Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology November 1996 ICH Guidance for Industry Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology Additional copies are available from:
竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法
 竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法 ABSTRACT The simplest way to determine whether two monoclonal antibodies bind to distinct sites on a protein antigen is to carry out a competition assay. The assay can
竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法 ABSTRACT The simplest way to determine whether two monoclonal antibodies bind to distinct sites on a protein antigen is to carry out a competition assay. The assay can
ab102884 FITC Conjugation Kit Protocol
 ab102884 FITC Conjugation Kit Protocol Antibody and protein modification This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 4 November 2013 Table of Contents
ab102884 FITC Conjugation Kit Protocol Antibody and protein modification This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 4 November 2013 Table of Contents
Theory of Binding Data Analysis
 Chapter 7 Theory of inding Data Analysis Clark s Theory......................................... 7-2 Non-specific inding.................................. 7-3 Determination of inding Constants...................
Chapter 7 Theory of inding Data Analysis Clark s Theory......................................... 7-2 Non-specific inding.................................. 7-3 Determination of inding Constants...................
OLIVÉR BÁNHIDI 1. Introduction
 Materials Science and Engineering, Volume 39, No. 1 (2014), pp. 5 13. DETERMINATION OF THE ANTIMONY- AND STRONTIUM- CONTENT OF ALUMINIUM ALLOYS BY INDUCTIVELY COUPLED PLASMA ATOM EMISSION SPECTROMETRY
Materials Science and Engineering, Volume 39, No. 1 (2014), pp. 5 13. DETERMINATION OF THE ANTIMONY- AND STRONTIUM- CONTENT OF ALUMINIUM ALLOYS BY INDUCTIVELY COUPLED PLASMA ATOM EMISSION SPECTROMETRY
Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Digestive Physiology: Amylase hydrolysis of starch
 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Digestive Physiology: Amylase hydrolysis of starch Introduction Enzymes are proteins composed of amino acid building blocks. Enzymes catalyze or increase the rate of metabolic
Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Digestive Physiology: Amylase hydrolysis of starch Introduction Enzymes are proteins composed of amino acid building blocks. Enzymes catalyze or increase the rate of metabolic
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service
 KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer. α-helix transmembrane domain. Multiple transmembrane helices in one polypeptide
 Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer α-helix transmembrane domain Hydrophobic R groups of a.a. interact with fatty acid chains Multiple transmembrane helices in one polypeptide Polar a.a. Hydrophilic
Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer α-helix transmembrane domain Hydrophobic R groups of a.a. interact with fatty acid chains Multiple transmembrane helices in one polypeptide Polar a.a. Hydrophilic
Supporting Information. The G-triplex DNA could function as a new variety of DNA peroxidase
 Supporting Information The G-triplex DNA could function as a new variety of DNA peroxidase Shaoru Wang +, Boshi Fu +, Shuang Peng, Xiaoe Zhang, Tian Tian*, Xiang Zhou* College of Chemistry and Molecular
Supporting Information The G-triplex DNA could function as a new variety of DNA peroxidase Shaoru Wang +, Boshi Fu +, Shuang Peng, Xiaoe Zhang, Tian Tian*, Xiang Zhou* College of Chemistry and Molecular
Peptide bonds: resonance structure. Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains. Dihedral angles. Peptide bond. Protein physics, Lecture 5
 Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
EdU Flow Cytometry Kit. User Manual
 User Manual Ordering information: (for detailed kit content see Table 2) EdU Flow Cytometry Kits for 50 assays: Product number EdU Used fluorescent dye BCK-FC488-50 10 mg 6-FAM Azide BCK-FC555-50 10 mg
User Manual Ordering information: (for detailed kit content see Table 2) EdU Flow Cytometry Kits for 50 assays: Product number EdU Used fluorescent dye BCK-FC488-50 10 mg 6-FAM Azide BCK-FC555-50 10 mg
Supporting Information. Rational design of Au nanorods assemblies for highly sensitive and selective SERS detection of prostate specific antigen
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rational design of Au nanorods assemblies for highly sensitive and selective
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rational design of Au nanorods assemblies for highly sensitive and selective
Two-photon FCS Tutorial. Berland Lab Department of Physics Emory University
 Two-photon FCS Tutorial Berland Lab Department of Physics Emory University What is FCS? FCS : Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy FCS is a technique for acquiring dynamical information from spontaneous
Two-photon FCS Tutorial Berland Lab Department of Physics Emory University What is FCS? FCS : Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy FCS is a technique for acquiring dynamical information from spontaneous
Co Extra (GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability) Outcomes of Co Extra
 GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit
 ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
HiPer Ion Exchange Chromatography Teaching Kit
 HiPer Ion Exchange Chromatography Teaching Kit Product Code: HTC001 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 5-6 hours Storage Instructions: The kit is stable for
HiPer Ion Exchange Chromatography Teaching Kit Product Code: HTC001 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 5-6 hours Storage Instructions: The kit is stable for
Spectrophotometry and the Beer-Lambert Law: An Important Analytical Technique in Chemistry
 Spectrophotometry and the Beer-Lambert Law: An Important Analytical Technique in Chemistry Jon H. Hardesty, PhD and Bassam Attili, PhD Collin College Department of Chemistry Introduction: In the last lab
Spectrophotometry and the Beer-Lambert Law: An Important Analytical Technique in Chemistry Jon H. Hardesty, PhD and Bassam Attili, PhD Collin College Department of Chemistry Introduction: In the last lab
Application of a New Immobilization H/D Exchange Protocol: A Calmodulin Study
 Application of a New Immobilization H/D Exchange Protocol: A Calmodulin Study Jiang Zhao; Mei Zhu; Daryl E. Gilblin; Michael L. Gross Washington University Center for Biomrdical and Bioorganic Mass Spectrometry:
Application of a New Immobilization H/D Exchange Protocol: A Calmodulin Study Jiang Zhao; Mei Zhu; Daryl E. Gilblin; Michael L. Gross Washington University Center for Biomrdical and Bioorganic Mass Spectrometry:
Related concepts Kohlrausch s law, equivalent conductivity, temperature dependence of conductivity, Ostwald s dilution law.
 Conductivity of strong and weak electrolytes TEC Related concepts Kohlrausch s law, equivalent conductivity, temperature dependence of conductivity, Ostwald s dilution law. Principle It is possible to
Conductivity of strong and weak electrolytes TEC Related concepts Kohlrausch s law, equivalent conductivity, temperature dependence of conductivity, Ostwald s dilution law. Principle It is possible to
BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES: FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURES & TRANSPORT
 BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES: FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURES & TRANSPORT UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BMLS II / B Pharm II / BDS II VJ Temple
BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES: FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURES & TRANSPORT UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BMLS II / B Pharm II / BDS II VJ Temple
Quantitation of Peptides and Amino Acids with a Synergy HT using UV Fluorescence
 Quantitation of Peptides and Amino Acids with a Synergy HT using UV Fluorescence Introduction Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells contain a number of compounds that are fluorescent with UV light excitation.
Quantitation of Peptides and Amino Acids with a Synergy HT using UV Fluorescence Introduction Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells contain a number of compounds that are fluorescent with UV light excitation.
How To Make A Molecular Encoder And Decoder
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Molecular Encoder - Decoder Based on Assembly of Graphene with Dye-labeled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Molecular Encoder - Decoder Based on Assembly of Graphene with Dye-labeled
Lab 2 Biochemistry. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Lipid Structure and Role in Food. The lab has the following learning objectives.
 1 Lab 2 Biochemistry Learning Objectives The lab has the following learning objectives. Investigate the role of double bonding in fatty acids, through models. Developing a calibration curve for a Benedict
1 Lab 2 Biochemistry Learning Objectives The lab has the following learning objectives. Investigate the role of double bonding in fatty acids, through models. Developing a calibration curve for a Benedict
Q.1 Classify the following according to Lewis theory and Brønsted-Lowry theory.
 Acid-base 2816 1 Acid-base theories ACIDS & BASES - IONIC EQUILIBRIA LEWIS acid electron pair acceptor H +, AlCl 3 base electron pair donor NH 3, H 2 O, C 2 H 5 OH, OH e.g. H 3 N: -> BF 3 > H 3 N + BF
Acid-base 2816 1 Acid-base theories ACIDS & BASES - IONIC EQUILIBRIA LEWIS acid electron pair acceptor H +, AlCl 3 base electron pair donor NH 3, H 2 O, C 2 H 5 OH, OH e.g. H 3 N: -> BF 3 > H 3 N + BF
CRITICAL ASPECTS OF STAINING FOR FLOW CYTOMETRY
 页 码,1/6 CRITICAL ASPECTS OF STAINING FOR FLOW CYTOMETRY From Givan, A.L. (2000), chapter in In Living Color: Protocols in Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting (R. Diamond and S. DeMaggio, eds). Springer, Berlin,
页 码,1/6 CRITICAL ASPECTS OF STAINING FOR FLOW CYTOMETRY From Givan, A.L. (2000), chapter in In Living Color: Protocols in Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting (R. Diamond and S. DeMaggio, eds). Springer, Berlin,
Determining the Identity of an Unknown Weak Acid
 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to observe and measure a weak acid neutralization and determine the identity of an unknown acid by titration. Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to identify
Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to observe and measure a weak acid neutralization and determine the identity of an unknown acid by titration. Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to identify
Enzymes. Enzymes are characterized by: Specificity - highly specific for substrates
 Enzymes Enzymes are characterized by: Catalytic Power - rates are 10 6-10 12 greater than corresponding uncatalyzed reactions Specificity - highly specific for substrates Regulation - acheived in many
Enzymes Enzymes are characterized by: Catalytic Power - rates are 10 6-10 12 greater than corresponding uncatalyzed reactions Specificity - highly specific for substrates Regulation - acheived in many
DNA Assembly and Enzymatic Cutting in Solutions: A Gold Nanoparticle Based SERS Detection Strategy
 Supporting Information DNA Assembly and Enzymatic Cutting in Solutions: A Gold Nanoparticle Based SERS Detection Strategy Elizabeth Crew 1, Hong Yan 1, Liqin Lin 1, Jun Yin 1, Zakiya Skeete 1, Timur Kotlyar
Supporting Information DNA Assembly and Enzymatic Cutting in Solutions: A Gold Nanoparticle Based SERS Detection Strategy Elizabeth Crew 1, Hong Yan 1, Liqin Lin 1, Jun Yin 1, Zakiya Skeete 1, Timur Kotlyar
High flexibility of DNA on short length scales probed by atomic force microscopy
 High flexibility of DNA on short length scales probed by atomic force microscopy Wiggins P. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnology (2006) presented by Anja Schwäger 23.01.2008 Outline Theory/Background Elasticity
High flexibility of DNA on short length scales probed by atomic force microscopy Wiggins P. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnology (2006) presented by Anja Schwäger 23.01.2008 Outline Theory/Background Elasticity
Biochemistry 462a Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading - Chapter 7 Practice problems - Chapter 7: 1-6; Proteins extra problems
 Biochemistry 462a Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading - Chapter 7 Practice problems - Chapter 7: 1-6; Proteins extra problems Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Oxygen is required for oxidative metabolism
Biochemistry 462a Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading - Chapter 7 Practice problems - Chapter 7: 1-6; Proteins extra problems Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Oxygen is required for oxidative metabolism
Chapter 3. Protein Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Collagen I Self-Assembly: Revealing the Developing Structures that Generate Turbidity. Supporting Material
 Collagen I Self-Assembly: Revealing the Developing Structures that Generate Turbidity Supporting Material Jieling Zhu and Laura J. Kaufman* Department of Chemistry, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027
Collagen I Self-Assembly: Revealing the Developing Structures that Generate Turbidity Supporting Material Jieling Zhu and Laura J. Kaufman* Department of Chemistry, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027
Spectrophotometry Practical Lesson on Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry
 Spectrophotometry Practical Lesson on Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry General Medicine Jiřina Crkovská (translated by Jan Pláteník) 2010/2011 1 Spectrophotometry is one of the most widely used instrumental
Spectrophotometry Practical Lesson on Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry General Medicine Jiřina Crkovská (translated by Jan Pláteník) 2010/2011 1 Spectrophotometry is one of the most widely used instrumental
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism
 Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Name Period Concept 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 1. Define metabolism. The totality of an organism
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Name Period Concept 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 1. Define metabolism. The totality of an organism
