CTA OF THE EXTRACORONARY HEART
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Bond
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CTA OF THE EXTRACORONARY HEART Charles White MD Director of Thoracic Imaging Department of Radiology University of Maryland NO DISCLOSURES
2 CARDIAC CASE DISTRIBUTION Coronary CTA 30% ED chest pain 10% Post-CABG -10% Other 50%» Congenital HD» Valves» Pulmonary Veins RF ablation» Tumor» Perfusion, dysplasia
3 CARDIAC CT Outline Technical Aspects Extra-coronary cardiac CT» Chambers» Valves» Masses» Congenital Function and perfusion Interactive Workstation
4 TECHNICAL ASPECTS CORONARY vs EXTRACORONARY CTA CONSIDERATIONS TYPE OF ECG-GATING CONTRAST INJECTION LENGTH OF SCAN
5 CLASSIC ECG-GATING IN MDCT Prospective part of cardiac cycle Lower radiation HR sensitive (<65bpm) Ca Scoring Retrospective entire cardiac cycle Higher radiation less sensitive to HR Coronary CTA Tube output ON Tube output OFF Tube output (x-ray) ON Spiral Acquisition
6 RETROSPECTIVE GATING DOSE MODULATION Retrospective ECG Tagging Tube output (x-ray) ON Spiral Acquisition Retrospective ECG Tagging With Dose Modulation Maximum tube output (100%) Reduced tube output (20%) Spiral Acquisition
7 ECG-GATING IN MDCT CORONARY VS EXTRCORONARY CTA Coronary CTA Prospective is preferred Retrospective if:» High or irregular heart rate» Large BMI» Need functional info Extracoronary CTA Indications often require function Retrospective more often used If prospective used, looser HR/BMI limitations 2º less strict IQ needs
8 TECHNICAL ASPECTS CONTRAST ADMINISTATION CARDIAC CTA (Majority) Test injection» 20 6 cc/sec Injection protocol» 80 ml 6 cc/sec» 40 ml 5 cc/sec» 50 ml 5 cc/sec Bolus tracking 100 CC CARDIAC CT (R sided) Test injection» 20 6 cc/sec Injection protocol» 80 ml 6 cc/sec» 50 ml 2 cc/sec» 50 ml 5 cc/sec Bolus tracking 130 CC Courtesy: MedRad
9 CONTRAST ADMINISTATION CARDIAC CTA (Majority) CARDIAC CT (R sided)
10 LENGTH OF SCAN
11 ITERATIVE RECONSTRUCTION (225 LB.) FBP Iterative Recon
12 SPECIFIC DISEASE OUTLINE Chambers Valves Masses Congenital LV analysis (function, perfusion)
13 CHAMBERS CARDIAC VIEWS 4CH Axial 2CH VLA 2CH SA
14 LEFT ATRIAL EVALUATION Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation Radiofrequency ablation Probing tool destroys abnormal conduction pathways in LA Risk of post-procedure pulmonary vein stenosis
15 LEFT ATRIAL EVALUATION
16 LEFT ATRIAL EVALUATION
17 LEFT ATRIAL EVALUATION NORMAL VARIANT
18 LEFT ATRIAL EVALUATION-COMPLICATION
19 LEFT ATRIAL EVALUATION - STENOSIS 18 (5%) of 335 pts developed pulmonary vein stenosis post RF ablation for AF From: Saad Ann Int Med, 2003
20 LA RF ABLATION COMPLICATION ATRIOESOPHAGEAL FISTULA Courtesy: S. Aquino MD
21 LA THROMBUS
22 LV ANEURYSM
23 PSEUDOANEURYSM
24
25 CARDIAC VALVES
26 AORTIC VALVE ASSESSMENT
27 CALCIFIED AORTIC VALVE
28 BICUSPID AORTIC VALVE 1-2% of population M:F = 2:1 Predisposition to AS, usually in middle age Assoc with coarctation, William s Sx
29 VALVES IN MOTION Normal Stenotic-bicuspid
30 AORTIC STENOSIS Planimetric measurements of AVA with retrospectively electrocardiographically gated 16-detector row CT allow classification of AS that is similar to that achieved with measurements by using echocardiographic methods Alkahdi H. Radiology. 2006;240:47-55.
31 AORTIC REGURGITATION
32 AORTIC REGURGITATION
33 AORTIC REGURGITATION Results of assessment of AR with 64- section CT are similar to those with TTE. Alkadhi H. Radiology. 2007;245:111
34 SUBAORTIC STENOSIS
35 REFORMATS
36 AORTIC VALVE PRE/POST-OP
37 TRANSCATHETER AORTIC VALVE IMPLANTATION (TAVI OR TAVR)
38 TAVI- POST-OPERATIVE
39 AORTIC VALVE COMPLICATION
40 AORTIC VALVE COMPLICATION
41 POST-OP ASSESSMENT
42 MITRAL VALVE ASSESSMENT
43 MITRAL VALVE ASSESSMENT
44 MITRAL VALVE IN MOTION
45 Mitral valve leaflet calcification on MDCT indicates mitral valve sclerosis or stenosis. Mahnken AH. AJR 2007; 188:
46 MITRAL VALVE PROSTHESES
47 PULMONIC VALVE ASSESSMENT
48 PULMONIC VALVE ASSESSMENT
49 TRICUSPID VALVE ASSESSMENT
50 TRICUSPID
51 MASSES
52 CARDIAC THROMBUS
53 CARDIAC THROMBUS
54 CARDIAC MASSES Lipomatous Hypertrophy
55 LARGE MASS
56 WHERE S THE MASS
57 CARDIAC TUMOR Hepatoma Liver
58 CARDIAC TUMOR Angiosarcoma
59 CARDIAC TUMOR Right atrial osteosarcoma
60 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Valvular» Bicuspid aortic valve» Pulmonic stenosis» Tricuspid (Ebstein s anomaly) Left to right shunts» Atrial septal defect (most common)» Ventricular septal defect» Patent ductus arteriosus Complex» Tetralogy of Fallot» Transposition of great vessels» Miscellaneous Post-operative
61 CT FOR CHD - PRINCIPLES Ideally, adults (radiation concern) Children for optimal 3D recons In younger children» Sedation» Hand injection» Non-gated often» mg/ml concentration
62 ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT Most common adult CHD F>M 3:1 Secundum (75%), primum, and sinus venosus types Fatigue, SOB, atrial arrhythmias Consider transcatheter closure
63 VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT 2 nd most common adult CHD Usually small Membranous, muscular, supracristal Dyspnea, pulmonary HTN Courtesy: L. Haramati MD
64 PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS Abnormal persistence after 10 days of life Fourth most common adult CHD abnormality Complications» Pulmonary hypertension» CHF» Aneurysm
65 PULMONIC STENOSIS 10% of CHD M=F Dysplastic leaflets Large Left PA, NL R PA due to post-stenotic jet Balloon dilatation
66 TETRALOGY OF FALLOT VSD/RVH Pulmonary Stenosis Aortic override Right aortic arch
67 LV ANALYSIS
68 LV FUNCTIONAL ASSESSMENT Strong correlation between CT and MRI LV function (r> 0.95) Yamamuro Radiology 2005
69 LV FUNCTION/PERFUSION
70 LV FUNCTION/PERFUSION
71 LV FUNCTION/PERFUSION
72 CARDIAC PERFUSION Perfusion defect
73 CARDIAC PERFUSION DEFECT
74 Courtesy: R. Yang MD
75 THANK YOU
020 // Congenital Heart Disease
 020 // Congenital Heart Disease CONTENTS 188 Basics 188 Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) 191 Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) 192 Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD) 194 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) 195 Coronary Fistulas
020 // Congenital Heart Disease CONTENTS 188 Basics 188 Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) 191 Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) 192 Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD) 194 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) 195 Coronary Fistulas
Common types of congenital heart defects
 Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Cardiology Fellowship Manual. Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 Page
 Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 Page 2015-2016 UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION
Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 Page 2015-2016 UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION
How to get insurance companies to work with you
 Paying for Quality ACHD Care How to get insurance companies to work with you Christy Sillman, RN, MSN ACHD nurse coordinator Inpatient ACHD Nurse Educator The Adult Congenital Heart Program Stanford Lucile
Paying for Quality ACHD Care How to get insurance companies to work with you Christy Sillman, RN, MSN ACHD nurse coordinator Inpatient ACHD Nurse Educator The Adult Congenital Heart Program Stanford Lucile
Workshop B: Essentials of Neonatal Cardiology and CHD Anthony C. Chang, MD, MBA, MPH CARDIAC INTENSIVE CARE
 SHUNT LESIONS NEONATAL : CONGENITAL CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS AND CARDIAC SURGERY ANTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF ORANGE COUNTY ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT LEFT TO RIGHT SHUNT INCREASED PULMONARY
SHUNT LESIONS NEONATAL : CONGENITAL CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS AND CARDIAC SURGERY ANTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF ORANGE COUNTY ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT LEFT TO RIGHT SHUNT INCREASED PULMONARY
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being
 Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. [email protected]
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. [email protected]
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery
 Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery Srinivasan Rajagopal M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Management of the Patient with Aortic Stenosis undergoing Non-cardiac Surgery Srinivasan Rajagopal M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis
 Variety Children s Heart Centre Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis Certain heart conditions and structural defects increase the risk of developing endocarditis (a heart valve infection)
Variety Children s Heart Centre Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis Certain heart conditions and structural defects increase the risk of developing endocarditis (a heart valve infection)
Resuscitation in congenital heart disease. Peter C. Laussen MBBS FCICM Department Critical Care Medicine Hospital for Sick Children Toronto
 Resuscitation in congenital heart disease Peter C. Laussen MBBS FCICM Department Critical Care Medicine Hospital for Sick Children Toronto Evolution of Congenital Heart Disease Extraordinary success: Overall
Resuscitation in congenital heart disease Peter C. Laussen MBBS FCICM Department Critical Care Medicine Hospital for Sick Children Toronto Evolution of Congenital Heart Disease Extraordinary success: Overall
Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular
 Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular Mitral Regurgitation Anatomy Mechanisms of MR Presentation Evaluation Management Repair Replace Clip
Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular Mitral Regurgitation Anatomy Mechanisms of MR Presentation Evaluation Management Repair Replace Clip
Nutrition in Paediatric Cardiology. Karen Hayes Paediatric Dietitian Addenbrooke s Hospital
 Nutrition in Paediatric Cardiology Karen Hayes Paediatric Dietitian Addenbrooke s Hospital Topics Who needs Nutrition support? Energy Requirements Meeting Energy and growth requirements Feeding Issues
Nutrition in Paediatric Cardiology Karen Hayes Paediatric Dietitian Addenbrooke s Hospital Topics Who needs Nutrition support? Energy Requirements Meeting Energy and growth requirements Feeding Issues
Auscultation of the Heart
 Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb.
 The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
Doc, I Am Fine, But I Have A Cardiac Condition
 Doc, I Am Fine, But I Have A Cardiac Condition Nevine Mahmoud, MD John Ludtke, MD Maj, USAFR, MC, FS RAM Class 2014 Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine Division of Aerospace Medicine Dayton,
Doc, I Am Fine, But I Have A Cardiac Condition Nevine Mahmoud, MD John Ludtke, MD Maj, USAFR, MC, FS RAM Class 2014 Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine Division of Aerospace Medicine Dayton,
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life
 Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Heart Murmurs. Outline. Basic Pathophysiology
 Heart Murmurs David Leder Outline I. Basic Pathophysiology II. Describing murmurs III. Systolic murmurs IV. Diastolic murmurs V. Continuous murmurs VI. Summary Basic Pathophysiology Murmurs = Math Q =
Heart Murmurs David Leder Outline I. Basic Pathophysiology II. Describing murmurs III. Systolic murmurs IV. Diastolic murmurs V. Continuous murmurs VI. Summary Basic Pathophysiology Murmurs = Math Q =
Read It, Code It, See It
 Read It, Code It, See It Richard L. Prager, M.D. University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan Dorothy Latham, R.N. Port Huron Hospital Port Huron, Michigan Nothing to Disclose Disclosure Preoperative diagnosis:
Read It, Code It, See It Richard L. Prager, M.D. University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan Dorothy Latham, R.N. Port Huron Hospital Port Huron, Michigan Nothing to Disclose Disclosure Preoperative diagnosis:
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging. Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet
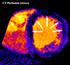 MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY PhD course in Medical Imaging Anne Günther Department of Radiology OUS Rikshospitalet CORONARY CT ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) Accurate method in the assessment of possible
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures Diagnostic and therapeutic cardiovascular s are central to the evaluation and management of patients with cardiovascular disease. Consistent with the other sections,
Cardiac Computed Tomographic Angiography (CCTA)
 Cardiac Computed Tomographic Angiography (CCTA) DESCRIPTION Contrast-enhanced computed tomography angiography (CTA) is a noninvasive imaging test that requires the use of intravenously administered contrast
Cardiac Computed Tomographic Angiography (CCTA) DESCRIPTION Contrast-enhanced computed tomography angiography (CTA) is a noninvasive imaging test that requires the use of intravenously administered contrast
Low-dose CT for Pulmonary Embolism
 Low-dose CT for Pulmonary Embolism Gautham Gautham P. P. Reddy, Reddy, MD, MD, MPH MPH University University of of Washington Washington Introduction Introduction CT CT accounts accounts for for > 50%
Low-dose CT for Pulmonary Embolism Gautham Gautham P. P. Reddy, Reddy, MD, MD, MPH MPH University University of of Washington Washington Introduction Introduction CT CT accounts accounts for for > 50%
Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging. Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469)
 Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469) Medical Review Note: Per InterQual, if any of the following are present,
Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469) Medical Review Note: Per InterQual, if any of the following are present,
Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management
 Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Dr Arvind Vasudeva Consultant Cardiologist Atrial Fibrillation An update on diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the commonest disturbance of cardiac rhythm seen in clinical practice.
Questions FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008
 FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
THE MARY ALLEN ENGLE, MD (1922-2008) PAPERS
 MEDICAL CENTER ARCHIVES OF NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN/WEILL CORNELL 1300 York Avenue # 34 New York, NY 10065 Finding Aid To THE MARY ALLEN ENGLE, MD (1922-2008) PAPERS Dates of Papers: 1948-1991 52.5 Linear
MEDICAL CENTER ARCHIVES OF NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN/WEILL CORNELL 1300 York Avenue # 34 New York, NY 10065 Finding Aid To THE MARY ALLEN ENGLE, MD (1922-2008) PAPERS Dates of Papers: 1948-1991 52.5 Linear
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology
 Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Cardiology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT 07/2006 Rev. BOT 03/2009 Rev. BOT 07/2011
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo. Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen
 RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology:
 Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS [email protected] Pediatric Cardiology What is Cyanosis? Bluish discoloration of skin that occurs when
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS [email protected] Pediatric Cardiology What is Cyanosis? Bluish discoloration of skin that occurs when
Left to Right Shunts and their Calculation. Ghada El Shahed, MD
 Left to Right Shunts and their Calculation Ghada El Shahed, MD Professor of Cardiology Ain Shams University Flow through systemic & pulmonary circulations is normally balanced and equal. Two circulations
Left to Right Shunts and their Calculation Ghada El Shahed, MD Professor of Cardiology Ain Shams University Flow through systemic & pulmonary circulations is normally balanced and equal. Two circulations
How To Treat A Single Ventricle And Fontan
 COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTS, STENTS, AND EXTRACORONARY CARDIAC DZ. Charles White MD
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTS, STENTS, AND EXTRACORONARY CARDIAC DZ Charles White MD Director of Thoracic Imaging Department of Radiology University of Maryland CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTS First performed
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTS, STENTS, AND EXTRACORONARY CARDIAC DZ Charles White MD Director of Thoracic Imaging Department of Radiology University of Maryland CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTS First performed
Atrial Septal Aneurysm: A Study in Five Hundred Adult Patients
 Premio al mejor Tema Libre Realizado por Médicos Residentes Atrial Septal Aneurysm: A Study in Five Hundred Adult Patients Olivares-Reyes Alexander; Al-Kamme Ahmad; Gonzalez Javier Cardiology Department
Premio al mejor Tema Libre Realizado por Médicos Residentes Atrial Septal Aneurysm: A Study in Five Hundred Adult Patients Olivares-Reyes Alexander; Al-Kamme Ahmad; Gonzalez Javier Cardiology Department
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children
 Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Adult Cardiac Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks
 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
Master s Program in Medical Physics. Physics of Imaging Systems Basic Principles of Computer Tomography (CT) III. Prof. Dr. Lothar Schad.
 1 12/9/2008 Page 1 Master s Program in Medical Physics Physics of Imaging Systems Basic Principles of Computer Tomography (CT) III Chair in Faculty of Medicine Mannheim University of Heidelberg Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer
1 12/9/2008 Page 1 Master s Program in Medical Physics Physics of Imaging Systems Basic Principles of Computer Tomography (CT) III Chair in Faculty of Medicine Mannheim University of Heidelberg Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer
scan: : a new tool to analyse
 Gated CT-scan scan: : a new tool to analyse the shape of the aortic annulus. SEROUSSI SAFAR K, JONDEAU G, LANSAC E., SERFATY JM Bichat Hospital, U698, Paris, France Anatomy: 3D + spatial resolution Retrospective
Gated CT-scan scan: : a new tool to analyse the shape of the aortic annulus. SEROUSSI SAFAR K, JONDEAU G, LANSAC E., SERFATY JM Bichat Hospital, U698, Paris, France Anatomy: 3D + spatial resolution Retrospective
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations. CardioCase presentation. Ethel s Case. Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC
 Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
Treating AF: The Newest Recommendations Wayne Warnica, MD, FACC, FACP, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Ethel s Case Ethel, 73, presents with rapid heart beating and mild chest discomfort. In the ED, ECG
25 Anomalies and Diseases of the Fetal Heart
 270 25 Anomalies and Diseases of the Fetal Heart Epidemiology and Indications for Fetal Echocardiography Epidemiologic Aspects It is generally known that approximately 15 20% of pregnancies in the second
270 25 Anomalies and Diseases of the Fetal Heart Epidemiology and Indications for Fetal Echocardiography Epidemiologic Aspects It is generally known that approximately 15 20% of pregnancies in the second
LEADING-EDGE Cardiovascular Care
 LEADING-Edge Cardiovascular Care Coral Gables Hospital North Shore Medical Center Hialeah Hospital Delray Medical Center Good Samaritan Medical Center Palm Beach Gardens Medical Center St. Mary s Medical
LEADING-Edge Cardiovascular Care Coral Gables Hospital North Shore Medical Center Hialeah Hospital Delray Medical Center Good Samaritan Medical Center Palm Beach Gardens Medical Center St. Mary s Medical
Heart Sounds & Murmurs
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
HEART MURMURS THROUGHOUT CHILDHOOD
 HEART MURMURS THROUGHOUT CHILDHOOD Frances R. Zappalla, D.O. Nemours Cardiac Center A.I. du Pont Hospital for Children Wilmington, DE Definition: HEART MURMURS An extra abnormal heart sound usually detected
HEART MURMURS THROUGHOUT CHILDHOOD Frances R. Zappalla, D.O. Nemours Cardiac Center A.I. du Pont Hospital for Children Wilmington, DE Definition: HEART MURMURS An extra abnormal heart sound usually detected
Heart valve repair and replacement
 16 Heart valve repair and replacement 222 Valvular heart disease can be treated in a variety of ways: valve replacement, in which an artificial (prosthetic) heart valve is implanted surgically to replace
16 Heart valve repair and replacement 222 Valvular heart disease can be treated in a variety of ways: valve replacement, in which an artificial (prosthetic) heart valve is implanted surgically to replace
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Explained Patient Information Contents What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 3 Normal heartbeat 4 How common
How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure
 Advances in Cardiac Arrhhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology Torino, 23/24 Ottobre 2015 How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure Matteo Anselmino Dipartimento Scienze Mediche Città
Advances in Cardiac Arrhhythmias and Great Innovations in Cardiology Torino, 23/24 Ottobre 2015 How should we treat atrial fibrillation in heart failure Matteo Anselmino Dipartimento Scienze Mediche Città
Low-gradient severe aortic stenosis with normal LVEF: A disturbing clinical entity
 Low-gradient severe aortic stenosis with normal LVEF: A disturbing clinical entity Jean-Luc MONIN, MD, PhD Henri Mondor University Hospital Créteil, FRANCE Disclosures : None 77-year-old woman, mild dyspnea
Low-gradient severe aortic stenosis with normal LVEF: A disturbing clinical entity Jean-Luc MONIN, MD, PhD Henri Mondor University Hospital Créteil, FRANCE Disclosures : None 77-year-old woman, mild dyspnea
Acquired Heart Disease: Prevention and Treatment
 Acquired Heart Disease: Prevention and Treatment Prevention and Treatment Sharon L. Roble, MD Assistant Professor Adult Congenital Heart Program The Ohio State University/Nationwide Children s Hospital
Acquired Heart Disease: Prevention and Treatment Prevention and Treatment Sharon L. Roble, MD Assistant Professor Adult Congenital Heart Program The Ohio State University/Nationwide Children s Hospital
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know
 Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London [email protected] CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
Purchasing a cardiac CT scanner: What the radiologist needs to know Maria Lewis ImPACT St George s Hospital, London [email protected] CT scanner development Slice wars 1998 Increased z-coverage
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
ST. DAVID S MEDICAL CENTER CARDIOLOGY - Special, Invasive, Diagnostic, or High-Risk Procedure Requirements
 ST. DAVID S MEDICAL CENTER CARDIOLOGY - Special, Invasive, Diagnostic, or High-Risk Procedure Requirements Cardiac Catheterization & Peripheral Angiography Completion of a fellowship in Cardiovascular
ST. DAVID S MEDICAL CENTER CARDIOLOGY - Special, Invasive, Diagnostic, or High-Risk Procedure Requirements Cardiac Catheterization & Peripheral Angiography Completion of a fellowship in Cardiovascular
1p36 and the Heart. John Lynn Jefferies, MD, MPH, FACC, FAHA
 1p36 and the Heart John Lynn Jefferies, MD, MPH, FACC, FAHA Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy Services Associate Professor, Pediatric Cardiology and Adult Cardiovascular Diseases Associate
1p36 and the Heart John Lynn Jefferies, MD, MPH, FACC, FAHA Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy Services Associate Professor, Pediatric Cardiology and Adult Cardiovascular Diseases Associate
Anatomy Review. Heart Murmurs. Surface Topography of the Heart 7/19/2011. The Base of the Heart and Erb s Point
 James A Mathey PA C, MPA CAPA WORKSHOP 2010 Heart Murmurs Anatomy Review 4 Classic Auscultatory Areas: Aortic 2ICS R SB Pulmonic 2ICS L SB Tricuspid 4 th L Lower SB Mitral 5ICS MCL Surface Topography of
James A Mathey PA C, MPA CAPA WORKSHOP 2010 Heart Murmurs Anatomy Review 4 Classic Auscultatory Areas: Aortic 2ICS R SB Pulmonic 2ICS L SB Tricuspid 4 th L Lower SB Mitral 5ICS MCL Surface Topography of
Heart Failure EXERCISES. Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it.
 Heart Failure EXERCISES Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it. ) 1. Heart rate increase is a kind of economic compensation, which should
Heart Failure EXERCISES Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it. ) 1. Heart rate increase is a kind of economic compensation, which should
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A Comprehensive Resource from the Heart Rhythm Society AF 360 provides a single, trusted resource for the most comprehensive and relevant information and
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
GE Healthcare. Revolution EVO. More than just high tech. Higher purpose.
 GE Healthcare Revolution EVO More than just high tech. Higher purpose. Revolution EVO. Designed with purpose. Today s healthcare environment is about creating new solutions to pressing needs. It s about
GE Healthcare Revolution EVO More than just high tech. Higher purpose. Revolution EVO. Designed with purpose. Today s healthcare environment is about creating new solutions to pressing needs. It s about
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts
 Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
Imaging of Thoracic Endovascular Stent-Grafts Tariq Hameed, M.D. Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana Disclosures: No relevant financial
How To Treat Aortic Stenosis
 2014 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease Developed in Collaboration with the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American Society of Echocardiography, Society
2014 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease Developed in Collaboration with the American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American Society of Echocardiography, Society
Cardiac CT Emerging Role and Current Indications
 Cardiac CT Emerging Role and Current Indications Dr. Felix Keng MBBS, FRCP (Lond), FAMS, Dip CBNC, Dip CBCCT, MMed (Int Med), FAPSC Director, Nuclear Cardiology National Heart Centre, Singapore Adjunct
Cardiac CT Emerging Role and Current Indications Dr. Felix Keng MBBS, FRCP (Lond), FAMS, Dip CBNC, Dip CBCCT, MMed (Int Med), FAPSC Director, Nuclear Cardiology National Heart Centre, Singapore Adjunct
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Anesthesia in Children with Congenital Heart Disease. Elliot Krane, M.D.
 Anesthesia in Children with Congenital Heart Disease Elliot Krane, M.D. Introduction The evolution of medicine to managed care and contracted medical services has often had the effect of shifting a sicker
Anesthesia in Children with Congenital Heart Disease Elliot Krane, M.D. Introduction The evolution of medicine to managed care and contracted medical services has often had the effect of shifting a sicker
INNOVATIONS IN THE ENVIRONMENT: HOW THE HYBRID OPERATING ROOM CAN INFLUENCE CARDIAC SURGERY
 CLAUDIO GROSSI Cardiac Surgery Ospedale Santa Croce CUNEO (Italy) INNOVATIONS IN THE ENVIRONMENT: HOW THE HYBRID OPERATING ROOM CAN INFLUENCE CARDIAC SURGERY Impossibile visualizzare l'immagine. La memoria
CLAUDIO GROSSI Cardiac Surgery Ospedale Santa Croce CUNEO (Italy) INNOVATIONS IN THE ENVIRONMENT: HOW THE HYBRID OPERATING ROOM CAN INFLUENCE CARDIAC SURGERY Impossibile visualizzare l'immagine. La memoria
Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness
 Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Disclosures Atrial Fibrillation Management Across the Spectrum of Illness NONE Barbara Birriel, MSN, ACNP-BC, FCCM The Pennsylvania State University Objectives AF Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis,
Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery
 Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery Stanford Health Care offers leading, superior options in cardiac surgery, including the latest techniques and research for Minimally Invasive Cardiac surgery. Advanced
Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery Stanford Health Care offers leading, superior options in cardiac surgery, including the latest techniques and research for Minimally Invasive Cardiac surgery. Advanced
Pediatric Congenital Cardiac Surgery
 Pediatric Congenital Cardiac Surgery in New York State 2006 2009 New York State Department of Health October 2011 Members of the New York State Cardiac Advisory Committee Chair Spencer King, M.D. Executive
Pediatric Congenital Cardiac Surgery in New York State 2006 2009 New York State Department of Health October 2011 Members of the New York State Cardiac Advisory Committee Chair Spencer King, M.D. Executive
Cardiac Masses and Tumors
 Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
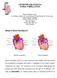 CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343 1952 Bay Street
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343 1952 Bay Street
How To Treat Heart Valve Disease
 The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines. Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center
 Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
Atrial Fibrillation Based on ESC Guidelines Moshe Swissa MD Kaplan Medical Center Epidemiology AF affects 1 2% of the population, and this figure is likely to increase in the next 50 years. AF may long
Congenital heart defects
 CONGENITAL ANOMALY REGISTER & INFORMATION SERVICE COFRESTR ANOMALEDDAU CYNHENID Congenital heart defects Cardiovascular defects are by far the commonest major group of congenital anomalies. Development
CONGENITAL ANOMALY REGISTER & INFORMATION SERVICE COFRESTR ANOMALEDDAU CYNHENID Congenital heart defects Cardiovascular defects are by far the commonest major group of congenital anomalies. Development
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain
 Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
Efficient Evaluation of Chest Pain Vikranth Gongidi, DO FACC FACOI Indian River Medical Center Vero Beach, FL No Disclosures Outline Background Chest pain pathway Indications for stress test Stress test
4/7/2015. Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door. Chicago, circa 1999. Objectives. No disclosures, no conflicts
 Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door No disclosures, no conflicts Charles X. Kim, MD, FACC, ABVM Objectives 1. Illustrate common CV benefits of CV rehab in real world practice.
Cardiac Rehabilitation: From the other side of the glass door No disclosures, no conflicts Charles X. Kim, MD, FACC, ABVM Objectives 1. Illustrate common CV benefits of CV rehab in real world practice.
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL)
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (RATE VS RHYTHM CONTROL) By Prof. Dr. Helmy A. Bakr Mansoura Universirty 2014 AF Classification: Mechanisms of AF : Selected Risk Factors and Biomarkers for AF: WHY AF? 1. Atrial fibrillation
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona
 Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
Christopher M. Wright, MD, MBA Pioneer Cardiovascular Consultants Tempe, Arizona Areas to be covered Historical, current, and future treatments for various cardiovascular disease: Atherosclerosis (Coronary
Anticoagulation: How Do I Pick From All the Choices? Jeffrey H. Neuhauser, DO, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014
 Anticoagulation: How Do I Pick From All the Choices? Jeffrey H. Neuhauser, DO, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Atrial Fibrillation 2 Atrial Fibrillation The most common arrhythmia encountered
Anticoagulation: How Do I Pick From All the Choices? Jeffrey H. Neuhauser, DO, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Atrial Fibrillation 2 Atrial Fibrillation The most common arrhythmia encountered
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Key priorities Identification and diagnosis Treatment for persistent AF Treatment for permanent AF Antithrombotic
UNMH Cardiothoracic Surgery Clinical Privileges
 All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 02/20/2015 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 02/20/2015 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
Nursing Care and Considerations for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Kris Kinghorn RN, MSN, ANP-BC
 Nursing Care and Considerations for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Kris Kinghorn RN, MSN, ANP-BC Case Study 66 y/o female (Mrs. Olus A. Blader) Admitted with c/o palpitations and lightheadedness PMH:
Nursing Care and Considerations for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Kris Kinghorn RN, MSN, ANP-BC Case Study 66 y/o female (Mrs. Olus A. Blader) Admitted with c/o palpitations and lightheadedness PMH:
HEART DISEASE IN THE YOUNG CHARLES S. KLEINMAN, M.D.
 CHAPTER 20 HEART DISEASE IN THE YOUNG CHARLES S. KLEINMAN, M.D. INTRODUCTION Congenital heart defects are relatively rare; seriously debilitating heart abnormalities rarer still. Approximately 8 babies
CHAPTER 20 HEART DISEASE IN THE YOUNG CHARLES S. KLEINMAN, M.D. INTRODUCTION Congenital heart defects are relatively rare; seriously debilitating heart abnormalities rarer still. Approximately 8 babies
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology
 Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
DOT Certification Handbook
 DOT Certification Handbook Updated January 1, 2014 ABSOLUTE DISQUALIFICATIONS EXEMPTIONS MEDICATIONS REQUIRING PRESCRIBING PHYSICIAN RECOMMENDATION LABORATORY/PROCEDURE TESTING REQUIREMENTS SPECIALTY REFERRAL
DOT Certification Handbook Updated January 1, 2014 ABSOLUTE DISQUALIFICATIONS EXEMPTIONS MEDICATIONS REQUIRING PRESCRIBING PHYSICIAN RECOMMENDATION LABORATORY/PROCEDURE TESTING REQUIREMENTS SPECIALTY REFERRAL
Adult Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Patient Information
 Adult Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patient Information WHAT IS CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE? Congenital heart disease (CHD) refers to a defect of the heart or major blood vessels
Adult Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patient Information WHAT IS CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE? Congenital heart disease (CHD) refers to a defect of the heart or major blood vessels
Example Theory Multiple Choice Questions
 Example Theory Multiple Choice Questions Q a). In an ultrasound imaging system: Sector width, sector depth and frame rate can all be controlled independently b) Frame rate falls as sector width increases
Example Theory Multiple Choice Questions Q a). In an ultrasound imaging system: Sector width, sector depth and frame rate can all be controlled independently b) Frame rate falls as sector width increases
5. Management of rheumatic heart disease
 5. Management of rheumatic heart disease The fundamental goal in the long-term management of RHD is to prevent ARF recurrences, and therefore, prevent the progression of RHD, and in many cases allow for
5. Management of rheumatic heart disease The fundamental goal in the long-term management of RHD is to prevent ARF recurrences, and therefore, prevent the progression of RHD, and in many cases allow for
Objectives. The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease. Lead II P-Wave Amplitude during COPD Exacerbation and after Treatment (50 pts.
 The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
17 Endocarditis. Infective endocarditis
 17 Endocarditis 234 Endocarditis refers to inflammation of the endocardium, the inner layer of the heart (including the heart valves). Endocarditis can be: infective (e.g. bacterial, fungal) non-infective
17 Endocarditis 234 Endocarditis refers to inflammation of the endocardium, the inner layer of the heart (including the heart valves). Endocarditis can be: infective (e.g. bacterial, fungal) non-infective
Chromosome Syndromes associated with Congenital Heart Defects
 National Birth Defects Prevention Network (NBPDN)/NBDPS Annual Meeting Feb. 26-29. 2012 Arlington, VA Chromosome Syndromes associated with Congenital Heart Defects Angela E. Lin, MD, FAAP, FACMG Associate
National Birth Defects Prevention Network (NBPDN)/NBDPS Annual Meeting Feb. 26-29. 2012 Arlington, VA Chromosome Syndromes associated with Congenital Heart Defects Angela E. Lin, MD, FAAP, FACMG Associate
MBCHB 3 Paediatrics and Child Health Rotation. Learning objectives
 MBCHB 3 Paediatrics and Child Health Rotation Learning objectives The overall objective is to introduce the student to basic paediatric clinical tools. By the end of the 4 week rotation the student will
MBCHB 3 Paediatrics and Child Health Rotation Learning objectives The overall objective is to introduce the student to basic paediatric clinical tools. By the end of the 4 week rotation the student will
HISTORY. Questions: 1. What diagnosis is suggested by this history? 2. How do you explain her symptoms during pregnancy?
 HISTORY 33-year-old woman. CHIEF COMPLAINT: months duration. Dyspnea, fatigue and nocturnal wheezing of six PRESENT ILLNESS: At ages 5 and 9, she had migratory arthritis. At age 29, in the third trimester
HISTORY 33-year-old woman. CHIEF COMPLAINT: months duration. Dyspnea, fatigue and nocturnal wheezing of six PRESENT ILLNESS: At ages 5 and 9, she had migratory arthritis. At age 29, in the third trimester
