HEART MURMURS THROUGHOUT CHILDHOOD
|
|
|
- Darcy Shelton
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HEART MURMURS THROUGHOUT CHILDHOOD Frances R. Zappalla, D.O. Nemours Cardiac Center A.I. du Pont Hospital for Children Wilmington, DE Definition: HEART MURMURS An extra abnormal heart sound usually detected while listening to the heartbeat with a stethoscope. 2 PARENTAL ANXIETY. Anxiety about need for medication (49%) Sports restrictions (41%) Cardiac surgery (29%), Cardiac risk for siblings (20%) Premature death (13%). 19% of mothers felt the murmur resulted from something they did wrong during pregnancy. After reassurance from the cardiologist, 7% of parents had persistent anxiety J Pediatr Jun;140(6):
2 HEART MURMURS Most systolic murmurs in otherwise healthy children are innocent and do not need a referral...however, see the previous slide. If findings are suspicious or in the present of parental anxiety. referral for a cardiology office visit is more cost effective than ordering an echocardiogram alone ECHO ONLY Slightly more than half of echocardiography studies (68%) performed in adult laboratories were technically adequate Of those 52% had the correct diagnosis 16% incorrect diagnosis Repeat echocardiography in 38% Abnormalities not diagnosed correctly in 14% 6 had important lesions Normal hearts were labeled as abnormal in 18% RA Hurwitz et al Peds 1998 DIASTOLIC MURMURS ARE PATHOLOGIC UNTIL PROVEN OTHERWISE 2
3 AUSCULTATION AREAS RUSB Aortic LUSB Pulmonic LLSB TV, Septum Apex - MV Fetal Circulation The colors indicate the oxygen saturation of the blood. The arrows show the course of the fetal circulation. FETAL CIRCULATION 55 % of the highly saturated umbilical venous returns via ductus venous to IVC - RA junction preferentially crosses the foramen ovale into the left atrium Highest oxygen content diverted to coronary arteries and the brain Remaining umbilical venous flow, portal venous blood, and SVC flow crosses the tricuspid valve 3
4 Circulation after Birth Arrows indicate the course of the neonatal circulation. TRANSITIONAL CIRCULATION Clamping of Umbilical cord Removes the low resistance placenta Decreases ductus venous flow and systemic venous return to IVC Increases systemic resistance Spontaneous respiration Decreases pulmonary vascular resistance Increases pulmonary venous return to LA TRANSITIONAL CIRCULATION Increased pulmonary venous return Increases in LA pressure Flap valve of foramen ovale closes PDA closes within 10 to 15 hours 4
5 PULSE OXIMETRY 20,055 newborn babies were screened 53 had major congenital heart disease (24 critical) Prevalence of 2 6 per 1000 livebirths. Sensitivity of pulse oximetry 75 00% (95% CI) for critical cases 49 06% for all major congenital heart defects. False-positive results noted for 169 (0 8%) 6 cases were significant, but not major, CHD 40 were other illnesses that required urgent medical intervention. The prevalence of major CHDs with normal pulse oximetry was 1.4 per 1000 live births Ewer et al LANCET 2011 NEONATES AND INFANTS LOW-RISK GROUP Otherwise well - no symptoms and no other signs Alert, active, feeding well, gaining weight Normal pulses, heart rate, respiratory rate and liver size. Normal blood pressures in all extremities Normal pulse oximeter saturation in upper and lower extremities in room air NEONATES AND INFANTS RED FLAGS Comfortable Tachypnea Diminished pulses Poor feeding Poor weight gain Pulse Oximetry <90% 5
6 BENIGN MURMURS IN THE NEONATE Physiologic peripheral pulmonary stenosis Transient patent ductus arteriosus murmur Tricuspid regurgitation murmur Flow Murmurs PERIPHERAL PULMONARYSTENOSIS Physiologic Grade 1-2/6 systolic ejection murmur Heard best in the upper left sternal border but radiates well to the axilla and back Most resolved within 6 weeks Remainder by 6 months TRANSIENT PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS Closing ductus arteriosus Usually a systolic ejection murmur of 1-2/6 intensity Heard best in the left upper sternal border Usually heard at hours of life and.. usually has disappears by the time the cardiologist comes to listen 6
7 TRICUSPID REGURGITATION MURMUR Infants with fetal distress or perinatal asphyxia Holosystolic murmur due to high right ventricular systolic pressure Sounds like a small ventricular septal defect PATENT FORAMEN OVALE Normal structure Functional closure occurs after birth as left atrial pressure exceeds right atrial pressure Right to left shunting may occur in neonatal period causing peri-oral cyanosis 7
8 PATHOLOGICAL MURMURS Most Common Ventricular septal defect Pulmonary stenosis Aortic stenosis PATHOLOGICAL MURMURS AV valve insufficiency in Complete AV Canal defect Tetralogy of Fallot Coarctation of the aorta Ebstein s Anomaly CHD WITHOUT MURMURS Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Tricuspid Atresia Critical Coarctation Interrupted aortic arch Complete Common AV canal 8
9 APPROACH TO THE CYANOTIC CHILD Pre- and post-ductal saturations measured on right arm and either leg detects shunting across the ductus arteriosus Arterial Blood Gas(es) Chest X-ray 12-lead ECG APPROACH TO THE CYANOTIC CHILD Hyperoxia test: Document PaO 2 in room air Administer 100% FiO 2 for 10 minutes Repeat PaO 2 in 100 % O 2 PaO 2 > 300 suggests intrapulmonary shunt PaO 2 < 150 suggests intracardiac shunt APPROACH TO THE CYANOTIC NEONATE Suspected Congenital Heart Disease Referral for pediatric cardiology evaluation in-house consult transport to tertiary center Telemedicine Echocardiography for detailed anatomic diagnosis Medical management and surgical strategies based on anatomic diagnosis 9
10 VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECTS Most common form of CHD 1.5 to 3.5 per 1000 term infants Slightly more common in females Most common defect in chromosomal syndromes however 95% of VSD not associated with chromosomal anomaly LOCATION OF VSD Perimembranous - most common (80%) Muscular (5-20%) Subpulmonary PV Subaortic TV Anterior Inlet AV canal type VSD (5-8%) Apex VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT Small ventricular septal defects Large ventricular septal defect NO murmur until pulmonary vascular resistance drops 10
11 AORTIC AND PULMONARY STENOSIS Murmurs may be heard soon after birth and persist Usually preceded by an ejection click Constant with aortic stenosis Louder during expiration with pulmonic stenosis PULMONARY VALVE STENOSIS Usually asymptomatic Variable systolic ejection click at LUSB Grade 2-5/6 SEM at LUSB to lung fields Soft, delayed pulmonary component of S2 May have increased RV impulse and thrill ECG: RVH BALLOON VALVULOPLASTY 11
12 BENIGN MURMURS IN CHILDREN Stills Murmur Venous Hum Pulmonary Flow Murmur STILL'S MURMUR Grade 1-2/6, musical or vibratory in nature Heard best at the lower left sternal border Murmurs are accentuated by anemia fever increased cardiac output VENOUS HUM Varies with neck position and compression Diff Dx of Continuous murmurs : PDA, shunt, AV fistula S 1 S2 S 1 12
13 PATHOLOGIC HEART MURMURS IN THE ADOLESCENT Atrial Septal Defects (ASD) Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECTS SVC Secundum ASD and PFO Sinus Venosus ASD Primum ASD IVC 13
14 ASD PULMONARY FLOW MURMUR Systolic flow murmur Widely split S2 Increased P2 rsr in V1 Right Axis deviation Systolic flow murmur Split S2 Normal P2 May have rsr in V1 Normal Axis deviation Right Arial Enlargement Normal P waves CLASSIC ASD ECG ASD CLOSURE 14
15 MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE Mid-systolic click at LLSB, maximal in upright position + late systolic regurgitant murmur at apex Look for associated skeletal abnormalities slender stature, scoliosis, pectus excavatum Marfan syndrome MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE Diagnosis often over-called Prognosis generally excellent Potential complications: Mitral valve regurgitation SBE Arrhythmia Central neurologic ischemic events High risk subset of patients: Males, age > 45 Presence of MR & leaflet thickening 15
16 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Most common cause of sudden death in US (35%) Sudden death usually occurs in teens and young adults < 35 years of age Occurs in about 2% (1:500) of general population Autosomal Dominant with > 400 mutations on 12 genes Variable expression and clinic course Competitive golf is permitted under guidelines HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Hyperdynamic precordium Murmur varies with maneuvers SEM at the LSB Softer with Hand-grip/ Louder with release Standing increases murmur /Squatting decreases murmur History of SOB or chest pain WITH exertion Family history of sudden death in a young relative HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Often don t develop hypertrophy until years old Absence of hypertrophy does NOT rule out HCM 90% have ECG changes which often precede echo findings Commercially available Genetic testing (50-60% yield) 16
17 Histopathology of heart sections showing significant myofibre disarray and interstitial fibrosis in HCM Cell Research (2003) 13,
18 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER New murmur or new onset of heart failure (tachypnea, S3 gallop, pulmonary edema) Murmur of mitral regurgitation at apex Diastolic decrescendo murmur of aortic regurgitation Pancarditis- can involve pericardium, myocardium and/or valves ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER 18
19 JONES CRITERIA Evidence of recent Group A hemolytic Strep infection Plus 2 major or one minor criteria MAJOR Carditis Polyarthritis Syndenham s chorea Erythema marginatum Subcutaneous nodules MINOR Athralgia Fever Elevated acute phase reactants Prolonged PR interval YEAR OLD WITH SEVERE MITRAL REGURGITATION NEW ENDOCARDITIS RECOMMENDATIONS Prosthetic material used for cardiac valve repair Previous endocarditis Unrepaired cyanotic CHD, including palliative shunts and conduits Completely repaired congenital heart defect with prosthetic material or device(surgical or catheter intervention ) for the first 6 months after the procedure Repaired CHD with residual defects at the site or adjacent to the site of a prosthetic patch or prosthetic device Cardiac transplantation recipients who develop cardiac valvulopathy 19
20 SUMMARY Most murmurs in childhood are innocent In sick patients the ECG and CXR will help differentiate a flow murmur due to fever versus a pathologic murmur When in doubt. Feel free to call for help 20
Common types of congenital heart defects
 Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Heart Sounds & Murmurs
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
Heart Murmurs. Outline. Basic Pathophysiology
 Heart Murmurs David Leder Outline I. Basic Pathophysiology II. Describing murmurs III. Systolic murmurs IV. Diastolic murmurs V. Continuous murmurs VI. Summary Basic Pathophysiology Murmurs = Math Q =
Heart Murmurs David Leder Outline I. Basic Pathophysiology II. Describing murmurs III. Systolic murmurs IV. Diastolic murmurs V. Continuous murmurs VI. Summary Basic Pathophysiology Murmurs = Math Q =
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology:
 Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS [email protected] Pediatric Cardiology What is Cyanosis? Bluish discoloration of skin that occurs when
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Right to Left Shunts aka Cyanotic Lesions Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS [email protected] Pediatric Cardiology What is Cyanosis? Bluish discoloration of skin that occurs when
Facts about Congenital Heart Defects
 Facts about Congenital Heart Defects Joseph A. Sweatlock, Ph.D., DABT New Jersey Department of Health Early Identification & Monitoring Program Congenital heart defects are conditions that are present
Facts about Congenital Heart Defects Joseph A. Sweatlock, Ph.D., DABT New Jersey Department of Health Early Identification & Monitoring Program Congenital heart defects are conditions that are present
Auscultation of the Heart
 Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
Review of Clinical Signs uscultation of the Heart Series Editor: Bernard Karnath, MD Bernard Karnath, MD William Thornton, MD uscultation of the heart can provide clues to the diagnosis of many cardiac
Questions FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008
 FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
Workshop B: Essentials of Neonatal Cardiology and CHD Anthony C. Chang, MD, MBA, MPH CARDIAC INTENSIVE CARE
 SHUNT LESIONS NEONATAL : CONGENITAL CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS AND CARDIAC SURGERY ANTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF ORANGE COUNTY ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT LEFT TO RIGHT SHUNT INCREASED PULMONARY
SHUNT LESIONS NEONATAL : CONGENITAL CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS AND CARDIAC SURGERY ANTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH CHILDREN S HOSPITAL OF ORANGE COUNTY ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT LEFT TO RIGHT SHUNT INCREASED PULMONARY
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being
 Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. [email protected]
Universal Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound At the Heart of Newborn Well-being Optimizes detection of congenital heart disease (chd) in the general low risk obstetrical population Daniel J. Cohen, M.D. [email protected]
Congenital heart defects
 CONGENITAL ANOMALY REGISTER & INFORMATION SERVICE COFRESTR ANOMALEDDAU CYNHENID Congenital heart defects Cardiovascular defects are by far the commonest major group of congenital anomalies. Development
CONGENITAL ANOMALY REGISTER & INFORMATION SERVICE COFRESTR ANOMALEDDAU CYNHENID Congenital heart defects Cardiovascular defects are by far the commonest major group of congenital anomalies. Development
Heart Sounds and Murmurs. Objectives. Valves. Wright, 2012 1
 Heart Sounds and Murmurs Wendy L. Wright, MS, RN, ARNP, FNP, FAANP Family Nurse Practitioner Owner Wright & Associates Family Healthcare Partner Partners in Healthcare Education 1 Objectives Upon completion
Heart Sounds and Murmurs Wendy L. Wright, MS, RN, ARNP, FNP, FAANP Family Nurse Practitioner Owner Wright & Associates Family Healthcare Partner Partners in Healthcare Education 1 Objectives Upon completion
Patient Possible differentials Recommended diagnostics Puppy or kitten with a soft systolic murmur
 Cardiac Auscultation 101 Terri DeFrancesco, DVM, DACVIM (Cardiology), DACVECC Associate Professor in Cardiology and Critical Care NC State University College of Veterinary Medicine Email: [email protected]
Cardiac Auscultation 101 Terri DeFrancesco, DVM, DACVIM (Cardiology), DACVECC Associate Professor in Cardiology and Critical Care NC State University College of Veterinary Medicine Email: [email protected]
The Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease among Neonates Referred for Echocardiography
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 ABSTRACT The Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease among Neonates Referred for Echocardiography Hussain Al Khawahur, MD* Hussain Al Sowaiket, MD** Thuria
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 2, June 2014 ABSTRACT The Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease among Neonates Referred for Echocardiography Hussain Al Khawahur, MD* Hussain Al Sowaiket, MD** Thuria
HEART MURMURS: INNOCENT OR GUILTY?
 HEART MURMURS: INNOCENT OR GUILTY? William A. Lutin, MD, PhD Section of Pediatric Cardiology Georgia Regents University Augusta, GA ([email protected]) DISCLOSURES I have no relevant financial relationships
HEART MURMURS: INNOCENT OR GUILTY? William A. Lutin, MD, PhD Section of Pediatric Cardiology Georgia Regents University Augusta, GA ([email protected]) DISCLOSURES I have no relevant financial relationships
Question 1: Interpret the rhythm strip above (comment on regularity, rate, P wave, PR interval and QRS)?
 It is your first month on your NICU rotation and you are prerounding on your patients. The nurse takes you aside and says she s been seeing something funny on the cardiac monitor. You walk to the bedside
It is your first month on your NICU rotation and you are prerounding on your patients. The nurse takes you aside and says she s been seeing something funny on the cardiac monitor. You walk to the bedside
How To Treat A Single Ventricle And Fontan
 COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
How to get insurance companies to work with you
 Paying for Quality ACHD Care How to get insurance companies to work with you Christy Sillman, RN, MSN ACHD nurse coordinator Inpatient ACHD Nurse Educator The Adult Congenital Heart Program Stanford Lucile
Paying for Quality ACHD Care How to get insurance companies to work with you Christy Sillman, RN, MSN ACHD nurse coordinator Inpatient ACHD Nurse Educator The Adult Congenital Heart Program Stanford Lucile
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Anatomy Review. Heart Murmurs. Surface Topography of the Heart 7/19/2011. The Base of the Heart and Erb s Point
 James A Mathey PA C, MPA CAPA WORKSHOP 2010 Heart Murmurs Anatomy Review 4 Classic Auscultatory Areas: Aortic 2ICS R SB Pulmonic 2ICS L SB Tricuspid 4 th L Lower SB Mitral 5ICS MCL Surface Topography of
James A Mathey PA C, MPA CAPA WORKSHOP 2010 Heart Murmurs Anatomy Review 4 Classic Auscultatory Areas: Aortic 2ICS R SB Pulmonic 2ICS L SB Tricuspid 4 th L Lower SB Mitral 5ICS MCL Surface Topography of
HISTORY. Questions: 1. What diagnosis is suggested by this history? 2. How do you explain her symptoms during pregnancy?
 HISTORY 33-year-old woman. CHIEF COMPLAINT: months duration. Dyspnea, fatigue and nocturnal wheezing of six PRESENT ILLNESS: At ages 5 and 9, she had migratory arthritis. At age 29, in the third trimester
HISTORY 33-year-old woman. CHIEF COMPLAINT: months duration. Dyspnea, fatigue and nocturnal wheezing of six PRESENT ILLNESS: At ages 5 and 9, she had migratory arthritis. At age 29, in the third trimester
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb.
 The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis
 Variety Children s Heart Centre Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis Certain heart conditions and structural defects increase the risk of developing endocarditis (a heart valve infection)
Variety Children s Heart Centre Dental Work and the Risk of Bacterial Endocarditis Certain heart conditions and structural defects increase the risk of developing endocarditis (a heart valve infection)
Normal Intracardiac Pressures. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
020 // Congenital Heart Disease
 020 // Congenital Heart Disease CONTENTS 188 Basics 188 Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) 191 Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) 192 Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD) 194 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) 195 Coronary Fistulas
020 // Congenital Heart Disease CONTENTS 188 Basics 188 Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) 191 Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) 192 Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD) 194 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) 195 Coronary Fistulas
Chest Pain in Young Athletes. Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.
 Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego [email protected] 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego [email protected] 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
Pulmonary Atresia With Intact Ventricular Septum - Anatomy, Physiology, and Diagnostic Imaging
 Pulmonary Atresia With Intact Ventricular Septum - Anatomy, Physiology, and Diagnostic Imaging Larry Latson MD Director of Pediatric Interventional Cardiology and Adult CHD Joe DiMaggio Children s Hospital
Pulmonary Atresia With Intact Ventricular Septum - Anatomy, Physiology, and Diagnostic Imaging Larry Latson MD Director of Pediatric Interventional Cardiology and Adult CHD Joe DiMaggio Children s Hospital
Delivery Planning for the Fetus with Congenital Heart Disease
 Delivery Planning for the Fetus with Congenital Heart Disease Mar y T. Donofrio MD, FAAP, FACC, FASE Director of the Fetal Heart Program Children s National Medical Center Washington DC Objectives Review
Delivery Planning for the Fetus with Congenital Heart Disease Mar y T. Donofrio MD, FAAP, FACC, FASE Director of the Fetal Heart Program Children s National Medical Center Washington DC Objectives Review
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children
 Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
HEART DISEASE IN THE YOUNG CHARLES S. KLEINMAN, M.D.
 CHAPTER 20 HEART DISEASE IN THE YOUNG CHARLES S. KLEINMAN, M.D. INTRODUCTION Congenital heart defects are relatively rare; seriously debilitating heart abnormalities rarer still. Approximately 8 babies
CHAPTER 20 HEART DISEASE IN THE YOUNG CHARLES S. KLEINMAN, M.D. INTRODUCTION Congenital heart defects are relatively rare; seriously debilitating heart abnormalities rarer still. Approximately 8 babies
Requirements for Provision of Outreach Paediatric Cardiology Service
 Requirements for Provision of Outreach Paediatric Cardiology Service Dr Shakeel A Qureshi, Consultant Paediatric Cardiologist, Evelina Children s Hospital, London, UK On behalf of British Congenital Cardiac
Requirements for Provision of Outreach Paediatric Cardiology Service Dr Shakeel A Qureshi, Consultant Paediatric Cardiologist, Evelina Children s Hospital, London, UK On behalf of British Congenital Cardiac
CARDIAC DISORDERS. Circulatory Changes at Birth 7/3/2008
 CARDIAC DISORDERS Circulatory Changes at Birth When the umbilical cord is clamped, the blood supply from the placenta is cut off, and oxygenation must then take place in the infant s lungs As the lungs
CARDIAC DISORDERS Circulatory Changes at Birth When the umbilical cord is clamped, the blood supply from the placenta is cut off, and oxygenation must then take place in the infant s lungs As the lungs
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo. Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen
 RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
Congenital Heart Disease. Mary Rummell, RN, MN, CPNP, CNS Clinical Nurse Specialist Pediatric Cardiology/Cardiac Surgery
 Congenital Heart Disease Mary Rummell, RN, MN, CPNP, CNS Clinical Nurse Specialist Pediatric Cardiology/Cardiac Surgery Objectives The learner will: Identify 3 areas in the developing heart that result
Congenital Heart Disease Mary Rummell, RN, MN, CPNP, CNS Clinical Nurse Specialist Pediatric Cardiology/Cardiac Surgery Objectives The learner will: Identify 3 areas in the developing heart that result
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
Critical Congenital Heart Disease (CCHD) Screening
 Critical Congenital Heart Disease (CCHD) Screening Screening The Florida Genetics and Newborn Screening Advisory Council recommended to the Department of Health that CCHD be added to the panel of disorders
Critical Congenital Heart Disease (CCHD) Screening Screening The Florida Genetics and Newborn Screening Advisory Council recommended to the Department of Health that CCHD be added to the panel of disorders
Dynamic Auscultation of Heart Sounds and Murmurs. Acknowledgement. Disclosures Real or Potential Conflicts of Interest
 Dynamic Auscultation of Heart Sounds and Murmurs W. Lane Edwards, Jr., MSN, ARNP, ANP Hospitalist Group of Southwest Florida Affiliate Professor of Nursing, University of Alaska at Anchorage Acknowledgement
Dynamic Auscultation of Heart Sounds and Murmurs W. Lane Edwards, Jr., MSN, ARNP, ANP Hospitalist Group of Southwest Florida Affiliate Professor of Nursing, University of Alaska at Anchorage Acknowledgement
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY
 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Most often diagnosed during infancy or adolescence, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the second most common form of heart muscle disease, is usually genetically transmitted,
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Most often diagnosed during infancy or adolescence, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the second most common form of heart muscle disease, is usually genetically transmitted,
How To Treat Heart Valve Disease
 The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
Cardiology Fellowship Manual. Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 Page
 Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 Page 2015-2016 UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION
Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 Page 2015-2016 UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease in the Apparently Healthy Newborn
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease in the Apparently Healthy Newborn A presentation of Texas Pulse Oximetry Project: A Joint Educational Initiative of The University of Texas Health Science
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease in the Apparently Healthy Newborn A presentation of Texas Pulse Oximetry Project: A Joint Educational Initiative of The University of Texas Health Science
5. Management of rheumatic heart disease
 5. Management of rheumatic heart disease The fundamental goal in the long-term management of RHD is to prevent ARF recurrences, and therefore, prevent the progression of RHD, and in many cases allow for
5. Management of rheumatic heart disease The fundamental goal in the long-term management of RHD is to prevent ARF recurrences, and therefore, prevent the progression of RHD, and in many cases allow for
1p36 and the Heart. John Lynn Jefferies, MD, MPH, FACC, FAHA
 1p36 and the Heart John Lynn Jefferies, MD, MPH, FACC, FAHA Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy Services Associate Professor, Pediatric Cardiology and Adult Cardiovascular Diseases Associate
1p36 and the Heart John Lynn Jefferies, MD, MPH, FACC, FAHA Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy Services Associate Professor, Pediatric Cardiology and Adult Cardiovascular Diseases Associate
Anesthesia in Children with Congenital Heart Disease. Elliot Krane, M.D.
 Anesthesia in Children with Congenital Heart Disease Elliot Krane, M.D. Introduction The evolution of medicine to managed care and contracted medical services has often had the effect of shifting a sicker
Anesthesia in Children with Congenital Heart Disease Elliot Krane, M.D. Introduction The evolution of medicine to managed care and contracted medical services has often had the effect of shifting a sicker
HEART MURMURS. Information Leaflet. Your Health. Our Priority.
 HEART MURMURS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is a heart murmur? The first important thing to note is that a heart murmur is not a diagnosis or an illness and it does not
HEART MURMURS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is a heart murmur? The first important thing to note is that a heart murmur is not a diagnosis or an illness and it does not
THE MARY ALLEN ENGLE, MD (1922-2008) PAPERS
 MEDICAL CENTER ARCHIVES OF NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN/WEILL CORNELL 1300 York Avenue # 34 New York, NY 10065 Finding Aid To THE MARY ALLEN ENGLE, MD (1922-2008) PAPERS Dates of Papers: 1948-1991 52.5 Linear
MEDICAL CENTER ARCHIVES OF NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN/WEILL CORNELL 1300 York Avenue # 34 New York, NY 10065 Finding Aid To THE MARY ALLEN ENGLE, MD (1922-2008) PAPERS Dates of Papers: 1948-1991 52.5 Linear
CTA OF THE EXTRACORONARY HEART
 CTA OF THE EXTRACORONARY HEART Charles White MD Director of Thoracic Imaging Department of Radiology University of Maryland NO DISCLOSURES [email protected] CARDIAC CASE DISTRIBUTION Coronary CTA 30% ED chest
CTA OF THE EXTRACORONARY HEART Charles White MD Director of Thoracic Imaging Department of Radiology University of Maryland NO DISCLOSURES [email protected] CARDIAC CASE DISTRIBUTION Coronary CTA 30% ED chest
What is echo? CHAPTER 1 1.1 BASIC NOTIONS. Ultrasound production and detection
 What is echo? CHAPTER 1 1.1 BASIC NOTIONS Echocardiography (echo) the use of ultrasound to examine the heart is a safe, powerful, non-invasive and painless technique. Echo is easy to understand as many
What is echo? CHAPTER 1 1.1 BASIC NOTIONS Echocardiography (echo) the use of ultrasound to examine the heart is a safe, powerful, non-invasive and painless technique. Echo is easy to understand as many
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Objectives. The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease. Lead II P-Wave Amplitude during COPD Exacerbation and after Treatment (50 pts.
 The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
ACYANOTIC HEART DEFECTS
 ACYANOTIC HEART DEFECTS Acyanotic congenital heart defects may be due to obstructive lesions (stenosis) or left-to-right shunts. Lesions with left-to-right shunts include atrial septal defect, ventricular
ACYANOTIC HEART DEFECTS Acyanotic congenital heart defects may be due to obstructive lesions (stenosis) or left-to-right shunts. Lesions with left-to-right shunts include atrial septal defect, ventricular
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Congenital Heart Defects Initial Diagnosis and
 Congenital Heart Defects Initial Diagnosis and Management age e Linda Risley, RN, MSN, CPNP Congenital Heart Defects Congenital heart defects are the most common type of birth defect ~1 out of 100 live
Congenital Heart Defects Initial Diagnosis and Management age e Linda Risley, RN, MSN, CPNP Congenital Heart Defects Congenital heart defects are the most common type of birth defect ~1 out of 100 live
DETECTION OF LEFT-TO-RIGHT INTRACARDIAC SHUNTS
 10/5/00 3:35 PM 9 Shunt Detection and Quantification William Grossman University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine; Division of Cardiology, University of California, San Francisco Medical
10/5/00 3:35 PM 9 Shunt Detection and Quantification William Grossman University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine; Division of Cardiology, University of California, San Francisco Medical
Acquired Heart Disease: Prevention and Treatment
 Acquired Heart Disease: Prevention and Treatment Prevention and Treatment Sharon L. Roble, MD Assistant Professor Adult Congenital Heart Program The Ohio State University/Nationwide Children s Hospital
Acquired Heart Disease: Prevention and Treatment Prevention and Treatment Sharon L. Roble, MD Assistant Professor Adult Congenital Heart Program The Ohio State University/Nationwide Children s Hospital
Screening for Congenital Heart Defects
 Screening for Congenital Heart Defects External review against programme appraisal criteria for the UK NSC Version 4.0, April 2014 Prepared by Dr Rachel L Knowles & Ms Rachael M Hunter University College
Screening for Congenital Heart Defects External review against programme appraisal criteria for the UK NSC Version 4.0, April 2014 Prepared by Dr Rachel L Knowles & Ms Rachael M Hunter University College
SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin
 SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin Product: SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin Cat. No.: 718-9007 Price: (Call for latest pricing) 281-488-5901 or 1-800-364-5901 in US and Canada; Email: [email protected]
SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin Product: SAM, Student Auscultation Manikin Cat. No.: 718-9007 Price: (Call for latest pricing) 281-488-5901 or 1-800-364-5901 in US and Canada; Email: [email protected]
BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April 15, 2008
 MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Feeding in Infants with Complex Congenital Heart Disease. Rachel Torok, MD Southeastern Pediatric Cardiology Society Conference September 6, 2014
 Feeding in Infants with Complex Congenital Heart Disease Rachel Torok, MD Southeastern Pediatric Cardiology Society Conference September 6, 2014 Objectives Discuss common feeding issues in patients with
Feeding in Infants with Complex Congenital Heart Disease Rachel Torok, MD Southeastern Pediatric Cardiology Society Conference September 6, 2014 Objectives Discuss common feeding issues in patients with
Cardiovascular diseases. pathology
 Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS
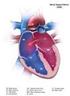 Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS [email protected] Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition
Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts Ismee A. Williams, MD, MS [email protected] Learning Objectives Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance Review the transition
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Introduction Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common congenital disorder in newborns [1]. Due to definitional issues, there are large variations in prevalence estimates.
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Introduction Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common congenital disorder in newborns [1]. Due to definitional issues, there are large variations in prevalence estimates.
Working Towards Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening to Detect Critical CHD
 Working Towards Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening to Detect Critical CHD Dalhousie Fall Refresher Course 2015 Kenny K Wong, MD, FRCPC Pediatric Cardiologist Associate Professor of Pediatrics Objectives
Working Towards Neonatal Pulse Oximetry Screening to Detect Critical CHD Dalhousie Fall Refresher Course 2015 Kenny K Wong, MD, FRCPC Pediatric Cardiologist Associate Professor of Pediatrics Objectives
Atrial Septal Aneurysm: A Study in Five Hundred Adult Patients
 Premio al mejor Tema Libre Realizado por Médicos Residentes Atrial Septal Aneurysm: A Study in Five Hundred Adult Patients Olivares-Reyes Alexander; Al-Kamme Ahmad; Gonzalez Javier Cardiology Department
Premio al mejor Tema Libre Realizado por Médicos Residentes Atrial Septal Aneurysm: A Study in Five Hundred Adult Patients Olivares-Reyes Alexander; Al-Kamme Ahmad; Gonzalez Javier Cardiology Department
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder. Chapter 14. Copyright 2008 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect
 Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
Right-sided infective endocarditis:tunisian experience
 Right-sided infective endocarditis:tunisian experience L. Ammari, A. Ghoubontini, A. Berriche, R. Abdelmalek, S.Aissa, F.Kanoun, B.Kilani, H.Tiouiri Benaissa, T.Ben chaabane Department of Infectious diseases,
Right-sided infective endocarditis:tunisian experience L. Ammari, A. Ghoubontini, A. Berriche, R. Abdelmalek, S.Aissa, F.Kanoun, B.Kilani, H.Tiouiri Benaissa, T.Ben chaabane Department of Infectious diseases,
Pulse Oximetry Screening for Congenital Heart Disease: Toolkit
 Pulse Oximetry Screening for Congenital Heart Disease: Toolkit Elizabeth Goetz MD, MPH John Hokanson, MD University of Wisconsin Department of Pediatrics Meriter Hospital Newborn Nursery University of
Pulse Oximetry Screening for Congenital Heart Disease: Toolkit Elizabeth Goetz MD, MPH John Hokanson, MD University of Wisconsin Department of Pediatrics Meriter Hospital Newborn Nursery University of
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Presentation of Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonate and Young Infant
 Presentation of Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonate and Young Infant Article cardiology Michael Silberbach, MD,* David Hannon, MD Author Disclosure Drs Silberbach and Hannon did not disclose any financial
Presentation of Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonate and Young Infant Article cardiology Michael Silberbach, MD,* David Hannon, MD Author Disclosure Drs Silberbach and Hannon did not disclose any financial
Congenital Heart Defects
 Congenital Heart Defects 1 Congenital Heart Defects CHD with Increased Pulmonary Blood Flow Patent Ductus Arteriosus - PDA...3 Atrial Septal Defect - ASD...4 Ventricular Septal Defect - VSD...5 Aorto-Pulmonary
Congenital Heart Defects 1 Congenital Heart Defects CHD with Increased Pulmonary Blood Flow Patent Ductus Arteriosus - PDA...3 Atrial Septal Defect - ASD...4 Ventricular Septal Defect - VSD...5 Aorto-Pulmonary
Doc, I Am Fine, But I Have A Cardiac Condition
 Doc, I Am Fine, But I Have A Cardiac Condition Nevine Mahmoud, MD John Ludtke, MD Maj, USAFR, MC, FS RAM Class 2014 Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine Division of Aerospace Medicine Dayton,
Doc, I Am Fine, But I Have A Cardiac Condition Nevine Mahmoud, MD John Ludtke, MD Maj, USAFR, MC, FS RAM Class 2014 Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine Division of Aerospace Medicine Dayton,
Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular
 Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular Mitral Regurgitation Anatomy Mechanisms of MR Presentation Evaluation Management Repair Replace Clip
Managing Mitral Regurgitation: Repair, Replace, or Clip? Michael Howe, MD Traverse Heart & Vascular Mitral Regurgitation Anatomy Mechanisms of MR Presentation Evaluation Management Repair Replace Clip
Current status of pediatric cardiac surgery
 Current status of pediatric cardiac surgery Sabine H. Daebritz Dept. of Cardio-vascular Surgery Heart Center Duisburg, Germany Normal circulation 1 Complex cardiac lesions Stenoses Shunts Malconnections
Current status of pediatric cardiac surgery Sabine H. Daebritz Dept. of Cardio-vascular Surgery Heart Center Duisburg, Germany Normal circulation 1 Complex cardiac lesions Stenoses Shunts Malconnections
Left to Right Shunts and their Calculation. Ghada El Shahed, MD
 Left to Right Shunts and their Calculation Ghada El Shahed, MD Professor of Cardiology Ain Shams University Flow through systemic & pulmonary circulations is normally balanced and equal. Two circulations
Left to Right Shunts and their Calculation Ghada El Shahed, MD Professor of Cardiology Ain Shams University Flow through systemic & pulmonary circulations is normally balanced and equal. Two circulations
Rheumatic Fever Vs. (?) Post Strep Reactive Arthritis ינואר 2009
 Rheumatic Fever Vs. (?) Post Strep Reactive Arthritis ינואר 2009 Agenda Introduction Articles Poststreptococcal reactive arthritis in children: is it really a different entity from rheumatic fever? Poststreptococcal
Rheumatic Fever Vs. (?) Post Strep Reactive Arthritis ינואר 2009 Agenda Introduction Articles Poststreptococcal reactive arthritis in children: is it really a different entity from rheumatic fever? Poststreptococcal
Evaluation and Management of Heart Murmurs in Children
 Evaluation and Management of Heart Murmurs in Children JENNIFER E. FRANK, MD, and KATHRYN M. JACOBE, MD, University of Wisconsin Fox Valley Family Medicine Residency Program, Appleton, Wisconsin Heart
Evaluation and Management of Heart Murmurs in Children JENNIFER E. FRANK, MD, and KATHRYN M. JACOBE, MD, University of Wisconsin Fox Valley Family Medicine Residency Program, Appleton, Wisconsin Heart
Resuscitation in congenital heart disease. Peter C. Laussen MBBS FCICM Department Critical Care Medicine Hospital for Sick Children Toronto
 Resuscitation in congenital heart disease Peter C. Laussen MBBS FCICM Department Critical Care Medicine Hospital for Sick Children Toronto Evolution of Congenital Heart Disease Extraordinary success: Overall
Resuscitation in congenital heart disease Peter C. Laussen MBBS FCICM Department Critical Care Medicine Hospital for Sick Children Toronto Evolution of Congenital Heart Disease Extraordinary success: Overall
Doppler Ultrasound in the Management of Fetal Growth Restriction Chukwuma I. Onyeije, M.D. Atlanta Perinatal Associates
 Doppler Ultrasound in the Management of Fetal Growth Restriction Chukwuma I. Onyeije, M.D. Atlanta Perinatal Associates 1 For your convenience a copy of this lecture is available for review and download
Doppler Ultrasound in the Management of Fetal Growth Restriction Chukwuma I. Onyeije, M.D. Atlanta Perinatal Associates 1 For your convenience a copy of this lecture is available for review and download
Acute heart failure may be de novo or it may be a decompensation of chronic heart failure.
 Management of Acute Left Ventricular Failure Acute left ventricular failure presents as pulmonary oedema due to increased pressure in the pulmonary capillaries. It is important to realise though that left
Management of Acute Left Ventricular Failure Acute left ventricular failure presents as pulmonary oedema due to increased pressure in the pulmonary capillaries. It is important to realise though that left
Nutrition in Paediatric Cardiology. Karen Hayes Paediatric Dietitian Addenbrooke s Hospital
 Nutrition in Paediatric Cardiology Karen Hayes Paediatric Dietitian Addenbrooke s Hospital Topics Who needs Nutrition support? Energy Requirements Meeting Energy and growth requirements Feeding Issues
Nutrition in Paediatric Cardiology Karen Hayes Paediatric Dietitian Addenbrooke s Hospital Topics Who needs Nutrition support? Energy Requirements Meeting Energy and growth requirements Feeding Issues
The physiology of cardiac auscultation
 Pediatr Clin N Am 51 (2004) 1515 1535 The physiology of cardiac auscultation Andrew N. Pelech, MD Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Medical College of Wisconsin, 8701 Watertown Plank Road Milwaukee, WI
Pediatr Clin N Am 51 (2004) 1515 1535 The physiology of cardiac auscultation Andrew N. Pelech, MD Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Medical College of Wisconsin, 8701 Watertown Plank Road Milwaukee, WI
Heart Failure EXERCISES. Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it.
 Heart Failure EXERCISES Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it. ) 1. Heart rate increase is a kind of economic compensation, which should
Heart Failure EXERCISES Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it. ) 1. Heart rate increase is a kind of economic compensation, which should
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Advanced Specialist Training (AST) Programme in Cardiology
 I. Definition Cardiology is a medical subspecialty concerned with the prevention, diagnosis, management, and rehabilitation of patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system. A cardiologist is a specialist
I. Definition Cardiology is a medical subspecialty concerned with the prevention, diagnosis, management, and rehabilitation of patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system. A cardiologist is a specialist
Consider the following 2 cases and discuss the questions below before reading the tutorial.
 Recognising Cardiac Disease in Children Name: Hospital: E-mail: Elizabeth Storey Leeds Teaching Hospitals, UK [email protected] Consider the following 2 cases and discuss the questions below before reading
Recognising Cardiac Disease in Children Name: Hospital: E-mail: Elizabeth Storey Leeds Teaching Hospitals, UK [email protected] Consider the following 2 cases and discuss the questions below before reading
Fellow TEE Review Workshop Hemodynamic Calculations 2013. Director, Intraoperative TEE Program. Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
 Fellow TEE Review Workshop Hemodynamic Calculations 2013 Mary Beth Brady, MD, FASE Director, Intraoperative TEE Program Johns Hopkins School of Medicine At the conclusion of the workshop, the participants
Fellow TEE Review Workshop Hemodynamic Calculations 2013 Mary Beth Brady, MD, FASE Director, Intraoperative TEE Program Johns Hopkins School of Medicine At the conclusion of the workshop, the participants
Pediatric Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider. Mary Anne Milbert, RN, MSN, CPNP-PC
 Pediatric Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider Mary Anne Milbert, RN, MSN, CPNP-PC 22nd Annual Northeast Regional Nurse Practitioner Conference May 6-8, 2015 DISCLOSURES There has been no commercial
Pediatric Cardiology for the Primary Care Provider Mary Anne Milbert, RN, MSN, CPNP-PC 22nd Annual Northeast Regional Nurse Practitioner Conference May 6-8, 2015 DISCLOSURES There has been no commercial
