Structural Classification of the Nervous System
|
|
|
- Anissa Judith Wiggins
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structural Classification of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) Brain and spinal cord Activates nerve responses Interprets sensations Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Composed of all the nerves and their branches Spinal nerves (12 pairs) Cranial nerves (31 pairs)
2 Peripheral Nervous System Voluntary (Somatic) Travels to and from the muscles Have some control over The brain sends impulses to nerves that travel down the spinal cord. Then, nerves leave the spinal cord and travel to your muscles, telling them to contract. 2 Subsystems Autonomic We have little or no control over these nerves Examples: Heart beating Food digesting Hormones Secreting 2 parts Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
3 Parasympathetic system Nerves originate in the brain and lowest part (the sacrum) of the spinal cord. Impulses tend to slow us down. Sympathetic system Nerves spring from the chest (thoracic) and lower back (lumbar) regions of the spinal cord. Impulses tend to speed us up, becoming really activated when we are in a fight or flight situation. These are situations in which we experience a sudden threat of danger (real or imagined) to our physical or mental well-being.
4 Three Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes = stimuli 2. Integration -To process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed 3. Motor output A response to integrated stimuli The response activates muscles or glands
5 Two Functional Classification of the Peripheral Nervous System 1. Sensory (afferent) division Nerve fibers that carry information to the central nervous system 2. Motor (efferent) division Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system Two subdivisions Somatic nervous system = voluntary Autonomic nervous system = involuntary
6 Nervous Tissue: Support Cells Support cells in the CNS are grouped together as neuroglia Function: to support, insulate, and protect neurons Control chemical environment of the brain. Unlike most nerve cells, neuroglia are able to replicate.
7 Astrocytes Nervous Tissue: Support Cells Abundant, star-shaped cells Brace neurons Form barrier between capillaries and neurons Control the chemical environment of the brain
8 Nervous Tissue: Support Cells Microglia Spiderlike phagocytes Dispose of debris
9 Nervous Tissue: Support Cells Ependymal cells Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord Circulate cerebrospinal fluid
10 Nervous Tissue: Support Cells Oligodendrocytes Wrap around nerve fibers in the central nervous system Produce myelin sheaths = insulation of the nerves
11 Nervous Tissue: Support Cells Satellite cells Protect neuron cell bodies Schwann cells Form myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system
12 Nervous Tissue: Neurons Neurons = nerve cells Cells specialized to transmit messages Most neurons of the CNS can not replicate Major regions of neurons Cell body nucleus and metabolic center of the cell Processes fibers that extend from the cell body The longest process in the human body is 3 to 4 feet long. The Sciatic nerve runs from the lower back to the big toe.
13 Nervous Tissue: Neurons Processes outside the cell body Dendrites conduct impulses toward the cell body Axons conduct impulses away from the cell body Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap Synaptic cleft gap between adjacent neurons Synapse junction between nerves
14 Neuron Cell Body Location Most neuron cell bodies are found in the central nervous system Gray matter cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers Nuclei clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system Ganglia collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system
15 Functional Classification of Neurons Sensory (afferent) neurons Carry impulses from the sensory receptors to the CNS Cutaneous sense organs Proprioceptors detect stretch or tension Motor (efferent) neurons Carry impulses from the central nervous system to viscera, muscles, or glands
16 Functional Properties of Neurons Irritability Ability to respond to stimuli Conductivity Ability to transmit an impulse Action potential If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon Impulses travel faster when fibers have a myelin sheath
17 Transmission of a Signal at Synapses Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve Neurotransmitter is released from a nerve s axon terminal The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter An action potential is started in the dendrite
18 Two Types of Reflexes and Regulation 1. Somatic reflexes Activation of skeletal muscles Example: When you move your hand away from a hot stove. 2. Autonomic reflexes Smooth muscle regulation Heart and blood pressure regulation Regulation of glands Digestive system regulation
19 Four Regions of the Brain 1. Cerebral hemispheres (cerebrum) 2. Diencephalon 3. Brain stem 4. Cerebellum
20 Cerebrum Cerebral Hemispheres (Cerebrum) Paired (left and right) superior parts of the brain Includes more than half of the brain mass The surface is made of ridges (gyri) and grooves (sulci) Lobes of the cerebrum Fissures (deep grooves) divide the cerebrum into lobes Surface lobes of the cerebrum Frontal lobe Parietal lobe *Occipital lobe *Temporal lobe
21 Cerebrum Specialized areas of the cerebrum Primary somatic sensory area Receives impulses from the body s sensory receptors Located in parietal lobe Primary motor area Sends impulses to skeletal muscles Located in frontal lobe Broca s area Involved in our ability to speak
22 Cerebrum Cerebral areas involved in special senses Gustatory area (taste) Visual area Auditory area Olfactory area Interpretation areas of the cerebrum Speech/language region Language comprehension region General interpretation area
23 Cerebrum Layers of the cerebrum Gray matter outer layer in the cerebral cortex composed mostly of neuron cell bodies White matter fiber tracts deep to the gray matter Corpus callosum connects hemispheres Basal nuclei islands of gray matter buried within the white matter
24 Diencephalon Sits on top of the brain stem Enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres Made of three parts Thalamus Hypothalamus Epithalamus
25 Thalamus Diencephalon The relay station for sensory impulses Transfers impulses to the correct part of the cortex for localization and interpretation Hypothalamus Under the thalamus Important autonomic nervous system center Helps regulate body temperature Controls water balance Regulates metabolism and emotions The pituitary gland is attached to the hypothalamus
26 Diencephalon Epithalamus Houses the pineal body (an endocrine gland) Forms cerebrospinal fluid
27 Regions of the Brain: Brain Stem Attaches to the spinal cord Parts of the brain stem Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata
28 Midbrain Brain Stem Reflex centers for vision and hearing Pons The bulging center part of the brain stem Includes nuclei involved in the control of breathing Reticular Formation Involved in motor control of visceral organs Reticular activating system (RAS) plays a role in awake/sleep cycles and consciousness
29 Regions of the Brain: Brain Stem Medulla Oblongata The lowest part of the brain stem Merges into the spinal cord Contains important control centers Heart rate control Blood pressure regulation Breathing Swallowing Vomiting
30 Regions of the Brain: Cerebellum Two hemispheres with convoluted surfaces Provides involuntary coordination of body movements
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes
 AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Chapter 4. The Brain
 Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
NERVOUS SYSTEM B 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C.
 NERVOUS SYSTEM B 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue D. movement of food
NERVOUS SYSTEM B 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue D. movement of food
Brain Power. Counseling and Mental Health
 Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
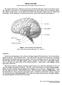 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Nervous System. from the Human Body Systems Series. catalog # 2890. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
NEURONS NEUROGLIAL CELLS.
 1 THE NERVOUS TISSUE Definition: The nervous tissue is an assemblage of cells and supportive elements (materials) in which there is a predominance of cells which are highly specialized in the property
1 THE NERVOUS TISSUE Definition: The nervous tissue is an assemblage of cells and supportive elements (materials) in which there is a predominance of cells which are highly specialized in the property
To understand the nervous system, start by thinking of your
 Chapter The Nervous System 6 To understand the nervous system, start by thinking of your body as a biological machine that runs on electricity. In fact, this is true; your body does run on electricity!
Chapter The Nervous System 6 To understand the nervous system, start by thinking of your body as a biological machine that runs on electricity. In fact, this is true; your body does run on electricity!
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Stress Psychophysiology. Introduction. The Brain. Chapter 2
 Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Chapter 2. The Biological Bases of Psychological Functioning
 Chapter 2 The Biological Bases of Psychological Functioning Outline I. Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System A. A neuron is a nerve cell that transmits information from one part of the body
Chapter 2 The Biological Bases of Psychological Functioning Outline I. Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System A. A neuron is a nerve cell that transmits information from one part of the body
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue
 12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture
 The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Best Teaching Practices Conference. Teacher ID: BTPC07_07 SUBJECT: BIOLOGY. Class: X. TOPIC: Exploring our Nervous System
 Best Teaching Practices Conference Teacher ID: BTPC07_07 SUBJECT: BIOLOGY Class: X TOPIC: Exploring our Nervous System OBJECTIVES: Use Information Technology to enable the students to: Explain the general
Best Teaching Practices Conference Teacher ID: BTPC07_07 SUBJECT: BIOLOGY Class: X TOPIC: Exploring our Nervous System OBJECTIVES: Use Information Technology to enable the students to: Explain the general
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
 Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input. Sensory receptors detects external and internal stimuli.
 FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input. Sensory receptors detects external and internal stimuli. 2. Integration. The brain and spinal cord process sensory input and produce responses. 3. Homeostasis.
FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input. Sensory receptors detects external and internal stimuli. 2. Integration. The brain and spinal cord process sensory input and produce responses. 3. Homeostasis.
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
The Brain of a Normal Human
 The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue Multiple Choice 1. The nervous system A) monitors internal and external stimuli. B) transmits information in the form of action potentials. C) interprets
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue Multiple Choice 1. The nervous system A) monitors internal and external stimuli. B) transmits information in the form of action potentials. C) interprets
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Brain & Mind. Bicester Community College Science Department
 B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 The Role of Experience on the Developing Brain Barb Jackson, Ph.D. Director, Education & Child Development Munroe-Meyer Institute University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE USA The purpose
Slide 1 The Role of Experience on the Developing Brain Barb Jackson, Ph.D. Director, Education & Child Development Munroe-Meyer Institute University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE USA The purpose
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Neurophysiology. 2.1 Equilibrium Potential
 2 Neurophysiology 2.1 Equilibrium Potential An understanding of the concepts of electrical and chemical forces that act on ions, electrochemical equilibrium, and equilibrium potential is a powerful tool
2 Neurophysiology 2.1 Equilibrium Potential An understanding of the concepts of electrical and chemical forces that act on ions, electrochemical equilibrium, and equilibrium potential is a powerful tool
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT
 PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT Chapter 2 Systems that control stress arousal Controlling Stress & Tension Girdano, Dusek & Everly Ligands Ligands (amino acid molecules) Biochemicals that carry information Neurohormones
PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT Chapter 2 Systems that control stress arousal Controlling Stress & Tension Girdano, Dusek & Everly Ligands Ligands (amino acid molecules) Biochemicals that carry information Neurohormones
Anatomy Review. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function.
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function.
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc).
 Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION THE TRIUNE BRAIN Neo? axon brain stem cerebral hemispheres cortex dendrite limbic system neural plasticity neurons neurotransmitter sensory flooding sensory gating
LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION THE TRIUNE BRAIN Neo? axon brain stem cerebral hemispheres cortex dendrite limbic system neural plasticity neurons neurotransmitter sensory flooding sensory gating
the puzzle packet! Brought to you by
 the puzzle packet! Brought to you by It s Mindboggling! word search The following brain-related words all appear in It s Mindboggling! How many can you find? Words may appear in all directions, including
the puzzle packet! Brought to you by It s Mindboggling! word search The following brain-related words all appear in It s Mindboggling! How many can you find? Words may appear in all directions, including
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Human Physiology Study Questions-2
 Human Physiology Study Questions-2 Action potentials: Handout-8, Chapter 8 1. Explain the positive feedback component of an action potential that is, how the opening of one voltage-gated sodium (or calcium)
Human Physiology Study Questions-2 Action potentials: Handout-8, Chapter 8 1. Explain the positive feedback component of an action potential that is, how the opening of one voltage-gated sodium (or calcium)
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system
 Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous system Central Nervous System relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information; Consists of brain and spinal cord Meninges connective tissue around
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Brain Matters: Brain Anatomy
 1 : Brain Anatomy Lesson Overview Students share what they already know about brain structure and function, and then, guided by descriptions of brain regions explore the G2C Online 3-D Brain to learn more
1 : Brain Anatomy Lesson Overview Students share what they already know about brain structure and function, and then, guided by descriptions of brain regions explore the G2C Online 3-D Brain to learn more
Chapter 3 The Brain and Behavior
 Chapter 3 The Brain and Behavior Learning Goals 1. Discuss the nature and basic functions of the nervous system. 2. Explain what neurons are and how they process information. 3. Identify the brain s levels
Chapter 3 The Brain and Behavior Learning Goals 1. Discuss the nature and basic functions of the nervous system. 2. Explain what neurons are and how they process information. 3. Identify the brain s levels
