Basic Brain Information
|
|
|
- Rosa Gilbert
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
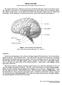
1 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem is the cerebellum The cerebral cortex is the largest part of your brain. It contains the frontal lobes, the motor cortex, sensory cortex and parietal lobes The brain is made up of around 100 billion nerve cells and even more support cells, which provide nourishment to the nerve cells. The diagram below shows which areas of your brain control different activities. Damage to a particular area can affect that activity. For example, damage to your frontal lobe could affect your personality. We also know that the left side of your brain controls your right side. So if someone had a stroke, which affected the left side of their brain, it would be likely that the right side of their body would be affected. For most of us, the left side controls speech, while the right side controls our artistic skills such as drawing and music.
2 Cranium and Brain Stem The brain is completely surrounded by a hard, protective, rounded shell of bone, known as the skull or cranium. The important thing to remember about the skull is that underneath the front there are a number of bony ridges. When the soft tissue of the brain is shaken around, these ridges have the unfortunate effect of lacerating and damaging the underside of the front of the brain. On the floor of the skull is a hole where the lower part of the brain or brain stem is connected to the spinal cord, and from there to the whole of the nervous system and the rest of the body. The brain stem is rather like a thick telecommunications cable, with countless nerve fibres like wires, carrying messages backwards and forwards. This brain stem area is also known to control such bodily functions as wakefulness, consciousness, tiredness, heartbeat and blood pressure. Damage to this area is thought to cause concussion and loss of consciousness. Texture and Blood Vessels The texture of the brain is rather like soft blancmange, but is held together in the skull by a number of layers of membrane called the dura, pia and arachnoid. Between the pia and arachnoid membranes is the subarachnoid space, in which run the blood vessels supplying and draining the brain. Like any organ, the brain is dependent on blood from the heart, and is criss-crossed by a network of large arteries, which divide into progressively smaller branches. When the brain is shaken about in a head injury, these vessels tear and bleed. As people get older, the blood vessels become more brittle and more likely to tear if shaken around. This bleeding leads to a build-up of blood clots, which pressurises and damages the delicate tissue of the brain. The brain in its membranous sack floats in a sea of cerebrospinal fluid, which fills in all the gaps around the brain and offers some protection and cushioning. Just behind the brain stem sits a curved lump of tissue called the cerebellum. This area regulates all of a person's fine motor co-ordination.
3 Cerebral Cortex The largest part of the brain is known as the cerebral cortex and is shaped like a large wrinkled walnut. It is divided into two halves and joined by a bridge in the middle. The two halves are known as the right and left cerebral hemispheres. It is known that the right side controls the left side of our body and the left side controls the right side of our body. Damage only to the right side may affect movement in the left arm and leg or hearing in the left ear. There is also evidence that for most people the left hemisphere contains the language centres involving speech, while the right hemisphere tends to control non-language, spatial skills such as drawing or musical ability. If a person received injuries only to the left side of the brain, by for example having a stroke, it is likely that speech would be affected, as would the ability to move the right side of the body. Strokes tend to affect a specific area, whereas a head injury due to a road traffic accident usually involves more general damage.
4 Nerve Cells The make up of the brain consists of billions of microscopic nerve cells. Under a powerful microscope these cells look like small dots with a network of hair like tentacles (axons and dendrites). They communicate with each other by passing electrical and chemical impulses between these tentacles. Highly complex patterns of communication, or pathways, build up as the brain develops throughout childhood. The effect of a head injury on this delicate substance is similar to that of vigorously shaking a plate of blancmange - it shears and tears, disrupting those pathways of communication. Apart from dividing into a left and right hemisphere, the cerebral cortex can be further divided into a number of areas known as lobes. The frontal lobe is the area behind the forehead and is heavily involved in intellectual activities such as planning and organising, as well as being involved in personality and the control of emotions and behaviour. Just behind and below the frontal lobes are the temporal lobes, nestled behind the ears. This area holds the bulk of memories, and the ability to understand things and speak. At the back of the brain above the ears sit the parietal lobes, which have an important role to play in our ability to understand spatial relationships and to read and write. Between the frontal and parietal lobes are areas that control movement and sensation. At the very back of the head are the occipital lobes, which are responsible for sight. Injury to this area can cause complete or partial blindness. Hidden in the middle of this walnut-like cerebral cortex are a number of small white nerve centres, collectively known as the diencephalon. In this area lies the small pea-sized hypothalamus, which controls appetite regulation, sexual arousal, thirst and temperature control, and some aspects of memory. Close to this area is another important set of nuclei, referred to as the limbic system. Damage to this area can play havoc with emotions, leaving the individual with dramatic and sudden mood swings.
5 Further Information The text and diagrams in this factsheet are adapted from the book Head Injury a practical guide by Trevor Powell, published by Speechmark. The book is available to buy from Headway for 15. If you would like to discuss any of the issues covered here, or any other aspects of brain injury, please call our free, confidential helpline on Alternatively, you can us on [email protected].
Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain
 Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain Acquired brain injury (also known as ABI) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth but has occurred since, and which is non-progressive. An
Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain Acquired brain injury (also known as ABI) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth but has occurred since, and which is non-progressive. An
Section 1. Understanding brain injury and the brain. What is acquired brain injury? Section 1
 Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain Section 1 What is acquired brain injury? Acquired brain injury (also known as ABI) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth but has occurred
Section 1 Understanding brain injury and the brain Section 1 What is acquired brain injury? Acquired brain injury (also known as ABI) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth but has occurred
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Homework Help Stroke
 The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Background on Brain Injury
 CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
BINSA Information on Brain Injury
 Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) There are a number of ways an individual can suffer an acquired brain injury (ABI) Figure one - ABI causes Significant causes of ABI Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Brain
Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) There are a number of ways an individual can suffer an acquired brain injury (ABI) Figure one - ABI causes Significant causes of ABI Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Brain
Brain Power. Counseling and Mental Health
 Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Types of Brain Injury
 Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
The Brain of a Normal Human
 The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration. Objectives. Traumatic Brain Injury. Which came first, the injury or the behavior?
 Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE
 HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE by Greg Doc TrojanIntroduction While motorcycling has been targeted as a public burden and garners most of the public attention concerning head injury, it is actually a minor
HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE by Greg Doc TrojanIntroduction While motorcycling has been targeted as a public burden and garners most of the public attention concerning head injury, it is actually a minor
Nervous System. from the Human Body Systems Series. catalog # 2890. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Functions of the Brain
 Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
It s All in the Brain!
 It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
Glossary. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding.
 Glossary Acoustic nerve: the nerve that is responsible for hearing. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding. Adaptive physical
Glossary Acoustic nerve: the nerve that is responsible for hearing. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding. Adaptive physical
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Chapter 4. The Brain
 Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Lecture One: Brain Basics
 Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
The Brain Injury Handbook. Sponsored by. The Brain Injury Handbook. sponsored by
 The Brain Injury Handbook sponsored by Sponsored by The Brain Injury Handbook a Suffered a serious head injury? We can help brighten your future. At Harris Fowler, we support you every step of the way.
The Brain Injury Handbook sponsored by Sponsored by The Brain Injury Handbook a Suffered a serious head injury? We can help brighten your future. At Harris Fowler, we support you every step of the way.
LECTURE 16 NEUROPATHOPHYSIOLOGY (HEAD INJURY)
 LECTURE 16 Copyright 2000 by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. The approach and organization of this material was developed by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. for specific use in online instruction. All rights reserved. No part
LECTURE 16 Copyright 2000 by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. The approach and organization of this material was developed by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. for specific use in online instruction. All rights reserved. No part
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
PE finding: Left side extremities mild weakness No traumatic wound No bloody otorrhea, nor rhinorrhea
 Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
B U R T & D A V I E S PERSONAL INJURY LAWYERS
 TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Table of Contents. Neurotra nsmission F act Sh eet Page 2. Neurotransmission Scavenger Hunt Page 4. Brain Parts Fact Sheet Page 6
 Table of Contents Neurotra nsmission F act Sh eet Page 2 Neurotransmission Scavenger Hunt Page 4 Brain Parts Fact Sheet Page 6 Nicotine and the Brain Page 8 Alcohol and the Brain Page 10 Puzzle Pieces
Table of Contents Neurotra nsmission F act Sh eet Page 2 Neurotransmission Scavenger Hunt Page 4 Brain Parts Fact Sheet Page 6 Nicotine and the Brain Page 8 Alcohol and the Brain Page 10 Puzzle Pieces
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes
 AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Posterior Cervical Decompression
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
The Brain Injury Handbook. sponsored by. The Brain Injury Handbook
 The Brain Injury Handbook sponsored by The Brain Injury Handbook a Supporting brain injured people and their carers We understand the impact a brain injury can have on the whole family. Our specialist
The Brain Injury Handbook sponsored by The Brain Injury Handbook a Supporting brain injured people and their carers We understand the impact a brain injury can have on the whole family. Our specialist
The Amazing Brain LEVELED BOOK Y. A Reading A Z Level Y Leveled Book Word Count: 1,470. www.readinga-z.com
 The Amazing Brain A Reading A Z Level Y Leveled Book Word Count: 1,470 LEVELED BOOK Y The Amazing Brain Visit for thousands of books and materials. Photo Photo Credits: Credits: Photo Credits: Front Front
The Amazing Brain A Reading A Z Level Y Leveled Book Word Count: 1,470 LEVELED BOOK Y The Amazing Brain Visit for thousands of books and materials. Photo Photo Credits: Credits: Photo Credits: Front Front
Brain & Mind. Bicester Community College Science Department
 B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
Patient Information. Posterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT
 PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT Chapter 2 Systems that control stress arousal Controlling Stress & Tension Girdano, Dusek & Everly Ligands Ligands (amino acid molecules) Biochemicals that carry information Neurohormones
PSK171 STRESS MANAGEMENT Chapter 2 Systems that control stress arousal Controlling Stress & Tension Girdano, Dusek & Everly Ligands Ligands (amino acid molecules) Biochemicals that carry information Neurohormones
How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function?
 How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function? Scientists have found That the basic anatomical components of brain function are related to brain size and shape. The brain is composed of two hemispheres.
How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function? Scientists have found That the basic anatomical components of brain function are related to brain size and shape. The brain is composed of two hemispheres.
Amazing AmMy Brain! DID YOU KNOW..
 My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
The Cranium Connection
 Your Brain! The brain is the command center of your body. It controls just about everything you do, even when you are sleeping. Weighing about 3 pounds, the brain is made up of many parts that all work
Your Brain! The brain is the command center of your body. It controls just about everything you do, even when you are sleeping. Weighing about 3 pounds, the brain is made up of many parts that all work
BINSA Information on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Mild traumatic brain injuries (MTBI) occur through sporting, car and workplace accidents. Mild brain injury is not easily diagnosed. This fact sheet explains how it may be recognised and assessed, and
Mild traumatic brain injuries (MTBI) occur through sporting, car and workplace accidents. Mild brain injury is not easily diagnosed. This fact sheet explains how it may be recognised and assessed, and
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3.
 Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
the puzzle packet! Brought to you by
 the puzzle packet! Brought to you by It s Mindboggling! word search The following brain-related words all appear in It s Mindboggling! How many can you find? Words may appear in all directions, including
the puzzle packet! Brought to you by It s Mindboggling! word search The following brain-related words all appear in It s Mindboggling! How many can you find? Words may appear in all directions, including
Anosmia Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Patient Information Booklet. Talis Consulting Limited
 Anosmia Following Traumatic Brain Injury Patient Information Booklet Talis Consulting Limited What is Anosmia? Anosmia literally means no smell and refers to any condition whereby a person loses their
Anosmia Following Traumatic Brain Injury Patient Information Booklet Talis Consulting Limited What is Anosmia? Anosmia literally means no smell and refers to any condition whereby a person loses their
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
Discuss risk factors and characteristics of various levels of brain injury from mild to severe
 Understanding Brain Injury and Effective Strategies for Communication Kristin A. King, PhD, CCC-SLP University of Tennessee [email protected] Objectives Participants will be able to: Discuss risk factors
Understanding Brain Injury and Effective Strategies for Communication Kristin A. King, PhD, CCC-SLP University of Tennessee [email protected] Objectives Participants will be able to: Discuss risk factors
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS
 CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd.
 About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
Brain Development. Genetic make-up... is not the major determiner
 Brain Development Presented by: Linda Alsop SKI-HI Institute Utah State University Genetic make-up... is not the major determiner Early experiences are so powerful that they can completely change the way
Brain Development Presented by: Linda Alsop SKI-HI Institute Utah State University Genetic make-up... is not the major determiner Early experiences are so powerful that they can completely change the way
Table of contents Topic Page
 Table of contents Topic Page Introduction 1 What is an acquired brain injury? 3 What type of damage has occurred? 4 How much damage has occurred? 5 What tests will my child need? 7 What happens when the
Table of contents Topic Page Introduction 1 What is an acquired brain injury? 3 What type of damage has occurred? 4 How much damage has occurred? 5 What tests will my child need? 7 What happens when the
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
E x p l a i n i n g Stroke
 Explaining Stroke Introduction Explaining Stroke is a practical step-by-step booklet that explains how a stroke happens, different types of stroke and how to prevent a stroke. Many people think a stroke
Explaining Stroke Introduction Explaining Stroke is a practical step-by-step booklet that explains how a stroke happens, different types of stroke and how to prevent a stroke. Many people think a stroke
BRAIN storming Copyright, Poliakoff and Bee, 2000
 by Ellen Poliakoff and Sally Bee Illustrations by Serena Korda BRAIN storming The 1990 s was hailed as the decade of the brain. We ask, what do we really know about the elusive workings of the grey matter
by Ellen Poliakoff and Sally Bee Illustrations by Serena Korda BRAIN storming The 1990 s was hailed as the decade of the brain. We ask, what do we really know about the elusive workings of the grey matter
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
