Chapter 17 Nervous Tissue
|
|
|
- Daisy Thomas
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 17 Nervous Tissue Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers. Neurology is the study of the normal functioning and disorders of the nervous system. Introduction The nervous system- brain, cranial nerves (and their branches), spinal cord, spinal nerves (and their branches), ganglia, enteric plexuses, and sensory receptors A nerve- a bundle of axons (plus associated connective tissue and blood vessels) located outside the brain and spinal cord Ganglia- neuron cell bodies, located outside the brain and spinal cord Enteric plexuses- networks of neurons n the walls of GI tract organs; they help regulate digestive system activities Sensory receptors- monitor changes in the internal and external environment 1
2 Components of the nervous system and anatomical organization of the nervous system. Figure 17.1 Organization of the Nervous System The nervous system consists of two major divisions: Central nervous system (CNS), consists of the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nervous system (PNS), ), cranial nerves that emerge from the brain spinal nerves that emerge from the spinal cord Contains sensory or afferent neurons which transmit nerve impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS motor or efferent neurons which transmit nerve impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands Functional organization of the nervous system Figure
3 The Function of the Nervous System Sensory function sensory receptors detect stimuli in the internal and external environments transmit sensory information by sensory or afferent neurons to the brain or spinal cord Integrative function interneurons analyze the sensory information to provide perception, storing some of it, and making decisions regarding appropriate behaviors Motor function motor or efferent neurons respond to integration decisions by initiating actions in effectors, including muscle fibers and glandular cells Somatic Nervous System The somatic nervous system (SNS) of the PNS consists of sensory and motor neurons. Somatic sensory neurons- information from sensory receptors to the CNS skin, skeletal muscles, joints, and for the special senses (vision, hearing, taste, and smell) Somatic motor neurons- information from the CNS to skeletal muscles only output of information resulting in a muscular contraction. Automonic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system of the PNS has sensory and motor components. Autonomic (Visceral) Sensory neurons- information from organs (smooth muscle organs in the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis) to the CNS. Autonomic motor neurons- information from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands cause the muscles to contract and the glands to secrete.. 3
4 The Motor Branch of the ANA The motor part of the ANS consists of two branches, the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. The sympathetic neurons increase heart rate, support exercise or emergency actions, so-called fight-or-flight responses. The parasympathetic neurons slow it down and the parasympathetic division takes care of rest and- digest activities. Enteric Nervous System The enteric nervous system (ENS) of the PNS- the brain of the gut over 100 million neurons throughout the length of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Sensory neurons of the ENS- monitor chemical changes within the GI tract ands the stretching of its walls. Motor neurons of the ENS- govern contraction of GI tract smooth muscle and secretions from the stomach, and endocrine cells. Histology Nervous tissue- comprised of two types of cells Neurons highly specialized cells. Neurons have lost the ability to undergo mitotic divisions. Neuroglia are smaller cells but greatly outnumber neurons. Neuroglia support, nourish, and protect neurons, and maintain the interstitial fluid Neuroglia continue to divide throughout an individual s lifetime. 4
5 Structure of a typical neuron Figure 17.3 Neurons Neurons possess electrical excitability. A nerve impulse travels rapidly and at a constant strength. Motor neurons cause muscles to contract. Sensory neurons allow you to feel sensations. Nerve impulses travel at speeds ranging from 0.5 to 130 meters per seconds (1 to 280 mi/hr) Parts of a Neuron Neuroglial cells Nucleus with Nucleolus Axons or Dendrites Cell body 5
6 Parts of a Neuron Cell body (perikaryon ) contains a nucleus Nissl bodies are for high levels of protein synthesis Lipofuscin, a pigment that occurs as clumps of yellowish brown granules in the cytoplasm. Dendrites are the receiving or input portions. Axon carries nerve impulses toward another neuron, a muscle fiber, or a gland cell. Axon hillock, a cylindrical projection that joins the cell body at a cone-shaped elevation. Parts of a Axon Trigger Zone- junction of axon hillock and the initial segment in most neurons, impulses arises and then travel along the axon. free of Nissl bodies numerous voltage-sensitive channels in the plasma membrane. Axoplasm- cytoplasm of an axon Axolemma- plasma membrane Axon terminals (telodendria)- axon and its collaterals end by dividing into many fine processes Synapse Synapse- The site of communication between two neurons. Presynaptic neuron- a nerve cell that carries an impulse toward a synapse. Postsynaptic neuron- a nerve cell or effector (muscle or gland) Neuromuscular junction- synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. synaptic vesicles release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) 6
7 Neurotransmitters About 100 substances are either known or suspected neurotransmitters. The presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft which act on the postsynaptic cell. Neurotransmitters include: acetylcholine (ACh), glutamate, aspartate, GABA, glycine, norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), serotonin, endorphins, nitric oxide (NO), etc. Structural Diversity in Neurons Neurons display great diversity in size and shape. Cell bodies range from 5 micrometers (um) to 135 mm. The pattern of dendritic branching is varied and distinctive for neurons in different parts. A few small neurons lack an axon, and many others have very short axons. Structural Diversity in Neurons Multipolar neurons usually have several dendrites and one axon Bipolar neurons have one main dendrite and one axon Unipolar neurons are sensory neurons have just one process extending from the cell body 7
8 Structural classification of neurons Figure 17.4 Neuroglia Neuroglia (glia)- half the volume of the CNS. smaller than neurons do not generate or propagate nerve impulses can multiply and divide in the mature nervous system. Six types: Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells- only in the CNS. Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes) and satellite cells- in the PNS. Neuroglia of the central nervous system Figure
9 Astrocytes Star-shaped cells Asterocytes Two types of astrocytes: Protoplasmic astrocytes found in gray matter Fibrous astrocytes are located mainly in white matter. The processes of astrocytes make contact with blood capillaries, neurons, and the pia mater. Functions of Astrocytes Contain microfilaments that provide strength for structural support of neurons. Their processes wrapped around blood capillaries secrete chemicals that maintain the unique permeability characteristics of the endothelial cells. In the embryo, astrocytes secrete chemicals that appear to regulate the growth, migration, and interconnections among neurons in the brain. Help maintain the appropriate chemical environment for the generation of nerve impulses. May also play a role in learning and memory by influencing the formation of neural synapses. 9
10 Oligodendrocytes Oligodendrocyte have process that form the myelin sheath a lipid and protein covering around some axons insulates the axon and increases the speed of nerve impulse conduction. Oligodendrocytes Most common glial cell type Analogous to Schwann cells of PNS Microglia Microglia originate in red bone marrow and migrate into the CNS as it develops (unlike other neuroglial cells, which develop from the neural tube). Microglia function as phagocytes and they remove cellular debris, microbes and damaged nervous tissue. 10
11 Microglia Small cells found near blood vessels Ependymal cells Ependymal cells line the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord produce, possibly monitor, and assist in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. form the blood cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Ependymal cells
12 Neuroglia of the PNS Completely surround axons and cell bodies. The two types of glial cells in the PNS: SCHWANN CELLS (neurolemmocytes) encircle PNS axons and form the myelin sheath participate in axon regeneration, which is more easily accomplished in the PNS. SATELLITE CELLS surround the cell bodies of neurons of PNS ganglia. regulate exchange of materials between neuronal cell bodies and interstitial fluid. Neuroglia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) Figure 17.7 Myelination Axons that are surrounded by a multilayered lipid and protein covering, called the myelin sheath, are myelinated. Axons without such a covering are unmyelinated. Two types of neuroglia produce myelin sheaths: Schwann cells (in the PNS) Oligodendrocytes (in the CNS). 12
13 Myelinated and unmyelinated axons Figure 17.8 Distribution of gray matter and white matter in the spinal cord Gray and White Matter The white matter is aggregations of myelinated and unmyelinated axons of many neurons. The gray matter of the nervous system contains neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, axon terminals, and neuroglia. 13
14 Neural Circuits The CNS contains billions of neurons organized into complex networks called neural circuits, each having its own function. Simple series circuit- a presynaptic neuron transmits a message to a single postsynaptic neuron, which in turn stimulates another neuron. Diverging circuit- a presynaptic neuron forms synapses with several postsynaptic cells. Converging circuit- presynaptic neurons form synapses with a single postsynaptic neuron Reverberating circuit- presynaptic neuron is stimulated causing the postsynaptic neuron to transmit a series of nerve impulses Parallel after-discharge circuit- a single presynaptic neuron stimulates a group of neurons, all of which form synapses with a common postsynaptic neuron. Neural Circuits 14
15 Regeneration and Neurogenesis The nervous system exhibits plasticity, the ability to change based on experience. Mammalian neurons have very limited powers of regeneration, the ability to replicate or repair themselves. Neurogenesis- formation of new neurons from stem cells known to occur in the adult hippocampus has not been shown to occur elsewhere in the brain or spinal cord. Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Autoimmune disorder causing destruction of myelin sheaths in CNS sheaths becomes scars or plaques 1/2 million people in the United States appears between ages 20 and 40 females twice as often as males Symptoms include muscular weakness, abnormal sensations or double vision Remissions & relapses result in progressive, cumulative loss of function Epilepsy The second most common neurological disorder affects 1% of population Characterized by short, recurrent attacks initiated by electrical discharges in the brain auras- lights, noise, or smells may be perceived prior skeletal muscles may contract involuntarily loss of consciousness Epilepsy has many causes, including; brain damage at birth, metabolic disturbances, infections, toxins, vascular disturbances, head injuries, and tumors
16 End of Chapter 17 All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permission Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publishers assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages caused by the use of theses programs or from the use of the information herein. 16
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
NEURONS NEUROGLIAL CELLS.
 1 THE NERVOUS TISSUE Definition: The nervous tissue is an assemblage of cells and supportive elements (materials) in which there is a predominance of cells which are highly specialized in the property
1 THE NERVOUS TISSUE Definition: The nervous tissue is an assemblage of cells and supportive elements (materials) in which there is a predominance of cells which are highly specialized in the property
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue
 12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input. Sensory receptors detects external and internal stimuli.
 FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input. Sensory receptors detects external and internal stimuli. 2. Integration. The brain and spinal cord process sensory input and produce responses. 3. Homeostasis.
FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input. Sensory receptors detects external and internal stimuli. 2. Integration. The brain and spinal cord process sensory input and produce responses. 3. Homeostasis.
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture
 The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue Multiple Choice 1. The nervous system A) monitors internal and external stimuli. B) transmits information in the form of action potentials. C) interprets
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue Multiple Choice 1. The nervous system A) monitors internal and external stimuli. B) transmits information in the form of action potentials. C) interprets
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
CELLS IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 NEURONS AND GLIA CELLS IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Glia Insulates, supports, and nourishes neurons Neurons Process information Sense environmental changes Communicate changes to other neurons Command body response
NEURONS AND GLIA CELLS IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Glia Insulates, supports, and nourishes neurons Neurons Process information Sense environmental changes Communicate changes to other neurons Command body response
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes
 AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions
 Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [ 1. Cell body] [2. Neuronal membrane] [3. Dendrites] [4. Axon] [5. Nerve ending] 1. Cell body The cell body (soma) is the factory
Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [ 1. Cell body] [2. Neuronal membrane] [3. Dendrites] [4. Axon] [5. Nerve ending] 1. Cell body The cell body (soma) is the factory
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Nervous Tissue Chapter 12
 Nervous Tissue Chapter 12 Overview of the Nervous System Cells of the Nervous System Electrophysiology of Neurons Synapses Subdivisions of the Nervous System Two major anatomical subdivisions: Central
Nervous Tissue Chapter 12 Overview of the Nervous System Cells of the Nervous System Electrophysiology of Neurons Synapses Subdivisions of the Nervous System Two major anatomical subdivisions: Central
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized
 Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized (ie) Electrical charge on the outside of the membrane is positive while the electrical charge on the inside of the membrane is negative Changes
Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized (ie) Electrical charge on the outside of the membrane is positive while the electrical charge on the inside of the membrane is negative Changes
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
You can t turn on the television or radio, much less go online, without seeing something
 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue You can t turn on the television or radio, much less go online, without seeing something to remind you of the nervous system. From advertisements
11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue You can t turn on the television or radio, much less go online, without seeing something to remind you of the nervous system. From advertisements
Neurophysiology. 2.1 Equilibrium Potential
 2 Neurophysiology 2.1 Equilibrium Potential An understanding of the concepts of electrical and chemical forces that act on ions, electrochemical equilibrium, and equilibrium potential is a powerful tool
2 Neurophysiology 2.1 Equilibrium Potential An understanding of the concepts of electrical and chemical forces that act on ions, electrochemical equilibrium, and equilibrium potential is a powerful tool
Nervous System: Nervous Tissue! (Chapter 12)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus!
 Nervous System: Nervous Tissue! (Chapter 12)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Neural Tissue! -3% of body mass! -cellular, ~20% extracellular
Nervous System: Nervous Tissue! (Chapter 12)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Neural Tissue! -3% of body mass! -cellular, ~20% extracellular
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Anatomy Review. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function.
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function.
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc).
 Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON. created by Dr. Joanne Hsu
 NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 3: Brain s Building Blocks. Module 3. Brain s Building Blocks
 Module 3 Brain s Building Blocks Structure of the Brain Genes chains of chemicals that are arranged like rungs on a twisting ladder there are about 100,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that
Module 3 Brain s Building Blocks Structure of the Brain Genes chains of chemicals that are arranged like rungs on a twisting ladder there are about 100,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system
 組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :[email protected]
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :[email protected]
Bio 348 Human Anatomy & Physiology Lapsansky 2014
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES NOTE: Please review the objectives for both the lecture and lab in preparation for lecture exams. Although lab questions will not be on the lecture exams, many of the objectives overlap,
LEARNING OBJECTIVES NOTE: Please review the objectives for both the lecture and lab in preparation for lecture exams. Although lab questions will not be on the lecture exams, many of the objectives overlap,
 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential
 Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944
 http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944 What are the nervous system s functions? The nervous system organizes and controls an individual s appropriate
http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944 What are the nervous system s functions? The nervous system organizes and controls an individual s appropriate
Chapter 4. The Brain
 Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
NERVOUS SYSTEM B 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C.
 NERVOUS SYSTEM B 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue D. movement of food
NERVOUS SYSTEM B 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue D. movement of food
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Psychology 3625 Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience. Dr Darren Hannesson
 Psychology 3625 Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience Dr Darren Hannesson Lecture 6 Cells of the nervous system Neurons Glia Other cell types Blood-brain barrier Types of nervous system cells Neurons The
Psychology 3625 Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience Dr Darren Hannesson Lecture 6 Cells of the nervous system Neurons Glia Other cell types Blood-brain barrier Types of nervous system cells Neurons The
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
MUSCULAR SYSTEM. A. K. Sengupta 9/9/2010 1/12
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
Brain & Mind. Bicester Community College Science Department
 B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange
 Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
BIO 201 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I with LAB
 BIO 201 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Presented and Approved: January 12, 2012 Effective: 2012-13 FA Prefix & Number BIO 201 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
BIO 201 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Presented and Approved: January 12, 2012 Effective: 2012-13 FA Prefix & Number BIO 201 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
Nerves and Conduction of Nerve Impulses
 A. Introduction 1. Innovation in Cnidaria - Nerve net a. We need to talk more about nerves b. Cnidaria have simple nerve net - 2 way conduction c. Basis for more complex system in Vertebrates B. Vertebrate
A. Introduction 1. Innovation in Cnidaria - Nerve net a. We need to talk more about nerves b. Cnidaria have simple nerve net - 2 way conduction c. Basis for more complex system in Vertebrates B. Vertebrate
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS.
 CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
Exploring Creation with Advanced Biology ~ Schedule for 2015-2016 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Date:
 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
Norepinephrine Effects On the System
 Norepinephrine Effects On the System NE Conversion to Epinephrine in the Circulation Under stress, the increased norepinephrine produced is transmitted throughout the system. This increased level represents
Norepinephrine Effects On the System NE Conversion to Epinephrine in the Circulation Under stress, the increased norepinephrine produced is transmitted throughout the system. This increased level represents
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to. women, and is a serious condition that can lead to. significant lifestyle changes.
 Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
I have also included the questions from the muscular system quiz 7AB and 8 AB in this practice set.
 1 Practice Questions for Exam 2 As you prepare for the exam you should review all of your lecture notes, study guides, key medical terms, blood test information, and previous quizzes. The following are
1 Practice Questions for Exam 2 As you prepare for the exam you should review all of your lecture notes, study guides, key medical terms, blood test information, and previous quizzes. The following are
The Neuron and the Synapse. The Neuron. Parts of the Neuron. Functions of the neuron:
 The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
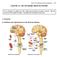 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
EXCITABILITY & ACTION POTENTIALS page 1
 page 1 INTRODUCTION A. Excitable Tissue: able to generate Action Potentials (APs) (e.g. neurons, muscle cells) B. Neurons (nerve cells) a. components 1) soma (cell body): metabolic center (vital, always
page 1 INTRODUCTION A. Excitable Tissue: able to generate Action Potentials (APs) (e.g. neurons, muscle cells) B. Neurons (nerve cells) a. components 1) soma (cell body): metabolic center (vital, always
Management in the pre-hospital setting
 Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
