Seismic Hazard Maps for the National Building Code of Canada past, present and future
|
|
|
- Maria Rice
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seismic Hazard Maps for the National Building Code of Canada past, present and future John Adams Geological Survey of Canada, Natural Resources Canada, Ottawa, CSRN 2011 Workshop 2012 Jan 13 Copyright. Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 2012
2 Seismology Background Movement on a fault plane causes vibrations The larger the area on which there is slip (rupture) the larger the magnitude of the earthquake M Lamontagne, GSC
3 Relative fault areas Haiti 2010 M7.0 Japan 2011 M9.1 M6.2. ~ 1000 times larger than M7.0 J Cassidy, GSC
4 Magnitude Magnitude depends on the size of the reactivated fault surface; as magnitude increases, the strength of ground shaking, duration, and area impacted increases very quickly. Ground shaking Increases by 10 times for every magnitude unit Energy released Increases by 32 times for every magnitude unit Duration of shaking From a few seconds (M 4) to several minutes (M 9) J Cassidy, GSC
5 Major earthquakes are related to movements at Plate Boundaries 7 M Lamontagne, GSC
6 Global Seismicity over 20 years: concentrated at plate boundaries Mw 6.0 Mw 7.7 M Lamontagne, GSC 8
7
8 Tectonic Context of Canada s West Coast Vancouver Transform Plates Divergent Plates Convergent Plates J Cassidy, GSC
9 Southeastern Canada Earthquakes since 1700 Timiskaming 1935 M6.1 Saguenay 1988 M5.9 Charlevoix 1663 M~7 Cornwall 1944 M5.8 Montreal 1732 M~6 Attica 1929 M4.9
10 Size described by magnitude (one magnitude per earthquake!) Effects described by shaking intensity (Modified Mercalli scale: IV, VII) Magnitude 5.9 Saguenay 1988 Nov 25 suppertime Damage in Montreal 250 km away
11 Cornwall 1944 Mw 5.7 Masonry damage School Gymnasium
12 Most recent sizable earthquake Val-des-Bois Mw 5.0 June 2010 Earthquakes magnitude 2.0 and larger, present
13 Val-des-Bois Earthquake June 23 rd shaking in Ottawa was strongest in Ottawa s history once-in-150-year level of shaking only 1/5 th as strong as current building code requires Response Spectral acceleartion (g) Earthquake design shaking in Ottawa on rock Val-des-Bois earthquake shaking on rock E-W component (Re9) N-S component (Re9) Design Spectrum (site class C) Design spectrum (site class A) Period (s) Only weakly felt into eastern Quebec Potentially felt by about 19 million people Web reports from 59,000 people Felt much farther to the southwest than to the northeast
14 Examples of Val-des-Bois earthquake effects At less than 70 km
15 While in Toronto, 400 km away.
16 How often do earthquakes happen? Magnitude-recurrence statistics near Toronto About once in 3000 years
17 Why do earthquakes happen here? Ancient Rifted margin Hot Spot
18 We can t stop earthquakes We can t forecast them in a useful way (yet!), So we must mitigate their effects Globally most deaths in earthquakes are from: People killed in collapsing buildings 77% Tsunamis 11% Earthquake-triggered landslides 8% Fire 4% Liquefaction; heart attacks ~1% 2.6 million fatalities, Source: Daniell 2011, Figure 10 We have done something about collapsing buildings, through Canada s National Building Code
19 National Building Code The minimum standard to protect the life and safety of building occupants and the general public as the building responds to strong ground shaking Expected shaking comes from seismic hazard maps
20 Probabilistic seismic hazard Earthquake Catalog Earthquake locations Earthquake number - sizes - rates magnitude Shaking vs distance relations Seismic hazard
21 National Building Code The minimum standard to protect the life and safety of building occupants and the general public as the building responds to strong ground shaking Expected shaking comes from seismic hazard maps 1953 One map Primarily a zoning map Peak Acceleration for 4 zones
22 1970 One map Peak Acceleration for 4 zones Probabilistic at 1/100 years 1985 Two maps Peak Acceleration & Velocity 7 zones Rock and Firm Ground Probabilistic 10% /50 years = 1/475 years
23 2005 Four maps Spectral Acceleration (plus Peak Acceleration) No zones Firm Ground (Site Class C) Probabilistic at 2%/50 years = 1/2475 years E Similar to 2005 (see next slide)
24 NBCC 2010 Issued at end of 2010 In process of being adopted by Provinces and Territories Similar parameters to 2005 Chief seismic difference: model for eastern ground motion shaking changed from Quadratic to 8-parameter fit because this reduced unnecessary conservatism Reduced hazard at short periods in low-hazard zones Increased hazard at long periods in low-hazard zones Reduced PGA (still used in geotechnical designs) Spectra tilted from the changes
25 Change in 2010 Blue = 2005 Red = 2010 Reduced PGA Reduced Sa(0.2) in lower hazard regions Increased Sa(2.0) in lower hazard regions
26 NRCan website for seismic hazard calculations
27
28 Web output plus singlepage pdf NBCC probability Other probabilities
29 NBCC 2015: 5 th Generation Seismic Hazard Maps Trial results: focus is on computing and understanding the hazard values for populated SE and SW Canada main cities Main changes Catalog 18 years more earthquakes Moment magnitude catalog Replacement of Robust approach Replacement of H and R models East West Probabilistic treatment of Cascadia Integrated treatment of Floor source New Ground Motion relations New spectral values (shorter and longer periods) Adjusted reference ground condition
30 New earthquakes Last model used earthquakes up to 1990/1991 Now will add earthquakes up to end of 2010 Adds lots of smaller earthquakes (GSC used to locate 1500 earthquakes a year, now locates per yr) Adds a number of significant earthquakes in the last decade (Denali, Nisqually, Queen Charlottes, Val-des-Bois ) New data for inslab earthquakes New data for moderate M5 earthquakes
31 Improved catalog in Moment magnitude (Mw) For 2015: largest events have had Mw assigned by inspection of data and publications Events smaller than Mw~4.7 converted from catalog values Sensitivity tests: East: centre of Gatineau zone Sa(0.2) = 0.26 g from mn catalog 0.25 g from Mw catalog West: Prince Rupert Sa(0.2) = 0.37 g from mn catalog 0.33 g from Mw catalog Sensitivity test: Not much effect on onshore hazard
32 Eastern source zones: Replacement of Robust approach The issue:
33 2005/2010 approach H Locations very different in H model, reflecting local Locations rather earthquake activity similar in R model Sa(0.2) in cm/s/s 2005 H 2005 R AG201 E-161 La Malbaie ? Quebec City * 260 R Trois Rivieres ?200 Montreal Ottawa * Low because IRM zone boundary badly placed
34 2015 draft Historical seismic source models GSC 2011 Atkinson
35 Earthquake rate considered in IRM source zone: Best estimate curve for IRM Source Zone Best estimate curve for CIE Work by Lan Lin, GSC Aug2009
36 Parameters considered in IRM source zone: Best estimate curve for IRM Source Zone Best estimate curve for CIE Work by Lan Lin, GSC Aug2009
37 Seismotectonic seismic source model from GSC 5 large zones as sources for Random Big Earthquakes (RBE)
38 Mw<6.8 Parameters considered in IRM source zone: M6.8 Composite seismic source model Best estimate curve for IRM Source Zone Mw 6.8 Best estimate curve for CIE Work by Lan Lin, GSC Aug2009
39 Historical seismic source models Composite Model We can use the H models directly, or composite with the RBE model The transition magnitude used doesn t matter very much
40 What rates for Random Big Earthquakes? Very little constraints from data, paleoseismic or otherwise St. Lawrence rift source: expect one Mw 6.8 per 300 years Other best rates for Mw 6.8 by judgement based on relative seismicity levels Large uncertainty taken as factor of 3 up and down Can infer unreasonable maximum rates from history (used to additionally constrain upper limits in blue) 1/1000 years 1/300 years 1/3000 years
41 Effect of Composite model is more evident in low seismicity regions like Trois Rivieres Montreal Trois Rivieres Contribution from Random Big Earthquakes Contribution from small local earthquakes Change in hazard still being modelled, but. Montreal not the same as Ottawa Trois Rivières lower than Montreal and Quebec City Charlevoix still high, but less high than before
42 Western sources 2011 model
43 Will remove areas of obvious induced events
44 Crustal and sub-crustal (mauve) sources
45 Probable replacement of 2010 deterministic Cascadia approach by 2015 probabilistic fault model 2010 Just replacing or by and increases hazard ~40% along this line Cascadia exceeds probabilistic
46 2015 Cascadia model Inboard edge of rupture
47 Rupture model for Cascadia and Explorer plates
48 Van 120 km 60 km Vic Rupture model for Cascadia and Explorer plates - detail Locus is at 30 km depth
49 Comparison of Cascadia inboard loci (best estimates) ~15 km closer to Victoria
50 Paleohistory of Great Cascadia Events after Goldfinger et al 201X Intervals for complete rupture events Dates for past events (10,000 year history)
51 Cascadia Magnitude-recurrence for complete rupture events 10,000 year history (we have one sample of the 1/10,000 year event!) Assume that each rupture of interest to Canada is complete, end-to-end (i.e. all M~9, not some M9 + many M~8) Use time interval * plate tectonic rate to get the slip per event magnitude Protypical event happens every 550 years, ruptures length of 1020 km and width of 125 km, has slip of 25 m and has magnitude of 9.3 Events range in magnitude from or depending on input assumptions but nearby seismic hazard is not very sensitive to exact magnitudes when earthquakes get this big
52 Magnitude-recurrence for complete rupture events using 2 sets of possible input parameters 1/550 yr 1/10,000 yr
53 Trial run Probabilistic Cascadia motions Sa(0.2) for 2%/50 years 2011 geometry Youngs GMPE Results indicative only Locus is uncertain by ~20 km, and results in ~15% change in hazard
54 Floor region and Maximum earthquake Mmax in nonextended-scr is M7.25±0.1 and in extended-scr is M7.65±0.1
55 Integrated Treatment of Floor source Will add as a source to the eastern and western models Will use two alternative models (probably 4 th Gen and Martens-Atkinson models, equally weighted) Will allow Mmax to (Leonard & Clark, 2011) Expect hazard to drop in centre of country, may increase it at margins, near other earthquake sources (e.g. Calgary, Sudbury) May still need a floor value?
56 New Ground Motion Prediction Equations Gail will talk about these Evolution of spectral periods In 1985 it was PGA and PGV In 2005/2010 Sa at 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 seconds For 2015 may add 0.15, 5, 10 seconds Important for very short rigid structures Important for tall buildings and bridges Not yet certain how these periods would be used in the Code
57 Adjusted reference ground condition In 1985 it was Rock or Firm Ground In 2005 Fa and Fv factors were introduced reference condition = Site Class C reduction factor of 20-50% for being on rock For 2015 the reference ground condition is likely to be the boundary between site class B and site Class C ( B/C = BslashC) for consistency with all recent Ground Motion relations Probably no design level implications (though the Fa and Fv values will change)
58 Summary Seismic hazard estimates are improving More data leads to improvements and increased confidence in our estimates 2015 estimates will provide an improved basis for the distribution of engineering anti-seismic measures across Canada
Earthquakes. Earthquakes: Big Ideas. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Measuring Earthquake Waves. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form?
 298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet
 Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE
 EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
Earthquake Hazards and Risks
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Name Date Class. By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter.
 CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel
 PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel Avigdor Rutenberg and Robert Levy Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel Avi Shapira International
PROHITECH WP3 (Leader A. IBEN BRAHIM) A short Note on the Seismic Hazard in Israel Avigdor Rutenberg and Robert Levy Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel Avi Shapira International
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
 Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Magnitude 7.2 GUERRERO, MEXICO
 A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
EARTHQUAKES. Compressional Tensional Slip-strike
 Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
How do scientists measure earthquakes?
 Name: Source: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=4892 http://gizmodo.com/5833688/what-do-earthquake-magnitudes-mean http://www.kids-fun-science.com/moment-magnitude-scale.html http://tremor.nmt.edu/faq/how.html
Name: Source: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=4892 http://gizmodo.com/5833688/what-do-earthquake-magnitudes-mean http://www.kids-fun-science.com/moment-magnitude-scale.html http://tremor.nmt.edu/faq/how.html
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy
 February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude
 Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Let s Talk about Earthquakes: Wellington Edition
 Let s Talk about Earthquakes: Wellington Edition Dr. Rob Langridge Dr. Graham Leonard Russ Van Dissen Kim Wright GNS Science What is this presentation about? Who we are Why we study earthquakes Wellington
Let s Talk about Earthquakes: Wellington Edition Dr. Rob Langridge Dr. Graham Leonard Russ Van Dissen Kim Wright GNS Science What is this presentation about? Who we are Why we study earthquakes Wellington
AFAD DEPREM DAİRESİ BAŞKANLIĞI TÜRKİYE KUVVETLİ YER HAREKETİ ve ÖN HASAR TAHMİN SİSTEMLERİ ÇALIŞMA GRUBU. (Rapid Estimation Damage)
 (Rapid Estimation Damage) AFAD-RED SYSTEM The technological advances in seismic instrumentation and telecommunication permit the development of rapid estimation of earthquake losses in order to enhance
(Rapid Estimation Damage) AFAD-RED SYSTEM The technological advances in seismic instrumentation and telecommunication permit the development of rapid estimation of earthquake losses in order to enhance
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel
 Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
CONTRASTING DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS OF DUCTILE STRUCTURES FROM TOHOKU SUBDUCTION TO CRUSTAL EARTHQUAKE RECORDS. Peter Dusicka 1 and Sarah Knoles 2
 CONTRASTING DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS OF DUCTILE STRUCTURES FROM TOHOKU SUBDUCTION TO CRUSTAL EARTHQUAKE RECORDS Abstract Peter Dusicka 1 and Sarah Knoles 2 With the impending Cascadia subduction zone event
CONTRASTING DISPLACEMENT DEMANDS OF DUCTILE STRUCTURES FROM TOHOKU SUBDUCTION TO CRUSTAL EARTHQUAKE RECORDS Abstract Peter Dusicka 1 and Sarah Knoles 2 With the impending Cascadia subduction zone event
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Science Grade 6. Unit Organizer: Geology: Inside the Earth (Approximate Time: 7 Weeks)
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY
 Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Locating the Epicenter and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake
 Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
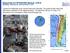 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
Seismic Risk Assessment Procedures for a System consisting of Distributed Facilities -Part three- Insurance Portfolio Analysis
 Seismic Risk Assessment Procedures for a System consisting of Distributed Facilities -Part three- Insurance Portfolio Analysis M. Achiwa & M. Sato Yasuda Risk Engineering Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan M. Mizutani
Seismic Risk Assessment Procedures for a System consisting of Distributed Facilities -Part three- Insurance Portfolio Analysis M. Achiwa & M. Sato Yasuda Risk Engineering Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan M. Mizutani
Site C Clean Energy Project Topic Specific Sessions: Presentation by Natural Resources Canada
 Site C Clean Energy Project Topic Specific Sessions: Presentation by Natural Resources Canada Fort St. John, British Columbia January 13, 2014 Outline 1. Context for NRCan s Participation in the Joint
Site C Clean Energy Project Topic Specific Sessions: Presentation by Natural Resources Canada Fort St. John, British Columbia January 13, 2014 Outline 1. Context for NRCan s Participation in the Joint
Client: Nederlandse Aardolie Maatschappij Arup Project Title: Groningen 2013 Seismic Risk Study - Earthquake Scenario-Based Risk Assessment
 Client: Nederlandse Aardolie Maatschappij Arup Project Title: Groningen 2013 Seismic Risk Study - Earthquake Scenario-Based Risk Assessment REP/229746/SR001 Issue 29 November 2013 This report was prepared
Client: Nederlandse Aardolie Maatschappij Arup Project Title: Groningen 2013 Seismic Risk Study - Earthquake Scenario-Based Risk Assessment REP/229746/SR001 Issue 29 November 2013 This report was prepared
Overview. NRC Regulations for Seismic. Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station. NRC History. How we Regulate
 Overview 1. NRC History and Overview NRC Regulations for Seismic Analysis and Design Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station Christie Hale Megan Williams 2. Regulations for Seismic Hazards 3.
Overview 1. NRC History and Overview NRC Regulations for Seismic Analysis and Design Applied to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station Christie Hale Megan Williams 2. Regulations for Seismic Hazards 3.
Glossary. continental crust: the sections of crust, the outermost layer of the earth, that include the continents
 aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
Scope of Insurance Premium for Residential Houses against Seismic Risk in Japan
 Scope of Insurance Premium for Residential Houses against Seismic Risk in Japan J. Kanda a) and K. Nishijima b) a) University of Tokyo, Japan [email protected] b) ETH, Switzerland ABSTRACT The premium
Scope of Insurance Premium for Residential Houses against Seismic Risk in Japan J. Kanda a) and K. Nishijima b) a) University of Tokyo, Japan [email protected] b) ETH, Switzerland ABSTRACT The premium
Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
EARTHQUAKE. Definition of Hazard. History of Hazard as it Affects the City of Kent. Hazard Identification
 EARTHQUAKE Definition of Hazard Earthquakes are defined as the sudden release of energy occurring from the collision or shifting of crustal plates on the earth s surface or from the fracture of stressed
EARTHQUAKE Definition of Hazard Earthquakes are defined as the sudden release of energy occurring from the collision or shifting of crustal plates on the earth s surface or from the fracture of stressed
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Echo Sounding Record. Measuring Bathymetry. CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II
 Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II 4. Which of the following statements about paleomagnetism at spreading ridges is FALSE? A. there is a clear pattern of paleomagnetic
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II 4. Which of the following statements about paleomagnetism at spreading ridges is FALSE? A. there is a clear pattern of paleomagnetic
The Dynamic Crust 2) EVIDENCE FOR CRUSTAL MOVEMENT
 The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface
 TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction. 2nd Edition
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2171210/ Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction. 2nd Edition Description: Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction,
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2171210/ Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction. 2nd Edition Description: Earthquake Resistant Design and Risk Reduction,
Assignment #3: Plate Tectonics
 Assignment #3: Plate Tectonics Overview: In this assignment we will examine the ideas of continental drift and of sea-floor spreading that lead to the Theory of Plate Tectonics. This assignment is in two
Assignment #3: Plate Tectonics Overview: In this assignment we will examine the ideas of continental drift and of sea-floor spreading that lead to the Theory of Plate Tectonics. This assignment is in two
PACIFIC CATASTROPHE RISK ASSESSMENT AND FINANCING INITIATIVE
 PACIFIC CATASTROPHE RISK ASSESSMENT AND FINANCING INITIATIVE NIUE SEPTEMBER 11 COUNTRY RISK PROFILE: NIUE Niue is expected to incur, on average,.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
PACIFIC CATASTROPHE RISK ASSESSMENT AND FINANCING INITIATIVE NIUE SEPTEMBER 11 COUNTRY RISK PROFILE: NIUE Niue is expected to incur, on average,.9 million USD per year in losses due to earthquakes and
Seismic Waves Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Chapter 2. Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics: Learning Goals
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q.
 Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
Step 2: Learn where the nearest divergent boundaries are located.
 What happens when plates diverge? Plates spread apart, or diverge, from each other at divergent boundaries. At these boundaries new ocean crust is added to the Earth s surface and ocean basins are created.
What happens when plates diverge? Plates spread apart, or diverge, from each other at divergent boundaries. At these boundaries new ocean crust is added to the Earth s surface and ocean basins are created.
SEISMIC RETROFITTING STRATEGIES FOR BRIDGES IN MODERATE EARTHQUAKE REGIONS
 SEISMIC RETROFITTING STRATEGIES FOR BRIDGES IN MODERATE EARTHQUAKE REGIONS ABSTRACT Ayaz H. Malik, P.E. Project Engineer New York State Department of Transportation Certain parts of the United States have
SEISMIC RETROFITTING STRATEGIES FOR BRIDGES IN MODERATE EARTHQUAKE REGIONS ABSTRACT Ayaz H. Malik, P.E. Project Engineer New York State Department of Transportation Certain parts of the United States have
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008
 Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
6.E.2.2 Plate Tectonics, Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Shaky Ground 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
ES Chapter 10 Review. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones
 Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Plate Tectonics. Introduction. Boundaries between crustal plates
 Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
Part 4: Seismic hazard assessment
 GIS CASE STUDY Application of GIS for earthquake hazard and risk assessment: Kathmandu, Nepal Part 4: Seismic hazard assessment Cees van Westen (E-mail : [email protected]) Siefko Slob (E-mail: [email protected])
GIS CASE STUDY Application of GIS for earthquake hazard and risk assessment: Kathmandu, Nepal Part 4: Seismic hazard assessment Cees van Westen (E-mail : [email protected]) Siefko Slob (E-mail: [email protected])
Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates.
 Notes on Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates. These plates move around the mantle. Plates are composed of the crust and
Notes on Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates. These plates move around the mantle. Plates are composed of the crust and
Using Remotely Sensed Data From ASTER to Look Impact of Recent Earth Quakes in Gujarat, India.
 Using Remotely Sensed Data From ASTER to Look Impact of Recent Earth Quakes in Gujarat, India. A major earth quake occurred in Gujarat, India on January 26,2000. (Origin time 03:16 GMT, Location 23.399N
Using Remotely Sensed Data From ASTER to Look Impact of Recent Earth Quakes in Gujarat, India. A major earth quake occurred in Gujarat, India on January 26,2000. (Origin time 03:16 GMT, Location 23.399N
Investigation 6: What happens when plates collide?
 Tectonics Investigation 6: Teacher Guide Investigation 6: What happens when plates collide? In this activity, students will use the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes in a Web GIS to learn about
Tectonics Investigation 6: Teacher Guide Investigation 6: What happens when plates collide? In this activity, students will use the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes in a Web GIS to learn about
Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological Disasters in Southeast Asia with a Focus on Thailand
 Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological Disasters in Southeast Asia with a Focus on Thailand Manfred Koch Department of Geohydraulics and Engineering Hydrology University of Kassel Germany
Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological Disasters in Southeast Asia with a Focus on Thailand Manfred Koch Department of Geohydraulics and Engineering Hydrology University of Kassel Germany
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery
 Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Earthquakes Natural and Induced. Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University
 Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
DECISION PROCESS AND OPTIMIZATION RULES FOR SEISMIC RETROFIT PROGRAMS. T. Zikas 1 and F. Gehbauer 2
 International Symposium on Strong Vrancea Earthquakes and Risk Mitigation Oct. 4-6, 2007, Bucharest, Romania DECISION PROCESS AND OPTIMIZATION RULES FOR SEISMIC RETROFIT PROGRAMS T. Zikas 1 and F. Gehbauer
International Symposium on Strong Vrancea Earthquakes and Risk Mitigation Oct. 4-6, 2007, Bucharest, Romania DECISION PROCESS AND OPTIMIZATION RULES FOR SEISMIC RETROFIT PROGRAMS T. Zikas 1 and F. Gehbauer
Interactive Plate Tectonics
 Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
SOFTWARE FOR GENERATION OF SPECTRUM COMPATIBLE TIME HISTORY
 3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 296 SOFTWARE FOR GENERATION OF SPECTRUM COMPATIBLE TIME HISTORY ASHOK KUMAR SUMMARY One of the important
3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 296 SOFTWARE FOR GENERATION OF SPECTRUM COMPATIBLE TIME HISTORY ASHOK KUMAR SUMMARY One of the important
II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013)
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra
 Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: [email protected]
Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: [email protected]
CyberShake Simulations for Path Effects near SONGS
 CyberShake Simulations for Path Effects near SONGS Feng Wang, Thomas H. Jordan, Robert Graves, Scott Callaghan, Philip Maechling, and the CME Collaboration 2 SCEC s CyberShake utilizes 3D simulations and
CyberShake Simulations for Path Effects near SONGS Feng Wang, Thomas H. Jordan, Robert Graves, Scott Callaghan, Philip Maechling, and the CME Collaboration 2 SCEC s CyberShake utilizes 3D simulations and
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey
 The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
Earthquakes in Saskatchewan and
 Page 1 of 7 Earthquakes in Saskatchewan and Canada by Don Gendzwill, University of Saskatchewan Contents A) NATURAL EARTHQUAKES IN SASKATCHEWAN Biggest History Table of natural seismic events in Saskatchewan
Page 1 of 7 Earthquakes in Saskatchewan and Canada by Don Gendzwill, University of Saskatchewan Contents A) NATURAL EARTHQUAKES IN SASKATCHEWAN Biggest History Table of natural seismic events in Saskatchewan
Where in the World Are All the Earthquakes?
 Curry School of Education, University of Virginia www.teacherlink.org/content/science/ Where in the World Are All the Earthquakes? In this activity, students go to the United States Geological Survey (USGS)
Curry School of Education, University of Virginia www.teacherlink.org/content/science/ Where in the World Are All the Earthquakes? In this activity, students go to the United States Geological Survey (USGS)
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk
 Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
A Preliminary Report The May 19, 2011 Simav, Turkey Earthquake
 A Preliminary Report The May 19, 2011 Simav, Turkey Earthquake Ömer AYDAN Tokai University, Shizuoka, Japan Visiting Professor, İstanbul Technical University Halil KUMSAR Pamukkale University May 24, 2011
A Preliminary Report The May 19, 2011 Simav, Turkey Earthquake Ömer AYDAN Tokai University, Shizuoka, Japan Visiting Professor, İstanbul Technical University Halil KUMSAR Pamukkale University May 24, 2011
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk. Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey
 Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Contents. Specific and total risk. Definition of risk. How to express risk? Multi-hazard Risk Assessment. Risk types
 Contents Multi-hazard Risk Assessment Cees van Westen United Nations University ITC School for Disaster Geo- Information Management International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation
Contents Multi-hazard Risk Assessment Cees van Westen United Nations University ITC School for Disaster Geo- Information Management International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
ABSG Consulting, Tokyo, Japan Email: [email protected] 2. Professor, Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan 3
 Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
A STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF SURFACE WAVES GENERATED
 A STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF SURFACE WAVES GENERATED IN DEEP SEDIMENTARY BASINS DURING A MAJOR EARTHQUAKE K. Eto ), K. Motoki 2) and K. Seo 3) )Graduate student, Department of Built Environment, Tokyo Institute
A STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF SURFACE WAVES GENERATED IN DEEP SEDIMENTARY BASINS DURING A MAJOR EARTHQUAKE K. Eto ), K. Motoki 2) and K. Seo 3) )Graduate student, Department of Built Environment, Tokyo Institute
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Does not include complete lecture notes. Continental drift: An idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed his continental drift hypothesis in 1915 Published The Origin
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Does not include complete lecture notes. Continental drift: An idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed his continental drift hypothesis in 1915 Published The Origin
Advanced GIS for Loss Estimation and Rapid Post-Earthquake Assessment of Building Damage
 Advanced GIS for Loss Estimation and Rapid Post-Earthquake Assessment of Building Damage Thomas D. O Rourke and Sang-Soo Jeon, Cornell University and Ronald T. Eguchi and Charles K. Huyck, Image Cat, Inc.
Advanced GIS for Loss Estimation and Rapid Post-Earthquake Assessment of Building Damage Thomas D. O Rourke and Sang-Soo Jeon, Cornell University and Ronald T. Eguchi and Charles K. Huyck, Image Cat, Inc.
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67)
 4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
Plate Tectonics Web-Quest
 Plate Tectonics Web-Quest Part I: Earth s Structure. Use the following link to find these answers: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html 1. Label the layers of Earth in the diagram
Plate Tectonics Web-Quest Part I: Earth s Structure. Use the following link to find these answers: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html 1. Label the layers of Earth in the diagram
Using GIS for Assessing Earthquake Hazards of San Francisco Bay, California, USA
 Using GIS for Assessing Earthquake Hazards of San Francisco Bay, California, USA Marzieh Zeinali Department of Resource Analysis, Saint Mary s University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55404 Keywords: San
Using GIS for Assessing Earthquake Hazards of San Francisco Bay, California, USA Marzieh Zeinali Department of Resource Analysis, Saint Mary s University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55404 Keywords: San
1. You are about to begin a unit on geology. Can anyone tell me what geology is? The study of the physical earth I.
 PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
Transform Boundaries
 Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system
 Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system October 2013 Japan Meteorological Agency Lessons learned from the
Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system October 2013 Japan Meteorological Agency Lessons learned from the
The earthquake source
 Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Improved Warnings for Natural Hazards: A Prototype System for Southern California
 Improved Warnings for Natural Hazards: A Prototype System for Southern California Yehuda Bock Research Geodesist Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California San Diego, La Jolla, Calif.
Improved Warnings for Natural Hazards: A Prototype System for Southern California Yehuda Bock Research Geodesist Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California San Diego, La Jolla, Calif.
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
Chincha and Cañete, Peru, Based
 Reconstruction of Ica, Pisco, Chincha and Cañete, Peru, Based on Updated Hazard Maps Julio Kuroiwa Professor emeritus National University of Engineering and UNDP Reconstruction Program/Sustainable Cities.
Reconstruction of Ica, Pisco, Chincha and Cañete, Peru, Based on Updated Hazard Maps Julio Kuroiwa Professor emeritus National University of Engineering and UNDP Reconstruction Program/Sustainable Cities.
EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION
 Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas. Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics. The unifying concept of the Earth sciences.
 Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas Our understanding of Earth is continuously refined. Earth s systems are dynamic; they continually react to changing influences from geological, hydrological, physical, chemical,
Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas Our understanding of Earth is continuously refined. Earth s systems are dynamic; they continually react to changing influences from geological, hydrological, physical, chemical,
The correct answers are given below. Some talking points have been added for the teachers use.
 Natural Resources Canada 2011: Lesson Plan Grades 11 and 12 Landslide activity 5b: Landslides in Canada quiz Description: This is an independent study activity for grades 11 and 12. Students will read
Natural Resources Canada 2011: Lesson Plan Grades 11 and 12 Landslide activity 5b: Landslides in Canada quiz Description: This is an independent study activity for grades 11 and 12. Students will read
