Estimating Acoustic Performance of a Cell Phone Speaker Using Abaqus
|
|
|
- Osborn Derick Bridges
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Estimating Acoustic Performance of a Cell Phone Speaker Using Abaqus C. Jackman 1, M. Zampino 1 D. Cadge 2, R. Dravida 2, V. Katiyar 2, J. Lewis 2 1 Foxconn Holdings LLC 2 DS SIMULIA Abstract: Consumers demand smaller electronics devices with more features and capabilities. Making devices smaller provides challenges to engineers to maintain the acoustic performances as enclosed acoustic volume sizes are reduced. This paper discusses the requirements for coupled structural-acoustic simulation and demonstrates the application of this technology to cell-phone acoustic design. Due to the smaller volume sizes, the low frequency response of the cell phone is affected. The frequency response rolls off faster at low frequencies when smaller microphone back volumes are used. The present work deals with studying this effect on a simple cell phone model with the finite element package, Abaqus. The results from the simulation can be used in better designing cell phone cavities for optimum performance. Keywords: Diaphragm, Acoustics, Impedance Boundary, Topology, Merge/Cut, Tie, Back Volume 1. Introduction Cell phone industry has been making great advances in terms of packing more features while reducing the size of the instrument itself. As the size reduces, it presents more challenges to the overall acoustic performance of the cell phone. At low frequencies, the acoustic pressure emitted by a cell phone device is affected by the size of the back volume which in turn is affected by the size of the instrument. Hence, in order to improve the acoustic performance cell phone designers often use more than one speaker. Additionally, the size of the back volume that would give the optimum acoustic performance has to be prototyped and developed. Fortunately the availability of finite element software codes, such as Abaqus, avoids the time consuming and expensive process of building and rebuilding of back volumes to physically test the optimum performance. 1
2 Abaqus s general nonlinear mechanics capabilities have been used for twist, hyperextension and drop test simulations (Nagaraj, 2002; Thiruppukuzhi, 2008; Theman, 2005). The general mechanics capabilities clubbed with the coupled structural-acoustic capabilities make Abaqus a powerful tool to solve the most important problems related to the cell phone industry. Powerful Abaqus/CAE modeling capabilities (including easy import of geometry from third party CAD software, a wide variety of meshing tools, virtual topology etc) along with a number of structural, acoustic element types and a broad range of material models make Abaqus a versatile software for these kinds of simulations. Additional features include nonconforming tie between structural and acoustic elements, and availability of a variety of acoustic output variables. In the present work, we setup a dual-speaker model in Abaqus and compare the simulation results of the acoustic pressure at a certain distance in the exterior of the diaphragm when the speakers are excited by a mechanical force. 2. Physics of the problem The geometry of the speaker is shown in the Figure 1. The diaphragm (yellow) is excited due to the rocking motion of the voice coil. By driving a current through the voice coil, a magnetic field is produced. This magnetic field causes the voice coil to react to the magnetic field from a permanent magnet fixed to the speaker's frame (Figure 1), thereby moving the diaphragm. A detailed plot of the diaphragm is shown in Figure 2. It can be seen that the annulus region of the diaphragm has corrugations. The corrugations are employed in most of the commercialized mobile speakers to enhance the high-frequency sensitivities to the required levels. In this way, a fairly flat frequency response over a broad range can be achieved to avoid sound distortion to human ears. Accurate modeling of such a response can be achieved only through a detailed finite element simulation. Other techniques such as the lumped parameter (Beranek, 1954; Small 1972; Small 1972) approach may not yield accurate results at high frequencies. Top surface of the voice coil Magnet Diaphragm Moving voice coil Figure 1. Geometry of the speaker used in the present work. 2
3 As the size of the cell phone decreases, the volume of air behind the diaphragm becomes smaller. This small amount of volume behind the speaker limits the range of motion of the diaphragm. The speaker does not produce enough force to compress the air beyond a certain point, hence causing the air to push back. This reduces the displacement of the speaker diaphragm, which in turn lowers the output. The frequencies affected the most by this are the ones with the largest amount of displacement, (low frequencies). This effect can be modeled in Abaqus using acoustic elements, which have predefined bulk properties to capture such volumetric effects automatically. Figure 2. Diaphragm. The function of the vents (shown in Figure 3) is to ensure that the diaphragm does not undergo static deformation due to changes in the atmospheric pressure while the back volume is maintained at a constant pressure when it is sealed. The static deformation would not only cause damage to the diaphragm but also can alter its acoustic performance. One disadvantage of the vent is that it excites an undesirable resonant peak called the Helmholtz resonance (Pierce, 1989), which may occur in the audio frequency range. When the diaphragm vibrates, part of its displacement compresses air inside the back volume and the remainder moves air outward through the vents. The mass of air displaced through the vent (acoustic mass) in combination with the stiffness (air in an enclosed volume tends to get compressed due an excitation) offered due to the air in the back 3
4 volume produces the Helmholtz resonance. In order to tune this peak to acceptable levels, the speaker manufacturers apply a netted material on the vent. Vents Figure 3. Bottom view of the speaker geometry showing the vents. 3. Model Setup We have taken two approaches to run the simulations. One is to replace the convoluted membrane with a planar membrane and tune the material properties (Young s modulus and density) and thickness of the membrane materials. The method relies on experimental data for two cases; case 1, when the speaker s back volume is enclosed such that the volume of air contained in it is 2cc and case 2, when the speaker s front and back volumes are separated such that there is no acoustic interaction between them (this condition is referred to as an infinite baffle in the literature). The thickness and density of the voice coil and the diaphragm are tuned such that the simulation results match the experimental results of both cases. The results obtained by 4
5 performing simulations with the tuned parameters have to be compared with another measurement with a different back volume. This is a work in progress as we will be comparing the tuned results with a 3.5 cc back volume case. The second approach is to model the actual dual-speaker geometry in Abaqus. This methodology is advantageous because the physics of the problem is captured accurately without the need for any approximations. Also since we are using the actual geometry and the material properties, the laborious tuning methodology employed in the first approach can be completely avoided. The original CAD speaker model was imported into Abaqus/CAE. Abaqus/CAE is a CAD neutral system, and is designed to be able to import and use geometry from many third party proprietary CAD systems, as well as neutral file formats. In some cases parts or part instances contain details such as very small faces and edges. These features, although important for machining and packaging of a component, have little impact on the mechanics of the problem. Including such features in the numerical analysis may lead to very fine mesh density leading to increased computation times. The virtual topology feature in Abaqus/CAE allowed us to exclude such small details by combining the feature with an adjacent larger feature. Nodes and elements are still created to conform to the original geometry. Boolean operation in assembly module of Abaqus/CAE was utilized to cut out the speaker geometry from the acoustic domain (Further details about virtual topology and Boolean operation can be obtained from Abaqus/CAE user s manual). The cut operation leaves holes in the acoustic domain for regions which will be filled later with the speaker geometry to create the complete system. The assembly of acoustic front and back volumes is shown in Figure 4. The diaphragm occupies the region in between the front and speaker s back volumes. The other speaker components which hold the diaphragm in place were considered rigid and so were not modeled, and boundary conditions were not applied to the acoustic regions that are in contact with the surfaces of these components to enforce this rigid assumption (In Abaqus acoustic domain without any boundary condition assumes a rigid termination). Enclosure s Back volume Front volume Speaker s Back volume Vent Figure 4. Speaker diaphragm assembled with front and back volumes of the acoustic domain. The green (dark) portions represent the acoustic 5
6 domain. Grey (light) portion represents the diaphragm and the moving coil. The void region represents the rigid components of the speaker. 3.1 Elements, Boundary Conditions, Loads and Domain Size: The diaphragm is modeled with modified three-dimensional solid elements (Abaqus keyword *ELEMENT, TYPE=C3D10M) and was assigned the physical properties for the material of the diaphragm given as per the manufacturer s specifications. Modeling the diaphragm with solid elements (instead of shell elements) allowed us to cut away the acoustic domain more easily. The acoustic domain, both in the back volume and the volume exterior to the diaphragm, is modeled with three-dimensional acoustic elements (*ELEMENT, TYPE=AC3D4). These elements were assigned the physical properties of air. For problems that include unbounded acoustic domain, a boundary condition has to be applied at the exterior boundary to minimize reflections. This can be achieved by applying nonreflecting surface impedance boundary conditions (*SIMPEDANCE, TYPE=SPHERICAL) to the exterior mesh as shown in Figure 5. A pinned boundary condition was applied on the outer surface of the diaphragm (red or dark region in Figure 2) which in the actual speaker geometry was sandwiched between two bodies. The accuracy of an acoustic analysis depends on two factors: element size in the acoustic domain and the overall size of the exterior domain. It is recommended that at least six representative inter nodal intervals fit into the shortest wavelength present in the analysis. Generally, if greater accuracy is desired 8 to 10 elements per wavelength should be used. If the domain size is many wavelengths at least 15 elements per wavelength have to be used to counter numerical dispersion. The numerical dispersion is the decay in acoustic pressure as a function of distance solely due to accumulation of numerical errors from one element to the next, which is a result of having fewer elements per wavelength (Figure 5 has an illustration of finite element mesh considerations for an acoustic analysis). In the present work, eight elements per wavelength were chosen to run the analysis. It is recommended that the domain size is at least 1/3 rd of the longest wavelength (lowest frequency present in the analysis). This number, although arbitrary, ensures that the reflections from the far field are minimized when the acoustic boundary is terminated with nonreflecting impedance boundary conditions. As the frequency range of interest grows the size of the model may approach the upper limit of memory and disk space on the computer. Hence, it is advisable to split the analysis into multiple runs with smaller frequency ranges of interest. In the present analysis our frequency range of interest from 200 Hz to 5000 Hz is split into two analyses; one from 200 Hz to 1000 Hz (Low frequency analysis) and the other from 1000 Hz to 5000 Hz (High frequency analysis). 6
7 Non-reflecting boundaries Radius of domain corresponds to onethird of the longest wavelength Element size corresponds to one-eighth of the shortest wavelength Speaker geometry Figure 5. Mesh properties for the acoustic domain driven by a single speaker. To provide coupling between the structural and the acoustic domains, tie constraints (*TIE) were applied between the acoustic medium and the front/back surfaces of the speaker diaphragm. Nonconformal tie constraints are used by Abaqus to provide a structural acoustic coupling without creating Acoustic Structural Interface (ASI) elements. This makes model setup simple whilst provides the necessary coupling between the acoustic and structural domains of the problem. A direct-solution steady state dynamic analysis (*STEADY STATE DYNAMICS, DIRECT) was used to run the analysis. This procedure conducts a frequency sweep by applying the loading at a series of frequencies and extracting the magnitude and phase response of the system (Refer to Abaqus Analysis User s Manual). A load (*CLOAD) of unit magnitude (constant value at all frequencies) was applied to the top surface of the voice coil (see Figure 1) in both the low frequency and high frequency analyses. 4. Analysis Methodology The mass of the voice coil (see Figure 1) is the only unknown in the model as it depends on the length and density of the coil wire and had to be chosen, by trial and error, to ensure that the resonant frequency matches the manufacturer s specifications. Tuning the mass of the voice coil required us to run a direct-solution steady state dynamics analysis (from 200Hz to 1000Hz) on the 7
8 diaphragm, without the acoustic domain, in the presence of high enough damping in order to obtain the displacement response at the center of the diaphragm. The damping of the diaphragm (*STRUCTURAL DAMPING) was chosen such that the quality factor (Pierce, 1989; Thiel, 1972) at the resonant peak matches with the manufacturer s specification. Additional damping was added to account for the electrical effects. The effect of the magnetic field, length of copper wire used to create the electro-magnet, as well as the resistance of this copper wire, is to create a resistance in series with the structural damping resistance provided by the diaphragm (See paper by Thiel: Loudspeakers in Vented Boxes: Part-1 Figure 3), and the applied excitation load is scaled independent of frequency. This means that the effect of the electro-magnetic parts of the system is to add damping to the system (Thiel, 1972). At the end of this process, the actual displacement may not match the experimental measurements but the general shape of the curve will align. This is because of using an approximate unit load as the forcing function. The physical forcing function on the diaphragm cannot be calculated in Abaqus as it is based on electrical excitation (If the electrical circuit is simple enough to be approximated by a lumped parameter model, it may be possible to calculate the equivalent mechanical components and run the complete electro-mechanical analysis in Abaqus. The static characteristics of the electromagnetic driver and its effect on the mechanical displacement of the diaphragm can be obtained by creating a user element) and hence the loading has to be approximated. It is also assumed that the force (as a function of frequency) is independent of the size of the back volume. Since the diaphragm displacement and the subsequent acoustic response are considered to be linear phenomena, the results can be scaled after the analysis to match the measurements. The following paragraph details the scaling procedure. The analysis is performed assuming a unit load on the top surface of the voice coil (see Figure 1) and a calibration vector, which is a linear ratio of the acoustic pressure measured to the acoustic pressure from the Abaqus results as a function of frequency, is calculated. This calibration vector can be multiplied with the acoustic pressure results from subsequent analyses (with different back volumes), provided that unit excitation is applied on the diaphragm in those cases as well. 5. Acoustic pressure and displacement calculations The acoustic pressure in the exterior domain at a distance of 10 cm away is shown in Figure 6. The mechanical force applied on the diaphragm (due to the electrical excitation) was not known and so an arbitrary value of 1 unit load was chosen to run the Abaqus simulation. Hence, the results in Figure 6 do not match but the general shape of the curves is identical. The calibration vector, 8
9 shown in Figure 7, is the ratio of Abaqus response (due to unit excitation) to the measurement. Figure 6. Comparison of Abaqus response with the measurements performed by Manufacturer B. An arbitrary excitation load of one unit was chosen in the Abaqus analysis as the excitation due to electrical load was not known and hence the results do not match. 9
10 Figure 7. Calibration vector computed by taking the ratio of measured to Abaqus responses from Figure 6. 10
11 Figure 8. Comparison of results when the speaker was enclosed in a 2cc back volume. In Figure 8 the results of Abaqus analysis have been compared with simulation results from a mobile device company (labeled in Figure 8 as Company A ), a speaker manufacturer (labeled in Figure 8 as Manufacturer B ) and measurements from the latter. The Company A results have been obtained by approximating the system as lumped parameters (effectively reducing the whole system into electrical equivalents). It can be seen that the low frequency analysis results of Abaqus simulation matches well with the other simulation results and reasonably well with the measurements. The Helmholtz resonance peak at 1500 Hz, in Abaqus and Company A simulations, is due to the interaction of vent holes (acoustic mass) with the 2cc back volume (acoustic compliance). The reason for suppression of the peak in Manufacturer B results is unknown at this time; we are in the process of obtaining this information. 11
12 6. Conclusions The present work shows that acoustic analysis in Abaqus can capture a) Helmholtz resonance and b) the reduction in acoustic pressure at low frequencies due to the presence of back volume. These effects play an important role in choosing the appropriate back-volume size during a cell phone design and in choosing the appropriate vent size during the speaker design. The results of Abaqus simulations have been compared to those from a mobile device company and a speaker manufacturer. The results below 1000 Hz agree very well between the three simulations and the measurement. The Helmholtz resonance peak that exists in Abaqus, Company A results is not seen in Manufacturer B results and the subsequent higher frequencies are also affected by the resonant peak. The reason for this discrepancy is being investigated. 7. Future work Several improvements can be made to the modeling strategy to reduce the analysis time. 1. Infinite elements can be employed instead of the nonreflecting impedance boundary conditions. The domain size required for infinite elements to work effectively is much smaller than the size required for nonreflecting boundaries. The infinite element formulation has a ninth-order truncation of the reflections, where as the nonreflecting boundaries have a zero-order approximation. 2. Use mode-based steady state dynamics (*STEADY STATE DYNAMICS, SUBSPACE) instead of the direct solution (*STEADY STATE DYNAMICS, DIRECT). 3. Model the diaphragm with shell elements instead of solid elements. This will reduce additional computation time associated with solving equations of the solid elements. 8. References 1. Beranek, L. L., Noise and vibration control, McGraw-Hill, New York, Nagaraj, B., Motorola, "Two Step Method of Analyzing Hyperextension Problems with Large Contact Interactions Using Abaqus/Explicit," Abaqus Users' Conference, pp. 1 7, Newport, Rhode Island, May Pierce, A. D., Acoustics: An Introduction to Physical Principles and Applications, Acoustical Society of America, pp. 121, 330,
13 4. Small, R. H, Direct-Radiator Loudspeaker System Analysis, Journal of Audio Engineering Society, Vol. 20, Num. 5, pp , June Small, R. H., Closed-box loudspeaker systems-part 1: analysis J Audio Eng Soc, Vol. 20, Num. 10, pp , Theman, M., and Poskiparta, P., Nokia, "Evolution of Mobile Phone Drop Test Simulation at Nokia," Abaqus Users' Conference, pp. 1 1, Stockholm, Sweden, May Thiel, A. N, Loudspeakers in Vented Boxes: Part I, Journal of Audio Engineering Society, Vol. 19, Num. 5, pp , May Thiel, A. N, Loudspeakers in Vented Boxes: Part II, Journal of Audio Engineering Society, Vol. 19, Num. 6, pp , June Thiruppukuzhi, S., Motorola," Probabilistic Simulation Applications in Product Design," Abaqus Users' Conference, pp , Newport, Rhode Island, May
Loudspeaker Parameters. D. G. Meyer School of Electrical & Computer Engineering
 Loudspeaker Parameters D. G. Meyer School of Electrical & Computer Engineering Outline Review of How Loudspeakers Work Small Signal Loudspeaker Parameters Effect of Loudspeaker Cable Sample Loudspeaker
Loudspeaker Parameters D. G. Meyer School of Electrical & Computer Engineering Outline Review of How Loudspeakers Work Small Signal Loudspeaker Parameters Effect of Loudspeaker Cable Sample Loudspeaker
Dispersion diagrams of a water-loaded cylindrical shell obtained from the structural and acoustic responses of the sensor array along the shell
 Dispersion diagrams of a water-loaded cylindrical shell obtained from the structural and acoustic responses of the sensor array along the shell B.K. Jung ; J. Ryue ; C.S. Hong 3 ; W.B. Jeong ; K.K. Shin
Dispersion diagrams of a water-loaded cylindrical shell obtained from the structural and acoustic responses of the sensor array along the shell B.K. Jung ; J. Ryue ; C.S. Hong 3 ; W.B. Jeong ; K.K. Shin
Abaqus Technology Brief. Automobile Roof Crush Analysis with Abaqus
 Abaqus Technology Brief Automobile Roof Crush Analysis with Abaqus TB-06-RCA-1 Revised: April 2007. Summary The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) mandates the use of certain test procedures
Abaqus Technology Brief Automobile Roof Crush Analysis with Abaqus TB-06-RCA-1 Revised: April 2007. Summary The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) mandates the use of certain test procedures
Section 5.0 : Horn Physics. By Martin J. King, 6/29/08 Copyright 2008 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved.
 Section 5. : Horn Physics Section 5. : Horn Physics By Martin J. King, 6/29/8 Copyright 28 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved. Before discussing the design of a horn loaded loudspeaker system, it is
Section 5. : Horn Physics Section 5. : Horn Physics By Martin J. King, 6/29/8 Copyright 28 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved. Before discussing the design of a horn loaded loudspeaker system, it is
AIR RESONANCE IN A PLASTIC BOTTLE Darrell Megli, Emeritus Professor of Physics, University of Evansville, Evansville, IN dm37@evansville.
 AIR RESONANCE IN A PLASTIC BOTTLE Darrell Megli, Emeritus Professor of Physics, University of Evansville, Evansville, IN [email protected] It is well known that if one blows across the neck of an empty
AIR RESONANCE IN A PLASTIC BOTTLE Darrell Megli, Emeritus Professor of Physics, University of Evansville, Evansville, IN [email protected] It is well known that if one blows across the neck of an empty
Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment
 Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
SIESMIC SLOSHING IN CYLINDRICAL TANKS WITH FLEXIBLE BAFFLES
 SIESMIC SLOSHING IN CYLINDRICAL TANKS WITH FLEXIBLE BAFFLES Kayahan AKGUL 1, Yasin M. FAHJAN 2, Zuhal OZDEMIR 3 and Mhamed SOULI 4 ABSTRACT Sloshing has been one of the major concerns for engineers in
SIESMIC SLOSHING IN CYLINDRICAL TANKS WITH FLEXIBLE BAFFLES Kayahan AKGUL 1, Yasin M. FAHJAN 2, Zuhal OZDEMIR 3 and Mhamed SOULI 4 ABSTRACT Sloshing has been one of the major concerns for engineers in
Solved with COMSOL Multiphysics 4.3
 Vibrating String Introduction In the following example you compute the natural frequencies of a pre-tensioned string using the 2D Truss interface. This is an example of stress stiffening ; in fact the
Vibrating String Introduction In the following example you compute the natural frequencies of a pre-tensioned string using the 2D Truss interface. This is an example of stress stiffening ; in fact the
Shell Elements in ABAQUS/Explicit
 ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics Appendix 2 Shell Elements in ABAQUS/Explicit ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics A2.2 Overview ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics A2.4 Triangular
ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics Appendix 2 Shell Elements in ABAQUS/Explicit ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics A2.2 Overview ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics ABAQUS/Explicit: Advanced Topics A2.4 Triangular
Linear Parameter Measurement (LPM)
 (LPM) Module of the R&D SYSTEM FEATURES Identifies linear transducer model Measures suspension creep LS-fitting in impedance LS-fitting in displacement (optional) Single-step measurement with laser sensor
(LPM) Module of the R&D SYSTEM FEATURES Identifies linear transducer model Measures suspension creep LS-fitting in impedance LS-fitting in displacement (optional) Single-step measurement with laser sensor
Section 6.0 : Design of a Front Loaded Exponential Horn By Martin J. King, 7/01/08 Copyright 2008 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved.
 Section 6.0 : Design of a Front Loaded Exponential Horn For a couple of years, a front loaded horn MathCad worksheet was available for downloading from my website. The worksheet was derived to simulate
Section 6.0 : Design of a Front Loaded Exponential Horn For a couple of years, a front loaded horn MathCad worksheet was available for downloading from my website. The worksheet was derived to simulate
Section 2.0 : Construction and Measurement of a Simple Test Transmission Line
 Section 2.0 : Construction and Measurement of a Simple Test Transmission Line After deciding to use a Focal 8V 4412 mid-bass driver for my first transmission line design, I started looking for a simple
Section 2.0 : Construction and Measurement of a Simple Test Transmission Line After deciding to use a Focal 8V 4412 mid-bass driver for my first transmission line design, I started looking for a simple
Finite Element Analysis for Acoustic Behavior of a Refrigeration Compressor
 Finite Element Analysis for Acoustic Behavior of a Refrigeration Compressor Swapan Kumar Nandi Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR, Chennai 600086, India Abstract When structures in contact with a fluid
Finite Element Analysis for Acoustic Behavior of a Refrigeration Compressor Swapan Kumar Nandi Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR, Chennai 600086, India Abstract When structures in contact with a fluid
Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance
 Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance CHRISTER HEED SD2165 Stockholm October 2008 Marcus Wallenberg Laboratoriet för Ljud- och Vibrationsforskning Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance
Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance CHRISTER HEED SD2165 Stockholm October 2008 Marcus Wallenberg Laboratoriet för Ljud- och Vibrationsforskning Sound absorption and acoustic surface impedance
Design Optimization of Printed Circuit Board Embedded Inductors through Genetic Algorithms with Verification by COMSOL
 Design Optimization of Printed Circuit Board Embedded Inductors through Genetic Algorithms with Verification by COMSOL Mickey P. Madsen *, Jakob D. Mønster, Arnold Knott and Michael A.E. Andersen Technical
Design Optimization of Printed Circuit Board Embedded Inductors through Genetic Algorithms with Verification by COMSOL Mickey P. Madsen *, Jakob D. Mønster, Arnold Knott and Michael A.E. Andersen Technical
A wave lab inside a coaxial cable
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 581 591 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)76273-X A wave lab inside a coaxial cable JoãoMSerra,MiguelCBrito,JMaiaAlves and A M Vallera
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 581 591 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)76273-X A wave lab inside a coaxial cable JoãoMSerra,MiguelCBrito,JMaiaAlves and A M Vallera
Section 1.0 : Introduction. By Martin J. King, 07/05/02 Copyright 2002 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved.
 Section 1.0 : Introduction Over the years, many articles have appeared in Speaker Builder (now audioxpress) presenting test data and theories related to transmission line loudspeaker behavior. In the issues
Section 1.0 : Introduction Over the years, many articles have appeared in Speaker Builder (now audioxpress) presenting test data and theories related to transmission line loudspeaker behavior. In the issues
ACCELERATING COMMERCIAL LINEAR DYNAMIC AND NONLINEAR IMPLICIT FEA SOFTWARE THROUGH HIGH- PERFORMANCE COMPUTING
 ACCELERATING COMMERCIAL LINEAR DYNAMIC AND Vladimir Belsky Director of Solver Development* Luis Crivelli Director of Solver Development* Matt Dunbar Chief Architect* Mikhail Belyi Development Group Manager*
ACCELERATING COMMERCIAL LINEAR DYNAMIC AND Vladimir Belsky Director of Solver Development* Luis Crivelli Director of Solver Development* Matt Dunbar Chief Architect* Mikhail Belyi Development Group Manager*
Edmund Li. Where is defined as the mutual inductance between and and has the SI units of Henries (H).
 INDUCTANCE MUTUAL INDUCTANCE If we consider two neighbouring closed loops and with bounding surfaces respectively then a current through will create a magnetic field which will link with as the flux passes
INDUCTANCE MUTUAL INDUCTANCE If we consider two neighbouring closed loops and with bounding surfaces respectively then a current through will create a magnetic field which will link with as the flux passes
An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis
 CHAPTER 1 An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis 1.1 Introduction Finite element analysis (FEA) involves solution of engineering problems using computers. Engineering structures that have complex geometry
CHAPTER 1 An Overview of the Finite Element Analysis 1.1 Introduction Finite element analysis (FEA) involves solution of engineering problems using computers. Engineering structures that have complex geometry
MASTER DEGREE PROJECT
 MASTER DEGREE PROJECT Finite Element Analysis of a Washing Machine Cylinder Thesis in Applied Mechanics one year Master Degree Program Performed : Spring term, 2010 Level Author Supervisor s Examiner :
MASTER DEGREE PROJECT Finite Element Analysis of a Washing Machine Cylinder Thesis in Applied Mechanics one year Master Degree Program Performed : Spring term, 2010 Level Author Supervisor s Examiner :
Comparison of the Bass Performance of Passive Open Baffle, U Frame, and H Frame Speakers
 Comparison of the Bass Performance of Passive Open Baffle, U Frame, and H Frame Speakers Martin J. King 40 Dorsman Dr. Clifton Park, NY 12065 [email protected] Introduction : My first article on OB design,
Comparison of the Bass Performance of Passive Open Baffle, U Frame, and H Frame Speakers Martin J. King 40 Dorsman Dr. Clifton Park, NY 12065 [email protected] Introduction : My first article on OB design,
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the SolidWorks Simulation finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the SolidWorks Simulation finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response
Motor-CAD Software for Thermal Analysis of Electrical Motors - Links to Electromagnetic and Drive Simulation Models
 Motor-CAD Software for Thermal Analysis of Electrical Motors - Links to Electromagnetic and Drive Simulation Models Dave Staton, Douglas Hawkins and Mircea Popescu Motor Design Ltd., Ellesmere, Shropshire,
Motor-CAD Software for Thermal Analysis of Electrical Motors - Links to Electromagnetic and Drive Simulation Models Dave Staton, Douglas Hawkins and Mircea Popescu Motor Design Ltd., Ellesmere, Shropshire,
Safakcan Tuncdemir 1, William M. Bradley *2. 1. Introduction
 Modeling and Experimental Verification of the Power Transfer and Thermal Characteristics of Piezoelectric Transformers Subjected to Combined Mechanical and Electrical Loading Safakcan Tuncdemir 1, William
Modeling and Experimental Verification of the Power Transfer and Thermal Characteristics of Piezoelectric Transformers Subjected to Combined Mechanical and Electrical Loading Safakcan Tuncdemir 1, William
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope
 Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
A novel sharp beam-forming flat panel loudspeaker using digitally driven speaker system
 Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper Presented at the 131st Convention 2011 October 20 23 New York, NY, USA This Convention paper was selected based on a submitted abstract and 750-word precis that
Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper Presented at the 131st Convention 2011 October 20 23 New York, NY, USA This Convention paper was selected based on a submitted abstract and 750-word precis that
Transmission Line and Back Loaded Horn Physics
 Introduction By Martin J. King, 3/29/3 Copyright 23 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved. In order to differentiate between a transmission line and a back loaded horn, it is really important to understand
Introduction By Martin J. King, 3/29/3 Copyright 23 by Martin J. King. All Rights Reserved. In order to differentiate between a transmission line and a back loaded horn, it is really important to understand
Mozart Grand. The elaborate spiked feet assemblies improve both the performance and appearance of this speaker worthy of its namesake.
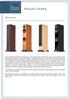 General The immediate appeal of the elegantly moving melodic lines of Mozart s music is grounded on subtly sophisticated musical structures. Similarly, while the elegant lines of the Mozart Grand cabinets
General The immediate appeal of the elegantly moving melodic lines of Mozart s music is grounded on subtly sophisticated musical structures. Similarly, while the elegant lines of the Mozart Grand cabinets
Mesh Moving Techniques for Fluid-Structure Interactions With Large Displacements
 K. Stein Department of Physics, Bethel College, St. Paul, MN 55112 T. Tezduyar Mechanical Engineering, Rice University, MS 321, Houston, TX 77005 R. Benney Natick Soldier Center, Natick, MA 01760 Mesh
K. Stein Department of Physics, Bethel College, St. Paul, MN 55112 T. Tezduyar Mechanical Engineering, Rice University, MS 321, Houston, TX 77005 R. Benney Natick Soldier Center, Natick, MA 01760 Mesh
International Journal of Engineering Research-Online A Peer Reviewed International Journal Articles available online http://www.ijoer.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2321-7758 DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF A DYNAMOMETER FOR MEASURING THRUST AND TORQUE IN DRILLING APPLICATION SREEJITH C 1,MANU RAJ K R 2 1 PG Scholar, M.Tech Machine Design, Nehru College
RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2321-7758 DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF A DYNAMOMETER FOR MEASURING THRUST AND TORQUE IN DRILLING APPLICATION SREEJITH C 1,MANU RAJ K R 2 1 PG Scholar, M.Tech Machine Design, Nehru College
3-D WAVEGUIDE MODELING AND SIMULATION USING SBFEM
 3-D WAVEGUIDE MODELING AND SIMULATION USING SBFEM Fabian Krome, Hauke Gravenkamp BAM Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing, Unter den Eichen 87, 12205 Berlin, Germany email: [email protected]
3-D WAVEGUIDE MODELING AND SIMULATION USING SBFEM Fabian Krome, Hauke Gravenkamp BAM Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing, Unter den Eichen 87, 12205 Berlin, Germany email: [email protected]
ABAQUS Tutorial. 3D Modeling
 Spring 2011 01/21/11 ABAQUS Tutorial 3D Modeling This exercise intends to demonstrate the steps you would follow in creating and analyzing a simple solid model using ABAQUS CAE. Introduction A solid undergoes
Spring 2011 01/21/11 ABAQUS Tutorial 3D Modeling This exercise intends to demonstrate the steps you would follow in creating and analyzing a simple solid model using ABAQUS CAE. Introduction A solid undergoes
Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31)
 Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31) Outline -1-! This part of the module consists of seven lectures and will focus
Plates and Shells: Theory and Computation - 4D9 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Office: Inglis building mezzanine level (INO 31) Outline -1-! This part of the module consists of seven lectures and will focus
The simulation of machine tools can be divided into two stages. In the first stage the mechanical behavior of a machine tool is simulated with FEM
 1 The simulation of machine tools can be divided into two stages. In the first stage the mechanical behavior of a machine tool is simulated with FEM tools. The approach to this simulation is different
1 The simulation of machine tools can be divided into two stages. In the first stage the mechanical behavior of a machine tool is simulated with FEM tools. The approach to this simulation is different
Figure 1 : Typical Computer Simulation of a Bass Reflex Speaker
 Introduction : Over the past few years, I have become very aware of the baffle step response phenomenon associated with drivers mounted in rectangular shaped baffles. My first quarter wavelength designs
Introduction : Over the past few years, I have become very aware of the baffle step response phenomenon associated with drivers mounted in rectangular shaped baffles. My first quarter wavelength designs
Voice Coil Impedance as a Function of Frequency and Displacement
 Voice Coil Impedance as a Function of Frequency and Displacement Mark Dodd 1, Wolfgang Klippel, and Jack Oclee-Brown. 3 1 KEF Audio UK (Ltd),Maidstone,Kent,ME15 6QP United Kingdom. [email protected] Klippel
Voice Coil Impedance as a Function of Frequency and Displacement Mark Dodd 1, Wolfgang Klippel, and Jack Oclee-Brown. 3 1 KEF Audio UK (Ltd),Maidstone,Kent,ME15 6QP United Kingdom. [email protected] Klippel
AN4427 Application note
 Application note Gasket design for optimal acoustic performance in MEMS microphones Introduction This application note serves as a reference for the design of gaskets in MEMS microphones, providing recommendations
Application note Gasket design for optimal acoustic performance in MEMS microphones Introduction This application note serves as a reference for the design of gaskets in MEMS microphones, providing recommendations
Physics 9e/Cutnell. correlated to the. College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives
 Physics 9e/Cutnell correlated to the College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring
Physics 9e/Cutnell correlated to the College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring
Calculation of Eigenfields for the European XFEL Cavities
 Calculation of Eigenfields for the European XFEL Cavities Wolfgang Ackermann, Erion Gjonaj, Wolfgang F. O. Müller, Thomas Weiland Institut Theorie Elektromagnetischer Felder, TU Darmstadt Status Meeting
Calculation of Eigenfields for the European XFEL Cavities Wolfgang Ackermann, Erion Gjonaj, Wolfgang F. O. Müller, Thomas Weiland Institut Theorie Elektromagnetischer Felder, TU Darmstadt Status Meeting
Physics in Entertainment and the Arts
 Physics in Entertainment and the Arts Chapter VII Wave Transfer and Waves incident on a rigid boundary almost completely reflect Almost all the wave s energy is reflected back the way it came Waves incident
Physics in Entertainment and the Arts Chapter VII Wave Transfer and Waves incident on a rigid boundary almost completely reflect Almost all the wave s energy is reflected back the way it came Waves incident
CHAPTER 3 MODAL ANALYSIS OF A PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD
 45 CHAPTER 3 MODAL ANALYSIS OF A PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the methodology for performing the modal analysis of a printed circuit board used in a hand held electronic
45 CHAPTER 3 MODAL ANALYSIS OF A PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the methodology for performing the modal analysis of a printed circuit board used in a hand held electronic
Doppler Effect Plug-in in Music Production and Engineering
 , pp.287-292 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2014.9.8.26 Doppler Effect Plug-in in Music Production and Engineering Yoemun Yun Department of Applied Music, Chungwoon University San 29, Namjang-ri, Hongseong,
, pp.287-292 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2014.9.8.26 Doppler Effect Plug-in in Music Production and Engineering Yoemun Yun Department of Applied Music, Chungwoon University San 29, Namjang-ri, Hongseong,
Frequecy Comparison and Optimization of Forged Steel and Ductile Cast Iron Crankshafts
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 11ǁ November2013 ǁ PP.38-45 Frequecy Comparison and Optimization of Forged Steel
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 11ǁ November2013 ǁ PP.38-45 Frequecy Comparison and Optimization of Forged Steel
Bending, Forming and Flexing Printed Circuits
 Bending, Forming and Flexing Printed Circuits John Coonrod Rogers Corporation Introduction: In the printed circuit board industry there are generally two main types of circuit boards; there are rigid printed
Bending, Forming and Flexing Printed Circuits John Coonrod Rogers Corporation Introduction: In the printed circuit board industry there are generally two main types of circuit boards; there are rigid printed
Strip Flatness Prediction in a 4 High Tandem Mill Using a Dynamic Model.
 Strip Flatness Prediction in a 4 High Tandem Mill Using a Dynamic Model. M. A. Bello-Gomez 1, M. P. Guerrero-Mata 1, L. A. Leduc Lezama 1, T. P. Berber- Solano 1, L. Nieves 2, F. Gonzalez 2, H. R. Siller
Strip Flatness Prediction in a 4 High Tandem Mill Using a Dynamic Model. M. A. Bello-Gomez 1, M. P. Guerrero-Mata 1, L. A. Leduc Lezama 1, T. P. Berber- Solano 1, L. Nieves 2, F. Gonzalez 2, H. R. Siller
STUDY OF DAM-RESERVOIR DYNAMIC INTERACTION USING VIBRATION TESTS ON A PHYSICAL MODEL
 STUDY OF DAM-RESERVOIR DYNAMIC INTERACTION USING VIBRATION TESTS ON A PHYSICAL MODEL Paulo Mendes, Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Portugal Sérgio Oliveira, Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia
STUDY OF DAM-RESERVOIR DYNAMIC INTERACTION USING VIBRATION TESTS ON A PHYSICAL MODEL Paulo Mendes, Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Portugal Sérgio Oliveira, Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia
Measurement of Soil Parameters by Using Penetrometer Needle Apparatus
 Vol.3, Issue.1, Jan-Feb. 2013 pp-284-290 ISSN: 2249-6645 Measurement of Soil Parameters by Using Penetrometer Needle Apparatus Mahmoud M. Abu zeid, 1 Amr M. Radwan, 2 Emad A. Osman, 3 Ahmed M.Abu-bakr,
Vol.3, Issue.1, Jan-Feb. 2013 pp-284-290 ISSN: 2249-6645 Measurement of Soil Parameters by Using Penetrometer Needle Apparatus Mahmoud M. Abu zeid, 1 Amr M. Radwan, 2 Emad A. Osman, 3 Ahmed M.Abu-bakr,
Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra
 Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra Erke Wang, Thomas Nelson, Rainer Rauch CAD-FEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract This paper presents some analytical results and some test results for different
Back to Elements - Tetrahedra vs. Hexahedra Erke Wang, Thomas Nelson, Rainer Rauch CAD-FEM GmbH, Munich, Germany Abstract This paper presents some analytical results and some test results for different
CRASH ANALYSIS OF AN IMPACT ATTENUATOR FOR RACING CAR IN SANDWICH MATERIAL
 F2008-SC-016 CRASH ANALYSIS OF AN IMPACT ATTENUATOR FOR RACING CAR IN SANDWICH MATERIAL Boria, Simonetta *, Forasassi, Giuseppe Department of Mechanical, Nuclear and Production Engineering, University
F2008-SC-016 CRASH ANALYSIS OF AN IMPACT ATTENUATOR FOR RACING CAR IN SANDWICH MATERIAL Boria, Simonetta *, Forasassi, Giuseppe Department of Mechanical, Nuclear and Production Engineering, University
 1 2 3 4 5 6 HIGHLIGHTS Woofer & midrange: Generously vented die-cast aluminium basket to prevent turbulence and compression effects Distortion-optimised magnet system with double induction rings and stray
1 2 3 4 5 6 HIGHLIGHTS Woofer & midrange: Generously vented die-cast aluminium basket to prevent turbulence and compression effects Distortion-optimised magnet system with double induction rings and stray
Fatigue Analysis and Optimization of Flexible Printed Circuits
 Fatigue Analysis and Optimization of Flexible Printed Circuits Alexander Ptchelintsev Nokia Research Center P.O. Box 407, FI-00045 NOKIA GROUP, Finland Email: [email protected] Abstract:
Fatigue Analysis and Optimization of Flexible Printed Circuits Alexander Ptchelintsev Nokia Research Center P.O. Box 407, FI-00045 NOKIA GROUP, Finland Email: [email protected] Abstract:
Manual Analysis Software AFD 1201
 AFD 1200 - AcoustiTube Manual Analysis Software AFD 1201 Measurement of Transmission loss acc. to Song and Bolton 1 Table of Contents Introduction - Analysis Software AFD 1201... 3 AFD 1200 - AcoustiTube
AFD 1200 - AcoustiTube Manual Analysis Software AFD 1201 Measurement of Transmission loss acc. to Song and Bolton 1 Table of Contents Introduction - Analysis Software AFD 1201... 3 AFD 1200 - AcoustiTube
www.integratedsoft.com Electromagnetic Sensor Design: Key Considerations when selecting CAE Software
 www.integratedsoft.com Electromagnetic Sensor Design: Key Considerations when selecting CAE Software Content Executive Summary... 3 Characteristics of Electromagnetic Sensor Systems... 3 Basic Selection
www.integratedsoft.com Electromagnetic Sensor Design: Key Considerations when selecting CAE Software Content Executive Summary... 3 Characteristics of Electromagnetic Sensor Systems... 3 Basic Selection
Heat Transfer and Thermal-Stress Analysis with Abaqus
 Heat Transfer and Thermal-Stress Analysis with Abaqus 2016 About this Course Course objectives Upon completion of this course you will be able to: Perform steady-state and transient heat transfer simulations
Heat Transfer and Thermal-Stress Analysis with Abaqus 2016 About this Course Course objectives Upon completion of this course you will be able to: Perform steady-state and transient heat transfer simulations
How SolidWorks Speeds Consumer Product Design
 white paper How SolidWorks Speeds Consumer Product Design inspiration SUMMARY SolidWorks Premium bridges the gap between industrial design and engineering by providing powerful surfacing capabilities,
white paper How SolidWorks Speeds Consumer Product Design inspiration SUMMARY SolidWorks Premium bridges the gap between industrial design and engineering by providing powerful surfacing capabilities,
Overview. also give you an idea of ANSYS capabilities. In this chapter, we will define Finite Element Analysis and. Topics covered: B.
 2. FEA and ANSYS FEA and ANSYS Overview In this chapter, we will define Finite Element Analysis and also give you an idea of ANSYS capabilities. Topics covered: A. What is FEA? B. About ANSYS FEA and ANSYS
2. FEA and ANSYS FEA and ANSYS Overview In this chapter, we will define Finite Element Analysis and also give you an idea of ANSYS capabilities. Topics covered: A. What is FEA? B. About ANSYS FEA and ANSYS
Linear Dynamics with Abaqus
 Linear Dynamics with Abaqus 2016 About this Course Course objectives Upon completion of this course you will be able to: Extract eigenmodes about a certain frequency Determine whether the number of extracted
Linear Dynamics with Abaqus 2016 About this Course Course objectives Upon completion of this course you will be able to: Extract eigenmodes about a certain frequency Determine whether the number of extracted
8.2 Elastic Strain Energy
 Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
Section 8. 8. Elastic Strain Energy The strain energy stored in an elastic material upon deformation is calculated below for a number of different geometries and loading conditions. These expressions for
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking
 The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
 41 CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Simulation is a powerful tool that engineers use to predict the result of a phenomenon or to simulate the working situation in which a part or machine will perform in
41 CHAPTER 4 4 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Simulation is a powerful tool that engineers use to predict the result of a phenomenon or to simulate the working situation in which a part or machine will perform in
Customer Training Material. Lecture 4. Meshing in Mechanical. Mechanical. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Lecture 4 Meshing in Mechanical Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical L4-1 Chapter Overview In this chapter controlling meshing operations is described. Topics: A. Global Meshing Controls B. Local Meshing Controls
Lecture 4 Meshing in Mechanical Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical L4-1 Chapter Overview In this chapter controlling meshing operations is described. Topics: A. Global Meshing Controls B. Local Meshing Controls
Copyright 2000 IEEE. Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000
 Copyright 2000 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
Copyright 2000 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF THICK PLATES SUBJECTED TO EARTQUAKE
 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF THICK PLATES SUBJECTED TO EARTQUAKE ÖZDEMİR Y. I, AYVAZ Y. Posta Adresi: Department of Civil Engineering, Karadeniz Technical University, 68 Trabzon, TURKEY E-posta: [email protected]
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF THICK PLATES SUBJECTED TO EARTQUAKE ÖZDEMİR Y. I, AYVAZ Y. Posta Adresi: Department of Civil Engineering, Karadeniz Technical University, 68 Trabzon, TURKEY E-posta: [email protected]
Active noise control in practice: transformer station
 Active noise control in practice: transformer station Edwin Buikema 1 ; Fokke D. van der Ploeg 2 ; Jan H. Granneman 3 1, 2, 3 Peutz bv, Netherlands ABSTRACT Based on literature and extensive measurements
Active noise control in practice: transformer station Edwin Buikema 1 ; Fokke D. van der Ploeg 2 ; Jan H. Granneman 3 1, 2, 3 Peutz bv, Netherlands ABSTRACT Based on literature and extensive measurements
Modeling Stents Using Abaqus
 Day 1 Lecture 1 Introduction Lecture 2 Geometry and Meshing Lecture 3 Element Selection and Mesh Convergence Workshop 1a Balloon-expanded stent geometry and meshing Workshop 1b Self-expanding stent geometry
Day 1 Lecture 1 Introduction Lecture 2 Geometry and Meshing Lecture 3 Element Selection and Mesh Convergence Workshop 1a Balloon-expanded stent geometry and meshing Workshop 1b Self-expanding stent geometry
Design and Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motors
 Design and Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motors İbrahim ŞENGÖR, Abdullah POLAT, and Lale T. ERGENE Electrical and Electronic Faculty, İstanbul Technical University, 34469, Istanbul, TURKEY [email protected],
Design and Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motors İbrahim ŞENGÖR, Abdullah POLAT, and Lale T. ERGENE Electrical and Electronic Faculty, İstanbul Technical University, 34469, Istanbul, TURKEY [email protected],
Sound Power Measurement
 Sound Power Measurement A sound source will radiate different sound powers in different environments, especially at low frequencies when the wavelength is comparable to the size of the room 1. Fortunately
Sound Power Measurement A sound source will radiate different sound powers in different environments, especially at low frequencies when the wavelength is comparable to the size of the room 1. Fortunately
Finite Element Formulation for Plates - Handout 3 -
 Finite Element Formulation for Plates - Handout 3 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Completed Version Definitions A plate is a three dimensional solid body with one of the plate dimensions much smaller than the
Finite Element Formulation for Plates - Handout 3 - Dr Fehmi Cirak (fc286@) Completed Version Definitions A plate is a three dimensional solid body with one of the plate dimensions much smaller than the
The Acoustical design of Mobile phones
 Proceedings of 20 th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia The Acoustical design of Mobile phones Yasuharu Onishi (1), Jun Kuroda (1), Yukio Murata (1), Motoyoshi
Proceedings of 20 th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia The Acoustical design of Mobile phones Yasuharu Onishi (1), Jun Kuroda (1), Yukio Murata (1), Motoyoshi
Analysis of Mobile Phone Reliability Based on Active Disassembly Using Smart Materials *
 Journal of Surface Engineered Materials and Advanced Technology, 2011, 1, 80-87 doi:10.4236/jsemat.2011.12012 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsemat) Analysis of Mobile Phone Reliability
Journal of Surface Engineered Materials and Advanced Technology, 2011, 1, 80-87 doi:10.4236/jsemat.2011.12012 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jsemat) Analysis of Mobile Phone Reliability
CONCEPT-II. Overview of demo examples
 CONCEPT-II CONCEPT-II is a frequency domain method of moment (MoM) code, under development at the Institute of Electromagnetic Theory at the Technische Universität Hamburg-Harburg (www.tet.tuhh.de). Overview
CONCEPT-II CONCEPT-II is a frequency domain method of moment (MoM) code, under development at the Institute of Electromagnetic Theory at the Technische Universität Hamburg-Harburg (www.tet.tuhh.de). Overview
Underwater Tablet Enclosure Final Report by Miguel de Villa
 Underwater Tablet Enclosure Final Report by Miguel de Villa Abstract: The underwater tablet enclosure is a device used to maximize the protection and survivability of a tablet underwater without losing
Underwater Tablet Enclosure Final Report by Miguel de Villa Abstract: The underwater tablet enclosure is a device used to maximize the protection and survivability of a tablet underwater without losing
Drum-Set Tuning Guide
 Drum-Set Tuning Guide Tune-Bot enables you to accurately tune your drums to a specific notes or frequencies and once you know the notes or frequencies you want, you can quickly tune and retune your drums.
Drum-Set Tuning Guide Tune-Bot enables you to accurately tune your drums to a specific notes or frequencies and once you know the notes or frequencies you want, you can quickly tune and retune your drums.
Tower Cross Arm Numerical Analysis
 Chapter 7 Tower Cross Arm Numerical Analysis In this section the structural analysis of the test tower cross arm is done in Prokon and compared to a full finite element analysis using Ansys. This is done
Chapter 7 Tower Cross Arm Numerical Analysis In this section the structural analysis of the test tower cross arm is done in Prokon and compared to a full finite element analysis using Ansys. This is done
An octave bandwidth dipole antenna
 An octave bandwidth dipole antenna Abstract: Achieving wideband performance from resonant structures is challenging because their radiation properties and impedance characteristics are usually sensitive
An octave bandwidth dipole antenna Abstract: Achieving wideband performance from resonant structures is challenging because their radiation properties and impedance characteristics are usually sensitive
BSEE Degree Plan Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering: 2015-16
 BSEE Degree Plan Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering: 2015-16 Freshman Year ENG 1003 Composition I 3 ENG 1013 Composition II 3 ENGR 1402 Concepts of Engineering 2 PHYS 2034 University Physics
BSEE Degree Plan Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering: 2015-16 Freshman Year ENG 1003 Composition I 3 ENG 1013 Composition II 3 ENGR 1402 Concepts of Engineering 2 PHYS 2034 University Physics
Chen. Vibration Motor. Application note
 Vibration Motor Application note Yangyi Chen April 4 th, 2013 1 Table of Contents Pages Executive Summary ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 1. Table
Vibration Motor Application note Yangyi Chen April 4 th, 2013 1 Table of Contents Pages Executive Summary ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 1. Table
CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION KARISMA BENCHMARK
 CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION KARISMA BENCHMARK Presented by F. Wang (CEA, France), CLUB CAST3M 2013 28/11/2013 5 DÉCEMBRE 2013 CEA 10 AVRIL 2012 PAGE 1 CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SSI
CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SOIL-STRUCTURE INTERACTION KARISMA BENCHMARK Presented by F. Wang (CEA, France), CLUB CAST3M 2013 28/11/2013 5 DÉCEMBRE 2013 CEA 10 AVRIL 2012 PAGE 1 CONTRIBUTION TO THE IAEA SSI
Loudspeaker Project Example n 1 A Simple Compact Subwoofer Concept for M-Force
 Loudspeaker Project Example n 1 A Simple Compact Subwoofer Concept for M-Force 2015 Powersoft powersoft_mforce_kit_en_v1.1 Keep This Manual For Future Reference 2 Page intentionally left blank M-Force
Loudspeaker Project Example n 1 A Simple Compact Subwoofer Concept for M-Force 2015 Powersoft powersoft_mforce_kit_en_v1.1 Keep This Manual For Future Reference 2 Page intentionally left blank M-Force
Numerical Simulation of CPT Tip Resistance in Layered Soil
 Numerical Simulation of CPT Tip Resistance in Layered Soil M.M. Ahmadi, Assistant Professor, [email protected] Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract The paper
Numerical Simulation of CPT Tip Resistance in Layered Soil M.M. Ahmadi, Assistant Professor, [email protected] Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran Abstract The paper
ENCLOSURE DESIGN I S 2008
 ENCLOSURE DESIGNS 2008 Beyma introduces a new range of enclosure designs created for obtaining the best performance from our latest loudspeakers and following the current trends in the market. The new
ENCLOSURE DESIGNS 2008 Beyma introduces a new range of enclosure designs created for obtaining the best performance from our latest loudspeakers and following the current trends in the market. The new
APPLICATION NOTE PROFESSIONAL LOUDSPEAKERS BUILDING AN EFFECTIVE, HIGH PERFORMANCES, 2 WAY, 12 LOUDSPEAKER SYSTEM
 APPLICATION NOTE PROFESSIONAL LOUDSPEAKERS BUILDING AN EFFECTIVE, HIGH PERFORMANCES, 2 WAY, 12 LOUDSPEAKER SYSTEM KEY FEATURES GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS THIELE SMALL PARAMETERS > An effective, high performance
APPLICATION NOTE PROFESSIONAL LOUDSPEAKERS BUILDING AN EFFECTIVE, HIGH PERFORMANCES, 2 WAY, 12 LOUDSPEAKER SYSTEM KEY FEATURES GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS THIELE SMALL PARAMETERS > An effective, high performance
Aeroelastic Investigation of the Sandia 100m Blade Using Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Aeroelastic Investigation of the Sandia 100m Blade Using Computational Fluid Dynamics David Corson Altair Engineering, Inc. Todd Griffith Sandia National Laboratories Tom Ashwill (Retired) Sandia National
Aeroelastic Investigation of the Sandia 100m Blade Using Computational Fluid Dynamics David Corson Altair Engineering, Inc. Todd Griffith Sandia National Laboratories Tom Ashwill (Retired) Sandia National
BOUNDARY INTEGRAL EQUATIONS FOR MODELING ARBITRARY FLAW
 BOUNDARY INTEGRAL EQUATIONS FOR MODELING ARBITRARY FLAW GEOMETRIES IN ELECTRIC CURRENT INJECTION NDE A. P. Ewingl,2, C. Hall Barbosa3.4, T. A. Cruse 2, A. C. Brun03 and 1. P. Wikswo, Jr.l ldepartment of
BOUNDARY INTEGRAL EQUATIONS FOR MODELING ARBITRARY FLAW GEOMETRIES IN ELECTRIC CURRENT INJECTION NDE A. P. Ewingl,2, C. Hall Barbosa3.4, T. A. Cruse 2, A. C. Brun03 and 1. P. Wikswo, Jr.l ldepartment of
Outer Diameter 23 φ mm Face side Dimension 20.1 φ mm. Baffle Opening. Normal 0.5 Watts Maximum 1.0 Watts Sine Wave.
 1. MODEL: 23CR08FH-50ND 2 Dimension & Weight Outer Diameter 23 φ mm Face side Dimension 20.1 φ mm Baffle Opening 20.1 φ mm Height Refer to drawing Weight 4.0Grams 3 Magnet Materials Rare Earth Size φ 9.5
1. MODEL: 23CR08FH-50ND 2 Dimension & Weight Outer Diameter 23 φ mm Face side Dimension 20.1 φ mm Baffle Opening 20.1 φ mm Height Refer to drawing Weight 4.0Grams 3 Magnet Materials Rare Earth Size φ 9.5
RF-thermal-structural-RF coupled analysis on the travelling wave disk-loaded accelerating structure
 RF-thermal-structural-RF coupled analysis on the travelling wave disk-loaded accelerating structure PEI Shi-Lun( 裴 士 伦 ) 1) CHI Yun-Long( 池 云 龙 ) ZHANG Jing-Ru( 张 敬 如 ) HOU Mi( 侯 汨 ) LI Xiao-Ping( 李 小
RF-thermal-structural-RF coupled analysis on the travelling wave disk-loaded accelerating structure PEI Shi-Lun( 裴 士 伦 ) 1) CHI Yun-Long( 池 云 龙 ) ZHANG Jing-Ru( 张 敬 如 ) HOU Mi( 侯 汨 ) LI Xiao-Ping( 李 小
Consideration of a high-capacity foil cable:
 Consideration of a high-capacity foil cable: Newly discovered ancient knowledge. The old RF-developers already knew the benefits of longplanar lines and have been used (electronic) Eonen (times) thin flat
Consideration of a high-capacity foil cable: Newly discovered ancient knowledge. The old RF-developers already knew the benefits of longplanar lines and have been used (electronic) Eonen (times) thin flat
3.0 Exhaust Muffler Design Principles. 3.1 Basic Concepts
 3.0 Exhaust Muffler Design Principles 3.1 Basic Concepts Internal combustion engines are typically equipped with an exhaust muffler to suppress the acoustic pulse generated by the combustion process. A
3.0 Exhaust Muffler Design Principles 3.1 Basic Concepts Internal combustion engines are typically equipped with an exhaust muffler to suppress the acoustic pulse generated by the combustion process. A
Rock Bolt Condition Monitoring Using Ultrasonic Guided Waves
 Rock Bolt Condition Monitoring Using Ultrasonic Guided Waves Bennie Buys Department of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering University of Pretoria Introduction Rock Bolts and their associated problems
Rock Bolt Condition Monitoring Using Ultrasonic Guided Waves Bennie Buys Department of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering University of Pretoria Introduction Rock Bolts and their associated problems
Audio Engineering Society. Convention Paper. Presented at the 119th Convention 2005 October 7 10 New York, New York USA
 Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper Presented at the 119th Convention 2005 October 7 10 New York, New York USA This convention paper has been reproduced from the author's advance manuscript, without
Audio Engineering Society Convention Paper Presented at the 119th Convention 2005 October 7 10 New York, New York USA This convention paper has been reproduced from the author's advance manuscript, without
An equivalent circuit of a loop antenna.
 3.2.1. Circuit Modeling: Loop Impedance A loop antenna can be represented by a lumped circuit when its dimension is small with respect to a wavelength. In this representation, the circuit parameters (generally
3.2.1. Circuit Modeling: Loop Impedance A loop antenna can be represented by a lumped circuit when its dimension is small with respect to a wavelength. In this representation, the circuit parameters (generally
Simulation of Couplers
 Simulation of Couplers by Søren Jønsson, Bin Liu, Lars B. Nielsen, Andreas Schuhmacher Brüel & Kjær AES, Workshop 7, 2003 March 23rd Brüel & Kjær 2003, 1 Agenda Introduction to Couplers Traditional Simulation
Simulation of Couplers by Søren Jønsson, Bin Liu, Lars B. Nielsen, Andreas Schuhmacher Brüel & Kjær AES, Workshop 7, 2003 March 23rd Brüel & Kjær 2003, 1 Agenda Introduction to Couplers Traditional Simulation
