Analysis of Underground Water Tank
|
|
|
- Tobias Franklin
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Analysis of Underground Water Tank Using SAP2000 (Metric Units)
2 Analysis of Underground Water Tank Using SAP2000 Table of Content Objective... 3 Problem... 3 Step by Step Start Model with Template Define Material Properties Define Shell Sections Modify Grid System Draw Top Slabs Draw Bottom Slabs Draw Wall Panels Define Load Cases Define and Assign Joint Pattern Assign Soil and Water Pressure on Wall Panels Assign Load on Top and Bottom Slabs Assign Spring Support Define Load Combinations Run Analysis View Analysis Results Analysis of Underground Water Tank 2/58
3 Objective To demonstrate and practice step-by-step on the modeling and static analysis of underground water tank Problem Carry out static analysis of underground water tank with the following details 3D View Plan View Analysis of Underground Water Tank 3/58
4 Section View 0.30 m 3.00 m 3.50 m 0.15 m Material Properties (Use Default Material) Compressive strength of concrete (f c ) = 281 kg/cm 2 Young Modulus of concrete (E c ) = 253,105 kg/cm 2 Unit Weight of Concrete = 2,403 kg/m 3 Unit Weight of Water = 1,000 kg/m 3 Unit Weight of Soil = 1,800 kg/m 3 Coefficient of Active Earth Pressure (Ka) = 0.6 (Assuming the back fill is cohesive) Modulus of Subgrade Reaction (K S ) Properties Direction Value (T/m 2 /m) Vertical (z) 1200 Horizontal (x and y) 500 Analysis of Underground Water Tank 4/58
5 Shell Section Properties Location Top Slabs Bottom Slabs Walls Section 15 cm 30 cm 25 cm Load Cases and Details Load Name Load Type Details DEAD Dead Load Self Weight: Calculate automatically using Self Weight Multiplier in SAP2000 LIVE Live Load 250 kg/m 2 on Top Slabs TANK1 TANK2 TANK3 SOIL Weight & Pressure of Fluid Weight & Pressure of Fluid Weight & Pressure of Fluid Weight & Pressure of Soil Weight and Pressure of Water on Walls and Bottom Slabs in Tank 1 Weight and Pressure of Water on Walls and Bottom Slabs in Tank 2 Weight and Pressure of Water on Walls and Bottom Slabs in Tank 3 Soil Pressure on All Side Walls and Cantilever Part of Base Slab (Not including any surcharge from service vehicles) UPLIFT Pressure of Water Uplift Pressure on Bottom Slabs (3.5 T/m 2 : Upward) Load Combinations (without Sanitary Durability Coefficient) Load Comb. No. Details 1 U = 1.4 DEAD WATER 2 U = 1.2 DEAD WATER LIVE +1.7 SOIL 3 U = 1.2 DEAD WATER LIVE +1.7 SOIL UPLIFT 4 U = 1.2 DEAD LIVE 5 U = 0.9 DEAD SOIL UPLIFT Sanitary Durability Coefficient (Modified ACI Capacity Factors for Water Retaining Structure) Reinforcement in Flexure Direct Tension/Hoop Reinforcement Excess Shear (for Stirrup) Compression + Flexure = 1.3 U = 1.6 U = 1.3 U = 1.0 U Analysis of Underground Water Tank 5/58
6 Step by Step 1. Start Model with Template Step 1-1: Select Working Unit and Start New Model with Template Start up screen of SAP2000, select working unit to be ton-m at drop-down menu on the bottom-right of screen and click on to start new model with template Step 1-2: Select Template Select Grid Only by clicking on it Analysis of Underground Water Tank 6/58
7 Step 1-3: Specify Grid System Specify grid system as shown in above figure and click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 7/58
8 2. Define Material Properties Step 2-1: Change Working Unit Change working unit to kg-cm Step 2-2: Modify Material Properties Go to Define >> Materials..., and select CONC, click on Modify/ Show Material... Analysis of Underground Water Tank 8/58
9 Step 2-3: Accept the Default Values Click OK to accept the default values. Next, also click OK in the preceding window (Define Materials). Analysis of Underground Water Tank 9/58
10 3. Define Shell Sections Three shell sections (thick. = 15, 25 and 30 cm) are required in this model. Step 3-1: Add New Shell Section Go to Define >> Area Section, select Shell from drop-down menu and click on Add New Section. Step 3-2: Specify Shell Section Properties Specify shell section properties as shown below for shell section thickness = 15 cm. Afterwards, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 10/58
11 Step 3-3: Add 2 New Shell Sections Repeat Step 3-1 and 3-2 to add two more shell sections with thicknesses of 25 and 30 cm, respectively. Next, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 11/58
12 4. Modify Grid System Step 4-1: Modify Grid System Select working unit to be Ton, m, C, go to Define >> Coordinate System/Grid and click on Modify/Show System... Analysis of Underground Water Tank 12/58
13 Step 4-2: Modify Grid System Modify grid system as shown below. Click OK button. Next, also click OK in the preceding window (Coordinate/ Grid Systems). Analysis of Underground Water Tank 13/58
14 5. Draw Top Slabs Step 5-1: Change Plan View to Top Slab Level Select left window, click on Set XY View button to change view to plan view and and click on or to move to move plan level to Z = 3.5 m. Plan elevation (X-Y Plane) is displayed at top-left of window. Step 5-2: Fill Object to Show Shell Element Go to View >> Set Display Options, select Fill Object and Apply to All Windows. Next, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 14/58
15 Step 5-3: Draw Roof Slab Click on Quick Draw Area Element button, select TH15CM and click on roof slab panel area as shown in figure below one by one. Step 5-4: Divide Roof Slab Click on Areas... Set Select Mode button, select all roof slab panels, go to Edit >> Divide Analysis of Underground Water Tank 15/58
16 Step 5-5: Specify Slab Meshing Size Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 16/58
17 6. Draw Bottom Slabs Step 6-1: Move Plan View to Bottom Level Click on twice to move plan view to the level Z = Step 6-2: Draw Bottom Slabs Click on Draw Rectangular Area Element button, select TH30CM and click on two nodes at the corners of bottom slab as shown below. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 17/58
18 Step 6-3: Mesh Bottom Slabs Select bottom slabs as shown in figure below and go to Edit >> Divide Areas... Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 18/58
19 Step 6-4: Mesh Bottom Slabs Select bottom slabs as shown below and go to Edit >> Divide Areas... Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 19/58
20 Step 6-5: Mesh Bottom Slabs Again, select bottom slabs as shown below and go to Edit >> Divide Areas... Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 20/58
21 Step 6-6: Mesh Bottom Slabs Once again, select bottom slabs as shown below and go to Edit >> Divide Areas... Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 21/58
22 7. Draw Wall Panels Step 7-1: Change View to Elevation View to XZ Plane Select left window, click on Set XZ View button to change view and click on or to move elevation view to Y = 0 m. Step 7-2: Draw Wall Panels Click on Quick Draw Area Element button, select TH25CM and draw area to cover wall panel area as shown in figure below. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 22/58
23 Step 7-3: Mesh Wall Panels Click on, select the top part of the wall panel as shown in figure below and go to Edit >> Divide Areas... Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 23/58
24 Step 7-4: Mesh Wall Panels Select bottom wall panels as shown in above figure and go to Edit >> Mesh Area. Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 24/58
25 Step 7-5: Copy Wall Panels Select all wall panels, go to Edit >> Replicate by drawing rectangular selection to cover all wall panels. Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 25/58
26 Step 7-6: Change View to Elevation View to YZ Plane Select left window, click on Set YZ View button to change view and click on or to move elevation view to X = 0 m. Step 7-7: Draw Wall Panels Click on Quick Draw Area Element button, select TH25CM and draw rectangular to cover wall areas as shown in above figure. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 26/58
27 Step 7-8: Mesh Wall Panels Click on Set Select Mode button, select top wall panels as shown in figure below and go to Edit >> Divide Areas... Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 27/58
28 Step 7-9: Mesh Wall Panels Select bottom wall panels as shown in figure below and go to Edit >> Divide Areas... Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 28/58
29 Step 7-10: Copy Wall Panels Select all wall panels and go to Edit >> Replicate Specify parameters as shown below. Then, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 29/58
30 8. Define Load Cases Water load in each tank will be assigned with difference load cases (TANK1, TANK2 and TANK3) for all possible loading condition. Step 8-1: Add Load Case Go to Define >> Load Cases. Then, specify load case name in text box Load Case and then click on Add New Load for each and every load case as shown in figure below Analysis of Underground Water Tank 30/58
31 9. Define and Assign Joint Pattern A joint pattern is simply a set of scalar values defined at the joints for assigning more complex distributions of temperature and pressure over the structure. Joint patterns by themselves create no loads on the structure. There are two types of joint pattern as described below. a. X Y, Z Multiplier Method. Type values in the Constant A, B, C and D edit boxes. The pattern value at each selected joint is calculated as Ax+By+Cz+D, where x, y and z are the joint coordinates of the selected joint in the current coordinate system. The units of constants A, B, and C are 1/Length and constant D is unitless. The calculated pattern value is also unitless. As an example of this assignment method, the following input defines the joint pattern values used to apply a varying soil pressure load on a wall. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 31/58
32 b. Z Coordinate at Zero Pressure and Weight Per Unit Volume Method. Type Z Coordinate and weight per unit volume (Wt per unit Vol) values in the edit boxes and select a Restriction from the drop down list, then click the Add button. If needed, check the Added Uniform Value per Unit Area check box to specify an added uniform value per unit area. The specified Z coordinate is assumed to be in the current coordinate system. The pattern value at each selected joint is calculated as: Zcoord = specified Z coordinate z = Z coordinate of the selected joint in the current coordinate system w = specified weight per unit volume A = specified added value per unit area All appropriate unit conversion factors are used when calculating the pattern value; however, after the pattern value has been obtained, it is thereafter assumed to be unitless. Note that positive and negative value restrictions can be specified individually for each set of Z coordinates and weight per unit volume in the summation as well as for the final calculated pattern value. As an example of this assignment method, the following input defines the joint pattern values used to apply a varying soil pressure load on a wall. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 32/58
33 Step 9-1: Add New Pattern Go to Define >> Joint Patterns, enter pattern name and click on Add New Pattern Name to add 2 new joint patterns ( SOIL and WATER ) Step 9-2: Select Only Wall Panels Activate 3D View Window by clicking on it, go to Select >> Select >> Area Section and select TH25CM from the list to select only wall panels. Go to View >> Selection Only to view only selected element (wall panels) Analysis of Underground Water Tank 33/58
34 Step 9-3: View and Select Only Wall Panels After viewing the selected elements only (wall panels), select all elements in 3D view. Step 9-4: Assign Joint Pattern ( SOIL ) Go to Assign >> Joint Patterns and specify parameters as shown in figure below. Afterwards, click OK. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 34/58
35 Step 9-5: Set View Limit Go to View >> Set Limit and enter Set Z Axis Limits as shown in figure below. Afterwards, click OK. Step 9-6: Select Wall Panels Select all shell elements in 3D view. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 35/58
36 Step 9-7: Assign Joint Pattern ( SOIL ) Go to Assign >> Joint Patterns and specify parameters as shown in figure below. Step 9-8: Clear Z Axis View Limit and Show All Elements Specify parameters as shown in figure below and go to View >> Show All. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 36/58
37 10. Assign Soil and Water Pressure on Wall Panels Pressure loads are assigned as triangular load using joint pattern. The direction of pressure depends on side of shell element (Positive pressures are directed toward the interior of the element.). In SAP2000, 2 sides of shell element (top and bottom) are represented as face 5 and face 6. Face 5 of shell element is the positive side of local axis 3, shown in blue color arrow. Local axes 1, 2, and 3 are marked with red, white and blue. Water pressures are assigned in the load cases separately for each tank (TANK1, TANK2 and TANK3). Note: To view local axis of shell element: Go to View >> Set Display Options and or click on Set Display Options button and select Local Axes in Areas To set color for face of shell element (Area): Go to Options >> Color >> Display Analysis of Underground Water Tank 37/58
38 Step 10-1: Change to in X-Z Plane at Y = 0.00 Select left window, click on Set XZ View button and move elevation view to Y = 0 by clicking or. The location of this elevation is displayed in blue outline in 3D view (right window). Step 10-2: Assign Water Pressure Load to Tank 1 Wall in XZ Plan at Y = 4.00 Select wall panels in tank 1, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 38/58
39 Step 10-3: Assign Water Pressure Load to Tank 2 Wall in XZ Plan at Y = 4.00 Select wall panels in tank 2, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below. Step 10-4: Assign Water Pressure Load to Tank 3 Wall in XZ Plan at Y = 4.00 Select wall panels in tank 3, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 39/58
40 Step 10-5: Assign Soil Pressure to All Tank Wall in XZ Plan at Y = 4.00 Soil pressure will be assigned to opposite face of water pressure (face 5). Select wall panels in all tanks, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All), select Add to Existing Loads options and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below (Multiplier = Ka x unit weight of soil = 0.6 x 1.8 = 1.08). Note: For more details on coefficient of active lateral earth pressure (K a ), please refer the standard book on geotechnical engineering (for example: page 478 of Foundation Analysis and Design by Joseph E. Bowles) Analysis of Underground Water Tank 40/58
41 Step 10-6: Change View to XZ Plan to Y = 4.00 Move elevation view to Y = 4.00 by clicking or. In this elevation view, face 5 of wall panels faces outside of water tank then water pressure load will be assigned at face 6 (water tank) and soil pressure will be assigned at face 5 (outside tank) by using same parameters as assigned at elevation Y = Step 10-7: Assign Water Pressure Load to Tank 1 Wall in XZ Plan at Y = 0.00 Select wall panels in tank 1, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 41/58
42 Step 10-8: Assign Water Pressure Load to Tank 2 Wall in XZ Plan at Y = 0.00 Select wall panels in tank 2, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below. Step 10-9: Assign Water Pressure Load to Tank 3 Wall in XZ Plan at Y = 0.00 Select wall panels in tank 3, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 42/58
43 Step 10-10: Assign Soil Pressure to All Tank Wall in XZ Plan at Y = 0.00 Soil pressure will be assigned to opposite face of water pressure (face 5). Select wall panels in all tanks, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All), select Add to Existing Loads options and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below (Multiplier = Ka x unit weight of soil = 0.6 x 1.8 = 1.08). Step 10-11: Change to in YZ Plan at X = 0 Select left window, click on and move elevation view to X= 0 by clicking or. In this elevation view, shows face 5 of wall panels is inside tank then water pressure will be assigned in face 5 and soil pressure will be assigned in face 6. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 43/58
44 Step 10-12: Assign Water and Soil Pressure to Tank 1 Wall in XZ Plan at X = 0 Select wall panels in tank 1, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below to assign pressure load one by one. Step 10-13: Assign Water Pressure for Tank 1 and 2 in XZ Plan at X = 5 Click on to move elevation view, select all wall panels, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below to assign pressure load one by one. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 44/58
45 Step 10-14: Assign Water Pressure for Tank 2 and 3 in XZ Plan at X = 10 Click on to move elevation view, select all wall panels, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below to assign pressure load one by one. Step 10-15: Assign Water and Soil Pressure to Tank 3 Wall in XZ Plan at X = 15 Click on to move elevation view, select all wall panels, go to Assign >> Area Load >> Surface Pressure (All) and specify pressure parameters as shown in figure below to assign pressure load one by one. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 45/58
46 11. Assign Load on Top and Bottom Slabs Step 11-1: Assign Live Load on Top Slabs (Z = 3.5) Change view to XY plan at Z = 3.5 by clicking on Set XY View button and move plan level to Z = 3.50 by clicking on. Select all slab panels, go to Assign >> Area Loads >> Uniform (Shell) and specify parameters as shown in figure below. Step 11-2: Assign Water Pressure in Bottom Slabs at Tank 1 (Z = 0.0) Click on to Z = 0, Select bottom slabs of tank 1, go to Assign >> Area Loads >> Uniform (Shell) and specify parameters as shown in figure below. Note: To do slab selection easier, deactivate snap option by deselect Intersections button Points and Grid Analysis of Underground Water Tank 46/58
47 Step 11-3: Assign Water Pressure in Bottom Slabs at Tank 2 (Z = 0.0) Select bottom slabs of tank 2, go to Assign >> Area Loads >> Assign >> Area Loads >> Uniform (Shell) and specify parameters as shown in figure below. Step 11-4: Assign Water Pressure in Bottom Slabs at Tank 3 (Z = 0.0) Select bottom slabs of tank 3, go to Assign >> Area Loads >> Uniform (Shell) and specify parameters as shown in figure below. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 47/58
48 Step 11-5: Assign Soil Pressure on Cantilever Slabs (Z = 0.0) Select cantilever slabs, go to Assign >> Area Loads >> Uniform (Shell) and specify parameters as shown in figure below. Note: Soil Pressure = ( / /2) x 1.8 = ton/m 2 Step 11-6: Assign Uplift Pressure in Bottom Slabs (Z = 0.0) Select all slabs, go to Assign >> Area Loads >> Uniform and specify parameters as shown in above figure. Negative value is assigned for Gravity direction. Note: Soil Pressure = / /2 = ton/m 2 Analysis of Underground Water Tank 48/58
49 12. Assign Spring Support Vertical Spring (Z Direction) Vertical spring support can be calculated from length and cross section of pile as shown in following details. Area (A) = 455 cm 2 Length (L) = 20 m Modulus of Concrete (E c ) = 253,150 kg/cm 2 K (Vertical) = 2 x E x A / L = 2 x 253,150 x 455 / 2000 = 115,183 kg/cm Horizontal Spring (X and Y Direction) Horizontal spring support will be assigned as line spring using dummy frame element (30 x 30 cm) and can be calculated from contact area between soil and foundation as shown in following detail Foundation Depth (D) = 0.30 m Modulus of Subgrade Reaction (K S ) = 500 T/m 2 /m K (Horizontal) = D x K S = 500 x 0.3 = 150 T/m/m Note: 1. The soil restraints on side walls have not been included. If the lateral soil restraint and water pressure are applied together the moment on the side walls will be less than when tank has water without back fill. 2. For more details on modulus of subgrade reaction (K s ), please refer the standard book on geotechnical engineering (for example: page 405 of Foundation Analysis and Design by Joseph E. Bowles) Step 12-1: Select Nodes at Pile Location to Assign Vertical Springs Select working unit = kg, cm, activate snap option by clicking on Points and Grid Intersections button and select support nodes by clicking on nodes at pile location as shown in above figure. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 49/58
50 Step 12-2: Assign Vertical Springs Go to Assign >> Joint >> Springs and specify parameters as shown in above figure. Step 12-3: Add DUMMY Frame Section Go to Define >> Frame Sections..., select Add Rectangular from second dropdown menu. Click Add New Property... and specify parameters as shown in figure below. Note: The beam does not exist in the tank in reality. The beam is defined only for the propose of applying lateral soil restraints. The dimensions of this beam are assumed based on the thickness of the base slab (30 cm). Analysis of Underground Water Tank 50/58
51 Step 12-4: Draw DUMMY Frame Section Click on Draw Frame/Cable Element button, select DUMMY and draw frame section as shown in figure below. Step 12-5: Assign Horizontal Springs Change working unit to Ton, m, click on Set Select Mode button, select DUMMY frames as shown in above figure, go to Assign >> Frame/Cable/Tendon >> Line Springs and specify parameter as shown in figure below. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 51/58
52 Step 12-6: Apply Automatic Frame Mesh to DUMMY Frames Select all DUMMY frames by clicking on Get Previous Selection button, go to Assign >> Frame/Cable/Tendon >> Automatic Frame Mesh and specify parameters as shown in figure below. 13. Define Load Combinations Envelop option is used in load combination ( WATER ) to find maximum and minimum results among of all possible full or empty water in each tank. Load combination details (without sanitary durability coefficient) are summarized in following table. Load Combination Name Combination Type Combination Details TANK120 Linear Add TANK1 + TANK2 TANK023 Linear Add TANK2 + TANK3 TANK103 Linear Add TANK1 + TANK3 TANK123 Linear Add TANK1 + TANK2 + TANK3 WATER Envelope TANK1, TANK2, TANK3, TANK120, TANK023, TANK103, TANK123 DESIGN1 Linear Add 1.4 DEAD WATER DESIGN2 Linear Add 1.2 DEAD WATER LIVE +1.7 SOIL DESIGN3 Linear Add 1.2 DEAD WATER LIVE +1.7 SOIL UPLIFT DESIGN4 Linear Add 1.2 DEAD LIVE DESIGN5 Linear Add 0.9 DEAD SOIL UPLIFT Analysis of Underground Water Tank 52/58
53 Step 13-1: Add New Load Combination Go to Define >> Combinations and click on Add New Combo Step 13-2: Define Load Combination Specify Name, select Combination Type, enter load and scale factor and click on Add to define load combination as shown in abovementioned table. Repeat this step to enter load combination as shown in table from previous page. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 53/58
54 14. Run Analysis Step 14-1: Start Analysis Go to Analyze > Run Analysis or click on Run Analysis button and click on Run Now button to start analysis and wait until analysis process complete. Step 14-2: Complete Analysis Wait until analysis status window display ANALYSIS COMPLETE. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 54/58
55 15. View Analysis Results Forces and stresses in shell element for slabs, walls and footing can be displayed in color contour. To use these results for design, sanitary durability coefficients need to be applied as following details. Reinforcement in Flexure Direct Tension/Hoop Reinforcement Excess Shear (for Stirrup) Compression + Flexure **U = Load Combination = 1.3 U = 1.6 U = 1.3 U = 1.0 U The direction and sign convention of forces/ stresses in shell element are described in SAP2000 Analysis Reference Manual page 131 to page 151 that is available in PDF format (file name SapRefer.pdf ) located at the Manual subfolder in folder that SAP2000 has been installed in your computer. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 55/58
56 How to Compute Reinforcement from Finite Element Output The direction of reinforcement for M11 and M 22 are as shown in left figure, Step 15-1: Select Shell Analysis Results to View in Graphic Go to Display >> Forces/Stresses >> Shells and select desired result parameters Analysis of Underground Water Tank 56/58
57 Step 15-2: View Shell Analysis Results in Contour Forces/Stresses in shell elements are displayed in contour color. Color tab at the bottom of screen indicates the value range of the results. Step 15-3: Select Shell Analysis Results to View in Tabular Form Forces/Stresses in shell elements are displayed in tabular form. Go to Display >> Show Table. Select Area Output, click on Select Analysis Cases to select desired load cases and combinations Analysis of Underground Water Tank 57/58
58 Step 15-4: View Shell Analysis Results to View in Tabular Form Shell analysis results are displayed in tabular form as shown in figure below. Analysis of Underground Water Tank 58/58
SAP2000 Getting Started Tutorial
 SAP2000 Getting Started Tutorial Learn how to define materials, sections, grids, and supports with basic modeling concepts for creating and modifying a concrete bent structure model using a nonprismatic
SAP2000 Getting Started Tutorial Learn how to define materials, sections, grids, and supports with basic modeling concepts for creating and modifying a concrete bent structure model using a nonprismatic
TABLE OF CONTENTS. INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE...
 Starting Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE... 7 ADVANCE CONCRETE USER INTERFACE... 7 Other important
Starting Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE... 7 ADVANCE CONCRETE USER INTERFACE... 7 Other important
METHODS FOR ACHIEVEMENT UNIFORM STRESSES DISTRIBUTION UNDER THE FOUNDATION
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 45-66, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 45-66, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
ETABS. Integrated Building Design Software. Concrete Shear Wall Design Manual. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA
 ETABS Integrated Building Design Software Concrete Shear Wall Design Manual Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 8 January 2002 Copyright The computer program ETABS and all
ETABS Integrated Building Design Software Concrete Shear Wall Design Manual Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 8 January 2002 Copyright The computer program ETABS and all
SECTION 5 ANALYSIS OF CONTINUOUS SPANS DEVELOPED BY THE PTI EDC-130 EDUCATION COMMITTEE LEAD AUTHOR: BRYAN ALLRED
 SECTION 5 ANALYSIS OF CONTINUOUS SPANS DEVELOPED BY THE PTI EDC-130 EDUCATION COMMITTEE LEAD AUTHOR: BRYAN ALLRED NOTE: MOMENT DIAGRAM CONVENTION In PT design, it is preferable to draw moment diagrams
SECTION 5 ANALYSIS OF CONTINUOUS SPANS DEVELOPED BY THE PTI EDC-130 EDUCATION COMMITTEE LEAD AUTHOR: BRYAN ALLRED NOTE: MOMENT DIAGRAM CONVENTION In PT design, it is preferable to draw moment diagrams
RFEM 5. Spatial Models Calculated acc. to Finite Element Method. of DLUBAL SOFTWARE GMBH. Dlubal Software GmbH Am Zellweg 2 D-93464 Tiefenbach
 Version July 2013 Program RFEM 5 Spatial Models Calculated acc. to Finite Element Method Tutorial All rights, including those of translations, are reserved. No portion of this book may be reproduced mechanically,
Version July 2013 Program RFEM 5 Spatial Models Calculated acc. to Finite Element Method Tutorial All rights, including those of translations, are reserved. No portion of this book may be reproduced mechanically,
Embankment Consolidation
 Embankment Consolidation 36-1 Embankment Consolidation In this tutorial, RS2 is used for a coupled analysis of a road embankment subject to loading from typical daily traffic. Model Start the RS2 9.0 Model
Embankment Consolidation 36-1 Embankment Consolidation In this tutorial, RS2 is used for a coupled analysis of a road embankment subject to loading from typical daily traffic. Model Start the RS2 9.0 Model
Layout Tutorial. Getting Started
 Getting Started Layout Tutorial This tutorial will explain how create a layout template, send views to a layout page, then save the document in PDF format. In this tutorial you will learn about: Creating
Getting Started Layout Tutorial This tutorial will explain how create a layout template, send views to a layout page, then save the document in PDF format. In this tutorial you will learn about: Creating
SLAB DESIGN. Introduction ACI318 Code provides two design procedures for slab systems:
 Reading Assignment SLAB DESIGN Chapter 9 of Text and, Chapter 13 of ACI318-02 Introduction ACI318 Code provides two design procedures for slab systems: 13.6.1 Direct Design Method (DDM) For slab systems
Reading Assignment SLAB DESIGN Chapter 9 of Text and, Chapter 13 of ACI318-02 Introduction ACI318 Code provides two design procedures for slab systems: 13.6.1 Direct Design Method (DDM) For slab systems
CH. 2 LOADS ON BUILDINGS
 CH. 2 LOADS ON BUILDINGS GRAVITY LOADS Dead loads Vertical loads due to weight of building and any permanent equipment Dead loads of structural elements cannot be readily determined b/c weight depends
CH. 2 LOADS ON BUILDINGS GRAVITY LOADS Dead loads Vertical loads due to weight of building and any permanent equipment Dead loads of structural elements cannot be readily determined b/c weight depends
DESIGN OF SLABS. 3) Based on support or boundary condition: Simply supported, Cantilever slab,
 DESIGN OF SLABS Dr. G. P. Chandradhara Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering Mysore 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional planar structural element having thickness small compared
DESIGN OF SLABS Dr. G. P. Chandradhara Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering Mysore 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional planar structural element having thickness small compared
How to create pop-up menus
 How to create pop-up menus Pop-up menus are menus that are displayed in a browser when a site visitor moves the pointer over or clicks a trigger image. Items in a pop-up menu can have URL links attached
How to create pop-up menus Pop-up menus are menus that are displayed in a browser when a site visitor moves the pointer over or clicks a trigger image. Items in a pop-up menu can have URL links attached
Design Of Reinforced Concrete Structures ii Two-Way Slabs
 1. Inroduction When the ratio (L/S) is less than 2.0, slab is called two-way slab, as shown in the fig. below. Bending will take place in the two directions in a dish-like form. Accordingly, main reinforcement
1. Inroduction When the ratio (L/S) is less than 2.0, slab is called two-way slab, as shown in the fig. below. Bending will take place in the two directions in a dish-like form. Accordingly, main reinforcement
Introductory Examples. InfoCAD Program System
 Introductory Examples InfoCAD Program System The description of program functions within this documentation should not be considered a warranty of product features. All warranty and liability claims arising
Introductory Examples InfoCAD Program System The description of program functions within this documentation should not be considered a warranty of product features. All warranty and liability claims arising
The following is an overview of lessons included in the tutorial.
 Chapter 2 Tutorial Tutorial Introduction This tutorial is designed to introduce you to some of Surfer's basic features. After you have completed the tutorial, you should be able to begin creating your
Chapter 2 Tutorial Tutorial Introduction This tutorial is designed to introduce you to some of Surfer's basic features. After you have completed the tutorial, you should be able to begin creating your
FOUNDATION DESIGN. Instructional Materials Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples
 FOUNDATION DESIGN Proportioning elements for: Transfer of seismic forces Strength and stiffness Shallow and deep foundations Elastic and plastic analysis Foundation Design 14-1 Load Path and Transfer to
FOUNDATION DESIGN Proportioning elements for: Transfer of seismic forces Strength and stiffness Shallow and deep foundations Elastic and plastic analysis Foundation Design 14-1 Load Path and Transfer to
Visual Tutorial Basic Edition 1. Visual. Basic Edition Tutorial. www.visuallightingsoftware.com
 Visual Tutorial Basic Edition 1 Visual Basic Edition Tutorial www.visuallightingsoftware.com Visual Tutorial Basic Edition 2 Basic Edition Tutorial Introduction In this tutorial, you will use the Visual
Visual Tutorial Basic Edition 1 Visual Basic Edition Tutorial www.visuallightingsoftware.com Visual Tutorial Basic Edition 2 Basic Edition Tutorial Introduction In this tutorial, you will use the Visual
REINFORCED CONCRETE. Reinforced Concrete Design. A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition. Walls are generally used to provide lateral support for:
 HANDOUT REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition RETAINING WALLS Fifth Edition A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
HANDOUT REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition RETAINING WALLS Fifth Edition A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 1 NON-CONCURRENT COPLANAR FORCE SYSTEMS 1. Be able to determine the effects
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 1 NON-CONCURRENT COPLANAR FORCE SYSTEMS 1. Be able to determine the effects
ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Analysis of an Aluminum Bracket
 H. Kim FEA Tutorial 1 ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Analysis of an Aluminum Bracket Hyonny Kim last updated: August 2004 In this tutorial, you ll learn how to: 1. Sketch 2D geometry & define part. 2. Define material
H. Kim FEA Tutorial 1 ABAQUS/CAE Tutorial: Analysis of an Aluminum Bracket Hyonny Kim last updated: August 2004 In this tutorial, you ll learn how to: 1. Sketch 2D geometry & define part. 2. Define material
SAFE. Key Features and Terminology DESIGN OF SLABS, BEAMS AND FOUNDATIONIS REINFORCED AND POST-TENSIONED CONCRETE
 SAFE DESIGN OF SLABS, BEAMS AND FOUNDATIONIS REINFORCED AND POST-TENSIONED CONCRETE Key Features and Terminology ISO SAF012209M1 Berkeley, California, USA Version 12.1.0 January 2009 Copyright Copyright
SAFE DESIGN OF SLABS, BEAMS AND FOUNDATIONIS REINFORCED AND POST-TENSIONED CONCRETE Key Features and Terminology ISO SAF012209M1 Berkeley, California, USA Version 12.1.0 January 2009 Copyright Copyright
Tension Development and Lap Splice Lengths of Reinforcing Bars under ACI 318-02
 ENGINEERING DATA REPORT NUMBER 51 Tension Development and Lap Splice Lengths of Reinforcing Bars under ACI 318-02 A SERVICE OF THE CONCRETE REINFORCING STEEL INSTITUTE Introduction Section 1.2.1 in the
ENGINEERING DATA REPORT NUMBER 51 Tension Development and Lap Splice Lengths of Reinforcing Bars under ACI 318-02 A SERVICE OF THE CONCRETE REINFORCING STEEL INSTITUTE Introduction Section 1.2.1 in the
Introduction to COMSOL. The Navier-Stokes Equations
 Flow Between Parallel Plates Modified from the COMSOL ChE Library module rev 10/13/08 Modified by Robert P. Hesketh, Chemical Engineering, Rowan University Fall 2008 Introduction to COMSOL The following
Flow Between Parallel Plates Modified from the COMSOL ChE Library module rev 10/13/08 Modified by Robert P. Hesketh, Chemical Engineering, Rowan University Fall 2008 Introduction to COMSOL The following
Module 5 (Lectures 17 to 19) MAT FOUNDATIONS
 Module 5 (Lectures 17 to 19) MAT FOUNDATIONS Topics 17.1 INTRODUCTION Rectangular Combined Footing: Trapezoidal Combined Footings: Cantilever Footing: Mat foundation: 17.2 COMMON TYPES OF MAT FOUNDATIONS
Module 5 (Lectures 17 to 19) MAT FOUNDATIONS Topics 17.1 INTRODUCTION Rectangular Combined Footing: Trapezoidal Combined Footings: Cantilever Footing: Mat foundation: 17.2 COMMON TYPES OF MAT FOUNDATIONS
Design of reinforced concrete columns. Type of columns. Failure of reinforced concrete columns. Short column. Long column
 Design of reinforced concrete columns Type of columns Failure of reinforced concrete columns Short column Column fails in concrete crushed and bursting. Outward pressure break horizontal ties and bend
Design of reinforced concrete columns Type of columns Failure of reinforced concrete columns Short column Column fails in concrete crushed and bursting. Outward pressure break horizontal ties and bend
Tutorial Plate Concrete
 Tutorial Plate Concrete Release: SCIA Engineer 2008.0 Req. Module: ESA.00 Base Modeller ESA.01 ESAS.00 ESA.08.x 2D Surfaces Linear Statics 2D a language module Manual: SCIA Engineer Tutorial Plate Concrete
Tutorial Plate Concrete Release: SCIA Engineer 2008.0 Req. Module: ESA.00 Base Modeller ESA.01 ESAS.00 ESA.08.x 2D Surfaces Linear Statics 2D a language module Manual: SCIA Engineer Tutorial Plate Concrete
Applying a circular load. Immediate and consolidation settlement. Deformed contours. Query points and query lines. Graph query.
 Quick Start Tutorial 1-1 Quick Start Tutorial This quick start tutorial will cover some of the basic features of Settle3D. A circular load is applied to a single soil layer and settlements are examined.
Quick Start Tutorial 1-1 Quick Start Tutorial This quick start tutorial will cover some of the basic features of Settle3D. A circular load is applied to a single soil layer and settlements are examined.
Egcobox Software Manuel Version 2.0. 2007-2010 Max Frank GmbH & Co. KG
 Egcobox Software Manuel Version 2.0 2007-2010 Max Frank GmbH & Co. KG Egcobox Software Contents Page Contents 3-4 Overview 5-13 Example calculation type 1: cantilever balcony 14-15 Language and standard
Egcobox Software Manuel Version 2.0 2007-2010 Max Frank GmbH & Co. KG Egcobox Software Contents Page Contents 3-4 Overview 5-13 Example calculation type 1: cantilever balcony 14-15 Language and standard
ETABS. Integrated Building Design Software. Concrete Frame Design Manual. Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA
 ETABS Integrated Building Design Software Concrete Frame Design Manual Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 8 January 2002 Copyright The computer program ETABS and all associated
ETABS Integrated Building Design Software Concrete Frame Design Manual Computers and Structures, Inc. Berkeley, California, USA Version 8 January 2002 Copyright The computer program ETABS and all associated
Correcting the Lateral Response Artifact in Radiochromic Film Images from Flatbed Scanners
 Correcting the Lateral Response Artifact in Radiochromic Film Images from Flatbed Scanners Background The lateral response artifact (LRA) in radiochromic film images from flatbed scanners was first pointed
Correcting the Lateral Response Artifact in Radiochromic Film Images from Flatbed Scanners Background The lateral response artifact (LRA) in radiochromic film images from flatbed scanners was first pointed
16. Beam-and-Slab Design
 ENDP311 Structural Concrete Design 16. Beam-and-Slab Design Beam-and-Slab System How does the slab work? L- beams and T- beams Holding beam and slab together University of Western Australia School of Civil
ENDP311 Structural Concrete Design 16. Beam-and-Slab Design Beam-and-Slab System How does the slab work? L- beams and T- beams Holding beam and slab together University of Western Australia School of Civil
Steady Flow: Laminar and Turbulent in an S-Bend
 STAR-CCM+ User Guide 6663 Steady Flow: Laminar and Turbulent in an S-Bend This tutorial demonstrates the flow of an incompressible gas through an s-bend of constant diameter (2 cm), for both laminar and
STAR-CCM+ User Guide 6663 Steady Flow: Laminar and Turbulent in an S-Bend This tutorial demonstrates the flow of an incompressible gas through an s-bend of constant diameter (2 cm), for both laminar and
COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING FOR AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATION USING ABAQUS
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 30 52, Article ID: IJARET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=7&itype=2
International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 30 52, Article ID: IJARET_07_02_004 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=7&itype=2
AASHTOWare Bridge Design and Rating Training. STL8 Single Span Steel 3D Example (BrDR 6.6)
 AASHTOWare Bridge Design and Rating Training STL8 Single Span Steel 3D Example (BrDR 6.6) Last Modified: 4/28/2015 STL8-1 AASHTOWare BrDR 6.5 AASHTOWare Bridge Design and Rating Training STL8 Single Span
AASHTOWare Bridge Design and Rating Training STL8 Single Span Steel 3D Example (BrDR 6.6) Last Modified: 4/28/2015 STL8-1 AASHTOWare BrDR 6.5 AASHTOWare Bridge Design and Rating Training STL8 Single Span
Home Designer. Creating a Pole Barn Structure. Software QUESTION. The information in this article applies to:
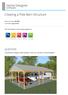 Home Designer Software Creating a Pole Barn Structure Reference Number: KB-01081 Last Modified: July 16, 2015 The information in this article applies to: QUESTION I would like to design a pole building.
Home Designer Software Creating a Pole Barn Structure Reference Number: KB-01081 Last Modified: July 16, 2015 The information in this article applies to: QUESTION I would like to design a pole building.
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Maps: Knowledge Worth Sharing Map Annotation A map is a graphic representation of some part of the earth. In our industry, it may represent either the surface or sub surface;
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Maps: Knowledge Worth Sharing Map Annotation A map is a graphic representation of some part of the earth. In our industry, it may represent either the surface or sub surface;
Manual for simulation of EB processing. Software ModeRTL
 1 Manual for simulation of EB processing Software ModeRTL How to get results. Software ModeRTL. Software ModeRTL consists of five thematic modules and service blocks. (See Fig.1). Analytic module is intended
1 Manual for simulation of EB processing Software ModeRTL How to get results. Software ModeRTL. Software ModeRTL consists of five thematic modules and service blocks. (See Fig.1). Analytic module is intended
Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS Workbench
 Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS Workbench 5.1 Introduction The problem selected to illustrate the use of ANSYS software for a three-dimensional steadystate
Essay 5 Tutorial for a Three-Dimensional Heat Conduction Problem Using ANSYS Workbench 5.1 Introduction The problem selected to illustrate the use of ANSYS software for a three-dimensional steadystate
Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures
 Chapter 8 Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures 8.1 Scope Provisions of Sec. 8.1 and 8.2 of Chapter 8 shall apply for detailing of reinforcement in reinforced concrete members, in general. For
Chapter 8 Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures 8.1 Scope Provisions of Sec. 8.1 and 8.2 of Chapter 8 shall apply for detailing of reinforcement in reinforced concrete members, in general. For
A Case Study Comparing Two Approaches for Applying Area Loads: Tributary Area Loads vs Shell Pressure Loads
 1 A Case Study Comparing Two Approaches for Applying Area Loads: Tributary Area Loads vs Shell Pressure Loads By Dr. Siriwut Sasibut (Application Engineer) S-FRAME Software Inc. #1158 13351 Commerce Parkway
1 A Case Study Comparing Two Approaches for Applying Area Loads: Tributary Area Loads vs Shell Pressure Loads By Dr. Siriwut Sasibut (Application Engineer) S-FRAME Software Inc. #1158 13351 Commerce Parkway
Element Property Definition for the Space Satellite
 LESSON 5 Element Property Definition for the Space Satellite Z Y X Objectives: Define shell, bar, and point mass element properties for the Space Satellite. Create and apply a Field to describe a spatially
LESSON 5 Element Property Definition for the Space Satellite Z Y X Objectives: Define shell, bar, and point mass element properties for the Space Satellite. Create and apply a Field to describe a spatially
Understand the Sketcher workbench of CATIA V5.
 Chapter 1 Drawing Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketcher Workbench-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Understand the Sketcher workbench of CATIA V5. Start a new file in the Part
Chapter 1 Drawing Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketcher Workbench-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Understand the Sketcher workbench of CATIA V5. Start a new file in the Part
Excel -- Creating Charts
 Excel -- Creating Charts The saying goes, A picture is worth a thousand words, and so true. Professional looking charts give visual enhancement to your statistics, fiscal reports or presentation. Excel
Excel -- Creating Charts The saying goes, A picture is worth a thousand words, and so true. Professional looking charts give visual enhancement to your statistics, fiscal reports or presentation. Excel
Type of Force 1 Axial (tension / compression) Shear. 3 Bending 4 Torsion 5 Images 6 Symbol (+ -)
 Cause: external force P Force vs. Stress Effect: internal stress f 05 Force vs. Stress Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-05 press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 1 Type of Force 1 Axial (tension /
Cause: external force P Force vs. Stress Effect: internal stress f 05 Force vs. Stress Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-05 press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 1 Type of Force 1 Axial (tension /
Layout Tutorial. Chapter 10: Getting Started
 Chapter 10: Layout Tutorial In this tutorial we will create a layout template, send a few views to a layout page, then save this document in PDF format. In this tutorial you will learn about: Creating
Chapter 10: Layout Tutorial In this tutorial we will create a layout template, send a few views to a layout page, then save this document in PDF format. In this tutorial you will learn about: Creating
DISTRIBUTION OF LOADSON PILE GROUPS
 C H A P T E R 7 DISTRIBUTION OF LOADSON PILE GROUPS Section I. DESIGN LOADS 7-1. Basic design. The load carried by an individual pile or group of piles in a foundation depends upon the structure concerned
C H A P T E R 7 DISTRIBUTION OF LOADSON PILE GROUPS Section I. DESIGN LOADS 7-1. Basic design. The load carried by an individual pile or group of piles in a foundation depends upon the structure concerned
AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 ESSENTIALS
 AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 ESSENTIALS SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. Visit our website to learn more about this and other books: AutoCAD Civil
AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 ESSENTIALS SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. Visit our website to learn more about this and other books: AutoCAD Civil
When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid.
 Fluid Statics When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid. Consider a small wedge of fluid at rest of size Δx, Δz, Δs
Fluid Statics When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid. Consider a small wedge of fluid at rest of size Δx, Δz, Δs
PDF Web Form. Projects 1
 Projects 1 In this project, you ll create a PDF form that can be used to collect user data online. In this exercise, you ll learn how to: Design a layout for a functional form. Add form fields and set
Projects 1 In this project, you ll create a PDF form that can be used to collect user data online. In this exercise, you ll learn how to: Design a layout for a functional form. Add form fields and set
9.3 Two-way Slabs (Part I)
 9.3 Two-way Slabs (Part I) This section covers the following topics. Introduction Analysis and Design Features in Modeling and Analysis Distribution of Moments to Strips 9.3.1 Introduction The slabs are
9.3 Two-way Slabs (Part I) This section covers the following topics. Introduction Analysis and Design Features in Modeling and Analysis Distribution of Moments to Strips 9.3.1 Introduction The slabs are
Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire 4.0 Basic Design
 Introduction Datum features are non-solid features used during the construction of other features. The most common datum features include planes, axes, coordinate systems, and curves. Datum features do
Introduction Datum features are non-solid features used during the construction of other features. The most common datum features include planes, axes, coordinate systems, and curves. Datum features do
Exercise: Building and zone geometry import from SketchUp
 Exercise: Building and zone geometry import from SketchUp Purpose Learn how to create and import building and zone geometry from SketchUp into IDA ICE. Learn how to work with imported building and zone
Exercise: Building and zone geometry import from SketchUp Purpose Learn how to create and import building and zone geometry from SketchUp into IDA ICE. Learn how to work with imported building and zone
Structure Design. Preface What's New? Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Workbench Description Customizing Glossary Index
 Structure Design Preface What's New? Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Workbench Description Customizing Glossary Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-2000. All rights reserved. Preface CATIA Version
Structure Design Preface What's New? Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Workbench Description Customizing Glossary Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-2000. All rights reserved. Preface CATIA Version
AB3080 L. Learning Objectives: About the Speaker:
 AB3080 L While architects have tested their designs in wind tunnels for many years, the process is typically outsourced to engineering firms and not easily accessible to architects during the conceptual
AB3080 L While architects have tested their designs in wind tunnels for many years, the process is typically outsourced to engineering firms and not easily accessible to architects during the conceptual
Open icon. The Select Layer To Add dialog opens. Click here to display
 Mosaic Introduction This tour guide gives you the steps for mosaicking two or more image files to produce one image file. The mosaicking process works with rectified and/or calibrated images. Here, you
Mosaic Introduction This tour guide gives you the steps for mosaicking two or more image files to produce one image file. The mosaicking process works with rectified and/or calibrated images. Here, you
Layout Tutorial. Chapter 10: Getting Started
 Chapter 10: Layout Tutorial In this tutorial we will create a layout template, send a few views to a layout page, then save this document in PDF format. In this tutorial you will learn about: Creating
Chapter 10: Layout Tutorial In this tutorial we will create a layout template, send a few views to a layout page, then save this document in PDF format. In this tutorial you will learn about: Creating
Draft Table of Contents. Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14
 Draft Table of Contents Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14 BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL CONCRETE (ACI 318 14) Chapter 1 General 1.1 Scope of ACI 318
Draft Table of Contents Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14 BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL CONCRETE (ACI 318 14) Chapter 1 General 1.1 Scope of ACI 318
National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying. Principles and Practice of Engineering Structural Examination
 Structural Effective Beginning with the April 2011 The structural engineering exam is a breadth and exam examination offered in two components on successive days. The 8-hour Vertical Forces (Gravity/Other)
Structural Effective Beginning with the April 2011 The structural engineering exam is a breadth and exam examination offered in two components on successive days. The 8-hour Vertical Forces (Gravity/Other)
4B-2. 2. The stiffness of the floor and roof diaphragms. 3. The relative flexural and shear stiffness of the shear walls and of connections.
 Shear Walls Buildings that use shear walls as the lateral force-resisting system can be designed to provide a safe, serviceable, and economical solution for wind and earthquake resistance. Shear walls
Shear Walls Buildings that use shear walls as the lateral force-resisting system can be designed to provide a safe, serviceable, and economical solution for wind and earthquake resistance. Shear walls
Learning Module 4 - Thermal Fluid Analysis Note: LM4 is still in progress. This version contains only 3 tutorials.
 Learning Module 4 - Thermal Fluid Analysis Note: LM4 is still in progress. This version contains only 3 tutorials. Attachment C1. SolidWorks-Specific FEM Tutorial 1... 2 Attachment C2. SolidWorks-Specific
Learning Module 4 - Thermal Fluid Analysis Note: LM4 is still in progress. This version contains only 3 tutorials. Attachment C1. SolidWorks-Specific FEM Tutorial 1... 2 Attachment C2. SolidWorks-Specific
Structural Axial, Shear and Bending Moments
 Structural Axial, Shear and Bending Moments Positive Internal Forces Acting Recall from mechanics of materials that the internal forces P (generic axial), V (shear) and M (moment) represent resultants
Structural Axial, Shear and Bending Moments Positive Internal Forces Acting Recall from mechanics of materials that the internal forces P (generic axial), V (shear) and M (moment) represent resultants
November 20, 2013. Heather Sustersic had132@psu.edu. Dear Professor Sustersic,
 November 20, 2013 Heather Sustersic had132@psu.edu Dear Professor Sustersic, The following technical report was written to fulfill the requirements specified in the Structural Technical Report 4 assignment
November 20, 2013 Heather Sustersic had132@psu.edu Dear Professor Sustersic, The following technical report was written to fulfill the requirements specified in the Structural Technical Report 4 assignment
Hands-On Practice. Using Notebook Software in the Office
 Using Notebook Software in the Office Before You Start Before you begin your meeting, ensure that your computer is turned on and the SMART Board interactive whiteboard is connected and oriented. The SMART
Using Notebook Software in the Office Before You Start Before you begin your meeting, ensure that your computer is turned on and the SMART Board interactive whiteboard is connected and oriented. The SMART
Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Using Beam Library (SI Units)
 APPENDIX A Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Using Beam Library (SI Units) Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a cantilever beam. Use the geometry model to define an MSC.Nastran
APPENDIX A Linear Static Analysis of a Cantilever Beam Using Beam Library (SI Units) Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a cantilever beam. Use the geometry model to define an MSC.Nastran
Roof Tutorial. Chapter 3:
 Chapter 3: Roof Tutorial The majority of Roof Tutorial describes some common roof styles that can be created using settings in the Wall Specification dialog and can be completed independent of the other
Chapter 3: Roof Tutorial The majority of Roof Tutorial describes some common roof styles that can be created using settings in the Wall Specification dialog and can be completed independent of the other
bi directional loading). Prototype ten story
 NEESR SG: Behavior, Analysis and Design of Complex Wall Systems The laboratory testing presented here was conducted as part of a larger effort that employed laboratory testing and numerical simulation
NEESR SG: Behavior, Analysis and Design of Complex Wall Systems The laboratory testing presented here was conducted as part of a larger effort that employed laboratory testing and numerical simulation
. Address the following issues in your solution:
 CM 3110 COMSOL INSTRUCTIONS Faith Morrison and Maria Tafur Department of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI USA 22 November 2012 Zhichao Wang edits 21 November 2013 revised
CM 3110 COMSOL INSTRUCTIONS Faith Morrison and Maria Tafur Department of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI USA 22 November 2012 Zhichao Wang edits 21 November 2013 revised
Plotting: Customizing the Graph
 Plotting: Customizing the Graph Data Plots: General Tips Making a Data Plot Active Within a graph layer, only one data plot can be active. A data plot must be set active before you can use the Data Selector
Plotting: Customizing the Graph Data Plots: General Tips Making a Data Plot Active Within a graph layer, only one data plot can be active. A data plot must be set active before you can use the Data Selector
Tutorial: 2D Pipe Junction Using Hexa Meshing
 Tutorial: 2D Pipe Junction Using Hexa Meshing Introduction In this tutorial, you will generate a mesh for a two-dimensional pipe junction, composed of two inlets and one outlet. After generating an initial
Tutorial: 2D Pipe Junction Using Hexa Meshing Introduction In this tutorial, you will generate a mesh for a two-dimensional pipe junction, composed of two inlets and one outlet. After generating an initial
An introduction to 3D draughting & solid modelling using AutoCAD
 An introduction to 3D draughting & solid modelling using AutoCAD Faculty of Technology University of Plymouth Drake Circus Plymouth PL4 8AA These notes are to be used in conjunction with the AutoCAD software
An introduction to 3D draughting & solid modelling using AutoCAD Faculty of Technology University of Plymouth Drake Circus Plymouth PL4 8AA These notes are to be used in conjunction with the AutoCAD software
ME 24-688 Week 11 Introduction to Dynamic Simulation
 The purpose of this introduction to dynamic simulation project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Inventor Professional. This environment allows you to perform rigid body dynamic
The purpose of this introduction to dynamic simulation project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Inventor Professional. This environment allows you to perform rigid body dynamic
PRO-MECHANICA. Lesson One < Structural > Beam Cantilever Beam
 PRO-MECHANICA Pro-Mechanica is a product of PTC. It works with Creo Pro/E in integrated mode to allow users to perform structural and thermal analyses. This tutorial was originally written for UNIX platform,
PRO-MECHANICA Pro-Mechanica is a product of PTC. It works with Creo Pro/E in integrated mode to allow users to perform structural and thermal analyses. This tutorial was originally written for UNIX platform,
Microsoft Access 2010 handout
 Microsoft Access 2010 handout Access 2010 is a relational database program you can use to create and manage large quantities of data. You can use Access to manage anything from a home inventory to a giant
Microsoft Access 2010 handout Access 2010 is a relational database program you can use to create and manage large quantities of data. You can use Access to manage anything from a home inventory to a giant
p atmospheric Statics : Pressure Hydrostatic Pressure: linear change in pressure with depth Measure depth, h, from free surface Pressure Head p gh
 IVE1400: n Introduction to Fluid Mechanics Statics : Pressure : Statics r P Sleigh: P..Sleigh@leeds.ac.uk r J Noakes:.J.Noakes@leeds.ac.uk January 008 Module web site: www.efm.leeds.ac.uk/ive/fluidslevel1
IVE1400: n Introduction to Fluid Mechanics Statics : Pressure : Statics r P Sleigh: P..Sleigh@leeds.ac.uk r J Noakes:.J.Noakes@leeds.ac.uk January 008 Module web site: www.efm.leeds.ac.uk/ive/fluidslevel1
Introduction. Background
 Introduction Welcome to CFS, the comprehensive cold-formed steel component design software. The endless variety of shapes and sizes of cold-formed steel members, combined with the complex failure modes
Introduction Welcome to CFS, the comprehensive cold-formed steel component design software. The endless variety of shapes and sizes of cold-formed steel members, combined with the complex failure modes
Design of diaphragm and sheet pile walls. D-Sheet Piling. User Manual
 Design of diaphragm and sheet pile walls D-Sheet Piling User Manual D-SHEET PILING Design of diaphragm and sheet pile walls User Manual Version: 14.1.34974 31 July 2014 D-SHEET PILING, User Manual Published
Design of diaphragm and sheet pile walls D-Sheet Piling User Manual D-SHEET PILING Design of diaphragm and sheet pile walls User Manual Version: 14.1.34974 31 July 2014 D-SHEET PILING, User Manual Published
Sheet Metal Design. Preface What's New? Getting Started Basic Tasks Workbench Description Customizing Glossary Index
 Sheet Metal Design Preface What's New? Getting Started Basic Tasks Workbench Description Customizing Glossary Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-99. All rights reserved. Preface The V5 CATIA - Sheet Metal Design
Sheet Metal Design Preface What's New? Getting Started Basic Tasks Workbench Description Customizing Glossary Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-99. All rights reserved. Preface The V5 CATIA - Sheet Metal Design
ANSYS FLUENT. Using Moving Reference Frames and Sliding Meshes WS5-1. Customer Training Material
 Workshop 5 Using Moving Reference Frames and Sliding Meshes Introduction to ANSYS FLUENT WS5-1 Introduction [1] Several solution strategies exist when there are moving parts in the domain. This workshop
Workshop 5 Using Moving Reference Frames and Sliding Meshes Introduction to ANSYS FLUENT WS5-1 Introduction [1] Several solution strategies exist when there are moving parts in the domain. This workshop
Statics of Structural Supports
 Statics of Structural Supports TYPES OF FORCES External Forces actions of other bodies on the structure under consideration. Internal Forces forces and couples exerted on a member or portion of the structure
Statics of Structural Supports TYPES OF FORCES External Forces actions of other bodies on the structure under consideration. Internal Forces forces and couples exerted on a member or portion of the structure
DESIGN OF SLABS. Department of Structures and Materials Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
 DESIGN OF SLABS Department of Structures and Materials Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Introduction Types of Slab Slabs are plate elements
DESIGN OF SLABS Department of Structures and Materials Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Introduction Types of Slab Slabs are plate elements
NIS-Elements Viewer. User's Guide
 NIS-Elements Viewer User's Guide Publication date 10.09.2013 v. 4.20.00 Laboratory Imaging, s. r. o., Za Drahou 171/17, CZ - 102 00 Praha 10 No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted
NIS-Elements Viewer User's Guide Publication date 10.09.2013 v. 4.20.00 Laboratory Imaging, s. r. o., Za Drahou 171/17, CZ - 102 00 Praha 10 No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted
AutoCAD Structural Detailing 2011. Getting Started with AutoCAD Structural Detailing, Reinforcement module
 AutoCAD Structural Detailing 2011 Getting Started with AutoCAD Structural Detailing, Reinforcement module 2010 Autodesk, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Except as otherwise permitted by Autodesk, Inc., this
AutoCAD Structural Detailing 2011 Getting Started with AutoCAD Structural Detailing, Reinforcement module 2010 Autodesk, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Except as otherwise permitted by Autodesk, Inc., this
Sample Table. Columns. Column 1 Column 2 Column 3 Row 1 Cell 1 Cell 2 Cell 3 Row 2 Cell 4 Cell 5 Cell 6 Row 3 Cell 7 Cell 8 Cell 9.
 Working with Tables in Microsoft Word The purpose of this document is to lead you through the steps of creating, editing and deleting tables and parts of tables. This document follows a tutorial format
Working with Tables in Microsoft Word The purpose of this document is to lead you through the steps of creating, editing and deleting tables and parts of tables. This document follows a tutorial format
digital project V1,R4 Quick Start
 digital project V1,R4 Quick Start Quick Starting Your Knowledge in Digital Project V1,R4 Nuri Miller May 2009 Copyright 2009 Gehry Technologies, Inc. Table of Contents Introduction...vi Creating a Part...2
digital project V1,R4 Quick Start Quick Starting Your Knowledge in Digital Project V1,R4 Nuri Miller May 2009 Copyright 2009 Gehry Technologies, Inc. Table of Contents Introduction...vi Creating a Part...2
TurboCAD Architectural
 TurboCAD Architectural Version 15 Getting Started Guide IMSI/Design LLC, US 100 Rowland Blvd. Novato. CA 94945, USA Tel: +1-415-878-4000 Fax: +1-415-897-2544 Web Site www.imsisoft.com www.turbocad.com
TurboCAD Architectural Version 15 Getting Started Guide IMSI/Design LLC, US 100 Rowland Blvd. Novato. CA 94945, USA Tel: +1-415-878-4000 Fax: +1-415-897-2544 Web Site www.imsisoft.com www.turbocad.com
Microsoft Excel 2010 Charts and Graphs
 Microsoft Excel 2010 Charts and Graphs Email: training@health.ufl.edu Web Page: http://training.health.ufl.edu Microsoft Excel 2010: Charts and Graphs 2.0 hours Topics include data groupings; creating
Microsoft Excel 2010 Charts and Graphs Email: training@health.ufl.edu Web Page: http://training.health.ufl.edu Microsoft Excel 2010: Charts and Graphs 2.0 hours Topics include data groupings; creating
CREATING EXCEL PIVOT TABLES AND PIVOT CHARTS FOR LIBRARY QUESTIONNAIRE RESULTS
 CREATING EXCEL PIVOT TABLES AND PIVOT CHARTS FOR LIBRARY QUESTIONNAIRE RESULTS An Excel Pivot Table is an interactive table that summarizes large amounts of data. It allows the user to view and manipulate
CREATING EXCEL PIVOT TABLES AND PIVOT CHARTS FOR LIBRARY QUESTIONNAIRE RESULTS An Excel Pivot Table is an interactive table that summarizes large amounts of data. It allows the user to view and manipulate
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL TUTORIAL 4 - COMPLEMENTARY SHEAR STRESS
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL TUTORIAL 4 - COMPLEMENTARY SHEAR STRESS This the fourth and final tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge our progress b completing the self assessment exercises.
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL TUTORIAL 4 - COMPLEMENTARY SHEAR STRESS This the fourth and final tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge our progress b completing the self assessment exercises.
SpaceClaim Introduction Training Session. A SpaceClaim Support Document
 SpaceClaim Introduction Training Session A SpaceClaim Support Document In this class we will walk through the basic tools used to create and modify models in SpaceClaim. Introduction We will focus on:
SpaceClaim Introduction Training Session A SpaceClaim Support Document In this class we will walk through the basic tools used to create and modify models in SpaceClaim. Introduction We will focus on:
Kitchen and Bath Design Tutorial
 Chapter 5: Kitchen and Bath Design Tutorial This tutorial continues where the Materials Tutorial left off. You should save this tutorial using a new name to archive your previous work. The tools and techniques
Chapter 5: Kitchen and Bath Design Tutorial This tutorial continues where the Materials Tutorial left off. You should save this tutorial using a new name to archive your previous work. The tools and techniques
6. If you want to enter specific formats, click the Format Tab to auto format the information that is entered into the field.
 Adobe Acrobat Professional X Part 3 - Creating Fillable Forms Preparing the Form Create the form in Word, including underlines, images and any other text you would like showing on the form. Convert the
Adobe Acrobat Professional X Part 3 - Creating Fillable Forms Preparing the Form Create the form in Word, including underlines, images and any other text you would like showing on the form. Convert the
 Edinburgh COLLEGE of ART ARCHITECTURE 3D Modelling in AutoCAD - tutorial exercise The screen The graphics area This is the part of the screen in which the drawing will be created. The command prompt area
Edinburgh COLLEGE of ART ARCHITECTURE 3D Modelling in AutoCAD - tutorial exercise The screen The graphics area This is the part of the screen in which the drawing will be created. The command prompt area
Leica 3D Disto Application Veranda / Conservatory
 Leica 3D Disto Application Veranda / Conservatory What do you need to know? 1) What position you are going to fit the Veranda in? 2) What is the height and width? 3) What is the length? 4) Is the wall
Leica 3D Disto Application Veranda / Conservatory What do you need to know? 1) What position you are going to fit the Veranda in? 2) What is the height and width? 3) What is the length? 4) Is the wall
Create a folder on your network drive called DEM. This is where data for the first part of this lesson will be stored.
 In this lesson you will create a Digital Elevation Model (DEM). A DEM is a gridded array of elevations. In its raw form it is an ASCII, or text, file. First, you will interpolate elevations on a topographic
In this lesson you will create a Digital Elevation Model (DEM). A DEM is a gridded array of elevations. In its raw form it is an ASCII, or text, file. First, you will interpolate elevations on a topographic
511 - Creating Structural Frame Designs
 4 th Generation VLC courtesy of Edison2 511 - Creating Structural Frame Designs Rahul Kulkarni, Manager, Product Design, Pune Center, Siemens PLM Software #SEU13 Agenda: 511 - Creating Structural Frame
4 th Generation VLC courtesy of Edison2 511 - Creating Structural Frame Designs Rahul Kulkarni, Manager, Product Design, Pune Center, Siemens PLM Software #SEU13 Agenda: 511 - Creating Structural Frame
Requirements for Building Application Submission
 THE DEVELOPMENT CONTROL AND PLANNING BOARD P O Box 597 Phone: 869 465-2277 Bladen Commercial Development Fax: 869 465-5842 Basseterre, St. Kitts Email: phyplskb@caribsurf.com To: Architects, Designers
THE DEVELOPMENT CONTROL AND PLANNING BOARD P O Box 597 Phone: 869 465-2277 Bladen Commercial Development Fax: 869 465-5842 Basseterre, St. Kitts Email: phyplskb@caribsurf.com To: Architects, Designers
How To Model A Shallow Foundation
 Finite Element Analysis of Elastic Settlement of Spreadfootings Founded in Soil Jae H. Chung, Ph.D. Bid Bridge Software Institute t University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA Content 1. Background 2.
Finite Element Analysis of Elastic Settlement of Spreadfootings Founded in Soil Jae H. Chung, Ph.D. Bid Bridge Software Institute t University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA Content 1. Background 2.
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the SolidWorks Simulation finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2012 SolidWorks Simulation Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the SolidWorks Simulation finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response
Generative Drafting. Page 1 1997 2001 DASSAULT SYSTEMES. IBM Product Lifecycle Management Solutions / Dassault Systemes
 Generative Drafting Page 1 Tutorial Objectives Description This Tutorial is an introduction to Generative Drafting. Message To show how CATIA V5 allows the user to automatically generate associative drafting
Generative Drafting Page 1 Tutorial Objectives Description This Tutorial is an introduction to Generative Drafting. Message To show how CATIA V5 allows the user to automatically generate associative drafting
