STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
|
|
|
- Rolf McKinney
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009
2 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong to? -They grow slowly -They notice many changes in their body -They look after their children -They have got white hair -They like to become less dependent -At around one year, they start to talk -It is the first stage of life -Friends become very important -They don t grow anymore
3 3. Make a list of three things to show how you have changed since you were a baby. a) When I was 3 years old, I couldn t..., now I can... b) When I was eight, I was..., now I am... c) When I was three months old, I didn t..., now I Think of people you know for the different stages: NAME STAGE 5. What do you think are the most important things you have learnt today?
4 PUBERTY: PHYSICAL CHANGES HANDOUT 2 1. Discuss with a classmate if the changes below occur in boys, in girls or in both: CHANGES BOYS GIRLS BOTH 1. You get hair in your pubic area and under your arms. 2. You start to produce sperm. 3. You will have more erections. 4. Your body shape changes and you get taller. 5. Your voice deepens or breaks. 6. Your penis gets longer and your testicles get bigger. 7. Your sweat glands start producing body odour. 8. Your breasts develop. 9. You get taller and heavier. 10. You put on weight. 11. Your periods start. 12. You get hair on your face and on your legs. 13. Your internal and external organs start to grow. 14. You get acne
5 Now visit the website: and find out what are the changes that occur at puberty. 2.Look at the pictures below. Use the numbers from the chart above to label the parts of the body that change at puberty.
6 3. Get in groups and look up in the books other changes that you think are interesting. Write down and discuss them with the rest of the class. WE HAVE FOUND OUT THAT BOYS GIRLS 4. Is there anything else you would like to know? If so, write your question on a piece of paper and put it into the class letter box. The questions can be anonymous. *I WOULD LIKE TO KNOW. *IS IT TRUE THAT..? 5. Write five things you have learnt in this session
7 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM HANDOUT 3 1. Match with the words below: penis vas deferens testicles urethra scrotum - seminal vesicles prostate gland - MASCULINE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS
8 2. Complete the chart with the words above. *They produce the male sex cells (sperms). *These tubes lead the sperm towards the penis. *They produce a liquid which gives the sperm energy. *It produces a fluid which helps the sperm to move *It has two functions: one, to carry the urine and two, it carries the semen(1) outside the penis *It is the male organ through which urine and sperm go out of the body *It is the bag that contains the testicles (1) Semen. It is the mixture of sperms and the fluids produced by the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland.
9 HANDOUT 4 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. Complete the picture with the words below: External female sex organs: Vagina opening urinary opening - vulva Internal female sex organs: Ovaries fallopian tubes uterus cervix - vagina EXTERNAL FEMININE ORGANS
10 INTERNAL FEMININE ORGANS 2. Complete the chart with the words above. EXTERNAL FEMALE SEX ORGANS *This is the opening of the urethra. It is where woman s urine comes out. *This is what the female genitals are called. *It is the opening that leads to the vagina.
11 INTERNAL FEMALE SEX ORGANS *They are the tubes at the top of the ovaries *It is where babies grow during pregnancy. *They produce the ovums. *It is a passageway between the uterus and the vagina. *It connects the uterus with the outside of the body.
12 OVULATION AND MENSTRUATION HANDOUT 5 1. Before watching the video Woman ovulation process, try to order the statements below -The ovum passes into the fallopian tubes. -The lining of the uterus thickens to receive a fertilised ovum. -Each month an ovum is released in one of the ovaries. -If the ovum is not fertilised, the lining and the ovum pass out of the woman s body. *When the egg passes from the ovaries to the fallopian tubes, it is called: *When the lining l of the uterus and the ovum go out the woman s body, it is called: Now, watch the video and check your answers.
13 2. Draw the cycle from the ovulation to the t menstruation. Then, explain each picture. Use the support to help you remember the stages. OVARY FALLOPIAN TUBES UTERUS CERVIX VAGINA 1) 2) 3) 4)
14 3. Now watch the video 28 days. Tick the statements that are true and correct the wrong statements: The menstrual cycles takes 18 days At the pre-ovulation stage girls feel bad. The ovum travels through the fallopian tubes. The lining of the uterus has no change during the cycle. At the pre-menstrual stage, girls eat a lot of sweet food, they are angry, they are tired, they are sensitive., they have headache and cramps. At the menstrual phase the ovum and the lining of the uterus pass out through the vagina outside. The girls have their menstruation. 4. Find out: a) When do girls start having menstruation? b) How long does it take? c) How long does menstruation last?
15 HANDOUT 6 WHERE DO WE COME FROM? 1. Listen to the story Where Willy went 2. Now, in pairs,, answer these questions: What are sperms? Where do they live? What is the prize for the sperm? How many sperms get the prize? What do you think is the journey shown in Map 1: Mr Browne? What do you think is the journey shown in Map 2: Mrs Browne? What happens when the sperm gets to the ovum? 3. Now watch the video Human Sexuality: Conception.
16 4. Write the path the sperm travels until it gets out of the man s body. Chain of Events Testicles Write a paragraph using the chain words in order to describe what happens at each step. Vas deferens 2 Semen-producing Glands Urethra Penis
17 5. Write the path the sperm travels until it gets to the ovum Chain of Events Vagina Write a paragraph using the chain words in order to describe what happens at each step. Cervix Uterus Fallopian tubes Ovum
18 PREGNANCY - 1 HANDOUT 7 1. Watch the video Human reproduction: fertilization ion and fetal development. Read the statements below and choose the correct answer: A) As the embryo divides, it continues its journey along: a) The fallopian tubes b) The ovary c) The cervix B) The embryo reaches the uterus: a) 1 week after fertilization b) 2 days after fertilization c) 2 weeks after fertilization C) When the embryo arrives at the uterus: a) The uterus is covered with a lining to receive the embryo b) The lining has disappeared c) The embryo goes towards the vagina D) The embryo consists of: a) 2 cells b) 1000 cells c) 100 cells E) The embryo gets attached to: a) The uterus b) The ovary c) The vagina F) At two months: a) The embryo is called a pea b) The embryo is called a foetus c) The embryo has not changed
19 G) The placenta is: a) The name of the embryo after 3 months b) The union of the ovum and the sperm c) A group of vessels and cells H) The umbilical cord: (2 correct answers) a) Joins the foetus to the placenta b) Joins the ovum and the sperm c) Will become the belly button 2. Complete the chart below with the missing information: WHAT IS THE.? DEFINITION WHAT IS ITS FUNCTION? EMBRYO FOETUS PLACENTA AMNIOTIC SAC UMBILICAL CORD
20 3. Label the pictures below with the words in the chart and say if they are an embryo or a foetus Placenta (x2) amniotic sac (x2) umbilical cord (x2) foetus - embryo It is a It is a.
21 4. Can you tell the differences between an embryo and a foetus? CHARACTERISTICS EMBRYO FOETUS
22 PREGNANCY - 2 HANDOUT 8. TRIMESTER MONTH.. (.-..WEEKS) HOW BIG IS IT? It is. cm long WHAT DOES IT LOOK LIKE? It is similar to WHAT IS IT LIKE? It is.. WHAT CAN IT DO? It can.. Other information
23 HANDOUT 9 WE ARE PARENTS NOW! *What is your child s name? *When was he/she born? *How old is he/she? *Where was he/she born? *What do you need to take care of him/her? *What is your role as a mother? *What is your role as a father?
24 SELF-ASSESSMENT HANDOUT 10 I can name all the stages of human life cycle I can say the characteristics of the different stages of human life cycle I know what physical changes boys have at puberty I know what physical changes girls have at puberty I can label the parts of the male reproductive system I can label the parts of the female reproductive system I can explain the menstrual cycle I know how and when fertilization happens I know the differences between an embryo and a foetus I can order the stages of pregnancy I know how to work in groups I participate in class I use English in class
25
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
Here we will talk about:
 Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Some activities need additional guidance, or can be expanded:
 GROWING UP This section includes: Teachers Notes Baby to adult Growing up What we need as we grow This is a toddler These are teenagers This is an adult These are older people or elderly people Body changes
GROWING UP This section includes: Teachers Notes Baby to adult Growing up What we need as we grow This is a toddler These are teenagers This is an adult These are older people or elderly people Body changes
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Some activities need additional guidance, or can be expanded: These are your testicles, this is where semen and sperm is made.
 P UBERTY This section includes: Teachers Notes changes - Female changes - Male Inside a boys body Inside a girls body Inside our bodies Boys growing up Girls growing up Hormones Coping with emotions Being
P UBERTY This section includes: Teachers Notes changes - Female changes - Male Inside a boys body Inside a girls body Inside our bodies Boys growing up Girls growing up Hormones Coping with emotions Being
Sexuality Education Lesson Plan #1
 Mary Wenstrom Sexuality Education Lesson Plan #1 Health Education Grade 10 Content Area: Sexuality Education Health Literacy: Effective Communicator and Critical Thinker Life Skills: Understanding Adolescence,
Mary Wenstrom Sexuality Education Lesson Plan #1 Health Education Grade 10 Content Area: Sexuality Education Health Literacy: Effective Communicator and Critical Thinker Life Skills: Understanding Adolescence,
II. III. 2004 Core Knowledge National Conference, Grade Level, (Unit Name Here) 1
 Teaching A Touchy Topic: Life Cycles and Reproduction Grade Level: Fifth Grade Written by: Kimberly Ruckh, Linda Cambra, Dallas Bankston; Challenge Charter School, Glendale, Az. Length of Unit: Five Lessons
Teaching A Touchy Topic: Life Cycles and Reproduction Grade Level: Fifth Grade Written by: Kimberly Ruckh, Linda Cambra, Dallas Bankston; Challenge Charter School, Glendale, Az. Length of Unit: Five Lessons
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-4.3:
 PUBERTY CHANGES Lesson 2 GRADE 4 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-4.3: Describe physical, emotional and social changes that occur during puberty; e.g., menstruation, secondary sexual characteristics, changing identity
PUBERTY CHANGES Lesson 2 GRADE 4 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-4.3: Describe physical, emotional and social changes that occur during puberty; e.g., menstruation, secondary sexual characteristics, changing identity
Unit #5 Human Growth and Development 6 th Grade - Chapter 7, 8 7 th Grade - Chapter 12 8 th Grade - Chapter 16, 17
 8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
FAMILY LIFE EDUCATION ACPS Fifth Grade
 Table of Contents UNIT I FAMILY...2 Relatives and Family Friends...2 Similarities and Differences among Families...2 UNIT II PERSONAL AND SEXUAL SAFETY... 3 Sexual Safety Good and Bad Touching... 3 UNIT
Table of Contents UNIT I FAMILY...2 Relatives and Family Friends...2 Similarities and Differences among Families...2 UNIT II PERSONAL AND SEXUAL SAFETY... 3 Sexual Safety Good and Bad Touching... 3 UNIT
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-6.3:
 GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
Growing up what s it all about?
 4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Puberty is the name given to the physical changes that happen between childhood and adulthood
 LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
Agenda: 1. Help students learn about health and major body systems. 2. Introduce the reproductive system
 FOURTH GRADE BODY SYSTEMS LESSON PLAN STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student will learn: That health has three parts: physical, mental and social About major body systems including an introduction to
FOURTH GRADE BODY SYSTEMS LESSON PLAN STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student will learn: That health has three parts: physical, mental and social About major body systems including an introduction to
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Let s talk aboutpuberty
 Let s talk aboutpuberty A booklet about growing up for young people who have a learning disability This booklet will tell you about what happens to your body as you grow up. This is called Puberty. A2
Let s talk aboutpuberty A booklet about growing up for young people who have a learning disability This booklet will tell you about what happens to your body as you grow up. This is called Puberty. A2
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up. (for boys and girls)
 What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3
 Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE
 Alabama Department of Public Health Mother s Milk Education Activity Package for Grades K-12 Level: 5 Adapted from New York Department of Health LEARNING OBJECTIVE FOR LEVEL 5 NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE Students
Alabama Department of Public Health Mother s Milk Education Activity Package for Grades K-12 Level: 5 Adapted from New York Department of Health LEARNING OBJECTIVE FOR LEVEL 5 NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE Students
associated with puberty for boys and girls.
 Lesson 5 Puberty Overview In this informational lesson, students learn about puberty. Small groups brainstorm physical, emotional and social changes they think occur The class discusses and evaluates the
Lesson 5 Puberty Overview In this informational lesson, students learn about puberty. Small groups brainstorm physical, emotional and social changes they think occur The class discusses and evaluates the
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3:
 GRADE 7-9 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT QUICK LESSON SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Quick Lesson GRADE 7-9 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual
GRADE 7-9 SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT QUICK LESSON SEXUAL DEVELOPMENT Quick Lesson GRADE 7-9 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-7.3: Examine the human reproductive process and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual
identify the physical, interpersonal, and emotional aspects of healthy human beings
 Lesson Four Title: Theme: Time: Materials: You, Your Body and Puberty Puberty for Boys and Girls 110 minutes External Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz External
Lesson Four Title: Theme: Time: Materials: You, Your Body and Puberty Puberty for Boys and Girls 110 minutes External Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz External
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Introduction to puberty
 Introduction to puberty Objective: Structure: Time: Materials: Participants will describe some of the common external changes associated with puberty. Presentation by educator with large group discussion.
Introduction to puberty Objective: Structure: Time: Materials: Participants will describe some of the common external changes associated with puberty. Presentation by educator with large group discussion.
SEXUALITY EDUCATION FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES
 SEXUALITY EDUCATION FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES AN INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL FOR PARENTS or CAREGIVERS OF AND INDIVIDUALS WITH DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES SEXUALITY ACROSS THE
SEXUALITY EDUCATION FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES AN INSTRUCTIONAL MANUAL FOR PARENTS or CAREGIVERS OF AND INDIVIDUALS WITH DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES SEXUALITY ACROSS THE
That being said, consider the following as you decide whether or not a vasectomy is your best option for birth control.
 Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 3 to 5 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Grades 3 to 5 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
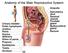 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Puberty is the bridge between childhood and adulthood.
 Puberty is the bridge between childhood and adulthood. Puberty can start as early as 8 or 9 years old or as late as 18 or 19 years old. The average age for girls is 10.5 years old. The average age for
Puberty is the bridge between childhood and adulthood. Puberty can start as early as 8 or 9 years old or as late as 18 or 19 years old. The average age for girls is 10.5 years old. The average age for
How does it all work?
 PREGNANCY How does it all work? How does it all work? reproductive organs bladder seminal vesicle prostate gland sperm duct epididymis testicle urethra fallopian tube uterus (womb) fallopian tube bladder
PREGNANCY How does it all work? How does it all work? reproductive organs bladder seminal vesicle prostate gland sperm duct epididymis testicle urethra fallopian tube uterus (womb) fallopian tube bladder
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
How Your Fertility Works
 How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Boys and. about body changes and other stuff! 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 1 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM
 Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 1 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 2 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM In
Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 1 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 2 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM In
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary
 X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Boys and Puberty. about body changes and other stuff!
 Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! In this booklet, we ve got together a heap of information so that you can be informed about the important stuff.
Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! In this booklet, we ve got together a heap of information so that you can be informed about the important stuff.
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The six life stages In the human lifespan, there are six life stages. You should know the names of each life stage and what ages each stage covers.
 The six life stages In the human lifespan, there are six life stages. You should know the names of each life stage and what ages each stage covers. 5 Infancy (0- years) Adolescence (9-8 years) Age in years
The six life stages In the human lifespan, there are six life stages. You should know the names of each life stage and what ages each stage covers. 5 Infancy (0- years) Adolescence (9-8 years) Age in years
Timing is everything. Ovulation Tracking. Patient Information Booklet
 Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion.
 Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
ALL ABOUT GROWING UP
 ALL ABOUT GROWING UP INTRODUCTION Sexuality is not just about the act of sex but about the values, beliefs, experiences and ideas a person has. Puberty is part of sexuality. It is the process of social,
ALL ABOUT GROWING UP INTRODUCTION Sexuality is not just about the act of sex but about the values, beliefs, experiences and ideas a person has. Puberty is part of sexuality. It is the process of social,
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
The Pregnancy Book Your complete guide to:
 The Pregnancy Book Your complete guide to: A healthy pregnancy Labour and childbirth The first weeks with your new baby The Department of Health would like to thank all those involved in shaping the updated
The Pregnancy Book Your complete guide to: A healthy pregnancy Labour and childbirth The first weeks with your new baby The Department of Health would like to thank all those involved in shaping the updated
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
WHERE DO BABIES COME FROM? Written by Margaret Sheffield Illustrated by Sheila Bewley
 WHERE DO BABIES COME FROM? Written by Margaret Sheffield Illustrated by Sheila Bewley ABOUT THE AUTHORS Margaret Sheffield was born in 1940 in New Zealand, where she received a Science Degree from the
WHERE DO BABIES COME FROM? Written by Margaret Sheffield Illustrated by Sheila Bewley ABOUT THE AUTHORS Margaret Sheffield was born in 1940 in New Zealand, where she received a Science Degree from the
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health October-December 2014 Let s Learn the Basics about Cervical Cancer What is cancer? The body is made up of millions and millions of living cells.
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
INTRODUCTION A PARTICIPATORY PROGRAMME ON SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FOR WOMEN AND GIRLS A TOOLKIT FOR FACILITATORS
 INTRODUCTION A PARTICIPATORY PROGRAMME ON SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FOR WOMEN AND GIRLS A TOOLKIT FOR FACILITATORS 01 02 Acknowledgements This toolkit was made possible through the financial support
INTRODUCTION A PARTICIPATORY PROGRAMME ON SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH FOR WOMEN AND GIRLS A TOOLKIT FOR FACILITATORS 01 02 Acknowledgements This toolkit was made possible through the financial support
Family Planning for Women and Couples following Fistula Repair
 Family Planning for Women and Couples following Fistula Repair Fistula Care at EngenderHealth 440 Ninth Avenue, 13th Floor New York, NY, USA 10001 Tel: 212-561-8000 E-mail: [email protected]
Family Planning for Women and Couples following Fistula Repair Fistula Care at EngenderHealth 440 Ninth Avenue, 13th Floor New York, NY, USA 10001 Tel: 212-561-8000 E-mail: [email protected]
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
contraception contraception contraception contracepti contraception contraception contraception aception contraception contraception contraception
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK
 Department of Health PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK This section describes week by week the way that your baby develops during your pregnancy. During the 40 weeks or so of pregnancy, your baby will grow from a
Department of Health PREGNANCY WEEK BY WEEK This section describes week by week the way that your baby develops during your pregnancy. During the 40 weeks or so of pregnancy, your baby will grow from a
Gonorrhoea. Looking after your sexual health
 Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Questions, Questions, Questions
 1 2 Puberty! Puberty is the biological transition from childhood to adulthood. Your body is changing to make it possible to have a baby in the future. Puberty affects your body, your thoughts and your
1 2 Puberty! Puberty is the biological transition from childhood to adulthood. Your body is changing to make it possible to have a baby in the future. Puberty affects your body, your thoughts and your
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Puberty in Adolescent Males Ready, Set, Develop
 Puberty in Adolescent Males Ready, Set, Develop By: Carol Friedl Reviewed by: Daniel Klein PhD, MSW When it comes to puberty; how much do you know? Have you learned anything from school? Can you talk to
Puberty in Adolescent Males Ready, Set, Develop By: Carol Friedl Reviewed by: Daniel Klein PhD, MSW When it comes to puberty; how much do you know? Have you learned anything from school? Can you talk to
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
it right? activity (page 4) to highlight ethical issues associated with IVF
 IN VITRO FERTILIZATION I V F In some cases, a sperm is directly injected into an egg IVF: THE MEETING OF SPERM AND EGG IN GLASS Louise Brown, the first test tube baby was born in 1978. Since then, there
IN VITRO FERTILIZATION I V F In some cases, a sperm is directly injected into an egg IVF: THE MEETING OF SPERM AND EGG IN GLASS Louise Brown, the first test tube baby was born in 1978. Since then, there
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo
 Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo 10 Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 379-380 in Science
Science 10-Biology Activity 15 The Development of the Human Embryo 10 Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 379-380 in Science
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
THE WELL. Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices WOMAN CENTRE
 THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
progestog progestogen stogen-only pill progestogen progestogen-only pill he progestogen-only pill progestogen-onl progestogen-o the progestogenonly
 your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
