progestog progestogen stogen-only pill progestogen progestogen-only pill he progestogen-only pill progestogen-onl progestogen-o the progestogenonly
|
|
|
- Tracey Sanders
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge pill gestogenly pill progestogen progesto progestog he progestogen-only pill the progestogen-only pill progestogen-onl progestog estogen progestogen-o progestogen
2 2 The progestogenonly pill (POP) This pill contains a progestogen hormone which is similar to the natural progesterone women produce in their ovaries. Progestogen-only pills (POPs) contain different types of progestogens. POPs containing desogestrel will be named specifically where relevant in this booklet. If you are not sure what type of progestogen is in your POP check the Contents How effective is the POP?...3 How does the POP work?...3 Where can I get the POP?...4 Can anyone use the POP?...4 What are the advantages of the POP?...5 What are the disadvantages of the POP?...5 Are there any risks?...5 How do I start the POP?...6 I ve just had a baby. Can I use the POP?...7 Can I use the POP after a miscarriage or abortion?...7 How do I take the POP?...7 What if I forget to take it on time?...7
3 3 patient information leaflet inside your pack or ask your doctor or nurse. POPs are different to combined pills because they do not contain any estrogen. How effective is the POP? How effective any contraceptive is depends on how old you are, how often you have sex and whether you follow the instructions. If 100 sexually active women don t use any contraception, 80 to 90 will become pregnant in a year. If taken according to instructions the POP is over 99 per cent effective. This means that less than one woman in 100 will get pregnant in a year. If the POP is not taken according to instructions, more women will become pregnant. How does the POP work? The POP works in a number of ways. O The main action of desogestrel POPs is to stop What if I want to change to a different pill?...7 What should I do if I am sick or have diarrhoea?...8 If I take other medicines will it affect my POP?...8 What should I do if I think I m pregnant?...8 What do I do if I miss a pill?...9 I want to have a baby. Can I try to get pregnant as soon as I stop taking the POP?...9 How often do I need to see a doctor or nurse?...10 Where can I get more information and advice?...10 Emergency contraception...11 Sexually transmitted infections...11 A final word...12
4 4 your ovaries releasing an egg (ovulation). Other types of POP sometimes stop you releasing an egg. O All POPs work by thickening the mucus from your cervix. This makes it difficult for sperm to move through it and reach an egg. O All POPs make the lining of your uterus (womb) thinner so it is less likely to accept a fertilised egg. Where can I get the POP? You can go to a contraception or sexual health clinic, or general practice. If you prefer not to go to your own general practice, or if they don t provide contraceptive services, they can give you information about another practice or clinic. All treatment is free and confidential. You don t need to have a vaginal or breast examination or cervical screening test when you are first prescribed the POP. Can anyone use the POP? Most women can use the POP but a doctor or nurse will ask you about your own and your family s medical history. Do mention any illness or operations you have had. Some of the conditions which may mean you should not use the POP are: O you think you might already be pregnant O you take certain medicines. You have now or had in the past: O heart disease or a stroke O disease of the liver O systemic lupus erythematosus O current breast cancer or breast cancer within the last five years. If you are healthy and there are no medical reasons for you not to take the POP, you can take it until your menopause or until you are 55 years.
5 5 What are the advantages of the POP? Some of the advantages of the POP are: O you can use it if you are breastfeeding O it is useful if you cannot take estrogens, like those found in the combined pill, contraceptive patch or contraceptive vaginal ring O you can use it at any age, but it is especially useful if you smoke and are 35 or over O it may help with premenstrual symptoms and painful periods. What are the disadvantages of the POP? There are no serious side effects with the POP. However: O It is common for your periods to change while you are taking the POP. Bleeding may be irregular, light, more frequent, last longer or stop altogether. This may settle down and is not harmful. If you have any concerns, see your doctor or nurse. Changing to a different POP may help. O The POP does not protect you against sexually transmitted infections, so you may need to use condoms as well. O You have to remember to take the pill at the same time every day. O You may get some side effects when you first start taking the POP, such as spotty skin, breast tenderness, weight change and headaches. These may stop within a few months. Are there any risks? The POP is a very safe pill to take but there are some risks.
6 6 O Some women may develop small fluid-filled cysts on their ovaries. These are not dangerous and do not usually need to be removed. Often there are no symptoms, but some women may have pelvic pain. These cysts usually disappear without treatment. O Research about the risk of breast cancer, cervical cancer and hormonal contraception is complex and contradictory. Research suggests that users of all hormonal contraception appear to have a small increase in risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer compared to non-users of hormonal contraception. O If you do become pregnant while you are using the POP there is a risk of you having an ectopic pregnancy (see page 9). How do I start the POP? You can start the POP any time in your menstrual cycle if it is certain you are not pregnant. If you start the POP on the first day of your period you will be protected from pregnancy immediately. You can also start the POP up to and including the fifth day of your period and you will be protected from pregnancy immediately. However, if you have a short menstrual cycle with your period coming every 23 days or less, starting the POP as late as the fifth day of your period may not provide you with immediate contraceptive protection. This is because you may ovulate early in your menstrual cycle. You may wish to talk to your doctor or nurse about this and whether you need to use an additional contraceptive method for the first two days. If you start the POP at any other time in your menstrual cycle, use another contraceptive method, such as condoms, for the first two days of pill-taking.
7 7 I ve just had a baby. Can I use the POP? The POP can be started any time after the birth. If you start the POP after day 21 you will need to use additional contraception for two days. You can breastfeed while you are taking the POP. A tiny amount of hormone enters your breast milk, but research has shown this will not harm your baby. Can I use the POP after a miscarriage or abortion? You can start taking the POP immediately after a miscarriage or abortion. You will be protected from pregnancy immediately. How do I take the POP? When taking your first pill choose a convenient time to take it. This can be any time of the day. Once you have chosen a time you must then take one POP each day at this same time until you finish all the pills in the pack. You then start a new pack the next day so there are no breaks between packs. What if I forget to take it on time? For your pill to work it is important not to take it more than three hours (12 hours for pills containing desogestrel) after your chosen time. If you remember later than this, see page 9. What if I want to change to a different pill? If you are changing to another POP (or from the combined pill) you may be advised to start the new pill immediately or start the day after you take your last pill. Do not have a break between packs. There is no need to wait for your period. You will
8 8 then continue to have protection from pregnancy. What should I do if I am sick or have diarrhoea? If you vomit within two hours of taking the POP, it will not have been absorbed by your body. Take another pill as soon you feel well enough. As long as you are not sick again your contraception will not be affected. Take your next pill at the normal time. If you continue to be sick, seek advice. If you have very severe diarrhoea that continues for more than 24 hours, this may make the POP less effective. Keep taking your pill at the normal time, but treat each day that you have severe diarrhoea as if you had missed a pill and follow the missed pill instructions in the box on page 9. If I take other medicines will it affect my POP? If you are given medicines by a doctor, nurse or hospital always say you are taking the POP. Commonly used antibiotics do not affect the POP. Medicines such as some of those used to treat epilepsy, HIV and TB and the complementary medicine St John s Wort may make it less effective. These types of drugs are called enzyme-inducers. If you take these medicines, talk to your doctor or nurse about how to take the POP - you may need to use a different method of contraception. What should I do if I think I m pregnant? If you took all your pills correctly and you didn t have an upset stomach or take any other medicines which might affect the POP, then it is unlikely you are pregnant. Continue to take your pills as normal. There is no evidence that if you
9 9 What do I do if I miss a pill? If you are more than three hours* late O Take a pill as soon as you remember. If you have missed more than one, only take one. O Take your next pill at the usual time. This may mean taking two pills in one day. This is not harmful. O You are not protected against pregnancy. Continue to take your pills as usual but use an additional method of contraception, such as condoms, for the next two days. O If you have had unprotected sex during this time you may need emergency contraception. Seek advice immediately. If you are less than three hours* late O Take a pill as soon as you remember, and take the next one at the usual time. You are protected from pregnancy. *12 hours if you are taking a desogestrel POP take the POP when you are pregnant it will harm the baby. If you are worried ask your doctor or nurse for advice or do a pregnancy test. Taking the POP does not affect a pregnancy test. If you do become pregnant there is a risk of ectopic pregnancy (where the pregnancy develops outside your uterus, usually in a fallopian tube). Seek medical advice as soon as possible if you have a sudden or unusual pain in your lower abdomen (this might be a warning sign of an ectopic pregnancy) or if you think you might be pregnant. I want to have a baby. Can I try to get pregnant as soon as I stop taking the POP? You can try to get pregnant as soon as you stop taking the POP. You can stop taking the pill at any time. Ideally you should wait for one natural
10 10 period before trying to get pregnant, so you will need to use another method of contraception, such as condoms. This means the pregnancy can be dated more accurately and you can start pre-pregnancy care such as taking folic acid and stopping smoking. You can ask your doctor or nurse for advice. Don t worry if you get pregnant sooner, it will not harm the baby. How often do I need to see a doctor or nurse? When you first start the POP you can be given up to a 12 months supply. After that you should go back to the doctor or nurse if you have any problems or concerns and when you need to get a new supply of the POP. Where can I get more information and advice? The Sexual Health Information Line provides confidential advice and information on all aspects of sexual health. The number is and the service is available from Monday to Friday from 9am - 8pm and at weekends from 11am - 4pm. For additional information on sexual health visit Information for young people can be found at Clinics To locate your closest clinic: O Use Find a Clinic at O Download FPA s Find a Clinic app for iphone or Android. You can find details of general practices and pharmacies in England at and in Wales
11 11 at In Scotland you can find details of general practices at and in Northern Ireland at Emergency contraception If you have had sex without contraception, or think your method might have failed, there are different types of emergency contraception you can use. O An emergency contraceptive pill containing levonorgestrel can be taken up to three days (72 hours) after sex. More effective the earlier it is taken after sex. Available with a prescription or to buy from a pharmacy. There are different brands but they all work the same way. O An emergency contraceptive pill containing ulipristal acetate can be taken up to five days (120 hours) after sex. Available with a prescription or to buy from a pharmacy. ellaone is the only brand in the UK. O An IUD - can be fitted up to five days after sex, or up to five days after the earliest time you could have released an egg (ovulation). Ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist about getting emergency pills in advance, just in case you need them. Sexually transmitted infections Most methods of contraception do not protect you from sexually transmitted infections. Male and female condoms, when used correctly and consistently, can help protect against sexually transmitted infections. If you can, avoid using spermicidally lubricated condoms. The spermicide commonly contains a chemical called Nonoxinol 9, which does not protect against HIV and may even increase the risk of infection.
12 A final word This booklet can only give you general information about the progestogen-only pill. The information is based on evidence-guided research from the World Health Organization and The Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. All methods of contraception come with a Patient Information Leaflet which provides detailed information about the method. Remember contact your doctor, practice nurse or a sexual health clinic if you are worried or unsure about anything. The Sexual Health Line is provided by the Department of Health. This booklet is produced by the sexual health charity FPA, registered charity number Limited liability company registered in England, number FPA does not run the Sexual Health Line. FPA. Printed June Crown Copyright Public Health England. ISBN The information in this booklet was accurate at the time of going to print. Booklets are reviewed regularly. Next edition available in If you would like information on the evidence used to produce this booklet or would like to provide us with feedback about this booklet [email protected] Ref: 1002
implant contraceptiv contraceptive contraceptive raceptiv contraceptive implant contraceptive contraceptive ontraceptive implant ontraceptive im
 your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
injections injections injections injections injections injection injections injections injections tions njections injections injections injections
 your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
ency emergency contra-
 your guide to emergency contraception Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you emergency cont gency contrace emergency contraception ency emergency contra- emergen mergency contraception
your guide to emergency contraception Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you emergency cont gency contrace emergency contraception ency emergency contra- emergen mergency contraception
the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
vagina vaginal r vaginal ring vaginal vaginal ring aginal ring vaginal ring vaginal ring vaginal ring the contraceptive vaginal rin vaginal ring
 your guide to the contraceptive vaginal ring Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you vagina vaginal ring vaginal r vaginal ring vaginal ring vaginal rin vaginal aginal ring
your guide to the contraceptive vaginal ring Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you vagina vaginal ring vaginal r vaginal ring vaginal ring vaginal rin vaginal aginal ring
patch contracep raceptiv contraceptive patch contraceptive patch contraceptiv patch contraceptive patch tch ontraceptive atch contraceptive p
 your guide to the contraceptive patch Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive pat contraceptive patch contraceptive patch ceptive patc atch contrace contracept
your guide to the contraceptive patch Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive pat contraceptive patch contraceptive patch ceptive patc atch contrace contracept
after you ve had you after you ve had your baby after you ve after you ve had your baby fter you ve had your baby after contraceptive choices
 your guide to contraceptive choices after you ve had your baby Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you after you ve had you ve had your bab after you ve had your baby after
your guide to contraceptive choices after you ve had your baby Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you after you ve had you ve had your bab after you ve had your baby after
l family plan natural natural family p natural family planning ily natural family plannin natural fami atural family planning your guide to
 your guide to natural family planning Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you natural family pla al family plannin natural family planning natural family plann atural fam natural
your guide to natural family planning Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you natural family pla al family plannin natural family planning natural family plann atural fam natural
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD the IUD. the IUD. the the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD.
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
contraception contraception contraception contracepti contraception contraception contraception aception contraception contraception contraception
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
pregnant pregnant pregnant pregnant pregnan pregnant ant pregnant pregnant pregnant egnant pregnant pregnant pregnant pregnant pregna
 Pregnant and don t know what to do? A guide to your options pregna regnant ant pregnan egnant 2 3 Are you but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about the options available
Pregnant and don t know what to do? A guide to your options pregna regnant ant pregnan egnant 2 3 Are you but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about the options available
abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion on abortio abortion ortion abortion abortion abortion abortion abortio
 Abortion Your questions answered abortio bortion ion ortion on abortio 2 Are you pregnant but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about your pregnancy choices? Unplanned pregnancy
Abortion Your questions answered abortio bortion ion ortion on abortio 2 Are you pregnant but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about your pregnancy choices? Unplanned pregnancy
Trichomonas vaginalis. Looking after your sexual health
 Trichomonas vaginalis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is sometimes referred to as trichomonas or trichomoniasis,
Trichomonas vaginalis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is sometimes referred to as trichomonas or trichomoniasis,
Gonorrhoea. Looking after your sexual health
 Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Diary Card. Cerazette. Keeping a record. For women prescribed Cerazette. How do I find out more? www.cerazette.co.uk
 Cerazette Keeping a record How do I find out more? You can ask for more information on Cerazette at your doctor s surgery or at family planning clinics. A diary card is attached. We suggest you keep a
Cerazette Keeping a record How do I find out more? You can ask for more information on Cerazette at your doctor s surgery or at family planning clinics. A diary card is attached. We suggest you keep a
condoms condoms male and fe male and female cond male and female condoms male and female male an male and female male and condoms
 your guide to male and female condoms Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you and male condoms female and female condom con dom male and female male an ale and female condoms
your guide to male and female condoms Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you and male condoms female and female condom con dom male and female male an ale and female condoms
Chlamydia. Looking after your sexual health
 Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
HIV. Looking after your sexual health
 HIV Looking after your sexual health 2 HIV HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Once someone is infected with HIV the virus will remain in their body for the rest of their life. There is currently
HIV Looking after your sexual health 2 HIV HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Once someone is infected with HIV the virus will remain in their body for the rest of their life. There is currently
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
HPV is very common and usually clears up on its own
 What is HPV? All cervical cancers are linked to a very common virus called the human papillomavirus or HPV. HPV usually doesn t cause any harm and most people will be infected with it at some point in
What is HPV? All cervical cancers are linked to a very common virus called the human papillomavirus or HPV. HPV usually doesn t cause any harm and most people will be infected with it at some point in
Combination Birth Control Pills - FAQ
 Combination Birth Control Pills - FAQ How does the birth control pill work? prevents ovulation thickens cervical mucus, which makes it hard for sperm to enter the uterus thins the lining of the uterus,
Combination Birth Control Pills - FAQ How does the birth control pill work? prevents ovulation thickens cervical mucus, which makes it hard for sperm to enter the uterus thins the lining of the uterus,
Genital warts. Looking after your sexual health
 Genital warts Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital warts Genital warts are the most common viral sexually transmitted infection (STI). They are caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV) which can
Genital warts Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital warts Genital warts are the most common viral sexually transmitted infection (STI). They are caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV) which can
Oral sex. Looking after your sexual health
 Oral sex Looking after your sexual health 2 What is this booklet about? This booklet gives you information about oral sex, the risk of getting and passing on sexually transmitted infections through oral
Oral sex Looking after your sexual health 2 What is this booklet about? This booklet gives you information about oral sex, the risk of getting and passing on sexually transmitted infections through oral
Syphilis. Looking after your sexual health
 Syphilis Looking after your sexual health 2 Syphilis Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is not as common as some sexually transmitted infections but if left untreated it can cause very
Syphilis Looking after your sexual health 2 Syphilis Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is not as common as some sexually transmitted infections but if left untreated it can cause very
Pubic lice and Scabies. Looking after your sexual health
 Pubic lice and Scabies Looking after your sexual health 2 Pubic lice and Scabies Pubic lice are tiny parasitic insects that live in coarse body hair, such as pubic hair. They are yellow-grey and about
Pubic lice and Scabies Looking after your sexual health 2 Pubic lice and Scabies Pubic lice are tiny parasitic insects that live in coarse body hair, such as pubic hair. They are yellow-grey and about
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
This is Jaydess. Patient Information. What is Jaydess? How does Jaydess work?
 , Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
, Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion.
 Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
THE WELL. Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices WOMAN CENTRE
 THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Guide for Using Lo Loestrin Fe WARNING TO WOMEN WHO SMOKE Do not use Lo Loestrin Fe if you smoke cigarettes and are over 35 years old. Smoking increases your risk of serious
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Guide for Using Lo Loestrin Fe WARNING TO WOMEN WHO SMOKE Do not use Lo Loestrin Fe if you smoke cigarettes and are over 35 years old. Smoking increases your risk of serious
Ask us about LARC. LARC stands for Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Types of LARC are: Contraceptive implant IUS IUD Contraceptive injection
 Ask us about LARC LARC stands for Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Types of LARC are: Contraceptive implant IUS IUD Contraceptive injection visit our website Long Acting Reversible Contraception (LARC)
Ask us about LARC LARC stands for Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Types of LARC are: Contraceptive implant IUS IUD Contraceptive injection visit our website Long Acting Reversible Contraception (LARC)
Intrauterine Device (IUD) THE FACTS
 Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
Information for you Abortion care
 Information for you Abortion care Published in February 2012 This information is for you if you are considering having an abortion. It tells you: how you can access abortion services the care you can expect
Information for you Abortion care Published in February 2012 This information is for you if you are considering having an abortion. It tells you: how you can access abortion services the care you can expect
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis. Looking after your sexual health
 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Why is Cerazette used? To prevent pregnancy.
 CERAZETTE Tablets for oral use Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again. This leaflet will provide information about the benefits and risks
CERAZETTE Tablets for oral use Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again. This leaflet will provide information about the benefits and risks
Abortion. just so you know
 Abortion just so you know Abortion can arouse strong feelings. This booklet aims to: help you understand more about abortion give you information about abortion that could help you, or someone you know,
Abortion just so you know Abortion can arouse strong feelings. This booklet aims to: help you understand more about abortion give you information about abortion that could help you, or someone you know,
BREAST CANCER. How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk. cruk.org
 BREAST CANCER How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk cruk.org Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Around 8 in 10 breast cancer cases are in women aged 50 and over. Men can
BREAST CANCER How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk cruk.org Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Around 8 in 10 breast cancer cases are in women aged 50 and over. Men can
CONSUMER INFORMATION IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ
 CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr MICRONOR norethindrone tablets, USP This leaflet is designed specifically for Consumers. This leaflet is a summary and will not tell you everything about MICRONOR. Contact your
CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr MICRONOR norethindrone tablets, USP This leaflet is designed specifically for Consumers. This leaflet is a summary and will not tell you everything about MICRONOR. Contact your
USER PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Exluton, tablets 0.5 mg Lynestrenol
 Lynestrenol 0.5mg tablets, (N.V.Organon), RH021 WHOPAR part 3 supplier s translation of original SRA approved text May 2012 USER PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Exluton, Lynestrenol Read this
Lynestrenol 0.5mg tablets, (N.V.Organon), RH021 WHOPAR part 3 supplier s translation of original SRA approved text May 2012 USER PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Exluton, Lynestrenol Read this
So you think you might be pregnant?
 So you think you might be pregnant? British Pregnancy Advisory Service British Pregnancy Advisory Service Contents What are the signs of pregnancy? 4 Where can I get a pregnancy test? 6 Who can I talk
So you think you might be pregnant? British Pregnancy Advisory Service British Pregnancy Advisory Service Contents What are the signs of pregnancy? 4 Where can I get a pregnancy test? 6 Who can I talk
abortion your questions answered
 abortion your questions answered About Marie Stopes International Marie Stopes International is a specialist reproductive healthcare organisation and a registered charity working in both the UK and overseas.
abortion your questions answered About Marie Stopes International Marie Stopes International is a specialist reproductive healthcare organisation and a registered charity working in both the UK and overseas.
Genital herpes. Looking after your sexual health
 Genital herpes Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital herpes Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is caused by a virus called Herpes simplex. Most people who get genital
Genital herpes Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital herpes Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is caused by a virus called Herpes simplex. Most people who get genital
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use IMPLANON does not protect against HIV infection (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases. Read this
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling IMPLANON (etonogestrel implant) Subdermal Use IMPLANON does not protect against HIV infection (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases. Read this
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Post-Coital Hormonal Contraception Instructions for Use of Plan B, Plan B One-Step, Next Choice One Dose, My Way, Generic Levonorgestrel and Ella
 Post-Coital Hormonal Contraception Instructions for Use of Plan B, Plan B One-Step, Next Choice One Dose, My Way, Generic Levonorgestrel and Ella Several options for emergency birth control exist for women
Post-Coital Hormonal Contraception Instructions for Use of Plan B, Plan B One-Step, Next Choice One Dose, My Way, Generic Levonorgestrel and Ella Several options for emergency birth control exist for women
what is an abortion where can I go for help? SAMPLE do my parents have to know?
 where can I go for help? what is an abortion? ask brook about abortion do my parents have to know? ask brook about abortion Finding out that you re pregnant might just be the news that you ve been waiting
where can I go for help? what is an abortion? ask brook about abortion do my parents have to know? ask brook about abortion Finding out that you re pregnant might just be the news that you ve been waiting
PILLS & RING INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS ON COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION INCLUDING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS & NUVA RING
 PILLS & RING INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS ON COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION INCLUDING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS & NUVA RING What is combined hormonal contraception? Birth control which contains two hormones
PILLS & RING INFORMATION AND INSTRUCTIONS ON COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION INCLUDING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS & NUVA RING What is combined hormonal contraception? Birth control which contains two hormones
Copper intra-uterine device (IUD)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
CYCLESSA Tablets (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP)
 DETAILED PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT CYCLESSA Tablets (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP) 28 Day Regimen This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy. It does not
DETAILED PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT CYCLESSA Tablets (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP) 28 Day Regimen This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy. It does not
Deciding whether to become a parent
 Deciding whether to become a parent This information is an extract from the booklet, Relationships, sex and fertility for young people affected by cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can
Deciding whether to become a parent This information is an extract from the booklet, Relationships, sex and fertility for young people affected by cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can
ABORTION WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
 ABORTION WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABORTION What you need to know Everyone who is pregnant has decisions to make. It might be unexpected. You might have many different feelings. It may be news that you re
ABORTION WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABORTION What you need to know Everyone who is pregnant has decisions to make. It might be unexpected. You might have many different feelings. It may be news that you re
Heavy menstrual bleeding and what you can do about it!
 Heavy menstrual bleeding and what you can do about it! The intrauterine system as an alternative to hysterectomy. What is heavy menstrual bleeding? Do I have it? A woman s menstrual periods are considered
Heavy menstrual bleeding and what you can do about it! The intrauterine system as an alternative to hysterectomy. What is heavy menstrual bleeding? Do I have it? A woman s menstrual periods are considered
So you think you might be pregnant?
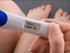 So you think you might be pregnant? About this booklet If you ve had sex in the last 5 days you may be able to use an emergency contraception method. See pages 22-25 for more information regarding emergency
So you think you might be pregnant? About this booklet If you ve had sex in the last 5 days you may be able to use an emergency contraception method. See pages 22-25 for more information regarding emergency
Combined Oral Contraceptives
 CHAPTER Combined Oral Contraceptives Key Points for Providers and Clients y Take one pill every day. For greatest effectiveness a woman must take pills daily and start each new pack of pills on time. y
CHAPTER Combined Oral Contraceptives Key Points for Providers and Clients y Take one pill every day. For greatest effectiveness a woman must take pills daily and start each new pack of pills on time. y
Drospirenone and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP, 3 mg/ 0.03 mg
 FDA Approved Patient Labeling Drospirenone and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP, 3 mg/ 0.03 mg Rx only Guide for Using Drospirenone and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets WARNING TO WOMEN WHO SMOKE Do not use drospirenone
FDA Approved Patient Labeling Drospirenone and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP, 3 mg/ 0.03 mg Rx only Guide for Using Drospirenone and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets WARNING TO WOMEN WHO SMOKE Do not use drospirenone
What could endometriosis mean for me?
 Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Birth Control Methods
 page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide
 NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
NHS cervical screening Helping you decide What is cervical cancer? 2 What causes cervical cancer? 2 What is cervical screening? 3 Cervical screening results 6 What is a colposcopy? 8 What are the benefits
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Cerazette, 75 microgram film-coated tablets desogestrel
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Cerazette, 75 microgram film-coated tablets desogestrel Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. Keep this leaflet. You may need
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Cerazette, 75 microgram film-coated tablets desogestrel Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. Keep this leaflet. You may need
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
the abortion pill by David Hager, M.D.
 the abortion pill by David Hager, M.D. A positive pregnancy test is one of the most life-changing moments for a woman. Never is it more important to base your decisions on accurate information. Try to
the abortion pill by David Hager, M.D. A positive pregnancy test is one of the most life-changing moments for a woman. Never is it more important to base your decisions on accurate information. Try to
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Gynaecology FAQ s. Correspondence address: 204 Fulham Road London SW10 9PJ Email: [email protected] Tel: 02077514489
 Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
HARMONET 75 microgram/20 microgram Coated Tablets Gestodene and Ethinylestradiol. PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET (Republic of Ireland)
 HARMONET 75 microgram/20 microgram Coated Tablets Gestodene and Ethinylestradiol PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET (Republic of Ireland) Please read this carefully before you start to take your tablets. Keep
HARMONET 75 microgram/20 microgram Coated Tablets Gestodene and Ethinylestradiol PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET (Republic of Ireland) Please read this carefully before you start to take your tablets. Keep
Where to get services How to use this brochure Questions to ask These choices don t work These choices might work Emergency Contraceptive Pills
 Where to get services How to use this brochure Questions to ask These choices don t work These choices might work Emergency Contraceptive Pills Abstinence Birth Control Pills Cervical Barriers Condoms
Where to get services How to use this brochure Questions to ask These choices don t work These choices might work Emergency Contraceptive Pills Abstinence Birth Control Pills Cervical Barriers Condoms
Alternatives to hormone replacement therapy for symptoms of the menopause
 Information for you Published in December 2011 (next review date: 2015) Alternatives to hormone replacement therapy for symptoms of the menopause This information is for you if you are considering alternatives
Information for you Published in December 2011 (next review date: 2015) Alternatives to hormone replacement therapy for symptoms of the menopause This information is for you if you are considering alternatives
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
What Are Fertility Awareness Methods?
 CHAPTER 17 Fertility Awareness Methods Key Points for Providers and Clients Fertility awareness methods require partners' cooperation. Couple must be committed to abstaining or using another method on
CHAPTER 17 Fertility Awareness Methods Key Points for Providers and Clients Fertility awareness methods require partners' cooperation. Couple must be committed to abstaining or using another method on
Mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept ): risks of miscarriage and birth defects. Patient guide. Key points to remember
 Mycophenolate (CellCept ): risks of miscarriage and birth defects Patient guide Key points to remember Mycophenolate (CellCept ) causes birth defects and miscarriages Follow the contraceptive advice given
Mycophenolate (CellCept ): risks of miscarriage and birth defects Patient guide Key points to remember Mycophenolate (CellCept ) causes birth defects and miscarriages Follow the contraceptive advice given
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
 National Patient Group Direction for the Supply of Levonorgestrel 1500 microgram tablet (Levonelle 1500), by Pharmacists, for Emergency Hormonal Contraception UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED EFFECTIVE FROM NOVEMBER
National Patient Group Direction for the Supply of Levonorgestrel 1500 microgram tablet (Levonelle 1500), by Pharmacists, for Emergency Hormonal Contraception UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED EFFECTIVE FROM NOVEMBER
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Gynaecology Service. Saint Mary s Hospital. The Whitworth Clinic. Information for patients
 Gynaecology Service Saint Mary s Hospital The Whitworth Clinic Information for patients Welcome to the Whitworth Clinic at Saint Mary s Hospital This leaflet will give you information about the service,
Gynaecology Service Saint Mary s Hospital The Whitworth Clinic Information for patients Welcome to the Whitworth Clinic at Saint Mary s Hospital This leaflet will give you information about the service,
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court. A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and
 Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Chlamydia THE FACTS. How do people get Chlamydia?
 What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
Menopause: should I take HRT?
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Menopause: should I take HRT? The menopause is when your periods stop for good. It isn't an illness. It's a normal part of every woman's life. But sometimes it causes
Patient information from the BMJ Group Menopause: should I take HRT? The menopause is when your periods stop for good. It isn't an illness. It's a normal part of every woman's life. But sometimes it causes
Polycystic ovary syndrome: what it means for your long-term health
 Polycystic ovary syndrome: what it means for your long-term health Information for you Published in February 2005, minor amendments in June 2005 Revised 2009 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? Polycystic
Polycystic ovary syndrome: what it means for your long-term health Information for you Published in February 2005, minor amendments in June 2005 Revised 2009 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? Polycystic
Making Sense of Your Pap and HPV Test Results
 Making Sense of Your Pap and HPV Test Results Keep this booklet until you get your test results back from your doctor. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Making Sense of Your Pap and HPV Test Results Keep this booklet until you get your test results back from your doctor. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Information on termination of pregnancy (abortion) A series of information leaflets on termination of pregnancy services in Greater Glasgow & Clyde
 Information on termination of pregnancy (abortion) A series of information leaflets on termination of pregnancy services in Greater Glasgow & Clyde Your first doctors appointment The assessment clinic
Information on termination of pregnancy (abortion) A series of information leaflets on termination of pregnancy services in Greater Glasgow & Clyde Your first doctors appointment The assessment clinic
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules. What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST?
 MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
MEDICATION GUIDE POMALYST (POM-uh-list) (pomalidomide) capsules What is the most important information I should know about POMALYST? Before you begin taking POMALYST, you must read and agree to all of
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
Birth Control M E T H O D S
 Birth Control M E T H O D S Adapted and reproduced with permission of Public Health, Region of Peel. Table of Contents z Introduction... 2 z Anatomy... 3 z Effectiveness... 4 z Hormonal Methods of Birth
Birth Control M E T H O D S Adapted and reproduced with permission of Public Health, Region of Peel. Table of Contents z Introduction... 2 z Anatomy... 3 z Effectiveness... 4 z Hormonal Methods of Birth
swine flu vaccination:
 swine flu vaccination: what you need to know Flu. Protect yourself and others. Contents What is swine flu?............... 3 About the swine flu vaccine....... 4 What else do I need to know?...... 8 What
swine flu vaccination: what you need to know Flu. Protect yourself and others. Contents What is swine flu?............... 3 About the swine flu vaccine....... 4 What else do I need to know?...... 8 What
Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know
 Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know First published December 2003 Revised edition published November 2008 What is chickenpox? Chickenpox is a very infectious illness caused by a virus called
Chickenpox in pregnancy: what you need to know First published December 2003 Revised edition published November 2008 What is chickenpox? Chickenpox is a very infectious illness caused by a virus called
