VITAMIN & MINERAL DEFICIENCY
|
|
|
- Calvin Armstrong
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VITAMIN & MINERAL Vitamin and mineral deficiencies affect a third of the world s people debilitating minds, bodies, energies, and the economic prospects of nations. But for once the world is confronted by a problem which could be brought under control in a relatively short time and at a relatively low cost. A global damage assessment report
2 It is no longer a question of treating severe deficiency in individuals. It is a question of reaching out to whole populations to protect them against the devastating consequences of even moderate forms of vitamin and mineral deficiency." Carol Bellamy, Executive Director, UNICEF We now have the knowledge and the solutions that can protect the muscles, brains, and blood of whole populations at an extraordinarily low cost. VITAMIN & MINERAL Venkatesh Mannar, President, The Micronutrient Initiative For nearly 40 years, food fortification has protected the populations of the United States, Canada, and many other countries. It is long past the time when the same protection was available to the peoples of the developing world. Nevin Scrimshaw, President, International Nutrition Foundation "Fortifying foods with basic vitamins and minerals is both essential and affordable. Bill Gates, co-founder, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation The case for the elimination of vitamin and mineral deficiency is compelling beyond description. The return on investment is without equal. Rolf Carriere, Executive Director, Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Probably no other technology available today offers as large an opportunity to improve lives and accelerate development at such low cost and in such a short time. The World Bank This is a vital economic and humanitarian cause and we in the food industry are uniquely positioned to help progress. Few outside specialist circles are aware of the scale and severity of vitamin and mineral deficiency, or of what it means for individuals and for nations. It means the impairment of hundreds of millions of growing minds and the lowering of national IQs. It means wholesale damage to immune systems, and the deaths of more than a million children a year. It means 200,000 serious birth defects annually, and the deaths of approximately 50,000 young women a year during pregnancy and childbirth. And it means the large-scale loss of national energies, intellects, productivity, and growth. This problem was largely controlled decades ago in the industrialised nations. It could now be controlled world-wide by means that are tried and tested, available and affordable. That is why the World Bank says that The control of vitamin and mineral deficiencies is one of the most extraordinary development-related scientific advances of recent years. Probably no other technology available today offers as large an opportunity to improve lives and accelerate development at such low cost and in such a short time. The Micronutrient Initiative and UNICEF will shortly be issuing a Global Progress Report on vitamin and mineral deficiency along with Damage Assessment Reports for 80 individual countries. This summary is being submitted to political leaders and major media in the belief that controlling vitamin and mineral deficiency is an affordable opportunity to improve the lives of two billion people and to strengthen the pulse of economic development. Brendan Stewart, Chairman, Australian Wheat Board The cost is minuscule. The benefit enormous. We have acted on this issue both because it is right and because it presents our business in a positive light. Philip Punarma, Chief Commercial Officer, Bogosari Flour Mills, Indonesia The road to regional health and life-long productivity cannot be passed without removing the obstacle of vitamin and mineral deficiency. Joseph Hunt, Health and Nutrition Adviser, Asian Development Bank Venkatesh Mannar President Micronutrient Initiative Ottawa Carol Bellamy Executive Director UNICEF New York 1
3 VITAMIN & MINERAL A Global Progress Report The Micronutrient Initiative and UNICEF will shortly be issuing a Global Progress Report on vitamin and mineral deficiency (VMD). At the same time, VMD Damage Assessment Reports for 80 individual countries are being distributed to national political leaders and major media. These nation-by-nation audits draw on latest information to present the most comprehensive picture to date of the toll being taken by VMD on developing nations. The findings, for countries that are home to approximately 80% of the world s population, are set out on pages 6 to 9. A summary that this is but the tip of a very large iceberg. Levels of mineral and vitamin deficiency that have no clinical symptoms can and do impair intellectual development, compromise immune systems, provoke birth defects, and consign perhaps 2 billion people to lives lived below their physical and mental potential. VMD therefore debilitates in some significant degree the energies, intellects, and economic prospects of nations. The implications of these findings are obviously far-reaching. Most fundamentally, as UNICEF Executive Director Carol Bellamy has said, "We have to leave behind the old thinking and act in the light of new knowledge: it is no longer a question of seeking out symptoms of severe deficiency in individuals and treating them. It is a question of reaching out to whole populations to protect them against the devastating consequences of even moderate forms of vitamin and mineral deficiency." Solutions But if it is clear that VMD represents a much greater problem than was imagined even a decade ago, it is also clear that for once the world is confronted by a problem for which there are available and affordable solutions. In summary those solutions are:- Iodine deficiency is estimated to have lowered the intellectual capacity of almost all of the nations reviewed by as much as 10 to 15 percentage points. Iron deficiency in the 6-to-24 month age group is impairing the mental development of 40% to 60% of the developing world s children. Vitamin A deficiency is compromising the immune systems of approximately 40% of the developing world s under-fives and leading to the early deaths of an estimated one million young children each year. Iodine deficiency in pregnancy is causing as many as 20 million babies a year to be born mentally impaired. Folate deficiency is causing approximately 200,000 severe birth defects every year and is associated with approximately 1 in every 10 adult deaths from heart disease. Severe iron deficiency anaemia is causing the deaths of an estimated 50,000 young women a year in pregnancy and childbirth. Iron deficiency in adults is so widespread that it is lowering the energies of nations and the productivity of workforces with estimated losses of up to 2% of GDP in the worst affected countries. Vitamin and mineral deficiencies, says the World Bank impose high economic costs on virtually every developing nation. In practice, vitamin and mineral deficiencies overlap and interact. Half of children with VMD are suffering from multiple deficiencies adding up an immeasurable burden on individuals, on health services, on education systems, and on millions of families caring for children who are disabled or mentally impaired. FORTIFICATION: Adding essential vitamins and minerals to foods that are regularly consumed by a significant proportion of the population (such as flour, salt, sugar, cooking oil and margarine). The cost can be as little as a few cents per person per year. SUPPLEMENTATION: Reaching out to vulnerable groups (particularly children and women of childbearing age) with vitamin and mineral supplements in the form of tablets, capsules and syrups costing only a few cents per person per year. EDUCATION: Informing communities about the kinds of foods that can increase the intake and absorption of vitamins and minerals. DISEASE CONTROL: Controlling diseases like malaria, measles, diarrhoea, and parasitic infections can also help the body to absorb and retain essential vitamins and minerals. These are the methods that have brought VMD under control in the industrialised nations and that could now be deployed to control the problem world-wide in a relatively short time and at a relatively low cost. As the forthcoming Global Progress Report on vitamin and mineral deficiency will show, each of the available solutions contains its own difficulties; none is a complete solution in itself; and all need to be pursued simultaneously and according to the particular contours of need and opportunity in each country. Targets In May 2002, the General Assembly of the United Nations agreed that the elimination or reduction of vitamin and mineral deficiencies should be one of the principal development goals to be achieved in the early years of the new millennium. Specifically, the UN has called for the elimination of iodine deficiency by 2005; the elimination of vitamin A deficiency by 2010; and a reduction of at least 30% in the global prevalence of iron deficiency anaemia by A new problem This damage assessment exercise confirms that we are here dealing with a global problem of enormous importance that is as yet little recognised. In large part this is because VMD is a new problem. For several decades it has been known that micronutrient deficiency the lack of key vitamins and minerals inflicts anaemia, cretinism and blindness on tens of millions of people. But the news of the last decade is The struggle to achieve these goals is already underway. Throughout the 1990s, international agencies have been working with governments, national institutions, and the private sector to fortify foods and extend the outreach of vitamin and mineral supplements. In that time, some remarkable advances have been made. These achievements, and the main lessons to be drawn from them, are also summarised in the forthcoming VMD Global Progress Report. The main burden of the report, however, is that the goals will not be achieved, and the impact of VMD will not be significantly reduced, without a more ambitious, visionary, and systematic commitment to deploy known solutions on the same scale as the known problems. 2 3
4 Achievement Alongside the VMD Damage Assessment Reports for individual countries, the Micronutrient Initiative and UNICEF are also issuing National Protection Audits to begin tracking the progress being made in putting solutions into effect. Much has already been achieved:- A summary The global prevalence of iodine deficiency has been halved from 30% to 15%. This has been brought about by a sustained effort to add iodine to two-thirds of the world s household salt. As a result, approximately 70 million new-borns a year are being protected, in some degree, against mental impairment. More than 40 developing countries are now reaching 70% or more of their young children with at least one vitamin A capsule every year. Two-dose coverage is significantly lower, but the effort to date is estimated to be saving the lives of more than 300,000 young children a year and preventing many hundreds of thousands of cases of irreversible blindness. An international movement to fortify all wheat flour with iron and folic acid (as in the United States and Canada) is beginning to gain momentum. Indonesia, Jordan, Nigeria and South Africa have recently acted, bringing to 49 the total number of countries adding iron to flour. Many more developing countries have begun the process of fortifying other staple foods and condiments from salt, sugar and margarine to noodles, cooking oil, and soy sauce with essential vitamins and minerals In addition to these advances, there are signs that the seriousness and urgency of the VMD issue is beginning to be more widely realised. The last year, for example, has seen the launch of the $70 million Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the Micronutrient Initiative, and the aid programmes of Canada, Germany, the Netherlands, and the United States. Many of these achievements stem from the resolutions made at the 1990 World Summit for Children. And they emphatically contradict the idea that that nothing ever comes of international conferences, resolutions, goals and targets. Nonetheless, with almost a third of the planet affected in some degree by a problem for which a clear solution beckons, anything less than rapid progress would be unconscionable. Indeed so serious is the VMD problem, and so affordable the solution, that not to act decisively against it would make a mockery of other, more difficult, development targets. The challenge for Despite the achievements, the fact remains that few nations have moved decisively against VMD by deploying the full range of known solutions on a systematic, nation-wide scale. If the goals set by the United Nations are to be achieved, action against VMD will therefore have to move onto a new level. Specifically, the major challenges are:- SUSTAINING RECENT ACHIEVEMENTS: The first priority is to maintain what has been achieved. There is nothing automatic about sustainability; salt iodisation levels, for example, have recently slipped back in Bolivia, India, Indonesia, Vietnam, Central Asia, and the Balkans. BUILDING A NEW AWARENESS: The next twelve months must be used to create a new public and political awareness of the scale and consequence of the problem. Action on the necessary scale will not happen unless VMD is seen for what it is not as an obscure nutritional issue but an assault on the mental and physical development of nations. MEETING THE IRON CHALLENGE: Much achieved, job less than half done might sum up recent progress against vitamin A and iodine deficiencies. But against iron deficiency there has been virtually no progress at all. With new knowledge about the consequences of the problem must come a new determination to move against it. To repeat, iron deficiency brings losses in productivity and cognitive development that no nation can afford. New solutions are becoming available, but will count for little without a new political determination to tackle the world s most stubborn public health problem. FORMING NATIONAL ALLIANCES: The best hope of sustained progress against VMD resides in the idea of national alliances to press for, plan, implement and monitor specific national solutions. Such alliances are most effective when they represent the full range of those who have the expertise, the authority, and the means to put particular solutions into effect on a national scale. National alliances need to embrace, for example, not only government departments but food companies, scientists and researchers, health and education professionals, print and broadcast media, consumer associations and non-governmental organisations. PARTNERING THE FOOD INDUSTRY: When it comes to deploying the powerful weapon of food fortification, it is the food companies, not governments, who own the solution. Only the food industry can develop, market, and distribute fortified food products for daily consumption by a significant proportion of the population. But if food fortification is to benefit the majority, then it will require public-private partnerships and government initiatives to create the legal and financial conditions and incentives that will allow the private sector to play its central role in defeating VMD. GETTING THE SCIENCE RIGHT: Controlling VMD also presents a challenge to the scientific and research community. Specifically, progress could be accelerated by: multi-vitamin and mineral tablets that can be administered less often and with higher acceptability; massively cheap and well-marketed home-mixes to add key vitamins and minerals to daily diets; improved pre-mixes and the identification of the most suitable staples for fortification in each nation; techniques to cheaply fortify rice with granulated vitamin and mineral pre-mixes; and progress in the bio-fortification of staple foods. MONITORING PROGRESS: The national VMD Damage Reports and Protection Audits about to be issued have brought together the best of currently available data for each individual country. But those data are not nearly good enough. In some countries, they are based on partial surveys, extrapolations, and statistical modelling techniques which are at present the only way of estimating the extent and consequences of VMD. To monitor progress and allocate resources, more accurate and up-to-date monitoring is needed. Conclusion VMD touches the lives of perhaps a third of the world s people. The effects on adults, and particularly on women, are subtle and insidious. The effects on nations, and on economic development, are only just beginning to be measured. But at the heart of the VMD problem is the fact that it is in the vital, vulnerable, earliest months of life that the lack of essential vitamins and minerals has its most devastating and durable effects. It is children who sustain the severest damage. One of the causes of poverty, and of its perpetuation from one generation to the next, is the fact that so many of the world s children do not have the kind of start in life that allows them to fulfil the potential with which they were born. It is in this sense that achieving UN goals for reducing vitamin and mineral deficiency would be a significant strike not only against one of poverty s most devastating effects but against one of its most insidious causes. After a decade of dramatic developments, the facts are known, the solutions are available, and the cause is one in which many individuals and organisations governments, the private sector, the medical and scientific community, civil society can all become involved. The challenge is therefore clear. And when so much could be achieved for so many and for so little, it would be a matter of global disgrace if vitamin and mineral deficiency were not brought under control in the years immediately ahead. 4 5
5 VMD: NATIONAL DAMAGE ASSESSMENTS VMD: NATIONAL PROTECTION AUDITS IRON IODINE VITAMIN A FOLATE ECONOMIC IMPACT FLOUR FORTIFICATION SALT IODISATION VITAMIN A SUPPLEMENTS anaemia in children under 5 years (%) anaemia in women age (%) of maternal deaths from severe anaemia of children born mentally impaired Total Goitre Rate (%) of child deaths precipitated children under 6 with sub-clinical vitamin A deficiency of neural tube birth defects GDP lost to all forms of VMD Type of programme (M = Mandatory, V = Voluntary, P = proposed) IRON FOLIC ACID household salt iodised children receiving at least one dose of vitamin A per year Afghanistan , Afghanistan Angola , Angola Armenia <100 3, < < Armenia Azerbaijan <100 22, V Azerbaijan Bangladesh , , P Bangladesh Benin , Benin Bhutan < Bhutan Bolivia ,000 < M Bolivia Botswana <100 9, Botswana Brazil , P, M 42 2 Brazil Burkina Faso , Burkina Faso Burundi , Burundi Cambodia , Cambodia Cameroon , Cameroon Central African Rep , Central African Rep. Chad , Chad China ,880, China Congo , Congo Congo, Dem. Rep Congo, Dem. Rep. Dominican Rep <100 23, V Dominican Rep. Egypt , Egypt El Salvador <100 17, M El Salvador Eritrea , Eritrea Ethiopia , , Ethiopia Gabon <100 11, < Gabon Gambia , Gambia Georgia <100 11, < Georgia Ghana , Ghana Guatemala <100 67, M Guatemala Guinea , Guinea Guinea-Bissau , Guinea-Bissau Haiti , V Haiti Honduras <100 24, M Honduras India ,000 6,600, India Indonesia , , M Indonesia Iran < , P Iran Kazakhstan <100 54, V Kazakhstan Kenya , Kenya Kyrgyzstan <100 23, V Kyrgyzstan Lao PDR , Lao PDR Lebanon <100 7, Lebanon Lesotho , Lesotho Liberia , Liberia Madagascar , Madagascar 6 7
6 VMD: NATIONAL DAMAGE ASSESSMENTS VMD: NATIONAL PROTECTION AUDITS IRON IODINE VITAMIN A FOLATE ECONOMIC IMPACT FLOUR FORTIFICATION SALT IODISATION VITAMIN A SUPPLEMENTS anaemia in children under 5 years (%) anaemia in women age (%) of maternal deaths from severe anaemia of children born mentally impaired Total Goitre Rate (%) of child deaths precipitated children under 6 with sub-clinical vitamin A deficiency of neural tube birth defects GDP lost to all forms of VMD Type of programme (M = Mandatory, V = Voluntary, P = proposed) IRON FOLIC ACID household salt iodised children receiving at least one dose of vitamin A per year Malawi , Malawi Mali , Mali Mauritania , Mauritania Mongolia <100 8, < V Mongolia Morocco P Morocco Mozambique , , Mozambique Myanmar , Myanmar Namibia <100 12, Namibia Nepal , Nepal Nicaragua <100 19, M Nicaragua Niger , M Niger Nigeria , Nigeria Pakistan ,100, Pakistan Papua New Guinea < Papua New Guinea Paraguay <100 22, M Paraguay Peru , M Peru Philippines , Philippines Rwanda , Rwanda Senegal , Senegal Sierra Leone , Sierra Leone South Africa , M South Africa Swaziland <100 4, < Swaziland Syria < , Syria Tajikistan <100 43, V Tajikistan Tanzania Tanzania Thailand < , Thailand Togo , Togo Turkey , Turkey Turkmenistan <100 11, Turkmenistan Uganda , Uganda Uzbekistan < , V Uzbekistan Venezuela <100 60, Venezuela Viet Nam , Viet Nam Yemen , Yemen Zambia , V Zambia Zimbabwe , Zimbabwe Totals 50, * ,000 Note: Data on vitamin and mineral deficiency are imperfect. The figures given in this table are drawn from the best information currently available. Prevalence data are based on a global review of existing surveys of vitamin and mineral deficiencies (VMD). Functional consequences of VMD are calculated using a specially-designed Profiles module. Some figures for individual countries may be subject to revision before official publication of national Damage Assessment Reports in cases where UNICEF country offices indicate that more recent national data is available. * This total may not yet reflect recent increases in the proportion of children receiving vitamin A supplements. Many nations have boosted vitamin A coverage by distributing capsules on National Polio Immunisation Days. Vitamin A supplementation is now estimated to be saving approximately 300,000 young lives each year, though there is a question mark over whether present levels of coverage can be maintained once polio is eradicated and National Immunisation Days are discontinued 8 9
7 Controlling VMD is an affordable opportunity to improve the lives of two billion people and strengthen the pulse of economic development The Micronutrient Initiative PO Box 56127, 250 Albert Street, Ottawa, Canada, K1R 7Z1 UNICEF 3 UN Plaza, New York, NY 10017, USA
Proforma Cost for international UN Volunteers for UN Partner Agencies for 2016. International UN Volunteers (12 months)
 Proforma Cost for international UN Volunteers for UN Partner Agencies for 2016 Country Of Assignment International UN Volunteers (12 months) International UN Youth Volunteers (12 months) University Volunteers
Proforma Cost for international UN Volunteers for UN Partner Agencies for 2016 Country Of Assignment International UN Volunteers (12 months) International UN Youth Volunteers (12 months) University Volunteers
Countries Ranked by Per Capita Income A. IBRD Only 1 Category iv (over $7,185)
 Page 1 of 5 Note: This OP 3.10, Annex C replaces the version dated September 2013. The revised terms are effective for all loans that are approved on or after July 1, 2014. Countries Ranked by Per Capita
Page 1 of 5 Note: This OP 3.10, Annex C replaces the version dated September 2013. The revised terms are effective for all loans that are approved on or after July 1, 2014. Countries Ranked by Per Capita
Eligibility List 2015
 The Global Fund adopted an allocation-based approach for funding programs against HIV/AIDS, TB and malaria in 2013. The Global Fund policy states that countries can receive allocation only if their components
The Global Fund adopted an allocation-based approach for funding programs against HIV/AIDS, TB and malaria in 2013. The Global Fund policy states that countries can receive allocation only if their components
Summary of GAVI Alliance Investments in Immunization Coverage Data Quality
 Summary of GAVI Alliance Investments in Immunization Coverage Data Quality The GAVI Alliance strategy and business plan for 2013-2014 includes a range of activities related to the assessment and improvement
Summary of GAVI Alliance Investments in Immunization Coverage Data Quality The GAVI Alliance strategy and business plan for 2013-2014 includes a range of activities related to the assessment and improvement
Bangladesh Visa fees for foreign nationals
 Bangladesh Visa fees for foreign nationals No. All fees in US $ 1. Afghanistan 5.00 5.00 10.00 2. Albania 2.00 2.00 3.00 3. Algeria 1.00 1.00 2.00 4. Angola 11.00 11.00 22.00 5. Argentina 21.00 21.00 42.00
Bangladesh Visa fees for foreign nationals No. All fees in US $ 1. Afghanistan 5.00 5.00 10.00 2. Albania 2.00 2.00 3.00 3. Algeria 1.00 1.00 2.00 4. Angola 11.00 11.00 22.00 5. Argentina 21.00 21.00 42.00
The Effective Vaccine Management Initiative Past, Present and Future
 EVM setting a standard for the vaccine supply chain The Effective Vaccine Management Initiative Past, Present and Future Paul Colrain TechNet meeting Dakar, Senegal, February 2013 February 2013 TechNet
EVM setting a standard for the vaccine supply chain The Effective Vaccine Management Initiative Past, Present and Future Paul Colrain TechNet meeting Dakar, Senegal, February 2013 February 2013 TechNet
Guidelines for DBA Coverage for Direct and Host Country Contracts
 Guidelines for DBA Coverage for Direct and Host Country Contracts An Additional Help document for ADS Chapter 302 New Reference: 06/14/2007 Responsible Office: OAA/P File Name: 302sap_061407_cd48 BACKGROUND:
Guidelines for DBA Coverage for Direct and Host Country Contracts An Additional Help document for ADS Chapter 302 New Reference: 06/14/2007 Responsible Office: OAA/P File Name: 302sap_061407_cd48 BACKGROUND:
International Fuel Prices 2012/2013
 International Fuel Prices 212/213 8 th Edition Published by International Fuel Prices 212/213 8 th Edition Disclaimer Findings, interpretation and conclusions expressed in this document are based on the
International Fuel Prices 212/213 8 th Edition Published by International Fuel Prices 212/213 8 th Edition Disclaimer Findings, interpretation and conclusions expressed in this document are based on the
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE USAID/TDA DEFENSE BASE ACT (DBA) APPLICATION
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE USAID/TDA DEFENSE BASE ACT (DBA) APPLICATION Full Name of Insured or Company and Complete Mailing Address: This is whoever has the contract with USAID. Generally, it is
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE USAID/TDA DEFENSE BASE ACT (DBA) APPLICATION Full Name of Insured or Company and Complete Mailing Address: This is whoever has the contract with USAID. Generally, it is
FDI performance and potential rankings. Astrit Sulstarova Division on Investment and Enterprise UNCTAD
 FDI performance and potential rankings Astrit Sulstarova Division on Investment and Enterprise UNCTAD FDI perfomance index The Inward FDI Performance Index ranks countries by the FDI they receive relative
FDI performance and potential rankings Astrit Sulstarova Division on Investment and Enterprise UNCTAD FDI perfomance index The Inward FDI Performance Index ranks countries by the FDI they receive relative
Expression of Interest in Research Grant Applications
 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR GENETIC ENGINEERING AND BIOTECHNOLOGY THE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES FOR THE DEVELOPING WORLD UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION ICGEB-TWAS-UNESCO/IBSP Joint
INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR GENETIC ENGINEERING AND BIOTECHNOLOGY THE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES FOR THE DEVELOPING WORLD UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION ICGEB-TWAS-UNESCO/IBSP Joint
OFFICIAL NAMES OF THE UNITED NATIONS MEMBERSHIP
 OFFICIAL NAMES OF THE UNITED NATIONS MEMBERSHIP Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Republic of Albania People s Democratic Republic of Algeria Principality of Andorra Republic of Angola Antigua and Barbuda
OFFICIAL NAMES OF THE UNITED NATIONS MEMBERSHIP Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Republic of Albania People s Democratic Republic of Algeria Principality of Andorra Republic of Angola Antigua and Barbuda
Appendix A. Crisis Indicators and Infrastructure Lending
 Appendix A. Crisis Indicators and Infrastructure Lending APPENDIX A Table A.1. Crisis Indicators (Case Study Countries) Country % as Share of GDP Share of in Bank Crisis Severity Score (principal factor
Appendix A. Crisis Indicators and Infrastructure Lending APPENDIX A Table A.1. Crisis Indicators (Case Study Countries) Country % as Share of GDP Share of in Bank Crisis Severity Score (principal factor
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table
 Updated 22/06/2016 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Updated 22/06/2016 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Population below the poverty line Rural % Population below $1 a day % Urban % Urban % Survey year. National %
 2.7 International the the Afghanistan.................... Albania 2002 29.6 19.8 25.4...... 2002 a
2.7 International the the Afghanistan.................... Albania 2002 29.6 19.8 25.4...... 2002 a
UNHCR, United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
 Belgium 22 Jul 1953 r 08 Apr 1969 a Belize 27 Jun 1990 a 27 Jun 1990 a Benin 04 Apr 1962 s 06 Jul 1970 a Bolivia 09 Feb 1982 a 09 Feb 1982 a Bosnia and Herzegovina 01 Sep 1993 s 01 Sep 1993 s Botswana
Belgium 22 Jul 1953 r 08 Apr 1969 a Belize 27 Jun 1990 a 27 Jun 1990 a Benin 04 Apr 1962 s 06 Jul 1970 a Bolivia 09 Feb 1982 a 09 Feb 1982 a Bosnia and Herzegovina 01 Sep 1993 s 01 Sep 1993 s Botswana
How To Calculate The Lorenz Curve
 FACT SHEET 1. Overview 1.1 Developed by an Italian statistician Corrado in the 1910s, is commonly used to indicate income inequality in a society. is a number which has a value between zero and one. As
FACT SHEET 1. Overview 1.1 Developed by an Italian statistician Corrado in the 1910s, is commonly used to indicate income inequality in a society. is a number which has a value between zero and one. As
Action required The Committee is requested to take note of the position of 2010 11 income and expenditure as of 30 September 2010.
 INTERNATIONAL LABOUR OFFICE Governing Body 309th Session, Geneva, November 2010 Programme, Financial and Administrative Committee GB.309/PFA/1 PFA FOR INFORMATION FIRST ITEM ON THE AGENDA Programme and
INTERNATIONAL LABOUR OFFICE Governing Body 309th Session, Geneva, November 2010 Programme, Financial and Administrative Committee GB.309/PFA/1 PFA FOR INFORMATION FIRST ITEM ON THE AGENDA Programme and
States Parties to the 1951 Convention relating to the Status of Refugees and the 1967 Protocol
 States Parties to the 1951 Convention relating to the Status of Refugees and the 1967 Protocol Date of entry into force: 22 April 1954 (Convention) 4 October 1967 (Protocol) As of 1 October 2008 Total
States Parties to the 1951 Convention relating to the Status of Refugees and the 1967 Protocol Date of entry into force: 22 April 1954 (Convention) 4 October 1967 (Protocol) As of 1 October 2008 Total
INDEX FOR RISK MANAGEMENT RESULTS 2015
 INDEX FOR RISK MANAGEMENT RESULTS 2015 INFORM 2015 INFORM MEASURES THE RISK OF HUMANITARIAN CRISES AND DISASTERS IN 191 COUNTRIES COUNTRY RISK 3 YR TREND Afghanistan 7.88 æ Albania 2.61 à Algeria 4.64
INDEX FOR RISK MANAGEMENT RESULTS 2015 INFORM 2015 INFORM MEASURES THE RISK OF HUMANITARIAN CRISES AND DISASTERS IN 191 COUNTRIES COUNTRY RISK 3 YR TREND Afghanistan 7.88 æ Albania 2.61 à Algeria 4.64
HEALTHIEST COUNTRIES 1 to 40
 BLOOMBERG RANKINGS THE WORLD'S HEALTHIEST COUNTRIES HEALTHIEST COUNTRIES 1 to 40 1 Singapore 89.45% 92.52% 3.07% 2 Italy 89.07 94.61 5.54 3 Australia 88.33 93.19 4.86 4 Switzerland 88.29 93.47 5.17 5 Japan
BLOOMBERG RANKINGS THE WORLD'S HEALTHIEST COUNTRIES HEALTHIEST COUNTRIES 1 to 40 1 Singapore 89.45% 92.52% 3.07% 2 Italy 89.07 94.61 5.54 3 Australia 88.33 93.19 4.86 4 Switzerland 88.29 93.47 5.17 5 Japan
New Technologies and services - Cable Television
 New Technologies and services - Cable Television WORLD: AFRICA provide service Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi applications. Cameroon The relevant licence must be obtained. Cape Verde Central
New Technologies and services - Cable Television WORLD: AFRICA provide service Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi applications. Cameroon The relevant licence must be obtained. Cape Verde Central
GLOBAL. 2014 Country Well-Being Rankings. D Social (% thriving) E Financial (% thriving) F Community (% thriving) G Physical (% thriving)
 0 0 GLOBAL 0 Country Rankings 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 : >0.0% 0.% 0.0% 0.% 0.0% 0.% 0.0% 0.0% A Country s global rank B in three or more elements of well-being C (% thriving) D (% thriving) E
0 0 GLOBAL 0 Country Rankings 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 : >0.0% 0.% 0.0% 0.% 0.0% 0.% 0.0% 0.0% A Country s global rank B in three or more elements of well-being C (% thriving) D (% thriving) E
INDEX FOR RISK MANAGEMENT
 INDEX FOR RISK MANAGEMENT RESULTS 2016 WELCOME Welcome to the INFORM (Index for Risk Management) 2016 global results report. INFORM is a way to understand and measure the risk of humanitarian crises and
INDEX FOR RISK MANAGEMENT RESULTS 2016 WELCOME Welcome to the INFORM (Index for Risk Management) 2016 global results report. INFORM is a way to understand and measure the risk of humanitarian crises and
Total Purchases in 2012
 Fighting Hunger Worldwide Food Procurement Annual Report 2012 Maize, Niger WFP/Rein Skullerud Procurement Mission Statement To ensure that appropriate commodities are available to WFP beneficiaries in
Fighting Hunger Worldwide Food Procurement Annual Report 2012 Maize, Niger WFP/Rein Skullerud Procurement Mission Statement To ensure that appropriate commodities are available to WFP beneficiaries in
COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING DECISION. of 24.5.2016
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 24.5.2016 C(2016) 3040 final COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING DECISION of 24.5.2016 amending Commission Implementing Decision C(2015) 8936 of 15.12.2015 on the financing of humanitarian
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 24.5.2016 C(2016) 3040 final COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING DECISION of 24.5.2016 amending Commission Implementing Decision C(2015) 8936 of 15.12.2015 on the financing of humanitarian
Country Briefing: Jordan Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) At a Glance
 Oxford and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) www.ophi.org.uk Oxford Dept of International Development, Queen Elizabeth House, University of Oxford Country Briefing: Jordan Multidimensional Index (MPI)
Oxford and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) www.ophi.org.uk Oxford Dept of International Development, Queen Elizabeth House, University of Oxford Country Briefing: Jordan Multidimensional Index (MPI)
Policy Paper 12. Education for All Global Monitoring Report. Increasing tax revenues to bridge the education financing gap
 Education for All Global Monitoring Report Policy Paper 12 March 2014 Increasing tax revenues to bridge the education financing gap Sustained economic growth has increased the resources that many of the
Education for All Global Monitoring Report Policy Paper 12 March 2014 Increasing tax revenues to bridge the education financing gap Sustained economic growth has increased the resources that many of the
Poorest Countries of the World: Projections upto 2018
 Poorest Countries of the World: Projections upto 2018 By Dunya News http://www.dunyanews.tv Author: Anis uddin Shiekh ([email protected]) December 2013 Copyright Dunya News 1 Introduction Poverty
Poorest Countries of the World: Projections upto 2018 By Dunya News http://www.dunyanews.tv Author: Anis uddin Shiekh ([email protected]) December 2013 Copyright Dunya News 1 Introduction Poverty
Fiscal Rules and Fiscal Responsibility Frameworks for Growth in Emerging and Low-Income Countries
 Fiscal Affairs Department Effects of Good Government, by Ambrogio Lorenzetti, Siena, Italy, 1338-39 Fiscal Rules and Fiscal Responsibility Frameworks for Growth in Emerging and Low-Income Countries Martine
Fiscal Affairs Department Effects of Good Government, by Ambrogio Lorenzetti, Siena, Italy, 1338-39 Fiscal Rules and Fiscal Responsibility Frameworks for Growth in Emerging and Low-Income Countries Martine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gini_coefficient
 Gini coefficient From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gini_coefficient Graphical representation of the Gini coefficient The Gini coefficient is a measure of inequality of
Gini coefficient From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gini_coefficient Graphical representation of the Gini coefficient The Gini coefficient is a measure of inequality of
The Education for All Fast Track Initiative
 The Education for All Fast Track Initiative Desmond Bermingham Introduction The Education for All Fast Track Initiative (FTI) is a global partnership to help low income countries to achieve the education
The Education for All Fast Track Initiative Desmond Bermingham Introduction The Education for All Fast Track Initiative (FTI) is a global partnership to help low income countries to achieve the education
Citizens of the following nationalities are exempted from holding a visa when crossing the external borders of the SCHENGEN area:
 WEB SUMMIT BULLETIN VISA The VISA requirement to cross the external borders of the SCHENGEN area it is one of the most important procedural steps for all those participants in the next Web Summit that
WEB SUMMIT BULLETIN VISA The VISA requirement to cross the external borders of the SCHENGEN area it is one of the most important procedural steps for all those participants in the next Web Summit that
Entrance Visas in Brazil (Updated on November, 24, 2015)
 Ministry of External Relations Immigration Division Padip Holders of diplomatic passports Pasof Holders of official or service passports Entrance Visas in Brazil (Updated on November, 24, 2015) Caption
Ministry of External Relations Immigration Division Padip Holders of diplomatic passports Pasof Holders of official or service passports Entrance Visas in Brazil (Updated on November, 24, 2015) Caption
LIST OF PAYMENT FOR VISA AND SECURITY BOND PAYMENT FOR VISA ( RM )
 LIST OF AND COUNTRY FOR Afghanistan 20 2000 Albania 20 2000 Algeria 20 2000 Angola 20 1500 Antigua and Bermuda - 2000 Argentina 20 2700 Armenia 20 2000 Australia - 1500 Austria ( Vienna ) 20 1500 Azerbaijan*
LIST OF AND COUNTRY FOR Afghanistan 20 2000 Albania 20 2000 Algeria 20 2000 Angola 20 1500 Antigua and Bermuda - 2000 Argentina 20 2700 Armenia 20 2000 Australia - 1500 Austria ( Vienna ) 20 1500 Azerbaijan*
(b) the details of those who have been given asylum of other country, country-wise during the last three years
 Annexure Table indicating country-wise data on asylum seekers (LS Starred Q No. 232 for answer on 5.8.2015 on Political Asylum ) S.No. Name of Country (a) the total number of Indians who have sought political
Annexure Table indicating country-wise data on asylum seekers (LS Starred Q No. 232 for answer on 5.8.2015 on Political Asylum ) S.No. Name of Country (a) the total number of Indians who have sought political
Entrance Visas in Brazil (Updated on July 08, 2014)
 Ministry of External Relations Immigration Division Padip Holders of diplomatic passports Pasof Holders of official or service passports Entrance Visas in Brazil (Updated on July 08, 2014) Caption Vitem
Ministry of External Relations Immigration Division Padip Holders of diplomatic passports Pasof Holders of official or service passports Entrance Visas in Brazil (Updated on July 08, 2014) Caption Vitem
Adobe Creative Cloud Availability
 Adobe Availability Countries/Regions for teams for teams United States Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua & Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas
Adobe Availability Countries/Regions for teams for teams United States Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua & Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas
AFR EUR MENA NAC SACA SEA WP
 250000 200000 Millions (USD) 150000 100000 50000 0 AFR EUR MENA NAC SACA SEA WP India China USA Russian Federation Brazil Germany Pakistan Japan Indonesia Mexico Bangladesh Egypt France Italy Turkey Thailand
250000 200000 Millions (USD) 150000 100000 50000 0 AFR EUR MENA NAC SACA SEA WP India China USA Russian Federation Brazil Germany Pakistan Japan Indonesia Mexico Bangladesh Egypt France Italy Turkey Thailand
KYOTO PROTOCOL STATUS OF RATIFICATION
 KYOTO PROTOCOL STATUS OF RATIFICATION Notes: R = Ratification At = Acceptance Ap = Approval Ac = Accession 1. ALBANIA ----- 01/04/05 (Ac) 30/06/05 2. ALGERIA ---- 16/02/05 (Ac) 17/05/05 3. ANTIGUA AND
KYOTO PROTOCOL STATUS OF RATIFICATION Notes: R = Ratification At = Acceptance Ap = Approval Ac = Accession 1. ALBANIA ----- 01/04/05 (Ac) 30/06/05 2. ALGERIA ---- 16/02/05 (Ac) 17/05/05 3. ANTIGUA AND
Outsource International Ltd
 Providing global technology solutions for: Carriers Systems Integrators Resellers Outsource Manufacturers International Ltd Government agencies Financial sector Global Technology Solutions Providing global
Providing global technology solutions for: Carriers Systems Integrators Resellers Outsource Manufacturers International Ltd Government agencies Financial sector Global Technology Solutions Providing global
THE WORLD FOOD PROGRAMME IN FACTS AND FIGURES
 THE WORLD FOOD PROGRAMME IN 2014 FACTS AND FIGURES WFP S KEY ACHIEVEMENTS 80 MILLION PEOPLE reached with food assistance in 82 COUNTRIES WFP S KEY ACHIEVEMENTS Children remained the primary focus of WFP
THE WORLD FOOD PROGRAMME IN 2014 FACTS AND FIGURES WFP S KEY ACHIEVEMENTS 80 MILLION PEOPLE reached with food assistance in 82 COUNTRIES WFP S KEY ACHIEVEMENTS Children remained the primary focus of WFP
What Can I Do With the Data?
 Profile of GMAT Testing: Report Five-Year Summary, TY2011 TY2015 November 2015 Globally, nearly 1.3 million Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT ) exams have been taken over the past five years by
Profile of GMAT Testing: Report Five-Year Summary, TY2011 TY2015 November 2015 Globally, nearly 1.3 million Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT ) exams have been taken over the past five years by
Time Warner Cable Date: 03/03/2014. Phone Product Management. BCP Standard International Rates
 Afghanistan $1.070 $1.100 Afghanistan Albania $1.040 $1.230 Albania Algeria $0.490 $0.560 Algeria Andorra $0.460 $0.750 Andorra Angola $1.440 $1.520 Angola Anguilla $0.570 $0.690 Anguilla Antarctica $3.010
Afghanistan $1.070 $1.100 Afghanistan Albania $1.040 $1.230 Albania Algeria $0.490 $0.560 Algeria Andorra $0.460 $0.750 Andorra Angola $1.440 $1.520 Angola Anguilla $0.570 $0.690 Anguilla Antarctica $3.010
Per Minute Rate Unlimited North America
 AT&T U-verse Calling Calling Rates Rates do not include taxes, fees, surcharges. Call destinations and rates are subject to change. An additional per minute rate for international calls terminating on
AT&T U-verse Calling Calling Rates Rates do not include taxes, fees, surcharges. Call destinations and rates are subject to change. An additional per minute rate for international calls terminating on
SPRINT CALL HOME PREPAID CALLING CARD
 Domestic Dial-1 Calling Dollar Increments Price Per Unit $10 and $20 $0.59 The same per minute rates apply when the card is refreshed. International Calling The cost per call is based on a $0.59 cost per
Domestic Dial-1 Calling Dollar Increments Price Per Unit $10 and $20 $0.59 The same per minute rates apply when the card is refreshed. International Calling The cost per call is based on a $0.59 cost per
Migration and Remittances: Top Countries
 Migration and Remittances: Top Countries Top Immigration Countries a, 010 number of immigrants, millions United States b Russian Federation b Germany b Saudi Arabia b Canada b United Kingdom b Spain b
Migration and Remittances: Top Countries Top Immigration Countries a, 010 number of immigrants, millions United States b Russian Federation b Germany b Saudi Arabia b Canada b United Kingdom b Spain b
CONVENTION ON INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION SIGNED AT CHICAGO ON 7 DECEMBER 1944
 State CONVENTION ON INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION SIGNED AT CHICAGO ON 7 DECEMBER 1944 Entry into force: The Convention entered into force on 4 April 1947. Status: 191 parties. This list is based on information
State CONVENTION ON INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION SIGNED AT CHICAGO ON 7 DECEMBER 1944 Entry into force: The Convention entered into force on 4 April 1947. Status: 191 parties. This list is based on information
Financing Education for All in Sub Saharan Africa: Progress and Prospects
 Financing Education for All in Sub Saharan Africa: Progress and Prospects Albert Motivans Education for All Working Group Paris, 3 February 211 1 Improving the coverage and quality of education finance
Financing Education for All in Sub Saharan Africa: Progress and Prospects Albert Motivans Education for All Working Group Paris, 3 February 211 1 Improving the coverage and quality of education finance
AAAS/ASPB 2009 Mass Media Science & Engineering Fellows Program
 AAAS/ASPB 2009 Mass Media Science & Engineering Fellows Program CALL FOR PAPERS Plant Physiology Focus Issue on Plant Interactions with Bacterial Pathogens Are you interested in science writing? Deadline
AAAS/ASPB 2009 Mass Media Science & Engineering Fellows Program CALL FOR PAPERS Plant Physiology Focus Issue on Plant Interactions with Bacterial Pathogens Are you interested in science writing? Deadline
LOCAL: INTRALATA RATES: COLLECT: PER CALL SERVICE CHARGE: $.75; PER MINUTE CHARGE: $.07 DEBIT: PER CALL SERVICE CHARGE: $.60; PER MINUTE CHARGE: $.
 RATE INFORMATION SHEET LOCAL: (COLLECT: PER CALL SERVICE CHARGE: $.75; CALL RATE $.25 unlimited (~otal $1.00) DEBIT: $.80 INTRALATA RATES: COLLECT: PER CALL SERVICE CHARGE: $.75; PER MINUTE CHARGE: $.07
RATE INFORMATION SHEET LOCAL: (COLLECT: PER CALL SERVICE CHARGE: $.75; CALL RATE $.25 unlimited (~otal $1.00) DEBIT: $.80 INTRALATA RATES: COLLECT: PER CALL SERVICE CHARGE: $.75; PER MINUTE CHARGE: $.07
1.1 LIST OF DAILY MAXIMUM AMOUNT PER COUNTRY WHICH IS DEEMED TO BEEN EXPENDED
 1 SUBSISTENCE ALLOWANCE FOREIGN TRAVEL 1.1 LIST OF DAILY MAXIMUM AMOUNT PER COUNTRY WHICH IS DEEMED TO BEEN EXPENDED Albania Euro 97 Algeria Euro 112 Angola US $ 322 Antigua and Barbuda US $ 220 Argentina
1 SUBSISTENCE ALLOWANCE FOREIGN TRAVEL 1.1 LIST OF DAILY MAXIMUM AMOUNT PER COUNTRY WHICH IS DEEMED TO BEEN EXPENDED Albania Euro 97 Algeria Euro 112 Angola US $ 322 Antigua and Barbuda US $ 220 Argentina
LIST OF RESOLUTIONS ADOPTED BY THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY AT ITS SIXTY-EIGHTH SESSION ON THE RECOMMENDATION OF THE THIRD COMMITTEE
 LIST OF AT THE LEVEL OF THE THIRD COMMITTEE ITEM 27: SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT ITEM 27 (a) Implementation of the outcome of the World Summit for Social Development and of the twenty-fourth special session of
LIST OF AT THE LEVEL OF THE THIRD COMMITTEE ITEM 27: SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT ITEM 27 (a) Implementation of the outcome of the World Summit for Social Development and of the twenty-fourth special session of
EMERGENCIES 911 ABROAD
 EMERGENCIES 911 ABROAD If you re in an emergency situation abroad, you ll need to know how to contact the police, an ambulance, or even the fire department. Not every county uses 911 as its emergency contact
EMERGENCIES 911 ABROAD If you re in an emergency situation abroad, you ll need to know how to contact the police, an ambulance, or even the fire department. Not every county uses 911 as its emergency contact
Lebara Unlimited Plan
 AFGHANISTAN $0.05 $0.19 ALBANIA $0.35 $0.43 ALGERIA $0.28 $0.38 AMERICAN SAMOA $0.15 $0.15 ANDORRA $0.07 $0.44 ANGOLA $0.25 $0.35 ANGUILLA $0.33 $0.33 ANTARCTICA $1.39 $0.00 ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA $0.25 $0.25
AFGHANISTAN $0.05 $0.19 ALBANIA $0.35 $0.43 ALGERIA $0.28 $0.38 AMERICAN SAMOA $0.15 $0.15 ANDORRA $0.07 $0.44 ANGOLA $0.25 $0.35 ANGUILLA $0.33 $0.33 ANTARCTICA $1.39 $0.00 ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA $0.25 $0.25
World Health Organization (WHO) estimates of tuberculosis incidence by country, 2014
 World Health Organization (WHO) estimates of tuberculosis incidence by country, 2014 Definition of high incidence With reference to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) recommendations
World Health Organization (WHO) estimates of tuberculosis incidence by country, 2014 Definition of high incidence With reference to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) recommendations
HEALTH HISTORY & IMMUNIZATION FORM
 HEALTH HISTORY & IMMUNIZATION FORM **Deadline to return this form is August 1 st ** Suffolk University Health & Wellness Services Tel: (617) 573-8260 Fax: (617) 305-1745 Mailing Address: Office Location:
HEALTH HISTORY & IMMUNIZATION FORM **Deadline to return this form is August 1 st ** Suffolk University Health & Wellness Services Tel: (617) 573-8260 Fax: (617) 305-1745 Mailing Address: Office Location:
country profiles WHO regions
 country profiles WHO regions AFR AMR EMR EUR SEAR WPR Algeria Total population: 37 63 aged years and older (+): 73% in urban areas: 66% Income group (World Bank): Upper middle income 196 196 197 197 198
country profiles WHO regions AFR AMR EMR EUR SEAR WPR Algeria Total population: 37 63 aged years and older (+): 73% in urban areas: 66% Income group (World Bank): Upper middle income 196 196 197 197 198
DEMOGRAPHIC AND SOCIOECONOMIC DETERMINANTS OF SCHOOL ATTENDANCE: AN ANALYSIS OF HOUSEHOLD SURVEY DATA
 BACKGROUND PAPER FOR FIXING THE BROKEN PROMISE OF EDUCATION FOR ALL DEMOGRAPHIC AND SOCIOECONOMIC DETERMINANTS OF SCHOOL ATTENDANCE: AN ANALYSIS OF HOUSEHOLD SURVEY DATA By Hiroyuki Hattori, UNICEF This
BACKGROUND PAPER FOR FIXING THE BROKEN PROMISE OF EDUCATION FOR ALL DEMOGRAPHIC AND SOCIOECONOMIC DETERMINANTS OF SCHOOL ATTENDANCE: AN ANALYSIS OF HOUSEHOLD SURVEY DATA By Hiroyuki Hattori, UNICEF This
EARLY MARRIAGE A HARMFUL TRADITIONAL PRACTICE A STATISTICAL EXPLORATION
 EARLY MARRIAGE A HARMFUL TRADITIONAL PRACTICE A STATISTICAL EXPLORATION EARLY MARRIAGE A HARMFUL TRADITIONAL PRACTICE A STATISTICAL EXPLORATION CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION......................................................1
EARLY MARRIAGE A HARMFUL TRADITIONAL PRACTICE A STATISTICAL EXPLORATION EARLY MARRIAGE A HARMFUL TRADITIONAL PRACTICE A STATISTICAL EXPLORATION CONTENTS I. INTRODUCTION......................................................1
Part II. Global health indicators
 2015 Part II Global health indicators 40 2015 General notes The following summary tables represent the best estimates of WHO for a broad range of key public health indicators based on evidence available
2015 Part II Global health indicators 40 2015 General notes The following summary tables represent the best estimates of WHO for a broad range of key public health indicators based on evidence available
Total merchandise trade
 Total merchandise trade October 214 213 213-13 212 213 Total exports f.o.b. 18 3 64 1 1 8 2 Total imports c.i.f. 18 49 1 1 7 1 an Union (28) 6 76 41 4 33 - extra-eu (28) exports 2 31 16 13 13 7 7 China
Total merchandise trade October 214 213 213-13 212 213 Total exports f.o.b. 18 3 64 1 1 8 2 Total imports c.i.f. 18 49 1 1 7 1 an Union (28) 6 76 41 4 33 - extra-eu (28) exports 2 31 16 13 13 7 7 China
UIS INFORMATION PAPER JUNE 2013. ADULT AND YOUTH LITERACY National, regional and global trends, 1985-2015
 UIS INFORMATION PAPER JUNE 213 ADULT AND YOUTH LITERACY National, regional and global trends, 1985-215 UNESCO The constitution of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
UIS INFORMATION PAPER JUNE 213 ADULT AND YOUTH LITERACY National, regional and global trends, 1985-215 UNESCO The constitution of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
Joint Initiative. International Partnerships for Sustainable Societies (IPaSS) Description
 Joint Initiative International Partnerships for Sustainable Societies (IPaSS) Description The International Partnerships for Sustainable Societies (IPaSS) are jointly funded by the International Development
Joint Initiative International Partnerships for Sustainable Societies (IPaSS) Description The International Partnerships for Sustainable Societies (IPaSS) are jointly funded by the International Development
JAMAICAN IMMIGRATION DEPARTMENT VISA REQUIREMENTS FOR JAMAICANS TRAVELLING OVERSEAS AND FOREIGNERS COMING TO JAMAICA
 JAMAICAN IMMIGRATION DEPARTMENT VISA REQUIREMENTS FOR JAMAICANS TRAVELLING OVERSEAS AND FOREIGNERS COMING TO JAMAICA COUNTRY ENTRY VISA Foreigners coming to Jamaica AFGHANISTAN Prior to arrival (pta) ALBANIA
JAMAICAN IMMIGRATION DEPARTMENT VISA REQUIREMENTS FOR JAMAICANS TRAVELLING OVERSEAS AND FOREIGNERS COMING TO JAMAICA COUNTRY ENTRY VISA Foreigners coming to Jamaica AFGHANISTAN Prior to arrival (pta) ALBANIA
TWC Phone Service International Rate Table Comparison
 Afghanistan $0.35 $0.35 Included* Included* $1.07 $1.10 Albania $0.15 $0.24 $1.04 $1.23 $1.04 $1.23 Algeria $0.17 $0.36 $0.49 $0.56 $0.49 $0.56 Andorra $0.05 $0.22 $0.46 $0.75 $0.46 $0.75 Angola $0.18
Afghanistan $0.35 $0.35 Included* Included* $1.07 $1.10 Albania $0.15 $0.24 $1.04 $1.23 $1.04 $1.23 Algeria $0.17 $0.36 $0.49 $0.56 $0.49 $0.56 Andorra $0.05 $0.22 $0.46 $0.75 $0.46 $0.75 Angola $0.18
VISA REQUIREMENTS FOR ALL COUNTRIES
 COUNTRY VISA REQUIRED REMARKS Afghanistan Islamic State of Afghanistan Albania Republic of Albania Business/Vacation Yes Visa not required for visits of up to thirty (30) days. Algeria Democratic and Popular
COUNTRY VISA REQUIRED REMARKS Afghanistan Islamic State of Afghanistan Albania Republic of Albania Business/Vacation Yes Visa not required for visits of up to thirty (30) days. Algeria Democratic and Popular
Global Online Business Intelligence Masterfile
 Size of Universe Cost Source Min Order Quantity 5,000 Update Frequency 6,074,363 Names USD 150.00 /M Addresses (Business Addresses Only) USD 175.00 /M Addresses (Named Executives) USD 150.00 /M Addresses
Size of Universe Cost Source Min Order Quantity 5,000 Update Frequency 6,074,363 Names USD 150.00 /M Addresses (Business Addresses Only) USD 175.00 /M Addresses (Named Executives) USD 150.00 /M Addresses
On-Net to On-Net Per. * Billed in 60 second increments. 1 Formerly found in Section 30.7.4
 1 The international usage rates below apply to Dial-1 calls from the U.S. Mainland, Hawaii, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. FONCARD international service is available from the U.S. Mainland,
1 The international usage rates below apply to Dial-1 calls from the U.S. Mainland, Hawaii, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. FONCARD international service is available from the U.S. Mainland,
SCALES OF ASSESSMENTS AND CURRENCY OF MEMBER STATES CONTRIBUTIONS FOR 2016-2017 OUTLINE
 38th Session, Paris, 2015 38 C 38 C/37 26 August 2015 Original: English Item 9.3 of the provisional agenda SCALES OF ASSESSMENTS AND CURRENCY OF MEMBER STATES CONTRIBUTIONS FOR 2016-2017 OUTLINE Source:
38th Session, Paris, 2015 38 C 38 C/37 26 August 2015 Original: English Item 9.3 of the provisional agenda SCALES OF ASSESSMENTS AND CURRENCY OF MEMBER STATES CONTRIBUTIONS FOR 2016-2017 OUTLINE Source:
Ensure that the HRTWS is included in the Declaration of the Post-2015 Development Agenda
 Ensure that the HRTWS is included in the Declaration of the Post-2015 Development Agenda SOCIAL MEDIA STRATEGY SHEET Join us for a weeklong Twitter campaign (Monday 27 April- Friday 1 May) Campaign background:
Ensure that the HRTWS is included in the Declaration of the Post-2015 Development Agenda SOCIAL MEDIA STRATEGY SHEET Join us for a weeklong Twitter campaign (Monday 27 April- Friday 1 May) Campaign background:
DEFINITION OF THE CHILD: THE INTERNATIONAL/REGIONAL LEGAL FRAMEWORK. The African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the Child, 1990
 DEFINITION OF THE CHILD: THE INTERNATIONAL/REGIONAL LEGAL FRAMEWORK Article 2: Definition of a Child The African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the Child, 1990 For tile purposes of this Charter.
DEFINITION OF THE CHILD: THE INTERNATIONAL/REGIONAL LEGAL FRAMEWORK Article 2: Definition of a Child The African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the Child, 1990 For tile purposes of this Charter.
Criteria rules. FTSE4Good Inclusion Criteria for the Marketing of Breast Milk Substitutes
 Criteria rules FTSE4Good Inclusion Criteria for the Marketing of Breast Milk Substitutes ftserussell.com Original January 2015; rebranded December 2015 Contents 1.0 Criteria... 3 2.0 Risk Categories...
Criteria rules FTSE4Good Inclusion Criteria for the Marketing of Breast Milk Substitutes ftserussell.com Original January 2015; rebranded December 2015 Contents 1.0 Criteria... 3 2.0 Risk Categories...
Quality of Government and Human Well Being: Some Surprises from Big Data
 Quality of Government and Human Well Being: Some Surprises from Big Data Bo Rothstein Head of Program Stefan Dahlberg Dataset Manager The Quality of Government Institute Department of Political Science
Quality of Government and Human Well Being: Some Surprises from Big Data Bo Rothstein Head of Program Stefan Dahlberg Dataset Manager The Quality of Government Institute Department of Political Science
JAMAICA IMMIGRATION UNIT
 AFGHANISTAN pta ALBANIA poe ALGERIA - pta ANDORRA poe ANGOLA pta ANTIGUA & BARBUDA ARGENTINA 30 days 30 days ARMENIA - poe pta AUSTRALIA AUSTRIA 90 days pta (Schengen AZERBAIJAN - poe pta BAHAMAS BAHRAIN
AFGHANISTAN pta ALBANIA poe ALGERIA - pta ANDORRA poe ANGOLA pta ANTIGUA & BARBUDA ARGENTINA 30 days 30 days ARMENIA - poe pta AUSTRALIA AUSTRIA 90 days pta (Schengen AZERBAIJAN - poe pta BAHAMAS BAHRAIN
Mineral Industry Surveys
 4 Mineral Industry Surveys For information contact: Robert L. Virta, Asbestos Commodity Specialist U.S. Geological Survey 989 National Center Reston, VA 20192 Telephone: 703-648-7726, Fax: (703) 648-7757
4 Mineral Industry Surveys For information contact: Robert L. Virta, Asbestos Commodity Specialist U.S. Geological Survey 989 National Center Reston, VA 20192 Telephone: 703-648-7726, Fax: (703) 648-7757
Brandeis University. International Student & Scholar Statistics
 1 Brandeis University International Student & Scholar Statistics 2014 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW OF INTERNATIONAL STUDENT & SCHOLAR POPULATION 3 DETAILED INFORMATION ON INTERNATIONAL STUDENT POPULATION
1 Brandeis University International Student & Scholar Statistics 2014 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW OF INTERNATIONAL STUDENT & SCHOLAR POPULATION 3 DETAILED INFORMATION ON INTERNATIONAL STUDENT POPULATION
ULTRA Mobile International Long Distance Rate Table
 Afghanistan 25 20 80 Afghanistan Mobile 23.5 21 85 Albania 8 63 250 Albania - Tirana 8 63 250 Albania Mobile 27.5 18 73 Algeria 6.5 77 308 Algeria Mobile 32 16 63 American Samoa 5 100 400 Andorra 22.5
Afghanistan 25 20 80 Afghanistan Mobile 23.5 21 85 Albania 8 63 250 Albania - Tirana 8 63 250 Albania Mobile 27.5 18 73 Algeria 6.5 77 308 Algeria Mobile 32 16 63 American Samoa 5 100 400 Andorra 22.5
CONVENTION FOR THE SUPPRESSION OF UNLAWFUL SEIZURE OF AIRCRAFT SIGNED AT THE HAGUE ON 16 DECEMBER 1970
 CONVENTION FOR THE SUPPRESSION OF UNLAWFUL SEIZURE OF AIRCRAFT SIGNED AT THE HAGUE ON 16 DECEMBER 1970 Entry into force: The Convention entered into force on 14 October 1971. Status: 185 Parties. This
CONVENTION FOR THE SUPPRESSION OF UNLAWFUL SEIZURE OF AIRCRAFT SIGNED AT THE HAGUE ON 16 DECEMBER 1970 Entry into force: The Convention entered into force on 14 October 1971. Status: 185 Parties. This
Standard Virgin Mobile Rates
 Standard Virgin Mobile National Out of Bundle * National Landlines National Mobiles National Texts Data per MB Calls to UPC Customer Care (1908) Voicemail 10c per text 1c per MB International ** UK Landlines
Standard Virgin Mobile National Out of Bundle * National Landlines National Mobiles National Texts Data per MB Calls to UPC Customer Care (1908) Voicemail 10c per text 1c per MB International ** UK Landlines
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts
 World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use WHO/ISH (World Health Organization/International
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use WHO/ISH (World Health Organization/International
Withholding Tax Rates 2016*
 Withholding Tax Rates 2016* International Tax Updated March 2016 Jurisdiction Dividends Interest Royalties Notes Albania 15% 15% 15% Algeria 15% 10% 24% Andorra 0% 0% 5% Angola 10% 15% 10% Anguilla 0%
Withholding Tax Rates 2016* International Tax Updated March 2016 Jurisdiction Dividends Interest Royalties Notes Albania 15% 15% 15% Algeria 15% 10% 24% Andorra 0% 0% 5% Angola 10% 15% 10% Anguilla 0%
2015 Update and MDG Assessment
 Update and MDG Assessment WHO Library CataloguinginPublication Data Progress on Sanitation and Drinking Water update and MDG assessment..water supply standards..sanitation trends..drinking water supply
Update and MDG Assessment WHO Library CataloguinginPublication Data Progress on Sanitation and Drinking Water update and MDG assessment..water supply standards..sanitation trends..drinking water supply
Progress and prospects
 Ending CHILD MARRIAGE Progress and prospects UNICEF/BANA213-182/Kiron The current situation Worldwide, more than 7 million women alive today were married before their 18th birthday. More than one in three
Ending CHILD MARRIAGE Progress and prospects UNICEF/BANA213-182/Kiron The current situation Worldwide, more than 7 million women alive today were married before their 18th birthday. More than one in three
Euler Hermes Country Risk Ratings JUNE 2014 REVIEW
 Euler Hermes Risk s Afghanistan D High Albania D High Algeria C Medium American Samoa A Low Andorra AA Low Angola C Sensitive Anguilla BB Low Antarctica AA Low Antigua & Barbuda C Sensitive Argentina D
Euler Hermes Risk s Afghanistan D High Albania D High Algeria C Medium American Samoa A Low Andorra AA Low Angola C Sensitive Anguilla BB Low Antarctica AA Low Antigua & Barbuda C Sensitive Argentina D
Euler Hermes Country Risk Ratings SEPTEMBER 2014 REVIEW
 Euler Hermes Risk s Afghanistan D 4 (High) Albania D 4 (High) Algeria C 2 (Medium) American Samoa A 1 (Low) Andorra AA 1 (Low) Angola C 3 (Sensitive) Anguilla BB 1 (Low) Antarctica AA 1 (Low) Antigua &
Euler Hermes Risk s Afghanistan D 4 (High) Albania D 4 (High) Algeria C 2 (Medium) American Samoa A 1 (Low) Andorra AA 1 (Low) Angola C 3 (Sensitive) Anguilla BB 1 (Low) Antarctica AA 1 (Low) Antigua &
Euler Hermes Country Risk Ratings JUNE 2016 REVIEW
 Euler Hermes Risk s Afghanistan D 4 (High) Albania D 4 (High) Algeria C 2 (Medium) American Samoa A 1 (Low) Andorra AA 1 (Low) Angola C 3 (Sensitive) Anguilla BB 1 (Low) Antarctica AA 1 (Low) Antigua &
Euler Hermes Risk s Afghanistan D 4 (High) Albania D 4 (High) Algeria C 2 (Medium) American Samoa A 1 (Low) Andorra AA 1 (Low) Angola C 3 (Sensitive) Anguilla BB 1 (Low) Antarctica AA 1 (Low) Antigua &
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers
 UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
VoIP Phone Calling Rates
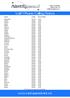 Afghanistan Default $0.52 Albania Default $0.24 Albania Mobile $0.71 Algeria Default $0.17 Algeria Mobile $0.86 Andorra Default $0.09 Andorra Mobile $0.48 Angola Default $0.21 Angola Mobile $0.24 Anguilla
Afghanistan Default $0.52 Albania Default $0.24 Albania Mobile $0.71 Algeria Default $0.17 Algeria Mobile $0.86 Andorra Default $0.09 Andorra Mobile $0.48 Angola Default $0.21 Angola Mobile $0.24 Anguilla
Abortion Policies and Reproductive Health around the World United Nations
 Abortion Policies and Reproductive Health around the World United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division DESA The Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United
Abortion Policies and Reproductive Health around the World United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division DESA The Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United
CONTENTS THE UNITED NATIONS' HIGH COMMISSIONER FOR REFUGEES (UNHCR)
 CONTENTS HIGH COMMISSIONER FOR REFUGEES (UNHCR) 1. INTRODUCTION...2 2. UNHCR HANDBOOK...2 3. CONTACT WITH UNHCR...2 4. UNHCR DATABASE...3 5. UNHCR HEADQUARTERS...3 ANNEX A. LIST OF STATES PARTY TO THE
CONTENTS HIGH COMMISSIONER FOR REFUGEES (UNHCR) 1. INTRODUCTION...2 2. UNHCR HANDBOOK...2 3. CONTACT WITH UNHCR...2 4. UNHCR DATABASE...3 5. UNHCR HEADQUARTERS...3 ANNEX A. LIST OF STATES PARTY TO THE
MCI Business Complete Unlimited
 MCI Business Complete Unlimited Only available in areas where MCI offers Local Service and customers must be enrolled in corresponding MCI Business Complete Local Product to receive benefits of this plan.
MCI Business Complete Unlimited Only available in areas where MCI offers Local Service and customers must be enrolled in corresponding MCI Business Complete Local Product to receive benefits of this plan.
MDRI HIPC. heavily indebted poor countries initiative. To provide additional support to HIPCs to reach the MDGs.
 Goal To ensure deep, broad and fast debt relief and thereby contribute toward growth, poverty reduction, and debt sustainability in the poorest, most heavily indebted countries. HIPC heavily indebted poor
Goal To ensure deep, broad and fast debt relief and thereby contribute toward growth, poverty reduction, and debt sustainability in the poorest, most heavily indebted countries. HIPC heavily indebted poor
Global Hotel Review (Media Version)
 United Kingdom United States Blue Fin Building 735 East Main Street 110 Southwark Street Hendersonville London SE1 0TA TN 37075 Phone: +44 (0)20 7922 1930 Phone: +1 (615) 824 8664 Fax: +44 (0)20 7922 1931
United Kingdom United States Blue Fin Building 735 East Main Street 110 Southwark Street Hendersonville London SE1 0TA TN 37075 Phone: +44 (0)20 7922 1930 Phone: +1 (615) 824 8664 Fax: +44 (0)20 7922 1931
Global Hotel Review (Media Version)
 United Kingdom United States Blue Fin Building 735 East Main Street 110 Southwark Street Hendersonville London SE1 0TA TN 37075 Phone: +44 (0)20 7922 1930 Phone: +1 (615) 824 8664 Fax: +44 (0)20 7922 1931
United Kingdom United States Blue Fin Building 735 East Main Street 110 Southwark Street Hendersonville London SE1 0TA TN 37075 Phone: +44 (0)20 7922 1930 Phone: +1 (615) 824 8664 Fax: +44 (0)20 7922 1931
