NANO INDENTERS FROM MICRO STAR TECHNOLOGIES
|
|
|
- Terence Jasper Simpson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
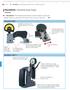
1 NANO INDENTERS FROM MICRO STAR TECHNOLOGIES Micro Star makes a variety of nano indenters following defined standards or custom requested geometries and dimensions. Micro Star calibration laboratory complies with the requirements of the International Standard ISO/IEC Standard nano indenters and custom indenters with applicable geometry are accepted only if the pertinent dimensions and angles are within the ranges specified by the ISO which defines internationally accepted micro and nano indenter tolerances. Figure 1 shows an example of a nano indenter with its three parts, the diamond, the holder and the bond. Micro Star can provide Standard Traceable Nano Indenters. They are inspected and measured with equipment and standards traceable to the NIST 3 or PTB 4 and supplied with a calibration certificate containing pertinent measurement records and references. TIP GEOMETRIES The tabulated illustrations show most of the indenter geometries available from Micro Star. Each type of indenter is designated by two letters in blue. There are examples of TEM 5 micrographs of critical measured dimensions, which are included with traceable indenters or per request. Figure 2 shows sharp point 3-sided pyramid geometry. The defining angle a is the angle between the axis and any of the faces. The 3 faces are symmetrically placed around the axis 120 apart. The Berkovich 6 indenter is designed to have the same area as the Vickers indenter at any given indentation depth. The modified Berkovich 7 indenter is designed to have the same projected area as the Vickers indenter at any given indentation depth. Micro Star makes a wide range of 3-sided indenters with custom angles and flat or round ends of any compatible size. Figure 3 shows sharp 4-sided geometries. Most 4-sided indenters have their faces symmetrically placed around the axis 90 apart and the defining angle a is measured between the axis and each face. The standard Knoop indenter has a special geometry as shown. Figure 1 Nano Indenter Example There are numerous geometries available for the indenter shape such as three sided pyramids, four sided pyramids, wedges, cones, cylinders or spheres. The tip end of the indenter can be made sharp, flat, or rounded to a cylindrical or spherical shape. Diamond and sapphire are the primary materials of Micro Star nano indenters but other hard materials can also be used such as quartz, silicone, tungsten, steel, tungsten carbide and almost any other hard metal or ceramic. Micro Star also has conductive diamond available. Nano indenters are mounted on holders which could be the standard design from a manufacturer of nano indenting equipment, or a custom design. Micro Star can design and make the holders or use the ones supplied by the customer. The holder material can be steel, titanium, machinable ceramic or other suitable material. In most cases Micro Star attaches the indenter to the holder using a rigid metal bonding process. A sharp 4-sided pyramid tip always ends in a small line (shown on the TEM micrograph) called the line of conjunction. Figure 4 shows 3 and 4-sided indenters with flat and rounded tips. Figure 5 shows wedge indenter configurations. Figure 6 shows the general cone geometry with sharp, flat or spherical end. There are no recognized standard angles or sizes for conical indenters. The taper cone configuration makes possible a very small cylindrical rod at the end of a large body as shown on Figure 7. Many Micro Star nano indenters are made at the end of a taper cone. The small volume of material to be shaped to a particular geometry provides higher precision and minimizes anisotropic 8 effects. Figure 8 shows a spherical indenter. Spheres made of various materials are attached to the indenter holder. Many available spheres are rough at microscopic scale. If required, the end surface of the sphere is polished up to a few nanometers and measured with the AFM 9. 1
2 BERKOVICH TB CUBE CORNER TC 3-SIDED CUSTOM TD SHARPNESS TEM micrograph Berkovich: a = Mod. Berkovich: a = Available as Traceable Standard Cube corner: a = Available as Traceable Standard Custom 3-sided indenters: 80 > a > 20 Micro Star 3-sided sharp indenters tip radius < 50nm. Figure 2 SHARP 3-SIDED INDENTERS VICKERS FV KNOOP INDENTER FK 4-SIDED CUSTOM FD END LINE TEM micrograph Standard Vickers indenter: a = Available as Traceable Standard Standard Knoop indenter defined by 2 angles: d = , g = Custom 4-sided indenters: 80 > a > 20 Micro Star indenters maximum line of conjunction: 400nm. Figure 3 SHARP 4-SIDED INDENTERS 4-SIDE FLAT END FP 4-SIDE ROUND END FR 3-SIDE FLAT END TP 3-SIDE ROUND END TR Flat square side from 500nm to any compatible size. End radius from 100nm to any compatible value. Flat triangle from 300nm side to any compatible size. End radius from 100nm to any compatible value. Figure 4 FLAT AND ROUND ED INDENTERS 2
3 WEDGE INDENTER WS TAPERED WEDGE WT CYLINDRICAL WEDGE WC ROUNDED WEDGE WR Edge length from 0.3mm to 3mm. Sharp edge radius less than 10nm. Included angle: 30 < i < 90 Wedge with tapered corners. Edge length from 0.5µ to 2mm. Angles: 30 < i < 90, 15 < s < 45 Wedge indenter with cylindrical edge angles same as WT. Radius from 200nm to 5µ. Wedge indenter with cylindrical edge and rounded corners. Radius from 200nm to 5µ. Figure 5 WEDGE INDENTERS CONE TIP VS POINT SHARPNESS TEM micrograph FLAT END CONE VP ROUND END CONE VR Included conical angle: 20 > c > 140 Micro Star sharp cone radius less than 300nm. Flat from 500nm diameter to larger compatible sizes. Spherical end radius <50nm to larger compatible sizes. Figure 6 CONE INDENTERS FILAMENT ROD YS CONE END ROD VS FLAT END ROD YP ROUND END ROD YR Thin cylindrical probe 0.4µ < diameter < 20µ Straight section up to 50µ long. End not defined. Straight cone at end of cylindrical section. Most Micro Star cone indenters (Type V) are made this way. Diameter from 20µ to larger sizes compatible with indenter. Straight section up to 0.3mm long. Spherical end rod. Diameter from 20µ to larger compatible sizes. Straight section up to 0.3mm long. Figure 7 TAPER CONE INDENTERS 3
4 possible to approach circular or spherical geometries but at higher cost. Figure 8 SPHERICAL INDENTER BR Spheres of sapphire and other materials metal bonded to the holder. Sphere diameters between 5µ and 2mm. Not all intermediate sizes available. Surface polished to < 20 nm roughness 10 on request. DIAMOND AND OTHER MATERIALS Diamond is the primary material for nano indentation. Only single crystal diamond, free of impurities or inclusions is used. Most Micro Star diamond nano indenters are shaped at one end of a large square section prism, as seen on some of the illustrations. Diamond indenters are accurately aligned with the atomic crystal orientation such that the axis is in line with the 100 direction. One face of 3-sided and all four faces of 4-sided indenters follow the 100 crystal direction. This is illustrated on Figure 9. Other crystal orientations are available at customer request. Figure 10 Diamond 4-sided Anisotropy - A diamond circular flat end becomes almost a square (left). Sapphire can approach a perfect circle. Micro Star has electrically conductive diamond available. The conductivity comes from Boron ions dispersed through the bulk of the material not just from surface coating. Conductivity is required in some special applications and to prevent static charge distortion of measurements. The resistivity is 0.04 Ohm m, similar to graphite. Sapphire is the second material available for Micro Star nano indenters. Although not as hard as diamond, sapphire can be shaped to similarly sharp points and edges. Micro Star sapphire indenters are made with the crystal C axis aligned with the indenter axis. The anisotropy of sapphire is much weaker than diamond permitting nearly perfect spherical and circular shapes. Figures 10 and 11 compare some diamond and sapphire properties. Property Diamond Sapphire Units Hardness 10 9 Mohs-scale Density g/cc Figure 9 Diamond Atomic 100 Crystal Directions (dotted lines) that Coincide with Micro Star Indenter s Axis Young Modulus E GPa Thermal conductivity W/(m K) The advantages of diamond for nano indentation come from its exceptional properties of hardness, thermal conductivity and chemical inertness, which surpass any other known material. Thermal expansion / C Electric resistivity Insulator Insulator Ohm m Figure 11 Some Diamond and Sapphire Properties The strong diamond anisotropy is a disadvantage for circular geometry nano indenters. This applies to conical, Most other hard materials can be used for making nano cylindrical and spherical indenters. Figure 10 shows the indenters, such are quartz, silicone, tungsten, steel, flat circular end of a diamond cone indenter (types VP tungsten carbide and almost any other hard metal or or YP), compared with the same indenter made of ceramic. sapphire. If a non circular perimeter shape is acceptable, the diamond indenter can be made to a precise area specification in square microns. With diamond, it is 4
5 INDENTER HOLDERS Micro Star has indenter holders available made to the specifications of some current nano indenting instrument manufacturers. Micro Star can also make holders for existing instruments, or design and make new ones based on customer requirements. Figure 12 shows 3 general holder design examples. The reference cylindrical and flat surfaces define the central axis and are the means of aligning the indenter with the axis of the instrument. Holders A and B are fastened with threads while C relies on a set screw in the instrument. Holder C has an orienting tab which aligns the indenter rotational angle with the instrument. Rotational orientation is not applicable for the majority of indentation measurements. b) Damaging the indenter as debris particles are crushed between the indenter and the sample, producing lateral forces which the nanometer size tip is not designed to withstand. Before shipment, Micro Star indenters are cleaned in vacuum and inspected at high magnification. The user needs to maintain the probe clean and undamaged in order to acquire accurate test results. Figure 13 Indenter Protective Packaging The indenters are supplied in special protective packaging, Figure 13. The tip is protected from contact with other objects by the tube as shown. This tube fits lightly on the cylindrical part of the holder. The tube may be used as a handle to attach the indenter to the instrument and then remove it with a straight motion avoiding to touch the tip. Figure 12 Indenter Holders Design Features Holders are made of steel, titanium, machinable ceramic, other metals or rigid materials. Micro Star attaches the indenters to the holder using a proprietary metal bonding process. The metal forms a molecular bond with both materials be it diamond-steel, diamondceramic, sapphire-steel, sapphire-diamond, etc. The bonding metal is rigid up to 500 C and has a tensile strength of 400 MPa. In some cases diamond can be pressed into a metal holder if, for instance, is to be used at higher temperatures. Figure 14 Indenter Cleaning with a Cotton Swab HANDLING AND CLEANING Micro Star nano indenters are made to probe materials properties at nanometer scale. It follows that a basic requirement is the total absence of debris and particle contamination which would affect the indenter s performance in two ways. a) Distorting the measurements because contaminating material adds an unknown factor negating the precise geometry of the clean indenter. If the diamond nano indenter is properly handled, it should not require cleaning. If it nevertheless becomes contaminated, clean as follows. Looking through a stereo microscope, rub the diamond with a cotton swab soaked with isopropyl alcohol, Figure 14. Before the alcohol dries, blow the tip with pressurized air or other clean gas. Inspect the diamond with an optical microscope at 400X. Repeat cleaning if necessary. Do not use the indenter unless the tip is totally clean and free of debris. 5
6 SPECIFICATIONS AND TOLERANCES Micro Star indenters are measured with instruments calibrated with traceable standards. The angles are measured with a specially designed goniometer. Linear dimensions are measured with calibrated optical microscopes or electron microscopes. Micro Star has a specially modified TEM for sub micron measurements, as well as a standard SEM 12 and field emission SEM. An AFM are used for surface roughness measurements which are available on request for some indenters. Each Micro Star indenter is measured individually for all pertinent dimensions. Figure 16 shows the angles and nomenclature used on a 3-sided indenter. Figure 17 is the specification sheet issued with each indenter. Sample data from a cube corner indenter is shown. Figure 18 is a table of the symbols used with Micro Star indenter measurements and specifications with the ISO required and Micro Star standard tolerances. Smaller tolerances are available for some indenters at extra cost. The tolerances of all specified angular or linear dimensions meet or exceed ISO which defines internationally accepted micro and nano indenter tolerances. STANDARD TRACEABLE NANO INDENTERS Micro Star can provide the Berkovich, Modified Berkovich, Cube Corner, and Vickers as standard traceable nano indenters following the definitions of ISO These indenters are inspected and measured with equipment and standards traceable to the NIST or PTB. A Calibration Certificate accompanying these indenters covers the following items pertaining to the particular indenter: Figure 16 Angle Measurements on a 3-sided Indenter (for clarity, not all the angles are shown). a) Table of measurements. b) Uncertainty of measurements. c) Confidence level of measurements. d) Measuring methods. e) Measuring instruments. f) Instrument calibration information. g) Standards used. h) Standards traceability. i) Inspector s signature and date. 6
7 SERIAL NUMBER INDENTER TYPE DESCRIPTION HOLDER TYPE NANO INDENTER SPECIFICATIONS TC CUBE CORNER MS1 DIAMOND CONDUCTIVE DIAMOND SAPPHIRE OTHER Dimension Nominal Value Measured Value Uncertainty Units Angle a ±0.025 deg Angle a ±0.025 deg Angle a ±0.025 deg Angle a 4 deg Angle b ±0.025 deg Angle b ±0.025 deg Angle b 14 deg Angle c deg Angle e* 0.15 ±0.025 deg Line L Radius R < 50 nm Diameter Area D A Indentation depth h >2 µ Surface roughness r* <20 nm Figure 17 Indenter Specification Sheet with Example Data in Blue *Measured on Request at an Extra Cost 7
8 SYMBOL DIMENSIONAL NOMENCLATURE AND TOLERANCES DESCRIPTION 1 (2, 3, 4) Face number 1. Face 1 can be marked on request. A 1 (A 2, A 3, A 4 ) Line perpendicular to face 1. B 1 (B 2, B 3, B 4 ) H T Projection of line A 1 on a plane perpendicular to the Indenter axis H. Indenter holder axis. Final angle measurements and user results refer to this axis. Indenter crystal axis. Ideally should be the same as H but in practice may differ by angle e. ISO REQUIRED TOLERANCE MST STANDARD TOLERANCE e Angle between T and H. ± 0.25 a 1 (a 2, a 3, a 4 ) b 12 (b 13, b 14 ) Face 1 tilt angle with respect to H, equal to angle between A 1 and B 1. Rotation angle between face 1 and face 2, equal to angle between B 1 and B 2. ± 0.3 ± 0.25 ± 0.3 ± 0.25 c Included angle on a cone. ± 5 ± 5 L Line of conjunction on 4-sided indenters. < 500 nm < 400 nm L (wedge indenter) Wedge length. ± 20% of L R (sharp tip) Tip radius. < 200 nm < 50 nm R (spherical tip ) Radius. ± 25% of R ± 10% of R D Diameter of a circular flat tip or cylinder. ± 10% of D A Area of a flat tip. ± 20% of A h (sharp tip) Valid indentation depth. > 200 nm > 1000 nm h (cone with spherical tip) h (spherical indenter or cylinder) Valid indentation depth. Valid indentation depth. >15 % of R (c = 90 ) >35 % of R (c = 40 ) >15 % of R (c = 90 ) >35 % of R (c = 40 ) >35 % of R r Surface roughness. <30nm Figure 18 Symbols in Figures 16 and 17 (ISO required tolerances and Micro Star standard tolerances are shown where applicable) 8
9 1 ISO/IEC = International standard comprising general requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. 2 ISO = Instrumented indentation test for hardness and materials parameters. Part 2: Verification and calibration of testing machines. In particular section 4: Direct verification and calibration. 3 NIST = National Institute of Standard and Technology. 4 PTB = Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (the counterpart of NIST in Germany). 5 TEM = Transmission Electron Microscope. 6 Berkovich, E. S., Three faceted diamond pyramid for micro hardness testing Industrial Diamond Review, 11, #127, June Oliver, W.C. and Pharr, G.M., An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J Mater. Res.,7, #6, June 1992, pp Anisotropy = The change of crystal properties with atomic directions. Anisotropy is especially pronounced in diamond with different abrasion resistance depending on the crystal orientation. 9 AFM = Atomic Force Microscope 10 Measured with a calibrated AFM. 11 Conductive diamond available from Micro Star. 12 SEM = Scanning Electron Microscope 9
Lapping and Polishing Basics
 Lapping and Polishing Basics Applications Laboratory Report 54 Lapping and Polishing 1.0: Introduction Lapping and polishing is a process by which material is precisely removed from a workpiece (or specimen)
Lapping and Polishing Basics Applications Laboratory Report 54 Lapping and Polishing 1.0: Introduction Lapping and polishing is a process by which material is precisely removed from a workpiece (or specimen)
Section. Tolerances. Aluminum Extrusion Manual. 4th Edition
 Section 8 Tolerances Aluminum Extrusion Manual 4th Edition Section 8 How straight is straight enough? How flat is flat enough? How uniform must a wall thickness be in order to be acceptable? These are
Section 8 Tolerances Aluminum Extrusion Manual 4th Edition Section 8 How straight is straight enough? How flat is flat enough? How uniform must a wall thickness be in order to be acceptable? These are
Nanotribology of Hard Thin Film Coatings: A Case Study Using the G200 Nanoindenter
 Nanotribology of Hard Thin Film Coatings: A Case Study Using the G200 Nanoindenter Application Note Introduction Thin film coatings are extensively used in various applications, such as microelectronics,
Nanotribology of Hard Thin Film Coatings: A Case Study Using the G200 Nanoindenter Application Note Introduction Thin film coatings are extensively used in various applications, such as microelectronics,
Hardness Testing at Elevated Temperatures. SJ Shaffer, Ph.D. Bruker-TMT [email protected]
 Hardness Testing at Elevated Temperatures SJ Shaffer, Ph.D. Bruker-TMT [email protected] Outline What is Hardness? How is Hardness Measured? Overview of Hardness Test Methods Hardness Testing
Hardness Testing at Elevated Temperatures SJ Shaffer, Ph.D. Bruker-TMT [email protected] Outline What is Hardness? How is Hardness Measured? Overview of Hardness Test Methods Hardness Testing
ME 111: Engineering Drawing
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture # 14 (10/10/2011) Development of Surfaces http://www.iitg.ernet.in/arindam.dey/me111.htm http://www.iitg.ernet.in/rkbc/me111.htm http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~psr/ Indian
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture # 14 (10/10/2011) Development of Surfaces http://www.iitg.ernet.in/arindam.dey/me111.htm http://www.iitg.ernet.in/rkbc/me111.htm http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~psr/ Indian
Shape Dictionary YR to Y6
 Shape Dictionary YR to Y6 Guidance Notes The terms in this dictionary are taken from the booklet Mathematical Vocabulary produced by the National Numeracy Strategy. Children need to understand and use
Shape Dictionary YR to Y6 Guidance Notes The terms in this dictionary are taken from the booklet Mathematical Vocabulary produced by the National Numeracy Strategy. Children need to understand and use
Mechanical Properties of Metals Mechanical Properties refers to the behavior of material when external forces are applied
 Mechanical Properties of Metals Mechanical Properties refers to the behavior of material when external forces are applied Stress and strain fracture or engineering point of view: allows to predict the
Mechanical Properties of Metals Mechanical Properties refers to the behavior of material when external forces are applied Stress and strain fracture or engineering point of view: allows to predict the
ABERLINK 3D MKIII MEASUREMENT SOFTWARE
 ABERLINK 3D MKIII MEASUREMENT SOFTWARE PART 1 (MANUAL VERSION) COURSE TRAINING NOTES ABERLINK LTD. EASTCOMBE GLOS. GL6 7DY UK INDEX 1.0 Introduction to CMM measurement...4 2.0 Preparation and general hints
ABERLINK 3D MKIII MEASUREMENT SOFTWARE PART 1 (MANUAL VERSION) COURSE TRAINING NOTES ABERLINK LTD. EASTCOMBE GLOS. GL6 7DY UK INDEX 1.0 Introduction to CMM measurement...4 2.0 Preparation and general hints
CATIA Functional Tolerancing & Annotation TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation...2 Pull-down Menus...3 Insert...3 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation Workbench...4 Bottom Toolbar Changes...5 3D Grid Toolbar...5
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation...2 Pull-down Menus...3 Insert...3 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation Workbench...4 Bottom Toolbar Changes...5 3D Grid Toolbar...5
Force measurement. Forces VECTORIAL ISSUES ACTION ET RÉACTION ISOSTATISM
 Force measurement Forces VECTORIAL ISSUES In classical mechanics, a force is defined as "an action capable of modifying the quantity of movement of a material point". Therefore, a force has the attributes
Force measurement Forces VECTORIAL ISSUES In classical mechanics, a force is defined as "an action capable of modifying the quantity of movement of a material point". Therefore, a force has the attributes
MEASUREMENT OF END FACE GEOMETRY ON FIBER OPTIC TERMINI...2
 MEASUREMENT OF END FACE GEOMETRY ON FIBER OPTIC TERMINI...2 IMPORTANCE OF END FACE GEOMETRY...2 FIBER OPTIC CONNECTOR END FACE GEOMETRY MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES...2 INTERFEROMETRIC MICROSCOPE TYPES...3 MEASUREMENT
MEASUREMENT OF END FACE GEOMETRY ON FIBER OPTIC TERMINI...2 IMPORTANCE OF END FACE GEOMETRY...2 FIBER OPTIC CONNECTOR END FACE GEOMETRY MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES...2 INTERFEROMETRIC MICROSCOPE TYPES...3 MEASUREMENT
The CVD diamond booklet
 available at: www.diamond-materials.com/download Content 1. General properties of diamond... 2 2. Optical Properties... 4 Optical transparency...4 Absorption coefficient at 10.6 µm...5 Refractive index:
available at: www.diamond-materials.com/download Content 1. General properties of diamond... 2 2. Optical Properties... 4 Optical transparency...4 Absorption coefficient at 10.6 µm...5 Refractive index:
5-Axis Test-Piece Influence of Machining Position
 5-Axis Test-Piece Influence of Machining Position Michael Gebhardt, Wolfgang Knapp, Konrad Wegener Institute of Machine Tools and Manufacturing (IWF), Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH), Zurich,
5-Axis Test-Piece Influence of Machining Position Michael Gebhardt, Wolfgang Knapp, Konrad Wegener Institute of Machine Tools and Manufacturing (IWF), Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH), Zurich,
TechCut 4 Precision Low Speed Saw
 Product Brochure TechCut 4 Precision Low Speed Saw 3" - 6" Blade Range Digital Speed Display 1-Micron Sample Indexing Spring-Loaded Dressing Stick Attachment All Aluminum & Stainless Steel Construction
Product Brochure TechCut 4 Precision Low Speed Saw 3" - 6" Blade Range Digital Speed Display 1-Micron Sample Indexing Spring-Loaded Dressing Stick Attachment All Aluminum & Stainless Steel Construction
Think precision, Think HSS REAMING
 Think precision, Think HSS REAMING SUMMARY REAMING TOOLS 2 Zoom on a reamer 3 Which HSS for maximum efficiency? 4 Coatings for the best performance 5 Vocabulary 6 Choose the right design 7 Types of bevel
Think precision, Think HSS REAMING SUMMARY REAMING TOOLS 2 Zoom on a reamer 3 Which HSS for maximum efficiency? 4 Coatings for the best performance 5 Vocabulary 6 Choose the right design 7 Types of bevel
COATED CARBIDE. TiN. Al 2 O 3
 COATED CARBIDE GENERAL INFORMATION CVD = Chemical Vapour Deposition coated grades GC2015, GC2025, GC2135, GC235, GC3005, GC3015, GC3020, GC3025, GC3115, GC4015, GC4025, GC4035, S05F, and CD1810. PVD =
COATED CARBIDE GENERAL INFORMATION CVD = Chemical Vapour Deposition coated grades GC2015, GC2025, GC2135, GC235, GC3005, GC3015, GC3020, GC3025, GC3115, GC4015, GC4025, GC4035, S05F, and CD1810. PVD =
Injection moulding and modelling on a micro scale
 Injection moulding and modelling on a micro scale Technology Update Injection moulding and welding of plastics 11 November 2014 Research Projects (National / European) Micro/Nano/Multimaterial Manufacturing
Injection moulding and modelling on a micro scale Technology Update Injection moulding and welding of plastics 11 November 2014 Research Projects (National / European) Micro/Nano/Multimaterial Manufacturing
How To Make A Diamond Diamond Wirehead From A Diamond
 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work would not have been possible without the advice and support of many people. First, and foremost, I would like to thank my advisor Dr. John Patten for providing me the opportunity
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work would not have been possible without the advice and support of many people. First, and foremost, I would like to thank my advisor Dr. John Patten for providing me the opportunity
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING BASIC ALGEBRA
 MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING BASIC ALGEBRA TUTORIAL 4 AREAS AND VOLUMES This is the one of a series of basic tutorials in mathematics aimed at beginners or anyone wanting to refresh themselves on fundamentals.
MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING BASIC ALGEBRA TUTORIAL 4 AREAS AND VOLUMES This is the one of a series of basic tutorials in mathematics aimed at beginners or anyone wanting to refresh themselves on fundamentals.
ELECTRIC FIELD LINES AND EQUIPOTENTIAL SURFACES
 ELECTRIC FIELD LINES AND EQUIPOTENTIAL SURFACES The purpose of this lab session is to experimentally investigate the relation between electric field lines of force and equipotential surfaces in two dimensions.
ELECTRIC FIELD LINES AND EQUIPOTENTIAL SURFACES The purpose of this lab session is to experimentally investigate the relation between electric field lines of force and equipotential surfaces in two dimensions.
TIE-31: Mechanical and thermal properties of optical glass
 PAGE 1/10 1 Density The density of optical glass varies from 239 for N-BK10 to 603 for SF66 In most cases glasses with higher densities also have higher refractive indices (eg SF type glasses) The density
PAGE 1/10 1 Density The density of optical glass varies from 239 for N-BK10 to 603 for SF66 In most cases glasses with higher densities also have higher refractive indices (eg SF type glasses) The density
Ion Beam Sputtering: Practical Applications to Electron Microscopy
 Ion Beam Sputtering: Practical Applications to Electron Microscopy Applications Laboratory Report Introduction Electron microscope specimens, both scanning (SEM) and transmission (TEM), often require a
Ion Beam Sputtering: Practical Applications to Electron Microscopy Applications Laboratory Report Introduction Electron microscope specimens, both scanning (SEM) and transmission (TEM), often require a
CHAPTER 6 WEAR TESTING MEASUREMENT
 84 CHAPTER 6 WEAR TESTING MEASUREMENT Wear is a process of removal of material from one or both of two solid surfaces in solid state contact. As the wear is a surface removal phenomenon and occurs mostly
84 CHAPTER 6 WEAR TESTING MEASUREMENT Wear is a process of removal of material from one or both of two solid surfaces in solid state contact. As the wear is a surface removal phenomenon and occurs mostly
CHAPTER 7 DISLOCATIONS AND STRENGTHENING MECHANISMS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 7-1 CHAPTER 7 DISLOCATIONS AND STRENGTHENING MECHANISMS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Basic Concepts of Dislocations Characteristics of Dislocations 7.1 The dislocation density is just the total dislocation length
7-1 CHAPTER 7 DISLOCATIONS AND STRENGTHENING MECHANISMS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Basic Concepts of Dislocations Characteristics of Dislocations 7.1 The dislocation density is just the total dislocation length
Length, Finland, MIKES (VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd, Centre for Metrology / Mittatekniikan keskus)
 absolute mise en pratigue: mise en pratigue: absolute absolute Level or Range 633 633 nm 0.04 fm 2 95% No 1 474 474 THz 24 khz 2 95% No 1 532 532 nm 0.08 fm 2 95% No 50 563 563 THz 0.08 MHz 2 95% No 51
absolute mise en pratigue: mise en pratigue: absolute absolute Level or Range 633 633 nm 0.04 fm 2 95% No 1 474 474 THz 24 khz 2 95% No 1 532 532 nm 0.08 fm 2 95% No 50 563 563 THz 0.08 MHz 2 95% No 51
Unit 6: EXTRUSION. Difficult to form metals like stainless steels, nickel based alloys and high temperature metals can also be extruded.
 1 Unit 6: EXTRUSION Introduction: Extrusion is a metal working process in which cross section of metal is reduced by forcing the metal through a die orifice under high pressure. It is used to produce cylindrical
1 Unit 6: EXTRUSION Introduction: Extrusion is a metal working process in which cross section of metal is reduced by forcing the metal through a die orifice under high pressure. It is used to produce cylindrical
Working Drawing and Assemblies. Chapter 10
 Working Drawing and Assemblies Chapter 10 Objectives 1.Define working drawings. 2. Describe how working drawings are used in industry. 3. List the major components of a complete set of working drawings.
Working Drawing and Assemblies Chapter 10 Objectives 1.Define working drawings. 2. Describe how working drawings are used in industry. 3. List the major components of a complete set of working drawings.
GEOMETRY OF SINGLE POINT TURNING TOOLS
 GEOMETRY OF SINGLE POINT TURNING TOOLS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Introduction to Features of single point cutting tool. Concept of rake and clearance angle and its importance System of description of Tool geometry
GEOMETRY OF SINGLE POINT TURNING TOOLS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Introduction to Features of single point cutting tool. Concept of rake and clearance angle and its importance System of description of Tool geometry
UNITED STATES CUTTING TOOL INSTITUTE Product Groupings for Standards Activities CUTTING TOOL PRODUCTS
 CUTTING TOOL PRODUCTS 1. BORING ISO 5609 Boring bars for indexable inserts Dimensions ISO 6261 Boring bars (tool holders with cylindrical shank) for indexable inserts Designation JIS B 4128 Boring bars
CUTTING TOOL PRODUCTS 1. BORING ISO 5609 Boring bars for indexable inserts Dimensions ISO 6261 Boring bars (tool holders with cylindrical shank) for indexable inserts Designation JIS B 4128 Boring bars
Lecture slides on rolling By: Dr H N Dhakal Lecturer in Mechanical and Marine Engineering, School of Engineering, University of Plymouth
 Lecture slides on rolling By: Dr H N Dhakal Lecturer in Mechanical and Marine Engineering, School of Engineering, University of Plymouth Bulk deformation forming (rolling) Rolling is the process of reducing
Lecture slides on rolling By: Dr H N Dhakal Lecturer in Mechanical and Marine Engineering, School of Engineering, University of Plymouth Bulk deformation forming (rolling) Rolling is the process of reducing
Chapter Outline. Mechanical Properties of Metals How do metals respond to external loads?
 Mechanical Properties of Metals How do metals respond to external loads? Stress and Strain Tension Compression Shear Torsion Elastic deformation Plastic Deformation Yield Strength Tensile Strength Ductility
Mechanical Properties of Metals How do metals respond to external loads? Stress and Strain Tension Compression Shear Torsion Elastic deformation Plastic Deformation Yield Strength Tensile Strength Ductility
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABORATORY
 ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABORATORY 01 Januarly 2000 / mgj MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND PERFORMANCE OF MATERIALS: HARDNESS TESTING* PURPOSE The purpose of this exercise is to obtain a number of experimental
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABORATORY 01 Januarly 2000 / mgj MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND PERFORMANCE OF MATERIALS: HARDNESS TESTING* PURPOSE The purpose of this exercise is to obtain a number of experimental
Micro-CT for SEM Non-destructive Measurement and Volume Visualization of Specimens Internal Microstructure in SEM Micro-CT Innovation with Integrity
 Micro-CT for SEM Non-destructive Measurement and Volume Visualization of Specimens Internal Microstructure in SEM Innovation with Integrity Micro-CT 3D Microscopy Using Micro-CT for SEM Micro-CT for SEM
Micro-CT for SEM Non-destructive Measurement and Volume Visualization of Specimens Internal Microstructure in SEM Innovation with Integrity Micro-CT 3D Microscopy Using Micro-CT for SEM Micro-CT for SEM
VICKERS HARDNESS TESTER. HBS HBW Kc
 ICKERS HARDNESS TESTER H HK HBS HBW Kc Clean Touch Panel coordinated with highly integrated PC board. Measuring procedures, conditions and data are displayed clearly. (F-800 Series) Accurate light load
ICKERS HARDNESS TESTER H HK HBS HBW Kc Clean Touch Panel coordinated with highly integrated PC board. Measuring procedures, conditions and data are displayed clearly. (F-800 Series) Accurate light load
ISO 1101 Geometrical product specifications (GPS) Geometrical tolerancing Tolerances of form, orientation, location and run-out
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1101 Third edition 2012-04-15 Geometrical product specifications (GPS) Geometrical tolerancing Tolerances of form, orientation, location and run-out Spécification géométrique
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1101 Third edition 2012-04-15 Geometrical product specifications (GPS) Geometrical tolerancing Tolerances of form, orientation, location and run-out Spécification géométrique
Be careful not to scratch or hit front edge of the side viewing micro prisms onto hard objects!
 Instructions Manual Flexia BGA Inspection Systems This manual describes how to use Flexia BGA Inspection System Optilia Instruments 1 AB Contents 1. Safety and maintenance Instructions 3 2. About Flexia
Instructions Manual Flexia BGA Inspection Systems This manual describes how to use Flexia BGA Inspection System Optilia Instruments 1 AB Contents 1. Safety and maintenance Instructions 3 2. About Flexia
Technical Product Specification (TPS)
 ISO Standards collection Technical Product Specification (TPS) Contents ISO 1:2002 Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) -- Standard reference temperature for geometrical product specification and verification
ISO Standards collection Technical Product Specification (TPS) Contents ISO 1:2002 Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) -- Standard reference temperature for geometrical product specification and verification
Specification for Rotary Drill Stem Elements
 Addendum 1 March 2007 Effective Date: September 1, 2007 Specification for Rotary Drill Stem Elements ANSI/API SPECIFICATION 7-1 FIRST EDITION, MARCH 2006 EFFECTIVE DATE: SEPTEMBER 2006 ISO 10424-1:2004
Addendum 1 March 2007 Effective Date: September 1, 2007 Specification for Rotary Drill Stem Elements ANSI/API SPECIFICATION 7-1 FIRST EDITION, MARCH 2006 EFFECTIVE DATE: SEPTEMBER 2006 ISO 10424-1:2004
Sheet metal operations - Bending and related processes
 Sheet metal operations - Bending and related processes R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Table of Contents 1.Quiz-Key... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.Bending
Sheet metal operations - Bending and related processes R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Table of Contents 1.Quiz-Key... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.Bending
The measuring of the hardness
 The measuring of the hardness In the field of mechanics one often meets with the notion of "hardness", and in fact the hardness is a fundamental characteristic to determine whether a certain material is
The measuring of the hardness In the field of mechanics one often meets with the notion of "hardness", and in fact the hardness is a fundamental characteristic to determine whether a certain material is
Platonic Solids. Some solids have curved surfaces or a mix of curved and flat surfaces (so they aren't polyhedra). Examples:
 Solid Geometry Solid Geometry is the geometry of three-dimensional space, the kind of space we live in. Three Dimensions It is called three-dimensional or 3D because there are three dimensions: width,
Solid Geometry Solid Geometry is the geometry of three-dimensional space, the kind of space we live in. Three Dimensions It is called three-dimensional or 3D because there are three dimensions: width,
SCREW THREADS C H A P T E R 17
 C H A P T E R 17 SCREW THREADS Screw threads are of prime importance in machine drawing. It is a functional element used as temporary fasteners such as bolt, stud, nut and screw etc. These are constructed
C H A P T E R 17 SCREW THREADS Screw threads are of prime importance in machine drawing. It is a functional element used as temporary fasteners such as bolt, stud, nut and screw etc. These are constructed
Machine Tool Inspection & Analyzer solutions
 Machine Tool Inspection & Analyzer solutions Introduction IBS Precision Engineering machine tool inspection series offers a range of products to provide peace of mind and control to machine operators by
Machine Tool Inspection & Analyzer solutions Introduction IBS Precision Engineering machine tool inspection series offers a range of products to provide peace of mind and control to machine operators by
MEASURING MACHINES. Pratt & Whitney METROLOGY LABORATORY. Measurement Systems, Inc.
 METROLOGY LABORATORY Pratt & Whitney Measurement s, Inc. METROLOGY LABORATORY The Standard of Accuracy Pratt & Whitney Metrology Laboratory Machines are the standard of accuracy to which all other gages
METROLOGY LABORATORY Pratt & Whitney Measurement s, Inc. METROLOGY LABORATORY The Standard of Accuracy Pratt & Whitney Metrology Laboratory Machines are the standard of accuracy to which all other gages
Coating Technology: Evaporation Vs Sputtering
 Satisloh Italy S.r.l. Coating Technology: Evaporation Vs Sputtering Gianni Monaco, PhD R&D project manager, Satisloh Italy 04.04.2016 V1 The aim of this document is to provide basic technical information
Satisloh Italy S.r.l. Coating Technology: Evaporation Vs Sputtering Gianni Monaco, PhD R&D project manager, Satisloh Italy 04.04.2016 V1 The aim of this document is to provide basic technical information
Milling. COPYRIGHT 2008, Seco Tools AB 1/111
 Milling 1/111 2/111 Milling A simple choice! Experts required? No Just follow some basic rules. 3/111 Face milling 4/111 Square shoulder milling 5/111 Disc milling 6/111 Copy milling 7/111 Plunge milling
Milling 1/111 2/111 Milling A simple choice! Experts required? No Just follow some basic rules. 3/111 Face milling 4/111 Square shoulder milling 5/111 Disc milling 6/111 Copy milling 7/111 Plunge milling
Chapter 6 Machining Center Carbide Insert Fundamentals
 This sample chapter is for review purposes only. Copyright The Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. N10G20G99G40 N20G96S800M3 N30G50S4000 N40T0100M8 N50G00X3.35Z1.25T0101 N60G01X3.25F.002 N70G04X0.5
This sample chapter is for review purposes only. Copyright The Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. N10G20G99G40 N20G96S800M3 N30G50S4000 N40T0100M8 N50G00X3.35Z1.25T0101 N60G01X3.25F.002 N70G04X0.5
INTERNATIONAL HOCKEY FEDERATION PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS AND TEST PROCEDURES FOR HOCKEY BALLS. Published: April 1999
 INTERNATIONAL HOCKEY FEDERATION PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS AND TEST PROCEDURES FOR HOCKEY BALLS Published: April 1999 CONTENTS 1 Introduction 2 Test Procedures General 3 Standards and Specific Test Procedures
INTERNATIONAL HOCKEY FEDERATION PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS AND TEST PROCEDURES FOR HOCKEY BALLS Published: April 1999 CONTENTS 1 Introduction 2 Test Procedures General 3 Standards and Specific Test Procedures
DiwiTherm, Resistance Thermometers Model TR75, with digital Display Battery or Solar Powered
 Electrical Temperature Measurement DiwiTherm, Resistance Thermometers Model TR75, with digital Display Battery or Solar Powered WIKA Data Sheet TE 60.75 Applications Machinery, plant and tank construction
Electrical Temperature Measurement DiwiTherm, Resistance Thermometers Model TR75, with digital Display Battery or Solar Powered WIKA Data Sheet TE 60.75 Applications Machinery, plant and tank construction
RAMAX S Prehardened stainless holder steel
 T O O L S T E E L F A C T S RAMAX S Prehardened stainless holder steel Wherever tools are made Wherever tools are used This information is based on our present state of knowledge and is intended to provide
T O O L S T E E L F A C T S RAMAX S Prehardened stainless holder steel Wherever tools are made Wherever tools are used This information is based on our present state of knowledge and is intended to provide
Valu Guide Sheaths. Valu Guide Inserts. Optional Valu Guide Inserts. Typical Properties of Valu Guide Rail. and Hardware.
 14 gauge stainless steel The Original, Long Life Sanitary Guide Rail Valu Guide rail incorporates two outstanding materials: stainless steel and UHMW. The 14 ga. stainless steel sheath provides rigid streamlined
14 gauge stainless steel The Original, Long Life Sanitary Guide Rail Valu Guide rail incorporates two outstanding materials: stainless steel and UHMW. The 14 ga. stainless steel sheath provides rigid streamlined
ASME Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Professional Certification
 ASME Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Professional Certification Applicant Information STATEMENT OF POLICY ON THE USE OF ASME GDTP SYMBOLS AND AUTHORIZATION IN ADVERTISING ASME has established procedures
ASME Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Professional Certification Applicant Information STATEMENT OF POLICY ON THE USE OF ASME GDTP SYMBOLS AND AUTHORIZATION IN ADVERTISING ASME has established procedures
Additional requirements and conditions for abrasive products to be marked with the osa symbol
 Appendix of paragraph 3 of the Conditions of Use for the osa Trademark Additional requirements and conditions for abrasive products to be marked with the osa symbol Conformance with the European safety
Appendix of paragraph 3 of the Conditions of Use for the osa Trademark Additional requirements and conditions for abrasive products to be marked with the osa symbol Conformance with the European safety
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Unit 7 Contact: Mr S C Sparks Solent Industrial Estate Tel: +44 (0)1489 790296 Hedge End Fax: +44 (0)1489 790294 Southampton E-Mail: [email protected]
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Unit 7 Contact: Mr S C Sparks Solent Industrial Estate Tel: +44 (0)1489 790296 Hedge End Fax: +44 (0)1489 790294 Southampton E-Mail: [email protected]
Usage of Carbon Nanotubes in Scanning Probe Microscopes as Probe. Keywords: Carbon Nanotube, Scanning Probe Microscope
 International Journal of Arts and Sciences 3(1): 18-26 (2009) CD-ROM. ISSN: 1944-6934 InternationalJournal.org Usage of Carbon Nanotubes in Scanning Probe Microscopes as Probe Bedri Onur Kucukyildirim,
International Journal of Arts and Sciences 3(1): 18-26 (2009) CD-ROM. ISSN: 1944-6934 InternationalJournal.org Usage of Carbon Nanotubes in Scanning Probe Microscopes as Probe Bedri Onur Kucukyildirim,
CVD SILICON CARBIDE. CVD SILICON CARBIDE s attributes include:
 CVD SILICON CARBIDE CVD SILICON CARBIDE is the ideal performance material for design engineers. It outperforms conventional forms of silicon carbide, as well as other ceramics, quartz, and metals in chemical
CVD SILICON CARBIDE CVD SILICON CARBIDE is the ideal performance material for design engineers. It outperforms conventional forms of silicon carbide, as well as other ceramics, quartz, and metals in chemical
TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13
 TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13 REFERENCE BOOK rel. 02.15 TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13 REL. 02.15 ENGLISH LANGUAGE 1 MACHINE DESCRIPTION TST.13 was designed and built for processing methacrylate.
TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13 REFERENCE BOOK rel. 02.15 TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13 REL. 02.15 ENGLISH LANGUAGE 1 MACHINE DESCRIPTION TST.13 was designed and built for processing methacrylate.
SCS Directory Accreditation number: SCS 0115
 International standard: ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Swiss standard: SN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 METRON SA Calibration Laboratory Via Luserte Sud 7 CH-6572 Quartino Head: Angelo Capone Responsible for MS: Angelo Capone
International standard: ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Swiss standard: SN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 METRON SA Calibration Laboratory Via Luserte Sud 7 CH-6572 Quartino Head: Angelo Capone Responsible for MS: Angelo Capone
Finding Volume of Rectangular Prisms
 MA.FL.7.G.2.1 Justify and apply formulas for surface area and volume of pyramids, prisms, cylinders, and cones. MA.7.G.2.2 Use formulas to find surface areas and volume of three-dimensional composite shapes.
MA.FL.7.G.2.1 Justify and apply formulas for surface area and volume of pyramids, prisms, cylinders, and cones. MA.7.G.2.2 Use formulas to find surface areas and volume of three-dimensional composite shapes.
Figure 1 Wafer with Notch
 Glass Wafer 2 SCHOTT is an international technology group with more than 125 years of experience in the areas of specialty glasses, materials and advanced technologies. With our high-quality products and
Glass Wafer 2 SCHOTT is an international technology group with more than 125 years of experience in the areas of specialty glasses, materials and advanced technologies. With our high-quality products and
MaraMeter. Indicating Snap Gages
 - 9-2 MaraMeter. Indicating Snap Gages Overview MaraMeter. The Indicating Snap Gage is ideal for highly accurate and reliable results on cylindrical work pieces with a narrow tolerance. MaraMeter 840 F
- 9-2 MaraMeter. Indicating Snap Gages Overview MaraMeter. The Indicating Snap Gage is ideal for highly accurate and reliable results on cylindrical work pieces with a narrow tolerance. MaraMeter 840 F
View of ΣIGMA TM (Ref. 1)
 Overview of the FESEM system 1. Electron optical column 2. Specimen chamber 3. EDS detector [Electron Dispersive Spectroscopy] 4. Monitors 5. BSD (Back scatter detector) 6. Personal Computer 7. ON/STANDBY/OFF
Overview of the FESEM system 1. Electron optical column 2. Specimen chamber 3. EDS detector [Electron Dispersive Spectroscopy] 4. Monitors 5. BSD (Back scatter detector) 6. Personal Computer 7. ON/STANDBY/OFF
BULLETIN. HIGH PURITY SYLVANIA s proprietary four-step sand purification process ensures consistently pure fused quartz tubing.
 FUSED QUARTZ HIGH PURITY SYLVANIA s proprietary four-step sand purification process ensures consistently pure fused quartz tubing. SUPERIOR SERVICE Manufacturing flexibility, backed by an experienced and
FUSED QUARTZ HIGH PURITY SYLVANIA s proprietary four-step sand purification process ensures consistently pure fused quartz tubing. SUPERIOR SERVICE Manufacturing flexibility, backed by an experienced and
To measure an object length, note the number of divisions spanned by the object then multiply by the conversion factor for the magnification used.
 STAGE MICROMETERS Introduction Whenever there is a need to make measurements with an eyepiece graticule, there is also a need to ensure that the microscope is calibrated. The use of a stage micrometer
STAGE MICROMETERS Introduction Whenever there is a need to make measurements with an eyepiece graticule, there is also a need to ensure that the microscope is calibrated. The use of a stage micrometer
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR KATTANKULATHUR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME2304 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR KATTANKULATHUR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME2304 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT QUESTION BANK UNIT I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT 1. What are the uses
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR KATTANKULATHUR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME2304 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT QUESTION BANK UNIT I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT 1. What are the uses
Angle - a figure formed by two rays or two line segments with a common endpoint called the vertex of the angle; angles are measured in degrees
 Angle - a figure formed by two rays or two line segments with a common endpoint called the vertex of the angle; angles are measured in degrees Apex in a pyramid or cone, the vertex opposite the base; in
Angle - a figure formed by two rays or two line segments with a common endpoint called the vertex of the angle; angles are measured in degrees Apex in a pyramid or cone, the vertex opposite the base; in
Material data sheet. EOS StainlessSteel GP1 for EOSINT M 270. Description, application
 EOS StainlessSteel GP1 for EOSINT M 270 A number of different materials are available for use with EOSINT M systems, offering a broad range of e-manufacturing applications. EOS StainlessSteel GP1 is a
EOS StainlessSteel GP1 for EOSINT M 270 A number of different materials are available for use with EOSINT M systems, offering a broad range of e-manufacturing applications. EOS StainlessSteel GP1 is a
Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV
 Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
Assessment For The California Mathematics Standards Grade 4
 Introduction: Summary of Goals GRADE FOUR By the end of grade four, students understand large numbers and addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of whole numbers. They describe and compare
Introduction: Summary of Goals GRADE FOUR By the end of grade four, students understand large numbers and addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of whole numbers. They describe and compare
ENGINEERING METROLOGY
 ENGINEERING METROLOGY ACADEMIC YEAR 92-93, SEMESTER ONE COORDINATE MEASURING MACHINES OPTICAL MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS; DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ISFAHAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Coordinate Measuring
ENGINEERING METROLOGY ACADEMIC YEAR 92-93, SEMESTER ONE COORDINATE MEASURING MACHINES OPTICAL MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS; DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ISFAHAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Coordinate Measuring
NEW SIX-SEALS CUTTING RING. INTERNATIONAL INDUSTRIAL PATENT Nr. 864061 of the 10/03/99 FLANKS AND DOES NOT REPLACE THE STANDARD RING CURRENTLY IN USE
 B4 NEW SIX-SEALS CUTTING RING. INTERNATIONAL INDUSTRIAL PATENT Nr. 864061 of the 10/03/99 FLANKS AND DOES NOT REPLACE THE STANDARD RING CURRENTLY IN USE AVAILABLE IN CARBON AND STAINLESS STEEL 23 THEORY
B4 NEW SIX-SEALS CUTTING RING. INTERNATIONAL INDUSTRIAL PATENT Nr. 864061 of the 10/03/99 FLANKS AND DOES NOT REPLACE THE STANDARD RING CURRENTLY IN USE AVAILABLE IN CARBON AND STAINLESS STEEL 23 THEORY
Formation of solids from solutions and melts
 Formation of solids from solutions and melts Solids from a liquid phase. 1. The liquid has the same composition as the solid. Formed from the melt without any chemical transformation. Crystallization and
Formation of solids from solutions and melts Solids from a liquid phase. 1. The liquid has the same composition as the solid. Formed from the melt without any chemical transformation. Crystallization and
Fiber Optic Terminus End Face Quality Standards
 Introduction Fiber Optic Terminus End Face Quality Standards Good fiber optic performance relies on connectors that are manufactured properly. Specifically, optimal optical performance requires that the
Introduction Fiber Optic Terminus End Face Quality Standards Good fiber optic performance relies on connectors that are manufactured properly. Specifically, optimal optical performance requires that the
SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES
 CHAPTER 1 SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES (A) Main Concepts and Results Cuboid whose length l, breadth b and height h (a) Volume of cuboid lbh (b) Total surface area of cuboid 2 ( lb + bh + hl ) (c) Lateral
CHAPTER 1 SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES (A) Main Concepts and Results Cuboid whose length l, breadth b and height h (a) Volume of cuboid lbh (b) Total surface area of cuboid 2 ( lb + bh + hl ) (c) Lateral
TIG torches... 3-2 to 3-5 Tungsten electrodes... 3-6 to 3-7 TIG consumables... 3-8 Miscellaneous... 3-9
 3- welding torches........................................................... 3-2 to 3-5 Tungsten electrodes........................................ 3-6 to 3-7 consumables........................................................
3- welding torches........................................................... 3-2 to 3-5 Tungsten electrodes........................................ 3-6 to 3-7 consumables........................................................
3 Nextel Textiles. Ceramic fiber products for outerspace applications.
 3 Nextel Textiles Ceramic fiber products for outerspace applications. Physical Properties 3M Nextel Fabrics, Tapes, and Sleevings are designed to meet the toughest thermal, mechanical and electrical performance
3 Nextel Textiles Ceramic fiber products for outerspace applications. Physical Properties 3M Nextel Fabrics, Tapes, and Sleevings are designed to meet the toughest thermal, mechanical and electrical performance
DRAFTING MANUAL. Gears (Bevel and Hypoid) Drafting Practice
 Page 1 1.0 General This section provides the basis for uniformity in engineering gears drawings and their technical data for gears with intersecting axes (bevel gears), and nonparallel, nonintersecting
Page 1 1.0 General This section provides the basis for uniformity in engineering gears drawings and their technical data for gears with intersecting axes (bevel gears), and nonparallel, nonintersecting
Geometry and dimensional tolerances of engine bearings
 Geometry and dimensional tolerances of engine bearings Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich (Research & Development Manager.) 1. Hydrodynamic lubrication Engine bearings operate mostly in the hydrodynamic regime of
Geometry and dimensional tolerances of engine bearings Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich (Research & Development Manager.) 1. Hydrodynamic lubrication Engine bearings operate mostly in the hydrodynamic regime of
HONING LATHE DUPLICATOR CUTTERS
 Lay the flat face of the cutter or bit on the flat top surface of the hone with the rest of the cutter overhanging the edge. Rub the cutter or bit up and down the hone (Figure 24-44). Be sure to hold the
Lay the flat face of the cutter or bit on the flat top surface of the hone with the rest of the cutter overhanging the edge. Rub the cutter or bit up and down the hone (Figure 24-44). Be sure to hold the
Specification of 5 Wire Analog Touch Panel
 Specification of 5 Wire Analog Touch Panel 5 WIRE ANALOG RESISTIVE TOUCH PANEL A. Application This specification applies to the 5 Wire Analog Resistive Touch Panel. B. Environmental Conditions 1. Operating
Specification of 5 Wire Analog Touch Panel 5 WIRE ANALOG RESISTIVE TOUCH PANEL A. Application This specification applies to the 5 Wire Analog Resistive Touch Panel. B. Environmental Conditions 1. Operating
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
Precision Vise Combinations
 Precision Vise Combinations PanaVise vises and work holding tools have hundreds of uses limited only by your imagination! Each vise allows the head to Tilt, Turn & Rotate and position your work anywhere
Precision Vise Combinations PanaVise vises and work holding tools have hundreds of uses limited only by your imagination! Each vise allows the head to Tilt, Turn & Rotate and position your work anywhere
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE COLLAR PRODUCTION ON THE PIERCED FLAT SHEET METAL USING LASER FORMING PROCESS
 JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN SCIENCE (ISSN 2322-5009) CODEN (USA): JCRSDJ 2014, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp:277-284 Available at www.jcrs010.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE COLLAR
JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN SCIENCE (ISSN 2322-5009) CODEN (USA): JCRSDJ 2014, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp:277-284 Available at www.jcrs010.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE COLLAR
General Allowances for Insulation & Cladding
 TRADE OF Industrial Insulation PHASE 2 Module 1 Sheet Metal and Insulation Fundamentals UNIT: 4 General Allowances for Insulation & Cladding Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Michael
TRADE OF Industrial Insulation PHASE 2 Module 1 Sheet Metal and Insulation Fundamentals UNIT: 4 General Allowances for Insulation & Cladding Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Michael
Renishaw 2008. apply innovation TM. Calibrating 5-axis machines to improve part accuracy. 5Align
 Calibrating 5-axis machines to improve part accuracy 5Align Productive Process Pyramid TM Understanding and tracking machine behaviour Process verification Thermal compensation In-cycle process control
Calibrating 5-axis machines to improve part accuracy 5Align Productive Process Pyramid TM Understanding and tracking machine behaviour Process verification Thermal compensation In-cycle process control
DMS 680. Universal length measuring system gauge inspection for»iso 9000«requirements
 DMS 680 Universal length measuring system gauge inspection for»iso 9000«requirements Universal length measuring system DMS 680 Wide range of applications For periodic inspection of gauges, reference gauges,
DMS 680 Universal length measuring system gauge inspection for»iso 9000«requirements Universal length measuring system DMS 680 Wide range of applications For periodic inspection of gauges, reference gauges,
Solid shape molding is not desired in injection molding due to following reasons.
 PLASTICS PART DESIGN and MOULDABILITY Injection molding is popular manufacturing method because of its high-speed production capability. Performance of plastics part is limited by its properties which
PLASTICS PART DESIGN and MOULDABILITY Injection molding is popular manufacturing method because of its high-speed production capability. Performance of plastics part is limited by its properties which
* This work is an official contribution of the National Institute of Standards and Technology and
 Variability in the Geometric Accuracy of Additively Manufactured Test Parts A.L. Cooke and J.A. Soons National Institute of Standards and Technology * Gaithersburg, MD, USA Abstract This paper describes
Variability in the Geometric Accuracy of Additively Manufactured Test Parts A.L. Cooke and J.A. Soons National Institute of Standards and Technology * Gaithersburg, MD, USA Abstract This paper describes
Activity Set 4. Trainer Guide
 Geometry and Measurement of Solid Figures Activity Set 4 Trainer Guide Mid_SGe_04_TG Copyright by the McGraw-Hill Companies McGraw-Hill Professional Development GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT OF SOLID FIGURES
Geometry and Measurement of Solid Figures Activity Set 4 Trainer Guide Mid_SGe_04_TG Copyright by the McGraw-Hill Companies McGraw-Hill Professional Development GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT OF SOLID FIGURES
Geometry Notes VOLUME AND SURFACE AREA
 Volume and Surface Area Page 1 of 19 VOLUME AND SURFACE AREA Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the volume of given geometric figures. Calculate
Volume and Surface Area Page 1 of 19 VOLUME AND SURFACE AREA Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the volume of given geometric figures. Calculate
Non-destructive testing of steel forgings - Part 2: Penetrant testing (BS EN 10228-2:1998)
 Non-destructive testing of steel forgings - Part 2: Penetrant testing (BS EN 10228-2:1998) 1 Scope This part of EN 10228 describes the method and acceptance criteria to be used for the penetrant testing
Non-destructive testing of steel forgings - Part 2: Penetrant testing (BS EN 10228-2:1998) 1 Scope This part of EN 10228 describes the method and acceptance criteria to be used for the penetrant testing
There is no upside to. down time
 EXPANDED and PERFORATED Data and Specifications 30 Similar to Type 302 with excellent mechanical properties, resistance to many corrosive agents. Useful where sanitation and cleanliness are important.
EXPANDED and PERFORATED Data and Specifications 30 Similar to Type 302 with excellent mechanical properties, resistance to many corrosive agents. Useful where sanitation and cleanliness are important.
Algebra Geometry Glossary. 90 angle
 lgebra Geometry Glossary 1) acute angle an angle less than 90 acute angle 90 angle 2) acute triangle a triangle where all angles are less than 90 3) adjacent angles angles that share a common leg Example:
lgebra Geometry Glossary 1) acute angle an angle less than 90 acute angle 90 angle 2) acute triangle a triangle where all angles are less than 90 3) adjacent angles angles that share a common leg Example:
Traditional Drawing Tools
 Engineering Drawing Traditional Drawing Tools DRAWING TOOLS DRAWING TOOLS 1. T-Square 2. Triangles DRAWING TOOLS HB for thick line 2H for thin line 3. Adhesive Tape 4. Pencils DRAWING TOOLS 5. Sandpaper
Engineering Drawing Traditional Drawing Tools DRAWING TOOLS DRAWING TOOLS 1. T-Square 2. Triangles DRAWING TOOLS HB for thick line 2H for thin line 3. Adhesive Tape 4. Pencils DRAWING TOOLS 5. Sandpaper
INFRARED MONITORING OF 110 GHz GYROTRON WINDOWS AT DIII D
 GA A23981 INFRARED MONITORING OF 110 GHz GYROTRON WINDOWS AT DIII D by Y. GORELOV, J. LOHR, R.W. CALLIS, and D. PONCE MAY 2002 DISCLAIMER This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an
GA A23981 INFRARED MONITORING OF 110 GHz GYROTRON WINDOWS AT DIII D by Y. GORELOV, J. LOHR, R.W. CALLIS, and D. PONCE MAY 2002 DISCLAIMER This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an
Defects Introduction. Bonding + Structure + Defects. Properties
 Defects Introduction Bonding + Structure + Defects Properties The processing determines the defects Composition Bonding type Structure of Crystalline Processing factors Defects Microstructure Types of
Defects Introduction Bonding + Structure + Defects Properties The processing determines the defects Composition Bonding type Structure of Crystalline Processing factors Defects Microstructure Types of
MOOG. MACHINING SUPPLIER WORKMANSHIP STANDARDS Issue: 1-APRIL- 2007
 INTRODUCTION Supported by valued suppliers, Moog has developed a reputation for quality, performance and delivery that has helped it to become a leading supplier of highly sophisticated control systems.
INTRODUCTION Supported by valued suppliers, Moog has developed a reputation for quality, performance and delivery that has helped it to become a leading supplier of highly sophisticated control systems.
NetShape - MIM. Metal Injection Molding Design Guide. NetShape Technologies - MIM Phone: 440-248-5456 31005 Solon Road FAX: 440-248-5807
 Metal Injection Molding Design Guide NetShape Technologies - MIM Phone: 440-248-5456 31005 Solon Road FAX: 440-248-5807 Solon, OH 44139 [email protected] 1 Frequently Asked Questions Page What
Metal Injection Molding Design Guide NetShape Technologies - MIM Phone: 440-248-5456 31005 Solon Road FAX: 440-248-5807 Solon, OH 44139 [email protected] 1 Frequently Asked Questions Page What
Product Information. QUADRA-CHEK 3000 Evaluation Electronics For Metrological Applications
 Product Information QUADRA-CHEK 3000 Evaluation Electronics For Metrological Applications April 2016 QUADRA-CHEK 3000 The evaluation electronics for intuitive 2-D measurement The QUADRA-CHEK 3000 evaluation
Product Information QUADRA-CHEK 3000 Evaluation Electronics For Metrological Applications April 2016 QUADRA-CHEK 3000 The evaluation electronics for intuitive 2-D measurement The QUADRA-CHEK 3000 evaluation
SAMPLE TEST PAPER - I
 SCHEME E SAMPLE TEST PAPER - I Course Name : Mechanical Engineering Group Course Code : AE/PG/PT/ME/MH/FE Semester : Third Subject : Mechanical Engineering Drawing 12042 Time : 90 Minutes Marks: 25 Instruction:
SCHEME E SAMPLE TEST PAPER - I Course Name : Mechanical Engineering Group Course Code : AE/PG/PT/ME/MH/FE Semester : Third Subject : Mechanical Engineering Drawing 12042 Time : 90 Minutes Marks: 25 Instruction:
