The Endocrine System
|
|
|
- Moses Lamb
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Endocrine System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3254 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL Hour Fax No Website: [email protected] 1
2 Grade Levels: 6-9 (Review for Grades 10-12) Viewing Time: 17 minutes with video quiz INTRODUCTION This video is designed for use in grades 6-9 as an introduction to the major ideas and concepts associated with the human endocrine system, and for use in grades as review. PROGRAM OBJECTIVES After viewing the video and participating in the accompanying activities, the students will be able to achieve the following objectives: Describe the function and workings of the endocrine system. Identify the main parts of the endocrine system. Identify the way the endocrine and nervous systems work together to regulate various body activities. Define key vocabulary terms associated with the endocrine system. SUMMARY OF THE VIDEO This video describes the functions of the endocrine system. The nervous and endocrine systems work together to regulate various body activities. The endocrine system is made up of eight glands located throughout the body. These glands make and release hormones, which are chemical messengers. These hormones move into the circulatory 2
3 system which carries them throughout the body. Each chemical is designed to affect or react with certain body tissues or organs and stimulate changes. Probably the most famous hormone is adrenaline which, when released from the adrenal glands, causes the body to prepare for a fight or flight condition. The heart beats faster, the lungs work harder, the muscles tense for action, and the blood pressure rises. This hormone is released when the nervous system senses danger or fear. So the two systems actually work together to prepare the body for an emergency situation. Some hormones trigger changes in the physical appearance of the body. INSTRUCTIONAL NOTES Before presenting this lesson to your students, we suggest that you preview the video and review this guide and the accompanying blackline master activities in order to familiarize yourself with their content. Duplicate any blackline masters you wish to distribute. If you choose to use the Video Quiz, which immediately follows the video presentation, you may wish to distribute Blackline Master 1, Video Quiz before showing the video. Also, plan to pause the tape between questions if students require more time. As you review the materials presented in this guide, you may find it necessary to make some changes, additions, or deletions to meet the specific needs of your class. We encourage you to do so, for only by tailoring this program to your class will they obtain the maximum instructional benefits afforded by the materials. It is also suggested that the video presentation take place before the entire group under your supervision. The lesson activities grow out of the context of the video; therefore, the presentation should be a common experience for all students. 3
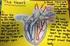
4 INTRODUCING THE VIDEO Ask students to share experiences they have had when their bodies have suddenly been surprised or scared. This might be a close call in a car or a terrifying experience. Tell the students that the video they will be watching today will describe how the nervous and endocrine systems work together to signal changes in the body. Present the video. The viewing time is 12 minutes for the program and about 5 minutes for the Video Quiz. BLACKLINE MASTER DESCRIPTIONS Most of the follow-up activities for this program are designed for middle school grades. If you use this program with an older audience, you will need to adapt the materials appropriately. Blackline Master 1, Video Quiz, is to be used at the end of the video program. At the completion of the video, there is a short quiz. The narrator will read the questions which are displayed on the screen. Students can use this sheet to record their answers. Answers to the questions are provided in the Answer Key on page 5. Blackline Master 2, Vocabulary, is a collection of important vocabulary words from the video. You may want to distribute this sheet before viewing the video so students can listen for definitions. Blackline Master 3, The Location of the Endocrine Glands, contains a diagram of the endocrine system. At the bottom of the page there is a box containing the names of the endocrine glands. Students are to place the names next to the appropriate lines on the diagram of the human endocrine system. 4
5 Blackline Master 4, Match, asks students to match the glands in column A with the functions listed in column B. Blackline Master 5, is the formal test for this unit of study. INTERNET ACTIVITIES 1. Visit the The Center for the Study of Environmental Endocrine Effects at for information on the latest and most significant scientific research and governmental policy developments on issues concerning adverse or beneficial effects that various environmental agents, both synthetic and natural, may have on the endocrine functions of humans, wildlife, and ecology. 2. The MedWeb's endocrinology page at endocrinology.html includes myriad sources for information on diabetes, endocrine diseases, environmental issues, discussion groups, publications, and information resources. DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. Discuss the relationship beween the nervous and endocrine systems. 2. Discuss how the negative-feedback mechanism helps to maintain proper balances of hormones in the blood. 3. Discuss how hormones can travel through the blood stream and reach their target tissues or organs. 5
6 ANSWER KEY Blackline Master 1, Video Quiz 1. Hormones are chemical messengers produced in the endocrine glands and released to the circulatory system. 2. They are released to the circulatory system, which carries them throughout the body. When they make contact with target tissues or organs, they are absorbed by the cells of those tissues or organs. 3. hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, thymus, adrenal, pancreas, parathyroids, gonads (ovaries or testes) 4. The negative-feedback mechanism is the endocrine system s method for regulating itself. Certain glands monitor the level of hormones in the blood. If a certain hormone level is too low or too high, then these glands release chemicals that stimulate or shut-off production of the hormone in question. 5. The hypothalamus regulates activities of the other endocrine glands. Blackline Master 2, Vocabulary 1. endocrine system - a system of eight glands that produce chemicals which regulate certain body activities 2. exocrine glands - glands which are responsible for things like tears, sweat, or digestive juices. These glands are usually located near the organs that they affect 3. hormones - chemical messengers produced by glands of the endocrine system 4. hypothalamus - considered the central control gland of the endocrine system 5. pituitary - gland located at the base of the brain which stimulates skeletal growth and the development of male and female sex organs 6. thymus - gland which regulates development and function of the immune system 7. thyroid - gland which increases metabolism and maintains the level of calcium in the blood 6
7 8. parathyroid - gland which regulates the level of calcium and phosphorus in the body 9. adrenal - gland which increases heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate 10. islets of Langerhans - produces insulin and glucagon, which regulate the level of sugar in the blood 11. ovary - gland which produces female secondary sex organs 12. testes - glands which produce male secondary sex organs 13. negative-feedback mechanism - method used by endocrine system to regulate itself; certain glands detect the level of hormones in the blood and release other hormones to either start or stop the production of the hormone being monitored Blackline Master 3, The Location of the Endocrine Glands 7
8 Blackline Master 4, Match Hypothalamus 11 Pituitary 10, 12 Thyroid 7, 8 Thymus 9 Adrenals 3 Pancreas 2, 5 Ovaries 4 Testes 1 Parathyroids 6 Blackline Master 5, Quiz 1. The endocrine system produces and releases hormones which are chemical messengers that affect various tissues and organs of the body. 2. hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, thymus, parathyroids, pancreas, gonads, adrenals 3. A hormone is a chemical messenger that regulates activities of tissues and organs in the body. 4. Negative-feedback is the method used by the endocrine system to regulate the level of hormones in the blood. Certain glands can detect how much of a given hormone is present in the blood. Based on this information, either the signal to create more or stop releasing that hormone is given. 5. Adrenaline is a hormone that has very dramatic effects on the body. It causes an increase in heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure. It is the flight or fight hormone. It prepares the body for an emergency. 6. The nervous system gathers information about what is happening around us and sends that information to the brain. The hypothalamus is an endocrine gland that is located in the brain. Much of the information sent by the nervous system goes through the hypothalamus. Based on that information, various other endocrine glands might be stimulated to produce hormones. 8
9 7. The flight or fight response is set into motion when the nervous system senses danger or an emergency. The adrenal glands respond by releasing adrenaline into the circulatory system. This chemical causes dramatic changes that include an increase of heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure levels. These changes occur so that if the human must run or fight, their bodies are ready for extreme measures. 8. The hormones travel throughout the body by way of the circulatory system. Each hormone has certain target cells located in various tissues or organs of the body. When a target cell detects the hormone in the blood, the cell absorbs the hormone. 9. Insulin is a chemical that helps cells convert sugar into energy. It decreases the sugar level in the blood. Glucagon does the opposite of insulin. It increases the blood sugar level by stimulating the conversion of stored sugar. 10. Some people can t produce enough insulin. The insulin helps the cells to convert sugar into energy. If there isn t enough insulin in the blood, then the blood sugar level goes too high. SCRIPT OF VIDEO NARRATION Have you ever been driving along when suddenly......watch OUT! You almost hit that car! That was a close call. You might remember that your heart was racing and your muscles felt all tensed up. In fact, you might have even been trembling. You might have wondered why your body felt so strange. This is one way the body reacts to danger or surprise. The nervous system and the endocrine system have worked together to prepare your body for an emergency situation. In this case, the nervous system sent a visual image from your eyes of a possible collision with another car. The brain 9
10 interpreted this information and sent messages to the glands of the endocrine system. These glands produced hormones that rushed to certain parts of the body to stimulate changes. For instance, a hormone rushed to the heart and caused it to beat faster, while other hormones signaled the lungs to work harder, and still other hormones caused the muscles to stiffen and prepare for action. In a case like the one described above, the hormones were sent to prepare the body for a flight or fight condition. This is a situation where the body is prepared to defend itself by either quickly running away or fighting. Once the danger was over, the body began to calm down because the brain stopped sending signals to the endocrine glands and the production of these flight or fight hormones stopped. Not everything the endocrine system does is in response to danger. In fact, the job of the system is to regulate or control various body functions and activities. The endocrine system is made up of a series of glands that produce hormones, which are chemical messengers. These hormones are responsible for speeding up or slowing down the activities of tissues and organs found throughout the body. The purpose of this program is to show how this system performs its job of helping to maintain a healthy body. There is another set of glands in the body called the exocrine glands. These glands don t produce hormones but rather they are responsible for things like tears, sweat, or digestive juices. These glands are usually located near the organs that they affect. For instance, the pancreas releases digestive juices into the small intestine through small tubes that connect the two organs. The chemicals produced by glands in the endocrine system travel through the blood stream to reach their destinations. Therefore, these glands don t need to be located near the 10
11 organs they will affect. There are eight endocrine glands found in the human body, each producing different hormones. The tissues of the body are able to identify which chemicals are meant for them and which to reject. Hormones that are not accepted continue to move through the circulatory system until they reach the tissue or organ they were designed to control. Hormones are chemical messengers that are very powerful. Hormones are responsible for three kinds of control. Some hormones speed up body processes. Some hormones are designed to slow down or stop certain processes. Still other hormones change body structure by stimulating growth. Only a small amount of a hormone is required to control various body activities. For instance, the growth of the skeleton is controled by the pituitary gland. If too much hormone is manufactured, a giant would result. If too little of the hormone is released, then a dwarf can result. If an endocrine gland isn t producing enough of a particular hormone, then medication can be used to supplement or supply the missing amount of chemicals. For instance, many people with diabetes must take insulin on a regular basis to maintain proper blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas. Actually the pancreas is more of an exocrine gland that produces digestive enzymes but there are special cells within the pancreas called the islets of Langerhans that produce the hormones insulin and glucagon, and therefore, are considered members of the endocrine system. Insulin is a hormone that lowers the sugar level in blood. It stimulates and helps body cells to take in sugar and use it as energy. It also helps excess sugar to be changed into glycogen in the liver so it can be stored for use later. The islets also produce glucagon, which stimulates the breakdown of glycogen to sugar when more energy is needed by cells. 11
12 So the insulin and glucagon work together to keep the level of sugar in the blood at a proper amount for normal body functions. When the sugar level is low, glucagon is released to change stored glycogen back into sugar. If the sugar level is too high, then insulin is released to encourage body cells to absorb and use the excess sugar. If insulin isn t present, the body cells can t absorb and use the sugar in the blood. The cells begin using their own proteins and fat for energy. If this happens, the level of sugar in the blood increases to abnormally high levels. This condition is called diabetes mellitus and can lead to heart disease, kidney failure, or blindness. In fact, this condition is the third major cause of death in the United States. THE HYPOTHALAMUS The hypothalamus is an endocrine gland located in the brain. It is considered the main control for the endocrine system because it affects the other seven glands in the system. It is the major link between the nervous system and the endocrine system. Messages sent to the brain by the nervous system go through the hypothalamus. So this gland receives information from all parts of the body. It uses this information to regulate the level of hormones in the circulatory system, the amount of nutrients in the body, and the temperature of the body. THE PITUITARY The pituitary gland is located just below the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. This gland controls bloood pressure, the overall chemical and physical activities of the body, growth, sexual development and reproduction. Because this gland is responsible for so much and it also controls many other glands, it was once refered to as the master gland. But this label is no longer used because it has been discovered that the hypothalamus actually controls the pituitary through nerve impulses. Though the pituitary is only the size of a pea, it is responsible for so much that goes on in our bodies. 12
13 THE THYROID The thyroid gland is located on the trachea. The hormone made by this gland helps to control metablism in the body and the production of protein. It is very important to the proper development of the nervous system and it affects the growth rate in children. THE PARATHYROIDS Located on the back of the thyroid are four small parathyroid glands. These glands secrete a hormone that regulates the amount of calcium in the blood. Calcium is important to the proper functioning of muscles and nerves in the body. THE THYMUS The thymus is located behind the breastbone and below the thyroid. It starts out large but shrinks to the size of a thumb by the time a person is an adult. The thymus is involved in the development of the immune system. The immune system is responsible for defending the body against germs and bacteria. The thymus produces white blood cells during infancy, but as the human gets older, other organs in the body take over the production of white blood cells. ADRENALS On top of each of the two kidneys is an adrenal gland. This gland produces the hormone adrenaline. This hormone raises the heart rate, increases breathing, and raises the blood sugar level. This is the flight or fight hormone that was discussed at the beginning of this tape. It is a part of the emergency response system of our bodies. There have been some very unusual cases where people have managed incredible feats of strength during an emergency or stressful situation. 13
14 For example, there was an account of two elderly women who carried their piano out of their burning home. When the fire was over, it took five fireman to carry the piano back inside. Another incident happened when a jack slipped and the car a man was working on fell on him. He had been working on the brakes, so the tire was gone and the axle was now lying on his chest. His wife lifted the side of the car and with her foot moved him from danger. GONADS The gonads are the reproductive glands of humans. The ovaries are the female gonads and the testes are the male gonads. The ovaries secrete estrogens that cause wider hips, enlarged breasts, and body hair. The testes secrete androgens, the most important of which is testosterone that deepens the voice, stimulates the growth of body hair, and enlarges muscles and bones. These hormones are released during puberty, which is a period during which boys and girls mature physically and sexually. NEGATIVE-FEEDBACK MECHANISM The endocrine system uses negative-feedback to regulate or control itself. How much hormone is present in the blood determines whether more or less of the hormone is produced. Think of a thermostat system as used in many cars of today. You set the thermostat to the desired temperature. Then the equipment reads the temperature inside the car and adjusts itself appropriately. If the car temperature is below the desired temperature on the thermostat, then the heater is turned on until that temperature is reached. If the temperature was higher than the setting, the air conditioner would kick on until the desired temperature is reached. This is similar to the way hormone level is controled in the blood. For instance, the pituitary gland monitors the level of thyroxine in the blood. Thyroxine is manufactured in the thyroid. If the level of the hormone thyroxine is detected to be too low, the 14
15 pituitary releases one of its hormones called TSH. This stands for thyroid-stimulating hormone. It travels to the thyroid by way of the circulatory system and stimulates the thyroid to produce more thyroxine. When the level of thyroxine in the blood returns to normal, the pituitary stops releasing the TSH and the thyroid stops making thyroxine. So the negative-feedback system keeps the body s internal environment operating smoothly. SUMMARY The endocrine and nervous systems work closely together to maintain a proper internal environment for humans. The endocrine system is made up of eight glands that work as a team to release various hormones throughout the body. The hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the circulatory system to specific tissues and organs of the body. The hormones stimulate changes that speed up or slow down various activities of the tissues and organs. The hypothalamus gland, located in the brain, receives information from the nervous system concerning everything that is happening to the body. It even gets information about fear and anger. Based on this stimulation, the hypothalamus sends hormones throughout the endocrine system to help keep the body balanced. The endocrine system is an important contributor to the health and maintenance of a very complicated living organism you. 15
16 VIDEO QUIZ Students may write the answers to the following questions on a separate piece of paper or on the duplicating master titled Video Quiz (Blackline Master 1). 1. What are hormones? 2. How do hormones move throughout the body? 3. Name the eight glands of the endocrine system. 4. What is the negative-feedback mechanism of the body? 5. Why is the hypothalamus considered the control center of the endocrine system? 16
17 1 Video Quiz Name Date Directions: At the end of the video production is a short quiz. Choose the correct answer or answers from the list below. Write your answers in the space provided. Not all options from the list will be used. 1. What are hormones? 2. How do hormones move throughout the body? 3. Name the eight glands of the endocrine system. 4. What is the negative-feedback mechanism of the body? 5. Why is the hypothalamus considered the control center of the endocrine system? Options: hypothalamus exocrine thyroid endocrine thymus pancreas gonads insulin adrenaline parathyroids adrenal flight-or-fight nervous system islets of Langerhans pituitary chemical messengers produced in the endocrine glands causes an increase in heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure regulates activities of other endocrine glands released to the circulatory system which carries them through the body endocrine system's method for regulating itself from The Human Body Systems Series 1998 AGC/United Learning 1560 Sherman Av., Suite 100 Evanston, IL Fax [email protected]
18 2 Vocabulary Name Date Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below. 1. endocrine system 2. exocrine glands 3. hormones 4. hypothalamus 5. pituitary 6. thymus 7. thyroid 8. parathyroid 9. adrenal 10. islets of Langerhans 11. ovary 12. testes 13. negative-feedback mechanism from The Human Body Systems Series 1998 AGC/United Learning 1560 Sherman Av., Suite 100 Evanston, IL Fax [email protected]
19 3 The Location of the Endocrine Glands Name Date Directions: Place the words from the box at the bottom of the page next to the appropriate lines on the diagram. Pancreas Hypothalamus Pituitary Parathyroid Ovaries Adrenal Thyroid Thymus Testes from The Human Body Systems Series 1998 AGC/United Learning 1560 Sherman Av., Suite 100 Evanston, IL Fax
20 4 Match Name Date Directions: Match the functions described in column B with the endocrine gland listed in column A. Column A Hypothalamus Column B 1. produces male sex characteristics 2. decreases blood sugar level 3. increases heart and breathing rate, Pituitary raises blood pressure 4. produces female sex characteristics 5. increases blood sugar level 6. regulates the level of calcium and Thyroid phosphorus 7. increases rate of metabolism 8. maintains the level of calcium and Thymus phosphorus in the blood Adrenals Pancreas Ovaries Testes 9. development of immune system 10. stimulates skeletal growth 11. regulates the activities of other glands 12. stimulates development of male and female sex organs Parathyroids from The Human Body Systems Series 1998 AGC/United Learning 1560 Sherman Av., Suite 100 Evanston, IL Fax [email protected]
21 5 Quiz Name Date Directions: Use the space provided to answer the following questions. Use the back of this sheet if necessary. 1. What is the function of the endocrine system? 2. Name the eight endocrine glands of the human body. 3. What is a hormone? 4. How does the negative-feedback mechanism work? 5. What are some of the effects of adrenaline? 6. How do the nervous and endocrine systems work together? 7. What is meant by the "flight or fight" response? 8. How do the hormones released by the endocrine glands get around the body? 9. Two of the hormones secreted by the pancreas are insulin and glucagon. These hormones work together to maintain a balanced blood sugar level. How do they do that? 10. Why must some people take insulin as a medication on a regular basis? from The Human Body Systems Series 1998 AGC/United Learning 1560 Sherman Av., Suite 100 Evanston, IL Fax [email protected]
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 Grades 9 to 12 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 9 to 12 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
 Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Class 10 NCERT Science Text Book Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus.
Chapter 45: Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Name Period Overview 1. What is a hormone? 2. Why does a hormone elicit a response only with target cells? 3. The body has two long-distance regulating systems. Which involves chemical signals by hormones?
Name Period Overview 1. What is a hormone? 2. Why does a hormone elicit a response only with target cells? 3. The body has two long-distance regulating systems. Which involves chemical signals by hormones?
The Endocrine System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Endocrine System Review Consists of discrete individual
Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Endocrine System Review Consists of discrete individual
Nervous System. from the Human Body Systems Series. catalog # 2890. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Fight or Flight Response: Play-by-Play
 One of the most remarkable examples of cell communication is the fight or flight response. When a threat occurs, cells communicate rapidly to elicit physiological responses that help the body handle extraordinary
One of the most remarkable examples of cell communication is the fight or flight response. When a threat occurs, cells communicate rapidly to elicit physiological responses that help the body handle extraordinary
Endocrine Responses to Resistance Exercise
 chapter 3 Endocrine Responses to Resistance Exercise Chapter Objectives Understand basic concepts of endocrinology. Explain the physiological roles of anabolic hormones. Describe hormonal responses to
chapter 3 Endocrine Responses to Resistance Exercise Chapter Objectives Understand basic concepts of endocrinology. Explain the physiological roles of anabolic hormones. Describe hormonal responses to
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
associated with puberty for boys and girls.
 Lesson 5 Puberty Overview In this informational lesson, students learn about puberty. Small groups brainstorm physical, emotional and social changes they think occur The class discusses and evaluates the
Lesson 5 Puberty Overview In this informational lesson, students learn about puberty. Small groups brainstorm physical, emotional and social changes they think occur The class discusses and evaluates the
II. 2005 Core Knowledge National Conference, The Endocrine System, 5 th Grade 1
 The Endocrine System: Who is in Control Here? Grade Level or Special Area: 5 th Grade Science Written by: Jan Guyer, Academy of Charter Schools, Denver, Colorado and Ernie Carroll, Lincoln Academy, Arvada,
The Endocrine System: Who is in Control Here? Grade Level or Special Area: 5 th Grade Science Written by: Jan Guyer, Academy of Charter Schools, Denver, Colorado and Ernie Carroll, Lincoln Academy, Arvada,
The Body Systems Lesson Plan
 The Body Systems Lesson Plan Science Standards Addressed (From the Colorado Department of Education) http://www2.cde.state.co.us/scripts/allstandards/costandards.asp?stid=7&stid2=0&glid2=0 Standard 2-Life
The Body Systems Lesson Plan Science Standards Addressed (From the Colorado Department of Education) http://www2.cde.state.co.us/scripts/allstandards/costandards.asp?stid=7&stid2=0&glid2=0 Standard 2-Life
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes?
 Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
Regulation of Metabolism. By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
DIABETES. Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys. www.kidney.org
 DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
Thyroid Problems after Childhood Cancer
 Thyroid Problems after Childhood Cancer Some people who were treated for cancer during childhood may develop endocrine (hormone) problems as a result of changes in the function of a complex system of glands
Thyroid Problems after Childhood Cancer Some people who were treated for cancer during childhood may develop endocrine (hormone) problems as a result of changes in the function of a complex system of glands
Introduction to puberty
 Introduction to puberty Objective: Structure: Time: Materials: Participants will describe some of the common external changes associated with puberty. Presentation by educator with large group discussion.
Introduction to puberty Objective: Structure: Time: Materials: Participants will describe some of the common external changes associated with puberty. Presentation by educator with large group discussion.
Testosterone Therapy for Women
 Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop: Stimulus. Production Cell. Hormone. Target Cell. Target Cell Action
 Hormonal Cycles Directions: a. Click the Contents button. b. Open the Endocrine System File. c. Click Animations. d. Click Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop:
Hormonal Cycles Directions: a. Click the Contents button. b. Open the Endocrine System File. c. Click Animations. d. Click Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop:
X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized
X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 3 to 5 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Grades 3 to 5 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
regulation of ECF composition and volume regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon
 Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
Systems of the Human Body
 . s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
. s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary
 X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Signs, symptoms, and treatments What is PCOS? Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects up to 1 in 10 women of reproductive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Signs, symptoms, and treatments What is PCOS? Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects up to 1 in 10 women of reproductive
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-4.3:
 PUBERTY CHANGES Lesson 2 GRADE 4 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-4.3: Describe physical, emotional and social changes that occur during puberty; e.g., menstruation, secondary sexual characteristics, changing identity
PUBERTY CHANGES Lesson 2 GRADE 4 LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-4.3: Describe physical, emotional and social changes that occur during puberty; e.g., menstruation, secondary sexual characteristics, changing identity
The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model
 The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 23, 2014 Outline The Background for
The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 23, 2014 Outline The Background for
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR
 ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
ARTICLE #1 PLEASE RETURN AT THE END OF THE HOUR Alcoholism By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/alcoholism/ds00340 Definition Alcoholism is a chronic and often progressive
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
7 Answers to end-of-chapter questions
 7 Answers to end-of-chapter questions Multiple choice questions 1 B 2 B 3 A 4 B 5 A 6 D 7 C 8 C 9 B 10 B Structured questions 11 a i Maintenance of a constant internal environment within set limits i Concentration
7 Answers to end-of-chapter questions Multiple choice questions 1 B 2 B 3 A 4 B 5 A 6 D 7 C 8 C 9 B 10 B Structured questions 11 a i Maintenance of a constant internal environment within set limits i Concentration
First Grade The Human Body Assessment
 First Grade The Human Body Assessment 1a. When we talk about the skeletal system we are talking about what part of our body? a. stomach b. bones 1b. How many bones in your skeleton? a. more than two hundred
First Grade The Human Body Assessment 1a. When we talk about the skeletal system we are talking about what part of our body? a. stomach b. bones 1b. How many bones in your skeleton? a. more than two hundred
Endocrine issues in FA SUSAN R. ROSE CINCINNATI CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER
 Endocrine issues in FA SUSAN R. ROSE CINCINNATI CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER 80% of children and adults with FA have an endocrine abnormality Endocrine cells make a hormone (message) Carried in bloodstream
Endocrine issues in FA SUSAN R. ROSE CINCINNATI CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER 80% of children and adults with FA have an endocrine abnormality Endocrine cells make a hormone (message) Carried in bloodstream
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Aging Well - Part V. Hormone Modulation -- Growth Hormone and Testosterone
 Aging Well - Part V Hormone Modulation -- Growth Hormone and Testosterone By: James L. Holly, MD (The Your Life Your Health article published in the December 4th Examiner was a first draft. It was sent
Aging Well - Part V Hormone Modulation -- Growth Hormone and Testosterone By: James L. Holly, MD (The Your Life Your Health article published in the December 4th Examiner was a first draft. It was sent
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of Hormone Action
 Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of Hormone Action Cai Li, Ph.D. Assistant professor Touchstone Center for Diabetes Research Departments of Physiology and Internal Medicine The University of
Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of Hormone Action Cai Li, Ph.D. Assistant professor Touchstone Center for Diabetes Research Departments of Physiology and Internal Medicine The University of
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Lesson 3: Blood glucose
 Lesson 3: Blood glucose Inquiry Focus: How does the body deliver the energy in food to its parts? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following: Describe
Lesson 3: Blood glucose Inquiry Focus: How does the body deliver the energy in food to its parts? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following: Describe
Puberty is the bridge between childhood and adulthood.
 Puberty is the bridge between childhood and adulthood. Puberty can start as early as 8 or 9 years old or as late as 18 or 19 years old. The average age for girls is 10.5 years old. The average age for
Puberty is the bridge between childhood and adulthood. Puberty can start as early as 8 or 9 years old or as late as 18 or 19 years old. The average age for girls is 10.5 years old. The average age for
Stress Psychophysiology. Introduction. The Brain. Chapter 2
 Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
It s time to TALK Targets A guide to taking control of your type 2 diabetes
 It s time to TALK Targets A guide to taking control of your type 2 diabetes The TALK Targets campaign was initiated and fully funded by Novo Nordisk. By supporting you and your healthcare team, TALK Targets
It s time to TALK Targets A guide to taking control of your type 2 diabetes The TALK Targets campaign was initiated and fully funded by Novo Nordisk. By supporting you and your healthcare team, TALK Targets
Benign Pituitary Tumor
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu The pituitary gland is a small, pea-sized endocrine gland in the center of the brain. Also known as the master gland, the pituitary gland helps control the
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu The pituitary gland is a small, pea-sized endocrine gland in the center of the brain. Also known as the master gland, the pituitary gland helps control the
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment
 Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
TEACHING Body Systems
 TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Body Systems 3rd Grade Reading Level ISBN: 978-0-8225-2324-6 Green 2 TEACHING BODY SYSTEMS Standards Health Language Arts Writing Language Arts Reading Science Visual Arts Knows
TEACHING GUIDE TEACHING Body Systems 3rd Grade Reading Level ISBN: 978-0-8225-2324-6 Green 2 TEACHING BODY SYSTEMS Standards Health Language Arts Writing Language Arts Reading Science Visual Arts Knows
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism. Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology
 A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form
 IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
glucose and fatty acids to raise your blood sugar levels.
 Endocrine & Cell Communication Part IV: Maintaining Balance (Homeostasis) TEACHER NOTES needs coding 1 Endocrine & Cell Communication Part IV: Maintaining Balance (Homeostasis) 2 AP Biology Curriculum
Endocrine & Cell Communication Part IV: Maintaining Balance (Homeostasis) TEACHER NOTES needs coding 1 Endocrine & Cell Communication Part IV: Maintaining Balance (Homeostasis) 2 AP Biology Curriculum
Hormone Restoration: Is It Right for You? Patricia A. Stafford, M.D. Founder, Wellness ReSolutions
 Hormone Restoration: Is It Right for You? Patricia A. Stafford, M.D. Founder, Wellness ReSolutions IMPORTANCE OF HORMONE BALANCE Importance of Hormone Balance Help you live a long, healthy life Help you
Hormone Restoration: Is It Right for You? Patricia A. Stafford, M.D. Founder, Wellness ReSolutions IMPORTANCE OF HORMONE BALANCE Importance of Hormone Balance Help you live a long, healthy life Help you
Part 1: Introduction Tell the name of your organ system and describe the major functions.
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Hormone Replacement Therapy For Men Consultation Information. Round Rock Jollyville Westlake 512-231-1444 www.urologyteam.com.
 Hormone Replacement Therapy For Men Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake 512-231-1444 www.urologyteam.com Rev 05/13 Table of Contents Biological Aging and Hormones 2 As we age.... 3
Hormone Replacement Therapy For Men Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake 512-231-1444 www.urologyteam.com Rev 05/13 Table of Contents Biological Aging and Hormones 2 As we age.... 3
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
MANAGING ANEMIA. When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure. www.kidney.org
 MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
Here we will talk about:
 Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Reader s Theater. I AM the Most Important. (A Script about the human body systems. By Amy Bowden) Characters
 Reader s Theater I AM the Most Important (A Script about the human body systems By Amy Bowden) Characters Judge (narrator) Digestive System Circulatory System Muscular System Respiratory System Nervous
Reader s Theater I AM the Most Important (A Script about the human body systems By Amy Bowden) Characters Judge (narrator) Digestive System Circulatory System Muscular System Respiratory System Nervous
Water Homeostasis. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
CAN DIABTES BE PREVENTED OR REVERSED?
 Knowledge is power if we use it to invest in our health and future. CAN DIABTES BE PREVENTED OR REVERSED? Old saying: An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure Did you know that over one-third of
Knowledge is power if we use it to invest in our health and future. CAN DIABTES BE PREVENTED OR REVERSED? Old saying: An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure Did you know that over one-third of
Biology 12 June 2003 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 June 2003 rovincial Examination ANWER KEY / CORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell rocesses and Applications 3. Human Biology ub-organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I, J, K,
Biology 12 June 2003 rovincial Examination ANWER KEY / CORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell rocesses and Applications 3. Human Biology ub-organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I, J, K,
Client Information for Informed Consent TESTOSTERONE FOR TRANSGENDER PATIENTS
 Client Information for Informed Consent TESTOSTERONE FOR TRANSGENDER PATIENTS You want to take testosterone to masculinize your body. Before taking it, there are several things you need to know about.
Client Information for Informed Consent TESTOSTERONE FOR TRANSGENDER PATIENTS You want to take testosterone to masculinize your body. Before taking it, there are several things you need to know about.
Second Grade The Human Body-Cells Assessment
 Second Grade The Human Body-Cells Assessment 1a. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell 1b. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell c. an egg d. a phone 1c. The basic unit of all
Second Grade The Human Body-Cells Assessment 1a. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell 1b. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell c. an egg d. a phone 1c. The basic unit of all
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
What Causes Cancer-related Fatigue?
 What Causes Cancer-related Fatigue? The causes of cancer-related fatigue are not fully understood. It may be the cancer and/or the cancer treatment. Cancer and cancer treatment can change normal protein
What Causes Cancer-related Fatigue? The causes of cancer-related fatigue are not fully understood. It may be the cancer and/or the cancer treatment. Cancer and cancer treatment can change normal protein
(1) Move the glucose from the blood into cells that need the glucose for its source of energy to survive; and,
 SOME INSIGHT INTO INSULIN Insulin is a major anabolic (tissue-building) hormone of metabolism and has many roles in the body. Unlike the anabolic effects of testosterone that builds muscle and bone, insulin
SOME INSIGHT INTO INSULIN Insulin is a major anabolic (tissue-building) hormone of metabolism and has many roles in the body. Unlike the anabolic effects of testosterone that builds muscle and bone, insulin
If you have type 1 diabetes, you will probably get symptoms quite suddenly, over a few days or weeks.
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Diabetes type 1 Type 1 diabetes is a long-term condition. It can lead to serious health problems. But making changes to your lifestyle and taking insulin can help
Patient information from the BMJ Group Diabetes type 1 Type 1 diabetes is a long-term condition. It can lead to serious health problems. But making changes to your lifestyle and taking insulin can help
What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body. Vitamin A
 What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body Vitamin A Prevents skin disorders, such as acne, wrinkling and age spots. Enhances the immune system protects against colds, flu, and infections to kidney,
What Each Vitamin & Mineral Does In Your Body Vitamin A Prevents skin disorders, such as acne, wrinkling and age spots. Enhances the immune system protects against colds, flu, and infections to kidney,
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource
 CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
CPI Links Content Guide & Five Items Resource Introduction The following information should be used as a companion to the CPI Links. It provides clarifications concerning the content and skills contained
About Andropause (Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome)
 About Andropause (Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome) There are many myths, misconceptions and a general lack of awareness about this easily treated hormonal imbalance that research shows affects 20% of
About Andropause (Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome) There are many myths, misconceptions and a general lack of awareness about this easily treated hormonal imbalance that research shows affects 20% of
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Micronutrient. Functio. Vitamin A
 EHPM Leaflet UK 25/4/00 14:50 Page 1 (1,1) Vitamin and mineral intake We cannot, however, afford to be complacent about our intake of vitamins and minerals. Poor diets with low quantities of fruit and
EHPM Leaflet UK 25/4/00 14:50 Page 1 (1,1) Vitamin and mineral intake We cannot, however, afford to be complacent about our intake of vitamins and minerals. Poor diets with low quantities of fruit and
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
Ch16 Endocrine part 2
 Ch16 Endocrine part 2 several separate organs release hormones into capillaries hormones are transported in the blood Hypothalamus Pituitary glands Pineal gland Thyroid Parathyroid Thymus Adrenal Cortex
Ch16 Endocrine part 2 several separate organs release hormones into capillaries hormones are transported in the blood Hypothalamus Pituitary glands Pineal gland Thyroid Parathyroid Thymus Adrenal Cortex
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Testosterone. Testosterone For Women
 Testosterone Testosterone is a steroid hormone. Popular use of the term steroid leads people to believe that it signifies a drug that s illegal and abused by some body builders and other athletes. While
Testosterone Testosterone is a steroid hormone. Popular use of the term steroid leads people to believe that it signifies a drug that s illegal and abused by some body builders and other athletes. While
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
Introduction to Animals Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What characteristics and traits define animals? 25.1 What is an animal? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Animals are different from other living things
The Testosterone Report
 The Testosterone Report Contents 1. What is Testosterone? 2. Why is Testosterone necessary? 3. Why do my Testosterone Levels decrease? 4. What does low Testosterone cause? 5. How Do I raise my Testosterone?
The Testosterone Report Contents 1. What is Testosterone? 2. Why is Testosterone necessary? 3. Why do my Testosterone Levels decrease? 4. What does low Testosterone cause? 5. How Do I raise my Testosterone?
Pregnancy and hypothyroidism
 Pregnancy and hypothyroidism Departments of Endocrinology & Obstetrics Patient Information What What is hypothyroidism? is hypothyroidism? Hypothyroidism means an underactive thyroid gland, which does
Pregnancy and hypothyroidism Departments of Endocrinology & Obstetrics Patient Information What What is hypothyroidism? is hypothyroidism? Hypothyroidism means an underactive thyroid gland, which does
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
The role of negative -ION in the improvement of our health
 What are IONS and where do they come from? IONS are particles with a positive or a negative electrical charge The percentage and number of +IONS and -IONS change depending on the time and place. IONS can
What are IONS and where do they come from? IONS are particles with a positive or a negative electrical charge The percentage and number of +IONS and -IONS change depending on the time and place. IONS can
Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Calcium. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nuf40101 Last reviewed: 02/19/2013 1
 Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
