The Emergence of Industrial Society in the West,
|
|
|
- Dominick Richardson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 23 The Emergence of Industrial Society in the West, The Age of Revolution Eighteenth-century faith in progress was reflected in Condorcet s Progress of the Human Mind,written in 1793 while the author was in hiding. The age of revolution was inspired by that spirit, but also shook its optimism. Three influences came to overturn Europe by the mid-19th century. Intellectual excitement was pervasive. The ideas of such philosophers as Jean-Jacques Rousseau were widely read. Secondly, more and more Europeans were part of the commercial economy. Commercial wealth challenged traditional notions of the right to rule. Thirdly, the population revolution resulting from better nutrition, and limited control of diseases, led to population pressure. Proto-industrialization was spurred by the wealth of labor resulting from the population revolution. When the British Atlantic colonies rebelled it was not truly a revolution, but a war of independence. The so-called American Revolution established a new government in 1776, and achieved its aims in The French Revolution soon followed, beginning a profound political restructuring. Ideology called for reforms, and social change added a dimension to the struggles. However, the French government was too slow to adapt. When Louis XVI finally called a parliament in the summer of 1789, reform was forced upon him. The Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen proclaimed the ideology of the reformers. The taking of the Bastille, a symbol of royal power, on July 14th began widespread uprisings. Calls for reform in 1789 turned to radicalism in The monarchy was abolished and the king beheaded by guillotine.maximilien Robespierre led the radical revolution. Leading the Terror, he also suppressed French Catholicism, but was finally guillotined himself. Universal male suffrage, abolition of colonial slavery, and universal conscription were among his policies. Nationalism added to calls for reform to crystallized adherence to the movement. The arrival on the scene of Napoleon Bonaparte in 1799 transformed the revolution. Monopolizing power, he nevertheless continued many of the liberal reforms. Legal reforms were promulgated under the Code Napoleon. Ambitious wars led to the undoing of Napoleon in Yet, the revolutionary legacy was great. Following the defeat of Napoleon, the Congress of Vienna met in 1815 to settle the peace. The principle of the balance of power was followed, and was successful for decades. The ascendancy of conservative goals was signaled by the 139
2 restoration of monarchies. Much of the Enlightenment ideology was pursued by Liberals, who formed in opposition to the Conservatives. Radicals wished to push reforms further. Nationalists allied sometimes with Radicals, sometimes with Liberals. The Greek Revolution in 1820 was one of many uprisings inspired by the French Revolution and the ideas of nationalism. The British Reform Bill of 1832 achieved many of the reformers goals without revolution. Industrialization, added to the social upheavals, creating a working class with its own agenda. The Chartist movement in Britain hoped to extend suffrage, enact educational reforms, and improve working conditions. However, in the revolutions, unrest peaked. Beginning with France, uprisings followed in Austria, Germany, Hungary, and Italy. These short-lived revolutions did not bear immediate fruit. In France itself, Napoleon III imposed authoritarian rule. The age of revolutions was over. Many of the goals of revolutionaries had been met, but governments had also learned how to control challenges. The Consolidation of the Industrial Order, The second half of the 19th century was marked by growth and a growing infrastructure linking European countries. Urban life was improved by better sanitation and attention to the needs of the poor and sick. Crime rates stabilized or fell. Industrialization changed every aspect of life. Material well-being rose. Mortality rates among infants fell, and more effective methods limited childhood diseases. The work of Louis Pasteur accounted in a large part for massive improvement in health. At the same time, corporations transformed business, drawing on capital. Their work forces became a major political and economic power, while the political power of peasants declined. Politically, the agenda changed radically after the 1848 revolutions. The Argument over absolutism and constitutions was resolved, and gave way to debates over workers rights and voting. Benjamin Disraeli, the British conservative prime minister, expanded the vote for men. Count Camillo di Cavour also responded to liberal demands. In Prussia, Otto von Bismarck extended the vote to all men, emancipated the Jews, and pushed mass education. These new conservatives also called upon nationalism to consolidate their power. National platforms often took the form of imperialism, as in the case of British and U.S. expansion. In Italy and Germany they were formative. Under Cavour s leadership, Italy was unified in spite of papal opposition. Bismarck similarly used nationalism to unite Prussia. He maneuvered the country into war with Denmark and Austria, culminating in German unity in The American Civil War, from , reaffirmed the Union and ended slavery. France returned to its republican system. Across Europe, parliamentary systems allowed continuity in spite of changes in leadership, a process the Italians called transformismo. Governments increased their domestic scope after Agencies regulating education, health, industry, and welfare became common. Germany was a leader, implementing social insurance for illness and old age. The social question came to dominate political debates, leading to the emergence of socialism. Earlier socialists had general aims, often taking shape in utopian communities. Inspired 140 PART II: TOPICAL REVIEW WITH SAMPLE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND EXPLANATIONS
3 Cultural Transformations by the ideas of Karl Marx,new generations focused on his idea of the centrality of the class struggle, and the necessity of violent protest. Socialism became an important force by the last decades of the 19th century. Revisionist socialism called for achieving Marx s ends without violence. Feminist movements added their agendas, demanding a political voice. Such leaders as Emmeline Pankhurst used strikes and protests to gain suffrage. While the growing working class copied middle-class tastes, they also demanded entertaining leisure pursuits. On the supply side, meanwhile, producers had to stimulate demand to find a market for their goods. Mass leisure culture, informed and shaped in part by high-circulation newspapers, called for entertainment. Team sports developed along with nationalism to create new loyalties. In many ways mass culture replaced religion. Unlike the sciences in the Enlightenment, in the late 19th century, the sciences moved away from other intellectual pursuits, and professional scientists took the place of amateurs. In 1859, Charles Darwin published his influential work on the theory of evolution. His ideas conflicted not only with religious notions, but with the Enlightenment idea of an orderly natural world. Meanwhile, work in physics included discoveries in electromagnetism, particle physics, and astronomy. Albert Einstein came up with the idea of relativity, also a challenge to accepted ideas of the physical world. The late 1800s were a period of great development in the social sciences, including economics, sociology, and psychology. Sigmund Freud advanced his ideas on the human subconscious. In the arts, the prevalent movement in the early 1800s was romanticism.in reaction to the Enlightenment, romanticism emphasized individual emotional responses in the plastic arts, music, and literature. The end of the century saw a move to challenge every canon of representation, harmony, rhyme, and narrative. Western Settler Societies Industrialization spurred the search for raw materials and markets. At the same time, it gave the West a military advantage, in its use of guns and steamships. These factors drove the expansion of settler societies in the United States, Canada, Australia, and South Africa. The new United States came to be a world power in the 19th century. Massively enlarging its territory with the Louisiana Purchase and settling the lands beyond the Mississippi, it was able to extend its influence partly due to a huge influx of Europeans. The American Civil War, , violently resolved the economic and cultural split between the north and south. The war pushed industrialization and the development of infrastructure. A railway linking the east and west coasts was key to exploiting western lands. Outside the Western Hemisphere, the influence of the United States was small. The British dominions of Canada, Australia, and New Zealand had been relatively sparsely-populated by indigenous peoples. In each area, governments followed western models. Canada was divided by French and British settlers. From 1839, the British began the process of giving Canada autonomy, to avoid an inde- CHAPTER 23: THE EMERGENCE OF INDUSTRIAL SOCIETY IN THE WEST,
4 pendence movement. As in the United States, railways facilitated settlement. Australia was originally colonized as a penal colony, but by the middle of the century was an important wool producer. Gold strikes spurred settlement. Britain granted self-rule, and the Australian parliamentary government developed. New Zealand was different. Its Maori people were politically organized, and resisted successfully for decades. Nevertheless, European immigration began in 1840, and the Maoris were defeated by New Zealand, Canada, and Australia remained closely linked to Britain, but developed along their own lines. With the United States and South America, they received the bulk of European immigrants in the 19th century. Diplomatic Tensions and World War I German unification undermined the balance of power in Europe. At the same time, European leaders were looking for solutions through imperialism. Yet by 1900, there was little territory left to take. The alliance system replaced the balance of power. The Triple Alliance Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy and the Triple Entente Britain, Russia, and France set the powers of Europe against each other. Militarization, spurred by nationalism and industrialists, made the face-off volatile. Russia and Austria- Hungary were the least stable elements, susceptible to internal upheavals. As provinces of the Ottoman Empire sought independence, Balkan nationalism also threatened the peace. Serbia emerged and then sought to expand its territory. The causes of the First World War included militant nationalism. Industrialization was an indirect cause, as leaders used international undertakings to appease social unrest. Militarization, an economic plus, also led to conflict. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. The chief intellectual cause of the French and American revolutions was the (A) Enlightenment. (B) economic ideas of mercantilism. (C) Renaissance. (D) 1688 Glorious Revolution in England. (E) economic system of mercantilism. 2. All of these were forces for change in Western Europe during the period EXCEPT: (A) the ideas of the Enlightenment. (B) the increasing wealth and success of the business classes. (C) religious innovation. (D) the population pressures caused by demographic shift. (E) industrialization and mechanization. 3. All of these led to the outbreak of the French Revolution in 1789 EXCEPT: (A) the inability of the French government to reform itself. (B) an invasion of France by Prussia and Austria. (C) a massive debt and need for tax reform. (D) a desire to limit the powers and rights of the king, nobles, and clergy. (E) bad harvests and rural (peasant) unrest. 4. The political ideology most favored by the victorious allied powers at the Congress of Vienna was: (A) nationalism. (B) radicalism. (C) liberalism. (D) conservatism. (E) revolution. 142 PART II: TOPICAL REVIEW WITH SAMPLE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND EXPLANATIONS
5 5. The older European loyalty to established religions and God was often replaced after the French Revolution by (A) devotion to the Pope. (B) support of the king and national rulers. (C) allegiance to local leaders. (D) allegiance to strong military leaders. (E) nationalism and loyalty to the nationstate. 6. The European Industrial Revolution directly influenced (A) the American Revolution. (B) the French Revolution. (C) the European revolutions of (D) the Greek nationalist revolution of (E) the Napoleonic Revolution. 7. All of these demands were advocated by the 1848 revolutionaries EXCEPT: (A) social reform. (B) an end to serfdom and manorialism. (C) nationalist independence and/or unification. (D) liberal constitutions with political rights and protections. (E) an end to colonialism and overseas acquisitions. 8. The new European power, which benefited from industrialization and nationalism, and which came to rival Great Britain in the 19th century, was (A) the United States. (B) Italy. (C) Russia. (D) France. (E) the German Empire. 9. The social questions, demands for reform, and the need for money to support the construction of railroads during the 19th century led to (A) the expansion of and increasing intervention by governments in society. (B) increasing radicalization of a majority of workers and peasants. (C) numerous violent, socialist revolutions. (D) the decrease in support for socialism, either Marxist or revisionist. (E) the bankruptcy of many governments. 10. All of these conditions led to the outbreak of World War I EXCEPT: (A) rival systems of alliance. (B) international courts of justice and organizations such as the Red Cross. (C) increased militarization of societies. (D) the rivalry for and expansion of colonial empires. (E) national rivalries between Balkan states. Free-Response Question What was the relationship between the French Revolution and the revolutions of ? ANSWERS AND EXPLANATIONS Multiple-Choice Questions 1. (A) is correct. The ideas of the Enlightenment, especially the innate right to freedom, were key in both revolutions. Critique of the clergy was an important part of the French revolution. 2. (C) is correct. There was no significant religious reform in the period, but all of the other factors were important. 3. (B) is correct. All of the answers except for B influenced the Revolution. The invasion by Prussia came later in the century. CHAPTER 23: THE EMERGENCE OF INDUSTRIAL SOCIETY IN THE WEST,
6 4. (D) is correct. The Congress of Vienna represented a reaction to the liberal ideas of the Enlightenment, as rulers attempted to stabilize their positions and suppress revolt. 5. (E) is correct. While the spiritual role of religion was little changed, Europeans increasingly gave their allegiance to, and formed their culture around, nationalism. 6. (C) is correct. Unlike the other revolutions, the revolutions of were inspired not by Enlightenment ideals but by unrest resulting from industrialization. 7. (E) is correct. The revolutions of concentrated on domestic reforms. 8. (E) is correct. The German empire achieved unity through nationalism, and its support of industrialization increased the power gained through unification. 9. (A) is correct. Governments intervened both to satisfy the needs of the population, and often in opposition to worker demands. 10. (B) is correct. World War I broke out in spite of the emergence of such international organizations. Free-Response Essay Sample Response What was the relationship between the French Revolution and the revolutions of ? The revolutions of 1848 and 1849 were fought over a different set of issues than the French Revolution. The French Revolution broke out because of economic conditions in France, and the inflexibility of the government when faced by calls for reform along Enlightenment lines. By 1848, industrialization had transformed Europe, and raised new issues about workers rights and other changes in society. The two revolutionary periods had some broad issues in common, but their most direct link was that the French revolution had demonstrated the efficacy of violent revolution for bringing about change. 144 PART II: TOPICAL REVIEW WITH SAMPLE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND EXPLANATIONS
ERA V 1750 1914 Revolution, Romanticism, Industrialization, and Imperialism
 CHAPTER 3 Chapter Summary Western society was dominated by four themes: political revolution, industrialization, nationalism, and the spread of Western institutions and values to other parts of the world.
CHAPTER 3 Chapter Summary Western society was dominated by four themes: political revolution, industrialization, nationalism, and the spread of Western institutions and values to other parts of the world.
Chapter 28. The Industrialization of the West, 1750-1914 OUTLINE. I. Introduction
 Chapter 28 The Industrialization of the West, 1750-1914 OUTLINE I. Introduction After 1750, the West underwent a series of dramatic transformations in politics, intellectual development, and industrialization.
Chapter 28 The Industrialization of the West, 1750-1914 OUTLINE I. Introduction After 1750, the West underwent a series of dramatic transformations in politics, intellectual development, and industrialization.
World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies. Semester 1
 World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies All World History courses (Honors or otherwise) utilize the same targets and indicators for student performance. However, students enrolled in Honors
World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies All World History courses (Honors or otherwise) utilize the same targets and indicators for student performance. However, students enrolled in Honors
Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government
 CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action 20:2 Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should
CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action 20:2 Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should
MT. DIABLO UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT COURSE OF STUDY
 COURSE TITLE: AP EUROPEAN HISTORY COURSE NUMBER: 3510 DEPARTMENT: History and Social Science GRADE LEVEL(S): 10-12 CREDITS PER SEMESTER: 5 credits LENGTH OF COURSE: One Year REQUIRED OR ELECTIVE: Elective-designed
COURSE TITLE: AP EUROPEAN HISTORY COURSE NUMBER: 3510 DEPARTMENT: History and Social Science GRADE LEVEL(S): 10-12 CREDITS PER SEMESTER: 5 credits LENGTH OF COURSE: One Year REQUIRED OR ELECTIVE: Elective-designed
UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON
 UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON NOTE: BASED ON 2X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON NOTE: BASED ON 2X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
Images of the French Revolution and Napoleon. Review A little information about Napoleon Map Work and the Congress of Vienna Reading
 Images of the French Revolution and Napoleon Review A little information about Napoleon Map Work and the Congress of Vienna Reading Who are these people? What do these images represent? What in the World
Images of the French Revolution and Napoleon Review A little information about Napoleon Map Work and the Congress of Vienna Reading Who are these people? What do these images represent? What in the World
Table of Contents. Part One: Social Studies Curriculum
 Table of Contents Part One: Social Studies Curriculum Chapter I: Social Studies Essay Questions and Prewriting Activities 1. Western Political Thought 1 2. The Age of Revolution 6 3. The Age of Napoleon
Table of Contents Part One: Social Studies Curriculum Chapter I: Social Studies Essay Questions and Prewriting Activities 1. Western Political Thought 1 2. The Age of Revolution 6 3. The Age of Napoleon
History programmes of study: key stage 3
 History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
World History: Essential Questions
 World History: Essential Questions Content Standard 1.0: Culture encompasses similarities and differences among people including their beliefs, knowledge, changes, values, and traditions. Students will
World History: Essential Questions Content Standard 1.0: Culture encompasses similarities and differences among people including their beliefs, knowledge, changes, values, and traditions. Students will
Soci250 Sociological Theory
 Soci250 Sociological Theory Module 1 Overview of Classical Sociological Theory François Nielsen University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Spring 2007 Outline Main Themes Social & historical forces Intellectual
Soci250 Sociological Theory Module 1 Overview of Classical Sociological Theory François Nielsen University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Spring 2007 Outline Main Themes Social & historical forces Intellectual
Note Taking Study Guide PHILOSOPHY IN THE AGE OF REASON
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide PHILOSOPHY IN THE AGE OF REASON Focus Question: What effects did Enlightenment philosophers have on government and society? As you read this section in your textbook,
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide PHILOSOPHY IN THE AGE OF REASON Focus Question: What effects did Enlightenment philosophers have on government and society? As you read this section in your textbook,
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Analyze various ways in which government policies during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic era contributed to a greater sense of French national identity
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Analyze various ways in which government policies during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic era contributed to a greater sense of French national identity
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT
 THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT To view this PDF as a projectable presentation, save the file, click View in the top menu bar of the file, and select Full Screen Mode To request an editable PPT version of this
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT To view this PDF as a projectable presentation, save the file, click View in the top menu bar of the file, and select Full Screen Mode To request an editable PPT version of this
TEACHER S KEY SESSION 1. THE WORLD BEFORE THE GREAT WAR. PRETASK. 3. Pre- listening.
 TEACHER S KEY SESSION 1. THE WORLD BEFORE THE GREAT WAR. PRETASK 3. Pre- listening. 1. Before 1914, the nations of Europe were involved in a race to obtain overseas colonies all over the world, mainly
TEACHER S KEY SESSION 1. THE WORLD BEFORE THE GREAT WAR. PRETASK 3. Pre- listening. 1. Before 1914, the nations of Europe were involved in a race to obtain overseas colonies all over the world, mainly
Chapter 22: World War I. Four most powerful European nations in the early 1900s were Great Britain, France, Germany, Russia.
 Chapter 22: World War I The Beginnings of World War I World War I was fought from 1914-1918. United States entered World War I in 1917. The Origins of Europe s Great War Nationalism Four most powerful
Chapter 22: World War I The Beginnings of World War I World War I was fought from 1914-1918. United States entered World War I in 1917. The Origins of Europe s Great War Nationalism Four most powerful
The French Revolution and the Idea of the Nation
 The French Revolution and the Idea of the Nation The first clear expression of nationalism came with the French Revolution in 1789. France, as you would remember, was a full-fledged territorial state in
The French Revolution and the Idea of the Nation The first clear expression of nationalism came with the French Revolution in 1789. France, as you would remember, was a full-fledged territorial state in
LEAGUE OF WOMEN VOTERS: OBJECTIVES
 Labor but were upset at the class divisions it encouraged between workers and bosses. That set people apart instead of bringing them together as citizens. They saw Labor as a selfish party, caring for
Labor but were upset at the class divisions it encouraged between workers and bosses. That set people apart instead of bringing them together as citizens. They saw Labor as a selfish party, caring for
To What Extent is The Cold War a Result of Two Conflicting Ideologies?
 Rahaf Alwattar Daniela Morales Kiley Smith Madison So To What Extent is The Cold War a Result of Two Conflicting Ideologies? The Cold War was an unceasing state of political and military tensions between
Rahaf Alwattar Daniela Morales Kiley Smith Madison So To What Extent is The Cold War a Result of Two Conflicting Ideologies? The Cold War was an unceasing state of political and military tensions between
Unit 01 - Study Questions 1. In what ways did geography and climate affect the development of human society? 2. What were the economic and social
 Unit 01 - Study Questions 1. In what ways did geography and climate affect the development of human society? 2. What were the economic and social results of the agricultural revolution? 3. What are the
Unit 01 - Study Questions 1. In what ways did geography and climate affect the development of human society? 2. What were the economic and social results of the agricultural revolution? 3. What are the
Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses
 Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses The AP social studies courses are intended to provide a rigorous college level introduction to the social sciences for high school students. While no official
Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses The AP social studies courses are intended to provide a rigorous college level introduction to the social sciences for high school students. While no official
Note Taking Study Guide ON THE EVE OF REVOLUTION
 SECTION 1 ON THE EVE OF REVOLUTION Focus Question: What led to the storming of the Bastille, and therefore, to the start of the French Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the
SECTION 1 ON THE EVE OF REVOLUTION Focus Question: What led to the storming of the Bastille, and therefore, to the start of the French Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the
ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES
 History S5 AOlution ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES Lesson 40 Developed by (Maxon J. Kasumba) Subtopic ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES Overview/general
History S5 AOlution ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES Lesson 40 Developed by (Maxon J. Kasumba) Subtopic ROLE OF KING WILLIAM I IN THE UNIFICATION OF GERMANY STATES Overview/general
History. Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment target (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007)
 History Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment target (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007 Curriculum aims
History Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment target (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007 Curriculum aims
Chapter 17 Outline revolutionary for the society that had already emerged, not for the revolution itself
 Chapter 17 Outline I. Comparing Atlantic Revolutions A. The revolutions of North America, Europe, Haiti, and Latin America influenced each other. 1. they also shared a set of common ideas 2. grew out of
Chapter 17 Outline I. Comparing Atlantic Revolutions A. The revolutions of North America, Europe, Haiti, and Latin America influenced each other. 1. they also shared a set of common ideas 2. grew out of
AP World History Class Notes Ch 30 Age of Revolutions December 27, 2011
 AP World History Class Notes The years 1776 and 1789 are pivotal dates in world history. The impact of e American Revolution and e French Revolution extended far beyond e borders of ose two countries.
AP World History Class Notes The years 1776 and 1789 are pivotal dates in world history. The impact of e American Revolution and e French Revolution extended far beyond e borders of ose two countries.
Course Title: AP European History Board Approval Date: 12/14/13 Credit / Hours: 1.5 credit
 Course Title: AP European History Board Approval Date: 12/14/13 Credit / Hours: 1.5 credit Course Description: The Advanced Placement course in European History is designed to give students a rigorous
Course Title: AP European History Board Approval Date: 12/14/13 Credit / Hours: 1.5 credit Course Description: The Advanced Placement course in European History is designed to give students a rigorous
Here is the list of history courses with cross listings and how they fit in each of the sections of the History Major.
 Here is the list of history courses with cross listings and how they fit in each of the sections of the History Major. Note: if you take a History course that is cross listed and you take it under the
Here is the list of history courses with cross listings and how they fit in each of the sections of the History Major. Note: if you take a History course that is cross listed and you take it under the
Addendum: American History I: The Founding Principles
 Addendum: American History I: The Founding Principles On June 23, 2011, the North Carolina General Assembly passed The Founding (SL 2011-273). This act calls for local boards of education to require, as
Addendum: American History I: The Founding Principles On June 23, 2011, the North Carolina General Assembly passed The Founding (SL 2011-273). This act calls for local boards of education to require, as
SOCIAL STUDIES TEST for e-lessons day 2
 SOCIAL STUDIES TEST for e-lessons day 2 Name Directions: Use your own piece of paper as your answer document. Do not print off the test. You will need to only turn in your answer document. 29. The Cold
SOCIAL STUDIES TEST for e-lessons day 2 Name Directions: Use your own piece of paper as your answer document. Do not print off the test. You will need to only turn in your answer document. 29. The Cold
Although the dominant military confrontations of the 20 th century were centered on the
 To what extent were the policies of the United States responsible for the outbreak and development of the Cold War between 1945 and 1949? Although the dominant military confrontations of the 20 th century
To what extent were the policies of the United States responsible for the outbreak and development of the Cold War between 1945 and 1949? Although the dominant military confrontations of the 20 th century
Ch 11-3 Worksheet 1The Berlin Conference 1884
 Ch 11-3 Worksheet 1The Berlin Conference 1884 THE BERLIN CONFERENCE Because of its size, surface features, climate, resources, and strategic importance, Africa became a prime candidate for conquest by
Ch 11-3 Worksheet 1The Berlin Conference 1884 THE BERLIN CONFERENCE Because of its size, surface features, climate, resources, and strategic importance, Africa became a prime candidate for conquest by
M.A. (Composite History)
 M.A. (Composite History) Semester I History of Europe, Renaissance to 1789 1. Renaissance 2. Reformation and Counter Reformation I 1. The Thirty Years war 2. Age of Louis XIV II 1. Conflict between King
M.A. (Composite History) Semester I History of Europe, Renaissance to 1789 1. Renaissance 2. Reformation and Counter Reformation I 1. The Thirty Years war 2. Age of Louis XIV II 1. Conflict between King
history (his) History
 history (his) Mark R. Correll, Chair Mark T. Edwards David Rawson Charles E. White The fundamental purpose of the department of history, politics, and geography is to aid the student in gaining an understanding
history (his) Mark R. Correll, Chair Mark T. Edwards David Rawson Charles E. White The fundamental purpose of the department of history, politics, and geography is to aid the student in gaining an understanding
Addendum: American History II:
 Addendum: American History II: On June 23, 2011, the North Carolina General Assembly passed The Founding Principles Act (SL 2011-273). This act calls for local boards of education to require, as a condition
Addendum: American History II: On June 23, 2011, the North Carolina General Assembly passed The Founding Principles Act (SL 2011-273). This act calls for local boards of education to require, as a condition
Late Medieval Period (WHI.12)
 Name Late Medieval Period (WHI.12) Label on Map: England, France, Spain, Russia, Holly Roman Empire, Paris, Rome, Mediterranean Sea, English Channel, Atlantic Ocean Term: Nation-state Describe: Draw: 1
Name Late Medieval Period (WHI.12) Label on Map: England, France, Spain, Russia, Holly Roman Empire, Paris, Rome, Mediterranean Sea, English Channel, Atlantic Ocean Term: Nation-state Describe: Draw: 1
Fundamental Principles of American Democracy
 Fundamental Principles of American Democracy Standard: 12.1 Students explain the fundamental principles and moral values of American democracy as expressed in the U.S. Constitution and other essential
Fundamental Principles of American Democracy Standard: 12.1 Students explain the fundamental principles and moral values of American democracy as expressed in the U.S. Constitution and other essential
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism in Africa and India?
 Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism in Africa and India? Unit X Quiz 2 1. When did the Suez Canal open? 2. Why was it initially difficult for European powers to control their
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism in Africa and India? Unit X Quiz 2 1. When did the Suez Canal open? 2. Why was it initially difficult for European powers to control their
UNIVERSAL ADULT FRANCHISE AND THE METHODS OF REPRESENTATION
 17 UNIVERSAL ADULT FRANCHISE AND THE METHODS OF REPRESENTATION I n an earlier lesson, you have studied that the opening words of the Preamble to the Indian Constitution are: We, the people of India. What
17 UNIVERSAL ADULT FRANCHISE AND THE METHODS OF REPRESENTATION I n an earlier lesson, you have studied that the opening words of the Preamble to the Indian Constitution are: We, the people of India. What
Chapter 11 Quiz- The Roaring 1920s
 Chapter 11 Quiz- The Roaring 1920s Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Ch. 11.1 The Republican Decade 1. Key features of Republican administrations
Chapter 11 Quiz- The Roaring 1920s Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Ch. 11.1 The Republican Decade 1. Key features of Republican administrations
Napoleonic France, 1799 1815. Napoleon Bonaparte as a young Officer
 Napoleonic France, 1799 1815 Napoleon Bonaparte as a young Officer 1 2 1796 Napoleon crossed the Alps & drove the Austrians out of Northern Italy. He then turned N. Italy into the Cisalpine Republic and
Napoleonic France, 1799 1815 Napoleon Bonaparte as a young Officer 1 2 1796 Napoleon crossed the Alps & drove the Austrians out of Northern Italy. He then turned N. Italy into the Cisalpine Republic and
The French Revolution Begins Close Read
 The French Revolution Begins Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may
The French Revolution Begins Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Social Studies
 Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Social Studies Mission Statement It is our belief that Social Studies education is ultimately to prepare students to assume the responsibilities
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Social Studies Mission Statement It is our belief that Social Studies education is ultimately to prepare students to assume the responsibilities
Running head: AMERICAN REVOLUTION 1
 Running head: AMERICAN REVOLUTION 1 American Revolution Persuasive Essay Student A. Sample Grand Canyon University: HIS 345 12/12/2012 AMERICAN REVOLUTION 2 American Revolution Persuasive Essay The American
Running head: AMERICAN REVOLUTION 1 American Revolution Persuasive Essay Student A. Sample Grand Canyon University: HIS 345 12/12/2012 AMERICAN REVOLUTION 2 American Revolution Persuasive Essay The American
Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline
 Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline 509 BCE: Tarquin the Proud, the last king of Rome, was overthrown by a group of patricians upset over his abuse of power. The Roman Republic was proclaimed. 494 BCE:
Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline 509 BCE: Tarquin the Proud, the last king of Rome, was overthrown by a group of patricians upset over his abuse of power. The Roman Republic was proclaimed. 494 BCE:
Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE. Course Title: Advanced Placement European History Course Number: 3452
 Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Advanced Placement European History Course Number: 3452 Department: Social Studies Grade(s): 11 & 12 Level(s): Advanced Placement Credit:
Wallingford Public Schools - HIGH SCHOOL COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Advanced Placement European History Course Number: 3452 Department: Social Studies Grade(s): 11 & 12 Level(s): Advanced Placement Credit:
Indian Independence Act 1947
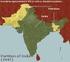 Indian Independence Act 1947 Independence Day, observed annually on 15 August, is a national holiday in India commemorating the nation s independence from British rule on 15 August 1947. India attained
Indian Independence Act 1947 Independence Day, observed annually on 15 August, is a national holiday in India commemorating the nation s independence from British rule on 15 August 1947. India attained
The failure of the Spanish Armada in 1588 permanently crippled the Spanish navy.
 AP European History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 15B Politics, Religion, and War (Note: only do the sections Politics, Religion, and War ; Changing Attitudes ; and Literature and Art ) A. True or False Where
AP European History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 15B Politics, Religion, and War (Note: only do the sections Politics, Religion, and War ; Changing Attitudes ; and Literature and Art ) A. True or False Where
International Relations / International Studies / European Studies
 International Relations / International Studies / European Studies Degree Courses BA International Relations and Politics 166 BA International Relations and Modern History 167 BA International Studies
International Relations / International Studies / European Studies Degree Courses BA International Relations and Politics 166 BA International Relations and Modern History 167 BA International Studies
FINAL ACT OF THE VIENNESE MINISTERIAL CONFERENCES (MAY 15, 1820)
 FINAL ACT OF THE VIENNESE MINISTERIAL CONFERENCES (MAY 15, 1820) The sovereign princes and free cities of Germany, mindful of the obligation they assumed upon founding the German Confederation to safeguard,
FINAL ACT OF THE VIENNESE MINISTERIAL CONFERENCES (MAY 15, 1820) The sovereign princes and free cities of Germany, mindful of the obligation they assumed upon founding the German Confederation to safeguard,
The Role of Trade and Empire in European Economic development to ca 1870
 The Role of Trade and Empire in European Economic development to ca 1870 Gerard M Koot, 2013 History Department, University of Massachusetts Dartmouth In recent years there has been a great deal of interest
The Role of Trade and Empire in European Economic development to ca 1870 Gerard M Koot, 2013 History Department, University of Massachusetts Dartmouth In recent years there has been a great deal of interest
AREA STUDIES - CHINA: REGIONAL SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT REVIEW Vol. III The Social Security System in China - Y. P. Liu
 THE SOCIAL SECURITY SYSTEM IN CHINA Y. P. Liu Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, P.R. China. Keywords: Social security system, China
THE SOCIAL SECURITY SYSTEM IN CHINA Y. P. Liu Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, P.R. China. Keywords: Social security system, China
Tennessee Curriculum Standards for High School World History Correlations to Wright Group/McGraw-Hill s World History
 Tennessee Curriculum Standards for High School World History Correlations to Wright Group/McGraw-Hill s World History Course Description: In World History High School, students study the history of humankind
Tennessee Curriculum Standards for High School World History Correlations to Wright Group/McGraw-Hill s World History Course Description: In World History High School, students study the history of humankind
THEMES/Learning Objectives
 PERIOD 2: 1607 1754 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 2. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
PERIOD 2: 1607 1754 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 2. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
: INTRODUCTION TO EUROPEAN HISTORY
 Course Title Course Code : INTRODUCTION TO EUROPEAN HISTORY : HST114 Recommended Study Year* : Year 1 No. of Credits/Term : 3 Mode of Tuition Class Contact Hours Category in Major Prog. Prerequisites Co-requisites
Course Title Course Code : INTRODUCTION TO EUROPEAN HISTORY : HST114 Recommended Study Year* : Year 1 No. of Credits/Term : 3 Mode of Tuition Class Contact Hours Category in Major Prog. Prerequisites Co-requisites
Note Taking Study Guide BUILDING A GERMAN NATION
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide BUILDING A GERMAN NATION Focus Question: How did Otto von Bismarck, the chancellor of Prussia, lead the drive for German unity? As you read this section in your textbook,
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide BUILDING A GERMAN NATION Focus Question: How did Otto von Bismarck, the chancellor of Prussia, lead the drive for German unity? As you read this section in your textbook,
Business. Democratic Socialism. Sponsoring Faculty Member: Professor Cindi Bearden. Levi Evans
 Business Levi Evans Democratic Socialism Sponsoring Faculty Member: Professor Cindi Bearden Levi Evans Democratic presidential primary candidate, Bernie Sanders, wants America to adopt the political and
Business Levi Evans Democratic Socialism Sponsoring Faculty Member: Professor Cindi Bearden Levi Evans Democratic presidential primary candidate, Bernie Sanders, wants America to adopt the political and
How To Learn About Politics At Sacred Heart University
 SACRED HEART UNIVERSITY UNDERGRADUATE CATALOG 2012-2013 POLITICAL SCIENCE The Political Science major seeks to awaken in students an appreciation and an understanding of politics and government in the
SACRED HEART UNIVERSITY UNDERGRADUATE CATALOG 2012-2013 POLITICAL SCIENCE The Political Science major seeks to awaken in students an appreciation and an understanding of politics and government in the
Name: Class: Global Studies Date: Mr. Wallace. The Enlightenment & The American Revolution Test Review
 Name: Class: Global Studies Date: Mr Wallace The Enlightenment & The American Revolution Test Review 1) The United States "founding fathers" were not influenced by the ideas of Enlightenment thinkers 2)
Name: Class: Global Studies Date: Mr Wallace The Enlightenment & The American Revolution Test Review 1) The United States "founding fathers" were not influenced by the ideas of Enlightenment thinkers 2)
The Printing Press: A Vehicle for Modernity
 The Printing Press: A Vehicle for Modernity November 3, 2010 Ailsa Lapp COMM345 Assignment #1 Professor: Virginia McKendry Throughout the history of civilization, the invention of printing has been argued
The Printing Press: A Vehicle for Modernity November 3, 2010 Ailsa Lapp COMM345 Assignment #1 Professor: Virginia McKendry Throughout the history of civilization, the invention of printing has been argued
THE EXECUTIVE AND LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT
 THE EXECUTIVE AND LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT The political institutions of the United Kingdom are divided into the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. The last of these will be developed
THE EXECUTIVE AND LEGISLATIVE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT The political institutions of the United Kingdom are divided into the legislative, the executive and the judiciary. The last of these will be developed
Chapter 8, Section 2 The Louisiana Purchase. Pages 272-277
 Chapter 8, Section 2 The Louisiana Purchase Pages 272-277 American Settlers Move West By the early 1800s, thousands of Americans settle in the area between the Appalachians and the Mississippi River. Kentucky,
Chapter 8, Section 2 The Louisiana Purchase Pages 272-277 American Settlers Move West By the early 1800s, thousands of Americans settle in the area between the Appalachians and the Mississippi River. Kentucky,
The Plight of Christians in the Middle East. Supporting Religious Freedom, Pluralism, and Tolerance During a Time of Turmoil
 AP PHOTO/HUSSEIN MALLA The Plight of Christians in the Middle East Supporting Religious Freedom, Pluralism, and Tolerance During a Time of Turmoil By Brian Katulis, Rudy deleon, and John Craig March 2015
AP PHOTO/HUSSEIN MALLA The Plight of Christians in the Middle East Supporting Religious Freedom, Pluralism, and Tolerance During a Time of Turmoil By Brian Katulis, Rudy deleon, and John Craig March 2015
Lesson # Overview Title /Standards. Big Question for lesson (from teaching thesis) Specific lesson Objectives (transfer from above).
 Lesson # Overview Title /Standards Big Question for lesson (from teaching thesis) Specific lesson Objectives (transfer from above). Content focused/action verbs Assessment of Objective(s) (you do not need
Lesson # Overview Title /Standards Big Question for lesson (from teaching thesis) Specific lesson Objectives (transfer from above). Content focused/action verbs Assessment of Objective(s) (you do not need
DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY. Add new courses:
 DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY Add new courses: HIST 299 Thinking Historically Fundamentals of the historian s craft. Variable content. Required for all majors except history honors students. Examines the origins
DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY Add new courses: HIST 299 Thinking Historically Fundamentals of the historian s craft. Variable content. Required for all majors except history honors students. Examines the origins
AP U.S. History Readiness Questions
 AP U.S. History Readiness Questions The following stimulus-based multiple choice questions should be able to be answered in 15 minutes. If after completing the items and checking your answers, you are
AP U.S. History Readiness Questions The following stimulus-based multiple choice questions should be able to be answered in 15 minutes. If after completing the items and checking your answers, you are
General Certificate of Education History
 General Certificate of Education History Unit HIS3D Report on the Examination (Specification 2040) June 2013 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2013 AQA
General Certificate of Education History Unit HIS3D Report on the Examination (Specification 2040) June 2013 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2013 AQA
Who Governs? CHAPTER 22 REVIEWING THE CHAPTER CHAPTER FOCUS STUDY OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 22 Who Governs? REVIEWING THE CHAPTER CHAPTER FOCUS This chapter provides an overview of American politics and central themes of the text, namely, Who Governs? To What Ends? A broad perspective
CHAPTER 22 Who Governs? REVIEWING THE CHAPTER CHAPTER FOCUS This chapter provides an overview of American politics and central themes of the text, namely, Who Governs? To What Ends? A broad perspective
The Approved List of Humanities and Social Science Courses For Engineering Degrees
 The Approved List of Humanities and Social Science Courses For Engineering Degrees Students should check the current catalog to ensure any prerequisite and departmental requirements are met. Approved Humanities
The Approved List of Humanities and Social Science Courses For Engineering Degrees Students should check the current catalog to ensure any prerequisite and departmental requirements are met. Approved Humanities
Mirror for Humanity by Kottack Quiz #10 C. Milner-Rose
 Mirror for Humanity by Kottack Quiz #10 C. Milner-Rose Chapter 10: The World System and Colonialism Multiple Choice Questions 1. What fueled the European Age of Discovery? A. A desire to save the souls
Mirror for Humanity by Kottack Quiz #10 C. Milner-Rose Chapter 10: The World System and Colonialism Multiple Choice Questions 1. What fueled the European Age of Discovery? A. A desire to save the souls
Colonialism and Imperialism
 Colonialism and Imperialism Juan Carlos Ocaña Aybar [4º ESO] Geography and History Bilingual Studies IES Parque de Lisboa, Alcorcón (Madrid) 1 Colonialism and Imperialism 1. Colonialism The Historical
Colonialism and Imperialism Juan Carlos Ocaña Aybar [4º ESO] Geography and History Bilingual Studies IES Parque de Lisboa, Alcorcón (Madrid) 1 Colonialism and Imperialism 1. Colonialism The Historical
History. Bachelor of Arts Major in History. Objectives. Degree Offered. Major Offered. Minor Offered. International Studies.
 History 123 History Thomas W. Taylor, PhD, Chair Objectives Defying classification as either humanity or social science, history functions as both. It focuses on the values, as well as the ideas, personalities,
History 123 History Thomas W. Taylor, PhD, Chair Objectives Defying classification as either humanity or social science, history functions as both. It focuses on the values, as well as the ideas, personalities,
I N V E S T I C E D O R O Z V O J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á N Í ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES
 ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES Absolutism: Louis XIV of France born in 1638, ruled 1643-1715 as a child, he had to face the Frondes Revolt when the French high nobles rebelled against him he managed to take control
ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES Absolutism: Louis XIV of France born in 1638, ruled 1643-1715 as a child, he had to face the Frondes Revolt when the French high nobles rebelled against him he managed to take control
The Approved List of Humanities and Social Science Courses For Engineering Degrees. Approved Humanities Courses
 The Approved List of Humanities and Social Science Courses For Engineering Degrees Students should check the current catalog to ensure any prerequisite and departmental requirements are met. ART Approved
The Approved List of Humanities and Social Science Courses For Engineering Degrees Students should check the current catalog to ensure any prerequisite and departmental requirements are met. ART Approved
Foreign Affairs and National Security
 Foreign Affairs and National Security Objectives: TLW understand and explain the following questions as it relates to the Foreign affairs of the American Government What is foreign policy? What is the
Foreign Affairs and National Security Objectives: TLW understand and explain the following questions as it relates to the Foreign affairs of the American Government What is foreign policy? What is the
GRADE 7 SOCIAL STUDIES. History
 GRADE 7 SOCIAL STUDIES History Standard 1 Historical Thinking Skills Students use information and concepts to interpret, analyze, and draw conclusions about United States history from 1763 1877. 7.1.1
GRADE 7 SOCIAL STUDIES History Standard 1 Historical Thinking Skills Students use information and concepts to interpret, analyze, and draw conclusions about United States history from 1763 1877. 7.1.1
Causes of World War One
 Suggested time: 75 Minutes What s important in this lesson: Causes of World War One The causes of World War One had been building up for many years. In June of 1914, the assassination of Franz Ferdinand
Suggested time: 75 Minutes What s important in this lesson: Causes of World War One The causes of World War One had been building up for many years. In June of 1914, the assassination of Franz Ferdinand
A CHARTER OF EUROPEAN IDENTITY. Foreword
 A CHARTER OF EUROPEAN IDENTITY 28 October 1995 Foreword In a speech to the European Parliament on March 8th, 1994, the poet Václav Havel, President of the Czech Republic, indicated the need for a Charter
A CHARTER OF EUROPEAN IDENTITY 28 October 1995 Foreword In a speech to the European Parliament on March 8th, 1994, the poet Václav Havel, President of the Czech Republic, indicated the need for a Charter
HONORS U. S. HISTORY II World War I - DBQ DUE December 13, 2013
 HONORS U. S. HISTORY II World War I - DBQ DUE December 13, 2013 TASK: Assess AT LEAST TWO of the causes for the United States entry into the conflict of World War I. How did the United States contribute
HONORS U. S. HISTORY II World War I - DBQ DUE December 13, 2013 TASK: Assess AT LEAST TWO of the causes for the United States entry into the conflict of World War I. How did the United States contribute
Federalizing Process in Italy Challenges from an International Perspective. Case Study Germany: How did Germany disentangle competences?
 Federalizing Process in Italy Challenges from an International Perspective Case Study Germany: How did Germany disentangle competences? Dr. Bernd Kuster, Federal Ministry of the Interior, Berlin At this
Federalizing Process in Italy Challenges from an International Perspective Case Study Germany: How did Germany disentangle competences? Dr. Bernd Kuster, Federal Ministry of the Interior, Berlin At this
The French Revolution and Napoleon
 The French Revolution and Napoleon Chapter 23 Marie Antoinette King Louis XVI Napoleon French Revolution Homework Schedule Wed 10/22 Thurs 10/23 Fri 10/24 Homework Schedule No Written HW Read p.215-216
The French Revolution and Napoleon Chapter 23 Marie Antoinette King Louis XVI Napoleon French Revolution Homework Schedule Wed 10/22 Thurs 10/23 Fri 10/24 Homework Schedule No Written HW Read p.215-216
Unit 9 Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church
 Unit 9 Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Directions Read each False statement below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word
Unit 9 Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Lesson 5 Popes, Kings and Challenges to the Church Directions Read each False statement below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word
Kansas Board of Regents Precollege Curriculum Courses Approved for University Admissions
 Kansas Board of Regents Precollege Curriculum Courses Approved for University Admissions Original Publication April 6, 2011 Revision Dates June 13, 2011 May 23, 2012 Kansas Board of Regents Precollege
Kansas Board of Regents Precollege Curriculum Courses Approved for University Admissions Original Publication April 6, 2011 Revision Dates June 13, 2011 May 23, 2012 Kansas Board of Regents Precollege
Take this Test! 1. The Aztec Empire was located in Canada or Central America?
 Take this Test! Round One 1. The Aztec Empire was located in Canada or Central America? 2. Where did Roger Williams eventually settle?...maryland or Rhode Island? 3. During the European settlement of the
Take this Test! Round One 1. The Aztec Empire was located in Canada or Central America? 2. Where did Roger Williams eventually settle?...maryland or Rhode Island? 3. During the European settlement of the
1. Which of the following is NOT an argument in support of imperialism or expansionism?
 U.S I Quarterly Assessment Practice Test Circle the best answer to each question. 1. Which of the following is NOT an argument in support of imperialism or expansionism? A. The United States should become
U.S I Quarterly Assessment Practice Test Circle the best answer to each question. 1. Which of the following is NOT an argument in support of imperialism or expansionism? A. The United States should become
Social 7 Ch 3 Study Guide /63 Name: Any goods being brought into the country
 Social 7 Ch 3 Study Guide /63 Name: Define the following terms. Use the glossary to help you. /13 Mercantilism- Sovereignty- Monopoly- Factories- allowed an imperial country to become rich in gold and
Social 7 Ch 3 Study Guide /63 Name: Define the following terms. Use the glossary to help you. /13 Mercantilism- Sovereignty- Monopoly- Factories- allowed an imperial country to become rich in gold and
PREREQUISITES FOR HEALTH
 Charter The first International Conference on Health Promotion, meeting in Ottawa this 21 st day of November 1986, hereby presents this CHARTER for action to achieve Health for All by the year 2000 and
Charter The first International Conference on Health Promotion, meeting in Ottawa this 21 st day of November 1986, hereby presents this CHARTER for action to achieve Health for All by the year 2000 and
Men from the British Empire in the First World War
 In 1914, Britain ruled over one quarter of the world s surface area and 434 million people. This was known as the British Empire. When war broke out, Britain was desperate for men to fight. Unlike France,
In 1914, Britain ruled over one quarter of the world s surface area and 434 million people. This was known as the British Empire. When war broke out, Britain was desperate for men to fight. Unlike France,
Call for Papers 6 th International Conference on Africa Unity for Renaissance (AUR) May 22-25, 2016 UNISA CAMPUS, Pretoria, South Africa
 Call for Papers 6 th International Conference on Africa Unity for Renaissance (AUR) May 22-25, 2016 UNISA CAMPUS, Pretoria, South Africa ORGANIZING SPONSORS Africa Unity for Renaissance Partners Network(AURPNET)
Call for Papers 6 th International Conference on Africa Unity for Renaissance (AUR) May 22-25, 2016 UNISA CAMPUS, Pretoria, South Africa ORGANIZING SPONSORS Africa Unity for Renaissance Partners Network(AURPNET)
The Approved List of Humanities and Social Science Courses For Engineering Degrees. Approved Humanities Courses
 The Approved List of Humanities and Social Science Courses For Engineering Degrees Students should check the current catalog to ensure any prerequisite and departmental requirements are met. NOTE: Some
The Approved List of Humanities and Social Science Courses For Engineering Degrees Students should check the current catalog to ensure any prerequisite and departmental requirements are met. NOTE: Some
Bettyann Foley Final Project: Book review, The Radical and the Republican, by James Oakes A More Perfect Union Year Two September 15, 2010
 1 Bettyann Foley Final Project: Book review, The Radical and the Republican, by James Oakes A More Perfect Union Year Two September 15, 2010 The book, The Radical and the Republican, written by James Oakes
1 Bettyann Foley Final Project: Book review, The Radical and the Republican, by James Oakes A More Perfect Union Year Two September 15, 2010 The book, The Radical and the Republican, written by James Oakes
2. Each of the above reasons helped to cause the creation of alliances throughout Europe. How? How do new alliances encourage tension?
 APEH Topic 10 Webquest Points Possible: 200 pts World War I Webquest Part I - M.A.I.N. Causes Name 1. Identify militarism, Imperialism, and Nationalism. Then, explain how each force creates tension in
APEH Topic 10 Webquest Points Possible: 200 pts World War I Webquest Part I - M.A.I.N. Causes Name 1. Identify militarism, Imperialism, and Nationalism. Then, explain how each force creates tension in
The Protestant Reformation
 The Protestant Reformation Mr. Montreuil April 2015 1 The Big Picture I can explain how the Protestant Reformation impacted Europe religiously, politically, & socially. This Lesson I can identify Reformation
The Protestant Reformation Mr. Montreuil April 2015 1 The Big Picture I can explain how the Protestant Reformation impacted Europe religiously, politically, & socially. This Lesson I can identify Reformation
ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS AND GOVERNMENT MAN IS BORN FREE, BUT EVERYWHERE IS IN CHAINS.
 ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS AND GOVERNMENT MAN IS BORN FREE, BUT EVERYWHERE IS IN CHAINS. Relevant Questions: Are people born good or bad? Are all people born equal? What is government? Why do societies have
ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS AND GOVERNMENT MAN IS BORN FREE, BUT EVERYWHERE IS IN CHAINS. Relevant Questions: Are people born good or bad? Are all people born equal? What is government? Why do societies have
DBQ on the Roaring Twenties Historical Context Task You are not limited to these suggestions.
 1 Mr. Saccullo 8 th grade Social Studies DBQ on the Roaring Twenties Historical Context The Great War was over and America s sons returned home having witnessed the horrors of war. The survivors brought
1 Mr. Saccullo 8 th grade Social Studies DBQ on the Roaring Twenties Historical Context The Great War was over and America s sons returned home having witnessed the horrors of war. The survivors brought
The Causes of the French and Indian War
 The Causes of the French and Indian War The End of the French Threat 1. relations between England & the colonies had been positive until the 1760s 2. England & France were the two main rivals for leadership
The Causes of the French and Indian War The End of the French Threat 1. relations between England & the colonies had been positive until the 1760s 2. England & France were the two main rivals for leadership
Rise of the Revolution Grade Nine
 Ohio Standards Connection: Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities Benchmark A Analyze ways people achieve governmental change, including political action, social protest, and revolution. Indicator 1 Analyze
Ohio Standards Connection: Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities Benchmark A Analyze ways people achieve governmental change, including political action, social protest, and revolution. Indicator 1 Analyze
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES FIFTH GRADE
 SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES FIFTH GRADE In fifth grade, students use their understanding of social studies concepts and cause-and-effect relationships to study the development of the United States up
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES FIFTH GRADE In fifth grade, students use their understanding of social studies concepts and cause-and-effect relationships to study the development of the United States up
