Roanoke Pinball Museum Key Concepts
|
|
|
- Jasmine Fields
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Roanoke Pinball Museum Key Concepts What are Pinball Machines Made of? SOL 3.3 Many different materials are used to make a pinball machine: 1. Steel: The pinball is made of steel, so it has a lot of mass. 2. Rubber: The bumpers are made of rubber, so the steel ball will bounce. 3. Wood and plastic: The colorful cabinet of the machine and many of the little parts are made of wood and plastic. 4. Glass: The playfield cover is made of glass. This cover keeps the ball in the machine allows the player to see what the ball is doing as it travels around the playfield. 5. Wiring: Wires serve as a highway do that the machine is provided with the electricity needed to power the lights, music, flippers, and other components. Simple pinball machines consist of components that are often studied in physics: inclined planes, pulleys, levers, wedges, and wheels. How Do Pinball Machines Work? SOL 4.2, 4.3, Ph.5 Key Terms: mass, speed, acceleration, force, kinetic energy, potential energy We can understand the operation of a pinball machine using the laws of physics. Physical concepts like mass, speed, acceleration, force, and energy are important to the understanding of pinball. Pinball uses a steel ball. Even though the ball is pretty small, it has a lot of mass, so it is heavy. During play, the ball is in motion, that is, it has a speed in a particular direction. Pinballs can go very fast - up to 90 miles/ hr (145 km/hr)! Newton s first law of motion tells us that any object that is in motion will stay in motion moving in a straight line, unless acted on by a force. A pinball machine works by using forces to change the motion of the ball. For example, we use the flippers to hit the ball, producing a force on the ball that makes it accelerate. Acceleration makes the ball speed up, slow down, or change direction. Other components like bumpers also hit the ball and produce forces, changing the direction or speed of the ball. When the ball is at the top of the sloped playfield, gravity exerts a force on it that makes it accelerate or speed up down the playfield toward the player (and the drain - watch out!). Because the ball has a lot of mass, we have to use a lot of force to make it accelerate. Pinball also utilizes the physical concept of energy. To make the game more fun and challenging, the playfield is tilted at a 6-7 degree angle toward the player. This means that the playfield is sloped, with the back of the playfield higher than at the front of the machine. First, we give the ball energy by putting a force on it (hitting it) with the plunger, making it travel up the playfield. When the ball is at the top, it has more gravitational potential energy because it is higher above the surface of the earth. This potential energy from gravity is converted into the kinetic energy of the ball as it rolls down the sloped playfield.
2 The total amount of energy is conserved - that means it is neither created nor destroyed, but only converted from one form to another. The energy you put into the ball by hitting it with the plunger is converted to the kinetic energy of the ball s motion and gravitational potential energy at the top of the slope. Then the gravitational energy is converted into kinetic energy at the bottom. The bumpers add additional energy by applying forces to the ball. Of course, some of the energy is converted to heat by friction, so it is not available for potential or kinetic energy of the ball. The playfields are made smooth to keep friction to a minimum. Think about it it is easier to ride your bicycle on smooth pavement than a gravel road (Diagram 1). An interesting use of electromechanical energy and electrical circuits is the tilt mechanism of pinball machines. This keeps players from excessively shaking the machine. It consists of a pendulum bob that hangs inside a conductive metal ring from a metal rod. If the rod touches the conductive ring, a current is created and a circuit is activated. The machine gives the player a warning, or immediately disables the flippers (Diagram 2). 1 2 Ball has more gravitational potential energy here Tilt Mechanism Metal Rod Conductive Ring Gravitational potential energy becomes kinetic energy (motion) Pendulum Bob Vocabulary 1. Mass: The amount of material an object contains. It can be thought of as the number of atoms in an object. In physics, mass is a measure of inertia, or something s resistance to being moved. Mass is what causes things to have weight in a gravitational field. 2. Speed: The rate at which something moves, defined in physics as the distance something moves in a given interval of time. 3. Acceleration: A change in an object s speed speeding up or slowing down. 4. Force: An influence on an object that causes it to accelerate, such as a push or pull. 5. Kinetic Energy: The energy associated with an object s motion. 6. Potential Energy: The energy associated with an object s position. Questions & Answers 1. Question: If you flick the ball straight uphill towards the top of the tilted playfield, it gradually slows to a stop and then begins to roll downhill. Which way is the ball accelerating as it rolls uphill? downhill? Answer: As it rolls on the surface, it always accelerates downhill - first slowing down, then speeding up. 2. Question: If a ball is rolling downhill on the playfield and friction between the ball and the surface is slowing it down, in which direction is the force of friction pointing? Answer: The friction force is pointing uphill.
3 Science & History of Pinball Pinball evolved out of a combination of billiards and bowling around 1700 in France. Table top ball games knocked down pins much like bowling. Forces were imparted to the balls, which, in turn, imparted their forces to the pins in order to knock them down. Soon, the pins became fixed so players would not have to pick them up and holes were created for scoring instead. Then, in the mid-1700s, the spring launcher was introduced. This used the stored potential energy of a spring to apply a force to the ball and launch it up an inclined playfield. About 100 years later, modern pinball was born using the same concepts, but with marbles and metal pins instead of billiard balls and pins. The game now fit on a small table and had a glass top. In the 1930s, the game became electrified. Electricity was used for lights and bells, making the game much more exciting. Solenoids were added to launch the ball. A solenoid is a wire wrapped around a metal bar. When a current is run through the wire, a magnetic field is produced. This field causes the spring in the plunger to contract. When it is released, the plunger puts a force on the ball which launches it up the ramp. In 1947 flippers were introduced. These allowed the players to interact with the game more by hitting the ball and keeping it in play much longer. Now players could exert forces on the ball and move it where they wanted it to go. In the 1970s, solid state electronics were introduced. Many of the simple electrical circuits were replaced with digital electronic components called microprocessors. These devices function as mini-computers and produce the recorded sounds and complicated flashing lights in pinball machines. Ramp Flippers Bumpers Score Reel (internal)
4 Make a Pinball Machine Supplies 1. Shoe box top 2. Scissors 3. 2 egg carton cups 4. Tape 5. Brass fasteners 6. Straws 7. Marble 8. Pencil Instructions 1. Tape the two egg carton cups to the bottom of the box, this creates an incline 2. Make a lever by folding a 2 inch long piece of cardboard in half and attach it with a brass fastener, this will launch the marble 3. Make a channel along one side of the box top by taping down straws. This is where the ball will be launched. 4. In the top left-hand corner, tape a small piece of paper to create a curve for the marble 5. Consider making obstacles out of pipe cleaners, straws, or cups. Holes can be placed in the box for scoring. Bumpers can be made from rubber stoppers used in sinks. Learning Objectives: Simple levers can be explained using the pinball machine. Explain how the force on one end of the lever makes it pivot around the fulcrum, and that mechanical advantage is obtained, amplifying the input force.
5 Balls & Ramps Supplies 1. Marbles of varying sizes 2. Ramp 3. Deflectors (cardboard and rubberbands) Instructions Start a ball from rest at the top of a ramp. Show how the gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. Raise and lower the ramp to show that different heights give different final velocities. Marble Ramp Friction can be studied different surfaces and sliding objects down them. Examples include a slick plastic surface that allows a small block to easily slide. The friction of the surface can be changed by taping on a piece of paper. Energy can be studied by building deflectors. These objects are made in the shape of an X using wood or stiff cardboard. Rubber bands are wrapped around the Xs and placed at the bottom of the ramps. Conservation of energy can be discussed - the rubber bands do not absorb all of the energy and it is redirected back to the ball. Learning Objectives: Friction and energy (conservation, transformation)
Compound Machine: Two or more simple machines working together to make work easier. Examples: Wheelbarrow, Can Opener, Bicycle
 Name SOL 4.2 Simple and Compound Machines NOTE - Simple machines are NOT included in the 5 th REVISED Science Standards Simple Machine: A machine with few or no moving parts. Simple machines make work
Name SOL 4.2 Simple and Compound Machines NOTE - Simple machines are NOT included in the 5 th REVISED Science Standards Simple Machine: A machine with few or no moving parts. Simple machines make work
What is Energy? 1 45 minutes Energy and You: Energy Picnic Science, Physical Education Engage
 Unit Grades K-3 Awareness Teacher Overview What is energy? Energy makes change; it does things for us. It moves cars along the road and boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps ice frozen
Unit Grades K-3 Awareness Teacher Overview What is energy? Energy makes change; it does things for us. It moves cars along the road and boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps ice frozen
7 TH GRADE SCIENCE REVIEW
 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE REVIEW The motion of an object is always judged with respect to some other object or point. When an object changes position over time relative to a reference point, the object is in
7 TH GRADE SCIENCE REVIEW The motion of an object is always judged with respect to some other object or point. When an object changes position over time relative to a reference point, the object is in
ANSWER KEY. Work and Machines
 Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. inclined plane, wedge, screw, lever, wheel and axle, pulley 2. pulley 3. lever 4. inclined plane 5. Answers will vary: top, side, or bottom 6. Answers will vary; only one
Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. inclined plane, wedge, screw, lever, wheel and axle, pulley 2. pulley 3. lever 4. inclined plane 5. Answers will vary: top, side, or bottom 6. Answers will vary; only one
5.1 The First Law: The Law of Inertia
 The First Law: The Law of Inertia Investigation 5.1 5.1 The First Law: The Law of Inertia How does changing an object s inertia affect its motion? Newton s first law states that objects tend to keep doing
The First Law: The Law of Inertia Investigation 5.1 5.1 The First Law: The Law of Inertia How does changing an object s inertia affect its motion? Newton s first law states that objects tend to keep doing
Pre and Post-Visit Activities
 Pre and Post-Visit Activities Simple Machines Table of Contents: Important Information: 2 Vocabulary: 3 Pre-Visit Activities: 4 Post-Visit Activities: 5 Vocabulary Word Search: 6 2 Important Information
Pre and Post-Visit Activities Simple Machines Table of Contents: Important Information: 2 Vocabulary: 3 Pre-Visit Activities: 4 Post-Visit Activities: 5 Vocabulary Word Search: 6 2 Important Information
Fulcrum Effort or Applied Force. Fulcrum Load or Resistance. Effort or Applied Force. Load or Resistance. Other First Class Lever Examples.
 First Class Lever Second Class Lever Load or Resistance Fulcrum Effort or Applied Force Fulcrum Load or Resistance Effort or Applied Force Other First Class Lever Examples Action Spring Force Load Applied
First Class Lever Second Class Lever Load or Resistance Fulcrum Effort or Applied Force Fulcrum Load or Resistance Effort or Applied Force Other First Class Lever Examples Action Spring Force Load Applied
Name: Partners: Period: Coaster Option: 1. In the space below, make a sketch of your roller coaster.
 1. In the space below, make a sketch of your roller coaster. 2. On your sketch, label different areas of acceleration. Put a next to an area of negative acceleration, a + next to an area of positive acceleration,
1. In the space below, make a sketch of your roller coaster. 2. On your sketch, label different areas of acceleration. Put a next to an area of negative acceleration, a + next to an area of positive acceleration,
PS-6.2 Explain the factors that determine potential and kinetic energy and the transformation of one to the other.
 PS-6.1 Explain how the law of conservation of energy applies to the transformation of various forms of energy (including mechanical energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, light energy, sound energy,
PS-6.1 Explain how the law of conservation of energy applies to the transformation of various forms of energy (including mechanical energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, light energy, sound energy,
Name Class Date. Pulley. Wedge
 CHAPTER 13 2 Simple Machines SECTION Work and Energy KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are simple machines? What simple machines are in the lever family? What simple
CHAPTER 13 2 Simple Machines SECTION Work and Energy KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are simple machines? What simple machines are in the lever family? What simple
At the skate park on the ramp
 At the skate park on the ramp 1 On the ramp When a cart rolls down a ramp, it begins at rest, but starts moving downward upon release covers more distance each second When a cart rolls up a ramp, it rises
At the skate park on the ramp 1 On the ramp When a cart rolls down a ramp, it begins at rest, but starts moving downward upon release covers more distance each second When a cart rolls up a ramp, it rises
3rd/4th Grade Science Unit: Forces and Motion. Melissa Gucker TE 804 Spring 2007
 3rd/4th Grade Science Unit: Forces and Motion Melissa Gucker TE 804 Spring 2007 Part I: Learning Goals Documentation Unit Title: Forces and Motion Grade Level: 3 rd Designer: Melissa Gucker The Main Idea(s)/Importance
3rd/4th Grade Science Unit: Forces and Motion Melissa Gucker TE 804 Spring 2007 Part I: Learning Goals Documentation Unit Title: Forces and Motion Grade Level: 3 rd Designer: Melissa Gucker The Main Idea(s)/Importance
Physics: Principles and Applications, 6e Giancoli Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion
 Physics: Principles and Applications, 6e Giancoli Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion Conceptual Questions 1) Which of Newton's laws best explains why motorists should buckle-up? A) the first law
Physics: Principles and Applications, 6e Giancoli Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion Conceptual Questions 1) Which of Newton's laws best explains why motorists should buckle-up? A) the first law
Simple Machines Quiz
 Simple Machines Quiz Part 1. Write the name of the simple machine that is described questions 1-4 below. Word Bank: Wheel & Axle Screw Pulley Inclined Plane Lever 1. These two parts act as one simple machine.
Simple Machines Quiz Part 1. Write the name of the simple machine that is described questions 1-4 below. Word Bank: Wheel & Axle Screw Pulley Inclined Plane Lever 1. These two parts act as one simple machine.
Chapter 5 Using Newton s Laws: Friction, Circular Motion, Drag Forces. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Using Newton s Laws: Friction, Circular Motion, Drag Forces Units of Chapter 5 Applications of Newton s Laws Involving Friction Uniform Circular Motion Kinematics Dynamics of Uniform Circular
Chapter 5 Using Newton s Laws: Friction, Circular Motion, Drag Forces Units of Chapter 5 Applications of Newton s Laws Involving Friction Uniform Circular Motion Kinematics Dynamics of Uniform Circular
Science Standard Articulated by Grade Level Strand 5: Physical Science
 Concept 1: Properties of Objects and Materials Classify objects and materials by their observable properties. Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 PO 1. Identify the following observable properties
Concept 1: Properties of Objects and Materials Classify objects and materials by their observable properties. Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 PO 1. Identify the following observable properties
Accelerometers: Theory and Operation
 12-3776C Accelerometers: Theory and Operation The Vertical Accelerometer Accelerometers measure accelerations by measuring forces. The vertical accelerometer in this kit consists of a lead sinker hung
12-3776C Accelerometers: Theory and Operation The Vertical Accelerometer Accelerometers measure accelerations by measuring forces. The vertical accelerometer in this kit consists of a lead sinker hung
9. The kinetic energy of the moving object is (1) 5 J (3) 15 J (2) 10 J (4) 50 J
 1. If the kinetic energy of an object is 16 joules when its speed is 4.0 meters per second, then the mass of the objects is (1) 0.5 kg (3) 8.0 kg (2) 2.0 kg (4) 19.6 kg Base your answers to questions 9
1. If the kinetic energy of an object is 16 joules when its speed is 4.0 meters per second, then the mass of the objects is (1) 0.5 kg (3) 8.0 kg (2) 2.0 kg (4) 19.6 kg Base your answers to questions 9
Directed Reading A. Section: Types of Machines LEVERS
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Types of Machines 1. A knife is actually a very sharp. 2. What are the six simple machines that all other machines are made from? LEVERS 3. A simple machine
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Types of Machines 1. A knife is actually a very sharp. 2. What are the six simple machines that all other machines are made from? LEVERS 3. A simple machine
Kinetic and Potential Energy
 Kinetic and Potential Energy Vocabulary: kinetic energy energy of movement potential energy stored energy potential chemical energy stored energy released by chemical changes Comprehension Questions 1.
Kinetic and Potential Energy Vocabulary: kinetic energy energy of movement potential energy stored energy potential chemical energy stored energy released by chemical changes Comprehension Questions 1.
Vocabulary: Familiarity with these terms and concepts will enhance students experience in the activity
 Energize your students with this exploration of the way energy transforms and transfers. Using household items and their knowledge, students will build fun contraptions that will make a ball move and hit
Energize your students with this exploration of the way energy transforms and transfers. Using household items and their knowledge, students will build fun contraptions that will make a ball move and hit
SCIENCE STD. V (2015) More About Force Energy and Simple Machines. Name Roll No. Date Std. V
 SCIENCE STD. V (2015) More About Force Energy and Simple Machines Name Roll No. Date Std. V Q1.What is Force? Force is a push or a pull that makes the things move. Q2.What effect does Force has on our
SCIENCE STD. V (2015) More About Force Energy and Simple Machines Name Roll No. Date Std. V Q1.What is Force? Force is a push or a pull that makes the things move. Q2.What effect does Force has on our
Friction and Gravity. Friction. Section 2. The Causes of Friction
 Section 2 Friction and Gravity What happens when you jump on a sled on the side of a snow-covered hill? Without actually doing this, you can predict that the sled will slide down the hill. Now think about
Section 2 Friction and Gravity What happens when you jump on a sled on the side of a snow-covered hill? Without actually doing this, you can predict that the sled will slide down the hill. Now think about
AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test
 AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A single conservative force F x = (6.0x 12) N (x is in m) acts on
AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A single conservative force F x = (6.0x 12) N (x is in m) acts on
EVALUAT ING ACADEMIC READINESS FOR APPRENTICESHIP TRAINING Revised for ACCESS TO APPRENTICESHIP
 EVALUAT ING ACADEMIC READINESS FOR APPRENTICESHIP TRAINING for ACCESS TO APPRENTICESHIP SCIENCE SKILLS SIMPLE MACHINES & MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE AN ACADEMIC SKILLS MANUAL for The Construction Trades: Mechanical
EVALUAT ING ACADEMIC READINESS FOR APPRENTICESHIP TRAINING for ACCESS TO APPRENTICESHIP SCIENCE SKILLS SIMPLE MACHINES & MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE AN ACADEMIC SKILLS MANUAL for The Construction Trades: Mechanical
LAB 6: GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES
 55 Name Date Partners LAB 6: GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly Bodies by the attraction
55 Name Date Partners LAB 6: GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly Bodies by the attraction
Mechanical Reasoning Review
 Mechanical Reasoning Review Work can be made easier or faster through practical applications of simple and/or compound machines. This is called mechanical advantage - in other words, using the principal
Mechanical Reasoning Review Work can be made easier or faster through practical applications of simple and/or compound machines. This is called mechanical advantage - in other words, using the principal
Force and Motion: Ramp It Up
 Force and Motion: Grade Level: 4-5 Time: 3 class periods By: Carrie D. Perry (Bedford County Public Schools) Overview After watching an engaging video on Olympic alpine skiers, students then participate
Force and Motion: Grade Level: 4-5 Time: 3 class periods By: Carrie D. Perry (Bedford County Public Schools) Overview After watching an engaging video on Olympic alpine skiers, students then participate
AP Physics C Fall Final Web Review
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP Physics C Fall Final Web Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. On a position versus time graph, the slope of
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP Physics C Fall Final Web Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. On a position versus time graph, the slope of
Bounce! Name. Be very careful with the balls. Do not throw them DROP the balls as instructed in the procedure.
 Bounce 1 Name Bounce! Be very careful with the balls. Do not throw them DROP the balls as instructed in the procedure. Background information: Energy causes things to happen. During the day, the sun gives
Bounce 1 Name Bounce! Be very careful with the balls. Do not throw them DROP the balls as instructed in the procedure. Background information: Energy causes things to happen. During the day, the sun gives
Inclined Plane: Distance vs. Force
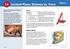 1a Inclined Plane: Distance vs. Force Look at the inclined plane model you built for Card 2. It s a ramp, so it s easy to slide or roll things up and down it. As you noticed, it is a little more difficult
1a Inclined Plane: Distance vs. Force Look at the inclined plane model you built for Card 2. It s a ramp, so it s easy to slide or roll things up and down it. As you noticed, it is a little more difficult
Force & Motion Activity Tub
 Force & Motion Activity Tub Designed to meet these objectives: Students will be able to describe Newton s First, Second, and Third Laws of Motion and identify examples of these laws at work in the world
Force & Motion Activity Tub Designed to meet these objectives: Students will be able to describe Newton s First, Second, and Third Laws of Motion and identify examples of these laws at work in the world
Simple Machines. Figure 2: Basic design for a mousetrap vehicle
 Mousetrap Vehicles Figure 1: This sample mousetrap-powered vehicle has a large drive wheel and a small axle. The vehicle will move slowly and travel a long distance for each turn of the wheel. 1 People
Mousetrap Vehicles Figure 1: This sample mousetrap-powered vehicle has a large drive wheel and a small axle. The vehicle will move slowly and travel a long distance for each turn of the wheel. 1 People
Chapter 3 Falling Objects and Projectile Motion
 Chapter 3 Falling Objects and Projectile Motion Gravity influences motion in a particular way. How does a dropped object behave?!does the object accelerate, or is the speed constant?!do two objects behave
Chapter 3 Falling Objects and Projectile Motion Gravity influences motion in a particular way. How does a dropped object behave?!does the object accelerate, or is the speed constant?!do two objects behave
Work, Energy & Momentum Homework Packet Worksheet 1: This is a lot of work!
 Work, Energy & Momentum Homework Packet Worksheet 1: This is a lot of work! 1. A student holds her 1.5-kg psychology textbook out of a second floor classroom window until her arm is tired; then she releases
Work, Energy & Momentum Homework Packet Worksheet 1: This is a lot of work! 1. A student holds her 1.5-kg psychology textbook out of a second floor classroom window until her arm is tired; then she releases
Using mechanical energy for daily
 unit 3 Using mechanical energy for daily activities Physics Chapter 3 Using mechanical energy for daily activities Competency Uses mechanical energy for day-to-day activities Competency level 3.1 Investigates
unit 3 Using mechanical energy for daily activities Physics Chapter 3 Using mechanical energy for daily activities Competency Uses mechanical energy for day-to-day activities Competency level 3.1 Investigates
Forces. Definition Friction Falling Objects Projectiles Newton s Laws of Motion Momentum Universal Forces Fluid Pressure Hydraulics Buoyancy
 Forces Definition Friction Falling Objects Projectiles Newton s Laws of Motion Momentum Universal Forces Fluid Pressure Hydraulics Buoyancy Definition of Force Force = a push or pull that causes a change
Forces Definition Friction Falling Objects Projectiles Newton s Laws of Motion Momentum Universal Forces Fluid Pressure Hydraulics Buoyancy Definition of Force Force = a push or pull that causes a change
Static Electricity Page 1. Static Electricity. Introduction: Structure of Atoms 2 Sample Curriculum, Materials Needed
 Static Electricity Page 1 Static Electricity Introduction: Structure of Atoms 2 Sample Curriculum, Materials Needed Experiment #1: Creating Static Charges 3 Experiment #2: Like Charges Repel and Unlike
Static Electricity Page 1 Static Electricity Introduction: Structure of Atoms 2 Sample Curriculum, Materials Needed Experiment #1: Creating Static Charges 3 Experiment #2: Like Charges Repel and Unlike
Educator Guide to S LAR SYSTEM. 1875 El Prado, San Diego CA 92101 (619) 238-1233 www.rhfleet.org
 Educator Guide to S LAR SYSTEM 1875 El Prado, San Diego CA 92101 (619) 238-1233 www.rhfleet.org Pre-Visit Activity: Orbital Paths Materials: Plastic Plate Marble Scissors To Do: 1. Put the plate on a flat
Educator Guide to S LAR SYSTEM 1875 El Prado, San Diego CA 92101 (619) 238-1233 www.rhfleet.org Pre-Visit Activity: Orbital Paths Materials: Plastic Plate Marble Scissors To Do: 1. Put the plate on a flat
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Equipment: Ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale. Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Equipment: Ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale. Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Physics 2A, Sec B00: Mechanics -- Winter 2011 Instructor: B. Grinstein Final Exam
 Physics 2A, Sec B00: Mechanics -- Winter 2011 Instructor: B. Grinstein Final Exam INSTRUCTIONS: Use a pencil #2 to fill your scantron. Write your code number and bubble it in under "EXAM NUMBER;" an entry
Physics 2A, Sec B00: Mechanics -- Winter 2011 Instructor: B. Grinstein Final Exam INSTRUCTIONS: Use a pencil #2 to fill your scantron. Write your code number and bubble it in under "EXAM NUMBER;" an entry
Unit 4 Practice Test: Rotational Motion
 Unit 4 Practice Test: Rotational Motion Multiple Guess Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How would an angle in radians be converted to an angle
Unit 4 Practice Test: Rotational Motion Multiple Guess Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How would an angle in radians be converted to an angle
Educational Innovations
 Educational Innovations Background Forces and Motion MAR-600 Wall Coaster Motion is caused by forces. Motion can be described. Motion follows rules. There are many forces and principles involved with motion.
Educational Innovations Background Forces and Motion MAR-600 Wall Coaster Motion is caused by forces. Motion can be described. Motion follows rules. There are many forces and principles involved with motion.
Chapter 6 Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 WORK AND ENERGY PREVIEW Work is the scalar product of the force acting on an object and the displacement through which it acts. When work is done on or by a system, the energy of that system
Chapter 6 WORK AND ENERGY PREVIEW Work is the scalar product of the force acting on an object and the displacement through which it acts. When work is done on or by a system, the energy of that system
Roller Coaster Mania!
 Overview Roller Coaster Mania! This series of educational programs was designed to simultaneously entertain and challenge gifted youth in their time outside of the school setting; however, the activities
Overview Roller Coaster Mania! This series of educational programs was designed to simultaneously entertain and challenge gifted youth in their time outside of the school setting; however, the activities
Tennessee State University
 Tennessee State University Dept. of Physics & Mathematics PHYS 2010 CF SU 2009 Name 30% Time is 2 hours. Cheating will give you an F-grade. Other instructions will be given in the Hall. MULTIPLE CHOICE.
Tennessee State University Dept. of Physics & Mathematics PHYS 2010 CF SU 2009 Name 30% Time is 2 hours. Cheating will give you an F-grade. Other instructions will be given in the Hall. MULTIPLE CHOICE.
LAB 6 - GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES
 L06-1 Name Date Partners LAB 6 - GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES OBJECTIVES And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly Bodies
L06-1 Name Date Partners LAB 6 - GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES OBJECTIVES And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly Bodies
Design Considerations for Water-Bottle Rockets. The next few pages are provided to help in the design of your water-bottle rocket.
 Acceleration= Force OVER Mass Design Considerations for Water-Bottle Rockets The next few pages are provided to help in the design of your water-bottle rocket. Newton s First Law: Objects at rest will
Acceleration= Force OVER Mass Design Considerations for Water-Bottle Rockets The next few pages are provided to help in the design of your water-bottle rocket. Newton s First Law: Objects at rest will
Lesson 3 - Understanding Energy (with a Pendulum)
 Lesson 3 - Understanding Energy (with a Pendulum) Introduction This lesson is meant to introduce energy and conservation of energy and is a continuation of the fundamentals of roller coaster engineering.
Lesson 3 - Understanding Energy (with a Pendulum) Introduction This lesson is meant to introduce energy and conservation of energy and is a continuation of the fundamentals of roller coaster engineering.
WORK DONE BY A CONSTANT FORCE
 WORK DONE BY A CONSTANT FORCE The definition of work, W, when a constant force (F) is in the direction of displacement (d) is W = Fd SI unit is the Newton-meter (Nm) = Joule, J If you exert a force of
WORK DONE BY A CONSTANT FORCE The definition of work, W, when a constant force (F) is in the direction of displacement (d) is W = Fd SI unit is the Newton-meter (Nm) = Joule, J If you exert a force of
Chapter 4: Newton s Laws: Explaining Motion
 Chapter 4: Newton s Laws: Explaining Motion 1. All except one of the following require the application of a net force. Which one is the exception? A. to change an object from a state of rest to a state
Chapter 4: Newton s Laws: Explaining Motion 1. All except one of the following require the application of a net force. Which one is the exception? A. to change an object from a state of rest to a state
Acceleration of Gravity Lab Basic Version
 Acceleration of Gravity Lab Basic Version In this lab you will explore the motion of falling objects. As an object begins to fall, it moves faster and faster (its velocity increases) due to the acceleration
Acceleration of Gravity Lab Basic Version In this lab you will explore the motion of falling objects. As an object begins to fall, it moves faster and faster (its velocity increases) due to the acceleration
Exam 2 is at 7 pm tomorrow Conflict is at 5:15 pm in 151 Loomis
 * By request, but I m not vouching for these since I didn t write them Exam 2 is at 7 pm tomorrow Conflict is at 5:15 pm in 151 Loomis There are extra office hours today & tomorrow Lots of practice exams
* By request, but I m not vouching for these since I didn t write them Exam 2 is at 7 pm tomorrow Conflict is at 5:15 pm in 151 Loomis There are extra office hours today & tomorrow Lots of practice exams
Rockets: Taking Off! Racing Balloon
 Rockets: Taking Off! For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Rockets and Balloons What happens when you blow up a balloon then let it go? Does the balloon move through the air? Did you
Rockets: Taking Off! For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Rockets and Balloons What happens when you blow up a balloon then let it go? Does the balloon move through the air? Did you
Date R. Mirshahi. Forces are all around us. Without forces, nothing can move and no work can be done.
 Name Date R. Mirshahi Forces and Movement: Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Forces are all around us. Without forces, nothing can move and no work can be done. There are different types of forces. Some forces
Name Date R. Mirshahi Forces and Movement: Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Forces are all around us. Without forces, nothing can move and no work can be done. There are different types of forces. Some forces
Energy Transfer in a Flash-Light. (Teacher Copy)
 Energy Transfer in a Flash-Light (Teacher Copy) Florida Sunshine State Standards Benchmark: SC.B. 1.3.1 AA The student identifies forms of energy and explains that they can be measured and compared. (Also
Energy Transfer in a Flash-Light (Teacher Copy) Florida Sunshine State Standards Benchmark: SC.B. 1.3.1 AA The student identifies forms of energy and explains that they can be measured and compared. (Also
Chapter 7: Momentum and Impulse
 Chapter 7: Momentum and Impulse 1. When a baseball bat hits the ball, the impulse delivered to the ball is increased by A. follow through on the swing. B. rapidly stopping the bat after impact. C. letting
Chapter 7: Momentum and Impulse 1. When a baseball bat hits the ball, the impulse delivered to the ball is increased by A. follow through on the swing. B. rapidly stopping the bat after impact. C. letting
Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING
 Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING Chapter 4 Table of Contents Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING... 4-1 DEFENSIVE DRIVING... 4-3 Positioning The Bus... 4-3 When Making a Turn at an Intersection... 4-3 Making the perfect
Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING Chapter 4 Table of Contents Chapter 4 DEFENSIVE DRIVING... 4-1 DEFENSIVE DRIVING... 4-3 Positioning The Bus... 4-3 When Making a Turn at an Intersection... 4-3 Making the perfect
Problem Set 1. Ans: a = 1.74 m/s 2, t = 4.80 s
 Problem Set 1 1.1 A bicyclist starts from rest and after traveling along a straight path a distance of 20 m reaches a speed of 30 km/h. Determine her constant acceleration. How long does it take her to
Problem Set 1 1.1 A bicyclist starts from rest and after traveling along a straight path a distance of 20 m reaches a speed of 30 km/h. Determine her constant acceleration. How long does it take her to
Physics 11 Assignment KEY Dynamics Chapters 4 & 5
 Physics Assignment KEY Dynamics Chapters 4 & 5 ote: for all dynamics problem-solving questions, draw appropriate free body diagrams and use the aforementioned problem-solving method.. Define the following
Physics Assignment KEY Dynamics Chapters 4 & 5 ote: for all dynamics problem-solving questions, draw appropriate free body diagrams and use the aforementioned problem-solving method.. Define the following
Levers and Pulleys. 5 th Grade Science Investigation. Unit
 Levers and Pulleys 5 th Grade Science Investigation Unit What Do We Already Know? A lever and pulley are mechanical advantages=makes work easier, and helps lift things you couldn t t normally lift Combined
Levers and Pulleys 5 th Grade Science Investigation Unit What Do We Already Know? A lever and pulley are mechanical advantages=makes work easier, and helps lift things you couldn t t normally lift Combined
10.1 Quantitative. Answer: A Var: 50+
 Chapter 10 Energy and Work 10.1 Quantitative 1) A child does 350 J of work while pulling a box from the ground up to his tree house with a rope. The tree house is 4.8 m above the ground. What is the mass
Chapter 10 Energy and Work 10.1 Quantitative 1) A child does 350 J of work while pulling a box from the ground up to his tree house with a rope. The tree house is 4.8 m above the ground. What is the mass
Let's Go Science Show
 Let's Go Science Show Take Home Materials *For Grades 4-8* What resource do you possess that grows as you learn? ATM OSPH ER E A transparent substance with EL EC TR ONS curved sides for concentrating or
Let's Go Science Show Take Home Materials *For Grades 4-8* What resource do you possess that grows as you learn? ATM OSPH ER E A transparent substance with EL EC TR ONS curved sides for concentrating or
5-Minute Refresher: FRICTION
 5-Minute Refresher: FRICTION Friction Key Ideas Friction is a force that occurs when two surfaces slide past one another. The force of friction opposes the motion of an object, causing moving objects to
5-Minute Refresher: FRICTION Friction Key Ideas Friction is a force that occurs when two surfaces slide past one another. The force of friction opposes the motion of an object, causing moving objects to
Activity: Building a Catapult
 Mechanical Engineering Activity: Building a Catapult In this activity, youth learn how to design and build a catapult that uses a pivot arm (lever) and a fulcrum to launch a Ping-Pong ball across the room.
Mechanical Engineering Activity: Building a Catapult In this activity, youth learn how to design and build a catapult that uses a pivot arm (lever) and a fulcrum to launch a Ping-Pong ball across the room.
Mechanical Systems. Grade 8 Unit 4 Test. 1. A wheelbarrow is an example of what simple machine? Class 1 lever. Class 2 lever.
 Mechanical Systems Grade 8 Unit 4 Test Student Class 1. A wheelbarrow is an example of what simple machine? D Wheel and Axle 2. A hockey stick is an example of what simple machine? D Inclined plane 3.
Mechanical Systems Grade 8 Unit 4 Test Student Class 1. A wheelbarrow is an example of what simple machine? D Wheel and Axle 2. A hockey stick is an example of what simple machine? D Inclined plane 3.
Student Reader. Energy Systems UNIT 7. E5 Student Reader v. 8.0 Unit 7 Page 1 2012 KnowAtom TM
 Student Reader UNIT 7 Energy Systems E5 Student Reader v. 8.0 Unit 7 Page 1 2012 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The cover shows a photograph of a sled that is not in motion. The movement of a sled from one place
Student Reader UNIT 7 Energy Systems E5 Student Reader v. 8.0 Unit 7 Page 1 2012 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The cover shows a photograph of a sled that is not in motion. The movement of a sled from one place
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Introduction to Energy. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types of energy: kinetic energy
Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types of energy: kinetic energy
4 Gravity: A Force of Attraction
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Matter in Motion 4 Gravity: A Force of Attraction BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is gravity? How are weight and mass different?
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Matter in Motion 4 Gravity: A Force of Attraction BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is gravity? How are weight and mass different?
Teacher notes/ activities. Gravity is the attractive force between all objects in the universe. It is the force that pulls objects to the earth.
 Gravity and forces unit Teacher notes/ activities Gravity is the attractive force between all objects in the universe. It is the force that pulls objects to the earth. Galileo, a famous Italian scientist
Gravity and forces unit Teacher notes/ activities Gravity is the attractive force between all objects in the universe. It is the force that pulls objects to the earth. Galileo, a famous Italian scientist
Levers for Lifting BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES. Grade 3 Quarter 3 Activity 23
 activity Levers for Lifting BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H... The
activity Levers for Lifting BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade Quarter Activity SC.C... The student understands that the motion of an object can be described and measured. SC.H... The
Acceleration due to Gravity
 Acceleration due to Gravity 1 Object To determine the acceleration due to gravity by different methods. 2 Apparatus Balance, ball bearing, clamps, electric timers, meter stick, paper strips, precision
Acceleration due to Gravity 1 Object To determine the acceleration due to gravity by different methods. 2 Apparatus Balance, ball bearing, clamps, electric timers, meter stick, paper strips, precision
physics 111N work & energy
 physics 111N work & energy conservation of energy entirely gravitational potential energy kinetic energy turning into gravitational potential energy gravitational potential energy turning into kinetic
physics 111N work & energy conservation of energy entirely gravitational potential energy kinetic energy turning into gravitational potential energy gravitational potential energy turning into kinetic
If you put the same book on a tilted surface the normal force will be less. The magnitude of the normal force will equal: N = W cos θ
 Experiment 4 ormal and Frictional Forces Preparation Prepare for this week's quiz by reviewing last week's experiment Read this week's experiment and the section in your textbook dealing with normal forces
Experiment 4 ormal and Frictional Forces Preparation Prepare for this week's quiz by reviewing last week's experiment Read this week's experiment and the section in your textbook dealing with normal forces
Catapult Engineering Pilot Workshop. LA Tech STEP 2007-2008
 Catapult Engineering Pilot Workshop LA Tech STEP 2007-2008 Some Background Info Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) did experiments regarding Acceleration. He realized that the change in velocity of balls rolling
Catapult Engineering Pilot Workshop LA Tech STEP 2007-2008 Some Background Info Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) did experiments regarding Acceleration. He realized that the change in velocity of balls rolling
Simple machines provide a mechanical advantage that makes our work faster and easier, and they are all around us every day.
 LEARNING MODULE: SIMPLE MACHINES Pre-Visit Activities We suggest that you use these pre-visit classroom acitivites to prepare your students for a rewarding Museum visit. Before your visit, introduce your
LEARNING MODULE: SIMPLE MACHINES Pre-Visit Activities We suggest that you use these pre-visit classroom acitivites to prepare your students for a rewarding Museum visit. Before your visit, introduce your
Name per due date mail box
 Name per due date mail box Rolling Momentum Lab (1 pt for complete header) Today in lab, we will be experimenting with momentum and measuring the actual force of impact due to momentum of several rolling
Name per due date mail box Rolling Momentum Lab (1 pt for complete header) Today in lab, we will be experimenting with momentum and measuring the actual force of impact due to momentum of several rolling
Engineer III Simple Machines
 Harford District 2014 Cub Scout Day Camp June 23-78 Knights of the Roundtable Engineer III Simple Machines Station Volunteer s Guide Thank you for being a station volunteer! The stations are the heart
Harford District 2014 Cub Scout Day Camp June 23-78 Knights of the Roundtable Engineer III Simple Machines Station Volunteer s Guide Thank you for being a station volunteer! The stations are the heart
Physics 201 Homework 8
 Physics 201 Homework 8 Feb 27, 2013 1. A ceiling fan is turned on and a net torque of 1.8 N-m is applied to the blades. 8.2 rad/s 2 The blades have a total moment of inertia of 0.22 kg-m 2. What is the
Physics 201 Homework 8 Feb 27, 2013 1. A ceiling fan is turned on and a net torque of 1.8 N-m is applied to the blades. 8.2 rad/s 2 The blades have a total moment of inertia of 0.22 kg-m 2. What is the
Energy and Energy Transformations Test Review
 Energy and Energy Transformations Test Review Completion: 1. Mass 13. Kinetic 2. Four 14. thermal 3. Kinetic 15. Thermal energy (heat) 4. Electromagnetic/Radiant 16. Thermal energy (heat) 5. Thermal 17.
Energy and Energy Transformations Test Review Completion: 1. Mass 13. Kinetic 2. Four 14. thermal 3. Kinetic 15. Thermal energy (heat) 4. Electromagnetic/Radiant 16. Thermal energy (heat) 5. Thermal 17.
Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams
 Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams Drawing Free-Body Diagrams Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation.
Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams Drawing Free-Body Diagrams Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation.
Work Energy & Power. September 2000 Number 05. 1. Work If a force acts on a body and causes it to move, then the force is doing work.
 PhysicsFactsheet September 2000 Number 05 Work Energy & Power 1. Work If a force acts on a body and causes it to move, then the force is doing work. W = Fs W = work done (J) F = force applied (N) s = distance
PhysicsFactsheet September 2000 Number 05 Work Energy & Power 1. Work If a force acts on a body and causes it to move, then the force is doing work. W = Fs W = work done (J) F = force applied (N) s = distance
III. Applications of Force and Motion Concepts. Concept Review. Conflicting Contentions. 1. Airplane Drop 2. Moving Ball Toss 3. Galileo s Argument
 III. Applications of Force and Motion Concepts Concept Review Conflicting Contentions 1. Airplane Drop 2. Moving Ball Toss 3. Galileo s Argument Qualitative Reasoning 1. Dropping Balls 2. Spinning Bug
III. Applications of Force and Motion Concepts Concept Review Conflicting Contentions 1. Airplane Drop 2. Moving Ball Toss 3. Galileo s Argument Qualitative Reasoning 1. Dropping Balls 2. Spinning Bug
general, accidents caused by misjudging
 Unit 3: The Effect of Natural Forces on your Vehicle Page 1 of 11 Purpose: Acquaint the student with some of the natural forces acting on a vehicle while stopping, maneuvering, and during a crash. Explain
Unit 3: The Effect of Natural Forces on your Vehicle Page 1 of 11 Purpose: Acquaint the student with some of the natural forces acting on a vehicle while stopping, maneuvering, and during a crash. Explain
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools
 Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools Supported by: National Science Foundation Simple Machines: 4.G.1 Introduction to Simple Machines
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools Supported by: National Science Foundation Simple Machines: 4.G.1 Introduction to Simple Machines
PHY231 Section 2, Form A March 22, 2012. 1. Which one of the following statements concerning kinetic energy is true?
 1. Which one of the following statements concerning kinetic energy is true? A) Kinetic energy can be measured in watts. B) Kinetic energy is always equal to the potential energy. C) Kinetic energy is always
1. Which one of the following statements concerning kinetic energy is true? A) Kinetic energy can be measured in watts. B) Kinetic energy is always equal to the potential energy. C) Kinetic energy is always
Potential / Kinetic Energy Remedial Exercise
 Potential / Kinetic Energy Remedial Exercise This Conceptual Physics exercise will help you in understanding the Law of Conservation of Energy, and its application to mechanical collisions. Exercise Roles:
Potential / Kinetic Energy Remedial Exercise This Conceptual Physics exercise will help you in understanding the Law of Conservation of Energy, and its application to mechanical collisions. Exercise Roles:
What Is Energy? Energy and Work: Working Together. 124 Chapter 5 Energy and Energy Resources
 1 What You Will Learn Explain the relationship between energy and work. Compare kinetic and potential energy. Describe the different forms of energy. Vocabulary energy kinetic energy potential energy mechanical
1 What You Will Learn Explain the relationship between energy and work. Compare kinetic and potential energy. Describe the different forms of energy. Vocabulary energy kinetic energy potential energy mechanical
B Answer: neither of these. Mass A is accelerating, so the net force on A must be non-zero Likewise for mass B.
 CTA-1. An Atwood's machine is a pulley with two masses connected by a string as shown. The mass of object A, m A, is twice the mass of object B, m B. The tension T in the string on the left, above mass
CTA-1. An Atwood's machine is a pulley with two masses connected by a string as shown. The mass of object A, m A, is twice the mass of object B, m B. The tension T in the string on the left, above mass
The Lever. The law of conservation of energy applies to all machines!
 Simple Machines A machine is a device for multiplying forces or simply changing the direction of forces. Many machines can increase the speed with which work is done. The Lever The law of conservation
Simple Machines A machine is a device for multiplying forces or simply changing the direction of forces. Many machines can increase the speed with which work is done. The Lever The law of conservation
PAScar Accessory Track Set (1.2m version)
 Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model ME-6955 012-07557A 1/01 PAScar Accessory Track Set (1.2m version) Model ME-9435
Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model ME-6955 012-07557A 1/01 PAScar Accessory Track Set (1.2m version) Model ME-9435
Conceptual Questions: Forces and Newton s Laws
 Conceptual Questions: Forces and Newton s Laws 1. An object can have motion only if a net force acts on it. his statement is a. true b. false 2. And the reason for this (refer to previous question) is
Conceptual Questions: Forces and Newton s Laws 1. An object can have motion only if a net force acts on it. his statement is a. true b. false 2. And the reason for this (refer to previous question) is
Resistance in the Mechanical System. Overview
 Overview 1. What is resistance? A force that opposes motion 2. In the mechanical system, what are two common forms of resistance? friction and drag 3. What is friction? resistance that is produced when
Overview 1. What is resistance? A force that opposes motion 2. In the mechanical system, what are two common forms of resistance? friction and drag 3. What is friction? resistance that is produced when
Integrated Physics & Chemistry Supply List (2010)
 Integrated Physics & Chemistry Supply List (2010) Integrated Physics and Chemistry is a physical science course covering basic concepts found in chemistry and physics. Topics included in the study are
Integrated Physics & Chemistry Supply List (2010) Integrated Physics and Chemistry is a physical science course covering basic concepts found in chemistry and physics. Topics included in the study are
F N A) 330 N 0.31 B) 310 N 0.33 C) 250 N 0.27 D) 290 N 0.30 E) 370 N 0.26
 Physics 23 Exam 2 Spring 2010 Dr. Alward Page 1 1. A 250-N force is directed horizontally as shown to push a 29-kg box up an inclined plane at a constant speed. Determine the magnitude of the normal force,
Physics 23 Exam 2 Spring 2010 Dr. Alward Page 1 1. A 250-N force is directed horizontally as shown to push a 29-kg box up an inclined plane at a constant speed. Determine the magnitude of the normal force,
Pushes and Pulls. TCAPS Created June 2010 by J. McCain
 Pushes and Pulls K i n d e r g a r t e n S c i e n c e TCAPS Created June 2010 by J. McCain Table of Contents Science GLCEs incorporated in this Unit............... 2-3 Materials List.......................................
Pushes and Pulls K i n d e r g a r t e n S c i e n c e TCAPS Created June 2010 by J. McCain Table of Contents Science GLCEs incorporated in this Unit............... 2-3 Materials List.......................................
Practice Exam Three Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01T Fall Term 2004 Practice Exam Three Solutions Problem 1a) (5 points) Collisions and Center of Mass Reference Frame In the lab frame,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01T Fall Term 2004 Practice Exam Three Solutions Problem 1a) (5 points) Collisions and Center of Mass Reference Frame In the lab frame,
What is a Mouse-Trap
 What is a Mouse-Trap Car and How does it Work? A mouse-trap car is a vehicle that is powered by the energy that can be stored in a wound up mouse-trap spring. The most basic design is as follows: a string
What is a Mouse-Trap Car and How does it Work? A mouse-trap car is a vehicle that is powered by the energy that can be stored in a wound up mouse-trap spring. The most basic design is as follows: a string
Work, Energy and Power Practice Test 1
 Name: ate: 1. How much work is required to lift a 2-kilogram mass to a height of 10 meters?. 5 joules. 20 joules. 100 joules. 200 joules 5. ar and car of equal mass travel up a hill. ar moves up the hill
Name: ate: 1. How much work is required to lift a 2-kilogram mass to a height of 10 meters?. 5 joules. 20 joules. 100 joules. 200 joules 5. ar and car of equal mass travel up a hill. ar moves up the hill
