Tornadoes Answer Sheet
|
|
|
- Maurice Murphy
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LEVEL 1 None LEVEL 2 Definitions for A Tornado Is Born anvil cloud: the upper portion of a cumulonimbus cloud that flattens spreads out, sometimes for hundreds of miles atmosphere: the mass of air surrounding the earth condense: to cause a gas or vapor to change into a liquid cumulonimbus cloud: a cloud that towers above ordinary cumulus clouds with stronger or severe storms. The cloud often has a more sharply outlined, defined appearance with relatively rapid rising motions that are visible. cumulus cloud: a column of rising air that has condensed into a dense cloud with distinct outlines. The cumulus cloud is the first stage of a developing thunderstorm, although most cumulus clouds do not form thunderstorms. downdraft: rapidly descending column of cooling air that causes heavy rains and violent wind gusts front: the boundary between two air masses with differing characteristics, such as temperature or humidity funnel cloud: a rotating, cone-shape column of air extending downward from the base of a thunderstorm. When a funnel cloud reaches the ground, it is called a tornado. mesocyclone: a rotating shaft of rapidly rising air within a storm. Under certain conditions, a mesocyclone can generate a tornado. supercell: a violent thunderstorm that has a persistent, rotating updraft and is capable of spawning tornadoes thunderhead: the upper portion of a swelling cumulus cloud, or the entire cumulonimbus cloud updraft: a column of warm, moist air that is rising in a thundercloud or supercell vertical wind shear: the change in the wind s direction and speed with height vortex: a whirling mass of air in the form of a column or spiral Answers to A Tornado Is Born, Pages 2 and 3 High in the atmosphere, cool air pushes against warm air. The place where the two kinds of air meet is called a front. A front can stretch over 100 miles (161 kilometers). On warm days, the air near the ground is much warmer than it is at higher elevations. Warm air rises by bubbling up from the ground, just like the bubbles in a pot of boiling water. If the air has enough moisture in it, the moisture condenses and forms cumulus clouds. Sometimes, the rising air is trapped by a layer of cooler air above it. As the day continues, the warm air builds up. If this pocket of warm air rises quickly, it can break through the cap of cooler air like water shooting up from a fountain and a thunderhead or cumulonimbus (kyu-mya-lo- NIM-buhs) cloud, grows, topped by an anvil cloud. The thunderheads most likely to cause tornadoes are those that form along and ahead of fronts. Strong, fast winds tend to blow along and above fronts. If slower surface winds blow opposite to the direction of the higher winds, a vertical wind shear forms. Vertical wind shear can cause the rising air in a thunderhead to begin to rotate. 1
2 A supercell is a thunderstorm with a constantly rotating updraft. Supercells are responsible for a high percentage of severe weather events, especially tornadoes. If the rising column of air in a thunderhead begins to rotate, it is called a mesocyclone (mez-uh-sy-klon). In a mesocyclone, the updrafts and down drafts are in near balance, allowing the storm to continue for several hours. As a mesocyclone rotates, it stretches toward warm air near the ground. The lower part of the mesocyclone narrows. The narrower it becomes, the faster it spins. When this vortex dips down from the mesocyclone, it draws in warm, moist air. The air cools as it is pulled up into the column. Tiny droplets of water form and a whirling cloud appears. This cloud is called a funnel cloud. Some funnel clouds hang straight down from the storm cloud. Others stretch sideways through the sky. A funnel cloud may dip down and then retract into the mesocyclone, or it may touch the ground. If it touches the ground, the funnel cloud is called a tornado. Answers to Hail Maker, page 2 Observation of Layers You can see the different layers within the frozen droplet. The layers farthest from the center are the clearest; the inner layer is white. The ice pellets resemble hail because of the layers of ice within each. They are different from hail because they are not round and the number of layers is not dependent on the winds and temperature changes within a cloud. Challenge: Temperature differences may have an effect, because the addition of warm water might partially melt the previous layer of the ice pellet before it is refrozen, blurring the layers. Using ice-cooled water might change the clarity of the layers. The actual demonstration may differ depending on the temperature of the water used. Answer to Wind Maker When you hold the spiral by the thread over the heat source, the spiral begins to swirl. When you move it away from the heat source, the spiral stops swirling. When the air around the heat source is heated, the warmer air rises (updraft) and the cooler air drops down (downdraft) causing air movement. This movement of air causes wind. Answer to Storm Cloud The warmer milk immediately rises toward the top of the container. It spreads into an anvilshaped cloud as it hits the cooler water of the container and the water s surface. As the milk cools, it sinks in pouches and then in tiny streams back into the water. A cumulonimbus cloud develops vertically (updrafts of moist air) and is often capped by an anvil-shaped cloud. This is a thunderstorm cloud, frequently accompanied by heavy rains, lightning, thunder and, sometimes, hail, tornadoes or strong winds. 2
3 Answer to Wind Shear When you move the books in opposite directions, the horizontal tube rolls between the books and then shears off vertically. Wind shear is the effect of winds moving in opposite directions. When the tube hits the ground, it represents a tornado. The power of the winds aloft and the slower winds closer to the ground can make the rising air in a thunderhead start spinning, forming a column of spinning air mesocyclone) that can be the basis of a tornado. Answer to Tornado in a Bottle The swirling motion builds energy and, as the water drops through the opening of the bottle, it forms a vortex (a spinning funnel shape). The energy of a real tornado comes from winds and wind shear that produce rotation, which results in the tornado vortex. As this energy is forced into the smaller opening, it becomes more violent because the molecules move closer to the center. Answers to Tornado Worksheet Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska and Missouri 6. Florida has many tornadoes simply because it experiences thunderstorms almost daily. In addition, tropical cyclones also affect the Florida peninsula. When these cyclones move ashore, the embedded thunderstorms often will produce tornadoes. However, despite the violent nature of a tropical cyclone, most of the tornadoes they spawn (some being water spouts) are normally relatively weak. 7. Yes. Tornadoes can strike anywhere if conditions are right. Some areas are more susceptble to tornado activity than others. LEVEL 3 Answers to A Cartographer s Guide to Tornadoes 1. Weather in the United States is influenced by four air masses. What are they? Tropical: These air masses form over the tropic latitudes. They are warm, humid and have low air pressure. Polar: These air masses form north of the 50o line of latitude. They are cold and have high pressure. Maritime: These air masses form over the oceans, so they are humid. Continental: These air masses form over land, so they tend to be drier than maritime air masses. 2. What forces move these air masses around? What direction will they take as they move toward and into the United States? The jet stream is a prevailing, upper-level, westerly wind. It moves from west to east in a sinuous line that changes with the strength of the cold fronts moving south. 3
4 A cyclone is an area of low pressure around which the winds flow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere. A developing cyclone is typically formed by a warm front pushing northward and a cold front pulling southward. Air masses move south from the arctic land mass, southwest from the northern Pacific, southeast from the northern Atlantic, north and then northeast from the Tropics. 3. How might the landforms of the United States affect the air masses moving through the area? When air is confronted by a mountain, it is lifted up and over the mountain; as it rises, it cools. If it reaches its dew point it will condense and form a cloud and probably precipitation. Usually, the wind releases its moisture on the west side of the mountains, and as it flows down onto the plains, the drier air begins to warm. There is no barrier to the movement of air masses between the Gulf of Mexico and the states of the Great Plains. 4. What is a cold front and what is a warm front? What happens when the two air masses collide? A cold front is an air mass characterized by cold, dense air. Cold fronts have winds that move in a clockwise direction. They are sometimes called anticyclones. A warm front is an air mass of light, warm air. Warm fronts have winds that move counterclockwise and are called cyclones. When a cold front collides with a warm front, it slides under the warm front and pushes the lighter, warmer air upward. The warm air cools down, condenses and forms cumulus clouds. If there is enough warm air, as in the summer, it may form cumulonimbus clouds and even tornadoes. 5. Based on information about the formation of cumulonimbus clouds, why does an occluded front create excellent conditions for the formation of severe thunderstorms and eventually tornadoes? An occluded front occurs when a warm air mass is trapped between two cold air masses. The warm air is pushed upward when the two cold air masses meet in a kind of squeeze action. The warm air mass is completely cut off from the ground by the colder air below. The warm air has nowhere to go but up, resulting in the creation of high, strong cumulus clouds. As it cools, it will fall and then be pushed up again, adding energy to the updraft. 6. Collisions between cold, dry air masses and warm, moist air masses take place in the Great Plains. This part of the United States is sometimes called Tornado Alley. Compare an alley in your town to Tornado Alley. How are they similar? Possible answer: An alley is a narrow street with walls on both sides. Tornado Alley is a geographic corridor in the United States, which stretches north from Texas to Nebraska and Iowa. In the case of Tornado Alley, the walls on either side of the alley are the two mountain ranges, the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains. 7. Tornado season tends to move north with the sun. That is, tornado season starts earlier in the southern part of Tornado Alley than in its northern regions. Why is spring the most active time for tornadoes? Use the same reasoning to explain why the southeastern states sometimes have a mini-tornado season in the fall. Spring and summer comprise the prime thunderstorm season; so it is also prime tornado season in the Great Plains. The reason is that because, during these seasons, the air temperature decreases dramatically as the air rises (called the temperature gradient). Moreover, as the earth rotates around the sun, the surface warms, releasing energy (heat) and water vapor. Severe thunderstorms need large infusions of energy to build into supercells and tornadoes. The warmer the surface, the more energy is available. Energy and water 4
5 vapor are released from the warm surface and rise in buoyant plumes which, when combined and organized, form a thunderstorm cell. Therefore, spring and summer have the greatest possibility for the development of thunderstorms. Answers to Real-life Tornadoes (1) EF3; (2) EF5; (3) EF1. Answers to The Truth About Tornadoes 1. True. There are three possible explanations for the greenish sky. As light from above travels through the storm, it is reflected and refracted by the water droplets and hailstones. The hail allows more of the green to get through and color the clouds. When the sun is low in the sky, such as before sunset when most severe storms occur, the reddening light of the sun when shining through the earth s atmosphere makes the bluish cloud tint turn green. Storm clouds may act as a kind of canvas upon which low sunlight, scattered by particles in the air, paints a greenish color. Hail can fall from severe thunderstorms. The rotation of a thunderstorm s updraft strengthens the upward wind motion, helping to hold larger ice particles aloft for a longer time. The longer a hailstone can remain suspended in a growth region of the thunderstorm, the bigger the hailstone will grow. 2. False. Tornadoes can happen in every state if there is warm, moist, unstable air along and ahead of cold fronts. 3. False. Waterspouts are weak tornadoes that form over warm water. The water drops in the waterspout are the result of condensation, not the body of water over which the spout has formed. They are most common along the Gulf Coast and southeastern states. Occasionally, waterspouts move inland becoming tornadoes that cause damage and injury. 4. False. Research has shown that buildings do not explode from the low air pressure of a tornado. Opening windows can increase the chance of high winds entering and causing more damage to your home and exposing you to injury. Leave the windows alone. 5. True. As the tornado moves over the ground, it stirs up dust and soil and other debris dragged in by the low pressure. 6. True. Never try to outdrive a tornado. Vehicles can be deadly in a tornado; the more surface they present to the wind, the more easily they are blown from the road. A tornado can pick up a car and toss it about like a toy. If you are in a car during a tornado, get out and find a safe place. 7. True. The whirling appearing near the cloud base is actually evidence of the mesocyclone that is responsible for the tornado s formation. Although the classic funnel shape is common, it can look like a jar or have more than one funnel. In fact, large tornadoes may have several narrow, twisting funnels circling around. 8. True. All that is needed for a tornado to form is warm, moist, unstable air along and ahead of cold fronts. 9. False. People who take shelter under a highway overpass can be killed because the overpass acts like a wind tunnel. The reality of a tornadic circulation in the atmosphere is that the wind has a very strong horizontal element. In most cases, the strongest horizontal and vertical components of the wind can be found not far above the surface. In addition, in almost ALL 5
6 tornadoes, the very strong wind extends outside the diameter of the visible funnel and in many cases, a considerable distance from the visible funnel. 10. True. The high winds of a tornado can cause a roar that is often compared to the sound of a freight train. However, what you hear depends on what the tornado is hitting, its size, intensity and distance from you. The most common tornado sound is a continuous rumble, like a nearby train. Sometimes a tornado produces a loud whooshing sound, like that of a waterfall or of open car windows while driving very fast. Tornadoes that are tearing through densely populated areas may be producing all kinds of loud noises at once which, collectively, may make a tremendous roar. 11. True. Tornadoes generally occur near the trailing edge of a thunderstorm. It is not uncommon to see clear, sunlit skies behind a tornado. The tornado circulation develops at midlevels about 20,000 feet (6,100 kilometers) in the storm where the storm s updraft and mesocyclone are strongest. The circulation gradually builds down (and up) within the storm. At about the same time, a downdraft develops at midlevels near the back edge of the storm. This downdraft, called a rear flank downdraft (RFD), descends to the ground along with the tornado circulation. 12. False. Tornadoes do happen in big cities. For example, St. Louis has had 22 tornadoes in the past 40 years; Oklahoma City and Salt Lake City have been struck by tornadoes. 6
Storms Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
2. The map below shows high-pressure and low-pressure weather systems in the United States.
 1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
Read and study the following information. After reading complete the review questions. Clouds
 Name: Pd: Read and study the following information. After reading complete the review questions. Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a large collection of very tiny droplets of water or ice crystals. The
Name: Pd: Read and study the following information. After reading complete the review questions. Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a large collection of very tiny droplets of water or ice crystals. The
Mid latitude Cyclonic Storm System. 08 _15 ab. jpg
 Mid latitude Cyclonic Storm System 08 _15 ab. jpg Mid Latitude Cyclone Storm System (MLCSS) It has several names. Cyclone, Cyclonic Storm, Cyclonic System, Depression. Cyclonic Storms are the weather maker
Mid latitude Cyclonic Storm System 08 _15 ab. jpg Mid Latitude Cyclone Storm System (MLCSS) It has several names. Cyclone, Cyclonic Storm, Cyclonic System, Depression. Cyclonic Storms are the weather maker
WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test
 WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What role does runoff play in the water cycle? a. It is the process in
WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What role does runoff play in the water cycle? a. It is the process in
Severe Weather. www.readinga-z.com. Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
 Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,801 LEVELED READER T Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrations by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,801 LEVELED READER T Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrations by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
THIRD GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 THIRD GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the different components of the water cycle. LAB: Contrasting water with hydrogen
THIRD GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the different components of the water cycle. LAB: Contrasting water with hydrogen
6 th Grade Science Assessment: Weather & Water Select the best answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this test.
 Select the be answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this te. 1. Weather is be defined as the A. changes that occur in cloud formations from day to day. B. amount of rain or snow that
Select the be answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this te. 1. Weather is be defined as the A. changes that occur in cloud formations from day to day. B. amount of rain or snow that
FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE!
 FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE! 1 NAME DATE GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water
FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE! 1 NAME DATE GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate?
 How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
FOURTH GRADE WEATHER
 FOURTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different reservoirs of water. LAB: Experimenting with surface tension and capillary
FOURTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different reservoirs of water. LAB: Experimenting with surface tension and capillary
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource
 Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
WeatherBug Vocabulary Bingo
 Type of Activity: Game: Interactive activity that is competitive, and allows students to learn at the same time. Activity Overview: WeatherBug Bingo is a fun and engaging game for you to play with students!
Type of Activity: Game: Interactive activity that is competitive, and allows students to learn at the same time. Activity Overview: WeatherBug Bingo is a fun and engaging game for you to play with students!
Air Masses and Fronts
 Air Masses and Fronts Air Masses The weather of the United States east of the Rocky Mountains is dominated by large masses of air that travel south from the wide expanses of land in Canada, and north from
Air Masses and Fronts Air Masses The weather of the United States east of the Rocky Mountains is dominated by large masses of air that travel south from the wide expanses of land in Canada, and north from
Temperature affects water in the air.
 KEY CONCEPT Most clouds form as air rises and cools. BEFORE, you learned Water vapor circulates from Earth to the atmosphere Warm air is less dense than cool air and tends to rise NOW, you will learn How
KEY CONCEPT Most clouds form as air rises and cools. BEFORE, you learned Water vapor circulates from Earth to the atmosphere Warm air is less dense than cool air and tends to rise NOW, you will learn How
SIXTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SIXTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Evaluating components of the water cycle. LAB: Experimenting with porosity and permeability.
SIXTH GRADE WEATHER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Evaluating components of the water cycle. LAB: Experimenting with porosity and permeability.
Basics of weather interpretation
 Basics of weather interpretation Safety at Sea Seminar, April 2 nd 2016 Dr. Gina Henderson Oceanography Dept., USNA [email protected] Image source: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/naturalhazards/view.php?id=80399,
Basics of weather interpretation Safety at Sea Seminar, April 2 nd 2016 Dr. Gina Henderson Oceanography Dept., USNA [email protected] Image source: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/naturalhazards/view.php?id=80399,
CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate
 Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
Analyze Weather in Cold Regions and Mountainous Terrain
 Analyze Weather in Cold Regions and Mountainous Terrain Terminal Learning Objective Action: Analyze weather of cold regions and mountainous terrain Condition: Given a training mission that involves a specified
Analyze Weather in Cold Regions and Mountainous Terrain Terminal Learning Objective Action: Analyze weather of cold regions and mountainous terrain Condition: Given a training mission that involves a specified
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: WEATHER BASICS: STATION MODELS: MOISTURE: PRESSURE AND WIND: Weather
 Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated, transpiration
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer, cyclone, dew point, front, isobar, isotherm, meteorology, precipitation, psychrometer, relative humidity, saturated, transpiration
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools
 Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools Supported by: National Science Foundation Weather: 4.H.3 Weather and Classical Instruments Grade
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools Supported by: National Science Foundation Weather: 4.H.3 Weather and Classical Instruments Grade
WEATHER THEORY Temperature, Pressure And Moisture
 WEATHER THEORY Temperature, Pressure And Moisture Air Masses And Fronts Weather Theory- Page 77 Every physical process of weather is a result of a heat exchange. The standard sea level temperature is 59
WEATHER THEORY Temperature, Pressure And Moisture Air Masses And Fronts Weather Theory- Page 77 Every physical process of weather is a result of a heat exchange. The standard sea level temperature is 59
What Causes Climate? Use Target Reading Skills
 Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
8.5 Comparing Canadian Climates (Lab)
 These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
7613-1 - Page 1. Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions
 Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions 7613-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) Equal quantities of water are placed in four uncovered containers with different shapes and left on a table at room temperature. From which
Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions 7613-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) Equal quantities of water are placed in four uncovered containers with different shapes and left on a table at room temperature. From which
Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Book Word Count: 1,775
 Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Book Word Count: 1,775 LEVELED BOOK T SEVERE WEATHER Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrated by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and
Severe Weather A Reading A Z Level T Leveled Book Word Count: 1,775 LEVELED BOOK T SEVERE WEATHER Written by Bruce D. Cooper Illustrated by Cende Hill Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and
Precipitation forms from water droplets or ice crystals.
 KEY CONCEPT Water falls to Earth s surface as precipitation. BEFORE, you learned Water moves between Earth's surface and the atmosphere Water vapor condenses into clouds NOW, you will learn How precipitation
KEY CONCEPT Water falls to Earth s surface as precipitation. BEFORE, you learned Water moves between Earth's surface and the atmosphere Water vapor condenses into clouds NOW, you will learn How precipitation
Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6
 Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6 Tropical Cyclones This document describes tropical cyclones and the dangers they pose to coastal populations. It is intended to help teachers improve
Exploring Florida: Teaching Resources for Science 1 of 6 Tropical Cyclones This document describes tropical cyclones and the dangers they pose to coastal populations. It is intended to help teachers improve
Chapter Overview. Seasons. Earth s Seasons. Distribution of Solar Energy. Solar Energy on Earth. CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Geography affects climate.
 KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
Thunderstorm Basics. Updraft Characteristics (Rising Air) Downdraft Characteristics (Air Descends to the Ground)
 Thunderstorm Basics Updraft Characteristics (Rising Air) Cumulus Tower Upward Cloud Motion Updraft Dominant Downdraft/Updraft Downdraft Dominant Rain-Free Base Downdraft Characteristics (Air Descends to
Thunderstorm Basics Updraft Characteristics (Rising Air) Cumulus Tower Upward Cloud Motion Updraft Dominant Downdraft/Updraft Downdraft Dominant Rain-Free Base Downdraft Characteristics (Air Descends to
Hurricanes. Characteristics of a Hurricane
 Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
Chapter 7 Stability and Cloud Development. Atmospheric Stability
 Chapter 7 Stability and Cloud Development Atmospheric Stability 1 Cloud Development - stable environment Stable air (parcel) - vertical motion is inhibited if clouds form, they will be shallow, layered
Chapter 7 Stability and Cloud Development Atmospheric Stability 1 Cloud Development - stable environment Stable air (parcel) - vertical motion is inhibited if clouds form, they will be shallow, layered
The Tornado Diaries. Tornadoes K-2. Tornado Science LESSON PLAN 2. Key Terms and Concepts. Purposes. Objectives
 LESSON PLAN 2 The Tornado Diaries Tornadoes K-2 A tornado is a violently rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm to the ground. Tornadoes have been reported in every state and, though they
LESSON PLAN 2 The Tornado Diaries Tornadoes K-2 A tornado is a violently rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm to the ground. Tornadoes have been reported in every state and, though they
Humidity, Condensation, Clouds, and Fog. Water in the Atmosphere
 Humidity, Condensation, Clouds, and Fog or Water in the Atmosphere The Hydrologic Cycle Where the Water Exists on Earth Evaporation From the Oceans and Land The Source of Water Vapor for the Atmosphere
Humidity, Condensation, Clouds, and Fog or Water in the Atmosphere The Hydrologic Cycle Where the Water Exists on Earth Evaporation From the Oceans and Land The Source of Water Vapor for the Atmosphere
UNIT VII--ATMOSPHERIC STABILITY AND INSTABILITY
 UNIT VII--ATMOSPHERIC STABILITY AND INSTABILITY The stability or instability of the atmosphere is a concern to firefighters. This unit discusses how changes in the atmosphere affect fire behavior, and
UNIT VII--ATMOSPHERIC STABILITY AND INSTABILITY The stability or instability of the atmosphere is a concern to firefighters. This unit discusses how changes in the atmosphere affect fire behavior, and
THE STORM CHASERS By Dr. Alicia L. Curry Dr. Michael L. Curry Tuskegee University Math & Science Partnership (NSF Funded Grant) Summer 2013
 THE STORM CHASERS By Dr. Alicia L. Curry Dr. Michael L. Curry Tuskegee University Math & Science Partnership (NSF Funded Grant) Summer 2013 STORM CHASERS PRE-TEST Name: Date: Reviewing Vocabulary Define
THE STORM CHASERS By Dr. Alicia L. Curry Dr. Michael L. Curry Tuskegee University Math & Science Partnership (NSF Funded Grant) Summer 2013 STORM CHASERS PRE-TEST Name: Date: Reviewing Vocabulary Define
Supercell Thunderstorm Structure and Evolution
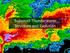 Supercell Thunderstorm Structure and Evolution Supercellular Convection Most uncommon, but most dangerous storm type Produces almost all instances of very large hail and violent (EF4-EF5) tornadoes Highly
Supercell Thunderstorm Structure and Evolution Supercellular Convection Most uncommon, but most dangerous storm type Produces almost all instances of very large hail and violent (EF4-EF5) tornadoes Highly
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures. Seasons & Sun's Distance. Solstice & Equinox. Seasons & Solar Intensity
 Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
Clouds. A simple scientific explanation for the weather-curious. By Kira R. Erickson
 Clouds A simple scientific explanation for the weather-curious By Kira R. Erickson Table of Contents 1 3 4 INTRO 2 Page 3 How Clouds Are Formed Types of Clouds Clouds and Weather More Information Page
Clouds A simple scientific explanation for the weather-curious By Kira R. Erickson Table of Contents 1 3 4 INTRO 2 Page 3 How Clouds Are Formed Types of Clouds Clouds and Weather More Information Page
The Atmosphere and Winds
 Oceanography 10, T. James Noyes, El Camino College 8A-1 The Atmosphere and Winds We need to learn about the atmosphere, because the ocean and atmosphere are tightly interconnected with one another: you
Oceanography 10, T. James Noyes, El Camino College 8A-1 The Atmosphere and Winds We need to learn about the atmosphere, because the ocean and atmosphere are tightly interconnected with one another: you
Multiple Choice For questions 1-10, circle only one answer.
 Test Bank - Chapter 1 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 1. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 1 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 1. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form?
 Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling. Why Clouds Form Cloud Types (from The Blue Planet ) Four Ways
Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling. Why Clouds Form Cloud Types (from The Blue Planet ) Four Ways
Lab Activity on Global Wind Patterns
 Lab Activity on Global Wind Patterns 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you should
Lab Activity on Global Wind Patterns 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you should
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS THINGS
 CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
The Water Cycle. 4 th Grade Pre-Visit Activity #1
 th Grade Pre-Visit Activity # The Water Cycle Overview Objectives Subjects Earth s water molecules circulate among air, plants, animals, and soil by way of the water cycle. This activity uses a game to
th Grade Pre-Visit Activity # The Water Cycle Overview Objectives Subjects Earth s water molecules circulate among air, plants, animals, and soil by way of the water cycle. This activity uses a game to
Convective Clouds. Convective clouds 1
 Convective clouds 1 Convective Clouds Introduction Convective clouds are formed in vertical motions that result from the instability of the atmosphere. This instability can be caused by: a. heating at
Convective clouds 1 Convective Clouds Introduction Convective clouds are formed in vertical motions that result from the instability of the atmosphere. This instability can be caused by: a. heating at
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the properties of water. LAB: Experimenting with different soap mixtures. POST: Analyzing
SECOND GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the properties of water. LAB: Experimenting with different soap mixtures. POST: Analyzing
This chapter discusses: 1. Definitions and causes of stable and unstable atmospheric air. 2. Processes that cause instability and cloud development
 Stability & Cloud Development This chapter discusses: 1. Definitions and causes of stable and unstable atmospheric air 2. Processes that cause instability and cloud development Stability & Movement A rock,
Stability & Cloud Development This chapter discusses: 1. Definitions and causes of stable and unstable atmospheric air 2. Processes that cause instability and cloud development Stability & Movement A rock,
Convection Currents in the Air
 LESSON 5 Convection Currents in the Air Hold on to your hat! Whether you are walking along a beach or flying a kite in an open field, a really windy day can make you feel like you are about to be swept
LESSON 5 Convection Currents in the Air Hold on to your hat! Whether you are walking along a beach or flying a kite in an open field, a really windy day can make you feel like you are about to be swept
6. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below, which shows the average monthly temperature of two cities A and B.
 1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
How do Scientists Forecast Thunderstorms?
 How do Scientists Forecast Thunderstorms? Objective In the summer, over the Great Plains, weather predictions often call for afternoon thunderstorms. While most of us use weather forecasts to help pick
How do Scientists Forecast Thunderstorms? Objective In the summer, over the Great Plains, weather predictions often call for afternoon thunderstorms. While most of us use weather forecasts to help pick
(Walter Glogowski, Chaz Shapiro & Reid Sherman) INTRODUCTION
 Convection (Walter Glogowski, Chaz Shapiro & Reid Sherman) INTRODUCTION You know from common experience that when there's a difference in temperature between two places close to each other, the temperatures
Convection (Walter Glogowski, Chaz Shapiro & Reid Sherman) INTRODUCTION You know from common experience that when there's a difference in temperature between two places close to each other, the temperatures
Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind
 Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind Pressure, Measurement, Distribution Forces Affect Wind Geostrophic Balance Winds in Upper Atmosphere Near-Surface Winds Hydrostatic Balance (why the sky isn t falling!) Thermal
Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind Pressure, Measurement, Distribution Forces Affect Wind Geostrophic Balance Winds in Upper Atmosphere Near-Surface Winds Hydrostatic Balance (why the sky isn t falling!) Thermal
Description: This competition will test the student's knowledge of meteorological terms, techniques, and events.
 Weather or Not Description: This competition will test the student's knowledge of meteorological terms, techniques, and events. Number of Participants: 2 Approximate Time: 45 minutes The Competition: 1.
Weather or Not Description: This competition will test the student's knowledge of meteorological terms, techniques, and events. Number of Participants: 2 Approximate Time: 45 minutes The Competition: 1.
1. The Kinetic Theory of Matter states that all matter is composed of atoms and molecules that are in a constant state of constant random motion
 Physical Science Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Practice Test for Unit 3: Ch. 3, and some of 15 and 16: Kinetic Theory of Matter, States of matter, and and thermodynamics, and gas laws. 1. The Kinetic
Physical Science Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Practice Test for Unit 3: Ch. 3, and some of 15 and 16: Kinetic Theory of Matter, States of matter, and and thermodynamics, and gas laws. 1. The Kinetic
Let s Make a Cloud. Objective Demonstrate the combination of three natural elements, to form a cloud: water vapor, smoke and air pressure.
 Let s Make a Cloud Related Subject: Climate and Weather Group Size: 10-15 Length of Activity: 45 minutes Objective Demonstrate the combination of three natural elements, to form a cloud: water vapor, smoke
Let s Make a Cloud Related Subject: Climate and Weather Group Size: 10-15 Length of Activity: 45 minutes Objective Demonstrate the combination of three natural elements, to form a cloud: water vapor, smoke
Climates are described by the same conditions used to describe
 58 The Causes of Climate R E A D I N G Climates are described by the same conditions used to describe weather, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind. You now know that oceans have an important effect
58 The Causes of Climate R E A D I N G Climates are described by the same conditions used to describe weather, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind. You now know that oceans have an important effect
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist. Introduction. Climatic controls
 Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
Clouds for pilots. Ed Williams. http://williams.best.vwh.net/
 Clouds for pilots Ed Williams http://williams.best.vwh.net/ Clouds are important to pilots! Many of our weather problems are associated with clouds: Fog Thunderstorms Cloud In flight icing Cloud physics
Clouds for pilots Ed Williams http://williams.best.vwh.net/ Clouds are important to pilots! Many of our weather problems are associated with clouds: Fog Thunderstorms Cloud In flight icing Cloud physics
In a majority of ice-crystal icing engine events, convective weather occurs in a very warm, moist, tropical-like environment. aero quarterly qtr_01 10
 In a majority of ice-crystal icing engine events, convective weather occurs in a very warm, moist, tropical-like environment. 22 avoiding convective Weather linked to Ice-crystal Icing engine events understanding
In a majority of ice-crystal icing engine events, convective weather occurs in a very warm, moist, tropical-like environment. 22 avoiding convective Weather linked to Ice-crystal Icing engine events understanding
5 th Grade Science Vocabulary Words
 5 th Grade Science Vocabulary Words abiotic factor A nonliving part of an ecosystem. acceleration Change in velocity with respect to time. action The force one object applies to a second, as in Newton
5 th Grade Science Vocabulary Words abiotic factor A nonliving part of an ecosystem. acceleration Change in velocity with respect to time. action The force one object applies to a second, as in Newton
UNIT IV--TEMPERATURE-MOISTURE RELATIONSHIP
 UNIT IV--TEMPERATURE-MOISTURE RELATIONSHIP Weather is the most variable and often the most critical determinant of fire behavior. This is the first of several units that will deal with weather and its
UNIT IV--TEMPERATURE-MOISTURE RELATIONSHIP Weather is the most variable and often the most critical determinant of fire behavior. This is the first of several units that will deal with weather and its
Clouds, Fog, & Precipitation
 firecatching.blogspot.com Kids.brittanica.com Clouds and fog are physically the same just location is different Fog is considered a stratus cloud at or near the surface What does one see when looking at
firecatching.blogspot.com Kids.brittanica.com Clouds and fog are physically the same just location is different Fog is considered a stratus cloud at or near the surface What does one see when looking at
Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms
 Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form Cloud Types (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling. Four Ways
Lecture 7a: Cloud Development and Forms Why Clouds Form Cloud Types (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling. Four Ways
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Natural Disasters 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms
 Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form Static Stability Cloud Types Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling.
Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form Static Stability Cloud Types Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling.
Formation & Classification
 CLOUDS Formation & Classification DR. K. K. CHANDRA Department of forestry, Wildlife & Environmental Sciences, GGV, Bilaspur What is Cloud It is mass of tiny water droplets or ice crystals or both of size
CLOUDS Formation & Classification DR. K. K. CHANDRA Department of forestry, Wildlife & Environmental Sciences, GGV, Bilaspur What is Cloud It is mass of tiny water droplets or ice crystals or both of size
1/2/3. Finding out about the Water Cycle
 The Water Cycle 1/2/3. Finding out about the Water Cycle Aims: To enable pupils to learn and understand what happens at each stage of the Water Cycle To introduce specific vocabulary related to the Water
The Water Cycle 1/2/3. Finding out about the Water Cycle Aims: To enable pupils to learn and understand what happens at each stage of the Water Cycle To introduce specific vocabulary related to the Water
Hazardous Weather Primer. CERT Basic Training Unit 0
 Hazardous Weather Primer Unit 0 Topic Overview: CERT Activation Basic Weather Weather Hazards: Flooding, Winter Weather, Extreme temperatures, severe thunderstorms, tornados Weather Safety Personal Preparedness
Hazardous Weather Primer Unit 0 Topic Overview: CERT Activation Basic Weather Weather Hazards: Flooding, Winter Weather, Extreme temperatures, severe thunderstorms, tornados Weather Safety Personal Preparedness
The Pennsylvania Observer
 The Pennsylvania Observer August 3, 2009 July 2009 - Pennsylvania Weather Recap Written by: Dan DePodwin After a cool month of June, some hoped July would bring usual summertime warmth to the state of
The Pennsylvania Observer August 3, 2009 July 2009 - Pennsylvania Weather Recap Written by: Dan DePodwin After a cool month of June, some hoped July would bring usual summertime warmth to the state of
Education and Outreach Lesson Plan
 Education and Outreach Lesson Plan Visit our online activities collection http://education.arm.gov/ Grade levels K 2 Common Covering Clouds Common Covering Clouds Approximate Time 1 1/2 hours, or two 45-minute
Education and Outreach Lesson Plan Visit our online activities collection http://education.arm.gov/ Grade levels K 2 Common Covering Clouds Common Covering Clouds Approximate Time 1 1/2 hours, or two 45-minute
[7] SD3.1 The student demonstrates an understanding of cycles influenced by energy from the
![[7] SD3.1 The student demonstrates an understanding of cycles influenced by energy from the [7] SD3.1 The student demonstrates an understanding of cycles influenced by energy from the](/thumbs/27/12373649.jpg) Cloud Types Levels Overview: During this project, students learn about different types of clouds and determine which type of cloud is most commonly overhead in their area over a period of four weeks. Objectives:
Cloud Types Levels Overview: During this project, students learn about different types of clouds and determine which type of cloud is most commonly overhead in their area over a period of four weeks. Objectives:
CHAPTER 5 Lectures 10 & 11 Air Temperature and Air Temperature Cycles
 CHAPTER 5 Lectures 10 & 11 Air Temperature and Air Temperature Cycles I. Air Temperature: Five important factors influence air temperature: A. Insolation B. Latitude C. Surface types D. Coastal vs. interior
CHAPTER 5 Lectures 10 & 11 Air Temperature and Air Temperature Cycles I. Air Temperature: Five important factors influence air temperature: A. Insolation B. Latitude C. Surface types D. Coastal vs. interior
The Water Cycle Now You See It, Now You Don t
 The Water Cycle Now You See It, Now You Don t Unit: Salinity Patterns & the Water Cycle l Grade Level: Elementary l Time Required: Introduction - 30 min. - Activity as groups 45min Wrap Up 20 min l Content
The Water Cycle Now You See It, Now You Don t Unit: Salinity Patterns & the Water Cycle l Grade Level: Elementary l Time Required: Introduction - 30 min. - Activity as groups 45min Wrap Up 20 min l Content
How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents
 How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents Before You Begin... 2 1. Identify H and L pressure systems... 3 2. Locate fronts and determine frontal activity... 5 3. Determine surface
How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents Before You Begin... 2 1. Identify H and L pressure systems... 3 2. Locate fronts and determine frontal activity... 5 3. Determine surface
Anticyclones, depressions, hot & drought, cold & snow
 AS/A2-Level Geography Anticyclones, depressions, hot & drought, cold & snow Learning Objectives: To describe and explain the weather associated with high and low pressure systems and their links to extreme
AS/A2-Level Geography Anticyclones, depressions, hot & drought, cold & snow Learning Objectives: To describe and explain the weather associated with high and low pressure systems and their links to extreme
Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air
 LESSON 4 Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air INTRODUCTION How can a hang glider stay up in the air for hours without a motor? How can a bird soar over an open field without flapping its wings? They can
LESSON 4 Heat Transfer and the Movement of Air INTRODUCTION How can a hang glider stay up in the air for hours without a motor? How can a bird soar over an open field without flapping its wings? They can
Chapter Test A. States of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE. a fixed amount of STAs2 a. a solid. b. a liquid. c. a gas. d. any type of matter.
 Assessment Chapter Test A States of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Boyle s law explains the relationship between volume and pressure for a fixed
Assessment Chapter Test A States of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Boyle s law explains the relationship between volume and pressure for a fixed
STUDY GUIDE: Earth Sun Moon
 The Universe is thought to consist of trillions of galaxies. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, has billions of stars. One of those stars is our Sun. Our solar system consists of the Sun at the center, and all
The Universe is thought to consist of trillions of galaxies. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, has billions of stars. One of those stars is our Sun. Our solar system consists of the Sun at the center, and all
BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE
 NATIONAL OCEANIC AND ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF
NATIONAL OCEANIC AND ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE BASIC SPOTTERS FIELD GUIDE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE U.S. DEPARTMENT OF
Perth Academy. Geography Department
 Perth Academy Geography Department Natural Hazards Tropical Storms Natural Hazards Natural Hazards affect a large percentage of the world s population. Despite the damage and destruction caused, there
Perth Academy Geography Department Natural Hazards Tropical Storms Natural Hazards Natural Hazards affect a large percentage of the world s population. Despite the damage and destruction caused, there
Water & Climate Review
 Water & Climate Review 1. The cross section below shows the direction of air flowing over a mountain. Points A and B are at the same elevation on opposite sides of the mountain. 4. The graph below shows
Water & Climate Review 1. The cross section below shows the direction of air flowing over a mountain. Points A and B are at the same elevation on opposite sides of the mountain. 4. The graph below shows
The Nature of Storms. What You ll Learn How thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes
 13 What You ll Learn How thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes form. What the effects of severe weather are. How repetitive weather patterns can cause droughts, floods, and other hazards. The Nature
13 What You ll Learn How thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes form. What the effects of severe weather are. How repetitive weather patterns can cause droughts, floods, and other hazards. The Nature
Third Grade Science Vocabulary Investigation Design & Safety
 recycle dispose reuse goggles data conclusion predict describe observe record identify investigate evidence analyze mass matter float sink attract force magnet magnetic magnetism pole pull push repel Third
recycle dispose reuse goggles data conclusion predict describe observe record identify investigate evidence analyze mass matter float sink attract force magnet magnetic magnetism pole pull push repel Third
Chapter 3: Weather Map. Weather Maps. The Station Model. Weather Map on 7/7/2005 4/29/2011
 Chapter 3: Weather Map Weather Maps Many variables are needed to described weather conditions. Local weathers are affected by weather pattern. We need to see all the numbers describing weathers at many
Chapter 3: Weather Map Weather Maps Many variables are needed to described weather conditions. Local weathers are affected by weather pattern. We need to see all the numbers describing weathers at many
Clouds and What They Mean
 Vocabulary and Writing Worksheet 1. Choose the best vocabulary word for each sentence and write it in the blank. dew point evaporation fog gas precipitation relative humidity a. Relative humidity refers
Vocabulary and Writing Worksheet 1. Choose the best vocabulary word for each sentence and write it in the blank. dew point evaporation fog gas precipitation relative humidity a. Relative humidity refers
Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze: Routing Considerations Table of Contents
 Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze: Routing Considerations Table of Contents Introduction Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze Description 2 3 Introduction Four Sea Breeze Quadrants (Figure 1) When considering a sea breeze and its
Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze: Routing Considerations Table of Contents Introduction Quadrant 1 Sea Breeze Description 2 3 Introduction Four Sea Breeze Quadrants (Figure 1) When considering a sea breeze and its
Clouds: What They Are and What They Mean. Susannah Lopez. Introduction to Meteorology. 2 December 2008
 Clouds: What They 1 Clouds: What They Are and What They Mean Susannah Lopez Introduction to Meteorology 2 December 2008 Clouds: What They 2 Clouds: What They Are and What They Mean Clouds are composed
Clouds: What They 1 Clouds: What They Are and What They Mean Susannah Lopez Introduction to Meteorology 2 December 2008 Clouds: What They 2 Clouds: What They Are and What They Mean Clouds are composed
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION THERMAL ENERGY
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION THERMAL ENERGY In general, when an object performs work on another object, it does not transfer all of its energy to that object. Some of the energy is lost as heat due to
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION THERMAL ENERGY In general, when an object performs work on another object, it does not transfer all of its energy to that object. Some of the energy is lost as heat due to
A Teaching Unit for Years 3 6 children
 A Teaching Unit for Years 3 6 children 1 SEREAD and ARGO: Concept Overview for Years 3-6 Teaching Programme This is the overview for the first part of the SEREAD programme link with ARGO. The overview
A Teaching Unit for Years 3 6 children 1 SEREAD and ARGO: Concept Overview for Years 3-6 Teaching Programme This is the overview for the first part of the SEREAD programme link with ARGO. The overview
UNIT 6a TEST REVIEW. 1. A weather instrument is shown below.
 UNIT 6a TEST REVIEW 1. A weather instrument is shown below. Which weather variable is measured by this instrument? 1) wind speed 3) cloud cover 2) precipitation 4) air pressure 2. Which weather station
UNIT 6a TEST REVIEW 1. A weather instrument is shown below. Which weather variable is measured by this instrument? 1) wind speed 3) cloud cover 2) precipitation 4) air pressure 2. Which weather station
Kindergarten Seasons and Weather Assessment
 Kindergarten Seasons and Weather Assessment 1a. Circle the pictures that represent the four seasons: snowman going to a teacher harvest fruits colorful flowers the beach 1b. Write the name of the season
Kindergarten Seasons and Weather Assessment 1a. Circle the pictures that represent the four seasons: snowman going to a teacher harvest fruits colorful flowers the beach 1b. Write the name of the season
Cumulifor m clouds develop as air slowly rises over Lake Powell in Utah.
 Cumulifor m clouds develop as air slowly rises over Lake Powell in Utah. Figure 6.1 Dew forms on clear nightswhen objects on the surface cool to a temperature below the dew point. If these beads of water
Cumulifor m clouds develop as air slowly rises over Lake Powell in Utah. Figure 6.1 Dew forms on clear nightswhen objects on the surface cool to a temperature below the dew point. If these beads of water
1. You are about to begin a unit on geology. Can anyone tell me what geology is? The study of the physical earth I.
 PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
Order of the Weather Experiments
 Order of the Weather Experiments 1. Staying Dry Towel in bottle--student i. Magic Air Pushing the stick down-- Student ii. Air Power Water in funnel--teacher 2. Tipping the Scale Weighing air--student
Order of the Weather Experiments 1. Staying Dry Towel in bottle--student i. Magic Air Pushing the stick down-- Student ii. Air Power Water in funnel--teacher 2. Tipping the Scale Weighing air--student
INTRODUCTION STORM CHRONOLOGY AND OBSERVATIONS
 THE MESOCYCLONE EVOLUTION OF THE WARREN, OKLAHOMA TORNADOES By Timothy P. Marshall and Erik N. Rasmussen (Reprinted from the 12th Conference on Severe Local Storms, American Meteorological Society, San
THE MESOCYCLONE EVOLUTION OF THE WARREN, OKLAHOMA TORNADOES By Timothy P. Marshall and Erik N. Rasmussen (Reprinted from the 12th Conference on Severe Local Storms, American Meteorological Society, San
The Clouds Outside My Window. National Weather Service NOAA
 The Clouds Outside My Window National Weather Service NOAA The Clouds Out My Window Written and illustrated by John Jensenius My window With help from Owlie Skywarn 1 The Clouds Outside My Window Whether
The Clouds Outside My Window National Weather Service NOAA The Clouds Out My Window Written and illustrated by John Jensenius My window With help from Owlie Skywarn 1 The Clouds Outside My Window Whether
