SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
|
|
|
- Bernard Bishop
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New cough; alteration in pre-existing cough; dyspnoea or worsening of previous dyspnoea; current pneumonia; symptoms from metastatic disease; paraneoplastic syndromes. 2. STAGING Staging should be recorded using the UICC, TNM, 7 th Edition 2009 definitions and the separate Veterans Administration Lung Group system which divides SCLC patients into either limited or extensive stages. Using current staging procedures, 30-40% of SCLC patients have limited stage SCLC. After the diagnosis of SCLC, accurate staging should be completed as expediently as possible. Limited Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer The original operational definition of limited disease was tumour quantity and configuration that could be encompassed by a "reasonable" radiotherapy treatment volume including the primary tumour site and the adjacent hilar, mediastinal and ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph nodes. The presence of massive intrathoracic tumour may preclude a "reasonable" thoracic radiotherapy volume and allow palliative therapy only. The tumour volume may change in response to chemotherapy and so regular review is mandatory. Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Disease beyond the limited stage criteria is defined as extensive stage. Patients with "regional" extensive stage disease (pleural effusion, contralateral supraclavicular nodes or cervical lymph nodes) have a prognosis that is intermediate between limited and extensive and may benefit from a limited stage type treatment plan. 3. HISTOPATHOLOGY WHO classification: Small cell carcinoma Intermediate cell type carcinoma Mixed small cell and non small cell carcinoma should be treated initially with chemotherapy for small cell component and then radiotherapy, depending on results. File Name: LU-02 Page 1 of 7 Date of Issue: April 2011
2 4. INVESTIGATIONS A full history and physical examination should precede any investigation. Initial investigations should include full blood count, serum biochemistry and C reactive protein; a chest X-ray and CT thorax and upper abdomen. Lung function testing (FEV1/FVC) should be performed. Because lesions thought to be lung cancer radiologically are sometimes shown to be a benign process and because of the difference in treatment for non-small cell and small cell lung cancer, histological or cytological verification of the diagnosis should be obtained wherever possible. Diagnostic procedures should be tailored to the individual patient and may include: i) Review of old chest X-rays to exclude a long-standing benign lesion or determine the rate of progression of a malignant lesion. ii) Bronchoscopy, biopsy of endobronchial lesions, brushings and washings, postbronchoscopy sputum cytology. iii) Percutaneous fine needle or core biopsy in selected cases where bronchoscopy unhelpful or via endoscopic bronchial or oesophageal ultrasound (EBUS / EUS) iv) Excisional or needle biopsy of readily accessible secondary deposits v) CT brain prior to commencing radical treatment All patients should be discussed at the lung cancer MDT meeting to confirm staging and histological diagnosis and to determine an appropriate management plan which should be recorded in the patient s notes. 5. CHEMOTHERAPY/ RADIOTHERAPY Limited stage disease: * CONSIDER CLINICAL TRIALS * Options include : a) Concurrent chemo-irradiation (1) : Leads to 5% improvement in 3 year survival (1) vs. sequential Limited disease PS 0, 1, or 2 Adequate pulmonary cardiac and renal function Disease volume that can safely be encompassed in a radical radiotherapy volume. Chemotherapy: Day 1: Cisplatin 80mg/m 2 IV Day 1 and 2: Etoposide 120mg/m 2 IV Every 21 days for 4 cycles File Name: LU-02 Page 2 of 7 Date of Issue: April 2011
3 If cisplatin contraindicated (GFR<50ml/min, significant ischaemic heart disease, previous major vascular episode, neuropathy): Day 1: Days 1, 2: Day 3: Carboplatin AUC 6 (Cockcroft-Gault) or AUC5 (measured GFR) Etoposide 120mg/m 2 IV Etoposide 240mg/m 2 orally Radiotherapy: Aim to start day 1 cycle 2 and no later than can be completed before end of last cycle of chemotherapy Gy in 20 fractions to a CT-planned volume. N.B. Thoracic irradiation should not be interrupted because of neutropenia (regardless of severity) in the absence of clinical evidence of infection. Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) should be given following completion of chemotherapy b) Sequential chemo-irradiation (2) Improved median survival from 11.6 to 15 months (2) Indication: PS 2-3 patients thought unlikely to tolerate concurrent treatment PS 0-1 patients with disease initially too bulky to encompass in a radical radiotherapy volume, and who have substantial tumour shrinkage following chemotherapy. Adequate pulmonary, cardiac, renal function to tolerate chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Chemotherapy: Day 1: Cisplatin 80mg/m 2 IV Day 1and 2: Etoposide 120mg/m 2 IV Every 21 days for 4 cycles If cisplatin contraindicated (GFR<50ml/min, significant ischaemic heart disease, previous major vascular episode, neuropathy): Carboplatin AUC 6 (Cockcroft-Gault) or AUC5 (measured GFR) Day 1 and 2: Etoposide 120mg/m 2 IV Every 21 days for 4 cycles File Name: LU-02 Page 3 of 7 Date of Issue: April 2011
4 Thoracic radiotherapy: 40Gy in 15 fractions AP/PA to include tumour and mediastinum or 45-50Gy in 20 fractions to CT-planned volume Aim to start no more than 4 weeks from day 1 of last cycle of chemotherapy. Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) should be considered and given concurrently with thoracic radiotherapy c) Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) (3) Improves 3 year survival from 15% to 20% and halves incidence of brain metastases from 50% to 25% Limited stage SCLC without evidence of progression on chemotherapy PS Gy in 10 fractions to whole brain Aim to start no more than 4 weeks from day 1 last cycle chemotherapy. NB must NOT be given concurrently with chemotherapy. N.B. Post op: Rarely patients with small cell carcinoma undergo surgery. If so, consideration should be given to 4 cycles of consolidation chemotherapy as detailed above, followed by prophylactic cranial irradiation and thoracic radiotherapy, all detailed above. Extensive stage disease: * CONSIDER CLINICAL TRIALS * Consider referral to Palliative Care for support and Information. a) First line palliative chemotherapy: Rationale (4,5) Median survival of 8 months using EP or CAV Extensive stage SCLC PS 0-2; Adequate renal, cardiac, and liver function to tolerate chemotherapy Day 1 Carboplatin AUC6 IV (AUC5 if EDTA GFR used) Days 1, 2: Etoposide 120mg/m 2 IV Every 21 days for up to 6 cycles if responding and well tolerated. File Name: LU-02 Page 4 of 7 Date of Issue: April 2011
5 If PS 3 consider Carboplatin AUC5 (Cockcroft-Gault) Etoposide 120 mg/m 2 IV d1, d2, 100 mg bd d3 In patients with poor renal function: Day 1 Adriamycin 40 mg/m 2 Day 1 Cyclophosphamide 750 mg/m 2 Days 1, 2 Etoposide 120 mg/m 2 IV Day 3 Etoposide 240 mg/m 2 orally b) Prophylactic cranial irradiation Improves 1 year survival from 13% to 27% (6) Extensive stage SCLC and evidence of some response to chemotherapy on chest x-ray. Good PS (0-2). Aim to start no more than 4-6 weeks from day 1 last cycle of chemotherapy 20Gy in 5 fractions to whole brain c) Second line chemotherapy: Selected patients of good PS (0-2) If >3 months since first line treatment: re-challenge with same first-line drugs If < 3 months since initial treatment: i) PS 0-1 Day 1 Cyclophosphamide 1000 mg/m 2 Day 1 Adriamycin 40 mg/m 2 Days 1 and 2 Etoposide 120 mg/m 2 IV Day 3 Etoposide 240 mg/m 2 orally ii) PS 2: Day 1 Cyclophosphamide 750mg/m 2 Day 1 Adriamycin 40mg/m 2, Day 1 Vincristine 1.4mg/m 2 (max 2mg) Every 21 days for 4-6 cycles depending on response. File Name: LU-02 Page 5 of 7 Date of Issue: April 2011
6 iii) In relapsed patients where re-treatment with first line regimen is not considered appropriate due to toxicities and in whom CAV is contra-indicated due to toxicities and who at the Oncologist s discretion are not fit for iv chemotherapy, consider: Oral Topotecan (7) 26 vs. 14 week median survival and improved symptom control vs. BSC (7) Regime: Topotecan 2.3mg /m 2 d1-5 q 21d orally up to 4 cycles * CONSIDER CLINICAL TRIALS * d) Palliative thoracic radiotherapy: Indications Progressive symptomatic disease during chemotherapy Symptomatic relapse in patient not fit for further chemotherapy 8Gy single fraction or 20Gy in 5 fractions over 5-7 days * CONSIDER CLINICAL TRIALS * e) Palliative radiotherapy to other sites: As per non-small cell lung cancer except: Fit patients who present with brain metastases from small cell lung cancer should be considered for chemotherapy as first line treatment with consolidation whole brain radiotherapy following this. References: (1) JP Pignon et al A meta-analysis of thoracic radiotherapy for small-cell lung cancer NEJM Volume 327: (2) PA Bunn et al Chemotherapy Alone or Chemotherapy with Chest Radiation Therapy in Limited Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann Intern Med May 1, 1987 vol. 106 no http:// (3) A Aupérin et al Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation for Patients with Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Complete Remission NEJM Volume 341: (4) BJ Roth et al Randomized study of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and vincristine versus etoposide and cisplatin versus alternation of these two regimens in extensive small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial of the South Eastern Cancer Study Group Journal of Clinical Oncology, Vol 10, File Name: LU-02 Page 6 of 7 Date of Issue: April 2011
7 (5) M Fukuoka et al Randomized Trial of Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, and Vincristine Versus Cisplatin and Etoposide Versus Alternation of These Regimens in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Journal of the National Cancer Institute, Vol. 83, No. 12, , June (6) B Slotman at al Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation in Extensive Small-Cell Lung Cancer NEJM Volume 357: (7) O Brien M et al Phase III Trial Comparing Supportive Care Alone with Supportive Care with Oral Topotecan in patients with Relapsed Small Cell Lug Cancer J Clin Oncol (34) Author: Signature:.. Chair: Signature:.. (on behalf of OHMMG) Date: Date: File Name: LU-02 Page 7 of 7 Date of Issue: April 2011
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Update on Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Welcome to Master Class for Oncologists Session 3: 2:45 PM - 3:30 PM Washington, DC March 28, 2009 Small Cell Lung Cancer: Best Practices & Recent Advances Speaker: Bruce E. Johnson, MD Professor of Medicine,
Welcome to Master Class for Oncologists Session 3: 2:45 PM - 3:30 PM Washington, DC March 28, 2009 Small Cell Lung Cancer: Best Practices & Recent Advances Speaker: Bruce E. Johnson, MD Professor of Medicine,
Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians
 Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians Background The Cancer Institute New South Wales Oncology Group Lung (NSWOG Lung) identified the need for the development
Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians Background The Cancer Institute New South Wales Oncology Group Lung (NSWOG Lung) identified the need for the development
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); [email protected] Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); [email protected] Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof.
 Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMA Summary of treatment approach * limited
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMA Summary of treatment approach * limited
Lung Cancer Treatment Guidelines
 Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of
 Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer
 Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Section 5 updated bullets 5.3 and 5.4 Section 6 updated
Guidelines for Management of Renal Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Section 5 updated bullets 5.3 and 5.4 Section 6 updated
REPORT ASCO 1998 LOS ANGELES : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group
 REPORT ASCO 1998 LOS ANGELES : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Educational session Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in
REPORT ASCO 1998 LOS ANGELES : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Educational session Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in
Stage I, II Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Stage I, II Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Best Results T1 (less 3 cm) N0 80% 5 year survival No Role Adjuvant Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Reduces Local Recurrence No Improvement in Survival 1 Staging Mediastinal
Stage I, II Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Best Results T1 (less 3 cm) N0 80% 5 year survival No Role Adjuvant Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Reduces Local Recurrence No Improvement in Survival 1 Staging Mediastinal
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline
 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Small cell Lung cancer New Chemotherapy options. Nicolas Mach, MD,PD
 Small cell Lung cancer New Chemotherapy options Nicolas Mach, MD,PD > 40 negative Phase III trials List of unsucessful drugs Pemetrexed, imatinib, bevacizumab, bcl-2 antagonist, ASCT, CASE PRESENTATION
Small cell Lung cancer New Chemotherapy options Nicolas Mach, MD,PD > 40 negative Phase III trials List of unsucessful drugs Pemetrexed, imatinib, bevacizumab, bcl-2 antagonist, ASCT, CASE PRESENTATION
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options. John Kuruvilla
 Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging
 The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging Peter Baik, DO Thoracic Surgery Cancer Treatment Centers of America Oklahoma Osteopathic Association 115th Annual Convention Financial Disclosures: None 2 Objectives
The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging Peter Baik, DO Thoracic Surgery Cancer Treatment Centers of America Oklahoma Osteopathic Association 115th Annual Convention Financial Disclosures: None 2 Objectives
Clinical Management Guideline Management of locally advanced or recurrent Renal cell carcinoma. Protocol for Planning and Treatment
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: LOCALLY ADVANCED OR METASTATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Patient information given at each stage following agreed information
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: LOCALLY ADVANCED OR METASTATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Patient information given at each stage following agreed information
Cesare Gridelli 1, Francesca Casaluce 2, Assunta Sgambato 2, Fabio Monaco 3, Cesare Guida 4
 Editorial Treatment of limited-stage small cell lung cancer in the elderly, chemotherapy vs. sequential chemoradiotherapy vs. concurrent chemoradiotherapy: that s the question Cesare Gridelli 1, Francesca
Editorial Treatment of limited-stage small cell lung cancer in the elderly, chemotherapy vs. sequential chemoradiotherapy vs. concurrent chemoradiotherapy: that s the question Cesare Gridelli 1, Francesca
Chapter 7: Lung Cancer
 Chapter 7: Lung Cancer Contents Chapter 7: Lung Cancer... 1 Small Cell... 2 Good PS + Limited stage... 2 Cisplatin/etoposide... 2 Concurrent chemotherapy + XRT... 2 Good / Intermediate PS... 2 Carboplatin
Chapter 7: Lung Cancer Contents Chapter 7: Lung Cancer... 1 Small Cell... 2 Good PS + Limited stage... 2 Cisplatin/etoposide... 2 Concurrent chemotherapy + XRT... 2 Good / Intermediate PS... 2 Carboplatin
Lung cancer LUNG CANCER. Box 1 Clinical signs
 22 LUNG CANCER Lung cancer Bronchial carcinoma refers to two distinct clinical entities small cell and non-small cell carcinoma. Although these conditions have much in common, with broadly similar presenting
22 LUNG CANCER Lung cancer Bronchial carcinoma refers to two distinct clinical entities small cell and non-small cell carcinoma. Although these conditions have much in common, with broadly similar presenting
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Network Chemotherapy Regimens
 Network Chemotherapy Regimens Lung Cancer Notes from the editor Thames Valley Cancer Network These protocols are available on the Network website www.tvcn.org.uk. Any correspondence about the protocols
Network Chemotherapy Regimens Lung Cancer Notes from the editor Thames Valley Cancer Network These protocols are available on the Network website www.tvcn.org.uk. Any correspondence about the protocols
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium pemetrexed 500mg infusion (Alimta ) No. (192/05) Eli Lilly 8 July 2005 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment of the above product and advises NHS
Scottish Medicines Consortium pemetrexed 500mg infusion (Alimta ) No. (192/05) Eli Lilly 8 July 2005 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment of the above product and advises NHS
Table of Contents. Data Supplement 1: Summary of ASTRO Guideline Statements. Data Supplement 2: Definition of Terms
 Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Aggressive lymphomas. Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital
 Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners
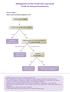 Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
What is neuroendocrine cervical cancer?
 Key Points: 1. Neuroendocrine cancer of the uterine cervix is a rare and aggressive disease. 2. Treatment for neuroendocrine cervical cancer is usually more intensive than that for most other types of
Key Points: 1. Neuroendocrine cancer of the uterine cervix is a rare and aggressive disease. 2. Treatment for neuroendocrine cervical cancer is usually more intensive than that for most other types of
Lung Tumours. Dr Emil Beltchev 07/03/2007 1
 Lung Tumours Dr Emil Beltchev 07/03/2007 1 Lung Cancer Primary carcinoma of the lung was an uncommon cancer until the 1930s. At that time a dramatic increase in the incidence of lung cancer began that
Lung Tumours Dr Emil Beltchev 07/03/2007 1 Lung Cancer Primary carcinoma of the lung was an uncommon cancer until the 1930s. At that time a dramatic increase in the incidence of lung cancer began that
4.8 Lung cancer. 4.8.5 In the UK, three fractionation regimens are most commonly used:
 4.8 Lung cancer 4.8.1 In 2005, both NICE (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence) and SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network) published guidelines on the management of lung cancer.
4.8 Lung cancer 4.8.1 In 2005, both NICE (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence) and SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network) published guidelines on the management of lung cancer.
B. Dingle MD, FRCPC, Brian Yaremko MD,FRCPC, R. Ash, MD, FRCPC, P. Truong, MD, FRCPC
 Lung Cancer B. Dingle MD, FRCPC, Brian Yaremko MD,FRCPC, R. Ash, MD, FRCPC, P. Truong, MD, FRCPC EPIDEMIOLOGY The estimated incidence of lung cancer in Canada for 2007 is 23,300 with 12,400 occurring in
Lung Cancer B. Dingle MD, FRCPC, Brian Yaremko MD,FRCPC, R. Ash, MD, FRCPC, P. Truong, MD, FRCPC EPIDEMIOLOGY The estimated incidence of lung cancer in Canada for 2007 is 23,300 with 12,400 occurring in
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Mesothelioma. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
 Mesothelioma William G. Richards, PhD Brigham and Women s Hospital Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma 2,000-3,000 cases per year (USA) Increasing incidence Asbestos (50-80%, decreasing) 30-40 year latency
Mesothelioma William G. Richards, PhD Brigham and Women s Hospital Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma 2,000-3,000 cases per year (USA) Increasing incidence Asbestos (50-80%, decreasing) 30-40 year latency
London Cancer. Mesothelioma Lung Protocols
 London Cancer Mesothelioma Lung Protocols Version 0.9 Contents 1. Staging... 3 2. Mesothelioma Summary of Chemotherapy Protocols... 4 3. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Protocols... 7 3.1. Pemetrexed (Alimta
London Cancer Mesothelioma Lung Protocols Version 0.9 Contents 1. Staging... 3 2. Mesothelioma Summary of Chemotherapy Protocols... 4 3. Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Protocols... 7 3.1. Pemetrexed (Alimta
Please see the LUCADA data manual v3.1.3, available in the downloads section
 National Lung Cancer Audit Frequently Asked Questions What dataset should be used? Please see the LUCADA data manual v3.1.3, available in the downloads section What does LUCADA stand for? LUCADA stands
National Lung Cancer Audit Frequently Asked Questions What dataset should be used? Please see the LUCADA data manual v3.1.3, available in the downloads section What does LUCADA stand for? LUCADA stands
The National Clinical Lung Cancer Audit (LUCADA)
 The National Clinical Lung Cancer Audit (LUCADA) DATA MANUAL Title: Version: 3.1.5 Date: September 2013 LUCADA Lung Cancer Audit VERSION HISTORY Version Date Issued Brief Summary of Change Owner s Name
The National Clinical Lung Cancer Audit (LUCADA) DATA MANUAL Title: Version: 3.1.5 Date: September 2013 LUCADA Lung Cancer Audit VERSION HISTORY Version Date Issued Brief Summary of Change Owner s Name
ST JOSEPH REGIONAL HEALTH CENTER LUNG CANCER ANALYSIS Incidence, Diagnosis, Treatment and Survival
 ST JOSEPH REGIONAL HEALTH CENTER LUNG CANCER ANALYSIS Incidence, Diagnosis, Treatment and Survival It is logical that the Cancer Program Committee choose to review the Lung Site, as Lung is the second
ST JOSEPH REGIONAL HEALTH CENTER LUNG CANCER ANALYSIS Incidence, Diagnosis, Treatment and Survival It is logical that the Cancer Program Committee choose to review the Lung Site, as Lung is the second
Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary
 TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
Carcinoma of the vagina is a relatively uncommon disease, affecting only about 2,000 women in
 EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
EVERYONE S GUIDE FOR CANCER THERAPY Malin Dollinger, MD, Ernest H. Rosenbaum, MD, Margaret Tempero, MD, and Sean Mulvihill, MD 4 th Edition, 2001 Vagina Jeffrey L. Stern, MD Carcinoma of the vagina is
Thames Valley Chemotherapy Regimens
 Chemotherapy Regimens Lung Cancer Notes from the editor These regimens are available on the Network website www.tvcn.org.uk. Any correspondence about the regimens should be addressed to: Sally Coutts,
Chemotherapy Regimens Lung Cancer Notes from the editor These regimens are available on the Network website www.tvcn.org.uk. Any correspondence about the regimens should be addressed to: Sally Coutts,
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer
 Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including anaplastic, gliosarcoma and glioblastoma multiforme)
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed when a course of chemotherapy is required to treat: PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed when a course of chemotherapy is required to treat: PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including
Lung cancer case study
 Change Presentation title and date in Footer dd.mm.yyyy Lung cancer case study Dr Jaishree Bhosle Consultant Medical Oncologist Change Presentation title and date in Footer dd.mm.yyyy 1 2 Part One Initial
Change Presentation title and date in Footer dd.mm.yyyy Lung cancer case study Dr Jaishree Bhosle Consultant Medical Oncologist Change Presentation title and date in Footer dd.mm.yyyy 1 2 Part One Initial
NCCN Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer V.1.2011 Update Meeting 07/09/10
 Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
An Overview of Lung Cancer Symptoms, Pathophysiology, And Treatment Linda H. Yoder
 CE Objectives and Evaluation Form appear on page 235. An Overview of Lung Cancer Symptoms, Pathophysiology, And Treatment Linda H. Yoder Patients with lung cancer can provide treatment challenges for even
CE Objectives and Evaluation Form appear on page 235. An Overview of Lung Cancer Symptoms, Pathophysiology, And Treatment Linda H. Yoder Patients with lung cancer can provide treatment challenges for even
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology. Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline
 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline Table of Contents Data Supplement 1: Summary of included
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline Table of Contents Data Supplement 1: Summary of included
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists
 Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
 Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
the standard of care 2009 5/1/2009 Mesothelioma: The standard of care take home messages PILC 2006 [email protected] Brussels, March 7, 2009
 Mesothelioma: The standard of care [email protected] Brussels, March 7, 2009 take home messages PILC 2006 All patients should receive adequate palliation of dyspnea and pain before starting chemotherapy
Mesothelioma: The standard of care [email protected] Brussels, March 7, 2009 take home messages PILC 2006 All patients should receive adequate palliation of dyspnea and pain before starting chemotherapy
a commitment in their practice to the roles and responsibilities of clinical oncologists X
 CLINICAL ONCOLOGY BLUEPRINT OF ASSESSMENT SYSTEM Good Medical Practice areas of curriculum - ST5 (Intermediate) Standards GMP criterion Workplace based assessment By the end of the third year of training
CLINICAL ONCOLOGY BLUEPRINT OF ASSESSMENT SYSTEM Good Medical Practice areas of curriculum - ST5 (Intermediate) Standards GMP criterion Workplace based assessment By the end of the third year of training
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Malignant Mesothelioma Current Approaches to a Difficult Problem. Raja M Flores, MD Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
 Malignant Mesothelioma Current Approaches to a Difficult Problem Raja M Flores, MD Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Clinical Presentation Insidious
Malignant Mesothelioma Current Approaches to a Difficult Problem Raja M Flores, MD Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Clinical Presentation Insidious
January 2013 LONDON CANCER NEW DRUGS GROUP RAPID REVIEW. Summary. Contents
 LONDON CANCER NEW DRUGS GROUP RAPID REVIEW Paclitaxel albumin (Abraxane ) as a substitute for docetaxel/paclitaxel for cancer Paclitaxel albumin (Abraxane ) as a substitute for docetaxel/ paclitaxel for
LONDON CANCER NEW DRUGS GROUP RAPID REVIEW Paclitaxel albumin (Abraxane ) as a substitute for docetaxel/paclitaxel for cancer Paclitaxel albumin (Abraxane ) as a substitute for docetaxel/ paclitaxel for
Prior Authorization Guideline
 Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: PS Inj - Alimta Therapeutic Class: Antineoplastic Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Antifolates Client: PS Inj Approval Date: 8/2/2004 Revision Date: 12/5/2006 I. BENEFIT
Prior Authorization Guideline Guideline: PS Inj - Alimta Therapeutic Class: Antineoplastic Agents Therapeutic Sub-Class: Antifolates Client: PS Inj Approval Date: 8/2/2004 Revision Date: 12/5/2006 I. BENEFIT
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners
 Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
Canine Lymphoma Frequently Asked Questions by Pet Owners What is lymphoma? The term lymphoma describes a diverse group of cancers in dogs that are derived from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer APPROVED BY THE NHMRC ON 18 MARCH 2004 The Cancer Council Australia 2004 ISBN Print: 1 86496 312 3 Online: 1 86496
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer APPROVED BY THE NHMRC ON 18 MARCH 2004 The Cancer Council Australia 2004 ISBN Print: 1 86496 312 3 Online: 1 86496
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal, D Landau, J Spicer
 Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
POLICY A. INDICATIONS
 Alimta (pemetrexed) Line(s) of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration Akamai Advantage Original Effective Date: 09/01/2007 Current Effective Date: 10/01/2015 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indications below
Alimta (pemetrexed) Line(s) of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration Akamai Advantage Original Effective Date: 09/01/2007 Current Effective Date: 10/01/2015 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indications below
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma
 Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC. Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai
 Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
5. Non small Cell Lung Cancer
 5. Non small Cell Lung Cancer Introduction The cancer registry in Sweden shows a continuous increase of lung cancer cases from 867 in 1958 when the registry started to 2 846 in 2000. The Swedish cancer
5. Non small Cell Lung Cancer Introduction The cancer registry in Sweden shows a continuous increase of lung cancer cases from 867 in 1958 when the registry started to 2 846 in 2000. The Swedish cancer
Surgeons Role in Symptom Management. A/Prof Cliff K. C. Choong Consultant Thoracic Surgeon Latrobe Regional Hospital GIPPSLAND
 Surgeons Role in Symptom Management A/Prof Cliff K. C. Choong Consultant Thoracic Surgeon Latrobe Regional Hospital GIPPSLAND Conditions PLEURAL Pleural effusion Pneumothorax ENDOBRONCHIAL Haemoptysis
Surgeons Role in Symptom Management A/Prof Cliff K. C. Choong Consultant Thoracic Surgeon Latrobe Regional Hospital GIPPSLAND Conditions PLEURAL Pleural effusion Pneumothorax ENDOBRONCHIAL Haemoptysis
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
A 32 year old woman comes to your clinic with neck masses for the last several weeks. Masses are discrete, non matted, firm and rubbery on
 A 32 year old woman comes to your clinic with neck masses for the last several weeks. Masses are discrete, non matted, firm and rubbery on examination. She also has fever, weight loss, and sweats. What
A 32 year old woman comes to your clinic with neck masses for the last several weeks. Masses are discrete, non matted, firm and rubbery on examination. She also has fever, weight loss, and sweats. What
