Update on Small Cell Lung Cancer
|
|
|
- Miles Webster
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Welcome to Master Class for Oncologists Session 3: 2:45 PM - 3:30 PM Washington, DC March 28, 2009 Small Cell Lung Cancer: Best Practices & Recent Advances Speaker: Bruce E. Johnson, MD Professor of Medicine, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Bruce E. Johnson has received consulting fees from Genzyme. Bruce E. Johnson receives patent royalties for a patent on epidermal growth factor receptor testing. Treatment Off Label/Investigational Discussion In accordance with Pri-Med Institute policy, faculty have been asked to disclose discussion of unlabeled or unapproved use(s) of drugs or devices during the course of their presentations. Pathology and Molecular Pathogenesis Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer 87% Small Cell Carcinoma 13% Small Cell Carcinoma >90% Variant (Combined Small Cell Carcinoma) <% Travis WD, et al. World Health Organisation Classification of Tumors. Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. 4th ed. WHO: Geneva, Switzerland;
2 Pathology and Molecular Pathogenesis Pathology and Molecular Pathogenesis: Smoking Markers of Neuroendocrine Differentiation Chromogrannin A Synaptophysin CD56 or Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule (NCAM) Travis WD, et al. World Health Organisation Classification of Tumors. Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. 4th ed. WHO: Geneva, Switzerland; Pathology and Molecular Pathogenesis: Smoking Pathology and Molecular Pathogenesis: Bcl-2 and Hedgehog Signaling Small Cell Lung is the Most Closely Linked with Cigarette Smoking >95% of Patient have a History of Cigarette Smoking Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Large Cell Carcinoma are Intermediate Approximately 80% of Patients have a History of Cigarette Smoking Adenocarcinoma is the Least Closely Linked to Cigarette Smoking 70% of Patients have a History of Cigarette Smoking Bcl-2 Overexpressed in Most Small Cell Lung Cancer Oral Bcl-2 Inhibitor, ABT-263 1, and an antisense nucleotide directed against Bcl-2, Oblimersen 2, are in Directed Phase I and II Trials for Patients with SCLC Hedgehog Signaling Present in Most Small Cell Lung Cancer 3 Systemic Hedgehog Signaling Antagonists are being Studied in Small Cell Lung Cancer in Phase I trials as well 1. Tse C, et al. Cancer Res. 2008;68(9): Rudin CM, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(6): Watkins DN, et al. Nature. 2003;422(6929): Presentation Treatment Lung Cancer Typically Presents in Patients after the Age of 50 and the Percentage of Women with SCLC has risen from 28% in the 1970s to 50% in 2002 The Symptoms and Signs of Lung Cancer are not Specific and are Commonly Found in Heavy Cigarette Smokers Govindan R, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(28):
3 Presentation Presentation; Paraneoplastic Syndromes Symptom or Sign Local Cough Percentage 50% Symptom or Sign Systemic Weight Loss Percentage 50% Syndrome Hyponatremia of Malignancy Protein Arginine Vasopressin and Atrial Natriuretic Peptide %Pts with SCLC 15 Dyspnea Chest Pain Hemoptysis Hoarseness 40% 35% 20% % Weakness Anorexia Paraneoplastic Syndrome Fever 40% 30% 15% % Hypercalcemia of Malignancy Ectopic ACTH Syndrome Acromegaly Parathyroid Hormone Related Peptide Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone <1% 3% <1% Presentation; Paraneoplastic Syndromes Sodium Serum SERUM LEVELS Feb-99 Mar-99 Apr-99 May-99 Jun-99 Jul-99 Treatment DATE ; Staging ; Staging Initial Evaluation: History Physical Examination, Complete blood counts, Chemistries including Liver Function Tests and Creatinine Imaging: Chest radiograph, Chest CT scan with Liver and Adrenals, Head MRI, Bone or PET Scan Diagnosis: Needle Aspiration of Chest Mass, Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy, or Mediastinoscopy Pathological Review by Experienced Pulmonary Pathologist The Staging Classification for These Patients Is a Simple Two-stage Veterans Administration Lung Study Group System, updated in 1989 by International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Limited Stage: Disease Confined to One Hemithorax with Regional Lymph Nodes including Either Ipsilateral or Bilateral Hilar, Mediastinal, and Supraclavicular Lymph Node Metastases and Without Ipsilateral Pleural Effusion That Fit Within a Tolerable Chest Radiation Field Extensive Stage: Disease Beyond these Boundaries 3
4 ; Metastatic Sites ; Prognostic Factors Bone-35% Liver-25% Bone Marrow-20% Brain-20% Extrathoracic Lymph Nodes-5% Subcutaneous Masses-5% Factors Consistently Reported Good Performance Status Limited Stage Disease Female Gender Caucasian Factors Inconsistently Reported Normal Serum Sodium Younger Age Absence of Liver or Brain Mets Normal Liver Function Tests 1. A patient presents with small cell lung cancer confined to the right upper lobe and mediastinum with adequate pulmonary reserve. Systemic combination chemotherapy with etoposide and cisplatin is recommended. The recommendations for chest radiotherapy are: 1. No chest radiotherapy is needed. 2. Chest radiotherapy should start with the first or second cycle of chemotherapy. 3. Chest radiotherapy should start with the third or fourth cycle of chemotherapy. 4. Chest radiotherapy should be given after the chemotherapy finishes.? : : Limited Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer BID randomize BID PCI Pretreatment 2 Years after Treatment Cisplatin - 80; Etoposide - 0 / Q 21 days in Sequential. Q28 days in Concurrent. PCI: 24 Gy 1.5 Gy BID to 45 Gy Takada M, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(14):
5 : : Limited Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer randomize BID QD PCI Platinum - 60; Etoposide / Cycle Q 21 days PCI: 25 Gy Takada M, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(14): Turrisi AT 3rd, et al. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(4): : : randomize CEV CEV CEV CEV QD CEV PE PCI CEV=Cyclo- 00; Epi 50; VCR 2.0 / Cycle Q 21 days PCI: 30 Gy PE=Cisplatin - 75; Etoposide - 0 / Cycle Q 21 days PCI: 30 Gy Turrisi AT 3rd, et al. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(4): Sundstrom S, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(24): : : Patients With Limited Stage SCLC Should Be Treated With Concurrent Chest Radiotherapy with Etoposide Plus Cisplatin. These Patients Lived Longer Than Patients Treated With Chemotherapy Alone. The Chest Radiotherapy Should Start with Cycle 1 or 2. The Chest Radiotherapy Should be Given Twice Daily over Three Weeks. Sundstrom S, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(24):
6 : Patients with a Solitary Pulmonary Nodule and a Diagnosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer Should Undergo Evaluation for Resection (2-3%) Patients Should have Mediastinoscopy Because 20% Will Have Positive Lymph Nodes Patients Should be Treated with Adjuvant Chemotherapy Following Resection Strand TE, et al. Thorax. 2006;61(8): A patient presents with small cell lung cancer confined to the right upper lobe and mediastinum with adequate pulmonary reserve. Systemic combination chemotherapy with etoposide and cisplatin is recommended. The recommendations for chest radiotherapy are: 1. No chest radiotherapy is needed. 2. Chest radiotherapy should start with the first or second cycle of chemotherapy. 3. Chest radiotherapy should start with the third or fourth cycle of chemotherapy. 4. Chest radiotherapy should be given after the chemotherapy finishes. 2. A patient presents with small cell lung cancer with involvement of the left upper lobe, mediastinum, and thoracic spine. Chemotherapy is recommended 1. Irinotecan plus cisplatin is more effective for patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer than etoposide plus cisplatin. 2. Etoposide cisplatin is as effective as other chemotherapy regimens that have been tested thus far. 3. Giving high doses of chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow transplantation will prolong their survival. 4. Adding the antiangiogenic agent, Thalidomide, to combination chemotherapy prolongs survival. Noda K, et al. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(2): Humblet Y, et al. J Clin Oncol. 1987;5(12): : Irinotecan for : Irinotecan for 144 Patients with Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Randomized to 4 cycles of Irinotecan 60 mg/m2 IV on Days 1, 8, and 15 plus Cisplatin 60 mg/m2 on Day 1 on 28 day cycle versus Etoposide 0 mg/m2 on Days 1, 2, and 3 plus Cisplatin 80 mg/m2 on Day 1 every 3 weeks Followed for Response, Time to Progression and von Pawel, et al. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:.658 Noda K, et al. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(2):
7 : Irinotecan for : Strategies for Number of Patients 154 Japanese NEJM Caucasian JCO Caucasian ASC Caucasian JCO 2008 Regimens of Etoposide Cisplatin versus Irinotecan Cisplatin Regimens Etop 0 mg X 3 and CP 80 mg q 3 wks versus Irinotecan 60 mg q wk X 3 and CP 60 mg q 4 wks Etop 120 mg X 3 and CP 60 mg q 3 wks Irinotecan 65 mg q wk X 2 and CP 30 mg q wk X 2 every 3 wks Etop 0 mg X 3 and CP 80 mg q 3 wks versus Irinotecan 60 mg q wk X 3 and CP 60 mg q 4 wks Oral Etop 120 mg X5 and Carbo AUC of 4 q 3 wks versus Irinotecan 175 mg/m2 IV and Carbo AUC of 4 every 3 weeks Median P= Mo 9.3 MO 8.9 Mo 9.7 Mo 7.1 Mo 8.5 Mo 1 Year 38% 58% 35% 35% 33% 39% Not Rep Not Rep Noda K, et al. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(2): Hanna N, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(13): Natale RB, et al. Presented at: American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting; Abstract 7512, Hermes et al. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: Given Oral Topotecan plus cisplatin versus Etoposide plus Cisplatin Limited and Extensive Stage Patients treated with Transplant Doses of Ifosfamide, Carboplatin and Etoposide (Tx) versus standard doses of the same drugs Patients with limited and extensive stage treated with etoposide and cisplatin +/- thalidomide 3 Eckardt JR, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(13):2044, 2006, Leyvraz S, et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;0(8): Siow-Ming L, et al. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2(8):S306-S307. : Patients With Should Be Treated With 2 Drugs Which Produce Moderate Myelosuppression. Etoposide Cisplatin remains the Standard Treatment. Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Intensive Chemotherapy (Adding Paclitaxel or Autologous Transplant Doses) Do Not Live Longer Than Patients Treated with Standard Doses. A patient presents with small cell lung cancer with involvement of the left upper lobe, mediastinum, and thoracic spine. Chemotherapy is recommended. 1. Irinotecan plus cisplatin is more effective for patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer than etoposide plus cisplatin. 2. Etoposide cisplatin is as effective as other chemotherapy regimens that have been tested thus far. 3. Giving high doses of chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow transplantation will prolong their survival. 4. Adding the antiangiogenic agent, Thalidomide to combination chemotherapy prolongs survival. Noda K, et al. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(2): Humblet Y, et al. J Clin Oncol. 1987;5(12): A patient with limited stage small cell lung cancer undergoes chemotherapy and chest radiotherapy. The radiographic imaging after the completion of treatment shows a complete response. The considerations about using prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small cell lung cancer and a response to treatment include: 1. Prophylactic cranial irradiation is recommended for only patients with limited stage small cell lung cancer with a response to treatment 2. Prophylactic cranial irradiation is recommended for patients with both limited and extensive stage small cell lung cancer after completion of their treatment 3. Prophylactic cranial irradiation has no impact on survival but reduces the chance of getting brain metastases 4. Prophylactic cranial irradiation can reduce the risk of brain metastases and prolong survival 7
8 : Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation for Limited Stage : Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation for Extensive Stage Auperin, et al. N Engl J Med. 1999;341: Slotman B, et al. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(7): : Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Pts With SCLC Have a 60-80% Actuarial Risk of Developing Brain Metastases Within 2 Years After the Start of Treatment PCI Has Been Shown to Prolong for Patients with both Limited and Extensive SCLC with a Response to Chemotherapy PCI ( cgy) Administered at the Time of Complete Remission Can Reduce the Chance of Developing the Brain Metastases by 50-67% A patient with limited stage small cell lung cancer undergoes chemotherapy and chest radiotherapy. The radiographic imaging after the completion of treatment shows a complete response. The considerations about using prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small cell lung cancer and a response to treatment include: 1. Prophylactic cranial irradiation is recommended for only patients with limited stage small cell lung cancer with a response to treatment 2. Prophylactic cranial irradiation is recommended for patients with both limited and extensive stage small cell lung cancer after completion of their treatment 3. Prophylactic cranial irradiation has no impact on survival but reduces the chance of getting brain metastases 4. Prophylactic cranial irradiation can reduce the risk of brain metastases and prolong survival : Relapsed Disease 211 Patients with Sensitive Relapsed SCLC (Complete or Partial Response and off Chemotherapy for > 60 Days) Randomized to Either Topotecan 1.5 mg/m2/day IV on Days 1-5 or Standard Doses of Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, and Vincristine (CAV) Followed for Response, Time to Progression and von Pawel, et al. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:.658 8
9 : Relapsed Disease : Relapsed Disease 141 Patients with Relapsed SCLC not Deemed to be Candidates for Further Intravenous Chemotherapy Randomized to Either Topotecan 2.3 mg/m2/day PO on Days 1-5 or Best Supportive Care Followed for Response, Time to Progression and von Pawel, et al. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:.658 O Brien ME, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(34): : Relapsed Disease O Brien ME, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(34): Questions & Answers Thank you for attending Master Class for Oncologists? 9
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed in the management of: SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient information given at each stage following agreed information pathway 1. DIAGNOSIS New
Stage I, II Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Stage I, II Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Best Results T1 (less 3 cm) N0 80% 5 year survival No Role Adjuvant Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Reduces Local Recurrence No Improvement in Survival 1 Staging Mediastinal
Stage I, II Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Best Results T1 (less 3 cm) N0 80% 5 year survival No Role Adjuvant Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Reduces Local Recurrence No Improvement in Survival 1 Staging Mediastinal
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof.
 Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMA Summary of treatment approach * limited
Corso Integrato di Clinica Medica ONCOLOGIA MEDICA AA 2010-2011 LUNG CANCER. VIII. THERAPY. V. SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Prof. Alberto Riccardi SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMA Summary of treatment approach * limited
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); [email protected] Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); [email protected] Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Small cell Lung cancer New Chemotherapy options. Nicolas Mach, MD,PD
 Small cell Lung cancer New Chemotherapy options Nicolas Mach, MD,PD > 40 negative Phase III trials List of unsucessful drugs Pemetrexed, imatinib, bevacizumab, bcl-2 antagonist, ASCT, CASE PRESENTATION
Small cell Lung cancer New Chemotherapy options Nicolas Mach, MD,PD > 40 negative Phase III trials List of unsucessful drugs Pemetrexed, imatinib, bevacizumab, bcl-2 antagonist, ASCT, CASE PRESENTATION
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline
 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians
 Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians Background The Cancer Institute New South Wales Oncology Group Lung (NSWOG Lung) identified the need for the development
Treatment Algorithms for the Management of Lung Cancer in NSW Guide for Clinicians Background The Cancer Institute New South Wales Oncology Group Lung (NSWOG Lung) identified the need for the development
REPORT ASCO 1998 LOS ANGELES : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group
 REPORT ASCO 1998 LOS ANGELES : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Educational session Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in
REPORT ASCO 1998 LOS ANGELES : LUNG CANCER Johan F. Vansteenkiste, MD, PhD, Univ. Hospital and Leuven Lung Cancer Group Educational session Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in
Lung Cancer Treatment Guidelines
 Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of
 Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
B. Dingle MD, FRCPC, Brian Yaremko MD,FRCPC, R. Ash, MD, FRCPC, P. Truong, MD, FRCPC
 Lung Cancer B. Dingle MD, FRCPC, Brian Yaremko MD,FRCPC, R. Ash, MD, FRCPC, P. Truong, MD, FRCPC EPIDEMIOLOGY The estimated incidence of lung cancer in Canada for 2007 is 23,300 with 12,400 occurring in
Lung Cancer B. Dingle MD, FRCPC, Brian Yaremko MD,FRCPC, R. Ash, MD, FRCPC, P. Truong, MD, FRCPC EPIDEMIOLOGY The estimated incidence of lung cancer in Canada for 2007 is 23,300 with 12,400 occurring in
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary
 TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
TUMOURS OF THE LUNG Primary -Benign - Malignant Secondary The incidence of lung cancer has been increasing almost logarithmically and is now reaching epidemic levels. The overall cure rate is very low
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA
 Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Neoplasms of the LUNG and PLEURA 2015-2016 FCDS Educational Webcast Series Steven Peace, BS, CTR September 19, 2015 2015 Focus o Anatomy o SSS 2000 o MPH Rules o AJCC TNM 1 Case 1 Case Vignette HISTORY:
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer. Mark A. Socinski, MD
 Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Epidemiology, Staging and Treatment of Lung Cancer Mark A. Socinski, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Program Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of
Lung Cancer: More than meets the eye
 Lung Cancer Education Program November 23, 2013 Lung Cancer: More than meets the eye Shantanu Banerji MD, FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Shantanu Banerji Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
Lung Cancer Education Program November 23, 2013 Lung Cancer: More than meets the eye Shantanu Banerji MD, FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Shantanu Banerji Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
Aggressive lymphomas. Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital
 Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
Mesothelioma. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
 Mesothelioma William G. Richards, PhD Brigham and Women s Hospital Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma 2,000-3,000 cases per year (USA) Increasing incidence Asbestos (50-80%, decreasing) 30-40 year latency
Mesothelioma William G. Richards, PhD Brigham and Women s Hospital Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma 2,000-3,000 cases per year (USA) Increasing incidence Asbestos (50-80%, decreasing) 30-40 year latency
Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART
 Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART Goals Discuss treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer: New and old Discuss new developments in personalized
Harmesh Naik, MD. Hope Cancer Clinic HOW DO I MANAGE STAGE 4 NSCLC IN 2012: STATE OF THE ART Goals Discuss treatment options for stage 4 lung cancer: New and old Discuss new developments in personalized
Lung Tumours. Dr Emil Beltchev 07/03/2007 1
 Lung Tumours Dr Emil Beltchev 07/03/2007 1 Lung Cancer Primary carcinoma of the lung was an uncommon cancer until the 1930s. At that time a dramatic increase in the incidence of lung cancer began that
Lung Tumours Dr Emil Beltchev 07/03/2007 1 Lung Cancer Primary carcinoma of the lung was an uncommon cancer until the 1930s. At that time a dramatic increase in the incidence of lung cancer began that
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer John delcharco, MD (Statistics based on CVMC data 2009-2013) Statistics Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer John delcharco, MD (Statistics based on CVMC data 2009-2013) Statistics Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates
Lung cancer LUNG CANCER. Box 1 Clinical signs
 22 LUNG CANCER Lung cancer Bronchial carcinoma refers to two distinct clinical entities small cell and non-small cell carcinoma. Although these conditions have much in common, with broadly similar presenting
22 LUNG CANCER Lung cancer Bronchial carcinoma refers to two distinct clinical entities small cell and non-small cell carcinoma. Although these conditions have much in common, with broadly similar presenting
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
 Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma
 Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
Lung Cancer and Mesothelioma Robert Kratzke, M.D. John C. Skoglund Professor of Lung Cancer Research Section of Heme/Onc/Transplant Department of Medicine University of Minnesota Medical School Malignant
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options. John Kuruvilla
 Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease Specific Biology and Treatment Options John Kuruvilla My Disclaimer This is where I work Objectives Pathobiology what makes HL different Diagnosis Staging Treatment Philosophy
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
NCCN Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer V.1.2011 Update Meeting 07/09/10
 Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
Guideline Page and Request NSCL-3 Stage IA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation. Stage IB, IIA, margins positive delete the recommendation for chemoradiation + Stage IIA, Stage
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Management of stage III A-B of NSCLC. Hamed ALHusaini Medical Oncologist
 Management of stage III A-B of NSCLC Hamed ALHusaini Medical Oncologist Global incidence, CA cancer J Clin 2011;61:69-90 Stage III NSCLC Includes heterogeneous group of patients with differences in the
Management of stage III A-B of NSCLC Hamed ALHusaini Medical Oncologist Global incidence, CA cancer J Clin 2011;61:69-90 Stage III NSCLC Includes heterogeneous group of patients with differences in the
Metastatic Breast Cancer 201. Carolyn B. Hendricks, MD October 29, 2011
 Metastatic Breast Cancer 201 Carolyn B. Hendricks, MD October 29, 2011 Overview Is rebiopsy necessary at the time of recurrence or progression of disease? How dose a very aggressive treatment upfront compare
Metastatic Breast Cancer 201 Carolyn B. Hendricks, MD October 29, 2011 Overview Is rebiopsy necessary at the time of recurrence or progression of disease? How dose a very aggressive treatment upfront compare
People Living with Cancer
 Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
How To Treat Lung Cancer At Cleveland Clinic
 Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists
 Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
Pediatric Oncology for Otolaryngologists Frederick S. Huang, M.D. Division of Hematology/Oncology Department of Pediatrics The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation to Department
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Chapter 7: Lung Cancer
 Chapter 7: Lung Cancer Contents Chapter 7: Lung Cancer... 1 Small Cell... 2 Good PS + Limited stage... 2 Cisplatin/etoposide... 2 Concurrent chemotherapy + XRT... 2 Good / Intermediate PS... 2 Carboplatin
Chapter 7: Lung Cancer Contents Chapter 7: Lung Cancer... 1 Small Cell... 2 Good PS + Limited stage... 2 Cisplatin/etoposide... 2 Concurrent chemotherapy + XRT... 2 Good / Intermediate PS... 2 Carboplatin
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
An Overview of Lung Cancer Symptoms, Pathophysiology, And Treatment Linda H. Yoder
 CE Objectives and Evaluation Form appear on page 235. An Overview of Lung Cancer Symptoms, Pathophysiology, And Treatment Linda H. Yoder Patients with lung cancer can provide treatment challenges for even
CE Objectives and Evaluation Form appear on page 235. An Overview of Lung Cancer Symptoms, Pathophysiology, And Treatment Linda H. Yoder Patients with lung cancer can provide treatment challenges for even
Lungenkrebs. Lungenkrebs Häufigkeit
 Lungenkrebs Prof. Dr. E.W. Russi Pneumologie 1.9.2008 Lungenkrebs Häufigkeit The Principles and Practice of Medicine William Osler New York D. Appleton and Company 1892 Section IV DISEASE OF THE RESPIRATORY
Lungenkrebs Prof. Dr. E.W. Russi Pneumologie 1.9.2008 Lungenkrebs Häufigkeit The Principles and Practice of Medicine William Osler New York D. Appleton and Company 1892 Section IV DISEASE OF THE RESPIRATORY
Case Number: RT2009-114(M) Potential Audiences: Intent Doctor, Oncology Special Nurse, Resident Doctor
 Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Post Full-Course Chemotherapy with Residual Locoregional Cancer Disease: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-114(M) Potential
Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Post Full-Course Chemotherapy with Residual Locoregional Cancer Disease: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-114(M) Potential
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC. Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai
 Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
Maintenance therapy in in Metastatic NSCLC Dr Amit Joshi Associate Professor Dept. Of Medical Oncology Tata Memorial Centre Mumbai Definition of Maintenance therapy The U.S. National Cancer Institute s
Tricia Cox on 7/18/2012 at Oncology Center. Sarah Randolf. Female
 SAMPLE This Survivorship Care Plan will facilitate cancer care following active treatment. It may include important contact information, a treatment summary, recommendations for follow-up care testing,
SAMPLE This Survivorship Care Plan will facilitate cancer care following active treatment. It may include important contact information, a treatment summary, recommendations for follow-up care testing,
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer
 Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
What is neuroendocrine cervical cancer?
 Key Points: 1. Neuroendocrine cancer of the uterine cervix is a rare and aggressive disease. 2. Treatment for neuroendocrine cervical cancer is usually more intensive than that for most other types of
Key Points: 1. Neuroendocrine cancer of the uterine cervix is a rare and aggressive disease. 2. Treatment for neuroendocrine cervical cancer is usually more intensive than that for most other types of
Cesare Gridelli 1, Francesca Casaluce 2, Assunta Sgambato 2, Fabio Monaco 3, Cesare Guida 4
 Editorial Treatment of limited-stage small cell lung cancer in the elderly, chemotherapy vs. sequential chemoradiotherapy vs. concurrent chemoradiotherapy: that s the question Cesare Gridelli 1, Francesca
Editorial Treatment of limited-stage small cell lung cancer in the elderly, chemotherapy vs. sequential chemoradiotherapy vs. concurrent chemoradiotherapy: that s the question Cesare Gridelli 1, Francesca
Male. Female. Death rates from lung cancer in USA
 Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
How To Know If You Have Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Lung cancer Lung cancer TABLE 85 1. MALIGNANT PULMONARY NEOPLASMS INCIDENCE (%) Common 99 Non small cell lung cancer ~75 Adenocarcinoma ~35 Squamous cell carcinoma ~30 Large cell carcinoma ~10 Small cell
Lung cancer Lung cancer TABLE 85 1. MALIGNANT PULMONARY NEOPLASMS INCIDENCE (%) Common 99 Non small cell lung cancer ~75 Adenocarcinoma ~35 Squamous cell carcinoma ~30 Large cell carcinoma ~10 Small cell
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners
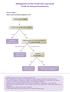 Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
Management of n-small Cell Lung Cancer Guide for General Practitioners Clinical Stage I Cancer only in one lobe of lung and
How To Treat Lung Cancer
 Case introduction 陳 先 生, 71y/0 96/10/9, Received TURP for BPH at 仁 愛 醫 院, pre-surgery CXR showed an abnormal mass over LUL. 96/10/19 TMUH, He went to Dr. 鍾 OPD for help Abnormal CXR finding Arrange chest
Case introduction 陳 先 生, 71y/0 96/10/9, Received TURP for BPH at 仁 愛 醫 院, pre-surgery CXR showed an abnormal mass over LUL. 96/10/19 TMUH, He went to Dr. 鍾 OPD for help Abnormal CXR finding Arrange chest
MOH Policy for dispensing NEOPLASTIC DISEASES DRUGS
 MOH Policy for dispensing NEOPLASTIC DISEASES DRUGS All prescriptions for antineoplastic drugs must be accompanied by the MOH special form. All the attachments mentioned on this form shall be submitted
MOH Policy for dispensing NEOPLASTIC DISEASES DRUGS All prescriptions for antineoplastic drugs must be accompanied by the MOH special form. All the attachments mentioned on this form shall be submitted
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide
 What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
ADJUVANT TREATMENT CLINICAL EVALUATION NEOADJUVANT TREATMENT
 te: Consider Clinical Trials as treatment options for eligible patients. Referral to a center with both pediatric oncology and orthopedic surgery is essential. CLINICAL EVALUATION This practice algorithm
te: Consider Clinical Trials as treatment options for eligible patients. Referral to a center with both pediatric oncology and orthopedic surgery is essential. CLINICAL EVALUATION This practice algorithm
PET/CT in Lung Cancer
 PET/CT in Lung Cancer Rodolfo Núñez Miller, M.D. Nuclear Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging Section Division of Human Health International Atomic Energy Agency Vienna, Austria GLOBOCAN 2012 #1 #3 FDG-PET/CT
PET/CT in Lung Cancer Rodolfo Núñez Miller, M.D. Nuclear Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging Section Division of Human Health International Atomic Energy Agency Vienna, Austria GLOBOCAN 2012 #1 #3 FDG-PET/CT
Lung cancer is not just one disease. There are two main types of lung cancer:
 1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
1. What is lung cancer? 2. How common is lung cancer? 3. What are the risk factors for lung cancer? 4. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? 5. How is lung cancer diagnosed? 6. What are the available
The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging
 The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging Peter Baik, DO Thoracic Surgery Cancer Treatment Centers of America Oklahoma Osteopathic Association 115th Annual Convention Financial Disclosures: None 2 Objectives
The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging Peter Baik, DO Thoracic Surgery Cancer Treatment Centers of America Oklahoma Osteopathic Association 115th Annual Convention Financial Disclosures: None 2 Objectives
Schedule: Drug Dose iv/infusion/oral q Carboplatin AUC 5 500mls 5% dex/1hr Day 1 Gemcitabine 1200mg/m 2 200mls N. Saline/30mins Days 1 & 8
 Carboplatin/Gemcitabine Lung Cancer (non-small cell) - Advanced Carboplatin AUC 5 500mls 5% dex/1hr Day 1 Gemcitabine 1200mg/m 2 200mls N. Saline/30mins Days 1 & 8 Cycle frequency: Every three weeks Total
Carboplatin/Gemcitabine Lung Cancer (non-small cell) - Advanced Carboplatin AUC 5 500mls 5% dex/1hr Day 1 Gemcitabine 1200mg/m 2 200mls N. Saline/30mins Days 1 & 8 Cycle frequency: Every three weeks Total
Lung cancer case study
 Change Presentation title and date in Footer dd.mm.yyyy Lung cancer case study Dr Jaishree Bhosle Consultant Medical Oncologist Change Presentation title and date in Footer dd.mm.yyyy 1 2 Part One Initial
Change Presentation title and date in Footer dd.mm.yyyy Lung cancer case study Dr Jaishree Bhosle Consultant Medical Oncologist Change Presentation title and date in Footer dd.mm.yyyy 1 2 Part One Initial
Extrapleural Pneumonectomy for Malignant Mesothelioma: Pro. Joon H. Lee 9/17/2012
 Extrapleural Pneumonectomy for Malignant Mesothelioma: Pro Joon H. Lee 9/17/2012 Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (Epidemiology) Incidence: 7/mil (Japan) to 40/mil (Australia) Attributed secondary to asbestos
Extrapleural Pneumonectomy for Malignant Mesothelioma: Pro Joon H. Lee 9/17/2012 Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (Epidemiology) Incidence: 7/mil (Japan) to 40/mil (Australia) Attributed secondary to asbestos
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015
 Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
Low dose capecitabine is effective and relatively nontoxic in breast cancer treatment.
 1 Low dose capecitabine is effective and relatively nontoxic in breast cancer treatment. John T. Carpenter, M.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham NP 2508 1720 Second Avenue South Birmingham, AL 35294-3300
1 Low dose capecitabine is effective and relatively nontoxic in breast cancer treatment. John T. Carpenter, M.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham NP 2508 1720 Second Avenue South Birmingham, AL 35294-3300
Summary of treatment benefits
 Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
Risk Management Plan PEMETREXED Powder for concentrate for Solution for infusion Pemetrexed is also indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non small cell
Sternotomy and removal of the tumor
 Sternotomy and removal of the tumor All thymomas originate from epithelial thymic cells 4% of them consist of a pure population of epithelial cells Most have mixed populations of lymphoid cells to a
Sternotomy and removal of the tumor All thymomas originate from epithelial thymic cells 4% of them consist of a pure population of epithelial cells Most have mixed populations of lymphoid cells to a
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies
 Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
Activity of pemetrexed in thoracic malignancies Results of phase III clinical studies of pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer show benefit P emetrexed (Alimta) is
Survival analysis of 220 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer
 窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
窑 Original Article 窑 Chinese Journal of Cancer Survival analysis of 22 patients with completely resected stage II non small cell lung cancer Yun Dai,2,3, Xiao Dong Su,2,3, Hao Long,2,3, Peng Lin,2,3, Jian
Case Number: RT2009-124(M) Potential Audiences: Intent Doctor, Oncology Special Nurse, Resident Doctor
 Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials)
 ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials) 3 Integrated Trials Testing Targeted Therapy in Early Stage Lung Cancer Part of NCI s Precision Medicine Effort in
ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials) 3 Integrated Trials Testing Targeted Therapy in Early Stage Lung Cancer Part of NCI s Precision Medicine Effort in
The National Clinical Lung Cancer Audit (LUCADA)
 The National Clinical Lung Cancer Audit (LUCADA) DATA MANUAL Title: Version: 3.1.5 Date: September 2013 LUCADA Lung Cancer Audit VERSION HISTORY Version Date Issued Brief Summary of Change Owner s Name
The National Clinical Lung Cancer Audit (LUCADA) DATA MANUAL Title: Version: 3.1.5 Date: September 2013 LUCADA Lung Cancer Audit VERSION HISTORY Version Date Issued Brief Summary of Change Owner s Name
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium pemetrexed 500mg infusion (Alimta ) No. (192/05) Eli Lilly 8 July 2005 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment of the above product and advises NHS
Scottish Medicines Consortium pemetrexed 500mg infusion (Alimta ) No. (192/05) Eli Lilly 8 July 2005 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment of the above product and advises NHS
LUNG CANCER. FCDS 2011 Educational Webcast Series November 17, 2011
 LUNG CANCER FCDS 2011 Educational Webcast Series November 17, 2011 Judy Bonner, RN, MS, CTR and Lynne Pearson, CTR, LHRM Steven Peace, CTR Updated for 2011 Requirements and CSv02.03.02 1 Presentation Outline
LUNG CANCER FCDS 2011 Educational Webcast Series November 17, 2011 Judy Bonner, RN, MS, CTR and Lynne Pearson, CTR, LHRM Steven Peace, CTR Updated for 2011 Requirements and CSv02.03.02 1 Presentation Outline
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology. Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline
 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline Table of Contents Data Supplement 1: Summary of included
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline Table of Contents Data Supplement 1: Summary of included
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
