Small cell lung cancer
|
|
|
- Juniper Rich
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the body when breathing in and take out carbon dioxide when breathing out. Each lung has sections called lobes. The left lung has two lobes. The right lung, which is slightly larger, has three. A thin membrane called the pleura surrounds the lungs. Two tubes called bronchi lead from the trachea (windpipe) to the right and left lungs. The bronchi are sometimes also involved in lung cancer. Small tubes called bronchioles and tiny air sacs called alveoli make up the inside of the lungs.
2 There are two types of lung cancer: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. This summary provides information on small cell lung cancer. (See the PDQ summary on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment for more information.) There are two types of small cell lung cancer.
3 These two types include many different types of cells. The cancer cells of each type grow and spread in different ways. The types of small cell lung cancer are named for the kinds of cells found in the cancer and how the cells look when viewed under a microscope: Small cell carcinoma (oat cell cancer). Combined small cell carcinoma. Smoking tobacco is the major risk factor for developing small cell lung cancer. Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn t mean that you will not get cancer. People who think they may be at risk should discuss this with their doctor. Cigarette smoking is the most common cause of lung cancer. Risk factors for small cell lung cancer include: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes now or in the past. Being exposed to secondhand smoke. Being exposed to asbestos or radon. Possible signs of small cell lung cancer include coughing, chest pain, and shortness of breath. These and other symptoms may be caused by small cell lung cancer. Other conditions may cause the same symptoms. A doctor should be consulted if any of the following problems occur: A cough that doesn t go away. Shortness of breath. Chest pain that doesn t go away. Wheezing. Coughing up blood. Hoarseness. Swelling of the face and neck. Loss of appetite. Weight loss for no known reason. Unusual tiredness. Tests and procedures that examine the lungs are used to detect (find), diagnose, and stage small cell lung cancer. The following tests and procedures may be used: Chest x-ray: An x-ray of the organs and bones inside the chest. An x-ray is a type of energy beam that can go through the body and onto film, making a picture of areas inside the body.
4 X-ray of the chest. X-rays are used to take pictures of organs and bones of the chest. X-rays pass through the patient onto film. Physical exam and history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient s health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken. CT scan (CAT scan) of the brain, chest, and abdomen: A procedure that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, taken from different angles. The pictures are made by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography. PET scan (positron emission tomography scan): A procedure to find malignant tumor cells in the body. A small amount of radioactive glucose (sugar) is injected into a vein. The PET scanner rotates around the body and makes a picture of where glucose is being used in the body. Malignant tumor cells show up brighter in the picture because they are more active and take up more glucose than normal cells do.
5 PET (positron emission tomography) scan. The patient lies on a table that slides through the PET machine. The head rest and white strap help the patient lie still. A small amount of radioactive glucose (sugar) is injected into the patient's vein, and a scanner makes a picture of where the glucose is being used in the body. Cancer cells show up brighter in the picture because they take up more glucose than normal cells do. Sputum cytology: A microscope is used to check for cancer cells in the sputum (mucus coughed up from the lungs). Bronchoscopy: A procedure to look inside the trachea and large airways in the lung for abnormal areas. A bronchoscope is inserted through the nose or mouth into the trachea and lungs. A bronchoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing. It may also have a tool to remove tissue samples, which are checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.
6 Bronchoscopy. A bronchoscope is inserted through the mouth, trachea, and major bronchi into the lung, to look for abnormal areas. A bronchoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing. It may also have a cutting tool. Tissue samples may be taken to be checked under a microscope for signs of disease. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy of the lung: The removal of tissue or fluid from the lung using a thin needle. A CT scan, ultrasound, or other imaging procedure is used to locate the abnormal tissue or fluid in the lung. A small incision may be made in the skin where the biopsy needle is inserted into the abnormal tissue or fluid. A sample is removed with the needle and sent to the laboratory. A pathologist then views the sample under a microscope to look for cancer cells. A chest x-ray is done after the procedure to make sure no air is leaking from the lung into the chest. Lung biopsy. The patient lies on a table that slides through the computed tomography (CT) machine which takes x-ray pictures of the inside of the body. The x-ray pictures help the doctor see where the abnormal tissue is in the lung. A biopsy needle is inserted through the chest wall and into the area of abnormal lung tissue. A small piece of tissue is removed through the needle and checked under the microscope for signs of cancer. Thoracoscopy: A surgical procedure to look at the organs inside the chest to check for abnormal areas. An incision (cut) is made between two ribs, and a thoracoscope is inserted into the chest. A thoracoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing. It may also have a tool to remove tissue or lymph node samples, which are checked under a microscope for signs of cancer. In some cases, this procedure is used to remove part of the esophagus or lung. If certain tissues, organs, or lymph nodes can t be reached, a thoracotomy may be done. In this procedure, a larger incision is made between the ribs and the chest is opened. Thoracentesis: The removal of fluid from the space between the lining of the chest and the lung, using a needle. A pathologist views the fluid under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options. The prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options depend on the following: The stage of the cancer (whether it is in the chest cavity only or has spread to other places in the body).
7 The patient s gender and general health. The blood level of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a substance found in the blood that may indicate cancer when the level is higher than normal. For most patients with small cell lung cancer, current treatments do not cure the cancer. If lung cancer is found, participation in one of the many clinical trials being done to improve treatment should be considered. Clinical trials are taking place in most parts of the country for patients with all stages of small cell lung cancer. Information about ongoing clinical trials is available from NCI Web site After small cell lung cancer has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread within the chest or to other parts of the body. The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the chest or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. Some of the tests used to diagnose small cell lung cancer are also used to stage the disease. (See the General Information section.) Other tests and procedures that may be used in the staging process include the following: Laboratory tests: Medical procedures that test samples of tissue, blood, urine, or other substances in the body. These tests help to diagnose disease, plan and check treatment, or monitor the disease over time. Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: The removal of bone marrow, blood, and a small piece of bone by inserting a hollow needle into the hipbone or breastbone. A pathologist views the bone marrow, blood, and bone under a microscope to look for signs of cancer. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain: A procedure that uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. This procedure is also called nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI). Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS): A procedure in which an endoscope is inserted into the body. An endoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing. A probe at the end of the endoscope is used to bounce high-energy sound waves (ultrasound) off internal tissues or organs and make echoes. The echoes form a picture of body tissues called a sonogram. This procedure is also called endosonography. EUS may be used to guide fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy of the lung, lymph nodes, or other areas.
8 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. An endoscope that has an ultrasound probe and a biopsy needle is inserted through the mouth and into the esophagus. The probe bounces sound waves off body tissues to make echoes that form a sonogram (computer picture) of the lymph nodes near the esophagus. The sonogram helps the doctor see where to place the biopsy needle to remove tissue from the lymph nodes. This tissue is checked under a microscope for signs of cancer. Lymph node biopsy: The removal of all or part of a lymph node. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Radionuclide bone scan: A procedure to check if there are rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, in the bone. A very small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive material collects in the bones and is detected by a scanner. There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body. The three ways that cancer spreads in the body are: Through tissue. Cancer invades the surrounding normal tissue. Through the lymph system. Cancer invades the lymph system and travels through the lymph vessels to other places in the body. Through the blood. Cancer invades the veins and capillaries and travels through the blood to other places in the body. When cancer cells break away from the primary (original) tumor and travel through the lymph or blood to other places in the body, another (secondary) tumor may form. This process is called metastasis. The secondary (metastatic) tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if breast cancer spreads to the bones, the cancer cells in the bones are actually breast cancer cells. The disease is metastatic breast cancer, not bone cancer. The following stages are used for small cell lung cancer:
9 Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer In limited-stage, cancer is found in one lung, the tissues between the lungs, and nearby lymph nodes only. Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer In extensive-stage, cancer has spread outside of the lung in which it began or to other parts of the body. After small cell lung cancer has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread within the chest or to other parts of the body. The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the chest or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. Some of the tests used to diagnose small cell lung cancer are also used to stage the disease. (See the General Information section.) Other tests and procedures that may be used in the staging process include the following: Laboratory tests: Medical procedures that test samples of tissue, blood, urine, or other substances in the body. These tests help to diagnose disease, plan and check treatment, or monitor the disease over time. Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: The removal of bone marrow, blood, and a small piece of bone by inserting a hollow needle into the hipbone or breastbone. A pathologist views the bone marrow, blood, and bone under a microscope to look for signs of cancer. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain: A procedure that uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. This procedure is also called nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI). Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS): A procedure in which an endoscope is inserted into the body. An endoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing. A probe at the end of the endoscope is used to bounce high-energy sound waves (ultrasound) off internal tissues or organs and make echoes. The echoes form a picture of body tissues called a sonogram. This procedure is also called endosonography. EUS may be used to guide fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy of the lung, lymph nodes, or other areas.
10 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. An endoscope that has an ultrasound probe and a biopsy needle is inserted through the mouth and into the esophagus. The probe bounces sound waves off body tissues to make echoes that form a sonogram (computer picture) of the lymph nodes near the esophagus. The sonogram helps the doctor see where to place the biopsy needle to remove tissue from the lymph nodes. This tissue is checked under a microscope for signs of cancer. Lymph node biopsy: The removal of all or part of a lymph node. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Radionuclide bone scan: A procedure to check if there are rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, in the bone. A very small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive material collects in the bones and is detected by a scanner. There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body. The three ways that cancer spreads in the body are: Through tissue. Cancer invades the surrounding normal tissue. Through the lymph system. Cancer invades the lymph system and travels through the lymph vessels to other places in the body. Through the blood. Cancer invades the veins and capillaries and travels through the blood to other places in the body. When cancer cells break away from the primary (original) tumor and travel through the lymph or blood to other places in the body, another (secondary) tumor may form. This process is called metastasis. The secondary (metastatic) tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if breast cancer spreads to the bones, the cancer cells in the bones are actually breast cancer cells. The disease is metastatic breast cancer, not bone cancer. The following stages are used for small cell lung cancer: Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer In limited-stage, cancer is found in one lung, the tissues between the lungs, and nearby lymph nodes only. Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer In extensive-stage, cancer has spread outside of the lung in which it began or to other parts of the body. There are different types of treatment for patients with small cell lung cancer. Different types of treatment are available for patients with small cell lung cancer. Some treatments are standard (the currently used treatment), and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard
11 treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment. Five types of standard treatment are used: Surgery Surgery may be used if the cancer is found in one lung and in nearby lymph nodes only. Because this type of lung cancer is usually found in both lungs, surgery alone is not often used. Occasionally, surgery may be used to help determine the patient s exact type of lung cancer. During surgery, the doctor will also remove lymph nodes to see if they contain cancer. Even if the doctor removes all the cancer that can be seen at the time of the operation, some patients may be given chemotherapy or radiation therapy after surgery to kill any cancer cells that are left. Treatment given after the surgery, to increase the chances of a cure, is called adjuvant therapy. Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body (systemic chemotherapy). When chemotherapy is placed directly into the spinal column, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas (regional chemotherapy). The way the chemotherapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated. Radiation therapy Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. There are two types of radiation therapy. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer. Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters that are placed directly into or near the cancer. Prophylactic cranial irradiation (radiation therapy to the brain to reduce the risk that cancer will spread to the brain) may also be given. The way the radiation therapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated. Laser therapy Laser therapy is a cancer treatment that uses a laser beam (a narrow beam of intense light) to kill cancer cells. Endoscopic stent placement An endoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument used to look at tissues inside the body. An endoscope has a light and a lens for viewing and may be used to place a stent in a body structure to keep the structure open. Endoscopic stent placement can be used to open an airway blocked by abnormal tissue. New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials. Information about clinical trials is available from the NCI Web site. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
12 For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment. Many of today's standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment. Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward. Patients can enter clinical trials before, during, or after starting their cancer treatment. Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring (coming back) or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment. Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. See the Treatment Options section that follows for links to current treatment clinical trials. These have been retrieved from NCI's clinical trials database. Follow-up tests may be needed. Some of the tests that were done to diagnose the cancer or to find out the stage of the cancer may be repeated. Some tests will be repeated in order to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests. This is sometimes called re-staging. Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred (come back). These tests are sometimes called follow-up tests or check-ups. Treatment Options by Stage Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer A link to a list of current clinical trials is included for each treatment section. For some types or stages of cancer, there may not be any trials listed. Check with your doctor for clinical trials that are not listed here but may be right for you. Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment of limited-stage small cell lung cancer may include the following: Combination chemotherapy and radiation therapy to the chest. Radiation therapy to the brain may later be given to patients with complete responses. Combination chemotherapy for patients with lung problems or who are very ill. Radiation therapy to the brain may later be given to patients with complete responses. Surgery followed by chemotherapy or chemotherapy plus radiation therapy to the chest. Radiation therapy to the brain may later be given to patients with complete responses.
13 Clinical trials of new chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation treatments. Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer may include the following: Combination chemotherapy. Radiation therapy to the brain may later be given to patients with complete responses. Radiation therapy to the brain, spine, bone, or other parts of the body where the cancer has spread, as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. Clinical trials of new chemotherapy treatments. Treatment Options for Recurrent Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment of recurrent small cell lung cancer may include the following: Chemotherapy. Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. Laser therapy, stent placement to keep airways open, and/or internal radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. Clinical trials of new chemotherapy treatments.
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
 Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of information
Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of information
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
 Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma
 Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Lung Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Mesothelioma: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Mesothelioma: Questions
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer About Your Lungs and Lung Cancer How do your lungs work? To understand lung cancer it is helpful to understand your lungs. Your lungs put oxygen into the blood, which the heart
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer About Your Lungs and Lung Cancer How do your lungs work? To understand lung cancer it is helpful to understand your lungs. Your lungs put oxygen into the blood, which the heart
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide
 What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
What If I Have a Spot on My Lung? Do I Have Cancer? Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 170,000
SMALL. 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org
 UNDERSTANDING Non- SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient I ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS The following image shows different parts that make up the lungs. Please use
UNDERSTANDING Non- SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A guide for the patient I ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS The following image shows different parts that make up the lungs. Please use
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
The lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Risks & symptoms Diagnosis & treatment options
 Why We re Here The lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Risks & symptoms Diagnosis & treatment options What Are Lungs? What Do They Do? 1 Located in the chest Allow you to breathe Provide oxygen
Why We re Here The lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Risks & symptoms Diagnosis & treatment options What Are Lungs? What Do They Do? 1 Located in the chest Allow you to breathe Provide oxygen
People Living with Cancer
 Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Patient Guide ASCOInformation for People Living with Cancer ADVANCED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Welcome The American Society of Clinical Oncology
Asbestos and your lungs
 This information describes what asbestos is and the lung conditions that are caused by exposure to it. It also includes information about what to do if you have been exposed to asbestos, and the benefits
This information describes what asbestos is and the lung conditions that are caused by exposure to it. It also includes information about what to do if you have been exposed to asbestos, and the benefits
How To Treat Lung Cancer At Cleveland Clinic
 Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Surgery. Wedge resection only part of the lung, not. not a lobe, is removed. Cancer Council NSW
 The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
The treatment you receive will depend on your lung cancer type, for example, whether you have a non-small cell lung cancer Adenocarcinoma or Squamous cell carcinoma, and if this is a sub-type with a mutation.
How To Understand How Cancer Works
 Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment.
 Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Lung Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
Lung Carcinoid Tumor
 Lung Carcinoid Tumor What are lung carcinoid tumors? Lung carcinoid tumors (also known as lung carcinoids) are a type of lung cancer, which is a cancer that starts in the lungs. Cancer starts when cells
Lung Carcinoid Tumor What are lung carcinoid tumors? Lung carcinoid tumors (also known as lung carcinoids) are a type of lung cancer, which is a cancer that starts in the lungs. Cancer starts when cells
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 [email protected] Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 [email protected] Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Facing Lung Cancer? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for lung cancer.
 Facing Lung Cancer? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for lung cancer. The Condition: Lung Cancer The lung is the organ that moves oxygen through your body. You have two lungs
Facing Lung Cancer? Learn why da Vinci Surgery may be your best treatment option for lung cancer. The Condition: Lung Cancer The lung is the organ that moves oxygen through your body. You have two lungs
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer
 Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
Main Page Risk Factors Reducing Your Risk Screening Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Overview Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgical Procedures Lifestyle Changes Managing Side Effects Talking to Your Doctor
About lung cancer. Contents. The lungs
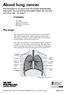 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
CEU Update. Pancreatic Cancer
 CEU Update A semi-annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals June 2015 Issue #0615 Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Inc. (PanCAN), established in 1999,
CEU Update A semi-annual publication of the National Association for Health Professionals June 2015 Issue #0615 Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Inc. (PanCAN), established in 1999,
Lung Cancer. Know how to stay strong
 Lung Cancer Know how to stay strong What is cancer? 2 Cancer is a disease when some cells in the body grow out of control Normal cells Your body has many tiny cells and keeps making new cells to keep you
Lung Cancer Know how to stay strong What is cancer? 2 Cancer is a disease when some cells in the body grow out of control Normal cells Your body has many tiny cells and keeps making new cells to keep you
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER
 dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
UNDERSTANDING YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...3 The Basics...4 Sections of a Pathology Report...7
Mesothelioma and Asbestos
 CANCER INFORMATION FACTSHEET Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
CANCER INFORMATION FACTSHEET Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer John delcharco, MD (Statistics based on CVMC data 2009-2013) Statistics Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer John delcharco, MD (Statistics based on CVMC data 2009-2013) Statistics Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates
TREATING LUNG CANCER AT VA PITTSBURGH HEALTHCARE SYSTEM A HERO S GUIDE
 Providing the best in cancer care for Veterans TREATING LUNG CANCER AT VA PITTSBURGH HEALTHCARE SYSTEM A HERO S GUIDE VA Pittsburgh s state-of-the-art TomoTherapy machine, which delivers radiation to patients.
Providing the best in cancer care for Veterans TREATING LUNG CANCER AT VA PITTSBURGH HEALTHCARE SYSTEM A HERO S GUIDE VA Pittsburgh s state-of-the-art TomoTherapy machine, which delivers radiation to patients.
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Esophageal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Mesothelioma and Asbestos
 Cancer information factsheet Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Cancer information factsheet Mesothelioma and Asbestos The information in this factsheet will help you to understand more about mesothelioma. It is an agreed view on this cancer by medical experts. We
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Malignant Mesothelioma
 Malignant Mesothelioma What is malignant mesothelioma? Malignant mesothelioma is a cancer that starts in cells in the linings of certain parts of the body, especially in the linings of the chest or abdomen.
Malignant Mesothelioma What is malignant mesothelioma? Malignant mesothelioma is a cancer that starts in cells in the linings of certain parts of the body, especially in the linings of the chest or abdomen.
This factsheet aims to outline the characteristics of some rare lung cancers, and highlight where each type of lung cancer may be different.
 There are several different kinds of lung cancer, often referred to as lung cancer subtypes. Some of these occur more often than others. In this factsheet we will specifically look at the subtypes of cancers
There are several different kinds of lung cancer, often referred to as lung cancer subtypes. Some of these occur more often than others. In this factsheet we will specifically look at the subtypes of cancers
Lung cancer (non-small-cell)
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
Patient information from the BMJ Group Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important decisions about
Learning about Mouth Cancer
 Learning about Mouth Cancer Creation of this material was made possible in part by a pioneering grant from CBCC-USA. Distributed by India Cancer Initiative What is mouth cancer? Our bodies are made up
Learning about Mouth Cancer Creation of this material was made possible in part by a pioneering grant from CBCC-USA. Distributed by India Cancer Initiative What is mouth cancer? Our bodies are made up
Colon and Rectal Cancer
 Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
Colon and Rectal Cancer What is colon or rectal cancer? Colon or rectal cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in your large intestine, which is also called the large bowel. The colon is the last 5 feet
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER. How Will I Know If My Prostate Cancer Returns?
 WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
WHEN PROSTATE CANCER RETURNS: ADVANCED PROSTATE CANCER (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) How Will I Know
Cancer of the Pancreas
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Cancer of the Pancreas U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Cancer of the Pancreas U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only
What is Mesothelioma?
 What is Mesothelioma? Mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that develops in the mesothelial cells found in one s body. These cells form membranous linings that surround and protect the body s organs and
What is Mesothelioma? Mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that develops in the mesothelial cells found in one s body. These cells form membranous linings that surround and protect the body s organs and
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Understanding Lung Cancer
 Lung Understanding Lung Cancer Information for individuals with lung cancer and their families Your Primary Team at the JCC Medical Oncologist Primary Nurse Radiation Oncologist Primary Nurse Other Oncology
Lung Understanding Lung Cancer Information for individuals with lung cancer and their families Your Primary Team at the JCC Medical Oncologist Primary Nurse Radiation Oncologist Primary Nurse Other Oncology
Esophageal Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis
 Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large
Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large
F r e q u e n t l y As k e d Qu e s t i o n s. Lung Disease
 Lung Disease page 1 Q: What is lung disease? A: Lung disease refers to disorders that affect the lungs, the organs that allow us to breathe. Breathing problems caused by lung disease may prevent the body
Lung Disease page 1 Q: What is lung disease? A: Lung disease refers to disorders that affect the lungs, the organs that allow us to breathe. Breathing problems caused by lung disease may prevent the body
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Melanoma The Skin Understanding Cancer
 Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide
 Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
Treating Mesothelioma - A Quick Guide Contents This is a brief summary of the information on Treating mesothelioma from CancerHelp UK. You will find more detailed information on the website. In this information
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis
 Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis Let s Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Pancreatic Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer you may feel alone
LUNG CANCER EVALUATION & TREATMENT. LungCancer. Prevention & Early Detection Save Lives. The Power Is Yours.
 LUNG CANCER EVALUATION & TREATMENT LungCancer Prevention & Early Detection Save Lives. The Power Is Yours. Prevention Lung cancer. It s one of the most common cancers in both men and women more deadly
LUNG CANCER EVALUATION & TREATMENT LungCancer Prevention & Early Detection Save Lives. The Power Is Yours. Prevention Lung cancer. It s one of the most common cancers in both men and women more deadly
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer?
 Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
National Cancer Institute. What You Need TM. To Know About. Stomach Cancer. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Stomach Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only one of
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Stomach Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute Services This is only one of
National Cancer Institute. What You Need TM. To Know About. Liver Cancer. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Liver Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
National Cancer Institute What You Need TM To Know About Liver Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health For more publications This is only one of many free booklets
Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer
 A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry
 National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry Instructions: This consent statement is to be signed and dated by the patient in the presence of a certified study staff
National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Consent for Screening and Patient Registry Instructions: This consent statement is to be signed and dated by the patient in the presence of a certified study staff
Malignant Mesothelioma
 Malignant Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Malignant Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Malignant Mesothelioma
 Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Malignant mesothelioma is a tumour originating from mesothelial cells. 85 95% of mesotheliomas are caused by asbestos exposure. It occurs much more commonly in the chest (malignant pleural mesothelioma)
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer?
 Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a
Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell) What is cancer? The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
