Topic 1: Internet Architecture & Addressing
|
|
|
- Nathan Mills
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topic 1: Internet Architecture & Addressing Objectives Understand the general architecture of Internet Identify the main actors in the Internet architecture Identify the main organizations implied in Internet Understand IPv4 address depletion problem Is it IPv6 the solution to IPv4 depletion problem?
2 Topic 1: Internet Architecture & Addressing Internet Architecture: ISP's, corporate networks and access networks. Organizations that manage the operation of businesses on the Internet: RIR (Regional Internet Registers), LIR (Local Internet Registries). Internet Addressing: IPv4 depletion and IPv6. Exchange Points.
3 Internet: global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard TCP/IP suite protocol to connect users and applications. Users are inter-connected through ISP (Internet Service Provider) Internet Service Provider (ISP) Provides connectivity and services to end users (Dial-up), corporative networks (IP-Net Clients) and other ISPs
4 Internet Service Provider End users (Dial-clients): Contract an access line (i.e., modem, ADLS, ). The ISP may be a telecom operator or has sub-contracts with telecom operators to offer service connectivity Corporative Networks (IP-Net-client) Local Area Networks (LANs) Contract switched/dedicated lines for linking their sites forming a VPN Contract one or several lines (backup, redundancy, load balancing, ) to the ISP ISP Peering between ISPs: ISPs act with con client-to-provider, peer-to-peer and provider-to-client relationships ISPs connections may be private (using Telecom operator lines) or public ( Exchange points ) Retail services (directly to customers) versus Wholesail services (in large quantities that later can be re-selled)
5 Internet Architecture
6 Internet Architecture ISP ISP ISP Internet Providers ISP ISP WAN Access Technologies WAN WAN WAN Users IP-Net clients IP-Net clients IP-Net clients Dial-up clients IP-Net clients
7 IANA The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is the body responsible for coordinating some of the key elements that keep the Internet running smoothly. Whilst the Internet is renowned for being a worldwide network free from central coordination, there is a technical need for some key parts of the Internet to be globally coordinated and this coordination role is undertaken by IANA.
8 IANA Activities Domain Names IANA manages the DNS root, the.int and.arpa domains, and an IDN practices resource. Number Resources IANA coordinates the global pool of IP and AS numbers, providing them to Regional Internet Registries. Protocol Assignments Internet protocols numbering systems are managed by IANA in conjunction with standards bodies.
9 Domain Names country code top-level domains (cctld): Used by a country or a dependent territory. It is two letters long, for example.us for the United States. With some historical exceptions, the code for any territory is the same as its two-letter ISO 3166 code. generic top-level domains (gtld): Used by a particular class of organizations (for example,.com for commercial organizations). It is three or more letters long. Most gtlds are available for use worldwide, but for historical reasons.mil (military) and.gov (governmental) are restricted to use by the respective U.S. authorities. gtlds are sub classified into sponsored top-level domains (stld), e.g..aero,.coop and.museum, and unsponsored top-level domains (utld), e.g..biz,.info, and.name. infrastructure top-level domains (itld): The top-level domain.arpa.int,.root.
10 Internet Numbers (addresses) Users are assigned IP addresses by Internet service providers (ISPs). ISPs obtain allocations of IP addresses from a local Internet registry (LIR) or national Internet registry (NIR), or from their appropriate Regional Internet Registry (RIR) IPv4: IPv6:
11 Protocol Numbers IANA is responsible for maintaining many of the codes and numbers contained in a variety of Internet protocols, enumerated below. We provide this service in coordination with the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). Address Family Numbers Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Parameters Autonomous System (AS) Numbers
12 IANA organization Regional Internet Registry (RIR) National Internet registry (NIR) Local Internet registry (LIR) RIR AfriNIC Africa Region APNIC Asia/Pacific Region ARIN North America Region LACNIC Latin America and some Caribbean Islands RIPE NCC Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia
13 Regional Internet Registries (RIRs): Independent organizations that supports Internet resources coordination in a geographical region and develop consistent policies and promote best current practice for the Internet. Each RIR manage: IPv4 and IPv6 Address blocks and AS number assignments DO NOT manage Name Domains (done by ICANN: Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers ) There are 5 Regions ARIN, RIPE, AFRINIC, LACNIC, APNIC
14 Regional Internet Registries (RIRs):
15 Regional Internet Registries (RIRs): LIR (Local Internet Registry) Members of RIR NIR (National Internet Registry) coordinate IP allocations at national level. There are no NIR in Europe, but APNIC and LACNIC have them. RIRs allocate IP address space and AS Numbers to Local Internet Registries (LIRs) that assign these resources to End Users
16 RIPE NCC ( Provides Internet resource allocations, registration services and coordination activities that support the operation of the Internet globally. Internet Governance: based on a commitment to enhance the cooperation between the public and private sectors LIR (Local Internet Register) Services: members of a RIR Data & Tools: provides databases and monitoring tools that support stable, reliable and secure Internet operations. RIPE Database support: contains registration details of IP addresses and AS Numbers originally allocated by the RIPE NCC Operates 1 of the 13 K-root Name Servers Provides high-quality measurements and analysis that can be used for a variety of operational, media, governmental and law enforcement activities.
17 Criteria to obtain an AS number Only when the routing policy is different from your ISP provider routing policy (RFC 1930) That implies that the customer has to be connected to at least two ISP (multi-homing) with different routing policies What is a LIR (Local Internet Registry)? Any member of a RIR is a LIR Typically ISP, Telecom Operators and Corporative Networks (Enterprise) Obligatory if you need IPv4 blocks higher or equal to /21 IPv4 blocks If you need lower blocks contact an ISP See in order to see ISP and LIR in any geographical zone covered by RIPE
18 AS numbers in Internet Data taken from IPJ Internet Protocol Journal (March 2006)
19 Autonomous Systems (AS) or Routing Domain: is a group of IP networks run by one or more network operators with a single, clearly defined routing policy. AS are identified with 16 bits (65535 AS s) AS s exchange routes (IP subnets) using Inter-domain Routing Protocols such as BGPv4 Internally, AS s exchange routes (IP subnets) using Intra-domain Routing Protocols such as OSPF, IS-IS, EIGRP, AS 1 AS 2 IGP EGP IGP AS 3 IGP
20 Internet Service Provider (ISP) and Autonomous Systems (AS): An ISP is an administrative entity that may have one or more AS numbers assigned depending of its architecture and geographical situation In general an AS number may be assigned to an ISP or to a Corporative Network, Thus, not all AS are ISP, however all ISPs have one or more AS number assigned We will clarify ISP in the next sections
21 Autonomous Systems
22 AS relationships The relationships between these networks are generally described by one of the following three categories: Transit - You pay money (or settlement) to another network for Internet access (or transit). Peer (or swap) - Two networks exchange traffic between each other's customers freely, and for mutual benefit. Customer (or sell) - Another network pays you money to provide them with Internet access.
23 Hierarchical Organization Tier 1 - A network that can reach every other network on the Internet without purchasing IP transit. Tier 2 - A network that peers with some networks, but still purchases IP transit to reach at least some portion of the Internet. Tier 3 - A network that solely purchases transit from other networks to reach the Internet.
24 Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Default Free Zone IPJ Vol2 March Geoff Huston MIRI: Computer Networks
25 Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Default Free Zone Default Free Zone MIRI: Computer Networks
26 ISP peering Private peering Point-to-point connections among two AS in order to transport routes and traffic Increase link reliability and offer high bandwidth but at cost increases Alleviate the traffic that crosses public exchange points Connections are bi-laterally negotiated among the ISP (peerto-peer basis) Routing and business treats are confidential and only known among partners (peers)
27 ISP peering Public peering National: inter-connect ISP belonging to the same country Espanix ( with 45 partners and 96 averaged Gb/s of traffic, Catnix ( with 24 partners and approx 700 switched Mb/s, EuskoNix with 7 partners and 100 Mb/s International: inter-connect National IXP; EuroIX ( with 105 European IXP The inter-connectivity matrix between IXP will give us information about ISP peering Not all ISP are connected to IXP
28 Motivations for peering Increased capacity for extremely large amounts of traffic (distributing traffic across many networks). Increased control over your traffic (reducing dependence on one or more transit providers). Improved performance (attempting to bypass potential bottlenecks with a "direct" path). Improved perception of your network (being able to claim a "higher tier"). Government regulations, or the desire to avoid the appearance of being a monopoly.
29 Exchange Points An Internet exchange point (IX or IXP) is a physical infrastructure that allows different Internet service providers (ISPs) to exchange traffic between their networks (autonomous systems) by means of mutual peering agreements, which allow traffic to be exchanged without cost. European Internet Exchange Association Espanix (punto neutro español)
30 Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Internet Exchange Point Requirements for an ISP to be member: One BGP router, at least, AS number With IPv4 and IPv6 One or more connections to the IXP switches MIRI: Computer Networks
31 Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Internet Exchange Point MIRI: Computer Networks
32 Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Internet Exchange Point MIRI: Computer Networks
33 Espanix (daily and weekly traffic)
34 Catnix:
35 Tiers: Tier 1 ISPs (troncales) are large and together hold all the world s Internet routes, and peer with each other to give each other access to all Internet routes. Tier 2 ISPs buy connectivity (upstream transit) to the world Internet routes from one or more tier 1 ISPs, and hence their IP network(s) becomes a sub-set of those tier 1 s IP networks. Tier 2 ISPs will also peer with each other to minimize the amount of traffic to and from the tier 1 ISPs from whom they buy upstream transit. Tier 3 ISPs buy upstream transit from Tier 2 ISPs and so on, however the model becomes increasingly vague, since an ISP may buy upstream transit from both a tier 1 ISP and a tier 2 ISP, and may peer with tier 2 and tier 3 ISP s and occasionally a tier 1 ISP, and so on. The term is really only of use to differentiate between tier1 ISPs who do not need to buy upstream transit due to their peerings with other tier 1 ISPs, and the rest of the ISPs, tier 2 and below. Tier 1 (International), Tier 2 (National/regional) and Tier 3 (regional/local)
36 The Cooperative Association for Internet Data Analysis (CAIDA): Provides statistics about AS organization, size, peering, etc E.g. AS rank by customer cone (number of AS s or IPv4 addresses ) reachable via customers or customers of customers of an AS (
37
38 Internet Arbor Networks. ATLAS Internet Observatory Annual Report. NANOG47
39 The new Internet Arbor Networks. ATLAS Internet Observatory Annual Report. NANOG47
40 Internet Service Provider ISP offer different types of services Dedicated Internet Access services T1/E1 lines (1.5, 2 Mbps), T3/E3 (45, 34 Mbps), OC3 (155 Mbps), OC12 (622 Mbps), OC48 (2.5 Gbps), etc Switched Internet Access services FR (Frame Relay) or ATM Other Internet Access services Modems, ADSL, RDSI (BRI, PRI), etc Hosting/housing Services and CPD services Racks, servers (e.g.; Web), equipment, etc End user services VPNs, , news, Web, IP multicast, etc Content Provider services (Content Distribution Networks such as Akamai)
41 SLA (Service Level Agreement): agreement that guarantees the contract offered by an ISP and that penalize the ISP if this one does not comply the contract Availability level (% of time that the customer agrees in losing connectivity) measured as the number of delivered packets respect to the transmitted Bandwidth contracted (Mb/s) Throughput (Mb/s) in high availability (rushy hours) Response time against connectivity failures (e.g. 24/7 service), penalize with respect the amount of time without connectivity Redundancy (multi-homing) Security Monitoring services Quality of Service (QoS): service levels (e.g. Gold, Silver, ) Packet marking, dropping, end-to-end delays,. El SLA is a customer support service
42 Corporative Networks or IP-Net Client Companies with end users and end services As any end user, they are connected to other end users and other corporative networks via an ISP A corporative network can be something ranging between: Small company with few users, to a large company with thousands of users A corporative network may: Manage their services in a CPD (Centre Processing Data) located in the Main Site Manage their services via others (e.g. either another corporative network or an ISP) that provides the service (e.g. hosting, housing, virtualization, )
43 Corporative Networks or IP-Net Client SERVER BLOCK WAN BLOCK BACKBONE CORE BLOCK DISTRIBUTED LAYER ACCESS LAYER SWITCH BLOCK SWITCH BLOCK SWITCH BLOCK * Internetwork Design Guide, CISCO documentation
The Internet Introductory material.
 The Internet Introductory material. An overview lecture that covers Internet related topics, including a definition of the Internet, an overview of its history and growth, and standardization and naming.
The Internet Introductory material. An overview lecture that covers Internet related topics, including a definition of the Internet, an overview of its history and growth, and standardization and naming.
Introduction to The Internet
 Introduction to The Internet ISP Workshops Last updated 5 September 2014 1 Introduction to the Internet p Topologies and Definitions p IP Addressing p Internet Hierarchy p Gluing it all together 2 Topologies
Introduction to The Internet ISP Workshops Last updated 5 September 2014 1 Introduction to the Internet p Topologies and Definitions p IP Addressing p Internet Hierarchy p Gluing it all together 2 Topologies
Introduction to The Internet. ISP/IXP Workshops
 Introduction to The Internet ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Introduction to the Internet Topologies and Definitions IP Addressing Internet Hierarchy Gluing it all together 2 Topologies and Definitions What does all
Introduction to The Internet ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Introduction to the Internet Topologies and Definitions IP Addressing Internet Hierarchy Gluing it all together 2 Topologies and Definitions What does all
The Internet. On October 24, 1995, the FNC unanimously passed a resolution defining the term Internet.
 The Internet Introductory material. An overview lecture that covers Internet related topics, including a definition of the Internet, an overview of its history and growth, and standardization and naming.
The Internet Introductory material. An overview lecture that covers Internet related topics, including a definition of the Internet, an overview of its history and growth, and standardization and naming.
BGP. 1. Internet Routing
 BGP 1. Internet Routing (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Internet Routing Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) not suitable for Inter-ISP routing Technical metrics only No policy features Inter-ISP routing is
BGP 1. Internet Routing (C) Herbert Haas 2005/03/11 1 Internet Routing Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) not suitable for Inter-ISP routing Technical metrics only No policy features Inter-ISP routing is
INTERNET ORGANIZATION OVERVIEW OF THE INTERNET'S ORGANIZATION AND MAIN STANDARD BODIES. Internet Organization. Peter R. Egli INDIGOO.COM. indigoo.
 INTERNET ORGANIZATION OVERVIEW OF THE INTERNET'S ORGANIZATION AND MAIN STANDARD BODIES Peter R. Egli INDIGOO.COM 1/17 Contents 1. Internet Organizations 2. Why the Internet is called Inter-Net 3. Internet
INTERNET ORGANIZATION OVERVIEW OF THE INTERNET'S ORGANIZATION AND MAIN STANDARD BODIES Peter R. Egli INDIGOO.COM 1/17 Contents 1. Internet Organizations 2. Why the Internet is called Inter-Net 3. Internet
Internet Structure and Organization
 Internet Structure and Organization Resources management and allocation [email protected] Introduction What s the Internet? Why organizations / bodies are needed? Define protocol specifications Agree
Internet Structure and Organization Resources management and allocation [email protected] Introduction What s the Internet? Why organizations / bodies are needed? Define protocol specifications Agree
IPv6 Address Planning
 eip604_v1.0 APNIC elearning: IPv6 Address Planning Contact: [email protected] Overview Where to Get IPv6 Addresses Addressing Plans ISP Infrastructure Addressing Plans Customer Example Address Plan Addressing
eip604_v1.0 APNIC elearning: IPv6 Address Planning Contact: [email protected] Overview Where to Get IPv6 Addresses Addressing Plans ISP Infrastructure Addressing Plans Customer Example Address Plan Addressing
IPv6 Addressing. ISP Training Workshops
 IPv6 Addressing ISP Training Workshops 1 Where to get IPv6 addresses p Your upstream ISP p Africa n AfriNIC http://www.afrinic.net p Asia and the Pacific n APNIC http://www.apnic.net p North America n
IPv6 Addressing ISP Training Workshops 1 Where to get IPv6 addresses p Your upstream ISP p Africa n AfriNIC http://www.afrinic.net p Asia and the Pacific n APNIC http://www.apnic.net p North America n
The Internet. Internet Technologies and Applications
 The Internet Internet Technologies and Applications Aim and Contents Aim: Review the main concepts and technologies used in the Internet Describe the real structure of the Internet today Contents: Internetworking
The Internet Internet Technologies and Applications Aim and Contents Aim: Review the main concepts and technologies used in the Internet Describe the real structure of the Internet today Contents: Internetworking
Introduction to Routing
 Introduction to Routing How traffic flows on the Internet Philip Smith [email protected] RIPE NCC Regional Meeting, Moscow, 16-18 18 June 2004 1 Abstract Presentation introduces some of the terminologies used,
Introduction to Routing How traffic flows on the Internet Philip Smith [email protected] RIPE NCC Regional Meeting, Moscow, 16-18 18 June 2004 1 Abstract Presentation introduces some of the terminologies used,
Ref: A. Leon Garcia and I. Widjaja, Communication Networks, 2 nd Ed. McGraw Hill, 2006 Latest update of this lecture was on 16 10 2010
 IPv4 Addressing There are several non-profit organizations in the world that have the authority for assigning IP addresses to institutions that need access to the Internet. These organizations are (for
IPv4 Addressing There are several non-profit organizations in the world that have the authority for assigning IP addresses to institutions that need access to the Internet. These organizations are (for
Internet Bodies. [email protected]
 Internet Bodies [email protected] Agenda Names, Acronyms in the Internet IETF organisation IESG, IAB, ISOC ICANN & IANA Standardisation process Standardisation compliance Internet Registries Requesting
Internet Bodies [email protected] Agenda Names, Acronyms in the Internet IETF organisation IESG, IAB, ISOC ICANN & IANA Standardisation process Standardisation compliance Internet Registries Requesting
An introduction to IANA Presentation Notes
 An introduction to IANA Presentation Notes Date 29 September 2008 Contact Kim Davies, Manager of Root Zone Services [email protected] While the Internet is renowned for being a worldwide network free
An introduction to IANA Presentation Notes Date 29 September 2008 Contact Kim Davies, Manager of Root Zone Services [email protected] While the Internet is renowned for being a worldwide network free
Internet Operations and the RIRs
 Internet Operations and the RIRs Overview ARIN and the Regional Internet Registry (RIR) System IP Number Resources, DNS and Routing IP Address Management Whois ARIN and the RIR System About ARIN One of
Internet Operations and the RIRs Overview ARIN and the Regional Internet Registry (RIR) System IP Number Resources, DNS and Routing IP Address Management Whois ARIN and the RIR System About ARIN One of
What's inside the cloud?!
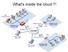 What's inside the cloud?! Initial Arpanet Initial Arpanet Interface Message Processors - DDP-516 mini-computers - 24 Kbyte of Core memory - Store-and-forward packet switching - Predecessors of present
What's inside the cloud?! Initial Arpanet Initial Arpanet Interface Message Processors - DDP-516 mini-computers - 24 Kbyte of Core memory - Store-and-forward packet switching - Predecessors of present
Address Scheme Planning for an ISP backbone Network
 Address Scheme Planning for an ISP backbone Network Philip Smith Consulting Engineering, Office of the CTO Version 0.1 (draft) LIST OF FIGURES 2 INTRODUCTION 3 BACKGROUND 3 BUSINESS MODEL 3 ADDRESS PLAN
Address Scheme Planning for an ISP backbone Network Philip Smith Consulting Engineering, Office of the CTO Version 0.1 (draft) LIST OF FIGURES 2 INTRODUCTION 3 BACKGROUND 3 BUSINESS MODEL 3 ADDRESS PLAN
The IANA Functions. An Introduction to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) Functions
 The IANA Functions An Introduction to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) Functions Contents SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION 4 SECTION 2: POLICY, STAKEHOLDERS AND STEWARDSHIP IMPLEMENTATION 6 SECTION
The IANA Functions An Introduction to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) Functions Contents SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION 4 SECTION 2: POLICY, STAKEHOLDERS AND STEWARDSHIP IMPLEMENTATION 6 SECTION
Chapter 9. Internet. Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc 10-1
 Chapter 9 Internet Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc 10-1 Outline 9.2 - How the Internet Works - Basic Architecture - Connecting to an ISP - Internet Today 9.3 - Internet Access Technologies - DSL
Chapter 9 Internet Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc 10-1 Outline 9.2 - How the Internet Works - Basic Architecture - Connecting to an ISP - Internet Today 9.3 - Internet Access Technologies - DSL
ICTTEN6172A Design and configure an IP- MPLS network with virtual private network tunnelling
 ICTTEN6172A Design and configure an IP- MPLS network with virtual private network tunnelling Release: 1 ICTTEN6172A Design and configure an IP-MPLS network with virtual private network tunnelling Modification
ICTTEN6172A Design and configure an IP- MPLS network with virtual private network tunnelling Release: 1 ICTTEN6172A Design and configure an IP-MPLS network with virtual private network tunnelling Modification
Simple Multihoming. ISP Workshops. Last updated 30 th March 2015
 Simple Multihoming ISP Workshops Last updated 30 th March 2015 1 Why Multihome? p Redundancy n One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: p Local router (configuration, software, hardware)
Simple Multihoming ISP Workshops Last updated 30 th March 2015 1 Why Multihome? p Redundancy n One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: p Local router (configuration, software, hardware)
BGP Terminology, Concepts, and Operation. Chapter 6 2007 2010, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
 BGP Terminology, Concepts, and Operation 1 IGP versus EGP Interior gateway protocol (IGP) A routing protocol operating within an Autonomous System (AS). RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP are IGPs. Exterior gateway
BGP Terminology, Concepts, and Operation 1 IGP versus EGP Interior gateway protocol (IGP) A routing protocol operating within an Autonomous System (AS). RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP are IGPs. Exterior gateway
IPv6 The Big Picture. Rob Evans, Janet [email protected]
 IPv6 The Big Picture Rob Evans, Janet [email protected] Where are we? IPv4 32 bit addresses 4,294,967,296 possible addresses In practice much less than this. History of large allocations /8s Inefficiency
IPv6 The Big Picture Rob Evans, Janet [email protected] Where are we? IPv4 32 bit addresses 4,294,967,296 possible addresses In practice much less than this. History of large allocations /8s Inefficiency
IPv6 and IPv4 Update from the RIPE NCC. Sandra Brás, Ferenc Csorba
 IPv6 and IPv4 Update from the RIPE NCC Sandra Brás, Ferenc Csorba RIPE NCC IPv6 Kongress - Frankfurt 22 May 2014 Schedule IPv6 Kongress 2 RIPE/RIPE NCC. Who are we? IPv4 exhaustion IPv4 transfers IPv6
IPv6 and IPv4 Update from the RIPE NCC Sandra Brás, Ferenc Csorba RIPE NCC IPv6 Kongress - Frankfurt 22 May 2014 Schedule IPv6 Kongress 2 RIPE/RIPE NCC. Who are we? IPv4 exhaustion IPv4 transfers IPv6
ISP Case Study. UUNET UK (1997) ISP/IXP Workshops. ISP/IXP Workshops. 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc.
 ISP Case Study UUNET UK (1997) ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Acknowledgements Thanks are due to UUNET UK for allowing the use of their configuration information and network
ISP Case Study UUNET UK (1997) ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Acknowledgements Thanks are due to UUNET UK for allowing the use of their configuration information and network
Internet Protocol version 4 Part I
 Internet Protocol version 4 Part I Claudio Cicconetti International Master on Information Technology International Master on Communication Networks Engineering Table of Contents
Internet Protocol version 4 Part I Claudio Cicconetti International Master on Information Technology International Master on Communication Networks Engineering Table of Contents
L4: ISPs, Backbones and Peering
 L4: ISPs, Backbones and Peering 15 September 2015 (From Kobe) Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 5 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia Norton2010 Paper Review
L4: ISPs, Backbones and Peering 15 September 2015 (From Kobe) Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 5 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia Norton2010 Paper Review
ISP & IXP Design. Philip Smith APNIC 34 21 st 31 st August 2012
 ISP & IXP Design Philip Smith APNIC 34 21 st 31 st August 2012 1 ISP & IXP Network Design p PoP Topologies and Design p Backbone Design p Upstream Connectivity & Peering p Addressing p Routing Protocols
ISP & IXP Design Philip Smith APNIC 34 21 st 31 st August 2012 1 ISP & IXP Network Design p PoP Topologies and Design p Backbone Design p Upstream Connectivity & Peering p Addressing p Routing Protocols
Network Level Multihoming and BGP Challenges
 Network Level Multihoming and BGP Challenges Li Jia Helsinki University of Technology [email protected] Abstract Multihoming has been traditionally employed by enterprises and ISPs to improve network connectivity.
Network Level Multihoming and BGP Challenges Li Jia Helsinki University of Technology [email protected] Abstract Multihoming has been traditionally employed by enterprises and ISPs to improve network connectivity.
Chapter 5. Data Communication And Internet Technology
 Chapter 5 Data Communication And Internet Technology Purpose Understand the fundamental networking concepts Agenda Network Concepts Communication Protocol TCP/IP-OSI Architecture Network Types LAN WAN
Chapter 5 Data Communication And Internet Technology Purpose Understand the fundamental networking concepts Agenda Network Concepts Communication Protocol TCP/IP-OSI Architecture Network Types LAN WAN
Internet Technical Governance: Orange s view
 Internet Technical Governance: Orange s view 1 Internet Technical Governance: Orange s view With the increasing use of IP technologies in the electronic communication networks and services, Internet Technical
Internet Technical Governance: Orange s view 1 Internet Technical Governance: Orange s view With the increasing use of IP technologies in the electronic communication networks and services, Internet Technical
Introducing Basic MPLS Concepts
 Module 1-1 Introducing Basic MPLS Concepts 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1-1 Drawbacks of Traditional IP Routing Routing protocols are used to distribute Layer 3 routing information. Forwarding
Module 1-1 Introducing Basic MPLS Concepts 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1-1 Drawbacks of Traditional IP Routing Routing protocols are used to distribute Layer 3 routing information. Forwarding
CORPORATE NETWORKING
 CORPORATE NETWORKING C. Pham Université de Pau et des Pays de l Adour Département Informatique http://www.univ-pau.fr/~cpham [email protected] Typical example of Ethernet local networks Mostly based
CORPORATE NETWORKING C. Pham Université de Pau et des Pays de l Adour Département Informatique http://www.univ-pau.fr/~cpham [email protected] Typical example of Ethernet local networks Mostly based
Chapter 3. TCP/IP Networks. 3.1 Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4)
 Chapter 3 TCP/IP Networks 3.1 Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) Internet Protocol version 4 is the fourth iteration of the Internet Protocol (IP) and it is the first version of the protocol to be widely
Chapter 3 TCP/IP Networks 3.1 Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) Internet Protocol version 4 is the fourth iteration of the Internet Protocol (IP) and it is the first version of the protocol to be widely
Law Enforcement and Internet Governance: An Ounce of Prevention Is Worth a Pound of Cure
 Law Enforcement and Internet Governance: An Ounce of Prevention Is Worth a Pound of Cure Supervisory Special Agent Robert Flaim Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) Operational Technology Division Global
Law Enforcement and Internet Governance: An Ounce of Prevention Is Worth a Pound of Cure Supervisory Special Agent Robert Flaim Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) Operational Technology Division Global
IPv6 Addressing. John Rullan Cisco Certified Instructor Trainer Thomas A. Edison CTE HS
 IPv6 Addressing John Rullan Cisco Certified Instructor Trainer Thomas A. Edison CTE HS Stephen Lynch Network Architect, CCIE #36243 ABS Technology Architects 128-bit hexadecimal format (0-9, A-F) Uses
IPv6 Addressing John Rullan Cisco Certified Instructor Trainer Thomas A. Edison CTE HS Stephen Lynch Network Architect, CCIE #36243 ABS Technology Architects 128-bit hexadecimal format (0-9, A-F) Uses
How To Get An Ipv6 Allocation On Ipv4 (Ipv4) From Ipv5) From The Ipvripe Ncc (Ip6) From A Ipvv6 Ipv2 (Ip4) To Ip
 What s hot at the RIPE NCC PLNOG6, March 2011 Sandra Brás Trainer, RIPE NCC [email protected] Hot topics - overview The registry system IPv4 depletion IPv6 policy update Independent resources 2 The five RIRs
What s hot at the RIPE NCC PLNOG6, March 2011 Sandra Brás Trainer, RIPE NCC [email protected] Hot topics - overview The registry system IPv4 depletion IPv6 policy update Independent resources 2 The five RIRs
CHAPTER 0 INTRODUCTION TO TCP/IP
 CHAPTER 0 INTRODUCTION TO TCP/IP This chapter gives an overview of TCP/IP networking principles that form the basis of discussion for many of the laboratories that are covered in this text. Using the example
CHAPTER 0 INTRODUCTION TO TCP/IP This chapter gives an overview of TCP/IP networking principles that form the basis of discussion for many of the laboratories that are covered in this text. Using the example
Draft WGIG Issue Paper on the Administration of Internet Names and IP Addresses
 Draft WGIG Issue Paper on the Administration of Internet Names and IP Addresses This paper is a 'draft working paper' reflecting the preliminary findings of the drafting team. It has been subject to review
Draft WGIG Issue Paper on the Administration of Internet Names and IP Addresses This paper is a 'draft working paper' reflecting the preliminary findings of the drafting team. It has been subject to review
MPLS Concepts. Overview. Objectives
 MPLS Concepts Overview This module explains the features of Multi-protocol Label Switching (MPLS) compared to traditional ATM and hop-by-hop IP routing. MPLS concepts and terminology as well as MPLS label
MPLS Concepts Overview This module explains the features of Multi-protocol Label Switching (MPLS) compared to traditional ATM and hop-by-hop IP routing. MPLS concepts and terminology as well as MPLS label
Enterprise Network Simulation Using MPLS- BGP
 Enterprise Network Simulation Using MPLS- BGP Tina Satra 1 and Smita Jangale 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, SAKEC, Chembur, Mumbai-88, India [email protected] 2 Department of Information Technolgy,
Enterprise Network Simulation Using MPLS- BGP Tina Satra 1 and Smita Jangale 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, SAKEC, Chembur, Mumbai-88, India [email protected] 2 Department of Information Technolgy,
Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) Scalable Infrastructure Workshop
 Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) Scalable Infrastructure Workshop Objectives p To be able to explain what an Internet Exchange Point (IXP) is p To be able to explain why ISPs participate in IXPs p To understand
Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) Scalable Infrastructure Workshop Objectives p To be able to explain what an Internet Exchange Point (IXP) is p To be able to explain why ISPs participate in IXPs p To understand
The Internet Ecosystem and ICANN!! Steve Sheng @ Stanford University, Center for Information and Society! 29 April 2013!
 The Internet Ecosystem and ICANN!! Steve Sheng @ Stanford University, Center for Information and Society! 29 April 2013! Ecosystem! + A network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and
The Internet Ecosystem and ICANN!! Steve Sheng @ Stanford University, Center for Information and Society! 29 April 2013! Ecosystem! + A network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and
Telecom and Internet Regulatory Challenges and Opportunities Names, Numbers, Internet Governance
 Telecom and Internet Regulatory Challenges and Opportunities Names, Numbers, Internet Governance Global Forum ICT & The Future of Internet Bucharest, Romania, 19-20 October 2009 Theresa Swinehart Vice-President
Telecom and Internet Regulatory Challenges and Opportunities Names, Numbers, Internet Governance Global Forum ICT & The Future of Internet Bucharest, Romania, 19-20 October 2009 Theresa Swinehart Vice-President
Networking Technology Online Course Outline
 Networking Technology Online Course Outline Introduction Networking Technology Introduction Welcome to InfoComm University About InfoComm International About Networking Technology Network Technology Course
Networking Technology Online Course Outline Introduction Networking Technology Introduction Welcome to InfoComm University About InfoComm International About Networking Technology Network Technology Course
Computer Networking Networks
 Page 1 of 8 Computer Networking Networks 9.1 Local area network A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area such as a home, school, office
Page 1 of 8 Computer Networking Networks 9.1 Local area network A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area such as a home, school, office
IP Addressing A Simplified Tutorial
 Application Note IP Addressing A Simplified Tutorial July 2002 COMPAS ID 92962 Avaya Labs 1 All information in this document is subject to change without notice. Although the information is believed to
Application Note IP Addressing A Simplified Tutorial July 2002 COMPAS ID 92962 Avaya Labs 1 All information in this document is subject to change without notice. Although the information is believed to
Fireware How To Dynamic Routing
 Fireware How To Dynamic Routing How do I configure my Firebox to use BGP? Introduction A routing protocol is the language a router speaks with other routers to share information about the status of network
Fireware How To Dynamic Routing How do I configure my Firebox to use BGP? Introduction A routing protocol is the language a router speaks with other routers to share information about the status of network
Simple Multihoming. ISP/IXP Workshops
 Simple Multihoming ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure,
Simple Multihoming ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure,
Demonstrating the high performance and feature richness of the compact MX Series
 WHITE PAPER Midrange MX Series 3D Universal Edge Routers Evaluation Report Demonstrating the high performance and feature richness of the compact MX Series Copyright 2011, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1 Table
WHITE PAPER Midrange MX Series 3D Universal Edge Routers Evaluation Report Demonstrating the high performance and feature richness of the compact MX Series Copyright 2011, Juniper Networks, Inc. 1 Table
IP Networking. Overview. Networks Impact Daily Life. IP Networking - Part 1. How Networks Impact Daily Life. How Networks Impact Daily Life
 Overview Dipl.-Ing. Peter Schrotter Institute of Communication Networks and Satellite Communications Graz University of Technology, Austria Fundamentals of Communicating over the Network Application Layer
Overview Dipl.-Ing. Peter Schrotter Institute of Communication Networks and Satellite Communications Graz University of Technology, Austria Fundamentals of Communicating over the Network Application Layer
Subnetting and Network Management Omer F. Rana. Networks and Data Communications 1
 Subnetting and Network Management Omer F. Rana Networks and Data Communications 1 Subnetting Subnetting is an important concept in establishing TCP/IP based networks important in integrating small Local
Subnetting and Network Management Omer F. Rana Networks and Data Communications 1 Subnetting Subnetting is an important concept in establishing TCP/IP based networks important in integrating small Local
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Topology A map of an internetwork that indicates network segments, interconnection points,
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Topology A map of an internetwork that indicates network segments, interconnection points,
MPLS/BGP Network Simulation Techniques for Business Enterprise Networks
 MPLS/BGP Network Simulation Techniques for Business Enterprise Networks Nagaselvam M Computer Science and Engineering, Nehru Institute of Technology, Coimbatore, Abstract Business Enterprises used VSAT
MPLS/BGP Network Simulation Techniques for Business Enterprise Networks Nagaselvam M Computer Science and Engineering, Nehru Institute of Technology, Coimbatore, Abstract Business Enterprises used VSAT
Build yourself an ISP
 Ouch what just bit me? So you ve been bitten by the Internet bug and want to dive into the world wide web by becoming what is called an Internet Service Provider (ISP). The good news is that it is actually
Ouch what just bit me? So you ve been bitten by the Internet bug and want to dive into the world wide web by becoming what is called an Internet Service Provider (ISP). The good news is that it is actually
QoS (Quality of Service)
 QoS (Quality of Service) QoS function helps you to control your network traffic for each application from LAN (Ethernet and/or Wireless) to WAN (Internet). It facilitates you to control the different quality
QoS (Quality of Service) QoS function helps you to control your network traffic for each application from LAN (Ethernet and/or Wireless) to WAN (Internet). It facilitates you to control the different quality
ISP Network Design. ISP Workshops. Last updated 16 September 2013
 ISP Network Design ISP Workshops Last updated 16 September 2013 1 ISP Network Design p PoP Topologies and Design p Backbone Design p Upstream Connectivity & Peering p Addressing p Routing Protocols p Security
ISP Network Design ISP Workshops Last updated 16 September 2013 1 ISP Network Design p PoP Topologies and Design p Backbone Design p Upstream Connectivity & Peering p Addressing p Routing Protocols p Security
WAN Technologies Based on CCNA 4 v3.1 Slides Compiled & modified by C. Pham
 WAN Technologies Based on CCNA 4 v3.1 Slides Compiled & modified by C. Pham 1 Wide-area Networks (WANs) 2 Metropolitan-Area Network (MANs) 3 Path Determination 4 Internetworking Any internetwork must include
WAN Technologies Based on CCNA 4 v3.1 Slides Compiled & modified by C. Pham 1 Wide-area Networks (WANs) 2 Metropolitan-Area Network (MANs) 3 Path Determination 4 Internetworking Any internetwork must include
Introduction to IP Numbers vs. Domain names. Adiel A. Akplogan CEO, AFRINIC. 2014
 Introduction to IP Numbers vs. Domain names Adiel A. Akplogan CEO, AFRINIC. 2014 Identifying an IP address Internet identifiers including information about how to reach a network location (via the Internet
Introduction to IP Numbers vs. Domain names Adiel A. Akplogan CEO, AFRINIC. 2014 Identifying an IP address Internet identifiers including information about how to reach a network location (via the Internet
The Internet Ecosystem
 The Internet Ecosystem 15 October 2010 Internet Society InternetSociety.org [email protected] Galerie Jean-Malbuisson, 15 CH-1204 Geneva Switzerland Tel: +41 22 807 1444 Fax: +41 22 807 1445 1775 Wiehle Ave.
The Internet Ecosystem 15 October 2010 Internet Society InternetSociety.org [email protected] Galerie Jean-Malbuisson, 15 CH-1204 Geneva Switzerland Tel: +41 22 807 1444 Fax: +41 22 807 1445 1775 Wiehle Ave.
Building MPLS VPNs with QoS Routing Capability i
 Building MPLS VPNs with QoS Routing Capability i Peng Zhang, Raimo Kantola Laboratory of Telecommunication Technology, Helsinki University of Technology Otakaari 5A, Espoo, FIN-02015, Finland Tel: +358
Building MPLS VPNs with QoS Routing Capability i Peng Zhang, Raimo Kantola Laboratory of Telecommunication Technology, Helsinki University of Technology Otakaari 5A, Espoo, FIN-02015, Finland Tel: +358
BGP Multihoming Techniques
 BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith SANOG 12 6th-14th August 2008 Kathmandu 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com /pfs/seminars/sanog12-multihoming.pdf And on the
BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith SANOG 12 6th-14th August 2008 Kathmandu 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com /pfs/seminars/sanog12-multihoming.pdf And on the
Routing in Small Networks. Internet Routing Overview. Agenda. Routing in Large Networks
 Routing in Small Networks Internet Routing Overview AS, IGP,, BGP in small networks distance vector or link state protocols like RIP or OSPF can be used for dynamic routing it is possible that every router
Routing in Small Networks Internet Routing Overview AS, IGP,, BGP in small networks distance vector or link state protocols like RIP or OSPF can be used for dynamic routing it is possible that every router
BT Internet Connect Global - Annex to the General Service Schedule
 1. Definitions The following definitions apply, in addition to those in the General Terms and Conditions and the General Services Schedule. ARP means Address Resolution Protocol. Border Gateway Protocol
1. Definitions The following definitions apply, in addition to those in the General Terms and Conditions and the General Services Schedule. ARP means Address Resolution Protocol. Border Gateway Protocol
IPv6 Deployment Strategies
 Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 10/15/2001 This document was created. 2 11/13/2001 Update to the explanation of NAT along tunnel paths. 3 03/08/2002 Update to the Related Documents section.
Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 10/15/2001 This document was created. 2 11/13/2001 Update to the explanation of NAT along tunnel paths. 3 03/08/2002 Update to the Related Documents section.
Introduction to LAN/WAN. Network Layer (part II)
 Introduction to LAN/WAN Network Layer (part II) Topics The Network Layer Introduction Routing (5.2) The Internet (5.5) IP, IP addresses ARP (5.5.4) OSPF (5.5.5) BGP (5.5.6) Congestion Control (5.3) Internetworking
Introduction to LAN/WAN Network Layer (part II) Topics The Network Layer Introduction Routing (5.2) The Internet (5.5) IP, IP addresses ARP (5.5.4) OSPF (5.5.5) BGP (5.5.6) Congestion Control (5.3) Internetworking
IPv6 and 4-byte ASN Update
 IPv6 and 4-byte ASN Update Philip Smith PacNOG 8 Pohnpei, FSM 22nd-27th November 2010 1 IPv6 Update 2 2004 Today Resurgence in demand for IPv4 address space 5% address space still unallocated
IPv6 and 4-byte ASN Update Philip Smith PacNOG 8 Pohnpei, FSM 22nd-27th November 2010 1 IPv6 Update 2 2004 Today Resurgence in demand for IPv4 address space 5% address space still unallocated
Guide to TCP/IP, Third Edition. Chapter 3: Data Link and Network Layer TCP/IP Protocols
 Guide to TCP/IP, Third Edition Chapter 3: Data Link and Network Layer TCP/IP Protocols Objectives Understand the role that data link protocols, such as SLIP and PPP, play for TCP/IP Distinguish among various
Guide to TCP/IP, Third Edition Chapter 3: Data Link and Network Layer TCP/IP Protocols Objectives Understand the role that data link protocols, such as SLIP and PPP, play for TCP/IP Distinguish among various
Distributed Systems. 09. Naming. Paul Krzyzanowski. Rutgers University. Fall 2015
 Distributed Systems 09. Naming Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2015 October 7, 2015 2014-2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Naming things Naming: map names to objects Helps with using, sharing, and communicating
Distributed Systems 09. Naming Paul Krzyzanowski Rutgers University Fall 2015 October 7, 2015 2014-2015 Paul Krzyzanowski 1 Naming things Naming: map names to objects Helps with using, sharing, and communicating
Balcan-IX Services Description
 Safe and easy communication Balcan-IX Services Description Annex B A. Balcan-IX Services Description Balcan-IX, countrywide Internet Exchange platform in Romania, offers access to IP networks connected
Safe and easy communication Balcan-IX Services Description Annex B A. Balcan-IX Services Description Balcan-IX, countrywide Internet Exchange platform in Romania, offers access to IP networks connected
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Third Edition Priscilla Oppenheimer Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 vi Тор-Down Network Design Contents at a Glance Introduction xxii Part I Identifying
Top-Down Network Design Third Edition Priscilla Oppenheimer Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 vi Тор-Down Network Design Contents at a Glance Introduction xxii Part I Identifying
An overview on Internet Measurement Methodologies, Techniques and Tools
 An overview on Internet Measurement Methodologies, Techniques and Tools AA 2012/2013 [email protected] (Agenda) Lezione 24/04/2013 Part 1 Intro basic concepts ISP Traffic exchange (peering)
An overview on Internet Measurement Methodologies, Techniques and Tools AA 2012/2013 [email protected] (Agenda) Lezione 24/04/2013 Part 1 Intro basic concepts ISP Traffic exchange (peering)
256 4 = 4,294,967,296 ten billion. 256 16 = 18,446,744,073,709,551,616 ten quintillion. IP Addressing. IPv4 Address Classes
 IP Addressing With the exception of multicast addresses, Internet addresses consist of a network portion and a host portion. The network portion identifies a logical network to which the address refers,
IP Addressing With the exception of multicast addresses, Internet addresses consist of a network portion and a host portion. The network portion identifies a logical network to which the address refers,
Understand Wide Area Networks (WANs)
 Understand Wide Area Networks (WANs) Lesson Overview In this lesson, you will review: Dial-up Integrated services digital networks (ISDN) Leased lines Virtual private networks (VPN) Wide area networks
Understand Wide Area Networks (WANs) Lesson Overview In this lesson, you will review: Dial-up Integrated services digital networks (ISDN) Leased lines Virtual private networks (VPN) Wide area networks
What is AfriNIC, IPv4 exhaustion & IPv6 transition
 AfriNIC 2005-2008 What is AfriNIC, IPv4 exhaustion & IPv6 transition The RIR System What is AfriNIC Adiel A. Akplogan CEO, AfriNIC cctld Forum, Paille (MU) March2009 Internet resources Number resources?
AfriNIC 2005-2008 What is AfriNIC, IPv4 exhaustion & IPv6 transition The RIR System What is AfriNIC Adiel A. Akplogan CEO, AfriNIC cctld Forum, Paille (MU) March2009 Internet resources Number resources?
WAN Technology. Heng Sovannarith [email protected]
 WAN Technology Heng Sovannarith [email protected] Introduction A WAN is a data communications network that covers a relatively broad geographic area and often uses transmission facilities provided
WAN Technology Heng Sovannarith [email protected] Introduction A WAN is a data communications network that covers a relatively broad geographic area and often uses transmission facilities provided
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Four Characterizing Network Traffic Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Network Traffic Factors Traffic flow unidirectional, bidirectional symmetric, asymmetric
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Four Characterizing Network Traffic Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Network Traffic Factors Traffic flow unidirectional, bidirectional symmetric, asymmetric
Advanced IP Addressing
 Advanced IP Addressing CS-765 A Aspects Of Systems Administration Spring-2005 Instructure: Jan Schauman Stevens Institute Of Technology, NJ. Prepared By: Modh, Jay A. M.S. NIS SID: 999-14-0352 Date: 05/02/2005
Advanced IP Addressing CS-765 A Aspects Of Systems Administration Spring-2005 Instructure: Jan Schauman Stevens Institute Of Technology, NJ. Prepared By: Modh, Jay A. M.S. NIS SID: 999-14-0352 Date: 05/02/2005
Glossary of Technical Terms Related to IPv6
 AAAA Record An AAAA record stores a 128-bit Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) address, which does not fit the standard A record format. For example, 2007:0db6:85a3:0000:0000:6a2e:0371:7234 is a valid
AAAA Record An AAAA record stores a 128-bit Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) address, which does not fit the standard A record format. For example, 2007:0db6:85a3:0000:0000:6a2e:0371:7234 is a valid
IMPLEMENTING CISCO IP ROUTING V2.0 (ROUTE)
 IMPLEMENTING CISCO IP ROUTING V2.0 (ROUTE) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v2.0 is an instructor-led five day training course developed to help students prepare for Cisco CCNP _
IMPLEMENTING CISCO IP ROUTING V2.0 (ROUTE) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) v2.0 is an instructor-led five day training course developed to help students prepare for Cisco CCNP _
CLASSLESS INTER DOMAIN ROUTING - CIDR
 CLASSLESS INTER DOMAIN ROUTING - CIDR Marko Luoma Helsinki University of Technology Laboratory of Telecommunications Technology [email protected] ABSTRACT As the Internet evolved and become more familiar
CLASSLESS INTER DOMAIN ROUTING - CIDR Marko Luoma Helsinki University of Technology Laboratory of Telecommunications Technology [email protected] ABSTRACT As the Internet evolved and become more familiar
NETE-4635 Computer Network Analysis and Design. Designing a Network Topology. NETE4635 - Computer Network Analysis and Design Slide 1
 NETE-4635 Computer Network Analysis and Design Designing a Network Topology NETE4635 - Computer Network Analysis and Design Slide 1 Network Topology Design Themes Hierarchy Redundancy Modularity Well-defined
NETE-4635 Computer Network Analysis and Design Designing a Network Topology NETE4635 - Computer Network Analysis and Design Slide 1 Network Topology Design Themes Hierarchy Redundancy Modularity Well-defined
How To Provide Qos Based Routing In The Internet
 CHAPTER 2 QoS ROUTING AND ITS ROLE IN QOS PARADIGM 22 QoS ROUTING AND ITS ROLE IN QOS PARADIGM 2.1 INTRODUCTION As the main emphasis of the present research work is on achieving QoS in routing, hence this
CHAPTER 2 QoS ROUTING AND ITS ROLE IN QOS PARADIGM 22 QoS ROUTING AND ITS ROLE IN QOS PARADIGM 2.1 INTRODUCTION As the main emphasis of the present research work is on achieving QoS in routing, hence this
How Routers Forward Packets
 Autumn 2010 [email protected] MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING (MPLS) AND MPLS VPNS How Routers Forward Packets Process switching Hardly ever used today Router lookinginside the packet, at the ipaddress,
Autumn 2010 [email protected] MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING (MPLS) AND MPLS VPNS How Routers Forward Packets Process switching Hardly ever used today Router lookinginside the packet, at the ipaddress,
R2. The word protocol is often used to describe diplomatic relations. How does Wikipedia describe diplomatic protocol?
 Chapter 1 Review Questions R1. What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end systems. Is a Web server an end system? 1. There is no difference. Throughout
Chapter 1 Review Questions R1. What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end systems. Is a Web server an end system? 1. There is no difference. Throughout
Textbook Required: Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 Lab Manual.
 Course: NET 251 Building Scalable Internetworks Credits: 3 Textbook Required: Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 Lab Manual. Course Description: In this course,
Course: NET 251 Building Scalable Internetworks Credits: 3 Textbook Required: Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 Lab Manual. Course Description: In this course,
Service Definition. Internet Service. Introduction. Product Overview. Service Specification
 Service Definition Introduction This Service Definition describes Nexium s from the customer s perspective. In this document the product is described in terms of an overview, service specification, service
Service Definition Introduction This Service Definition describes Nexium s from the customer s perspective. In this document the product is described in terms of an overview, service specification, service
AT&T Managed IP Network Service (MIPNS) MPLS Private Network Transport Technical Configuration Guide Version 1.0
 AT&T Managed IP Network Service (MIPNS) MPLS Private Network Transport Technical Configuration Guide Version 1.0 Introduction...2 Overview...2 1. Technology Background...2 2. MPLS PNT Offer Models...3
AT&T Managed IP Network Service (MIPNS) MPLS Private Network Transport Technical Configuration Guide Version 1.0 Introduction...2 Overview...2 1. Technology Background...2 2. MPLS PNT Offer Models...3
The Internet and Its Uses
 CHAPTER 1 The Internet and Its Uses Objectives After completing this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: How is the Internet evolving? How do businesses and individuals use the
CHAPTER 1 The Internet and Its Uses Objectives After completing this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: How is the Internet evolving? How do businesses and individuals use the
