Hyung Hun Kim, 1 Gwang Ha Kim, 2 Ji Hyun Kim, 3 Myung-Gyu Choi, 1 Geun Am Song, 2 and Sung Eun Kim Introduction
|
|
|
- Roland Morrison
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Article ID , 7 pages Clinical Study The Efficacy of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Type I Gastric Carcinoid Tumors Compared with Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Hyung Hun Kim, 1 Gwang Ha Kim, 2 Ji Hyun Kim, 3 Myung-Gyu Choi, 1 Geun Am Song, 2 and Sung Eun Kim 4 1 DepartmentofInternalMedicine,TheCatholicUniversityofKoreaCollegeofMedicine,Seoul ,RepublicofKorea 2 Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University, School of Medicine, Busan , Republic of Korea 3 Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan Paik Hospital, Gaegeum-dong, Busanjin-Gu, Busan , Republic of Korea 4 Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan , Republic of Korea Correspondence should be addressed to Ji Hyun Kim; zep2000@inje.ac.kr Received 28 October 2013; Accepted 9 January 2014; Published 17 February 2014 Academic Editor: Michelle Kang Kim Copyright 2014 Hyung Hun Kim et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Background and Aims. Conventional endoscopic submucosal resection (EMR) of carcinoid tumors often involves the resection margin, which necessitates further intervention. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is widely accepted for removing carcinoid tumors. We aimed to evaluate the clinical usefulness of ESD with that of EMR for resection of type I gastric carcinoid tumors. Patients and Methods. The study enrolled 62 patients (37 males, 25 females; median age, 50 years; range, years) who were treated with EMR or ESD at three hospitals; the study group had 87 type I gastric carcinoid tumors with an estimated size of 10 mm. The complete resection rate and the complications associated with these two procedures were analyzed. Results.Theoverall ESD complete resection rate was higher than that of the EMR rate (94.9% versus 83.3%, P value=0.174).astatisticallylowervertical margin involvement rate was achieved when ESD was performed compared to when EMR was performed (2.6% versus 16.7%, P value = 0.038). The complication rate was not significantly different between the two groups. Conclusions. ESD showed a higher complete resection rate, particularly for the vertical margin, with a similar complication rate. We mildly recommend ESD rather than EMR for removing type I gastric carcinoid tumors. 1. Introduction Although being rare, the incidence of gastric carcinoid tumors has significantly increased over the past 50 years. The percentage of gastric carcinoid tumors among all gastric malignancies has increased from 0.3 to 1.77% since the 1950s, and the proportion of gastric carcinoid tumors among all gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors has increased from 2.4 to 8.7% [1]. Undoubtedly, increased endoscopic surveillance and enhanced evaluation of gastric biopsies are partially responsible for this observed increase [2]. As knowledge of the pathogenesis and clinical significance of gastric carcinoid tumors evolves,cliniciansarebetterabletoidentifyandmanagethese tumors [2]. Gastric carcinoid tumors are classified into three categories: type I, arising in atrophic body gastritis, type II, a manifestation of type I multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN- I), and type III, with no specific background disease [3]. The type I variety comprises 70 to 80% of gastric carcinoid tumors. Type I gastric carcinoid tumors are often associated with chronic atrophic gastritis. Approximately 5% of patients with autoimmune chronic atrophic gastritis develop gastric carcinoid tumors [4 6]. Most type I gastric carcinoid tumors have a benign course, withmetastasisoccurringin <10% of tumors measuring <2cm and in 20%of larger tumors[2]. Given this low potential for malignancy, the medical and surgical treatments are controversial. Even with no treatment, there is little
2 2 Gastroenterology Research and Practice risk for local or distant metastases, and the carcinoid tumors may even regress over time [7]. In general, most clinicians would agree that type I gastric carcinoid tumors that measure <1 cm are fewer than five in number, and with no lesions extending beyond the submucosa, endoscopic resection is the optimal treatment choice [2, 8 12]. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has been approved for en bloc and complete resection of early gastric cancer, particularly in Korea and Japan, and it is considered to be the best technique for these lesions [13 15]. Moreover, this technique has been used to remove rectal carcinoid tumors and has demonstrated a superior efficacy to conventional endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), particularly for less vertical margin involvement [16, 17]. However, few reports have evaluated the efficacy of ESD comparedwithemrintypeigastriccarcinoidtumors[18]. TheaimofthisstudywastoinvestigatewhetherESDis superior to EMR for removing type I gastric carcinoid tumors as a means of complete resection. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1. Patients and Lesions. Between January 2004 and December 2012, 62 patients (37 males, 25 females; median age, 50 years; range, years) were treated with EMR or ESD at threehospitals;thestudygrouphad87typeigastriccarcinoid tumors with an estimated size of 10 mm. The tumor size was estimatedendoscopicallywithmeasuringforceps(olympus Co., Tokyo, Japan). No patient had carcinoid syndrome symptoms. All tumors were found incidentally during a screening endoscopy. No tumor invasion beyond the submucosal layer was observed on the endoscopic ultrasonography before ESD or EMR (Figure 1). Computed tomography (CT) revealed that none of the tumors were associated with lymph node metastasis or with distant metastasis. All patients provided written informed consent for the endoscopic treatment of type I gastric carcinoid tumors. The patients medical records were reviewed retrospectively to extract clinical information, including endoscopic findings (e.g., the tumor characteristics and type of surrounding gastric mucosal atrophy), laboratory findings, resection techniques, and any complications. This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board of each participating institution: Kosin University College of Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, and Pusan University College of Medicine ESD and EMR Procedures. All ESD practitioners are experts who performed over 300 cases of ESD. The ESD procedures were performed as described previously in detail with room air insufflations (Figure 2) [19]. After marking around the lesion, normal saline containing epinephrine was injected into the submucosal layer of the lesion. A circumferential mucosal incision around the lesion and submucosal dissection for the complete removal of the lesion were performed using various knives. To control bleeding during the procedure or to prevent possible bleeding from visible vessels in the artificial ulcer immediately after the resection, hemostatic forceps were used. EMR was performed, as follows (Figure 3). After a submucosal injection of saline with epinephrine, the Figure 1: An approximately 1 cm 0.8 cm, round, homogenous hypoechoic lesion located in the submucosal layer was detected using endoscopic ultrasonography. open snare was placed around a portion of the lesion and was gently pressed against the mucosa. The excess air was aspirated to decrease the distension and facilitate grasping of the targeted lesion. After snare excision, the lumen was insufflated again to visualize the resection area. Hemostatic forceps were applied to ablate any possible bleeding foci in the EMRrelated ulcers Evaluation of the Complete Resection and Complications. Endoscopic complete resection was defined as the en bloc resection of the lesion. All resected specimens were evaluated histologically using light microscopy at low-power and highpower magnifications. Histologic complete resection was defined as the lateral and vertical margin of the specimens (i.e., free of tumor invasion). Procedure-related bleeding was classified as immediate or delayed. Immediate bleeding was defined as bleeding during the procedure that did not cease spontaneously and that required hemostatic intervention, such as argon plasma/hemostatic forceps coagulation or clips (Easy clip, Olympus Co., Tokyo, Japan). Delayed bleeding was defined as the occurrence of hematemesis, hematochezia, or melena (after completing ESD or EMR) that required endoscopic and/or angiographic hemostasis or transfusions. Perforation was defined as gastric wall penetration recognized during the endoscopic procedure or detected after procedure via a radiological examination, such as X-ray or CT Statistical Analyses. All statistical analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software (version 16.0, SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Significant between-group differences were tested using Fisher s exact test and Student s t-test. P values for two-tailed tests were considered to be significant if they were < Results 3.1. Patients and Tumors. Among the 87 lesions, 48 were resected using EMR and 39 were resected using ESD. No evidence of metastasis to the lymph nodes or other organs
3 Gastroenterology Research and Practice 3 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Figure 2: (a) An approximately 1 cm, round, slightly elevated subepithelial lesion with a central hyperemic depression was observed at the anterior wall side of the lower body. (b) The marking was performed using an argon plasma coagulator. (c) A circumferential mucosal incision was performed after a submucosal injection. (d) A submucosal dissection being performed. (e) A large artificial ulcer created by endoscopic submucosal dissection for a type I gastric carcinoid tumor was observed. (f) Endoscopic en bloc resection was achieved. (g) Histologic findings (hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain, 40) showed complete resection: negative lateral and negative deep resection margin. was found in the initial evaluation of any patient. The mean tumor size was 7.6 ± 4.1 mm, and according to the KimuraTakemoto classification, open type atrophic gastritis was observed in 75.8% of the lesions. Tumors in the stomach body were more common (89%). There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the EMR and ESD groups, including age and gender (Table 1). in the ESD group (2.6%) and in two cases in the EMR group (4.2%; 𝑃 value > 0.999). The rate of vertical resection margin involvement was significantly lower in the ESD group (one case, 2.6%) than it was in the EMR group (eight cases, 16.7%; 𝑃 value = 0.038; Table 2). The complete resection rate of the vertical margin achieved using ESD was 7.6-fold greater than that for EMR Endoscopic and Histologic Complete Resection Rates. The endoscopic complete resection rate was higher in the ESD group (38 lesions, 97.4%) than in the EMR group (45 lesions, 93.7%), but this difference was not statistically significant (𝑃 value = 0.624). The histologic complete resection rate was much higher in the ESD group (37 lesions, 94.9%) than it was in the EMR group (40 lesions, 83.3%; 𝑃 value = 0.174). Involvement of the lateral resection margin was found in one case 3.3. Microscopic Findings. Lymphatic invasion was observed in 1 case (1.1%); the patient underwent surgery regardless of histologic complete resection. No vascular invasion was identified in any patient. In no case did the tumor invade the muscular propria. The mitotic index findings were as follows: <2/high power field (HPF) 83 cases (95.4%) and 2 20/HPF, four cases (4.5%). In measuring the Ki 67 index, 72 cases (82.8%) showed <2% expression and 15 cases (17.2%)
4 4 Gastroenterology Research and Practice (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Figure 3: (a) A hyperemic polypoid subepithelial lesion measuring approximately 1 cm was detected at the greater curvature side of the upper body. (b) Submucosal injection was performed. After then, an endoscopic mucosal resection was performed using a snare. (c) A small artificial ulcer produced by endoscopic mucosal resection was detected. (d) Endoscopic en bloc resection was achieved, but a yellowish vertical resection margin that was not covered with submucosal tissue was manifested (blue arrow). (e) The histologic findings (H&E stain, 10) showed a positive deep resection margin (red arrow). presented 3 20% expression. No difference was observed between the EMR and ESD groups (Table 3) Complications and Procedure Duration. There were three immediate bleedings in the EMR group and six immediate bleedings in the ESD group that occurred during the procedures (𝑃 value = 0.288). Two cases of delayed bleeding occurred eight hours after the procedure in both the ESD and EMR groups, respectively (𝑃 value > 0.999). All bleeding cases were controlled endoscopically using clips and/or hemostatic forceps, and blood transfusions were not necessary. One perforation occurred in the ESD group; it was managed successfully by clipping. The procedure duration is much longer in ESD group (26.1 ± 10.5 min versus 9.5 ± 3.6 min, 𝑃 value < 0.001, Table 4). 4. Discussion The present study found that ESD resulted in histologically complete resection in 94.9% of patients with type I gastric
5 Gastroenterology Research and Practice 5 Table 1: Baseline characteristics of patients with EMR and ESD groups. EMR (n =48) ESD(n=39) P value Age, mean ± SD, year 53.2 ± ± Male, n (%) 18 (37.5) 22 (56.4) Dyspepsia, n (%) 12 (25.0) 9 (23.1) Endoscopic findings Open type atrophic gastritis, n (%) 38 (79.1) 28 (71.8) Size of the tumor, mean ± SD, mm 7.8 ± ± Location Antrum 10 (20.8) 8 (20.5) Body 32 (66.7) 28 (71.8) Fundus 6 (12.5) 3 (7.7) According to Kimura-Takemoto classification in white light endoscopy image. EMR: endoscopic mucosal resection and ESD: endoscopic submucosal dissection. Table 2: Complete resection rate in endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection groups. EMR (n =48) ESD(n=39) P value Endoscopic complete resection, n (%) 45 (93.7) 38 (97.4) Histologic complete resection, n (%) 40 (83.3) 37 (94.9) Lateral margin involvement, n (%) 2 (4.2) 1 (2.6) >0.999 Vertical margin involvement, n (%) 8 (16.7) 1 (2.6) EMR: endoscopic mucosal resection and ESD: endoscopic submucosal dissection; odd ratio was 7.6. Table 3: Microscopic findings of resected carcinoid tumors. EMR (n =48) ESD(n=39) P value Lymphovascular findings Lymphatic invasion, n (%) 1 (2.1) 0 (0.0) Vascular invasion, n (%) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) NA Invading to muscular propria, n (%) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) NA Mitotic index <2/HPF, n (%) 46 (95.8) 37 (94.9) 2 20/HPF, n (%) 2 (4.1) 2 (5.1) >0.999 Ki 67 index <2%, n (%) 38 (79.2) 34 (87.2) 3 20%, n (%) 10 (42.7) 5 (12.8) EMR: endoscopic mucosal resection, ESD: endoscopic submucosal dissection, and NA: not accessible. Table 4: Complication and procedure duration in endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection groups. EMR (n =48) ESD(n=39) P value Immediate bleeding, n (%) 3 (6.3) 6 (15.4) Delayed bleeding, n (%) 2 (4.2) 2 (5.1) >0.999 Perforation, n (%) 0 (0.0) 1 (2.6) Surgery due to complication, n (%) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) NA Procedure time, mean ± SD, min 26.1 ± ± 3.6 <0.001 EMR: endoscopic mucosal resection, ESD: endoscopic submucosal dissection, and NA: not accessible. carcinoid tumors; this result was greater than the 83.3% rate achieved by using EMR. Although there were no significant differences in the overall complete resection rate and lateral margin involvement, a significantly lower vertical resection margin involvement was observed. The higher histologically complete resection rate associated with ESD is clinically significant given the advantage of complete histological resection of type I gastric carcinoid tumors. First, complete resection is essential for determining the subsequent management options. Although the risk of
6 6 Gastroenterology Research and Practice metastasis from small type I gastric carcinoid tumors is generally low, some patients, even those with carcinoid tumors measuring <10 mm in diameter, may have metastases [20]. One recent study reported that 3.4% of tumors measuring <1cminvadingintothelaminapropriaorsubmucosahad lymph node metastases [20]. This observation demonstrates that it is safe to recommend additional resection with lymph node dissection if the endoscopically resected gastric carcinoid tumor specimens show lymphovascular invasion. To understand lymphovascular invasion accurately, it is necessary to acquire a substantial amount of submucosal tissue. For this reason, ESD is the better option compared with EMR. A second advantage provided by complete histologic resection is that frequent endoscopic follow-up may not be required. Although a consensus protocol has yet to be established, it is recommended that follow-up endoscopy should not be delayed for too long after an incomplete gastric carcinoid tumor resection. Incomplete resection inevitably requires additional medical resources and inconveniences the patient. Finally, a repeat of endoscopic resection of a remnant tumor after an initial incomplete endoscopic resection may be difficult (and even dangerous) because fibrosis prevents lifting the lesion using submucosal injection [21, 22]. Therefore, itwouldbereasonabletorecommendacquiringhistologically complete resection of type I gastric carcinoid tumors in the first trial when the lesions are small. This study showed that ESD may produce the most desirable patient outcomes. In the ESD group, there were two instances of delayed bleeding and one case of perforation. The complication rate in theesdgroupwassimilartothatintheemrgroupandwas similar to the rates that have been described in previous reports [23 25]. Therefore, we concluded that ESD can be a useful strategy for managing type I gastric carcinoid tumors basedontheriskofcomplications. The present study had several limitations. First, a retrospective study was used; a thorough review of available information was performed from the medical records. Therefore, we were unable to describe some intricate details about the procedures. However, we are certain that important data, including the resection rate and complications, were included. Second, some specific aspects of the ESD and EMR procedures might be different because we collected information from three different university hospitals, but this limitationwasaninevitablepartoftheprocesstoevaluateenough cases to produce a substantial statistical power, which was not acquired in the previous studies [18, 23 25]. Alternatively, this multicenter study has the advantage of producing data that can be generalized across centers. Third, the follow-up result for recurrence should be considered to adequately evaluate the efficacy of the practice. However, many patients were lost to follow up; therefore differences in recurrence rates with each technique could not be determined. In conclusion, ESD need to be considered when treating type I gastric carcinoid tumors for the following two reasons despiteoflongerproceduredurationcomparedwithemr. First, ESD yielded a significantly higher histologic complete resection rate than EMR, particularly in the vertical resection margin, resulting in complete histologic evaluation, less frequent endoscopic follow-up, and the prevention of additional endoscopic procedures. Second, the complication rates of ESD and EMR were similar. The long-term results after ESD and EMR treatments should be addressed in future prospective studies. Abbreviations EMR: Endoscopic mucosal resection ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection CT: Computed tomography. Conflict of Interests The authors do have no conflict of interests regarding this paper. Authors Contribution HyungHunKimandGwangHaKimcontributedtothis paper equally. Acknowledgment This work was supported by the 2013 Inje University research grant. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2013R1A1A and NRF ). References [1] I. M. Modlin, K. D. Lye, and M. Kidd, A 50-year analysis of 562 gastric carcinoids: small tumor or larger problem? The American Gastroenterology,vol.99,no.1,pp.23 32,2004. [2]L.Zhang,J.Ozao,R.Warner,andC.Divino, Reviewofthe pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of type I gastric carcinoid tumor, World Surgery,vol.35, no.8,pp , [3] G.DelleFave,G.Capurso,M.Milione,andF.Panzuto, Endocrine tumours of the stomach, Best Practice and Research: Clinical Gastroenterology,vol.19,no.5,pp ,2005. [4] K.Borch,B.Ahrén,H.Ahlman,S.Falkmer,G.Granérus, and L. Grimelius, Gastric carcinoids: biologic behavior and prognosis after differentiated treatment in relation to type, Annals of Surgery,vol.242,no.1,pp.64 73,2005. [5] O. Hosokawa, Y. Kaizaki, M. Hattori et al., Long-term follow up of patients with multiple gastric carcinoids associated with type Agastritis, Gastric Cancer,vol.8,no.1,pp.42 46,2005. [6] D.B.Gough,G.B.Thompson,T.B.Crottyetal., Diverseclinical and pathologic features of gastric carcinoid and the relevance of hypergastrinemia, World Surgery,vol.18,no. 4, pp , [7] R. Bründler,J.O.Gebbers,andD.Criblez, Multiplegastric carcinoid tumours in chronic atrophic gastritis: long-term follow-up under conservative management, Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift,vol.129,no.25,pp ,1999. [8] C.J.Gilligan,G.P.Lawton,L.H.Tang,A.B.West,andI.M. Modlin, Gastric carcinoid tumors: the biology and therapy of
7 Gastroenterology Research and Practice 7 an enigmatic and controversial lesion, The American Gastroenterology,vol.90,no.3,pp ,1995. [9] G.Kadikoylu,I.Yavasoglu,V.Yukselen,E.Ozkara,andZ.Bolaman, Treatment of solitary gastric carcinoid tumor by endoscopic polypectomy in a patient with pernicious anemia, World Gastroenterology,vol.12,no.26,pp ,2006. [10] M. Schindl, K. Kaserer, and B. Niederle, Treatment of gastric neuroendocrine tumors: the necessity of a type-adapted treatment, Archives of Surgery,vol.136,no. 1,pp.49 54,2001. [11] S. Manfredi, M. Pagenault, A. de Lajarte-Thirouard, and J. Bretagne, Type 1 and 2 gastric carcinoid tumors: long-term followup of the efficacy of treatment with a slow-release somatostatin analogue, European Gastroenterology and Hepatology,vol.19,no.11,pp ,2007. [12] P. Guillem, Gastric carcinoid tumours. Is there a place for antrectomy? Annales de Chirurgie,vol.130,no.5, pp , [13] T. Gotoda, H. Yamamoto, and R. M. Soetikno, Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer, Gastroenterology,vol.41,no.10,pp ,2006. [14] S. Oka, S. Tanaka, I. Kaneko et al., Advantage of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer, Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, vol.64,no.6,pp , [15] Y. Onozato, H. Ishihara, H. Iizuka et al., Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancers and large flat adenomas, Endoscopy, vol. 38, no. 10, pp , [16] D. S. Lee, S. W. Jeon, S. Y. Park et al., The feasibility of endoscopic submucosal dissection for rectal carcinoid tumors: comparison with endoscopic mucosal resection, Endoscopy,vol.42, no. 8, pp , [17] H.W.Park,J.S.Byeon,Y.S.Parketal., Endoscopicsubmucosal dissection for treatment of rectal carcinoid tumors, Gastrointestinal Endoscopy,vol.72,no.1,pp ,2010. [18] Y. Sato, M. Takeuchi, S. Hashimoto et al., Usefulness of endoscopic submucosal dissection for type I gastric carcinoid tumors compared with endoscopic mucosal resection, Hepatogastroenterology,vol.60,no.126,pp ,2013. [19] H. Isomoto, S. Shikuwa, N. Yamaguchi et al., Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: a large-scale feasibility study, Gut, vol. 58, no. 3, pp , [20] M. S. Saund, R. H. Al Natour, A. M. Sharma, Q. Huang, V. A. Boosalis, and J. S. Gold, Tumor size and depth predict rate of lymph node metastasis and utilization of lymph node sampling in surgically managed gastric carcinoids, Annals of Surgical Oncology, vol. 18, no. 10, pp , [21] M. Higashimaya, S. Oka, S. Tanaka et al., Outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric neoplasm in relationship to endoscopic classification of submucosal fibrosis, Gastric Cancer, vol. 16, no. 3, pp , [22] K. S. Han, D. K. Sohn, D. H. Choi et al., Prolongation of the period between biopsy and EMR can influence the nonlifting sign in endoscopically resectable colorectal cancers, Gastrointestinal Endoscopy,vol.67,no.1,pp ,2008. [23] Q. L. Li, Y. Q. Zhang, W. F. Chen et al., Endoscopic submucosal dissection for foregut neuroendocrine tumors: an initial study, World Gastroenterology, vol.18,no.40,pp , [24]W.F.Chen,P.H.Zhou,Q.L.Li,M.D.Xu,andL.Q.Yao, Clinical impact of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric neuroendocrine tumors: a retrospective study from mainland of China, The Scientific World Journal, vol. 2012, ArticleID , 6 pages, [25] C. W. Choi, D. H. Kang, H. W. Kim et al., Comparison of endoscopic resection therapies for rectal carcinoid tumor: endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection using band ligation, Clinical Gastroenterology,vol.47,no.5,pp ,2013.
8 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Learning Luncheon 7: Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: When, Where and How?
 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): When, Where, and Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) EMR developed for removal of sessile or flat neoplasms
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): When, Where, and Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) EMR developed for removal of sessile or flat neoplasms
How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens
 Section of Pathology and Tumour Biology How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens Dr.H.Grabsch Warning. Most of the criteria, methodologies, evidence presented in this talk are based on studies in early
Section of Pathology and Tumour Biology How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens Dr.H.Grabsch Warning. Most of the criteria, methodologies, evidence presented in this talk are based on studies in early
EMR Can anyone do this?
 EMR Can anyone do this? Norio Fukami, MD University of Colorado Piecemeal resection? 1 Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) Endoscopic removal of premalignant or
EMR Can anyone do this? Norio Fukami, MD University of Colorado Piecemeal resection? 1 Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) Endoscopic removal of premalignant or
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (E.S.D.) vs. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (E.M.R.) in Colombia. Advocating E.M.R.
 Controversies in Gastroenterology Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (E.S.D.) vs. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (E.M.R.) in Colombia. Advocating E.M.R. Raúl Cañadas Garrido, MD. 1 1 Internist-Gastroenterologist.
Controversies in Gastroenterology Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (E.S.D.) vs. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (E.M.R.) in Colombia. Advocating E.M.R. Raúl Cañadas Garrido, MD. 1 1 Internist-Gastroenterologist.
Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer
 Gut 2001;48:225 229 225 Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer H Ono, H Kondo, T Gotoda, K Shirao, H Yamaguchi, D Saito, K Hosokawa, T Shimoda, S Yoshida Department of Endoscopy
Gut 2001;48:225 229 225 Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer H Ono, H Kondo, T Gotoda, K Shirao, H Yamaguchi, D Saito, K Hosokawa, T Shimoda, S Yoshida Department of Endoscopy
These parameters cannot, at the present time, be determined by non-invasive imaging techniques.
 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Upper Gastrointestinal Lesions Kenneth K. Wang, M.D. Chairman, WEO Publication and Guidelines Committee Professor of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota Upper gastrointestinal
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Upper Gastrointestinal Lesions Kenneth K. Wang, M.D. Chairman, WEO Publication and Guidelines Committee Professor of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota Upper gastrointestinal
ESD for colorectal lesions I am in favour. Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy
 ESD for colorectal lesions I am in favour Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy Surgery for early colonic lesions 51 pts referred for lap colectomy
ESD for colorectal lesions I am in favour Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy Surgery for early colonic lesions 51 pts referred for lap colectomy
BAISHIDENG PUBLISHING GROUP INC
 Reviewer s code: 01714224 Reviewer s country: Italy Date reviewed: 2015-01-30 20:36 [ Y] Grade A: Priority publishing [ ] Accept [ ] Grade C: Good [ Y] Grade D: Fair language [ Y] Major revision The article
Reviewer s code: 01714224 Reviewer s country: Italy Date reviewed: 2015-01-30 20:36 [ Y] Grade A: Priority publishing [ ] Accept [ ] Grade C: Good [ Y] Grade D: Fair language [ Y] Major revision The article
Thursday, November 3, 2005
 Thursday, November 3, 2005 8:30-10:30 a. m. Gastric Tumors, Session 1 Chairman: P. Ruszniewski, Clichy, France 9:00-9:30 a. m. Working Group Sessions Pathology and Genetics Group leaders: G. Rindi, Parma,
Thursday, November 3, 2005 8:30-10:30 a. m. Gastric Tumors, Session 1 Chairman: P. Ruszniewski, Clichy, France 9:00-9:30 a. m. Working Group Sessions Pathology and Genetics Group leaders: G. Rindi, Parma,
Endoscopic Therapy for Early Esophageal Cancer: EMR and ESD
 Endoscopic Therapy for Early Esophageal Cancer: EMR and ESD AATS Toronto April 26, 2014 Lorenzo Ferri MD PhD David S. Mulder Chair in Surgery Associate Professor of Surgery and Oncology Disclosures Olympus
Endoscopic Therapy for Early Esophageal Cancer: EMR and ESD AATS Toronto April 26, 2014 Lorenzo Ferri MD PhD David S. Mulder Chair in Surgery Associate Professor of Surgery and Oncology Disclosures Olympus
Challenges in gastric, appendiceal and rectal NETs Leuven, 29.11.2014
 Challenges in gastric, appendiceal and rectal NETs Leuven, 29.11.2014 Prof. Dr. Chris Verslype, Leuven Prof. Dr. Aurel Perren, Bern Menue Challenges: 1. Gastric NET 2. Appendiceal NET 3. Rectal NET SEER,
Challenges in gastric, appendiceal and rectal NETs Leuven, 29.11.2014 Prof. Dr. Chris Verslype, Leuven Prof. Dr. Aurel Perren, Bern Menue Challenges: 1. Gastric NET 2. Appendiceal NET 3. Rectal NET SEER,
The utility of endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy in the endoscopic mucosal resection of early gastric cancer
 Gut 1999;45:599 604 599 The utility of endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy in the endoscopic mucosal resection of early gastric cancer S Ohashi, K Segawa, S Okamura, M Mitake, H Urano, M Shimodaira,
Gut 1999;45:599 604 599 The utility of endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy in the endoscopic mucosal resection of early gastric cancer S Ohashi, K Segawa, S Okamura, M Mitake, H Urano, M Shimodaira,
Captivator EMR Device
 Device Clinical Article and Abstract Summary Endoscopic Mucosal Bergman et al: EMR Training Tips Bergman et al: EMR Learning Curve ASGE: EMR & ESD Guidelines Bergman et al: Captivator EMR vs Cook Duette
Device Clinical Article and Abstract Summary Endoscopic Mucosal Bergman et al: EMR Training Tips Bergman et al: EMR Learning Curve ASGE: EMR & ESD Guidelines Bergman et al: Captivator EMR vs Cook Duette
Evolution of Barrett s esophagus
 Endoscopic Treatment and Surveillance of Esophageal Cancer: GI Perspective Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Evolution of Barrett s esophagus Squamous esophagus Chronic inflammation
Endoscopic Treatment and Surveillance of Esophageal Cancer: GI Perspective Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Evolution of Barrett s esophagus Squamous esophagus Chronic inflammation
ERBEJET 2. The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY
 ERBEJET 2 The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY Gentle interventions in surgery and endoscopy Waterjet surgery with hybrid technology Waterjet surgery
ERBEJET 2 The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY Gentle interventions in surgery and endoscopy Waterjet surgery with hybrid technology Waterjet surgery
Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus and Early Cancer 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery
 Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus and Early Cancer 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery Matthew Hartwig, M.D. Duke Cancer Institute Case Presentation: Patient ER 51 y/o man with schizophrenia
Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus and Early Cancer 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery Matthew Hartwig, M.D. Duke Cancer Institute Case Presentation: Patient ER 51 y/o man with schizophrenia
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of colorectal neoplasms ENDOSCOPY CORNER
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:22 26 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Efficacy of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection With Circumferential Incision for Patients With Large Colorectal Tumors TAKU SAKAMOTO, TAKAHISA
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:22 26 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Efficacy of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection With Circumferential Incision for Patients With Large Colorectal Tumors TAKU SAKAMOTO, TAKAHISA
Format for ANSWERING REVIEWERS
 Format for ANSWERING REVIEWERS July 15, 2015 Dear Editor, Please find enclosed the edited manuscript in Word format (file name: 19935-revised manuscript). Title: Management and associated factors of delayed
Format for ANSWERING REVIEWERS July 15, 2015 Dear Editor, Please find enclosed the edited manuscript in Word format (file name: 19935-revised manuscript). Title: Management and associated factors of delayed
Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate
 Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate Hironori Yamamoto, MD, Hiroshi Kawata, MD, Keijiro Sunada,
Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate Hironori Yamamoto, MD, Hiroshi Kawata, MD, Keijiro Sunada,
The digestive system. Medicine and technology. Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies
 The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
Magnetic Anchor for More Effective Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2004;34(3)118 123 Magnetic Anchor for More Effective Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Toshiaki Kobayashi 1, Takushi Gotohda 1, Katsunori Tamakawa 2, Hirohisa Ueda 3 and Tadao Kakizoe 1 1 National
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2004;34(3)118 123 Magnetic Anchor for More Effective Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Toshiaki Kobayashi 1, Takushi Gotohda 1, Katsunori Tamakawa 2, Hirohisa Ueda 3 and Tadao Kakizoe 1 1 National
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com. Digestive and Liver Disease 41 (2009) 201 209. Digestive Endoscopy
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Digestive and Liver Disease 41 (2009) 201 209 Digestive Endoscopy Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for treating early gastric cancer:
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Digestive and Liver Disease 41 (2009) 201 209 Digestive Endoscopy Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for treating early gastric cancer:
How to treat early gastric cancer. Surgery
 How to treat early gastric cancer Surgery Mark I. van Berge Henegouwen Department of Surgery, AMC, Amsterdam Director upper GI surgical unit Academic Medical Center Upper GI surgery at AMC 100 oesophagectomies
How to treat early gastric cancer Surgery Mark I. van Berge Henegouwen Department of Surgery, AMC, Amsterdam Director upper GI surgical unit Academic Medical Center Upper GI surgery at AMC 100 oesophagectomies
Bridging Techniques. What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS
 Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
ENDOSCOPIC SUBMUCOSAL DISSECTION FOR THE TREATMENT OF EARLY ESOPHAGEAL AND GASTRIC CANCER - INITIAL EXPERIENCE OF A WESTERN CENTER
 CLINICS 2010;65(4):377-82 CLINICAL SCIENCE ENDOSCOPIC SUBMUCOSAL DISSECTION FOR THE TREATMENT OF EARLY ESOPHAGEAL AND GASTRIC CANCER - INITIAL EXPERIENCE OF A WESTERN CENTER Dalton Marques Chaves, I Fauze
CLINICS 2010;65(4):377-82 CLINICAL SCIENCE ENDOSCOPIC SUBMUCOSAL DISSECTION FOR THE TREATMENT OF EARLY ESOPHAGEAL AND GASTRIC CANCER - INITIAL EXPERIENCE OF A WESTERN CENTER Dalton Marques Chaves, I Fauze
Case Report Concurrent Esophageal Dysplasia and Leiomyoma
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine, Article ID 804175, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/804175 Case Report Concurrent Esophageal Dysplasia and Leiomyoma Asim Shuja 1 and Khalid A. Alkimawi
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine, Article ID 804175, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/804175 Case Report Concurrent Esophageal Dysplasia and Leiomyoma Asim Shuja 1 and Khalid A. Alkimawi
Post-DDW OAG Course - Therapeutic Endoscopy
 Post-DDW OAG Course - Therapeutic Endoscopy June 13, 2015 Jeffrey Mosko Division of Gastroenterology St. Michael's Hospital University of Toronto moskoj@smh.ca Program Name: Post-DDW OAG course CanMEDS
Post-DDW OAG Course - Therapeutic Endoscopy June 13, 2015 Jeffrey Mosko Division of Gastroenterology St. Michael's Hospital University of Toronto moskoj@smh.ca Program Name: Post-DDW OAG course CanMEDS
Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options
 Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options Michael A Smith, MD Associate Chief Thoracic Surgery Center for Thoracic Disease St Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center Phoenix, AZ Michael Smith, MD
Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options Michael A Smith, MD Associate Chief Thoracic Surgery Center for Thoracic Disease St Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center Phoenix, AZ Michael Smith, MD
2/49; 4.1% 7/41; PATIENTS AND METHODS
 A new technique for endoscopic mucosal resection with an insulated-tip electrosurgical knife improves the completeness of resection of intramucosal gastric neoplasms Received July 6, 2001. For revision
A new technique for endoscopic mucosal resection with an insulated-tip electrosurgical knife improves the completeness of resection of intramucosal gastric neoplasms Received July 6, 2001. For revision
Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline
 Guideline 829 Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline Authors Institutions Pedro Pimentel-Nunes 1, Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1, Thierry Ponchon 2, Alessandro
Guideline 829 Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline Authors Institutions Pedro Pimentel-Nunes 1, Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1, Thierry Ponchon 2, Alessandro
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Combination Therapy After EMR/ESD for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Submucosal Invasion
 Combination Therapy After EMR/ESD for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Submucosal Invasion 8 Ota M., Nakamura T. and Yamamoto M. Department of Surgery, Institute of Gastroenterology, Tokyo Women's
Combination Therapy After EMR/ESD for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Submucosal Invasion 8 Ota M., Nakamura T. and Yamamoto M. Department of Surgery, Institute of Gastroenterology, Tokyo Women's
Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm
 Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm Shinji Tanaka, MD, Ken Haruma, MD, Shiro Oka, MD, Ryoji Takahashi, MD, Masaki Kunihiro,
Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm Shinji Tanaka, MD, Ken Haruma, MD, Shiro Oka, MD, Ryoji Takahashi, MD, Masaki Kunihiro,
Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Evidence tabel Early Gastric Cancer
 Evidence tabel Early Gastric Cancer Auteurs, jaartal Mate van bewijs Studie type Follow-up Wang, 2006 Systematic review Search up to Feb 2006 Mean 35.3 months (range 18-66) Populatie (incl. steekproefgrootte)
Evidence tabel Early Gastric Cancer Auteurs, jaartal Mate van bewijs Studie type Follow-up Wang, 2006 Systematic review Search up to Feb 2006 Mean 35.3 months (range 18-66) Populatie (incl. steekproefgrootte)
Endo Conference: Large Polypectomy & EMR
 Endo Conference: Large Polypectomy & EMR Dr. Whang Feb 3, 2015 VOGELGRAM: genetic pathway of colorectal cancer & genes affected by point mutations Outline I. Baseline Colonoscopy II. Colon Polyps III.
Endo Conference: Large Polypectomy & EMR Dr. Whang Feb 3, 2015 VOGELGRAM: genetic pathway of colorectal cancer & genes affected by point mutations Outline I. Baseline Colonoscopy II. Colon Polyps III.
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after
 Sample Peer-Review of a Fictitious Manuscript Reviewer A s Comments to Authors: This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after EMR of Barrett s esophagus
Sample Peer-Review of a Fictitious Manuscript Reviewer A s Comments to Authors: This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after EMR of Barrett s esophagus
Developing an endoscopic mucosal resection service in a district general hospital
 RESEARCH Developing an endoscopic mucosal resection service in a district general hospital Chris A Lamb, 1 Jamie A Barbour 2 1 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University, The Medical School,
RESEARCH Developing an endoscopic mucosal resection service in a district general hospital Chris A Lamb, 1 Jamie A Barbour 2 1 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University, The Medical School,
Billing Guideline. Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16
 Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16 Billing Guideline Background Health First administers benefit packages with full coverage
Subject: Colorectal Cancer Screening Exams (Invasive Procedures) Effective Date: 1/1/2012 Last Update Effective: 4/16 Billing Guideline Background Health First administers benefit packages with full coverage
Case Report Pleural Mesothelioma Presenting as Periumbilical Metastasis: The First Clinical Documentation
 Volume 2013, Article ID 198729, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/198729 Case Report Pleural Mesothelioma Presenting as Periumbilical Metastasis: The First Clinical Documentation R. F. Falkenstern-Ge,
Volume 2013, Article ID 198729, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/198729 Case Report Pleural Mesothelioma Presenting as Periumbilical Metastasis: The First Clinical Documentation R. F. Falkenstern-Ge,
Research Article Prevalence of Provocative Seizures in Persons with Epilepsy: A Longitudinal Study at Khon Kaen University Hospital, Thailand
 Neurology Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 659189, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/659189 Research Article Prevalence of Provocative Seizures in Persons with Epilepsy: A Longitudinal
Neurology Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 659189, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/659189 Research Article Prevalence of Provocative Seizures in Persons with Epilepsy: A Longitudinal
Received June 18, 2007; Revised August 30, 2007; Accepted August 30, 2007; Published September 17, 2007
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 1575 1578 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.253 Unusual Complication of Suprapubic Cystostomy in a Male Patient with Tetraplegia: Traction
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 1575 1578 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.253 Unusual Complication of Suprapubic Cystostomy in a Male Patient with Tetraplegia: Traction
Correspondence should be addressed to Heinz-Jakob Langen; hj.langen@missioklinik.de
 Radiology Research and Practice, Article ID 312846, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/312846 Research Article Performing Chest X-Rays at Inspiration in Uncooperative Children: The Effect of Exercises
Radiology Research and Practice, Article ID 312846, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/312846 Research Article Performing Chest X-Rays at Inspiration in Uncooperative Children: The Effect of Exercises
POEM Procedure for. Esophageal Achalasia
 POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
Research Article Inconsistencies Exist in National Estimates of Eye Care Services Utilization in the United States
 Ophthalmology Volume 2015, Article ID 435606, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/435606 Research Article Inconsistencies Exist in National Estimates of Eye Care Services Utilization in the United States
Ophthalmology Volume 2015, Article ID 435606, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/435606 Research Article Inconsistencies Exist in National Estimates of Eye Care Services Utilization in the United States
Case Report Chronic Neck Pain Associated with an Old Odontoid Fracture: A Rare Presentation
 Case Reports in Emergency Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 372723, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/372723 Case Report Chronic Neck Pain Associated with an Old Odontoid Fracture: A Rare Presentation
Case Reports in Emergency Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 372723, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/372723 Case Report Chronic Neck Pain Associated with an Old Odontoid Fracture: A Rare Presentation
Endoscopic caps are commonly used for both diagnosis
 Endoscopic Caps Kazuki Sumiyama, MD, and Elizabeth Rajan, MD Endoscopic caps are commonly used accessories for both endoscopic therapy and diagnosis. Many variations of endoscopic caps are available. Cap
Endoscopic Caps Kazuki Sumiyama, MD, and Elizabeth Rajan, MD Endoscopic caps are commonly used accessories for both endoscopic therapy and diagnosis. Many variations of endoscopic caps are available. Cap
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD
 SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
Selection of appropriate endoscopic therapies for duodenal tumors: An open-label study, single-center experience
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8624 World J Gastroenterol 2014 July 14; 20(26): 8624-8630 ISSN 1007-9327 (print)
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8624 World J Gastroenterol 2014 July 14; 20(26): 8624-8630 ISSN 1007-9327 (print)
THYROID CANCER. I. Introduction
 THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
Neuroendocrine Tumors
 Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Captivator II. Single-Use Snares
 Captivator II Single-Use Snares Captivator II Snares are the first line of stiff and rounded snares available in multiple sizes with both a hot and cold snaring indication. The Captivator II Snare line
Captivator II Single-Use Snares Captivator II Snares are the first line of stiff and rounded snares available in multiple sizes with both a hot and cold snaring indication. The Captivator II Snare line
HOW I DO IT Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in the esophagus
 HOW I DO IT (EMR) in the esophagus AUTHORSHIP How I do it: Horst Neuhaus, MD Department of Internal Medicine Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf Germany Comment Hiroyasu Makuuchi, MD Professor and Chairman
HOW I DO IT (EMR) in the esophagus AUTHORSHIP How I do it: Horst Neuhaus, MD Department of Internal Medicine Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf Germany Comment Hiroyasu Makuuchi, MD Professor and Chairman
Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics
 Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics 5758 South Maryland Avenue (MC9028) Chicago, Illinois 60637 (773) 702-1459 www.uchospitals.edu Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics To refer a patient
Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics 5758 South Maryland Avenue (MC9028) Chicago, Illinois 60637 (773) 702-1459 www.uchospitals.edu Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics To refer a patient
Case Report Laser Vision Correction on Patients with Sick Optic Nerve: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 796463, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/796463 Case Report Laser Vision Correction on Patients with Sick Optic Nerve: A Case Report Ming Chen
Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 796463, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/796463 Case Report Laser Vision Correction on Patients with Sick Optic Nerve: A Case Report Ming Chen
LOWER GI ENDOSCOPIES So why is CMS yanking our chain? General Concepts for all GI Endoscopy Procedures
 LOWER GI ENDOSCOPIES We have lots of changes to lower GI coding for 2015 to talk about. Code definitions have been revised and many new codes have been added to this chapter. First the good news: All these
LOWER GI ENDOSCOPIES We have lots of changes to lower GI coding for 2015 to talk about. Code definitions have been revised and many new codes have been added to this chapter. First the good news: All these
Endotherapy for high grade dysplasia & early oesophageal neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: A single centre retrospective audit
 Endotherapy for high grade dysplasia & early oesophageal neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: A single centre retrospective audit U Duffy, K Gowland, AI Morris, HL Smart Department of Gastroenterology, Royal
Endotherapy for high grade dysplasia & early oesophageal neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: A single centre retrospective audit U Duffy, K Gowland, AI Morris, HL Smart Department of Gastroenterology, Royal
Tumor Budding as a Useful Prognostic Marker in T1-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus
 2013;108:42 46 Tumor Budding as a Useful Prognostic Marker in T1-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus HITOSHI TERAMOTO, MD, 1 * MASAHIKO KOIKE, MD, PhD, 1 CHIE TANAKA, MD, PhD, 1 SUGURU YAMADA,
2013;108:42 46 Tumor Budding as a Useful Prognostic Marker in T1-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus HITOSHI TERAMOTO, MD, 1 * MASAHIKO KOIKE, MD, PhD, 1 CHIE TANAKA, MD, PhD, 1 SUGURU YAMADA,
Gastrointestinal and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth
 Gastrointestinal and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth What is the definition of neuroendocrine tumours? Neuroendocrine tumours are neoplastic lesions, composed either by
Gastrointestinal and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth What is the definition of neuroendocrine tumours? Neuroendocrine tumours are neoplastic lesions, composed either by
The Captivator II Snares are the first line of stiff and rounded snares available in multiple sizes with both a hot and cold snaring indication.
 Captivator II Single-Use Snares The Captivator II Snares are the first line of stiff and rounded snares available in multiple sizes with both a hot and cold snaring indication. The Captivator II Snare
Captivator II Single-Use Snares The Captivator II Snares are the first line of stiff and rounded snares available in multiple sizes with both a hot and cold snaring indication. The Captivator II Snare
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Research Article Frequency of Surgery in Black Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
 Disease Markers Volume 2015, Article ID 282145, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/282145 Research Article Frequency of Surgery in Black Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Emanuela Taioli,
Disease Markers Volume 2015, Article ID 282145, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/282145 Research Article Frequency of Surgery in Black Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Emanuela Taioli,
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
Argon plasma coagulation for successful treatment of early gastric cancer with intramucosal invasion
 334 CANCER Argon plasma coagulation for successful treatment of early gastric cancer with intramucosal invasion T Sagawa, T Takayama, T Oku, T Hayashi, H Ota, T Okamoto, H Muramatsu, S Katsuki, Y Sato,
334 CANCER Argon plasma coagulation for successful treatment of early gastric cancer with intramucosal invasion T Sagawa, T Takayama, T Oku, T Hayashi, H Ota, T Okamoto, H Muramatsu, S Katsuki, Y Sato,
Surgical Management of Papillary Microcarcinoma 趙 子 傑 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 林 口 總 院 一 般 外 科
 Surgical Management of Papillary Microcarcinoma 趙 子 傑 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 林 口 總 院 一 般 外 科 Papillary microcarcinoma of thyroid Definition latent aberrant thyroid occult thyroid carcinoma latent papillary carcinoma)
Surgical Management of Papillary Microcarcinoma 趙 子 傑 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 林 口 總 院 一 般 外 科 Papillary microcarcinoma of thyroid Definition latent aberrant thyroid occult thyroid carcinoma latent papillary carcinoma)
Male. Female. Death rates from lung cancer in USA
 Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Male Female Death rates from lung cancer in USA Smoking represents an interesting combination of an entrenched industry and a clearly drug-induced cancer Tobacco Use in the US, 1900-2000 5000 100 Per Capita
Clinical Study The Risk of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection in the Setting of Clopidogrel Use
 ISRN Gastroenterology, Article ID 494157, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/494157 Clinical Study The Risk of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection in the Setting of Clopidogrel Use Vikneswaran Namasivayam,
ISRN Gastroenterology, Article ID 494157, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/494157 Clinical Study The Risk of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection in the Setting of Clopidogrel Use Vikneswaran Namasivayam,
NET della mammella: realtà o fantasia
 NET della mammella: realtà o fantasia Roberto BALDELLI M.D., Ph.D. Regina Elena, Italian National Cancer Institute, Rome Unit of Endocrinology baldelli@ifo.it Tumors arising from enterochromaffin cells
NET della mammella: realtà o fantasia Roberto BALDELLI M.D., Ph.D. Regina Elena, Italian National Cancer Institute, Rome Unit of Endocrinology baldelli@ifo.it Tumors arising from enterochromaffin cells
Endoscopic Management of Barrett s High-Grade Dysplasia and Early Stage Esophageal Cancer
 VOLUME 10, ISSUE 2, YEAR 2011 Endoscopic Management of Barrett s High-Grade Dysplasia and Early Stage Esophageal Cancer James L. Wise, MD Duluth, MN. Introduction: In recent years there has been intense
VOLUME 10, ISSUE 2, YEAR 2011 Endoscopic Management of Barrett s High-Grade Dysplasia and Early Stage Esophageal Cancer James L. Wise, MD Duluth, MN. Introduction: In recent years there has been intense
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory
 The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory Dr Edward Sheffield Christmas Select 74 Meeting, Queen s Hotel Cheltenham, 3 rd December 2014 Agenda Overview of the pathology of cancer How specimens
The Diagnosis of Cancer in the Pathology Laboratory Dr Edward Sheffield Christmas Select 74 Meeting, Queen s Hotel Cheltenham, 3 rd December 2014 Agenda Overview of the pathology of cancer How specimens
E L E C T R O S U R G E R G Y / W A T E R J E T S U R G E R Y. Endoscopic Submucosal Dissec tion
 E L E C T R O S U R G E R G Y / W A T E R J E T S U R G E R Y E S D W o r k s t a t i o n w i t h H y b r i d K n i f e Endoscopic Submucosal Dissec tion fast, safe and easy with the HybridKnife. introduc
E L E C T R O S U R G E R G Y / W A T E R J E T S U R G E R Y E S D W o r k s t a t i o n w i t h H y b r i d K n i f e Endoscopic Submucosal Dissec tion fast, safe and easy with the HybridKnife. introduc
Evidence tabel Lokaal palliatieve behandelingen
 Auteurs, jaartal Mate van bewijs Studie type Follow-up Populatie (incl. steekproef-grootte) Patienten kenmerken Interventie Controle Resultaten Conclusie Opmerkingen, commentaar Hartgrink, 2002 The Netherlands
Auteurs, jaartal Mate van bewijs Studie type Follow-up Populatie (incl. steekproef-grootte) Patienten kenmerken Interventie Controle Resultaten Conclusie Opmerkingen, commentaar Hartgrink, 2002 The Netherlands
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY
 PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS
 WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
WHAT S WRONG WITH MY GALL BLADDER? GALL BLADDER POLYPS This is a patient information booklet providing specific practical information about gall bladder polyps in brief. Its aim is to provide the patient
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical
 Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE. Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What?
 RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
Contents. Updated July 2011
 - Updated July 2011 Guideline Authors: Todd S. Crocenzi, M.D.; Mark Whiteford, M.D.; Matthew Solhjem, M.D.; Carlo Bifulco, M.D.; Melissa Li, M.D.; Christopher Cai, M.D.; and James Durham, M.D. Contents
- Updated July 2011 Guideline Authors: Todd S. Crocenzi, M.D.; Mark Whiteford, M.D.; Matthew Solhjem, M.D.; Carlo Bifulco, M.D.; Melissa Li, M.D.; Christopher Cai, M.D.; and James Durham, M.D. Contents
Research Article Analysis of the Power of Common Diagnostic Tools in the Management of Acute Pancreatitis
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Article ID 438697, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/438697 Research Article Analysis of the Power of Common Diagnostic Tools in the Management of Acute Pancreatitis
Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Article ID 438697, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/438697 Research Article Analysis of the Power of Common Diagnostic Tools in the Management of Acute Pancreatitis
Clinical Outcomes of Gastrectomy after Incomplete EMR/ESD
 J Gastric Cancer 2011;11(3):162-166 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2011.11.3.162 Original Article Clinical Outcomes of Gastrectomy after Incomplete EMR/ESD Hye-Jeong Lee, You-Jin Jang, Jong-Han Kim, Sung-Soo
J Gastric Cancer 2011;11(3):162-166 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2011.11.3.162 Original Article Clinical Outcomes of Gastrectomy after Incomplete EMR/ESD Hye-Jeong Lee, You-Jin Jang, Jong-Han Kim, Sung-Soo
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
CHAPTER 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014. 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc.
 Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
Current Status of Esophageal Cancer Treatment
 Cancer Current Status of Esophageal Cancer Treatment JMAJ 46(11): 497 503, 2003 Hiroyasu MAKUUCHI Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Tokai University School of Medicine Abstract: The diagnosis
Cancer Current Status of Esophageal Cancer Treatment JMAJ 46(11): 497 503, 2003 Hiroyasu MAKUUCHI Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Tokai University School of Medicine Abstract: The diagnosis
Flexible sigmoidoscopy the procedure explained Please bring this booklet with you
 Flexible sigmoidoscopy the procedure explained Please bring this booklet with you Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction You have been advised by your GP or hospital doctor to have an
Flexible sigmoidoscopy the procedure explained Please bring this booklet with you Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Introduction You have been advised by your GP or hospital doctor to have an
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D.
 Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
Early Colonoscopy in Patients with Acute Diverticulitis Simon Bar-Meir, M.D. Professor of Medicine Germanis Kaufman Chair of Gastroenterology Director, Dept. of Gastroenterology Chaim Sheba Medical Center,
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
GI Bleed. Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System. Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital
 October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
Non-surgical treatment of severe varicose veins
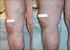 Non-surgical treatment of severe varicose veins Yasu Harasaki UCHSC Department of Surgery General Surgery Grand Rounds March 19, 2007 Definition Dilated, palpable, subcutaneous veins generally >3mm in
Non-surgical treatment of severe varicose veins Yasu Harasaki UCHSC Department of Surgery General Surgery Grand Rounds March 19, 2007 Definition Dilated, palpable, subcutaneous veins generally >3mm in
Colonoscopy Data Collection Form
 Identifier: Sociodemographic Information Type: Zip Code: Gender: Height: (inches) Race: Ethnicity Inpatient Outpatient Male Female Birth Date: Weight: (pounds) American Indian (Native American) or Alaska
Identifier: Sociodemographic Information Type: Zip Code: Gender: Height: (inches) Race: Ethnicity Inpatient Outpatient Male Female Birth Date: Weight: (pounds) American Indian (Native American) or Alaska
Earn 20 ABIM MOC Points! Perform with Confidence Expand your Practice. Lower GI EMR: June 27-28, 2015 Upper GI EMR: August 22-23, 2015
 Skills Training Assessment Reinforcement ASGE Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Earn 20 ABIM MOC Points! Perform with Confidence Expand your Practice ASGE An Assessment-Based Curriculum Lower GI : June 27-28,
Skills Training Assessment Reinforcement ASGE Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Earn 20 ABIM MOC Points! Perform with Confidence Expand your Practice ASGE An Assessment-Based Curriculum Lower GI : June 27-28,
Post-PET Restaging Cancer Form National Oncologic PET Registry
 Post-PET Restaging Cancer Form National Oncologic PET Registry Facility ID #: Registry Case Number: Patient Name: Your patient had a PET scan on: mm/dd/yyyy. The PET scan was done for restaging of (cancer
Post-PET Restaging Cancer Form National Oncologic PET Registry Facility ID #: Registry Case Number: Patient Name: Your patient had a PET scan on: mm/dd/yyyy. The PET scan was done for restaging of (cancer
Barrett s oesophagus: specimen handling and reporting
 Barrett s oesophagus: specimen handling and reporting Professor Neil A Shepherd Gloucester and Cheltenham, UK The role of the pathologist in Barrett s oesophagus 1. Diagnosis 2. Typing 3. Assessing response
Barrett s oesophagus: specimen handling and reporting Professor Neil A Shepherd Gloucester and Cheltenham, UK The role of the pathologist in Barrett s oesophagus 1. Diagnosis 2. Typing 3. Assessing response
PSA Testing 101. Stanley H. Weiss, MD. Professor, UMDNJ-New Jersey Medical School. Director & PI, Essex County Cancer Coalition. weiss@umdnj.
 PSA Testing 101 Stanley H. Weiss, MD Professor, UMDNJ-New Jersey Medical School Director & PI, Essex County Cancer Coalition weiss@umdnj.edu September 23, 2010 Screening: 3 tests for PCa A good screening
PSA Testing 101 Stanley H. Weiss, MD Professor, UMDNJ-New Jersey Medical School Director & PI, Essex County Cancer Coalition weiss@umdnj.edu September 23, 2010 Screening: 3 tests for PCa A good screening
