Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer
|
|
|
- Arnold Jeffrey Marsh
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gut 2001;48: Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer H Ono, H Kondo, T Gotoda, K Shirao, H Yamaguchi, D Saito, K Hosokawa, T Shimoda, S Yoshida Department of Endoscopy and Gastrointestinal Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo, Japan H Ono H Kondo T Gotoda K Shirao H Yamaguchi D Saito K Hosokawa Division of Pathology, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo, Japan T Shimoda National Cancer Center Hospital East, Tokyo, Japan S Yoshida Correspondence to: Dr H Kondo, Department of Endoscopy and Gastrointestinal Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tsukiji, Chuo-ku, Tokyo , Japan. htkondoh@ncc.go.jp Accepted for publication 18 July 2000 Abstract Background In Japan, endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is accepted as a treatment option for cases of early gastric cancer (EGC) where the probability of lymph node metastasis is low. The results of EMR for EGC at the National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo, over a 11 year period are presented. Methods EMR was applied to patients with early cancers up to 30 mm in diameter that were of a well or moderately histologically diverentiated type, and were superficially elevated and/or depressed (types I, IIa, and IIc) but without ulceration or definite signs of submucosal invasion. The resected specimens were carefully examined by serial sections at 2 mm intervals, and if histopathology revealed submucosal invasion and/or vessel involvement or if the resection margin was not clear, surgery was recommended. Results Four hundred and seventy nine cancers in 445 patients were treated by EMR from 1987 to 1998 but submucosal invasion was found on subsequent pathological examination in 74 tumours. Sixty nine percent of intramucosal cancers (278/ 405) were resected with a clear margin. Of 127 cancers without complete resection, 14 underwent an additional operation and nine were treated endoscopically; the remainder had intensive follow up. Local recurrence in the stomach occurred in 17 lesions followed conservatively, in one lesion treated endoscopically, and in five lesions with complete resection. All tumours were diagnosed by follow up endoscopy and subsequently treated by surgery. There were no gastric cancer related deaths during a median follow up period of 38 months (3 120 months). Bleeding and perforation (5%) were two major complications of EMR but there were no treatment related deaths. Conclusion In our experience, EMR allows us to perform less invasive treatment without sacrificing the possibility of cure. (Gut 2001;48: ) Keywords: endoscopic mucosal resection; early gastric cancer Early gastric cancer (EGC) is defined as that confined to the mucosa or submucosa, regardless of the presence or absence of regional lymph node metastasis. It has been increasing in Japan, 1 accounting for approximately 60% of all resected cases in our institution. In Japan, the five year survival rate of patients with EGC is more than 90% after gastrectomy with complete removal of primary and secondary lymph nodes. 2 3 The incidence of nodal metastasis of intramucosal and submucosal EGC has been reported as 3% and 20%, respectively, 4 and therefore major surgery may be inappropriate in many of these patients. It has been shown that lymphatic vessel invasion, histological ulceration of the tumour, and tumour diameter (>30 mm) are independent risk factors for regional lymph node metastasis, and in the absence of these risk factors the incidence of lymph node involvement in patients with intramucosal EGC is 0.36%. 5 These patients may be appropriate for endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Fifteen years have passed since EMR was introduced in Japan. 6 However, there are still unsolved problems with regard to its indications, techniques, evaluation of curability, and follow up. In this paper, we present the results of EMR for EGC at the National Cancer Center Hospital (NCCH) over an 11 year period. Patients and methods A prospective analysis of 479 EGCs in 445 patients resected by EMR at NCCH, Tokyo, from March 1987 to December 1998 was performed. These were 413 solitary, 17 double, one triple, one quadruple, and 13 metachronous tumours. Mean age of the patients was 67.6 years (range 34 92), the male to female ratio was 4.13 (357/88), and the follow up period was months (median 45 months). The Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma was used for tumour description. 1 The indications for EMR are determined by the risk of lymph node metastasis 5 and such technical considerations as the size and position of the lesion, and the equipment and expertise available locally. Current indications for EMR at the NCCH are shown in table 1. When EMR was introduced to the NCCH in 1987, the indication size was 15 mm or less in diameter, and multifragment resection was not accepted. However, it was increased to 30 mm because multifragment resection was introduced based on a review of resected cancers and the development of appropriate endoscopic techniques. Abbreviations used in this paper: EGC, early gastric cancer; EMR, endoscopic mucosal resection; NCCH, National Cancer Center Hospital.
2 226 Ono, Kondo, Gotoda, et al Table 1 resection Indication criteria for endoscopic mucosal Table 2 Evaluation of resected specimens by endoscopic mucosal resection Early gastric cancer meeting all of the following: (1) Well or moderately diverentiated type adenocarcinoma (2) Superficial, elevated, or depressed macroscopic appearance (types I, IIa, IIc) (3) No ulceration (4) Diameter <30 mm (5) No apparent invasive findings The following must be confirmed histologically for complete resection : (1) Intramucosal cancer (2) Well or moderately diverentiated type adenocarcinoma (3) No histological ulceration (4) No lymphatic or venous invasion (5) No tumour invasion to the lateral margin As it is sometimes diycult to accurately assess the depth of invasion prior to EMR, 7 we are prepared to remove any lesion that appears to be confined to the mucosa if it meets the other criteria. In this series, most EMRs were performed by the so called strip biopsy method, a relatively simple technique that has been described elsewhere. 6 8 Since 1997, a new EMR procedure using an insulation tipped diathermic knife (IT knife) was used in the majority of cases 9 (fig 1). Follow up endoscopy was performed at three and six months after EMR in the first year, and yearly thereafter to diagnose local recurrence. EVALUATION OF RESECTED SPECIMENS AND RESECTABILITY The resectability of EMR specimens was carefully evaluated both endoscopically and histopathologically in slices at 2 mm intervals according to the Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma After resection in multiple fragments, resectability was evaluated based on completely reconstructed specimens. The current definition of resection EA, 10 which means a high probability of cure, is demonstrated in table 2. As submucosal invasion and/or vessel involvement are regarded as high risks of positive nodes or distant metastasis, surgical intervention was strongly recommended. Evaluation of invasion to the lateral margin was classified into the following three groups using endoscopic and histopathological evidence: (1) Complete resection: when the lateral margin was clear endoscopically and pathologically (minimum probability of local recurrence). (2) Incomplete resection: when the tumour definitely invaded to the lateral margin endoscopically and pathologically (high probability of local recurrence). (3) Not evaluable: when the tumour was removed endoscopically but its lateral margin was not pathologically evaluable due to a burn evect (burned by diathermic treatment) or mechanical damage, or when reconstruction was diycult due to multifragment resection. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS The SAS program (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, North Carolina, USA) was used for all analyses; p<0.05 was taken as significant. Figure 1 Endoscopic mucosal resection procedure using an IT knife. (A) Superficial elevated (IIa type) early gastric cancer (EGC) located on the lesser curvature of the lower body after spraying with indigo carmine dye. (B) Marking dots were made using a precut knife on the circumference of the target lesion to clarify the margin. (C) After injection of saline with epinephrine (0.025 mg/ml) into the submucosal layer, an initial cut was made with a conventional needle knife outside of the dots. The IT knife was inserted into this cut and operated to cut around the lesion. (D) The tumour marked by dots was separated from the surrounding normal mucosa. (E) The tumour was removed by standard polypectomy with a combination of cutting and coagulation current in a single fragment. (F) The resected specimen showed well diverentiated adenocarcinoma (20 25 mm) with a clear lateral margin. (G) The specifications of the insulation tipped diathermic knife, which was developed by Dr Hosokawa in The knife consists of a conventional diathermic needle knife (KD-1L; Olympus, Japan) with a ceramic ball at the top to minimise the risk of perforation.
3 Endoscopic mucosal resection for gastric cancer 227 Table 3 Macroscopic features of the resected tumours Results Tumour size (mm) Type Mean Total 0-I type (protruded) IIa type (superficial elevated) IIc type (superficial depressed) Total Complete resection 278 (69%) Figure 2 cancer. Table 4 Local recur. 5 (2%) 13 Intramucosal cancer: 405 (100%) Not evaluable 84 (20%) 5 EMR 479 Follow up 67 Local recur. 9 (13%) No recurrence 44 Follow up sm invasion 74 Incomplete resection 43 (11%) 4 Clinical courses after endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) for early gastric Follow up 28 Local recur. Local recur. 1 (25%) 8 (37%) Tumour size and invasion to the resection margin of intramucosal cancer Tumour size (mm) Total Complete resection 170 (72%) 86 (67%) 19 (58%) 3 (38%) 278 (69%) Incomplete resection 21 (9%) 16 (13%) 2 (6%) 4 (50%) 43 (11%) Not evaluable 45 (19%) 26 (20%) 12 (36%) 1 (13%) 84 (21%) Total 236 (100%) 128 (100%) 33 (100%) 8 (100%) 405 (100%) Table 5 Tumour location and invasion to the resection margin of intramucosal cancer Location in the stomach Lower Middle Upper Total Complete resection 151 (75%) 94 (65%) 33 (57%) 278 (69%) Incomplete resection 20 (10%) 17 (12%) 6 (10%) 43 (11%) Not evaluable 31 (15%) 34 (23%) 19 (33%) 84 (21%) Total 202 (100%) 145 (100%) 58 (100%) 405 (100%) EVALUATION OF RESECTED SPECIMENS The macroscopic appearances of the resected tumours are summarized in table 3. A total of 429 lesions (90%) were less than 20 mm in diameter while 280 lesions (58%) were of the superficial depressed type (0-IIc type). The tumours were located in the upper third (82 lesions, 17%), middle third (166 lesions, 35%), and lower third (231 lesions, 48%) of the stomach. Submucosal invasion was found in 74 lesions on subsequent pathological examination by serial sections (fig 2). These patients were strongly recommended to undergo additional gastrectomy with D2 lymph node dissection. However, 30 patients were merely followed because of minute submucosal invasion, advanced age, other diseases, or the patient s refusal of an additional operation. Among 405 intramucosal cancers, 278 (69%) were resected with a clear lateral margin (table 4). The rate of complete resection was lower when lesions had a diameter exceeding 20 mm and were situated in the upper third of the stomach (tables 4, 5). Forty three tumours were incompletely resected as there was definite invasion to the lateral margin endoscopically and histologically. Although EMR appeared to be successful endoscopically, 84 lesions could not be evaluated histologically because of diathermic burn, mechanical damage, or failure to retrieve multiple fragments. CLINICAL OUTCOMES (FIG 2) Of 278 lesions which were completely resected, five (2%) developed local recurrence, and all were subsequently treated with curative intent. The remainder are disease free at a median follow up period of 38 months (3 120 months). Of 127 lesions whose complete resection was not confirmed, 24 underwent resection and no lymph node metastases were found in these patients, and nine were treated by endoscopic therapy and one developed local recurrence after laser ablation. Among the 95 lesions that were followed conservatively, there were 17 local recurrences (18%) after a median follow up of four months (2 12 months). All of these patients with recurrence underwent surgery and remain disease free. There were no treatment related or gastric cancer related deaths. COMPLICATIONS Bleeding and perforation were two major complications of EMR. All bleeding was controlled by endoscopic treatment with ethanol injection, endoscopic clipping (HX5LR-1, Olympus, Japan), and spraying of thrombin solution into the stomach. There were 25 cases of perforation (5%); the first four were converted to open surgery. Since then, all perforations have been successfully treated with endoscopic clipping, intubation of a nasogastric tube, and administration of antibiotics. Discussion The EMR technique has been developed mainly in Japan where there is a high incidence of EGC. It is used infrequently in the West. It is important to carefully evaluate the current status of EMR and promote the appropriate use of this technique around the world. The number of patients undergoing EMR is increasing, with about 500 procedures performed in our hospital over the past 11 years. Considering that it generally takes one hour for resection and one week for admission, EMR is a minimally invasive procedure (a patient undergoing surgical resection is hospitalised for approximately three weeks). Our experience suggests that EMR can provide comparable long term survival rates to traditional therapy, provided adherence to strict inclusion
4 228 Ono, Kondo, Gotoda, et al Case No Figure 3 Hospital. Surgical operation Endoscopic resection Year Trends in treatment for early gastric cancer at the National Cancer Center criteria is followed. As shown in fig 3, the proportion of EGC cases treated by EMR at the NCCH has risen, and this accounted for about 40% of all EGC cases in This is probably due to improved diagnostic techniques. As there are still several unsolved problems in EMR, we will address specific concerns. Patient eligibility for EMR should be considered in relation to the risk of lymph node metastasis. As shown in table 1, EGCs fulfilling the criteria for EMR have a lower incidence of lymph node metastasis (0.36%) than the mortality rate of surgery for EGC (approximately 0.5% at the NCCH). In this study, the Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma was used for tumour description, 1 which is widely used in our country. Western pathologists use the term high grade dysplasia for neoplastic lesions that have not breached the basement membrane to the lamina propria. Japanese pathologists, however, classify them as intramucosal cancer on the grounds that the cells are of a malignant type and have the potential to invade. 11 A recent analysis showed that the histological type, macroscopic appearance, degree of invasion, and lymph node metastases are the same although many more EGCs are detected in Japan than in the West. 12 We usually perform EMR for intramucosal cancer using the Japanese criteria, and it is important to have the same diagnostic criteria for gastric neoplastic lesions to propagate EMR around the world. As it is sometimes diycult to accurately assess the depth of invasion prior to EMR, we remove any lesion without apparent endoscopic findings of submucosal invasion 7 but 15% (74/479) of all lesions invaded to the submucosa. We do not use endoscopic ultrasonography routinely as it is not sensitive enough to evaluate minute invasion to the submucosa. Although histological examination revealed minute submucosal invasion in resected EGC, some patients refused to undergo an additional treatment. As no lymph node metastasis was demonstrated in tumours with less than 300 µm of submucosal invasion, 13 and no recurrence has been observed during follow up of these patients, it may be reasonable to treat patients with minute submucosal invasion by EMR. In our series, most EMRs were performed by the so called strip biopsy method. However, we had five local recurrences in complete resection, all of which had been resected in multiple fragments by this method. Single fragment resection is preferable because with multifragment specimens it is often diycult to reconstruct the entire lesion. We believe it is likely that local recurrence can often be attributed to inappropriate assessment of the multiple fragments of resected specimens. There have been several reports on endo scopic resection of larger lesions. In addition, we have found that the insulation tipped diathermy knife (IT knife) can allow safe resection of a larger lesion in a single piece. The average rate of complete resection increased to more than 90% and histological evaluation became easier following introduction of this technique. A follow up programme is important for finding local recurrence and other cancers in the stomach. Thirteen metachronous early cancers were included in our series, which were diagnosed a median period of 23 months after the initial EMR (3 67 months). The incidence of multiple primary lesions in surgically treated EGC is approximately 10% at the NCCH. 16 As EGC is frequently associated with synchronous tumours that may be missed at an initial endoscopic examination, and the stomach may also contain premalignant conditions such as intestinal metaplasia, we should pay attention not only to recurrence but also to other cancers in the stomach. In summary, based on our experience, it is clear that EMR can provide the same favourable long term survival rates as traditional therapy and is now the treatment of choice for mucosal EGC. We hope to promote its use around the world. We are indebted to Drs M Sasako, T Sano, and H Katai, and K Maruyama for helpful suggestions. The work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Cancer Research and for the 2nd Term Comprehensive 10-year Strategy of Cancer Control from the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Japan 1 Nishi M, Omori Y, Miwa K, eds. Japanese Research Society for Gastric Cancer. Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma. Tokyo: Kanehara and Co., Ltd, Okamura T, Tsujitani S, Korenaga D, et al. Lymphadenectomy for cure in patients with early gastric cancer and lymph node metastasis. Am J Surg 1998;155: Noguchi Y, Imada T, Matsumoto A, et al. Radical surgery for gastric cancer: a review of Japanese experience. Cancer 1989;64: Sano T, Kobori O, Muto T. Lymph node metastasis from early gastric cancer: endoscopic resection of tumor. Br J Surg 1992;79: Yamao T, Shirao K, Ono H, et al. Risk factors for lymph node metastasis from intramucosal gastric carcinoma. Cancer 1996;77: Tada M, Mukrakami A, Karita M, et al. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Endoscopy 1993;25: Sano T, Okuyama Y, Kobori O, et al. Early gastric cancer; endoscopic diagnosis of depth of invasion. Dig Dis Sci 1990;35: Tada M, Shimada M, Murakami F. Development of the strip-ov biopsy. Gastroenterol Endosc 1984;26: Gotoda T, Kondo H, Ono H, et al. A new endoscopic mucosal resection procedure using an insulation-tipped diathermic knife for rectal flat lesions. Gastrointestinal Endosc 1999;50: Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma, 2nd English edn. Gastric Cancer 1998;1:10 24.
5 Endoscopic mucosal resection for gastric cancer Schlemper RJ, Itabashi M, Kato Y, et al. DiVerences in diagnosis criteria for gastric carcinoma between Japanese and Western pathologists. Lancet 1997;349: Everett SM, Axon ATR. Early gastric cancer in Europe. Gut 1997;41: Yasuda K, Shiraishi N, Suemasu T, et al. Rate of detection of lymph node metastasis is correlated with the depth of submucosal invasion in early gastric cancer. Cancer 1999;85: Inoue H, Tani M, Nagai K, et al. Treatment of esophageal and gastric tumors. Endoscopy 1999;31: Hirao M, Matsuda K, Asanuma T, et al. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer and other tumors with local injection of hypertonic saline-epinephrine. Gastrointest Endosc 1998;34: Oda I, Kondo H, Gotoda T, et al. Endoscopic diagnosis for multiple early gastric cancer [abstract]. Proceeding of the 3rd International Gastric Cancer Congress, 1999:343;AO4069.
The utility of endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy in the endoscopic mucosal resection of early gastric cancer
 Gut 1999;45:599 604 599 The utility of endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy in the endoscopic mucosal resection of early gastric cancer S Ohashi, K Segawa, S Okamura, M Mitake, H Urano, M Shimodaira,
Gut 1999;45:599 604 599 The utility of endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy in the endoscopic mucosal resection of early gastric cancer S Ohashi, K Segawa, S Okamura, M Mitake, H Urano, M Shimodaira,
Early gastric cancer: endoscopic mucosal resection
 Early gastric cancer: endoscopic mucosal resection Ann. Ital. Chir., LXXII, 1, 2001 HITOSHI KONDO*, TAKUJI GOTODA, HIROYUKI ONO, ICHIRO ODA, HAJIME YAMAGUCHI, DAIZO SAITO, SHIGEAKI YOSHIDA** *Department
Early gastric cancer: endoscopic mucosal resection Ann. Ital. Chir., LXXII, 1, 2001 HITOSHI KONDO*, TAKUJI GOTODA, HIROYUKI ONO, ICHIRO ODA, HAJIME YAMAGUCHI, DAIZO SAITO, SHIGEAKI YOSHIDA** *Department
How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens
 Section of Pathology and Tumour Biology How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens Dr.H.Grabsch Warning. Most of the criteria, methodologies, evidence presented in this talk are based on studies in early
Section of Pathology and Tumour Biology How to report Upper GI EMR/ESD specimens Dr.H.Grabsch Warning. Most of the criteria, methodologies, evidence presented in this talk are based on studies in early
Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate
 Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate Hironori Yamamoto, MD, Hiroshi Kawata, MD, Keijiro Sunada,
Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosal incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate Hironori Yamamoto, MD, Hiroshi Kawata, MD, Keijiro Sunada,
Learning Luncheon 7: Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: When, Where and How?
 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): When, Where, and Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) EMR developed for removal of sessile or flat neoplasms
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): When, Where, and Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) EMR developed for removal of sessile or flat neoplasms
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (E.S.D.) vs. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (E.M.R.) in Colombia. Advocating E.M.R.
 Controversies in Gastroenterology Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (E.S.D.) vs. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (E.M.R.) in Colombia. Advocating E.M.R. Raúl Cañadas Garrido, MD. 1 1 Internist-Gastroenterologist.
Controversies in Gastroenterology Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (E.S.D.) vs. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (E.M.R.) in Colombia. Advocating E.M.R. Raúl Cañadas Garrido, MD. 1 1 Internist-Gastroenterologist.
EMR Can anyone do this?
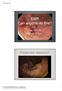 EMR Can anyone do this? Norio Fukami, MD University of Colorado Piecemeal resection? 1 Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) Endoscopic removal of premalignant or
EMR Can anyone do this? Norio Fukami, MD University of Colorado Piecemeal resection? 1 Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) Endoscopic removal of premalignant or
2/49; 4.1% 7/41; PATIENTS AND METHODS
 A new technique for endoscopic mucosal resection with an insulated-tip electrosurgical knife improves the completeness of resection of intramucosal gastric neoplasms Received July 6, 2001. For revision
A new technique for endoscopic mucosal resection with an insulated-tip electrosurgical knife improves the completeness of resection of intramucosal gastric neoplasms Received July 6, 2001. For revision
ENDOSCOPIC SUBMUCOSAL DISSECTION FOR THE TREATMENT OF EARLY ESOPHAGEAL AND GASTRIC CANCER - INITIAL EXPERIENCE OF A WESTERN CENTER
 CLINICS 2010;65(4):377-82 CLINICAL SCIENCE ENDOSCOPIC SUBMUCOSAL DISSECTION FOR THE TREATMENT OF EARLY ESOPHAGEAL AND GASTRIC CANCER - INITIAL EXPERIENCE OF A WESTERN CENTER Dalton Marques Chaves, I Fauze
CLINICS 2010;65(4):377-82 CLINICAL SCIENCE ENDOSCOPIC SUBMUCOSAL DISSECTION FOR THE TREATMENT OF EARLY ESOPHAGEAL AND GASTRIC CANCER - INITIAL EXPERIENCE OF A WESTERN CENTER Dalton Marques Chaves, I Fauze
These parameters cannot, at the present time, be determined by non-invasive imaging techniques.
 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Upper Gastrointestinal Lesions Kenneth K. Wang, M.D. Chairman, WEO Publication and Guidelines Committee Professor of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota Upper gastrointestinal
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Upper Gastrointestinal Lesions Kenneth K. Wang, M.D. Chairman, WEO Publication and Guidelines Committee Professor of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota Upper gastrointestinal
Magnetic Anchor for More Effective Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2004;34(3)118 123 Magnetic Anchor for More Effective Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Toshiaki Kobayashi 1, Takushi Gotohda 1, Katsunori Tamakawa 2, Hirohisa Ueda 3 and Tadao Kakizoe 1 1 National
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2004;34(3)118 123 Magnetic Anchor for More Effective Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Toshiaki Kobayashi 1, Takushi Gotohda 1, Katsunori Tamakawa 2, Hirohisa Ueda 3 and Tadao Kakizoe 1 1 National
Endoscopic Therapy for Early Esophageal Cancer: EMR and ESD
 Endoscopic Therapy for Early Esophageal Cancer: EMR and ESD AATS Toronto April 26, 2014 Lorenzo Ferri MD PhD David S. Mulder Chair in Surgery Associate Professor of Surgery and Oncology Disclosures Olympus
Endoscopic Therapy for Early Esophageal Cancer: EMR and ESD AATS Toronto April 26, 2014 Lorenzo Ferri MD PhD David S. Mulder Chair in Surgery Associate Professor of Surgery and Oncology Disclosures Olympus
Captivator EMR Device
 Device Clinical Article and Abstract Summary Endoscopic Mucosal Bergman et al: EMR Training Tips Bergman et al: EMR Learning Curve ASGE: EMR & ESD Guidelines Bergman et al: Captivator EMR vs Cook Duette
Device Clinical Article and Abstract Summary Endoscopic Mucosal Bergman et al: EMR Training Tips Bergman et al: EMR Learning Curve ASGE: EMR & ESD Guidelines Bergman et al: Captivator EMR vs Cook Duette
ESD for colorectal lesions I am in favour. Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy
 ESD for colorectal lesions I am in favour Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy Surgery for early colonic lesions 51 pts referred for lap colectomy
ESD for colorectal lesions I am in favour Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy Surgery for early colonic lesions 51 pts referred for lap colectomy
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of colorectal neoplasms ENDOSCOPY CORNER
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:22 26 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Efficacy of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection With Circumferential Incision for Patients With Large Colorectal Tumors TAKU SAKAMOTO, TAKAHISA
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:22 26 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Efficacy of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection With Circumferential Incision for Patients With Large Colorectal Tumors TAKU SAKAMOTO, TAKAHISA
Clinical Outcomes of Gastrectomy after Incomplete EMR/ESD
 J Gastric Cancer 2011;11(3):162-166 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2011.11.3.162 Original Article Clinical Outcomes of Gastrectomy after Incomplete EMR/ESD Hye-Jeong Lee, You-Jin Jang, Jong-Han Kim, Sung-Soo
J Gastric Cancer 2011;11(3):162-166 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2011.11.3.162 Original Article Clinical Outcomes of Gastrectomy after Incomplete EMR/ESD Hye-Jeong Lee, You-Jin Jang, Jong-Han Kim, Sung-Soo
Do we have enough evidence for expanding the indications of ESD for EGC?
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i21.2597 World J Gastroenterol 2011 June 7; 17(21): 2597-2601 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online)
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i21.2597 World J Gastroenterol 2011 June 7; 17(21): 2597-2601 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com. Digestive and Liver Disease 41 (2009) 201 209. Digestive Endoscopy
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Digestive and Liver Disease 41 (2009) 201 209 Digestive Endoscopy Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for treating early gastric cancer:
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Digestive and Liver Disease 41 (2009) 201 209 Digestive Endoscopy Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for treating early gastric cancer:
How to treat early gastric cancer. Surgery
 How to treat early gastric cancer Surgery Mark I. van Berge Henegouwen Department of Surgery, AMC, Amsterdam Director upper GI surgical unit Academic Medical Center Upper GI surgery at AMC 100 oesophagectomies
How to treat early gastric cancer Surgery Mark I. van Berge Henegouwen Department of Surgery, AMC, Amsterdam Director upper GI surgical unit Academic Medical Center Upper GI surgery at AMC 100 oesophagectomies
Combination Therapy After EMR/ESD for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Submucosal Invasion
 Combination Therapy After EMR/ESD for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Submucosal Invasion 8 Ota M., Nakamura T. and Yamamoto M. Department of Surgery, Institute of Gastroenterology, Tokyo Women's
Combination Therapy After EMR/ESD for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Submucosal Invasion 8 Ota M., Nakamura T. and Yamamoto M. Department of Surgery, Institute of Gastroenterology, Tokyo Women's
Evolution of Barrett s esophagus
 Endoscopic Treatment and Surveillance of Esophageal Cancer: GI Perspective Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Evolution of Barrett s esophagus Squamous esophagus Chronic inflammation
Endoscopic Treatment and Surveillance of Esophageal Cancer: GI Perspective Charles J. Lightdale, MD Columbia University New York, NY Evolution of Barrett s esophagus Squamous esophagus Chronic inflammation
Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options
 Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options Michael A Smith, MD Associate Chief Thoracic Surgery Center for Thoracic Disease St Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center Phoenix, AZ Michael Smith, MD
Cancer of the Cardia/GE Junction: Surgical Options Michael A Smith, MD Associate Chief Thoracic Surgery Center for Thoracic Disease St Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center Phoenix, AZ Michael Smith, MD
Tumor Budding as a Useful Prognostic Marker in T1-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus
 2013;108:42 46 Tumor Budding as a Useful Prognostic Marker in T1-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus HITOSHI TERAMOTO, MD, 1 * MASAHIKO KOIKE, MD, PhD, 1 CHIE TANAKA, MD, PhD, 1 SUGURU YAMADA,
2013;108:42 46 Tumor Budding as a Useful Prognostic Marker in T1-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus HITOSHI TERAMOTO, MD, 1 * MASAHIKO KOIKE, MD, PhD, 1 CHIE TANAKA, MD, PhD, 1 SUGURU YAMADA,
Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus and Early Cancer 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery
 Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus and Early Cancer 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery Matthew Hartwig, M.D. Duke Cancer Institute Case Presentation: Patient ER 51 y/o man with schizophrenia
Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus and Early Cancer 2014 Masters of Minimally Invasive Surgery Matthew Hartwig, M.D. Duke Cancer Institute Case Presentation: Patient ER 51 y/o man with schizophrenia
Argon plasma coagulation for successful treatment of early gastric cancer with intramucosal invasion
 334 CANCER Argon plasma coagulation for successful treatment of early gastric cancer with intramucosal invasion T Sagawa, T Takayama, T Oku, T Hayashi, H Ota, T Okamoto, H Muramatsu, S Katsuki, Y Sato,
334 CANCER Argon plasma coagulation for successful treatment of early gastric cancer with intramucosal invasion T Sagawa, T Takayama, T Oku, T Hayashi, H Ota, T Okamoto, H Muramatsu, S Katsuki, Y Sato,
Endoscopic mucosal resection with a multiband ligator for the treatment of Barrett s high-grade dysplasia and early gastric cancer
 1130-0108/2009/101/6/403-407 REVISTA ESPAÑOLA DE ENFERMEDADES DIGESTIVAS Copyright 2009 ARÁN EDICIONES, S. L. REV ESP ENFERM DIG (Madrid) Vol. 101. N. 6, pp. 403-407, 2009 Endoscopic mucosal resection
1130-0108/2009/101/6/403-407 REVISTA ESPAÑOLA DE ENFERMEDADES DIGESTIVAS Copyright 2009 ARÁN EDICIONES, S. L. REV ESP ENFERM DIG (Madrid) Vol. 101. N. 6, pp. 403-407, 2009 Endoscopic mucosal resection
Current Status of Esophageal Cancer Treatment
 Cancer Current Status of Esophageal Cancer Treatment JMAJ 46(11): 497 503, 2003 Hiroyasu MAKUUCHI Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Tokai University School of Medicine Abstract: The diagnosis
Cancer Current Status of Esophageal Cancer Treatment JMAJ 46(11): 497 503, 2003 Hiroyasu MAKUUCHI Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Tokai University School of Medicine Abstract: The diagnosis
Format for ANSWERING REVIEWERS
 Format for ANSWERING REVIEWERS July 15, 2015 Dear Editor, Please find enclosed the edited manuscript in Word format (file name: 19935-revised manuscript). Title: Management and associated factors of delayed
Format for ANSWERING REVIEWERS July 15, 2015 Dear Editor, Please find enclosed the edited manuscript in Word format (file name: 19935-revised manuscript). Title: Management and associated factors of delayed
Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm
 Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm Shinji Tanaka, MD, Ken Haruma, MD, Shiro Oka, MD, Ryoji Takahashi, MD, Masaki Kunihiro,
Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm Shinji Tanaka, MD, Ken Haruma, MD, Shiro Oka, MD, Ryoji Takahashi, MD, Masaki Kunihiro,
Hyung Hun Kim, 1 Gwang Ha Kim, 2 Ji Hyun Kim, 3 Myung-Gyu Choi, 1 Geun Am Song, 2 and Sung Eun Kim 4. 1. Introduction
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Article ID 253860, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/253860 Clinical Study The Efficacy of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Type I Gastric Carcinoid Tumors
Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Article ID 253860, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/253860 Clinical Study The Efficacy of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Type I Gastric Carcinoid Tumors
Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Carcinoma of the Stomach
 Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Carcinoma of the Stomach April 2004 edition Edited by the Japanese Gastric Cancer Society Overview Objective of Guidelines Principles of Guidelines Guideline Process
Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Carcinoma of the Stomach April 2004 edition Edited by the Japanese Gastric Cancer Society Overview Objective of Guidelines Principles of Guidelines Guideline Process
BAISHIDENG PUBLISHING GROUP INC
 Reviewer s code: 01714224 Reviewer s country: Italy Date reviewed: 2015-01-30 20:36 [ Y] Grade A: Priority publishing [ ] Accept [ ] Grade C: Good [ Y] Grade D: Fair language [ Y] Major revision The article
Reviewer s code: 01714224 Reviewer s country: Italy Date reviewed: 2015-01-30 20:36 [ Y] Grade A: Priority publishing [ ] Accept [ ] Grade C: Good [ Y] Grade D: Fair language [ Y] Major revision The article
Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline
 Guideline 829 Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline Authors Institutions Pedro Pimentel-Nunes 1, Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1, Thierry Ponchon 2, Alessandro
Guideline 829 Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline Authors Institutions Pedro Pimentel-Nunes 1, Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1, Thierry Ponchon 2, Alessandro
Endoscopic Management of Barrett s High-Grade Dysplasia and Early Stage Esophageal Cancer
 VOLUME 10, ISSUE 2, YEAR 2011 Endoscopic Management of Barrett s High-Grade Dysplasia and Early Stage Esophageal Cancer James L. Wise, MD Duluth, MN. Introduction: In recent years there has been intense
VOLUME 10, ISSUE 2, YEAR 2011 Endoscopic Management of Barrett s High-Grade Dysplasia and Early Stage Esophageal Cancer James L. Wise, MD Duluth, MN. Introduction: In recent years there has been intense
Evidence tabel Early Gastric Cancer
 Evidence tabel Early Gastric Cancer Auteurs, jaartal Mate van bewijs Studie type Follow-up Wang, 2006 Systematic review Search up to Feb 2006 Mean 35.3 months (range 18-66) Populatie (incl. steekproefgrootte)
Evidence tabel Early Gastric Cancer Auteurs, jaartal Mate van bewijs Studie type Follow-up Wang, 2006 Systematic review Search up to Feb 2006 Mean 35.3 months (range 18-66) Populatie (incl. steekproefgrootte)
Barrett s oesophagus: specimen handling and reporting
 Barrett s oesophagus: specimen handling and reporting Professor Neil A Shepherd Gloucester and Cheltenham, UK The role of the pathologist in Barrett s oesophagus 1. Diagnosis 2. Typing 3. Assessing response
Barrett s oesophagus: specimen handling and reporting Professor Neil A Shepherd Gloucester and Cheltenham, UK The role of the pathologist in Barrett s oesophagus 1. Diagnosis 2. Typing 3. Assessing response
The Royal Marsden. Surgery for Gastric and GE Junction Cancer: primary palliative where and when? William Allum
 The Royal Marsden Surgery for Gastric and GE Junction Cancer: primary palliative where and when? William Allum Any surgeon can cure Surgeon - dependent No surgeon can cure EMR D2 GASTRECTOMY H N SN. WEDGE
The Royal Marsden Surgery for Gastric and GE Junction Cancer: primary palliative where and when? William Allum Any surgeon can cure Surgeon - dependent No surgeon can cure EMR D2 GASTRECTOMY H N SN. WEDGE
Endo Conference: Large Polypectomy & EMR
 Endo Conference: Large Polypectomy & EMR Dr. Whang Feb 3, 2015 VOGELGRAM: genetic pathway of colorectal cancer & genes affected by point mutations Outline I. Baseline Colonoscopy II. Colon Polyps III.
Endo Conference: Large Polypectomy & EMR Dr. Whang Feb 3, 2015 VOGELGRAM: genetic pathway of colorectal cancer & genes affected by point mutations Outline I. Baseline Colonoscopy II. Colon Polyps III.
EMR is not inferior to ESD for early Barrett s and EGJ neoplasia: An extensive review on outcome, recurrence and complication rates
 E58 EMR is not inferior to ESD for early Barrett s and EGJ neoplasia: An extensive review on outcome, recurrence and complication rates Authors Institution Yoriaki Komeda, Marco Bruno, Arjun Koch Department
E58 EMR is not inferior to ESD for early Barrett s and EGJ neoplasia: An extensive review on outcome, recurrence and complication rates Authors Institution Yoriaki Komeda, Marco Bruno, Arjun Koch Department
Surgical Management of Papillary Microcarcinoma 趙 子 傑 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 林 口 總 院 一 般 外 科
 Surgical Management of Papillary Microcarcinoma 趙 子 傑 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 林 口 總 院 一 般 外 科 Papillary microcarcinoma of thyroid Definition latent aberrant thyroid occult thyroid carcinoma latent papillary carcinoma)
Surgical Management of Papillary Microcarcinoma 趙 子 傑 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 林 口 總 院 一 般 外 科 Papillary microcarcinoma of thyroid Definition latent aberrant thyroid occult thyroid carcinoma latent papillary carcinoma)
Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment for Colorectal Cancer
 17 Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment for Colorectal Cancer Hiroyuki Kato, Teruhiko Sakamoto, Hiroko Otsuka, Rieko Yamada and Kiyo Watanabe Tokyo Women s Medical University, Medical Center East, Department
17 Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment for Colorectal Cancer Hiroyuki Kato, Teruhiko Sakamoto, Hiroko Otsuka, Rieko Yamada and Kiyo Watanabe Tokyo Women s Medical University, Medical Center East, Department
Endotherapy for high grade dysplasia & early oesophageal neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: A single centre retrospective audit
 Endotherapy for high grade dysplasia & early oesophageal neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: A single centre retrospective audit U Duffy, K Gowland, AI Morris, HL Smart Department of Gastroenterology, Royal
Endotherapy for high grade dysplasia & early oesophageal neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: A single centre retrospective audit U Duffy, K Gowland, AI Morris, HL Smart Department of Gastroenterology, Royal
HOW I DO IT Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in the esophagus
 HOW I DO IT (EMR) in the esophagus AUTHORSHIP How I do it: Horst Neuhaus, MD Department of Internal Medicine Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf Germany Comment Hiroyasu Makuuchi, MD Professor and Chairman
HOW I DO IT (EMR) in the esophagus AUTHORSHIP How I do it: Horst Neuhaus, MD Department of Internal Medicine Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf Germany Comment Hiroyasu Makuuchi, MD Professor and Chairman
Bridging Techniques. What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS
 Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
ENDOSCOPY IN GASTRIC CANCER: NEW IMAGING TECHNIQUES, NEW TREATMENT MODALITIES (EMR, ESD)
 ENDOSCOPY IN GASTRIC CANCER: NEW IMAGING TECHNIQUES, NEW TREATMENT MODALITIES (EMR, ESD) Fabrice Caillol Paoli Calmettes Institute, Marseille, France June 10th, Prague, Czech Republic EUS AND STAGING 1980:
ENDOSCOPY IN GASTRIC CANCER: NEW IMAGING TECHNIQUES, NEW TREATMENT MODALITIES (EMR, ESD) Fabrice Caillol Paoli Calmettes Institute, Marseille, France June 10th, Prague, Czech Republic EUS AND STAGING 1980:
This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after
 Sample Peer-Review of a Fictitious Manuscript Reviewer A s Comments to Authors: This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after EMR of Barrett s esophagus
Sample Peer-Review of a Fictitious Manuscript Reviewer A s Comments to Authors: This is a prospective study that analyzed the factors associated with cancer progression after EMR of Barrett s esophagus
Post-DDW OAG Course - Therapeutic Endoscopy
 Post-DDW OAG Course - Therapeutic Endoscopy June 13, 2015 Jeffrey Mosko Division of Gastroenterology St. Michael's Hospital University of Toronto moskoj@smh.ca Program Name: Post-DDW OAG course CanMEDS
Post-DDW OAG Course - Therapeutic Endoscopy June 13, 2015 Jeffrey Mosko Division of Gastroenterology St. Michael's Hospital University of Toronto moskoj@smh.ca Program Name: Post-DDW OAG course CanMEDS
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE. Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What?
 RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Adiuwantowe i neoadiuwantowe leczenie chorych na zaawansowanego raka żołądka
 Adiuwantowe i neoadiuwantowe leczenie chorych na zaawansowanego raka żołądka Neoadiuvant and adiuvant therapy for advanced gastric cancer Franco Roviello, IT Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for advanced
Adiuwantowe i neoadiuwantowe leczenie chorych na zaawansowanego raka żołądka Neoadiuvant and adiuvant therapy for advanced gastric cancer Franco Roviello, IT Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for advanced
Endoscopic caps are commonly used for both diagnosis
 Endoscopic Caps Kazuki Sumiyama, MD, and Elizabeth Rajan, MD Endoscopic caps are commonly used accessories for both endoscopic therapy and diagnosis. Many variations of endoscopic caps are available. Cap
Endoscopic Caps Kazuki Sumiyama, MD, and Elizabeth Rajan, MD Endoscopic caps are commonly used accessories for both endoscopic therapy and diagnosis. Many variations of endoscopic caps are available. Cap
ERBEJET 2. The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY
 ERBEJET 2 The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY Gentle interventions in surgery and endoscopy Waterjet surgery with hybrid technology Waterjet surgery
ERBEJET 2 The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY Gentle interventions in surgery and endoscopy Waterjet surgery with hybrid technology Waterjet surgery
What is Barrett s esophagus? How does Barrett s esophagus develop?
 Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
Barrett s Esophagus What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a pre-cancerous condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy Endotherapy for superficial adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: an American experience Shreyas Saligram, MD, MRCP, 1 Jennifer Chennat, MD, 1 Huankai Hu, MD, 2 Jon M. Davison,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy Endotherapy for superficial adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: an American experience Shreyas Saligram, MD, MRCP, 1 Jennifer Chennat, MD, 1 Huankai Hu, MD, 2 Jon M. Davison,
POEM Procedure for. Esophageal Achalasia
 POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
POEM Procedure for Esophageal Achalasia POEM (Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy) is an incisionless procedure to treat esophageal achalasia, totally performed by endoscopy, without cutting the surface of the
Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50
 General Data Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50 The vast majority of the patients in this study were diagnosed
General Data Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50 The vast majority of the patients in this study were diagnosed
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination
 Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer (Review)
 Endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer (Review) Bennett C, Wang Y, Pan T This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The
Endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer (Review) Bennett C, Wang Y, Pan T This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
The digestive system. Medicine and technology. Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies
 The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 2005 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology
 Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
Oncology Annual Report: Prostate Cancer 25 Update By: John Konefal, MD, Radiation Oncology Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, with 232,9 new cases projected to be diagnosed in the U.S. in
9. Discuss guidelines for follow-up post-thyroidectomy for cancer (labs/tests) HH
 9. Discuss guidelines for follow-up post-thyroidectomy for cancer (labs/tests) HH Differentiated thyroid cancer expresses the TSH receptor on the cell membrane and responds to TSH stimulation by increasing
9. Discuss guidelines for follow-up post-thyroidectomy for cancer (labs/tests) HH Differentiated thyroid cancer expresses the TSH receptor on the cell membrane and responds to TSH stimulation by increasing
PANCREATIC AND PERIAMPULLARY TUMORS: PANCREATICODUODENECTOMY. Dr. Shailesh V. Shrikhande
 PANCREATIC AND PERIAMPULLARY TUMORS: PANCREATICODUODENECTOMY Dr. Shailesh V. Shrikhande Associate Professor & Consultant Surgeon GI and HPB Surgical Oncology Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai INDIA HELICAL
PANCREATIC AND PERIAMPULLARY TUMORS: PANCREATICODUODENECTOMY Dr. Shailesh V. Shrikhande Associate Professor & Consultant Surgeon GI and HPB Surgical Oncology Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai INDIA HELICAL
International Journal of Cancer Studies & Research (IJCR) ISSN: 2167-9118
 International Journal of Cancer Studies & Research (IJCR) ISSN: 2167-9118 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection after Circumferential Mucosal Incision of Large Colorectal Tumors: Comparison With Endoscopic Submucosal
International Journal of Cancer Studies & Research (IJCR) ISSN: 2167-9118 Endoscopic Mucosal Resection after Circumferential Mucosal Incision of Large Colorectal Tumors: Comparison With Endoscopic Submucosal
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
Ulcerative colitis patients with low grade dysplasia should undergo frequent surveillance colonoscopies
 Ulcerative colitis patients with low grade dysplasia should undergo frequent surveillance colonoscopies David T. Rubin, MD, FACG, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Co-Director, Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Ulcerative colitis patients with low grade dysplasia should undergo frequent surveillance colonoscopies David T. Rubin, MD, FACG, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Co-Director, Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
 Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Features of esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer is an abnormal growth that arises
Use of stents in esophageal cancer" Hans Gerdes, M.D. Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Features of esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer is an abnormal growth that arises
Selection of appropriate endoscopic therapies for duodenal tumors: An open-label study, single-center experience
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8624 World J Gastroenterol 2014 July 14; 20(26): 8624-8630 ISSN 1007-9327 (print)
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8624 World J Gastroenterol 2014 July 14; 20(26): 8624-8630 ISSN 1007-9327 (print)
How To Treat Lung Cancer At Cleveland Clinic
 Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Treatment Guide Lung Cancer Management The Chest Cancer Center at Cleveland Clinic, which includes specialists from the Respiratory Institute, Taussig Cancer Institute and Miller Family Heart & Vascular
Contents. Updated July 2011
 - Updated July 2011 Guideline Authors: Todd S. Crocenzi, M.D.; Mark Whiteford, M.D.; Matthew Solhjem, M.D.; Carlo Bifulco, M.D.; Melissa Li, M.D.; Christopher Cai, M.D.; and James Durham, M.D. Contents
- Updated July 2011 Guideline Authors: Todd S. Crocenzi, M.D.; Mark Whiteford, M.D.; Matthew Solhjem, M.D.; Carlo Bifulco, M.D.; Melissa Li, M.D.; Christopher Cai, M.D.; and James Durham, M.D. Contents
A Comparison of Endoscopic Treatment and Surgery in Early Esophageal Cancer: An Analysis of Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Data
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2008 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01889.x Published by Blackwell Publishing ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Esophagus A Comparison
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2008 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01889.x Published by Blackwell Publishing ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Esophagus A Comparison
LifeProtect. Cancer Cover. For Intermediary Use Only
 LifeProtect Cancer Cover For Intermediary Use Only There are few families in Ireland that have been unaffected by cancer. In fact, 1 in 3 men and 1 in 4 women in Ireland* will suffer from cancer at some
LifeProtect Cancer Cover For Intermediary Use Only There are few families in Ireland that have been unaffected by cancer. In fact, 1 in 3 men and 1 in 4 women in Ireland* will suffer from cancer at some
Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics
 Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics 5758 South Maryland Avenue (MC9028) Chicago, Illinois 60637 (773) 702-1459 www.uchospitals.edu Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics To refer a patient
Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics 5758 South Maryland Avenue (MC9028) Chicago, Illinois 60637 (773) 702-1459 www.uchospitals.edu Center for Endoscopic Research & Therapeutics To refer a patient
New strategies in anticancer therapy
 癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
GENERAL CODING. When you review old cases that were coded to unknown, make corrections based on guidelines in effect at the time of diagnosis.
 GENERAL CODING When you review old cases that were coded to unknown, make corrections based on guidelines in effect at the time of diagnosis. Exception: You must review and revise EOD coding for prostate
GENERAL CODING When you review old cases that were coded to unknown, make corrections based on guidelines in effect at the time of diagnosis. Exception: You must review and revise EOD coding for prostate
Luis D. Carcorze Soto, MD PGY-3
 Luis D. Carcorze Soto, MD PGY-3 Peritoneal Surface Malignancies Peritoneum Patient Selection Operative Technique HIPEC EPIC Primary: Primary Peritoneal Carcinoma Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Metastatic:
Luis D. Carcorze Soto, MD PGY-3 Peritoneal Surface Malignancies Peritoneum Patient Selection Operative Technique HIPEC EPIC Primary: Primary Peritoneal Carcinoma Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Metastatic:
Breast cancer close to the nipple: Does this carry a higher risk ofaxillary node metastasesupon diagnosis?
 Breast cancer close to the nipple: Does this carry a higher risk ofaxillary node metastasesupon diagnosis? Erin I. Lewis, BUSM 2010 Cheri Nguyen, BUSM 2008 Priscilla Slanetz, M.D., MPH Al Ozonoff, Ph.d.
Breast cancer close to the nipple: Does this carry a higher risk ofaxillary node metastasesupon diagnosis? Erin I. Lewis, BUSM 2010 Cheri Nguyen, BUSM 2008 Priscilla Slanetz, M.D., MPH Al Ozonoff, Ph.d.
HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer?
 Ask the Experts HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer? Bharat Jasani MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Marco Novelli MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Josef Rüschoff, MD Robert Y. Osamura, MD, FIAC
Ask the Experts HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer? Bharat Jasani MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Marco Novelli MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Josef Rüschoff, MD Robert Y. Osamura, MD, FIAC
Evidence tabel Lokaal palliatieve behandelingen
 Auteurs, jaartal Mate van bewijs Studie type Follow-up Populatie (incl. steekproef-grootte) Patienten kenmerken Interventie Controle Resultaten Conclusie Opmerkingen, commentaar Hartgrink, 2002 The Netherlands
Auteurs, jaartal Mate van bewijs Studie type Follow-up Populatie (incl. steekproef-grootte) Patienten kenmerken Interventie Controle Resultaten Conclusie Opmerkingen, commentaar Hartgrink, 2002 The Netherlands
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
General Information About Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing
Diagnosing vascular (venous) invasion in colorectal carcinomas
 Diagnosing vascular (venous) invasion in colorectal carcinomas Improving reproducibility and potential pitfalls Gábor Cserni Bács-Kiskun County Teaching Hospital, Kecskemét & University of Szeged Hungary
Diagnosing vascular (venous) invasion in colorectal carcinomas Improving reproducibility and potential pitfalls Gábor Cserni Bács-Kiskun County Teaching Hospital, Kecskemét & University of Szeged Hungary
Challenges in gastric, appendiceal and rectal NETs Leuven, 29.11.2014
 Challenges in gastric, appendiceal and rectal NETs Leuven, 29.11.2014 Prof. Dr. Chris Verslype, Leuven Prof. Dr. Aurel Perren, Bern Menue Challenges: 1. Gastric NET 2. Appendiceal NET 3. Rectal NET SEER,
Challenges in gastric, appendiceal and rectal NETs Leuven, 29.11.2014 Prof. Dr. Chris Verslype, Leuven Prof. Dr. Aurel Perren, Bern Menue Challenges: 1. Gastric NET 2. Appendiceal NET 3. Rectal NET SEER,
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma
 A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
A918: Prostate: adenocarcinoma General facts of prostate cancer The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The tube that carries urine (the urethra)
THYROID CANCER. I. Introduction
 THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
The Whipple Operation for Pancreatic Cancer: Optimism vs. Reality. Franklin Wright UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds September 11, 2006
 The Whipple Operation for Pancreatic Cancer: Optimism vs. Reality Franklin Wright UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds September 11, 2006 Overview Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Pancreaticoduodenectomy
The Whipple Operation for Pancreatic Cancer: Optimism vs. Reality Franklin Wright UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds September 11, 2006 Overview Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Pancreaticoduodenectomy
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY
 PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
Colorectal cancer. A guide for journalists on colorectal cancer and its treatment
 Colorectal cancer A guide for journalists on colorectal cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Colorectal cancer 4 i. What is colorectal cancer? 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 4 iii.
Colorectal cancer A guide for journalists on colorectal cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Colorectal cancer 4 i. What is colorectal cancer? 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 4 iii.
Surgery for oesophageal cancer
 Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Surgery for oesophageal cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding oesophageal cancer (cancer of the gullet). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Risk factors for bleeding after endoscopic mucosal resection
 PO Box 2345, Beijing 100023, China World J Gastroenterol 2005;11(46):7335-7339 www.wjgnet.com World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 1007-9327 wjg@wjgnet.com ELSEVIER 2005 The WJG Press and Elsevier Inc.
PO Box 2345, Beijing 100023, China World J Gastroenterol 2005;11(46):7335-7339 www.wjgnet.com World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 1007-9327 wjg@wjgnet.com ELSEVIER 2005 The WJG Press and Elsevier Inc.
Case Report Concurrent Esophageal Dysplasia and Leiomyoma
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine, Article ID 804175, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/804175 Case Report Concurrent Esophageal Dysplasia and Leiomyoma Asim Shuja 1 and Khalid A. Alkimawi
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine, Article ID 804175, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/804175 Case Report Concurrent Esophageal Dysplasia and Leiomyoma Asim Shuja 1 and Khalid A. Alkimawi
restricted to certain centers and certain patients, preferably in some sort of experimental trial format.
 Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
Barrett s ALIMENTARY TRACT. Subsquamous Extension of Intestinal Metaplasia Is Detected in 98% of Cases of Neoplastic Barrett s Esophagus
 Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2014;12:405 410 ALIMENTARY TRACT Subsquamous Extension of Intestinal Metaplasia Is Detected in 98% of Cases of Neoplastic Barrett s Esophagus Mario Anders,* Yasmin
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2014;12:405 410 ALIMENTARY TRACT Subsquamous Extension of Intestinal Metaplasia Is Detected in 98% of Cases of Neoplastic Barrett s Esophagus Mario Anders,* Yasmin
National Bowel Cancer Audit Report 2008 Public and Executive Summary
 National Bowel Cancer Audit Report 2008 Public and Executive Summary Prepared in association with: Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership HQIP Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland
National Bowel Cancer Audit Report 2008 Public and Executive Summary Prepared in association with: Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership HQIP Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland
Update on thyroid cancer surveillance and management of recurrent disease. Minimally invasive thyroid surgery
 Update on thyroid cancer surveillance and management of recurrent disease Minimally invasive thyroid surgery July 2006 Michael W. Yeh, MD Program Director, Endocrine Surgery Assistant Professor, David
Update on thyroid cancer surveillance and management of recurrent disease Minimally invasive thyroid surgery July 2006 Michael W. Yeh, MD Program Director, Endocrine Surgery Assistant Professor, David
LOWER GI ENDOSCOPIES So why is CMS yanking our chain? General Concepts for all GI Endoscopy Procedures
 LOWER GI ENDOSCOPIES We have lots of changes to lower GI coding for 2015 to talk about. Code definitions have been revised and many new codes have been added to this chapter. First the good news: All these
LOWER GI ENDOSCOPIES We have lots of changes to lower GI coding for 2015 to talk about. Code definitions have been revised and many new codes have been added to this chapter. First the good news: All these
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma
 A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
