Assessing short-term individual consistency using IRT-based statistics
|
|
|
- Margaret Goodman
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pscológca (2010), 31, Assessng short-term ndvdual consstency usng IRT-based statstcs Pere J. Ferrando * Rovra Vrgl Unversty, Span Ths artcle proposes a procedure, based on a global statstc, for assessng ntra-ndvdual consstency n a test-retest desgn wth a short-term retest nterval. The procedure s developed wthn the framework of parametrc tem response theory, and the statstc s a lkelhood-based measure that can be consdered as an extenson of the well-known lz person-ft ndex. The ratonale for usng and nterpretng the proposed statstc s dscussed, and an adapted standardzed resdual at the tem level s also proposed to obtan clues about the possble causes of the detected nconsstency. The procedure s llustrated wth a real-data example and a parallel smulaton n the personalty doman. In recent decades n appled psychometrcs nterest n the assessment of the ntra-ndvdual consstency of the responses over a set of test tems has been growng. Wthn the framework of parametrc tem response theory (IRT), whch s the one consdered here, most of the research on ths topc has focused on developng and evaluatng global statstcs (.e. scalar measures based on the complete pattern of tem responses) that measure the extent to whch the answerng behavor of a respondent s consstent wth the psychometrc model whch was ftted to the data. These statstcs were ntally known as approprateness measures (Levne & Rubn, 1979), but now they are usually referred to as person-ft ndces (e.g. Meer & Stsma, 1995, 2001). Most of these model-based statstcs can be classfed n two broad classes (see Meer & Stsma, 1995). The measures n the frst class are based on a resdual that reflects the dfferences between the observed tem scores and the scores expected from the model. The measures n the second * Ths research was partally supported by a grant from the Spansh Mnstry of Educaton and Scence (PSI /PSIC). Correspondence: Pere Joan Ferrando. Unversdad 'Rovra Vrgl'. Departamento de Pscología. Carretera Valls s/n Tarragona (Span). E-mal: pereoan.ferrando@urv.cat
2 320 P.J. Ferrando class are based on the lkelhood functon. In ths second class, two of the bestknown and most commonly used person-ft ndces are the lo and lz measures ntally proposed by Levne and Rubn (1979). Person-ft ndces were ntally ntended for the ablty and apttude doman and manly for practcal purposes. However, over tme they have also been used n the personalty doman (Ferrando & Chco, 2001, Rese, 1995, Rese & Flannery, 1996, Rese & Waller, 1993, Meer et al., 2008). The assessment of ntra-ndvdual consstency n personalty s more than a practcal ssue, because n ths doman consstency s a topc of central theoretcal relevance (e.g. Tellegen, 1988). In personalty measurement three types of ntra-ndvdual consstency are generally dstngushed dependng on the temporal framework n whch the assessment takes place (e.g. Fske & Rce, 1955, Lumsden 1977, Watson, 2004). The frst type s momentary consstency, whch s assessed by analyzng the responses of the ndvdual over the set of tems durng a sngle test admnstraton. The second type s short-term consstency, usually assessed by usng a two-wave or a mult-wave retest desgn wth a short retest nterval (generally from a few days to a few weeks). Fnally, the thrd type s long-term consstency, whch s concerned wth trat stablty, and whch s generally assessed by usng two-wave or mult-wave desgns wth long retest perods (e.g. Conley, 1984). Cattell (1986) made a more specfc dfferentaton and dstngushed between dependablty (a retest nterval shorter than two months) and stablty (a retest nterval of two months or more). Now, accordng to these dstnctons, standard person-ft ndces appear to be useful measures for assessng the frst type of consstency at the ndvdual level (Rese, 1995, Rese & Flannery, 1996, Rese & Waller, 1993). However, statstcs for measurng the other two types also seem to be of potental nterest. In partcular, ths paper s concerned wth the assessment of short-term ndvdual consstency. In personalty measurement, ths assessment s of both theoretcal and practcal nterest. Theoretcally, the degree of short-term consstency can be consdered partly as a property of the trat (Cattell, 1986), and, for a personalty theorst the dfferences of trats n ther degree of consstency s mportant nformaton. In expermental and clncal settngs, short-term desgns are commonly used to assess the effects of expermental condtons or treatments. Also, n the selecton doman, short-term desgns are used to gauge the effects of test-coachng and practce. The classcal approach for assessng short-term consstency n personalty s to assume that the ndvduals are perfectly stable over tme: hence, all nconsstency s due solely to measurement error (see e.g.
3 Short-term consstency 321 Watson, 2004). However, ths ratonale s surely too smple. Frst, even wth short retest ntervals, ndvdual transent fluctuatons such as mood changes, cogntve energy varatons, mental atttude changes, etc are expected to occur (Lumsden 1977, Schmdt & Hunter, 1996). Second, changes n the assessment condtons (e.g. nstructons, pressures or motvatng condtons) mght gve rase to true or smulated temporary changes n the trat levels (e.g. Schuldberg, 1990, Zckar & Drasgow, 1996). Thrd, even f condtons reman the same over dfferent admnstratons, the mere fact of havng responded at Tme 1 (pror exposure) mght lead to systematc changes at the retest (e.g. Knowles, 1988). Fnally, we also need to consder the retest effects, understood here as the tendency for ndvduals to duplcate ther former responses (Gullksen, 1950). Ths tendency mght be due to memory effects, or to ncdental tem features whch are unrelated to the trat, but whch tend to elct the same response on each occason (Thorndke, 1951). So, overall, t seems more realstc to assume that short-term nconsstency arses as a result of a complex tem respondent nteracton process (e.g. Ferrando, Lorenzo-Seva & Molna, 2001, Schuldberg, 1990). In spte of ths assumpton, however, most of the research on the causes of short-term nconsstent respondng has focused solely on tem characterstcs (see Ferrando et al for a revew). The present paper develops and proposes an IRT-based statstc for assessng short-term consstency at the ndvdual level. Ths statstc s lkelhood-based, and can be consdered as an extenson of the lz person-ft ndex mentoned above. It s ntended for bnary tems whch are calbrated wth a undmensonal IRT model. Of the exstng parametrc IRT models, bnary undmensonal models are the smplest and best known. So, they seem to be an approprate startng framework for developng new measures. The number of questonnares based on bnary tems s stll substantal n personalty, so the potental nterest of the statstc n appled research seems clear. The statstc proposed here s expected to be of both theoretcal and practcal nterest. At the practcal level, t can be used for flaggng ndvduals for whom the estmated trat level at Tme 1 mght be napproprate for makng vald nferences n the short term. A second practcal use s for detectng outlers (.e. nconsstent ndvduals) n longtudnal studes. It s well known that the estmated parameters and ft results n structural equaton models are easly dstorted f outlers are present (e.g. Bollen & Armnger, 1991). At a more theoretcal level, the statstc can provde addtonal nformaton about the nconsstency of the response behavor of the ndvdual beyond that provded n a sngle test
4 322 P.J. Ferrando admnstraton, and can be useful for assessng dfferent types of ndvdual change as well as retest effects. Ratonale and Descrpton of the lz-ch Statstc Consder a personalty test that measures a sngle trat θ and whch s made up of 1,, n tems scored as 0 or 1. The tem responses are assumed to behave accordng to a specfc parametrc IRT model, and are ndependent for fxed trat level (local ndependence). Let P (θ) be the tem response functon correspondng to the IRT model, and let x =(x 1..x n ) be the response pattern of ndvdual. Then, the log lkelhood of x s n L θ ) = x ln( P ( θ )) + (1 x ) ln(1 P ( θ )) (1) ( Furthermore, the mean and varance of L(θ ) are (Drasgow, Levne & Wllams, 1985) E n L( θ )) = P ( θ ) ln( P ( θ )) + (1 P ( θ )) ln(1 P ( θ )) (2) ( and n P ( ) θ Var ( L( θ )) = P ( θ )(1 P ( θ )) ln (3) 1 P ( θ ) 2 Levne and Rubn (1979) defned the lo person-ft ndex as the log lkelhood (1) computed usng the maxmum lkelhood (ML) estmate of θ. The ratonale for ths choce s that when a pattern s nconsstent, no value of θ makes the lkelhood of ths pattern large. So, even when evaluated at the maxmum, the value of (1) s stll relatvely small. A lmtaton of lo that can be noted by nspecton of (2) s that ts value depends generally on the trat level. Furthermore, the ndex has no mmedate theoretcal reference dstrbuton for assessng the values
5 Short-term consstency 323 obtaned. To overcome these problems, Drasgow et al. (1985) proposed a standardzed verson of lo, whch they named lz. It s gven by l z lo E ( lo ) = (4) [ Var ( l )] 1 / 2 o where the mean and varance are obtaned from (2) and (3) computed usng the ML estmate of θ. The standardzaton provdes a known scale and s ntended to reduce the dependency of the values on θ. Furthermore, because the terms n (1) are ndependent for fxed θ, as the number of tems ncreases the dstrbuton of lz s expected to approach the standard normal. Ths approxmaton requres some condtons to be fulflled (see below). As for nterpretaton, typcally only the left tal of the dstrbuton s consdered: large negatve values ndcate potental person msft. Large postve values would ndcate an over-consstent, determnstc (.e. Guttman-type) respondng, however they are seldom nterpreted. Consder now that the test s admnstered to the same respondents at two ponts of tme wth a gven retest nterval. The present development s based on the addtonal assumpton that the local ndependence prncple also holds for repeated measurements of the same tem, or, more specfcally, that for fxed θ the condtonal dstrbutons of the responses to the same tem n two repeated admnstratons are ndependent of each other. If ths s so, the condtonal probablty of a response change to tem s gven by Pch θ ) = 2 P ( θ )( 1 P ( θ )) (5) (.e. the probablty of the 1-0 pattern of change plus the probablty of the 0-1 pattern (Ferrando et al., 2001, Nowakowska, 1983). We shall now defne the ndcator varable y to denote response change to tem as 1, f response of tem was changed y = 0, otherwse at Tme2 (6) and y =(y 1..y n ) as the change response pattern of ndvdual. Under the assumptons stated so far, the log lkelhood of the change response pattern y s
6 324 P.J. Ferrando L n θ ) = y ln( Pch ( θ )) + ( 1 y ) ln( 1 Pch ( θ )). (7) ch ( By usng the same ratonale as Levne and Rubn s, the short-term consstency counterpart of the lz person-ft ndex, whch we shall name lzch, s now defned as l E ( l ) = (8) o ch o ch l z ch / o ch [ Var ( l )] 1 2 where lo-ch s the value of (7) evaluated at the ML estmate of θ, and the mean and varance are gven respectvely by E = n ( l ) ( ˆ ) ln( ( ˆ )) ( ( ˆ 0 ch Pch θ Pch θ + 1 Pch θ )) ln( 1 Pch ( θˆ )) (9) Var ( l 0 ch ) n = Pch Pch ( θˆ ) ( θ ˆ )( 1 Pch ( θˆ )) ln (10) 1 Pch ˆ ( θ ) 2 and θˆ s the ML estmate of θ. Because the terms n (7) are ndependent for fxed θ, under the null hypothess that all respondents follow the postulated model, the dstrbuton of lz-ch s expected to approach the standard normal as the number of tems ncreases. Ths expectaton, however, s based on the same two strong assumptons that Drasgow et al. used when dervng the dstrbuton of lz. Frst, the tem parameters are assumed to be fxed and known. Second, the ML estmate of θ s expected to concde wth the true value. To see these ponts, note that the Pch(θ) terms n (7) are treated as constants when dervng the mean and varance (9) and (10). And ths treatment s only strctly correct when the two above assumptons are met. The lz-ch statstc s ntended to be used n a retest desgn n whch the tems are calbrated at Tme 1, and the ndvduals are also scored at Tme 1
7 Short-term consstency 325 by usng the tem estmates as fxed and known values. It s also assumed that the sample at Tme 1 s large and representatve enough for the assumpton of known tem parameters to be reasonable. However, the problem of usng ndvdual trat estmates n place of the true levels stll remans. In the context of lz, some correctons have been proposed (e.g. Snders, 2001). At the moment, however, we shall not stll consder these correctons for reasons whch are dscussed below. In summary, lz-ch s ntended to be used n a stuaton n whch a large and representatve group of respondents s avalable at Tme 1. The IRT model s calbrated n ths group and the ft of the model s checked. Next, ndvdual trat estmates are obtaned at Tme 1 by takng the tem parameter estmates as fxed and known values. Some or all of the ndvduals of the group are then retested after a short-term retest nterval, and, for these ndvduals, the lz-ch values are obtaned based on the tem and person estmates at Tme 1, and the observed responses at Tme 1 and at Tme 2. These values are used to flag those respondents that are potentally nconsstent n the short term. As for possble cut scores, the standard normal dstrbuton of lz-ch requres the fulfllment of some condtons that can never be fulflled wth real data. As well as the condtons dscussed above (known tem and person parameters), the model s assumed to be correct and the data s expected to contan no truly nconsstent respondents (.e. the null hypothess stated above). Models, however, are at best reasonable approxmatons, and the data s expected to contan a certan unknown proporton of nconsstent respondents. So, t seems unrealstc to expect normal dstrbutons wth real data, and, n the wrter s opnon, t s napproprate to suggest cut scores based on theoretcal nomnal levels. Future ntensve research may make headway n ths respect, ncludng the correctons dscussed above. For the moment t seems better to consder the standard normal dstrbuton only as a useful reference. Interpretaton Issues and Further Extensons Inspecton of equatons (7) to (10) shows that lz-ch values are negatve when the respondent changes hs/her tem responses more often than expected. On the other hand, values are postve when the respondent tends to duplcate the responses gven at Tme 1 more often than would be expected gven the IRT model and hs/her trat estmate. Ths result suggests than n the lz-ch case both tals of the dstrbuton should be examned, as large and postve values would probably ndcate retest
8 326 P.J. Ferrando effects of the type dscussed above. Furthermore, examnaton of the lz-ch dstrbuton over respondents mght also be useful for assessng retest effects. If the retest nterval s too short for avodng memory effects, the respondents as a group would tend to behave more consstently than expected. As a result, the mean of lz-ch n ths group would be expected to shft toward postve values. As mentoned above, one of the ams of lz-ch s to provde more nformaton about consstency than can be obtaned wth lz. In prncple, t seems clear that both ndces assess dfferent aspects of consstency. The lz ndex assesses consstency on a same-tme/dfferent-tem bass, whereas lzch manly assesses consstency on a dfferent-tme/same-tem bass (although the consstency contrbuton s then summed over tems). In spte of ths dstncton, however, f the assumptons on whch both ndces are based are fulflled, then lz and lz-ch are probablstcally related. To see ths pont, consder a sngle tem. If the response to ths tem at Tme 1 s consstent, then lz wll be postve (.e. above the mean). If t s, accordng to the assumptons, the probablty of also obtanng a postve lz-ch value s greater than the probablty of obtanng a negatve value. On the other hand, f the response at Tme 1 s nconsstent, lz wll be negatve. And the probablty of also obtanng a negatve lz-ch value s greater than the probablty of obtanng a postve value. From these results t follows that n a group of consstent respondents, lz and lz-ch are expected to be postvely correlated. Ths result s theoretcally sound. It seems reasonable to expect that those respondents who are the most consstent when respondng n a sngle test stuaton also tend to be the most consstent under repetton. Indeed, the ndex proposed here wll be most useful when the respondent behaves nconsstently and there are dscrepances between lz and lz-ch. As a frst example, consder a stuaton reported n the lterature (Jorm, Duncan-Jones & Scott, 1989). The ndvdual responds consstently at Tme 1, but at Tme 2 hs/her motvaton decreases and he/she responds more randomly or mechancally. In ths case lz would probably ndcate consstency, but lz-ch would not. As a second example consder the thetashft model (Zckar & Drasgow, 1996). Assume that the admnstraton condtons are neutral on the frst occason but that there s a strong motvaton for fakng good on the second occason. Assume further that, under ths pressure, the ndvdual responds as f hs/her trat level s more adapted than t really s. In ths case lz would probablty ndcate consstency, perhaps even when t s computed on both occasons. However, because the lz-ch values are obtaned based on the person estmates at the
9 Short-term consstency 327 frst occason, lz-ch would be expected to flag ths respondent as nconsstent gven the temporary changes n hs/her trat level. Whle the nformaton obtaned wth lz-ch seems useful, once a response pattern has been detected as potentally nconsstent, t also seems to be useful to collect more nformaton about the specfc tem responses n whch the nconsstent respondng s more pronounced. Informaton of ths type can be obtaned by usng ndvdual tem statstcs. In partcular, I propose to assess nconsstency at the ndvdual tem level by adaptng the standardzed resdual statstc proposed by Wrght (Wrght & Stone, 1979) n the context of the Rasch model. In the framework used here (see equatons 5 and 6), the standardzed change resdual for respondent on tem, denoted by Zch s obtaned as y Pch ( θˆ ) =. (11) Z ch / [ Pch ( θˆ )( 1 Pch ( θˆ ))] 1 2 The Zch measures the tem response contrbuton to the short-term nconsstency of ndvdual. So, a large postve value would be obtaned f the ndvdual changed a response to an tem n whch a change was very unlkely gven the model and trat estmate. The am of ths paper s not to derve the specfc relatons between (8) and (11). However, we note that lzch n (8) can be re-expressed as a weghted sum of the dscrepancy terms n the numerator of (11) (e.g. Snders, 2001). So, t seems clear that the ndvdual tem nconsstences drectly contrbute to the global nconsstency as measured by lz-ch. As for possble cut scores, t should be stressed that the scalng n (11) (.e. zero mean and unt varance) s only made so as to make the resduals more nterpretable. However, t cannot be sad that the Zch values are dstrbuted as a standard normal varable because, n fact, Zch s smply a transformed bnary varable. So, no attempt s made here to provde crtcal values based on exact probabltes. What s expected, however, s that the Zch values wll be regular enough to dentfy outlyng responses relably, and ths pont s consdered n the llustratve example below. Fnally, as a reference, we may consder that a Zch value of +3 would be obtaned f a respondent changed a response to an tem for whch the expected probablty of change was as low as 0.10.
10 328 P.J. Ferrando An Illustratve Example The statstcs and procedure dscussed so far are llustrated usng data collected by the author n personalty research. A 60-tem Neurotcsm scale was admnstered twce n the same condtons to a sample of undergraduate students wth a 4-week retest nterval. The analyses that follow were based on the 436 respondents who were present at both admnstratons. As dscussed above, tems were calbrated and respondents were scored usng the Tme 1 data. The tems of the scale were domnance-based, of the type whch are generally well ftted by the two-parameter IRT model (2PM, see e.g. Ferrando, 1994). Items were calbrated accordng to the 2PM n the normal-ogve metrc by usng BILOG MG-3 (Zmowsk et al. 2003), and the undmensonalty assumpton and the global model-data ft were assessed wth NOHARM (Fraser & McDonald, 1988). The ft of the model, both at the global level and at the ndvdual-tem level was reasonably good (detals of the goodness-of-ft results are avalable from the author). The tem locatons ranged from to 4.15, wth a mean of The average of the tem dscrmnatons was The tem parameter estmates obtaned n the calbraton stage were used n a real-parameter smulaton study, whch was parallel to the man emprcal study. Ths parallel study smulated the responses of 436 ndvduals at two ponts of tme to a test that behaved accordng to the 2PM, wth tem parameter values equal to those obtaned n the calbraton of the emprcal data. In the smulated data all of the assumptons used n the dervaton of lz-ch were met: The model was totally correct, the tem responses were locally ndependent under repetton, and the sample dd not contan truly nconsstent respondents. So, the smulated results were used to check the predctons about the behavor of lz-ch and to assess the dscrepances wth respect to the real-data results. Fgure 1 shows the dstrbuton of lz-ch wth the smulated data (thck dashed curve) and wth the emprcal data (thck sold curve). The dstrbutons were obtaned by usng Gaussan kernel densty estmaton (Slverman, 1986), whch essentally provdes smoothed mproved hstograms. The dstrbuton based on the smulated data agreed qute well wth the expected standard normal dstrbuton. The mean and the standard devatons were 0.05 and The adherence of the lz-ch values to the correspondng theoretcal dstrbuton was further assessed by usng the Kolmogorov-Smrnov statstc. The Kolmogorov dstance was 0.05, wth an assocated probablty of 0.13.
11 Short-term consstency 329 Note:.. : Real data; : Smulated data Fgure 1. Dstrbuton of lz-ch wth the real data and the smulated data. At frst sght, the dfference between the curves n fgure 1 does not seem to be too great. However, the dstrbuton based on real data, (a) s clearly shfted to the rght (the mean was 1.38), (b) s somewhat asymmetrcal wth a heaver left tal, and (c) tends to have more dsperson than the standard normal dstrbuton (the standard devaton was 1.17). Prevous studes wth lz show that when ndvdual trat estmates are used n place of the true levels the varance usually decreases (Snders, 2001, van Krmpen-Stoop & Meer, 1999). So, the true effect (c) mght be even larger. Results (b) and (c) are to be expected. The dstrbuton of lz-ch s obtaned by assumng that there are no nconsstent respondents n the group whch s assessed. However, real data s expected to contan a certan, unknown proporton of nconsstent respondents. These are precsely the
12 330 P.J. Ferrando ones we wsh to dentfy and who are expected to be found n the tals (partcularly the left tal) of the dstrbutons, thus ncreasng the dsperson. As dscussed above, result (a) would be expected f respondents tended to behave more consstently as a group than the model predcts. To further assess ths ssue, the expected number of response changes was obtaned for each respondent by evaluatng (5) at the estmated trat level, and summng the values over the 60 tems. The values obtaned were then compared to the observed number of response changes. The medan of the expected number of changes over respondents was 20, whereas the medan of the observed values was 10. The respondents clearly tended to behave more consstently n the short term than the model and the trat estmates would lead us to expect. Overall, these results suggest that the 4-week nterval was nsuffcent to avod retest (probably memory) effects. The next factor to be assessed was the extent to whch the proposed standardzaton (8) acheved ndependence from the trat levels estmated at Tme 1. For the smulated data, the product-moment correlaton between the θ estmates and lz-ch was For the real data t was Inspecton of the scatterplots dd not reveal a trend of any sort. So, the ntal results suggest that the values of lz-ch are essentally ndependent from the trat levels. Indeed, far more research s needed on ths ssue. We turn now to the relatons between lz-ch and the lz values estmated at Tme 1. For the smulated data the scatterplot suggested a lnear relaton wthout outlers, and the correlaton was Ths result agrees wth the theoretcal expectatons dscussed above. As for the real data, the scatterplot s shown n fgure 2 Unlke the smulated case, fgure 2 reveals the presence of outlers that affect the product-moment correlaton, whch n ths case was only These outlers are marked n fgure 2 and are presumably respondents who behaved consstently at Tme 1 (acceptable lz values) but nconsstently n the short-term. As dscussed above, these are precsely the most nterestng cases. The lz-ch values for the ndvduals flagged n fgure 2 were (respondent 56), (respondent 88) and (respondent 357). These hgh negatve values suggest that these respondents changed responses at Tme 2 more often than expected. To further assess the type of nconsstency that was potentally detected by lz-ch, the standardzed change resduals (11) were assessed for each tem. For respondents 56 and 88, t was found that nconsstences were located n a small group of tems (15, 17, and 34 for respondent 56, and 28, 41, 46 and 51 for respondent 88). For these tems, the Zch values were far above 4 n all cases. In contrast,
13 Short-term consstency 331 the Zch values for respondent 357 were systematcally hgh (around 2) for most tems but wthout the extremely hgh values obtaned n the two prevous cases. In appled research, further nformaton should be collected to determne the cause of the unexpected changes of respondents 56 and 88. The behavor of respondent 357, on the other hand, rather suggests some type of systematc change n the trat levels. Fgure 2. Relaton between lz at Tme 1 and lz-ch. Real data. DISCUSSIO In personalty measurement, short-term consstency s an mportant topc that has been the obect of consderable research. Earler studes used a classcal test theory framework, whereas most modern research tends to be based on IRT. In both cases, however, the focus has generally been on the tem characterstcs that tend to elct nconsstent respondng (e.g. Ferrando et al. 2001). Furthermore, the respondents have only been studed at the group level, not at the ndvdual level (e.g. Fscher, 1995). As far as the wrter
14 332 P.J. Ferrando knows, no procedures at the ndvdual level of the type dscussed here have been proposed so far. The present procedure s based on a lkelhood-type ndex that can be consdered as the short-term counterpart of the well known lz statstc. So, lzch can be assumed to have the same advantages and shortcomngs as lz. Its advantages are that t has a clear ratonale, s easy to nterpret and s expected to have a relatvely good power for detectng nconsstent respondents. Its dsadvantages are that t only adheres to the standard normal reference dstrbuton under strong assumptons that can never be fulflled wth real data. So, at present t does not seem approprate to use the statstc for conductng strct tests of ft; rather t can be used at the descrptve level as a useful screenng tool. Once a respondent has been flagged as potentally nconsstent, the standardzed change resduals also proposed n ths paper can be used to further assess the type of nconsstency detected by the global ndex, and perhaps to explan the reasons behnd the nconsstences. Further extensons can also be consdered. One revewer suggested that the ndvdual estmates obtaned separately at Tme 1 and at Tme 2 should be used for assessng specfc sources of nconsstency. For example, for the theta-shft case, lz-ch could be modfed so that t would take nto account the estmated ndvdual change. If so, the statstc would detect nconsstency beyond that due to the temporal change n the trat level. The results obtaned n the emprcal study supported the expectatons about the behavor of lz-ch. In the smulated data, based on a 60-tem test wth moderate dscrmnaton and a wde range of tem dffcultes, the dstrbuton of lz-ch approached the theoretcal reference dstrbuton qute well. In fact the departure from ths dstrbuton was non-sgnfcant accordng to the Kolmogorov-Smrnov test. Furthermore, the values of the statstc were vrtually ndependent from the estmated trat level. Wth the real data, the departure from the reference dstrbuton was clear. However, the dscrepances could be reasonably explaned, and they provded useful nformaton. Fnally, the man purpose of ths paper s to provde a useful tool for appled researchers. In ths respect, the procedure s relatvely smple, and the proposed statstcs can be easly programmed. At present, the wrter s developng a user-frendly program that wll be avalable at no cost.
15 Short-term consstency 333 RESUME Evaluacón de la consstenca ndvdual a corto plazo medante estadístcos basados en la TRI. Se propone un procedmento, basado en un estadístco global para evaluar la consstenca ntra-ndvdual en un dseño retest basado en un ntervalo de retest corto. El procedmento se desarrolla en el marco de los modelos paramétrcos de TRI, y el estadístco, que se basa en la funcón de verosmltud, puede ser consderado como una extensón del estadístco lz. Se dscute la ustfcacón para el uso e nterpretacón del estadístco y se propone además un estadístco estandarzado a nvel de ítem para obtener claves acerca de las posbles causas de la nconsstenca detectada medante el índce global. El procedmento se lustra con un eemplo real y una smulacón paralela en el domno de la personaldad. REFERE CES Bollen, K.A. & Armnger, G. (1991). Observatonal resduals n factor analyss and structural equaton models. In P.V. Marsden (ed.) Socologcal Methodology 1991 (pp ). New York: Basl Blackwell. Cattell, R.B. (1986). The psychometrc propertes of tests: consstency, valdty and effcency. In R.B. Cattell and R.C. Johnson (eds.) Functonal Psychologcal Testng (pp 54-78). New York: Brunner/Mazel. Conley, J.J. (1984). The herarchy of consstency: a revew and model of longtudnal fndngs on adult ndvdual dfferences n ntellgence, personalty and self-opnon. Personalty and Indvdual Dfferences, 5, Drasgow, F., Levne, M.V. & Wllams, E.A. (1985). Approprateness measurement wth polychotomous tem response models and standardzed ndces. Brtsh Journal of Mathematcal and Statstcal Psychology, 38, Ferrando, P.J. & Chco, E. (2001).Detectng dssmulaton n personalty test scores: A comparson between person-ft ndces and detecton scales. Educatonal and Psychologcal Measurement, 61, Ferrando, P.J.(1994). Fttng tem response models to the EPI-A mpulsvty subscale. Educatonal and Psychologcal Measurement. 54, Ferrando, P.J., Lorenzo-Seva, U., & Molna, G. (2001). An tem response theory analyss of response stablty n personalty measurement. Appled Psychologcal Measurement. 25, Fscher, G.H. (1995). Some neglected problems n IRT. Psychometrka, 60, Fske, D.W. & Rce, L. (1955). Intra-ndvdual response varablty. Psychologcal Bulletn, 52, Fraser, C. & McDonald, R.P. (1988). NOHARM: least squares tem factor analyss. Multvarate Behavoral Research, 23, Gullksen, H. (1950). Theory of mental tests. New York: Wley. Jorm, A.F., Duncan-Jones, P. & Scout, R. (1989). An analyss of the re-test artfact n longtudnal studes of psychatrc symptoms and personalty. Psychologcal Medcne, 19, Knowles, E.S. (1988). Item context effects on personalty scales: measurng changes the measure. Journal of Personalty and Socal Psychology, 55,
16 334 P.J. Ferrando Levne, M.V. & Rubn, D.B. (1979). Measurng the approprateness of multple choce test scores. Journal of Educatonal Statstcs, 4, Lumsden, J. (1977). Person relablty. Appled Psychologcal Measurement, 1, Meer, R.R.& Stsma, K. (1995). Detecton of aberrant tem scores patterns: A revew and new developments. Appled Measurement n Educaton. 8, Meer, R.R.& Stsma, K. (2001). Methodology revew: Evaluatong person ft. Appled Psychologcal Measurement. 25, Meer, R.R., Egbernk, I.J.K., Emons, W.H.M. & Stsma, K. (2008). Detecton and valdaton of unscalable tem score patterns usng tem response theory: An llustraton wth Harter s self-percepton profle for chldren. Journal of Personalty Assessment, 90, Nowakowska, M. (1983). Quanttatve pschology: some chosen problems and new deas. Amsterdam: North-Holland. Rese, S.P. & Waller, N.G. (1993). Tratedness and the assessment of response pattern scalablty. Journal of Personalty and Socal Psychology, 65, Rese, S.P. (1995). Scorng method and the detecton of person msft n a personalty assessment context. Appled Psychologcal Measurement, 19, Rese, S.P. & Flannery, W.P. (1996). Assessng person-ft on measures of typcal performance. Appled Measurement n Educaton, 9, Schmdt, F.L. & Hunter, J.E. (1996). Measurement error n psychologcal research: Lessons from 26 research scenaros. Psychologcal Methods, 1, Schuldberg, D. (1990). Varetes of nconsstency across test occasons: Effects of computerzed test admnstraton and repeated testng. Journal of Personalty Assessment, 55, Slverman, B.W. (1986). Densty estmaton for statstcs and data analyss. London: Chapman & Hall. Snders, T.A.B. (2001). Asymptotc null dstrbuton of person ft statstcs wth estmated person parameter. Psychometrka, 66, Tellegen, A. (1988). The analyss of consstency n personalty assessment. Journal of Personalty, 56, Thorndke, R.L. (1951). Relablty. In E.F. Lndqust (ed.) Educatonal Measurement (pp ). Washngton: Amercan Councl on Educaton. van Krmpen-Stoop, E.M.L.A. & Meer, R.R. (1999). The null dstrbuton of person-ft statstcs for conventonal and adaptve tests. Appled Psychologcal Measurement, 23, Watson, D. (2004). Stablty versus change, dependablty versus error: Issues n the assessment of personalty over tme. Journal of Research n Personalty, 38, Wrght, B. & Stone, C.H. (1979). Best test desgn. Chcago: Mesa press. Zckar, M. J. & Drasgow, F. (1996). Detectng fakng on a personalty nstrument usng aproprateness measurement. Appled Psychologcal Measurement, 20, Zmowsk, M., Murak, E., Mslevy, R. J., & Bock, R. D. (2003). BILOG-MG 3: Item analyss and test scorng wth bnary logstc models. Chcago: Scentfc Software. (Manuscrpt receved: 10 March 2009; accepted: 14 Aprl 2009)
Can Auto Liability Insurance Purchases Signal Risk Attitude?
 Internatonal Journal of Busness and Economcs, 2011, Vol. 10, No. 2, 159-164 Can Auto Lablty Insurance Purchases Sgnal Rsk Atttude? Chu-Shu L Department of Internatonal Busness, Asa Unversty, Tawan Sheng-Chang
Internatonal Journal of Busness and Economcs, 2011, Vol. 10, No. 2, 159-164 Can Auto Lablty Insurance Purchases Sgnal Rsk Atttude? Chu-Shu L Department of Internatonal Busness, Asa Unversty, Tawan Sheng-Chang
benefit is 2, paid if the policyholder dies within the year, and probability of death within the year is ).
 REVIEW OF RISK MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS LOSS DISTRIBUTIONS AND INSURANCE Loss and nsurance: When someone s subject to the rsk of ncurrng a fnancal loss, the loss s generally modeled usng a random varable or
REVIEW OF RISK MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS LOSS DISTRIBUTIONS AND INSURANCE Loss and nsurance: When someone s subject to the rsk of ncurrng a fnancal loss, the loss s generally modeled usng a random varable or
An Alternative Way to Measure Private Equity Performance
 An Alternatve Way to Measure Prvate Equty Performance Peter Todd Parlux Investment Technology LLC Summary Internal Rate of Return (IRR) s probably the most common way to measure the performance of prvate
An Alternatve Way to Measure Prvate Equty Performance Peter Todd Parlux Investment Technology LLC Summary Internal Rate of Return (IRR) s probably the most common way to measure the performance of prvate
Causal, Explanatory Forecasting. Analysis. Regression Analysis. Simple Linear Regression. Which is Independent? Forecasting
 Causal, Explanatory Forecastng Assumes cause-and-effect relatonshp between system nputs and ts output Forecastng wth Regresson Analyss Rchard S. Barr Inputs System Cause + Effect Relatonshp The job of
Causal, Explanatory Forecastng Assumes cause-and-effect relatonshp between system nputs and ts output Forecastng wth Regresson Analyss Rchard S. Barr Inputs System Cause + Effect Relatonshp The job of
Analysis of Premium Liabilities for Australian Lines of Business
 Summary of Analyss of Premum Labltes for Australan Lnes of Busness Emly Tao Honours Research Paper, The Unversty of Melbourne Emly Tao Acknowledgements I am grateful to the Australan Prudental Regulaton
Summary of Analyss of Premum Labltes for Australan Lnes of Busness Emly Tao Honours Research Paper, The Unversty of Melbourne Emly Tao Acknowledgements I am grateful to the Australan Prudental Regulaton
Latent Class Regression. Statistics for Psychosocial Research II: Structural Models December 4 and 6, 2006
 Latent Class Regresson Statstcs for Psychosocal Research II: Structural Models December 4 and 6, 2006 Latent Class Regresson (LCR) What s t and when do we use t? Recall the standard latent class model
Latent Class Regresson Statstcs for Psychosocal Research II: Structural Models December 4 and 6, 2006 Latent Class Regresson (LCR) What s t and when do we use t? Recall the standard latent class model
PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PYC 304-C) Lecture 12
 14 The Ch-squared dstrbuton PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PYC 304-C) Lecture 1 If a normal varable X, havng mean µ and varance σ, s standardsed, the new varable Z has a mean 0 and varance 1. When ths standardsed
14 The Ch-squared dstrbuton PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PYC 304-C) Lecture 1 If a normal varable X, havng mean µ and varance σ, s standardsed, the new varable Z has a mean 0 and varance 1. When ths standardsed
CHAPTER 14 MORE ABOUT REGRESSION
 CHAPTER 14 MORE ABOUT REGRESSION We learned n Chapter 5 that often a straght lne descrbes the pattern of a relatonshp between two quanttatve varables. For nstance, n Example 5.1 we explored the relatonshp
CHAPTER 14 MORE ABOUT REGRESSION We learned n Chapter 5 that often a straght lne descrbes the pattern of a relatonshp between two quanttatve varables. For nstance, n Example 5.1 we explored the relatonshp
The Development of Web Log Mining Based on Improve-K-Means Clustering Analysis
 The Development of Web Log Mnng Based on Improve-K-Means Clusterng Analyss TngZhong Wang * College of Informaton Technology, Luoyang Normal Unversty, Luoyang, 471022, Chna wangtngzhong2@sna.cn Abstract.
The Development of Web Log Mnng Based on Improve-K-Means Clusterng Analyss TngZhong Wang * College of Informaton Technology, Luoyang Normal Unversty, Luoyang, 471022, Chna wangtngzhong2@sna.cn Abstract.
An Investigation of the Performance of the Generalized S-X 2 Item-Fit Index for Polytomous IRT Models. Taehoon Kang Troy T. Chen
 An Investgaton of the Performance of the eneralzed S-X Item-Ft Index for Polytomous IRT Models Taehoon Kang Troy T. Chen Abstract Orlando and Thssen (, 3) proposed an tem-ft ndex, S-X, for dchotomous
An Investgaton of the Performance of the eneralzed S-X Item-Ft Index for Polytomous IRT Models Taehoon Kang Troy T. Chen Abstract Orlando and Thssen (, 3) proposed an tem-ft ndex, S-X, for dchotomous
THE DISTRIBUTION OF LOAN PORTFOLIO VALUE * Oldrich Alfons Vasicek
 HE DISRIBUION OF LOAN PORFOLIO VALUE * Oldrch Alfons Vascek he amount of captal necessary to support a portfolo of debt securtes depends on the probablty dstrbuton of the portfolo loss. Consder a portfolo
HE DISRIBUION OF LOAN PORFOLIO VALUE * Oldrch Alfons Vascek he amount of captal necessary to support a portfolo of debt securtes depends on the probablty dstrbuton of the portfolo loss. Consder a portfolo
STATISTICAL DATA ANALYSIS IN EXCEL
 Mcroarray Center STATISTICAL DATA ANALYSIS IN EXCEL Lecture 6 Some Advanced Topcs Dr. Petr Nazarov 14-01-013 petr.nazarov@crp-sante.lu Statstcal data analyss n Ecel. 6. Some advanced topcs Correcton for
Mcroarray Center STATISTICAL DATA ANALYSIS IN EXCEL Lecture 6 Some Advanced Topcs Dr. Petr Nazarov 14-01-013 petr.nazarov@crp-sante.lu Statstcal data analyss n Ecel. 6. Some advanced topcs Correcton for
CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK. Sample Stability Protocol
 CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK Sample Stablty Protocol Background The Cholesterol Reference Method Laboratory Network (CRMLN) developed certfcaton protocols for total cholesterol, HDL
CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK Sample Stablty Protocol Background The Cholesterol Reference Method Laboratory Network (CRMLN) developed certfcaton protocols for total cholesterol, HDL
How To Calculate The Accountng Perod Of Nequalty
 Inequalty and The Accountng Perod Quentn Wodon and Shlomo Ytzha World Ban and Hebrew Unversty September Abstract Income nequalty typcally declnes wth the length of tme taen nto account for measurement.
Inequalty and The Accountng Perod Quentn Wodon and Shlomo Ytzha World Ban and Hebrew Unversty September Abstract Income nequalty typcally declnes wth the length of tme taen nto account for measurement.
DEFINING %COMPLETE IN MICROSOFT PROJECT
 CelersSystems DEFINING %COMPLETE IN MICROSOFT PROJECT PREPARED BY James E Aksel, PMP, PMI-SP, MVP For Addtonal Informaton about Earned Value Management Systems and reportng, please contact: CelersSystems,
CelersSystems DEFINING %COMPLETE IN MICROSOFT PROJECT PREPARED BY James E Aksel, PMP, PMI-SP, MVP For Addtonal Informaton about Earned Value Management Systems and reportng, please contact: CelersSystems,
Calculation of Sampling Weights
 Perre Foy Statstcs Canada 4 Calculaton of Samplng Weghts 4.1 OVERVIEW The basc sample desgn used n TIMSS Populatons 1 and 2 was a two-stage stratfed cluster desgn. 1 The frst stage conssted of a sample
Perre Foy Statstcs Canada 4 Calculaton of Samplng Weghts 4.1 OVERVIEW The basc sample desgn used n TIMSS Populatons 1 and 2 was a two-stage stratfed cluster desgn. 1 The frst stage conssted of a sample
Module 2 LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Lesson 3 Lossless Compresson: Huffman Codng Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:. Defne and measure source entropy..
Module LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Lesson 3 Lossless Compresson: Huffman Codng Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:. Defne and measure source entropy..
THE METHOD OF LEAST SQUARES THE METHOD OF LEAST SQUARES
 The goal: to measure (determne) an unknown quantty x (the value of a RV X) Realsaton: n results: y 1, y 2,..., y j,..., y n, (the measured values of Y 1, Y 2,..., Y j,..., Y n ) every result s encumbered
The goal: to measure (determne) an unknown quantty x (the value of a RV X) Realsaton: n results: y 1, y 2,..., y j,..., y n, (the measured values of Y 1, Y 2,..., Y j,..., Y n ) every result s encumbered
1. Measuring association using correlation and regression
 How to measure assocaton I: Correlaton. 1. Measurng assocaton usng correlaton and regresson We often would lke to know how one varable, such as a mother's weght, s related to another varable, such as a
How to measure assocaton I: Correlaton. 1. Measurng assocaton usng correlaton and regresson We often would lke to know how one varable, such as a mother's weght, s related to another varable, such as a
Statistical Methods to Develop Rating Models
 Statstcal Methods to Develop Ratng Models [Evelyn Hayden and Danel Porath, Österrechsche Natonalbank and Unversty of Appled Scences at Manz] Source: The Basel II Rsk Parameters Estmaton, Valdaton, and
Statstcal Methods to Develop Ratng Models [Evelyn Hayden and Danel Porath, Österrechsche Natonalbank and Unversty of Appled Scences at Manz] Source: The Basel II Rsk Parameters Estmaton, Valdaton, and
The Current Employment Statistics (CES) survey,
 Busness Brths and Deaths Impact of busness brths and deaths n the payroll survey The CES probablty-based sample redesgn accounts for most busness brth employment through the mputaton of busness deaths,
Busness Brths and Deaths Impact of busness brths and deaths n the payroll survey The CES probablty-based sample redesgn accounts for most busness brth employment through the mputaton of busness deaths,
Risk-based Fatigue Estimate of Deep Water Risers -- Course Project for EM388F: Fracture Mechanics, Spring 2008
 Rsk-based Fatgue Estmate of Deep Water Rsers -- Course Project for EM388F: Fracture Mechancs, Sprng 2008 Chen Sh Department of Cvl, Archtectural, and Envronmental Engneerng The Unversty of Texas at Austn
Rsk-based Fatgue Estmate of Deep Water Rsers -- Course Project for EM388F: Fracture Mechancs, Sprng 2008 Chen Sh Department of Cvl, Archtectural, and Envronmental Engneerng The Unversty of Texas at Austn
What is Candidate Sampling
 What s Canddate Samplng Say we have a multclass or mult label problem where each tranng example ( x, T ) conssts of a context x a small (mult)set of target classes T out of a large unverse L of possble
What s Canddate Samplng Say we have a multclass or mult label problem where each tranng example ( x, T ) conssts of a context x a small (mult)set of target classes T out of a large unverse L of possble
INVESTIGATION OF VEHICULAR USERS FAIRNESS IN CDMA-HDR NETWORKS
 21 22 September 2007, BULGARIA 119 Proceedngs of the Internatonal Conference on Informaton Technologes (InfoTech-2007) 21 st 22 nd September 2007, Bulgara vol. 2 INVESTIGATION OF VEHICULAR USERS FAIRNESS
21 22 September 2007, BULGARIA 119 Proceedngs of the Internatonal Conference on Informaton Technologes (InfoTech-2007) 21 st 22 nd September 2007, Bulgara vol. 2 INVESTIGATION OF VEHICULAR USERS FAIRNESS
Institute of Informatics, Faculty of Business and Management, Brno University of Technology,Czech Republic
 Lagrange Multplers as Quanttatve Indcators n Economcs Ivan Mezník Insttute of Informatcs, Faculty of Busness and Management, Brno Unversty of TechnologCzech Republc Abstract The quanttatve role of Lagrange
Lagrange Multplers as Quanttatve Indcators n Economcs Ivan Mezník Insttute of Informatcs, Faculty of Busness and Management, Brno Unversty of TechnologCzech Republc Abstract The quanttatve role of Lagrange
CHAPTER 5 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITATIVE VARIABLES
 CHAPTER 5 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITATIVE VARIABLES In ths chapter, we wll learn how to descrbe the relatonshp between two quanttatve varables. Remember (from Chapter 2) that the terms quanttatve varable
CHAPTER 5 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITATIVE VARIABLES In ths chapter, we wll learn how to descrbe the relatonshp between two quanttatve varables. Remember (from Chapter 2) that the terms quanttatve varable
Forecasting the Direction and Strength of Stock Market Movement
 Forecastng the Drecton and Strength of Stock Market Movement Jngwe Chen Mng Chen Nan Ye cjngwe@stanford.edu mchen5@stanford.edu nanye@stanford.edu Abstract - Stock market s one of the most complcated systems
Forecastng the Drecton and Strength of Stock Market Movement Jngwe Chen Mng Chen Nan Ye cjngwe@stanford.edu mchen5@stanford.edu nanye@stanford.edu Abstract - Stock market s one of the most complcated systems
Recurrence. 1 Definitions and main statements
 Recurrence 1 Defntons and man statements Let X n, n = 0, 1, 2,... be a MC wth the state space S = (1, 2,...), transton probabltes p j = P {X n+1 = j X n = }, and the transton matrx P = (p j ),j S def.
Recurrence 1 Defntons and man statements Let X n, n = 0, 1, 2,... be a MC wth the state space S = (1, 2,...), transton probabltes p j = P {X n+1 = j X n = }, and the transton matrx P = (p j ),j S def.
SPEE Recommended Evaluation Practice #6 Definition of Decline Curve Parameters Background:
 SPEE Recommended Evaluaton Practce #6 efnton of eclne Curve Parameters Background: The producton hstores of ol and gas wells can be analyzed to estmate reserves and future ol and gas producton rates and
SPEE Recommended Evaluaton Practce #6 efnton of eclne Curve Parameters Background: The producton hstores of ol and gas wells can be analyzed to estmate reserves and future ol and gas producton rates and
ANALYZING THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUALITY, TIME, AND COST IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
 ANALYZING THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUALITY, TIME, AND COST IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING Matthew J. Lberatore, Department of Management and Operatons, Vllanova Unversty, Vllanova, PA 19085, 610-519-4390,
ANALYZING THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUALITY, TIME, AND COST IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING Matthew J. Lberatore, Department of Management and Operatons, Vllanova Unversty, Vllanova, PA 19085, 610-519-4390,
How To Understand The Results Of The German Meris Cloud And Water Vapour Product
 Ttel: Project: Doc. No.: MERIS level 3 cloud and water vapour products MAPP MAPP-ATBD-ClWVL3 Issue: 1 Revson: 0 Date: 9.12.1998 Functon Name Organsaton Sgnature Date Author: Bennartz FUB Preusker FUB Schüller
Ttel: Project: Doc. No.: MERIS level 3 cloud and water vapour products MAPP MAPP-ATBD-ClWVL3 Issue: 1 Revson: 0 Date: 9.12.1998 Functon Name Organsaton Sgnature Date Author: Bennartz FUB Preusker FUB Schüller
Exhaustive Regression. An Exploration of Regression-Based Data Mining Techniques Using Super Computation
 Exhaustve Regresson An Exploraton of Regresson-Based Data Mnng Technques Usng Super Computaton Antony Daves, Ph.D. Assocate Professor of Economcs Duquesne Unversty Pttsburgh, PA 58 Research Fellow The
Exhaustve Regresson An Exploraton of Regresson-Based Data Mnng Technques Usng Super Computaton Antony Daves, Ph.D. Assocate Professor of Economcs Duquesne Unversty Pttsburgh, PA 58 Research Fellow The
The OC Curve of Attribute Acceptance Plans
 The OC Curve of Attrbute Acceptance Plans The Operatng Characterstc (OC) curve descrbes the probablty of acceptng a lot as a functon of the lot s qualty. Fgure 1 shows a typcal OC Curve. 10 8 6 4 1 3 4
The OC Curve of Attrbute Acceptance Plans The Operatng Characterstc (OC) curve descrbes the probablty of acceptng a lot as a functon of the lot s qualty. Fgure 1 shows a typcal OC Curve. 10 8 6 4 1 3 4
IDENTIFICATION AND CORRECTION OF A COMMON ERROR IN GENERAL ANNUITY CALCULATIONS
 IDENTIFICATION AND CORRECTION OF A COMMON ERROR IN GENERAL ANNUITY CALCULATIONS Chrs Deeley* Last revsed: September 22, 200 * Chrs Deeley s a Senor Lecturer n the School of Accountng, Charles Sturt Unversty,
IDENTIFICATION AND CORRECTION OF A COMMON ERROR IN GENERAL ANNUITY CALCULATIONS Chrs Deeley* Last revsed: September 22, 200 * Chrs Deeley s a Senor Lecturer n the School of Accountng, Charles Sturt Unversty,
Staff Paper. Farm Savings Accounts: Examining Income Variability, Eligibility, and Benefits. Brent Gloy, Eddy LaDue, and Charles Cuykendall
 SP 2005-02 August 2005 Staff Paper Department of Appled Economcs and Management Cornell Unversty, Ithaca, New York 14853-7801 USA Farm Savngs Accounts: Examnng Income Varablty, Elgblty, and Benefts Brent
SP 2005-02 August 2005 Staff Paper Department of Appled Economcs and Management Cornell Unversty, Ithaca, New York 14853-7801 USA Farm Savngs Accounts: Examnng Income Varablty, Elgblty, and Benefts Brent
Regression Models for a Binary Response Using EXCEL and JMP
 SEMATECH 997 Statstcal Methods Symposum Austn Regresson Models for a Bnary Response Usng EXCEL and JMP Davd C. Trndade, Ph.D. STAT-TECH Consultng and Tranng n Appled Statstcs San Jose, CA Topcs Practcal
SEMATECH 997 Statstcal Methods Symposum Austn Regresson Models for a Bnary Response Usng EXCEL and JMP Davd C. Trndade, Ph.D. STAT-TECH Consultng and Tranng n Appled Statstcs San Jose, CA Topcs Practcal
PRACTICE 1: MUTUAL FUNDS EVALUATION USING MATLAB.
 PRACTICE 1: MUTUAL FUNDS EVALUATION USING MATLAB. INDEX 1. Load data usng the Edtor wndow and m-fle 2. Learnng to save results from the Edtor wndow. 3. Computng the Sharpe Rato 4. Obtanng the Treynor Rato
PRACTICE 1: MUTUAL FUNDS EVALUATION USING MATLAB. INDEX 1. Load data usng the Edtor wndow and m-fle 2. Learnng to save results from the Edtor wndow. 3. Computng the Sharpe Rato 4. Obtanng the Treynor Rato
Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Statistical Association, August 5-9, 2001
 Proceedngs of the Annual Meetng of the Amercan Statstcal Assocaton, August 5-9, 2001 LIST-ASSISTED SAMPLING: THE EFFECT OF TELEPHONE SYSTEM CHANGES ON DESIGN 1 Clyde Tucker, Bureau of Labor Statstcs James
Proceedngs of the Annual Meetng of the Amercan Statstcal Assocaton, August 5-9, 2001 LIST-ASSISTED SAMPLING: THE EFFECT OF TELEPHONE SYSTEM CHANGES ON DESIGN 1 Clyde Tucker, Bureau of Labor Statstcs James
Risk Model of Long-Term Production Scheduling in Open Pit Gold Mining
 Rsk Model of Long-Term Producton Schedulng n Open Pt Gold Mnng R Halatchev 1 and P Lever 2 ABSTRACT Open pt gold mnng s an mportant sector of the Australan mnng ndustry. It uses large amounts of nvestments,
Rsk Model of Long-Term Producton Schedulng n Open Pt Gold Mnng R Halatchev 1 and P Lever 2 ABSTRACT Open pt gold mnng s an mportant sector of the Australan mnng ndustry. It uses large amounts of nvestments,
How Sets of Coherent Probabilities May Serve as Models for Degrees of Incoherence
 1 st Internatonal Symposum on Imprecse Probabltes and Ther Applcatons, Ghent, Belgum, 29 June 2 July 1999 How Sets of Coherent Probabltes May Serve as Models for Degrees of Incoherence Mar J. Schervsh
1 st Internatonal Symposum on Imprecse Probabltes and Ther Applcatons, Ghent, Belgum, 29 June 2 July 1999 How Sets of Coherent Probabltes May Serve as Models for Degrees of Incoherence Mar J. Schervsh
An Evaluation of the Extended Logistic, Simple Logistic, and Gompertz Models for Forecasting Short Lifecycle Products and Services
 An Evaluaton of the Extended Logstc, Smple Logstc, and Gompertz Models for Forecastng Short Lfecycle Products and Servces Charles V. Trappey a,1, Hsn-yng Wu b a Professor (Management Scence), Natonal Chao
An Evaluaton of the Extended Logstc, Smple Logstc, and Gompertz Models for Forecastng Short Lfecycle Products and Servces Charles V. Trappey a,1, Hsn-yng Wu b a Professor (Management Scence), Natonal Chao
Psicológica Universidad de Valencia psicologica@uv.es ISSN (Versión impresa): 0211-2159 ISSN (Versión en línea): 1576-8597 ESPAÑA
 Pscológca Unversdad de Valenca pscologca@uv.es ISSN (Versón mpresa): 02-259 ISSN (Versón en línea): 576-8597 ESPAÑA 2000 Vcenta Serra / Vcenç Quera / Anton Solanas AUTOCORRELATION EFFECT ON TYPE I ERROR
Pscológca Unversdad de Valenca pscologca@uv.es ISSN (Versón mpresa): 02-259 ISSN (Versón en línea): 576-8597 ESPAÑA 2000 Vcenta Serra / Vcenç Quera / Anton Solanas AUTOCORRELATION EFFECT ON TYPE I ERROR
Portfolio Loss Distribution
 Portfolo Loss Dstrbuton Rsky assets n loan ortfolo hghly llqud assets hold-to-maturty n the bank s balance sheet Outstandngs The orton of the bank asset that has already been extended to borrowers. Commtment
Portfolo Loss Dstrbuton Rsky assets n loan ortfolo hghly llqud assets hold-to-maturty n the bank s balance sheet Outstandngs The orton of the bank asset that has already been extended to borrowers. Commtment
Calculating the high frequency transmission line parameters of power cables
 < ' Calculatng the hgh frequency transmsson lne parameters of power cables Authors: Dr. John Dcknson, Laboratory Servces Manager, N 0 RW E B Communcatons Mr. Peter J. Ncholson, Project Assgnment Manager,
< ' Calculatng the hgh frequency transmsson lne parameters of power cables Authors: Dr. John Dcknson, Laboratory Servces Manager, N 0 RW E B Communcatons Mr. Peter J. Ncholson, Project Assgnment Manager,
Estimation of Dispersion Parameters in GLMs with and without Random Effects
 Mathematcal Statstcs Stockholm Unversty Estmaton of Dsperson Parameters n GLMs wth and wthout Random Effects Meng Ruoyan Examensarbete 2004:5 Postal address: Mathematcal Statstcs Dept. of Mathematcs Stockholm
Mathematcal Statstcs Stockholm Unversty Estmaton of Dsperson Parameters n GLMs wth and wthout Random Effects Meng Ruoyan Examensarbete 2004:5 Postal address: Mathematcal Statstcs Dept. of Mathematcs Stockholm
Traffic State Estimation in the Traffic Management Center of Berlin
 Traffc State Estmaton n the Traffc Management Center of Berln Authors: Peter Vortsch, PTV AG, Stumpfstrasse, D-763 Karlsruhe, Germany phone ++49/72/965/35, emal peter.vortsch@ptv.de Peter Möhl, PTV AG,
Traffc State Estmaton n the Traffc Management Center of Berln Authors: Peter Vortsch, PTV AG, Stumpfstrasse, D-763 Karlsruhe, Germany phone ++49/72/965/35, emal peter.vortsch@ptv.de Peter Möhl, PTV AG,
Gender differences in revealed risk taking: evidence from mutual fund investors
 Economcs Letters 76 (2002) 151 158 www.elsever.com/ locate/ econbase Gender dfferences n revealed rsk takng: evdence from mutual fund nvestors a b c, * Peggy D. Dwyer, James H. Glkeson, John A. Lst a Unversty
Economcs Letters 76 (2002) 151 158 www.elsever.com/ locate/ econbase Gender dfferences n revealed rsk takng: evdence from mutual fund nvestors a b c, * Peggy D. Dwyer, James H. Glkeson, John A. Lst a Unversty
An Interest-Oriented Network Evolution Mechanism for Online Communities
 An Interest-Orented Network Evoluton Mechansm for Onlne Communtes Cahong Sun and Xaopng Yang School of Informaton, Renmn Unversty of Chna, Bejng 100872, P.R. Chna {chsun,yang}@ruc.edu.cn Abstract. Onlne
An Interest-Orented Network Evoluton Mechansm for Onlne Communtes Cahong Sun and Xaopng Yang School of Informaton, Renmn Unversty of Chna, Bejng 100872, P.R. Chna {chsun,yang}@ruc.edu.cn Abstract. Onlne
A Probabilistic Theory of Coherence
 A Probablstc Theory of Coherence BRANDEN FITELSON. The Coherence Measure C Let E be a set of n propostons E,..., E n. We seek a probablstc measure C(E) of the degree of coherence of E. Intutvely, we want
A Probablstc Theory of Coherence BRANDEN FITELSON. The Coherence Measure C Let E be a set of n propostons E,..., E n. We seek a probablstc measure C(E) of the degree of coherence of E. Intutvely, we want
Rate-Based Daily Arrival Process Models with Application to Call Centers
 Submtted to Operatons Research manuscrpt (Please, provde the manuscrpt number!) Authors are encouraged to submt new papers to INFORMS journals by means of a style fle template, whch ncludes the journal
Submtted to Operatons Research manuscrpt (Please, provde the manuscrpt number!) Authors are encouraged to submt new papers to INFORMS journals by means of a style fle template, whch ncludes the journal
Traditional versus Online Courses, Efforts, and Learning Performance
 Tradtonal versus Onlne Courses, Efforts, and Learnng Performance Kuang-Cheng Tseng, Department of Internatonal Trade, Chung-Yuan Chrstan Unversty, Tawan Shan-Yng Chu, Department of Internatonal Trade,
Tradtonal versus Onlne Courses, Efforts, and Learnng Performance Kuang-Cheng Tseng, Department of Internatonal Trade, Chung-Yuan Chrstan Unversty, Tawan Shan-Yng Chu, Department of Internatonal Trade,
PRIVATE SCHOOL CHOICE: THE EFFECTS OF RELIGIOUS AFFILIATION AND PARTICIPATION
 PRIVATE SCHOOL CHOICE: THE EFFECTS OF RELIIOUS AFFILIATION AND PARTICIPATION Danny Cohen-Zada Department of Economcs, Ben-uron Unversty, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel Wllam Sander Department of Economcs, DePaul
PRIVATE SCHOOL CHOICE: THE EFFECTS OF RELIIOUS AFFILIATION AND PARTICIPATION Danny Cohen-Zada Department of Economcs, Ben-uron Unversty, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel Wllam Sander Department of Economcs, DePaul
Economic Interpretation of Regression. Theory and Applications
 Economc Interpretaton of Regresson Theor and Applcatons Classcal and Baesan Econometrc Methods Applcaton of mathematcal statstcs to economc data for emprcal support Economc theor postulates a qualtatve
Economc Interpretaton of Regresson Theor and Applcatons Classcal and Baesan Econometrc Methods Applcaton of mathematcal statstcs to economc data for emprcal support Economc theor postulates a qualtatve
Statistical algorithms in Review Manager 5
 Statstcal algorthms n Reve Manager 5 Jonathan J Deeks and Julan PT Hggns on behalf of the Statstcal Methods Group of The Cochrane Collaboraton August 00 Data structure Consder a meta-analyss of k studes
Statstcal algorthms n Reve Manager 5 Jonathan J Deeks and Julan PT Hggns on behalf of the Statstcal Methods Group of The Cochrane Collaboraton August 00 Data structure Consder a meta-analyss of k studes
RESEARCH ON DUAL-SHAKER SINE VIBRATION CONTROL. Yaoqi FENG 1, Hanping QIU 1. China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) yaoqi.feng@yahoo.
 ICSV4 Carns Australa 9- July, 007 RESEARCH ON DUAL-SHAKER SINE VIBRATION CONTROL Yaoq FENG, Hanpng QIU Dynamc Test Laboratory, BISEE Chna Academy of Space Technology (CAST) yaoq.feng@yahoo.com Abstract
ICSV4 Carns Australa 9- July, 007 RESEARCH ON DUAL-SHAKER SINE VIBRATION CONTROL Yaoq FENG, Hanpng QIU Dynamc Test Laboratory, BISEE Chna Academy of Space Technology (CAST) yaoq.feng@yahoo.com Abstract
Characterization of Assembly. Variation Analysis Methods. A Thesis. Presented to the. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Brigham Young University
 Characterzaton of Assembly Varaton Analyss Methods A Thess Presented to the Department of Mechancal Engneerng Brgham Young Unversty In Partal Fulfllment of the Requrements for the Degree Master of Scence
Characterzaton of Assembly Varaton Analyss Methods A Thess Presented to the Department of Mechancal Engneerng Brgham Young Unversty In Partal Fulfllment of the Requrements for the Degree Master of Scence
The Application of Fractional Brownian Motion in Option Pricing
 Vol. 0, No. (05), pp. 73-8 http://dx.do.org/0.457/jmue.05.0..6 The Applcaton of Fractonal Brownan Moton n Opton Prcng Qng-xn Zhou School of Basc Scence,arbn Unversty of Commerce,arbn zhouqngxn98@6.com
Vol. 0, No. (05), pp. 73-8 http://dx.do.org/0.457/jmue.05.0..6 The Applcaton of Fractonal Brownan Moton n Opton Prcng Qng-xn Zhou School of Basc Scence,arbn Unversty of Commerce,arbn zhouqngxn98@6.com
Evaluating credit risk models: A critique and a new proposal
 Evaluatng credt rsk models: A crtque and a new proposal Hergen Frerchs* Gunter Löffler Unversty of Frankfurt (Man) February 14, 2001 Abstract Evaluatng the qualty of credt portfolo rsk models s an mportant
Evaluatng credt rsk models: A crtque and a new proposal Hergen Frerchs* Gunter Löffler Unversty of Frankfurt (Man) February 14, 2001 Abstract Evaluatng the qualty of credt portfolo rsk models s an mportant
Chapter XX More advanced approaches to the analysis of survey data. Gad Nathan Hebrew University Jerusalem, Israel. Abstract
 Household Sample Surveys n Developng and Transton Countres Chapter More advanced approaches to the analyss of survey data Gad Nathan Hebrew Unversty Jerusalem, Israel Abstract In the present chapter, we
Household Sample Surveys n Developng and Transton Countres Chapter More advanced approaches to the analyss of survey data Gad Nathan Hebrew Unversty Jerusalem, Israel Abstract In the present chapter, we
Conceptual and Practical Issues in the Statistical Design and Analysis of Usability Tests
 Conceptual and Practcal Issues n the Statstcal Desgn and Analyss of Usablty Tests John J. Bosley (Bosley_J@bls.gov), BLS, John L. Eltnge (Eltnge_J@bls.gov), BLS, Jean E. Fox (Fox_J@bls.gov), BLS, Scott
Conceptual and Practcal Issues n the Statstcal Desgn and Analyss of Usablty Tests John J. Bosley (Bosley_J@bls.gov), BLS, John L. Eltnge (Eltnge_J@bls.gov), BLS, Jean E. Fox (Fox_J@bls.gov), BLS, Scott
Properties of Indoor Received Signal Strength for WLAN Location Fingerprinting
 Propertes of Indoor Receved Sgnal Strength for WLAN Locaton Fngerprntng Kamol Kaemarungs and Prashant Krshnamurthy Telecommuncatons Program, School of Informaton Scences, Unversty of Pttsburgh E-mal: kakst2,prashk@ptt.edu
Propertes of Indoor Receved Sgnal Strength for WLAN Locaton Fngerprntng Kamol Kaemarungs and Prashant Krshnamurthy Telecommuncatons Program, School of Informaton Scences, Unversty of Pttsburgh E-mal: kakst2,prashk@ptt.edu
Binomial Link Functions. Lori Murray, Phil Munz
 Bnomal Lnk Functons Lor Murray, Phl Munz Bnomal Lnk Functons Logt Lnk functon: ( p) p ln 1 p Probt Lnk functon: ( p) 1 ( p) Complentary Log Log functon: ( p) ln( ln(1 p)) Motvatng Example A researcher
Bnomal Lnk Functons Lor Murray, Phl Munz Bnomal Lnk Functons Logt Lnk functon: ( p) p ln 1 p Probt Lnk functon: ( p) 1 ( p) Complentary Log Log functon: ( p) ln( ln(1 p)) Motvatng Example A researcher
) of the Cell class is created containing information about events associated with the cell. Events are added to the Cell instance
 Calbraton Method Instances of the Cell class (one nstance for each FMS cell) contan ADC raw data and methods assocated wth each partcular FMS cell. The calbraton method ncludes event selecton (Class Cell
Calbraton Method Instances of the Cell class (one nstance for each FMS cell) contan ADC raw data and methods assocated wth each partcular FMS cell. The calbraton method ncludes event selecton (Class Cell
High Correlation between Net Promoter Score and the Development of Consumers' Willingness to Pay (Empirical Evidence from European Mobile Markets)
 Hgh Correlaton between et Promoter Score and the Development of Consumers' Wllngness to Pay (Emprcal Evdence from European Moble Marets Ths paper shows that the correlaton between the et Promoter Score
Hgh Correlaton between et Promoter Score and the Development of Consumers' Wllngness to Pay (Emprcal Evdence from European Moble Marets Ths paper shows that the correlaton between the et Promoter Score
Single and multiple stage classifiers implementing logistic discrimination
 Sngle and multple stage classfers mplementng logstc dscrmnaton Hélo Radke Bttencourt 1 Dens Alter de Olvera Moraes 2 Vctor Haertel 2 1 Pontfíca Unversdade Católca do Ro Grande do Sul - PUCRS Av. Ipranga,
Sngle and multple stage classfers mplementng logstc dscrmnaton Hélo Radke Bttencourt 1 Dens Alter de Olvera Moraes 2 Vctor Haertel 2 1 Pontfíca Unversdade Católca do Ro Grande do Sul - PUCRS Av. Ipranga,
Demographic and Health Surveys Methodology
 samplng and household lstng manual Demographc and Health Surveys Methodology Ths document s part of the Demographc and Health Survey s DHS Toolkt of methodology for the MEASURE DHS Phase III project, mplemented
samplng and household lstng manual Demographc and Health Surveys Methodology Ths document s part of the Demographc and Health Survey s DHS Toolkt of methodology for the MEASURE DHS Phase III project, mplemented
Adaptive Clinical Trials Incorporating Treatment Selection and Evaluation: Methodology and Applications in Multiple Sclerosis
 Adaptve Clncal Trals Incorporatng Treatment electon and Evaluaton: Methodology and Applcatons n Multple cleross usan Todd, Tm Frede, Ngel tallard, Ncholas Parsons, Elsa Valdés-Márquez, Jeremy Chataway
Adaptve Clncal Trals Incorporatng Treatment electon and Evaluaton: Methodology and Applcatons n Multple cleross usan Todd, Tm Frede, Ngel tallard, Ncholas Parsons, Elsa Valdés-Márquez, Jeremy Chataway
Sketching Sampled Data Streams
 Sketchng Sampled Data Streams Florn Rusu, Aln Dobra CISE Department Unversty of Florda Ganesvlle, FL, USA frusu@cse.ufl.edu adobra@cse.ufl.edu Abstract Samplng s used as a unversal method to reduce the
Sketchng Sampled Data Streams Florn Rusu, Aln Dobra CISE Department Unversty of Florda Ganesvlle, FL, USA frusu@cse.ufl.edu adobra@cse.ufl.edu Abstract Samplng s used as a unversal method to reduce the
SIMPLE LINEAR CORRELATION
 SIMPLE LINEAR CORRELATION Smple lnear correlaton s a measure of the degree to whch two varables vary together, or a measure of the ntensty of the assocaton between two varables. Correlaton often s abused.
SIMPLE LINEAR CORRELATION Smple lnear correlaton s a measure of the degree to whch two varables vary together, or a measure of the ntensty of the assocaton between two varables. Correlaton often s abused.
An Introduction to 3G Monte-Carlo simulations within ProMan
 An Introducton to 3G Monte-Carlo smulatons wthn ProMan responsble edtor: Hermann Buddendck AWE Communcatons GmbH Otto-Llenthal-Str. 36 D-71034 Böblngen Phone: +49 70 31 71 49 7-16 Fax: +49 70 31 71 49
An Introducton to 3G Monte-Carlo smulatons wthn ProMan responsble edtor: Hermann Buddendck AWE Communcatons GmbH Otto-Llenthal-Str. 36 D-71034 Böblngen Phone: +49 70 31 71 49 7-16 Fax: +49 70 31 71 49
1 De nitions and Censoring
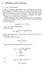 De ntons and Censorng. Survval Analyss We begn by consderng smple analyses but we wll lead up to and take a look at regresson on explanatory factors., as n lnear regresson part A. The mportant d erence
De ntons and Censorng. Survval Analyss We begn by consderng smple analyses but we wll lead up to and take a look at regresson on explanatory factors., as n lnear regresson part A. The mportant d erence
Diagnostic Tests of Cross Section Independence for Nonlinear Panel Data Models
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2756 Dagnostc ests of Cross Secton Independence for Nonlnear Panel Data Models Cheng Hsao M. Hashem Pesaran Andreas Pck Aprl 2007 Forschungsnsttut zur Zukunft der Arbet
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2756 Dagnostc ests of Cross Secton Independence for Nonlnear Panel Data Models Cheng Hsao M. Hashem Pesaran Andreas Pck Aprl 2007 Forschungsnsttut zur Zukunft der Arbet
Calibration and Linear Regression Analysis: A Self-Guided Tutorial
 Calbraton and Lnear Regresson Analyss: A Self-Guded Tutoral Part The Calbraton Curve, Correlaton Coeffcent and Confdence Lmts CHM314 Instrumental Analyss Department of Chemstry, Unversty of Toronto Dr.
Calbraton and Lnear Regresson Analyss: A Self-Guded Tutoral Part The Calbraton Curve, Correlaton Coeffcent and Confdence Lmts CHM314 Instrumental Analyss Department of Chemstry, Unversty of Toronto Dr.
Abstract. 260 Business Intelligence Journal July IDENTIFICATION OF DEMAND THROUGH STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION MODELING FOR IMPROVED DEMAND FORECASTING
 260 Busness Intellgence Journal July IDENTIFICATION OF DEMAND THROUGH STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION MODELING FOR IMPROVED DEMAND FORECASTING Murphy Choy Mchelle L.F. Cheong School of Informaton Systems, Sngapore
260 Busness Intellgence Journal July IDENTIFICATION OF DEMAND THROUGH STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION MODELING FOR IMPROVED DEMAND FORECASTING Murphy Choy Mchelle L.F. Cheong School of Informaton Systems, Sngapore
"Research Note" APPLICATION OF CHARGE SIMULATION METHOD TO ELECTRIC FIELD CALCULATION IN THE POWER CABLES *
 Iranan Journal of Scence & Technology, Transacton B, Engneerng, ol. 30, No. B6, 789-794 rnted n The Islamc Republc of Iran, 006 Shraz Unversty "Research Note" ALICATION OF CHARGE SIMULATION METHOD TO ELECTRIC
Iranan Journal of Scence & Technology, Transacton B, Engneerng, ol. 30, No. B6, 789-794 rnted n The Islamc Republc of Iran, 006 Shraz Unversty "Research Note" ALICATION OF CHARGE SIMULATION METHOD TO ELECTRIC
Feature selection for intrusion detection. Slobodan Petrović NISlab, Gjøvik University College
 Feature selecton for ntruson detecton Slobodan Petrovć NISlab, Gjøvk Unversty College Contents The feature selecton problem Intruson detecton Traffc features relevant for IDS The CFS measure The mrmr measure
Feature selecton for ntruson detecton Slobodan Petrovć NISlab, Gjøvk Unversty College Contents The feature selecton problem Intruson detecton Traffc features relevant for IDS The CFS measure The mrmr measure
ESTIMATING THE MARKET VALUE OF FRANKING CREDITS: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM AUSTRALIA
 ESTIMATING THE MARKET VALUE OF FRANKING CREDITS: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM AUSTRALIA Duc Vo Beauden Gellard Stefan Mero Economc Regulaton Authorty 469 Wellngton Street, Perth, WA 6000, Australa Phone: (08)
ESTIMATING THE MARKET VALUE OF FRANKING CREDITS: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM AUSTRALIA Duc Vo Beauden Gellard Stefan Mero Economc Regulaton Authorty 469 Wellngton Street, Perth, WA 6000, Australa Phone: (08)
Damage detection in composite laminates using coin-tap method
 Damage detecton n composte lamnates usng con-tap method S.J. Km Korea Aerospace Research Insttute, 45 Eoeun-Dong, Youseong-Gu, 35-333 Daejeon, Republc of Korea yaeln@kar.re.kr 45 The con-tap test has the
Damage detecton n composte lamnates usng con-tap method S.J. Km Korea Aerospace Research Insttute, 45 Eoeun-Dong, Youseong-Gu, 35-333 Daejeon, Republc of Korea yaeln@kar.re.kr 45 The con-tap test has the
Forecasting the Demand of Emergency Supplies: Based on the CBR Theory and BP Neural Network
 700 Proceedngs of the 8th Internatonal Conference on Innovaton & Management Forecastng the Demand of Emergency Supples: Based on the CBR Theory and BP Neural Network Fu Deqang, Lu Yun, L Changbng School
700 Proceedngs of the 8th Internatonal Conference on Innovaton & Management Forecastng the Demand of Emergency Supples: Based on the CBR Theory and BP Neural Network Fu Deqang, Lu Yun, L Changbng School
L10: Linear discriminants analysis
 L0: Lnear dscrmnants analyss Lnear dscrmnant analyss, two classes Lnear dscrmnant analyss, C classes LDA vs. PCA Lmtatons of LDA Varants of LDA Other dmensonalty reducton methods CSCE 666 Pattern Analyss
L0: Lnear dscrmnants analyss Lnear dscrmnant analyss, two classes Lnear dscrmnant analyss, C classes LDA vs. PCA Lmtatons of LDA Varants of LDA Other dmensonalty reducton methods CSCE 666 Pattern Analyss
HOUSEHOLDS DEBT BURDEN: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON MICROECONOMIC DATA*
 HOUSEHOLDS DEBT BURDEN: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON MICROECONOMIC DATA* Luísa Farnha** 1. INTRODUCTION The rapd growth n Portuguese households ndebtedness n the past few years ncreased the concerns that debt
HOUSEHOLDS DEBT BURDEN: AN ANALYSIS BASED ON MICROECONOMIC DATA* Luísa Farnha** 1. INTRODUCTION The rapd growth n Portuguese households ndebtedness n the past few years ncreased the concerns that debt
On the allocation of resources for secondary education schools
 On the allocaton of resources for secondary educaton schools C. Haelermans, K. De Wtte and J. Blank TIER WORKING PAPER SERIES TIER WP /08 On the allocaton of resources for secondary educaton schools Carla
On the allocaton of resources for secondary educaton schools C. Haelermans, K. De Wtte and J. Blank TIER WORKING PAPER SERIES TIER WP /08 On the allocaton of resources for secondary educaton schools Carla
Social Nfluence and Its Models
 Influence and Correlaton n Socal Networks Ars Anagnostopoulos Rav Kumar Mohammad Mahdan Yahoo! Research 701 Frst Ave. Sunnyvale, CA 94089. {ars,ravkumar,mahdan}@yahoo-nc.com ABSTRACT In many onlne socal
Influence and Correlaton n Socal Networks Ars Anagnostopoulos Rav Kumar Mohammad Mahdan Yahoo! Research 701 Frst Ave. Sunnyvale, CA 94089. {ars,ravkumar,mahdan}@yahoo-nc.com ABSTRACT In many onlne socal
Scale Dependence of Overconfidence in Stock Market Volatility Forecasts
 Scale Dependence of Overconfdence n Stoc Maret Volatlty Forecasts Marus Glaser, Thomas Langer, Jens Reynders, Martn Weber* June 7, 007 Abstract In ths study, we analyze whether volatlty forecasts (judgmental
Scale Dependence of Overconfdence n Stoc Maret Volatlty Forecasts Marus Glaser, Thomas Langer, Jens Reynders, Martn Weber* June 7, 007 Abstract In ths study, we analyze whether volatlty forecasts (judgmental
Quantization Effects in Digital Filters
 Quantzaton Effects n Dgtal Flters Dstrbuton of Truncaton Errors In two's complement representaton an exact number would have nfntely many bts (n general). When we lmt the number of bts to some fnte value
Quantzaton Effects n Dgtal Flters Dstrbuton of Truncaton Errors In two's complement representaton an exact number would have nfntely many bts (n general). When we lmt the number of bts to some fnte value
Multiple-Period Attribution: Residuals and Compounding
 Multple-Perod Attrbuton: Resduals and Compoundng Our revewer gave these authors full marks for dealng wth an ssue that performance measurers and vendors often regard as propretary nformaton. In 1994, Dens
Multple-Perod Attrbuton: Resduals and Compoundng Our revewer gave these authors full marks for dealng wth an ssue that performance measurers and vendors often regard as propretary nformaton. In 1994, Dens
CS 2750 Machine Learning. Lecture 3. Density estimation. CS 2750 Machine Learning. Announcements
 Lecture 3 Densty estmaton Mlos Hauskrecht mlos@cs.ptt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Next lecture: Matlab tutoral Announcements Rules for attendng the class: Regstered for credt Regstered for audt (only f there
Lecture 3 Densty estmaton Mlos Hauskrecht mlos@cs.ptt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Next lecture: Matlab tutoral Announcements Rules for attendng the class: Regstered for credt Regstered for audt (only f there
The Use of Analytics for Claim Fraud Detection Roosevelt C. Mosley, Jr., FCAS, MAAA Nick Kucera Pinnacle Actuarial Resources Inc.
 Paper 1837-2014 The Use of Analytcs for Clam Fraud Detecton Roosevelt C. Mosley, Jr., FCAS, MAAA Nck Kucera Pnnacle Actuaral Resources Inc., Bloomngton, IL ABSTRACT As t has been wdely reported n the nsurance
Paper 1837-2014 The Use of Analytcs for Clam Fraud Detecton Roosevelt C. Mosley, Jr., FCAS, MAAA Nck Kucera Pnnacle Actuaral Resources Inc., Bloomngton, IL ABSTRACT As t has been wdely reported n the nsurance
NPAR TESTS. One-Sample Chi-Square Test. Cell Specification. Observed Frequencies 1O i 6. Expected Frequencies 1EXP i 6
 PAR TESTS If a WEIGHT varable s specfed, t s used to replcate a case as many tmes as ndcated by the weght value rounded to the nearest nteger. If the workspace requrements are exceeded and samplng has
PAR TESTS If a WEIGHT varable s specfed, t s used to replcate a case as many tmes as ndcated by the weght value rounded to the nearest nteger. If the workspace requrements are exceeded and samplng has
Fragility Based Rehabilitation Decision Analysis
 .171. Fraglty Based Rehabltaton Decson Analyss Cagdas Kafal Graduate Student, School of Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng, Cornell Unversty Research Supervsor: rcea Grgoru, Professor Summary A method s presented
.171. Fraglty Based Rehabltaton Decson Analyss Cagdas Kafal Graduate Student, School of Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng, Cornell Unversty Research Supervsor: rcea Grgoru, Professor Summary A method s presented
BERNSTEIN POLYNOMIALS
 On-Lne Geometrc Modelng Notes BERNSTEIN POLYNOMIALS Kenneth I. Joy Vsualzaton and Graphcs Research Group Department of Computer Scence Unversty of Calforna, Davs Overvew Polynomals are ncredbly useful
On-Lne Geometrc Modelng Notes BERNSTEIN POLYNOMIALS Kenneth I. Joy Vsualzaton and Graphcs Research Group Department of Computer Scence Unversty of Calforna, Davs Overvew Polynomals are ncredbly useful
A multiple objective test assembly approach for exposure control problems in Computerized Adaptive Testing
 Pscológca (2), 3, 335-355. A multple objectve test assembly approach for exposure control problems n Computerzed Adaptve Testng Bernard P. Veldkamp * (), Angela J. Verschoor (2) & Theo J.H.M. Eggen (2)
Pscológca (2), 3, 335-355. A multple objectve test assembly approach for exposure control problems n Computerzed Adaptve Testng Bernard P. Veldkamp * (), Angela J. Verschoor (2) & Theo J.H.M. Eggen (2)
Discount Rate for Workout Recoveries: An Empirical Study*
 Dscount Rate for Workout Recoveres: An Emprcal Study* Brooks Brady Amercan Express Peter Chang Standard & Poor s Peter Mu** McMaster Unversty Boge Ozdemr Standard & Poor s Davd Schwartz Federal Reserve
Dscount Rate for Workout Recoveres: An Emprcal Study* Brooks Brady Amercan Express Peter Chang Standard & Poor s Peter Mu** McMaster Unversty Boge Ozdemr Standard & Poor s Davd Schwartz Federal Reserve
FREQUENCY OF OCCURRENCE OF CERTAIN CHEMICAL CLASSES OF GSR FROM VARIOUS AMMUNITION TYPES
 FREQUENCY OF OCCURRENCE OF CERTAIN CHEMICAL CLASSES OF GSR FROM VARIOUS AMMUNITION TYPES Zuzanna BRO EK-MUCHA, Grzegorz ZADORA, 2 Insttute of Forensc Research, Cracow, Poland 2 Faculty of Chemstry, Jagellonan
FREQUENCY OF OCCURRENCE OF CERTAIN CHEMICAL CLASSES OF GSR FROM VARIOUS AMMUNITION TYPES Zuzanna BRO EK-MUCHA, Grzegorz ZADORA, 2 Insttute of Forensc Research, Cracow, Poland 2 Faculty of Chemstry, Jagellonan
MARKET SHARE CONSTRAINTS AND THE LOSS FUNCTION IN CHOICE BASED CONJOINT ANALYSIS
 MARKET SHARE CONSTRAINTS AND THE LOSS FUNCTION IN CHOICE BASED CONJOINT ANALYSIS Tmothy J. Glbrde Assstant Professor of Marketng 315 Mendoza College of Busness Unversty of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556
MARKET SHARE CONSTRAINTS AND THE LOSS FUNCTION IN CHOICE BASED CONJOINT ANALYSIS Tmothy J. Glbrde Assstant Professor of Marketng 315 Mendoza College of Busness Unversty of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556
Return decomposing of absolute-performance multi-asset class portfolios. Working Paper - Nummer: 16
 Return decomposng of absolute-performance mult-asset class portfolos Workng Paper - Nummer: 16 2007 by Dr. Stefan J. Illmer und Wolfgang Marty; n: Fnancal Markets and Portfolo Management; March 2007; Volume
Return decomposng of absolute-performance mult-asset class portfolos Workng Paper - Nummer: 16 2007 by Dr. Stefan J. Illmer und Wolfgang Marty; n: Fnancal Markets and Portfolo Management; March 2007; Volume
RELIABILITY, RISK AND AVAILABILITY ANLYSIS OF A CONTAINER GANTRY CRANE ABSTRACT
 Kolowrock Krzysztof Joanna oszynska MODELLING ENVIRONMENT AND INFRATRUCTURE INFLUENCE ON RELIABILITY AND OPERATION RT&A # () (Vol.) March RELIABILITY RIK AND AVAILABILITY ANLYI OF A CONTAINER GANTRY CRANE
Kolowrock Krzysztof Joanna oszynska MODELLING ENVIRONMENT AND INFRATRUCTURE INFLUENCE ON RELIABILITY AND OPERATION RT&A # () (Vol.) March RELIABILITY RIK AND AVAILABILITY ANLYI OF A CONTAINER GANTRY CRANE
Vasicek s Model of Distribution of Losses in a Large, Homogeneous Portfolio
 Vascek s Model of Dstrbuton of Losses n a Large, Homogeneous Portfolo Stephen M Schaefer London Busness School Credt Rsk Electve Summer 2012 Vascek s Model Important method for calculatng dstrbuton of
Vascek s Model of Dstrbuton of Losses n a Large, Homogeneous Portfolo Stephen M Schaefer London Busness School Credt Rsk Electve Summer 2012 Vascek s Model Important method for calculatng dstrbuton of
This study examines whether the framing mode (narrow versus broad) influences the stock investment decisions
 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 54, No. 6, June 2008, pp. 1052 1064 ssn 0025-1909 essn 1526-5501 08 5406 1052 nforms do 10.1287/mnsc.1070.0845 2008 INFORMS How Do Decson Frames Influence the Stock Investment Choces
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 54, No. 6, June 2008, pp. 1052 1064 ssn 0025-1909 essn 1526-5501 08 5406 1052 nforms do 10.1287/mnsc.1070.0845 2008 INFORMS How Do Decson Frames Influence the Stock Investment Choces
Traffic-light a stress test for life insurance provisions
 MEMORANDUM Date 006-09-7 Authors Bengt von Bahr, Göran Ronge Traffc-lght a stress test for lfe nsurance provsons Fnansnspetonen P.O. Box 6750 SE-113 85 Stocholm [Sveavägen 167] Tel +46 8 787 80 00 Fax
MEMORANDUM Date 006-09-7 Authors Bengt von Bahr, Göran Ronge Traffc-lght a stress test for lfe nsurance provsons Fnansnspetonen P.O. Box 6750 SE-113 85 Stocholm [Sveavägen 167] Tel +46 8 787 80 00 Fax
